Metabolic Bone Disease in Captive Flying Foxes: A Comprehensive Survey Across Zoological Parks
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey Development
2.2. Participant Recruitment and Survey Distribution
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Descriptive Analysis
2.3.2. Statistical Comparative Analysis of Symptomatic and Healthy Groups
3. Results
3.1. General Descriptive Analysis
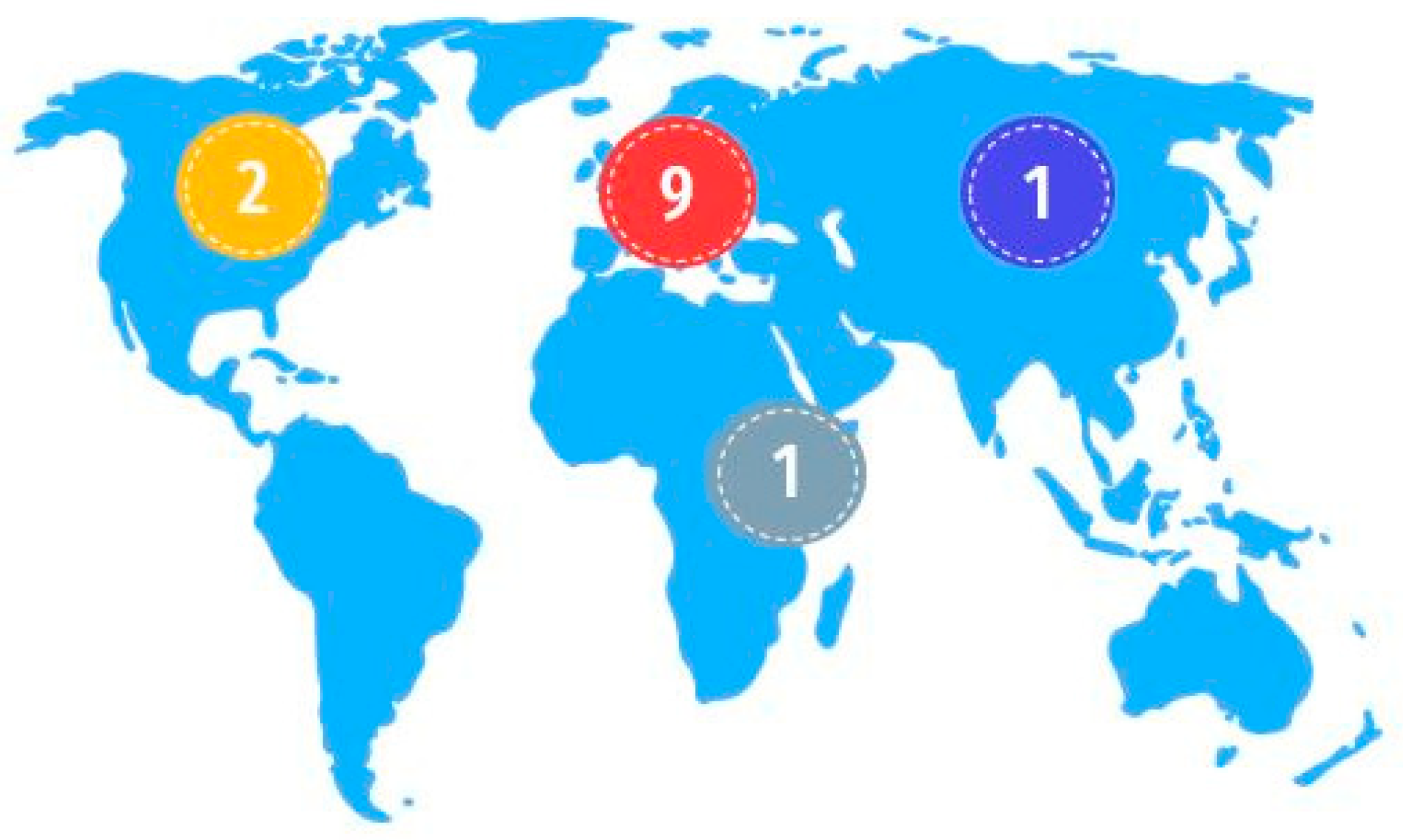
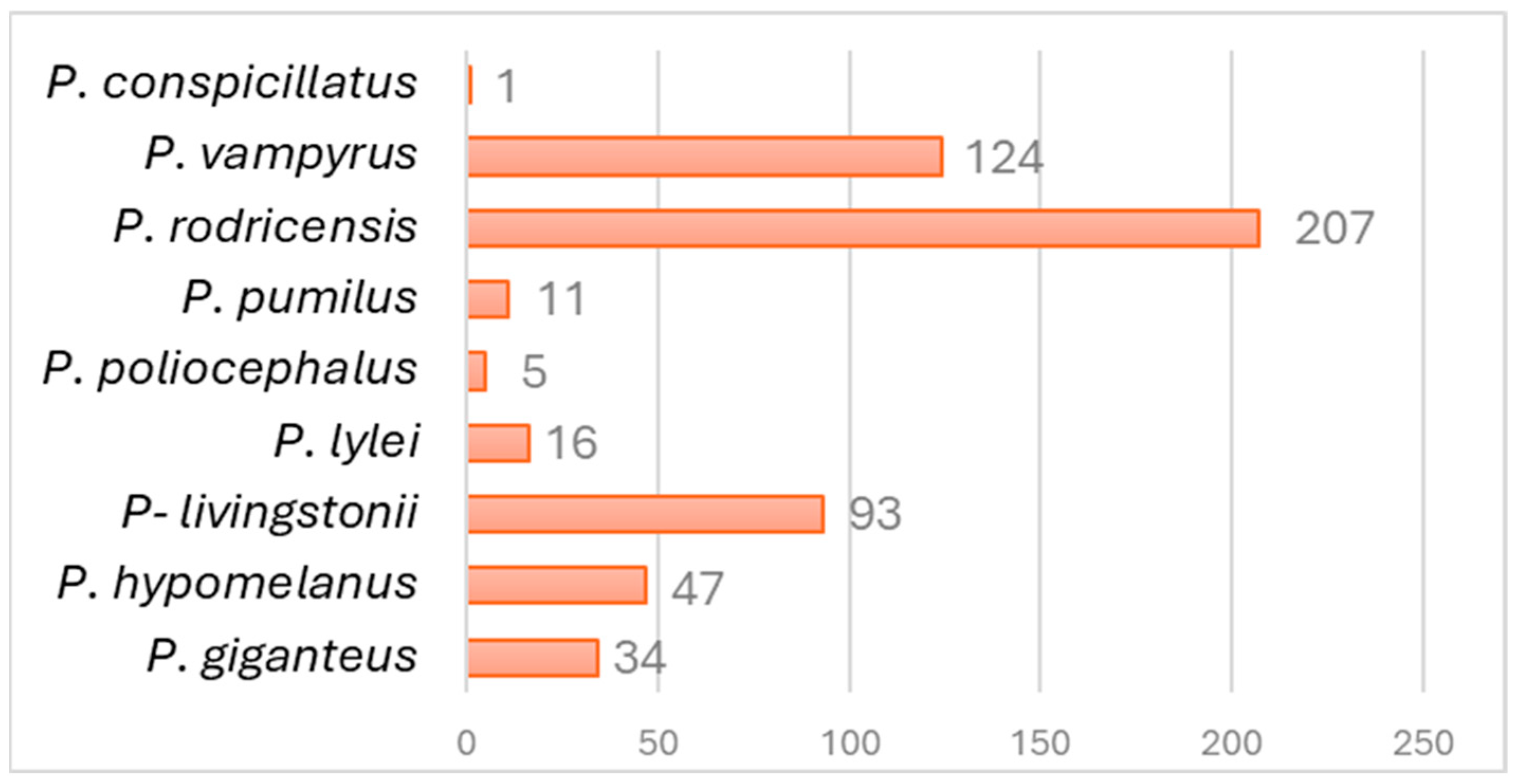
3.1.1. Zoological Parks: Location and Species
3.1.2. Diet
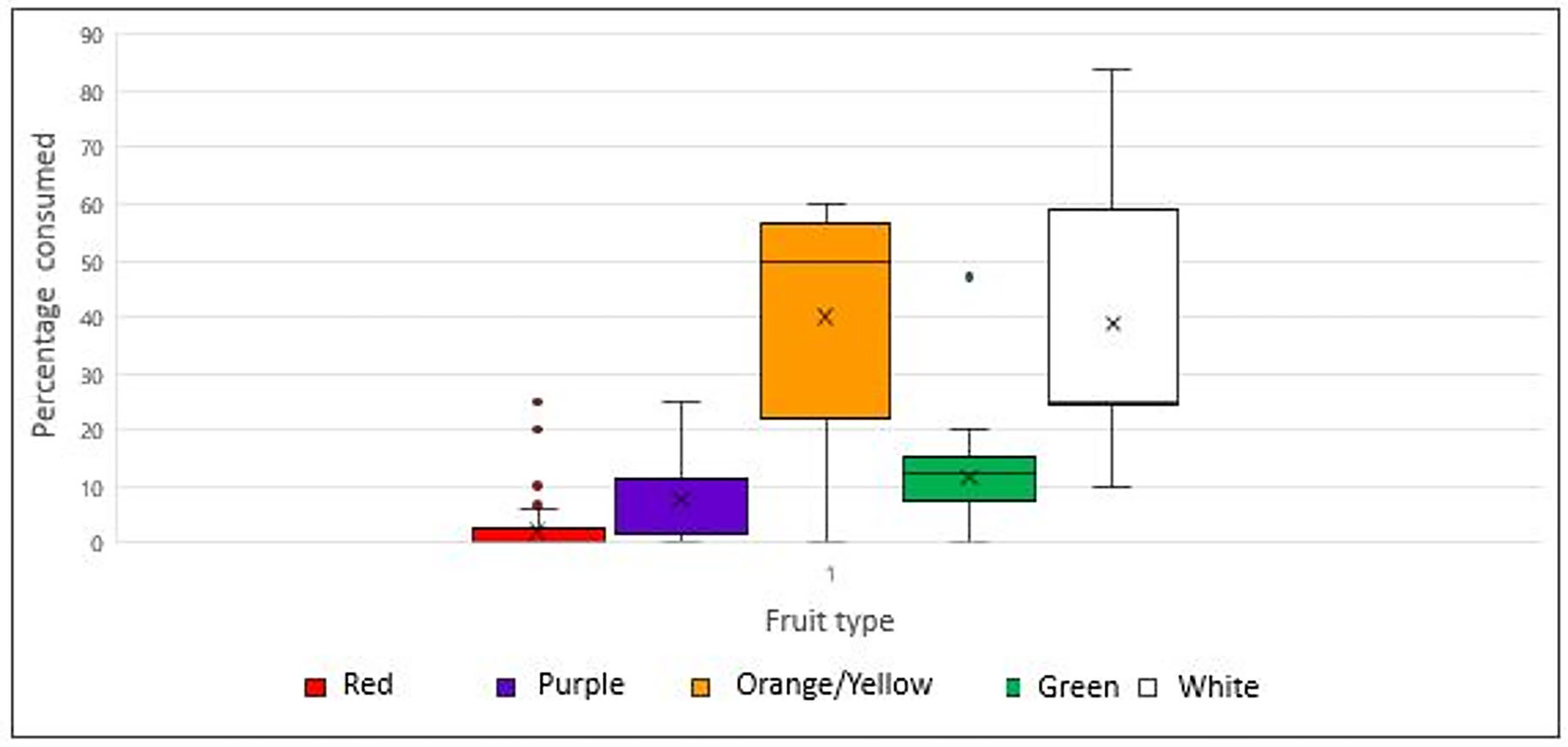
- Fruit and vegetables
- Animal products and other types of food used
- Use of nutritional supplements
3.1.3. Flying Fox Enclosures
- Enclosure dimensions (space per animal)
- Enclosure temperature
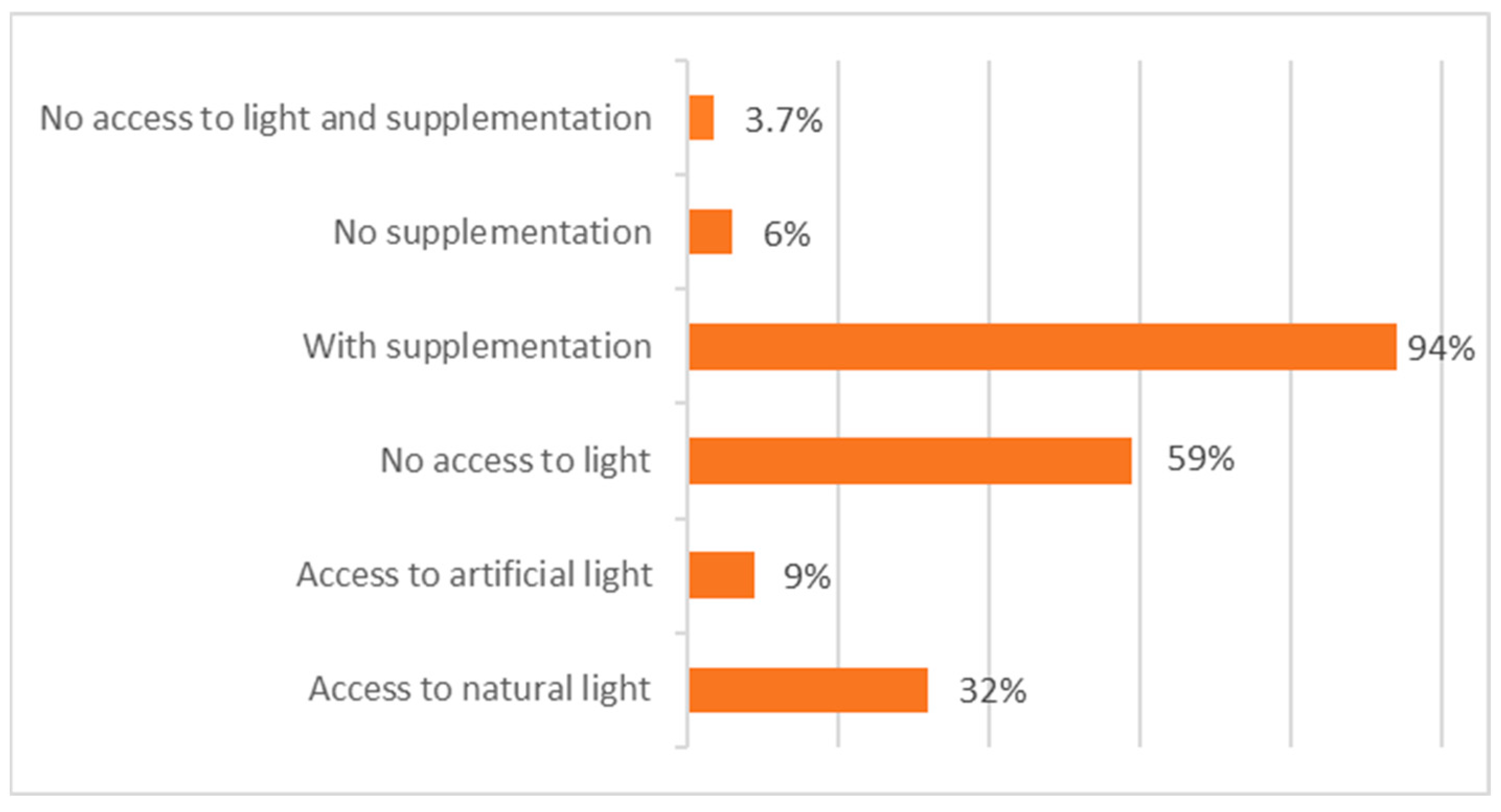
- Access to natural/artificial light (UVB radiation)
3.2. Descriptive Analysis of Metabolic Bone Disease Animals
3.2.1. Animals Affected
3.2.2. Diet
3.2.3. Enclosures
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Symptomatic and Healthy Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-8018-8221-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mickleburgh, S.P.; Hutson, A.M.; Racey, P.A. Old World Fruit Bats: An Action Plan for Their Conservation; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/en (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Cahyadi, D.; Nurhidayat, N.; Nisa, C.; Supratikno, S.; Novelina, S.; Setijanto, H.; Agungpriyono, S. Musculoskeletal Structure of the Shoulder and Arm in Large Flying Fox (Pteropus vampyrus). Biodivers. J. Biol. Divers. 2022, 23, 5902–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalyova, I. Key Morphofunctional Transformations in the Evolution of Bats (Mammalia, Chiroptera). Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 45, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.; Bernard, J.; Crissey, S.; Dierenfeld, E. Fruit Bats: Nutrition and Dietary Husbandrya. 2004. Available online: https://nagonline.