Computed Tomographic Characteristics of Feline Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Case Selection
2.2. Computed Tomography Scan Techniques
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Characteristics
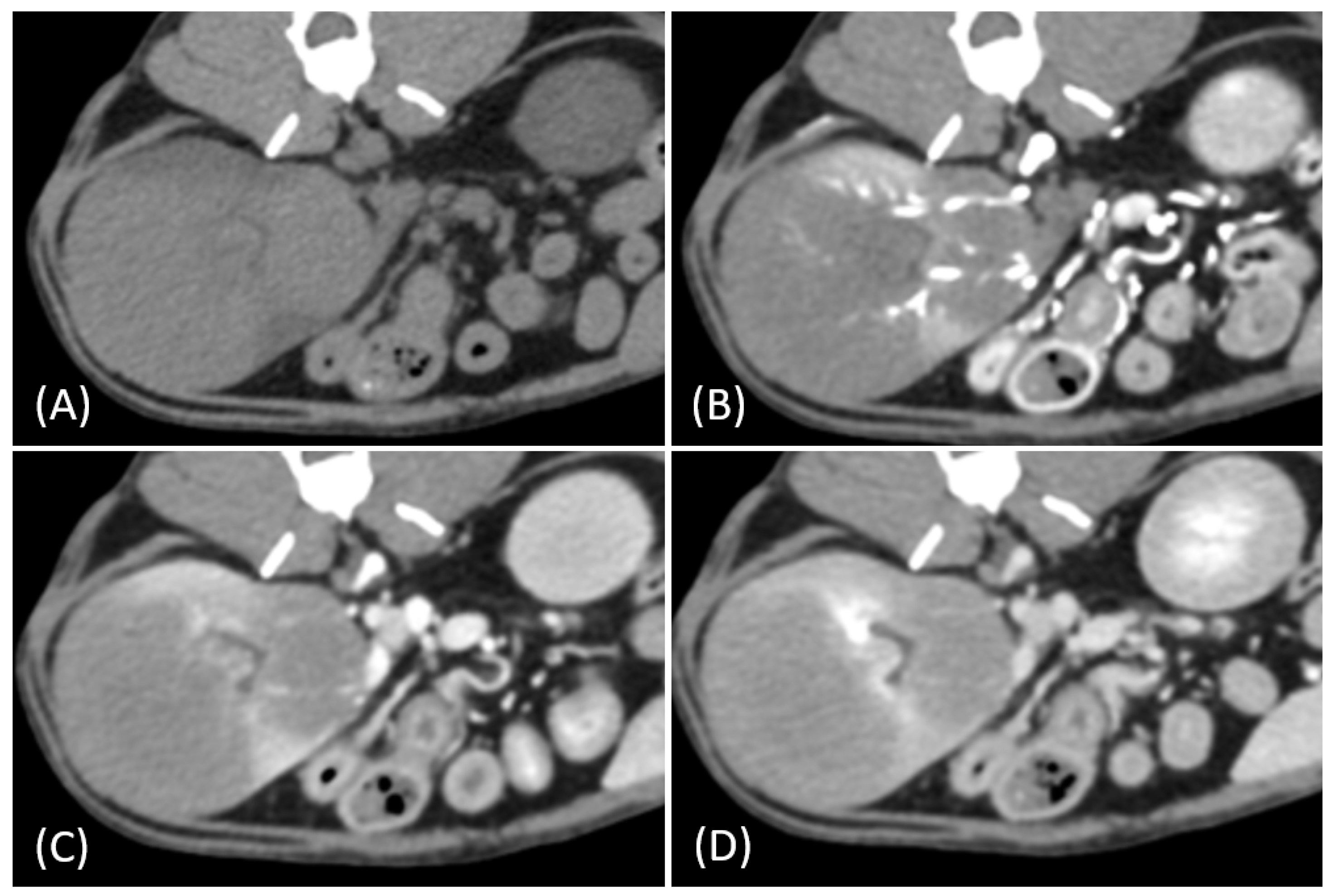
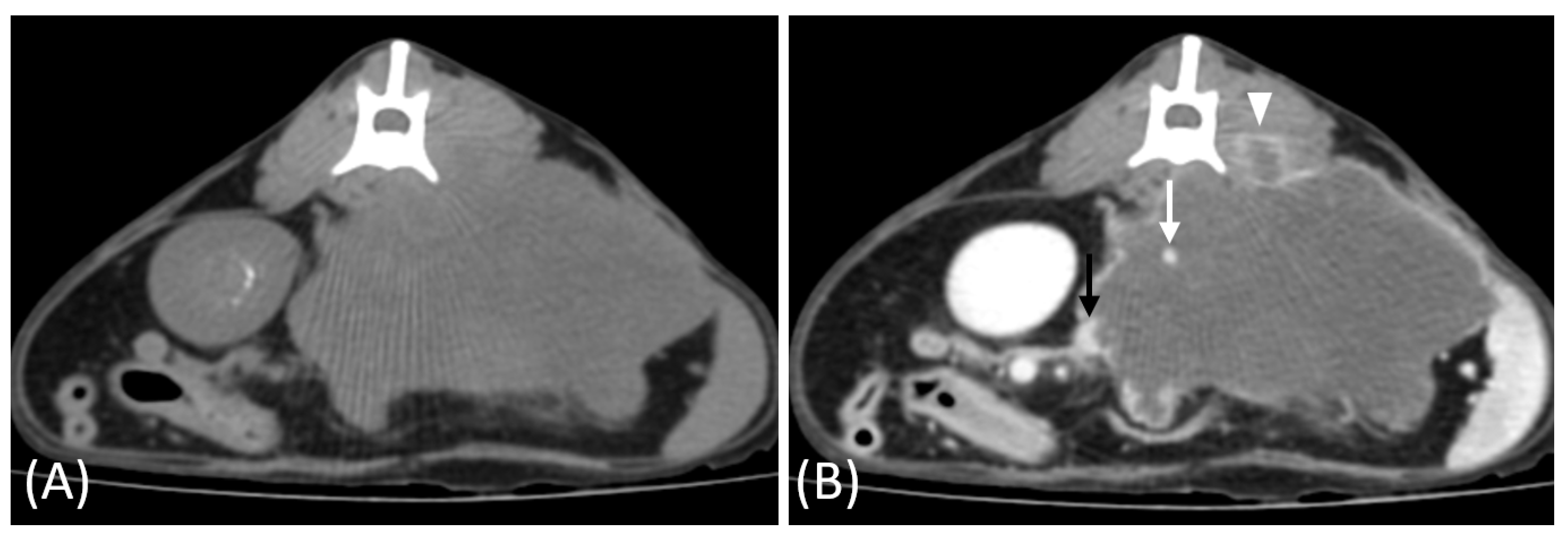
3.2. Qualitative CT Features
3.3. Quantitative CT Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crow, S.E. Urinary Tract Neoplasms in Dogs and Cats. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. 1985, 7, 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Yırgın, I.K. Primary Renal Lymphoma: CT Findings of a Rare Case. Int. J. Radiol. Radiat. Ther. 2018, 5, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Gianni, B.; Marconato, L.; Sabattini, S.; Caleri, E.; Mattolini, M.; Camosci, V.; Carozzi, G. Comparison of Sonographic and CT Findings for the Identification of Renal Nodules in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2023, 64, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, H.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, J.W.; Jang, Y.; Chhoey, S.; Choi, J. Split-Bolus CT Urography with Synchronous Nephrographic and Excretory Phase in Dogs: Comparison of Image Quality with Three-Phase CT Urography and Optimal Allocation Ratio of Contrast Medium. J. Vet. Sci 2020, 21, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, E.L.; Robertson, I.D.; Osborne, J.A.; Brown, J.C. Comparison of Abdominal Computed Tomography and Abdominal Ultrasound in Sedated Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2012, 53, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Akiyoshi, H.; Nishida, H.; Mie, K.; Lin, L.S.; Iimori, Y.; Okamoto, M. Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Findings of Canine Primary Renal Tumors Including Renal Cell Carcinoma, Lymphoma, and Hemangiosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, R.E.; Zagoria, R.J. Imaging Approach to Staging of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 24, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, A.L.; Sartor, L.K. Imaging of Kidney Cancer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 116–227. [Google Scholar]
- Muglia, V.F.; Prando, A. Renal Cell Carcinoma: Histological Classification and Correlation with Imaging Findings. Radiol. Bras. 2015, 48, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, M.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Cho, S.H. Differentiation of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma from Other Subtypes and Fat-Poor Angiomyolipoma by Use of Quantitative Enhancement Measurement during Three-Phase MDCT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, W21–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, I.; Chambers, J.K.; Nibe, K.; Kinoshita, R.; Nishimura, R.; Nakayama, H.; Uchida, K. Histopathologic and Immunohistochemistry Findings in Feline Renal Cell Carcinoma. Vet. Pathol. 2018, 55, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Lee, D.H.; Cha, A.Y.; Kim, D.E.; Chang, D.W.; Choi, J. Optimization of Scan Delay for Multi-Phase Computed Tomography by Using Bolus Tracking in Normal Canine Kidney. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 19, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jung, J.; Chang, J.; Yoon, J.; Choi, M. Evaluation of Triphasic Helical Computed Tomography of the Kidneys in Clinically Normal Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, D.; Shim, J.; Choi, S.; Choi, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K. Computed Tomographic Findings of Primary Renal Tumors in Dogs and Cats. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2022, 52, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Tamada, T.; Higaki, A.; Arita, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Murakami, T.; Jinzaki, M. Evaluation of the Clinical Behavior of Unclassified Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Imaging Findings on Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based on World Health Organization (WHO). Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 42, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillas, V.J.; Amendola, M.A.; Gascue, A.; Pinnar, N.; Levi, J.U.; Perez, J.M. Imaging of Nontraumatic Hemorrhagic Hepatic Lesions. RadioGraphics 2000, 20, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, S.G.; Mortele, K.J.; Tuncali, K.; Jinzaki, M.; Cibas, E.S. Hyperattenuating Renal Masses: Etiologies, Pathogenesis, and Imaging Evaluation. Radiographics 2007, 27, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlo, C.A.; Kou, L.; Di Paolo, P.L.; Kattan, M.W.; Motzer, R.J.; Russo, P.; Tickoo, S.K.; Akin, O.; Hricak, H. Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Nomogram for the CT Imaging-Inclusive Prediction of Indolent, Non-Clear Cell Renal Cortical Tumors. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 59, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlini, M.; Bugbee, A.; Secrest, S. Computed Tomographic Appearance of Abdominal Lymph Nodes in Healthy Cats. J. Vet. Intern Med. 2018, 32, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, E.; Amasyalı, A.S.; Erol, B.; Acikgozoglu, S.; Kucukdurmaz, F.; Nayman, A.; Erol, H. Role of Contrast Enhancement and Corrected Attenuation Values of Renal Tumors in Predicting Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) Subtypes: Protocol for a Triphasic Multi-Slice Computed Tomography (CT) Procedure. Pol. J. Radiol. 