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/NAG-FS014-FRUIT-BATS-AUG-2004.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Buckles, E.L. Chiroptera (Bats). In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine; Eric Miller, R., Fowler, M.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 8, pp. 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Duque-Márquez, A.; Ruiz-Ramoni, D.; Ramoni-Perazzi, P.; Muñoz-Romo, M. Bat Folivory in Numbers: How Many, How Much, and How Long? Acta Chiropterol. 2019, 21, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.G.; Gutierrez, E.; Hobson, K.A.; Altube, B.; Díaz, W.G.; Sánchez-Cordero, V. Sources of Assimilated Protein in Five Species of New World Frugivorous Bats. Oecologia 2002, 133, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellón, J.J.; Medina-Espinoza, E.F.; Lim, B.K.; Cornejo, F.; Medellín, R.A. Eat What You Can, When You Can: Relatively High Arthropod Consumption by Frugivorous Bats in Amazonian Peru. Mamm. Biol. 2023, 103, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, S.M. Bats in Captivity, Volume 3: Diet and Feeding—Environment and Housing; Bats in Captivity; Logos Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 3, ISBN 978-1-934899-07-6. [Google Scholar]
- AZA BAT TAG. Standardized Guidelines for Fruit and Nectar Bat Care 2004. Available online: https://www.battag.org/husbandry.html (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- LeBlanc, D. Fruit Bat Enrichment at The Lubee Foundation, Inc.; The Lubee Foundation, Inc.: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Welch; Smith, T.; Hosie, C.; Wormell, D.; Price, E.; Stanley, C.R. Social Experience of Captive Livingstone’s Fruit Bats (Pteropus livingstonii). Animals 2020, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.E.; Dittmer, K.E.; Thompson, K.G. Chapter 2—Bones and Joints. In Jubb, Kennedy & Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals: Volume 1, 6th ed.; Maxie, M.G., Saunders, W.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 16–163.e1. ISBN 978-0-7020-5317-7. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; McDonald, J.M. Disorders of Bone Remodeling. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünberg, W. Dystrophies Associated with Calcium, Phosphorus, and Vitamin D in Animals—Musculoskeletal System. Available online: https://www.msdvetmanual.com/musculoskeletal-system/dystrophies-associated-with-calcium,-phosphorus,-and-vitamin-d/dystrophies-associated-with-calcium,-phosphorus,-and-vitamin-d-in-animals (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Saliba, W.; El-Haddad, B. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Pathophysiology and Treatment. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. JABFM 2009, 22, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmel, B.; Johnson, R. Nutritional and Metabolic Diseases. In Reptile Medicine and Surgery in Clinical Practice; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 185–195. ISBN 978-1-118-97770-5. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams, D.; Leeson, S. Metabolic Bone Disease in Lizards: Prevalence and Potential for Monitoring Bone Health. Clin. Nutr. Reptil. Amphib. 2014, 120–129. Available online: https://nagonline.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/McWilliams-MetabolicBoneDiseaseinLizards.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Hoby, S.; Wenker, C.; Robert, N.; Jermann, T.; Hartnack, S.; Segner, H.; Aebischer, C.-P.; Liesegang, A. Nutritional Metabolic Bone Disease in Juvenile Veiled Chameleons (Chamaeleo calyptratus) and Its Prevention. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleros, M.; Buffenstein, R.; Ross, F.P.; Pettifor, J.M. Vitamin D Metabolism in a Frugivorous Nocturnal Mammal, the Egyptian Fruit Bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 133, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiecinski, G.G.; Zhiren, L.; Chen, T.C.; Holick, M.F. Observations on Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Calcium Concentrations from Wild-Caught and Captive Neotropical Bats, Artibeus Jamaicensis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2001, 122, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southworth, L.O.; Holick, M.F.; Chen, T.-C.; Kunz, T.H. Variation in Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in Free-Ranging New-World Tropical Bats. Acta Chiropterol. 2009, 11, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, L.O.; Holick, M.F.; Chen, T.C.; Kunz, T.H. Effects of Sunlight on Behavior and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Two Species of Old World Fruit Bats. Dermato-Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.A.; Freitas, M.B.; da Matta, S.L.P.; Novaes, R.D.; Gonçalves, R.V. Is Bone Loss a Physiological Cost of Reproduction in the Great Fruit-Eating Bat Artibeus Lituratus? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, G.G.; Krook, L.; Wimsatt, W.A. Annual Skeletal Changes in the Little Brown Bat, Myotis Lucifugus Lucifugus, with Particular Reference to Pregnancy and Lactation. Am. J. Anat. 1987, 178, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, V.R. Pathological Conditions in British Bats. In Proceedings of the European Wildlife Disease Association 1st Conference, Paris, France, 22–24 November 1994; Available online: https://ewda.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/EWDA-1st-Conference-Paris-22-24-Nov-1994-Abstracts-part-1_rotated.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Lollar, A. The Rehabilitation and Captive Care of Insectivorous Bats 2018. Available online: https://batworld.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/E-Book-The-Rehabilitation-and-Captive-Care-of-Insectivorous-Bats.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Kirejczyk, S.G.M.; Goodwin, C.; Gyimesi, Z.S.; Zachariah, T.T.; Sturgeon, G.L.; Armwood, A.R.; Frontera-Acevedo, K.; Kokosinksa, A.; Seguel, M.; Fogelson, S.B.; et al. A Retrospective Study of Pathology in Bats Submitted to an Exotic and Zoo Animal Diagnostic Service in Georgia, USA (2008–2019). J. Comp. Pathol. 