2017, 82, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, F.; Garcia, M.; Silva, V.G.e.; Rossa, A.P.; Alves, T.L.; Sousa, R.S.d.; Albernaz, V.G.P.; Sousa, M.G.; Stedile, S.T.d.O. Primary Renal Lymphoma in Two Cats: Case Report. Arch. Vet. Sci. 2021, 26, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur Muniz, I.; Andrade, E.R.; Voigt, P.R. Primary Renal Lymphoma in Domestic Cat (Felis Catus): Case Report. Vet. Zootec. 2017, 24, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, S.A.; Cook, M.R.; Lenz, J.A.; Maritato, K.C.; Skorupski, K.A.; Wustefeld-Janssens, B.G.; Pellin, M.A.; Silveira, C.J.; Veytsman, S.; Selmic, L.E.; et al. Clinical Outcomes in Cats with Renal Carcinoma Undergoing Nephrectomy: A Retrospective Study. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2023, 21, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.G.; Hohenhaus, A.E.; Lamb, K.E. Incidence and Treatment of Feline Renal Lymphoma: 27 Cases. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 23, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A. Extranodal Lymphoma in the Cat: Prognostic Factors and Treatment Options. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.E.; Sola, M.F. Pathology in Practice. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 259, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Gupta, A.; Bhatt, S. Multimodality Imaging of Renal Lymphoma and Its Mimics. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, G.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Moloo, Z.; Girgis, S. Review of Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Common Subtypes in Radiology. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.; Ali, S.; Fishman, E. Imaging of Renal Lymphoma: Patterns of Disease with Pathologic Correlation. Radiographics 2006, 26, 1151–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickhardt, P.J.; Lonergan, G.J.; Davis, C.J.; Kashitani, N.; Wagner, B.J. From the Archives of the AFIP. Infiltrative Renal Lesions: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Radiographics 2000, 20, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufau, B.P.; Cerqueda, C.S.; Villalba, L.B.; Izquierdo, R.S.; González, B.M.; Molina, C.N. Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Radiologic Findings and Assessment of Response to Targeted Antiangiogenic Therapy by Using Multidetector CT. Radiographics 2013, 33, 1691–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.M.; Khajehasani, F.; Fatemi, I.; Ayoubpour, M.R. Tumoral Vascular Pattern in Renal Cell Carcinoma and Fat-Poor Renal Angiomyolipoma as a Novel Helpful Differentiating Factor on Contrast-Enhanced CT Scan. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317733144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolaki, E.; Bertazzo, S. Pathological Mineralization: The Potential of Mineralomics. Materials 2019, 12, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, B.A.; Fishman, E.K. Renal Lymphoma: CT Patterns with Emphasis on Helical CT. Radiographics 2000, 20, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.S.; Akin, O.; Shaish, H.; Luk, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, H.; Zabor, E.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Hakimi, A.A.; Zhao, B.; et al. Non-Enhancing Component of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma on CT Correlates with Tumor Necrosis, Stage, and as a Size-Independent Prognostic Biomarker. HHS Public Access. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2019, 43, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, D.S.; David, C.J.; Goldman, S.M.; Friedman, A.C.; Fritzsche, P. Renal Lymphoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation of 21 Cases. Radiology 1982, 144, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouh, M.A.A.M.; Inui, M.; Kakehi, Y. Renal Cell Carcinoma with IVC Thrombi; Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Clin. Med. Oncol. 2008, 2, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficarra, V.; Righetti, R.; D’Amico, A.; Rubilotta, E.; Novella, G.; Malossini, G.; Mobilio, G. Renal Vein and Vena Cava Involvement Does Not Affect Prognosis in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncology 2001, 61, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawindy, S.M.; Kurian, T.; Kim, T.; Mangar, D.; Armstrong, P.A.; Alsina, A.E.; Sheffield, C.; Sexton, W.J.; Spiess, P.E. Important Surgical Considerations in the Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) with Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Tumour Thrombus. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.N.; Henry, C.J.; Turnquist, S.E.; Tyler, J.W.; Liptak, J.M.; Rizzo, S.A.; Sfiligoi, G.; Steinberg, S.J.; Smith, A.N.; Jackson, T. Primary Renal Neoplasia of Dogs. J. Vet. Intern Med. 2006, 20, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, E.F.; Hess, A.M.; Powers, B.E. Prognostic Significance of Histologic Features in Canine Renal Cell Carcinomas: 70 Nephrectomies. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Kastl, B.; Cino-Ozuna, A.G.; Springer, N.L.; Thakkar, R.; Biller, D.; Whitehouse, W.; Easterwood, L.; Nguyen, T.A. Brief Report Feline Sarcomatoid Renal Cell Carcinoma with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis and Effusion. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 2022, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; He, W.; Guan, X.; Zu, X.; et al. Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Sarcomatoid Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
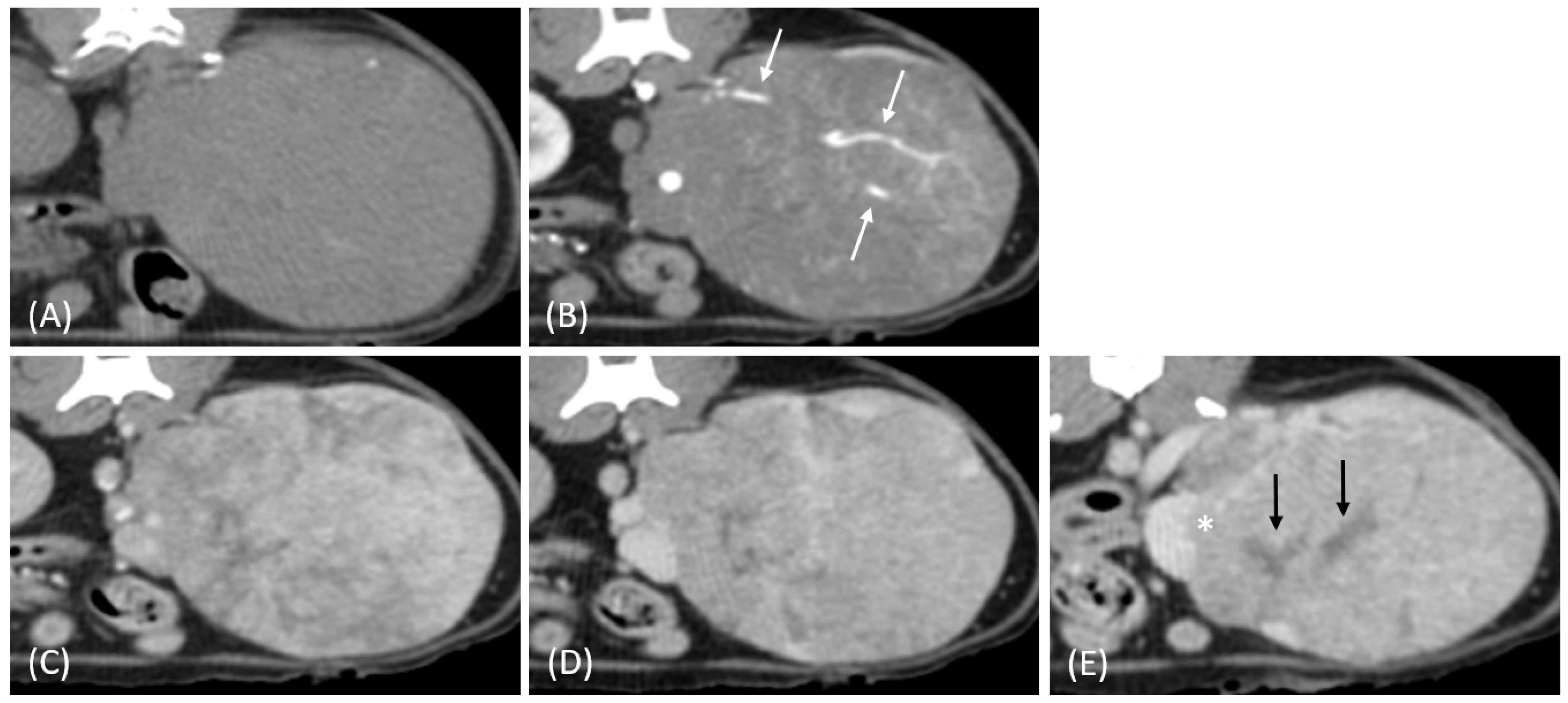
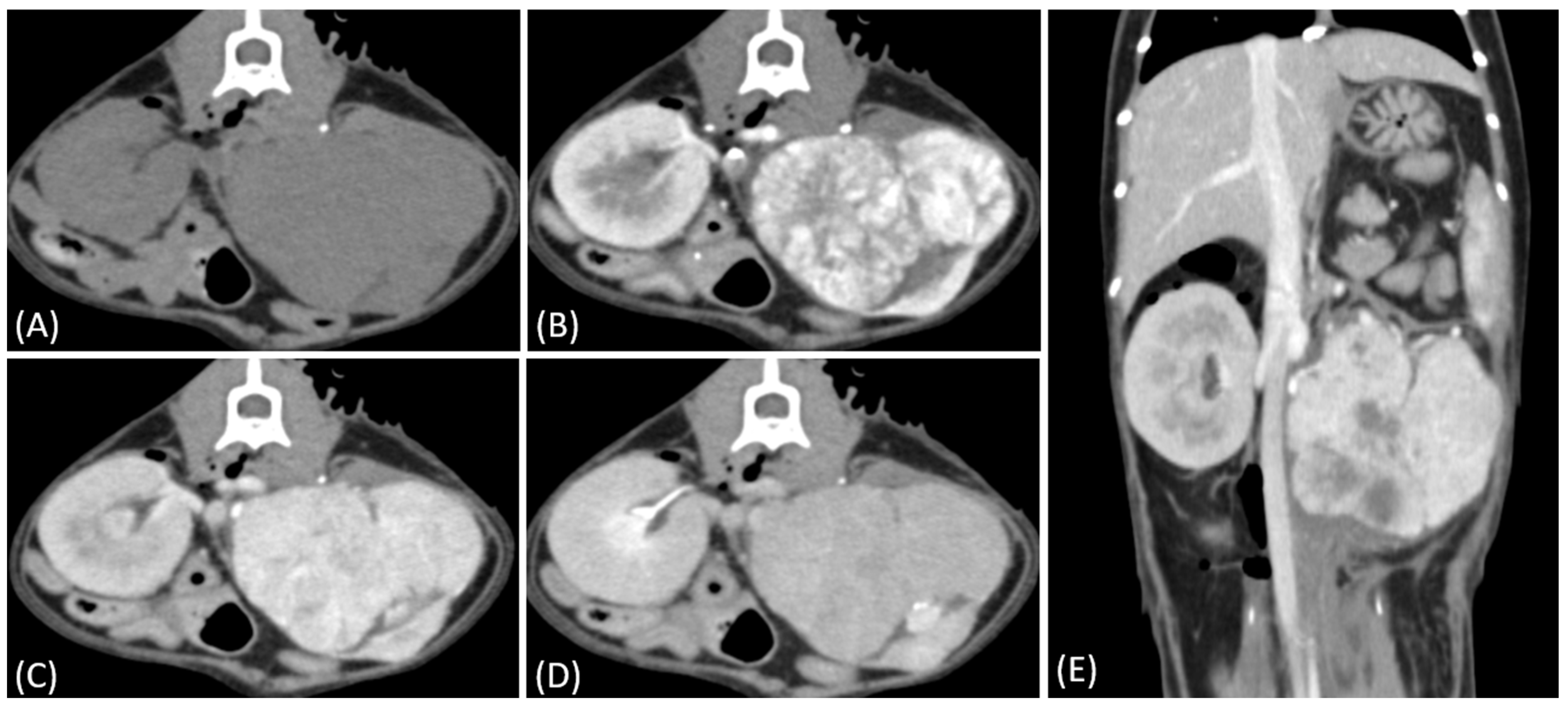
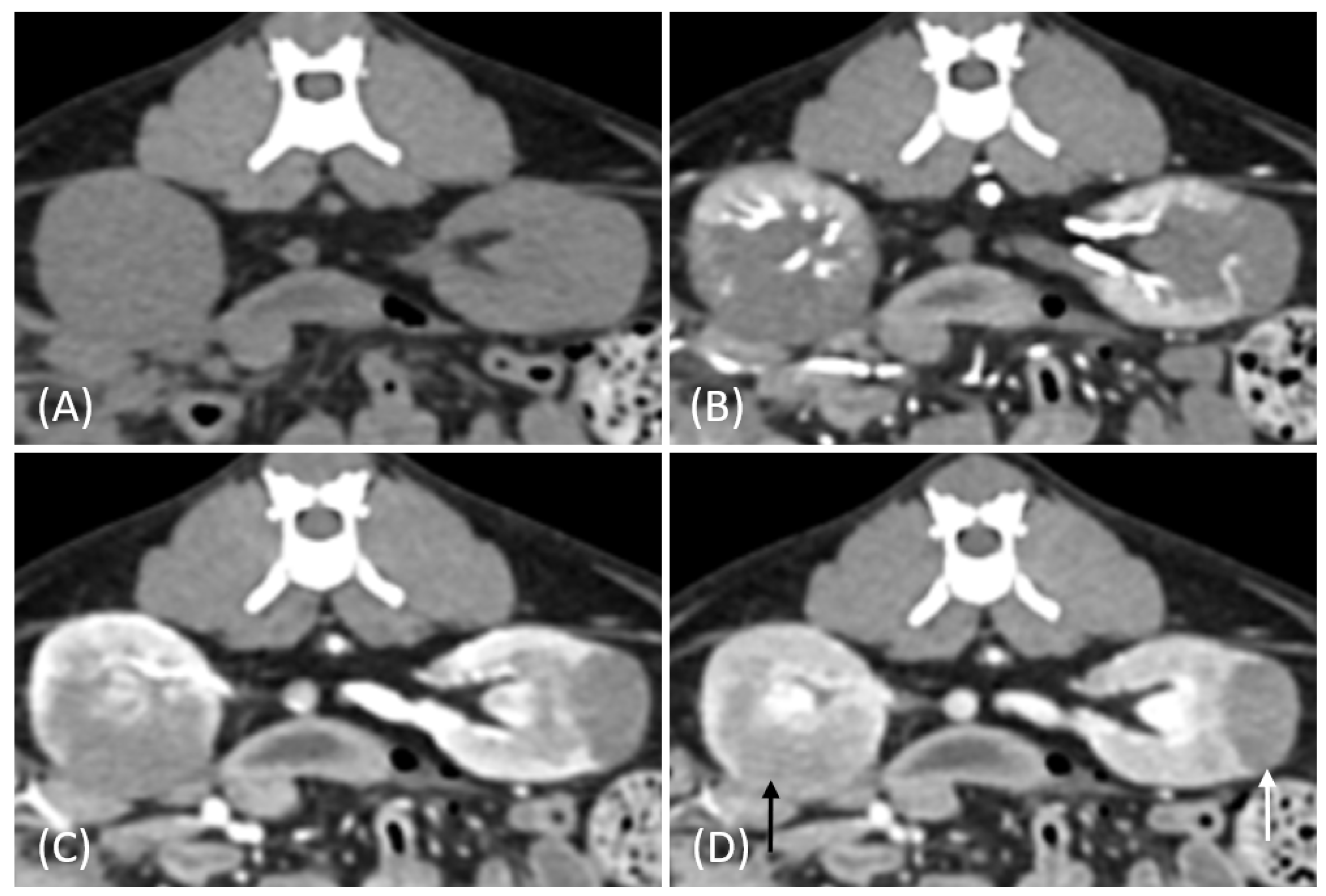
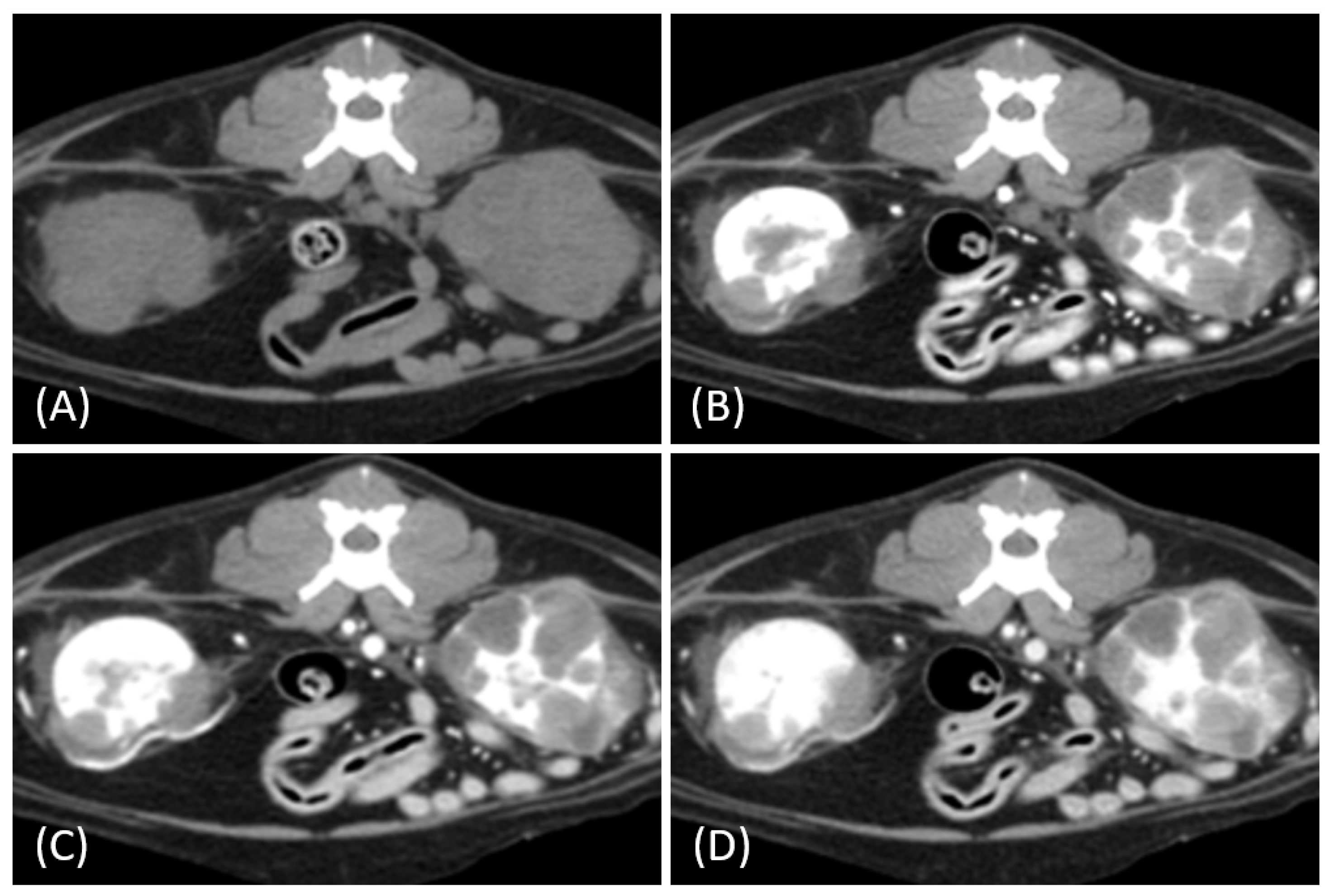


| CT Features | Distribution of Tumor Types | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCC | Lymphoma | ||
| Renal tumor involvement | Right (4/15) Left (10/15), Bilateral (1/15) | Right (2/10), Left (2/10), Bilateral (6/10) | 0.009 * |
| Number of lesions | Solitary (14/15) Multiple (1/15) | Solitary (2/10) Multiple (8/10) | <0.001 * |
| Growth pattern | Expansile (11/15) Infiltrative (3/15) Combined (1/15) | Expansile (2/10) Infiltrative (5/10) Combined (3/10) | 0.015 * |
| Hemorrhage | Present (8/15) | Present (1/10) | 0.040 * |
| Necrosis | Present (14/15) | Present (1/10) | <0.001 * |
| Spatial enhancement pattern | Homogeneous (0/13) Heterogeneous (13/13) | Homogeneous (9/10) Heterogeneous (1/10) | <0.001 * |
| Time-course enhancement pattern | Progressive (3/5) Plateau (2/5) | Progressive (6/6) Plateau (0/6) | 0.182 |
| Tumor vessel enhancement | Present (corticomedullary) (4/5) | Absent (0/6) | 0.015 * |
| Vascular invasion | Present (1/13) | Absent (0/10) | 1.000 |
| Mineralization | Present (4/15) | Absent (0/10) | 0.125 |
| Lymphadenopathy | Present (1/15) | Present (5/10) | 0.023 * |
| Pulmonary metastases | Present (1/15) | Present (1/10) | 1.000 |