2021, 185, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Species360. Zoological Information Management System (ZIMS) 2023. Available online: https://species360.org/zims/ (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Barnard, S.M. Bats in Captivity 1: Biological and Medical Aspets; Logos Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 1, ISBN 978-1-934899-03-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, A.; Ravasco, F.; Oliveira, L.; Dias, M.G. Tabela da Composição de Alimentos portuguesa: Da compilação à atualização. 2023. Available online: https://www.rcaap.pt/detail.jsp?id=oai:repositorio.insa.pt:10400.18/8750 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Courts, S.E. Dietary Strategies of Old World Fruit Bats (Megachiroptera, Pteropodidae): How Do They Obtain Sufficient Protein? Mammal Rev. 1998, 28, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulscher, L.A.; Dierenfeld, E.S.; Welbergen, J.A.; Rose, K.A.; Phalen, D.N. A Comparison of Nutritional Value of Native and Alien Food Plants for a Critically Endangered Island Flying-Fox. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.E. Stress. In Restraint and Handling of Wild and Domestic Animals; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, A.R.; Holick, M.F. The Role of Sunlight in the Cutaneous Production of Vitamin D3. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1988, 8, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, D.; Stabenfeldt, G.H. Metabolismo do cálcio e do fosfato. In Tratado de Fisiologia Veterinária; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, A.R. Who, What, Where and When-Influences on Cutaneous Vitamin D Synthesis. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2006, 92, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enderli, T.A.; Burtch, S.R.; Templet, J.N.; Carriero, A. Animal Models of Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Applications in Clinical Research. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Other Food Items | Number of Animals |