| CT Phases | Mean Attenuation Value (HU) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCC | Lymphoma | |||
| Pre-contrast | 42.5 ± 6.2 (n = 13) | 42.3 ± 5.7 (n = 10) | 0.942 | |
| CMP | 107.0 ± 85.5 (n = 5) | 56.2 ± 8.3 (n = 6) | 0.255 | |
| NP | 143.2 ± 86.2 (n = 5) | 72.7 ± 22.0 (n = 6) | 0.142 | |
| Delayed NP/ Early EP | 175.2 ± 72.8 (n = 13) | 89.9 ± 24.2 (n = 10) | 0.001 * | |
| Aorta-based corrected AV | CMP | 180.2 ± 204.9 (n = 5) | 62.9 ± 46.1 (n = 6) | 0.126 |
| NP | 147.0 ± 89.4 (n = 5) | 84.1 ± 28.8 (n = 6) | 0.195 | |
| Delayed NP/ Early EP | 184.1 ± 63.2 (n = 13) | 93.7 ± 20.4 (n = 10) | <0.001 * | |
| Aorta-based relative AV | CMP | 4.1 ± 4.9 (n = 5) | 1.4 ± 1.1 (n = 6) | 0.126 |
| NP | 3.6 ± 2.2 (n = 5) | 1.8 ± 0.6 (n = 6) | 0.150 | |
| Delayed NP/ Early EP | 4.3 ± 1.2 (n = 13) | 2.2 ± 0.5 (n = 10) | <0.001 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, C.; Eom, K.; Kim, J.; Nam, A.; Joo, Y.; Jung, I.; Park, J.; Park, N.-w.; Lee, M.; Lee, D.-g.; et al. Computed Tomographic Characteristics of Feline Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040360
Shin C, Eom K, Kim J, Nam A, Joo Y, Jung I, Park J, Park N-w, Lee M, Lee D-g, et al. Computed Tomographic Characteristics of Feline Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040360
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Choye, Kidong Eom, Jaehwan Kim, Aryung Nam, Yewon Joo, Inseong Jung, Jihee Park, Noh-won Park, Minsu Lee, Dong-gil Lee, and et al. 2025. "Computed Tomographic Characteristics of Feline Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040360
APA StyleShin, C., Eom, K., Kim, J., Nam, A., Joo, Y., Jung, I., Park, J., Park, N.-w., Lee, M., Lee, D.-g., Yeo, S., & Yu, H. (2025). Computed Tomographic Characteristics of Feline Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040360