|---|---|
| Cereal (oatmeal) | 6 |
| Primate food | 297 |
| Dry feed of frugivorous birds | 30 |
| Dry dog food | 32 |
| Characteristics | Zoological Park 1 | Zoological Park 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Species | Pteropus vampyrus | Pteropus vampyrus |
| Number MBD/total animals | 6/23 animals | 3/12 animals |
| Onset age | <3 month | <3 month |
| Diet | ||
| Orange/yellow fruits (%) | 37.03 | 44.5 |
| White fruits (%) | 51.87 | 33.3 |
| Red fruits (%) | 3.7 | 11.1 |
| Purple/blue fruits (%) | 3.7 | 11.1 |
| Green fruits (%) | 3.7 | Not provided |
| Other types of food used | Cottage cheese, yogurt, raw eggs, nectar | Not provided |
| Nutritional supplements | Calcium, vitamin D3, yeast, human supplements | Calcium |
| Nutritional plan | Yes | Yes |
| Enclosures | ||
| Dimensions | Not ideal | Ideal |
| Temperature | Not ideal | Not ideal |
| Natural light | No | No |
| Artificial light | Yes | No |
| Outcome | All alive | 2/3 Euthanized |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faim, D.; Silva, F.; Weissenbacher, A.; Starnberger, I.; Pires, I. Metabolic Bone Disease in Captive Flying Foxes: A Comprehensive Survey Across Zoological Parks. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030271
Faim D, Silva F, Weissenbacher A, Starnberger I, Pires I. Metabolic Bone Disease in Captive Flying Foxes: A Comprehensive Survey Across Zoological Parks. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030271
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaim, Diana, Filipe Silva, Anton Weissenbacher, Iris Starnberger, and Isabel Pires. 2025. "Metabolic Bone Disease in Captive Flying Foxes: A Comprehensive Survey Across Zoological Parks" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030271
APA StyleFaim, D., Silva, F., Weissenbacher, A., Starnberger, I., & Pires, I. (2025). Metabolic Bone Disease in Captive Flying Foxes: A Comprehensive Survey Across Zoological Parks. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030271








