Quantitative Analysis of 137 MRI Images in Hydrocephalic Dogs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Data Acquisition
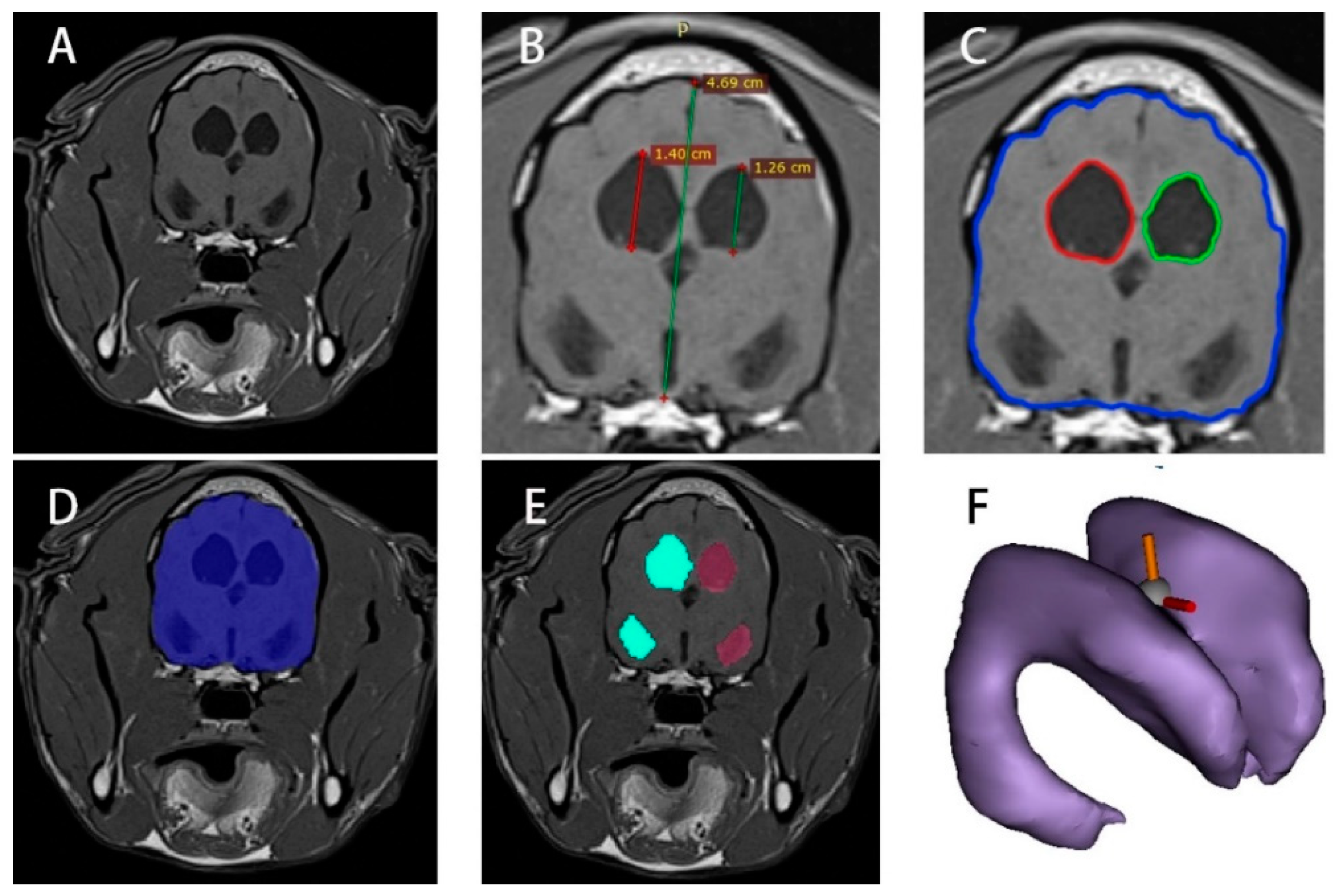
2.2. MRI Image Height Processing of Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
2.3. MRI Image Area Processing of Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
2.4. MRI Image Volume Processing of Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
2.5. Quantitative Analysis of Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
2.6. Regression Analysis of Hydrocephalus Cases
3. Results
3.1. Retrospective Analysis of Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
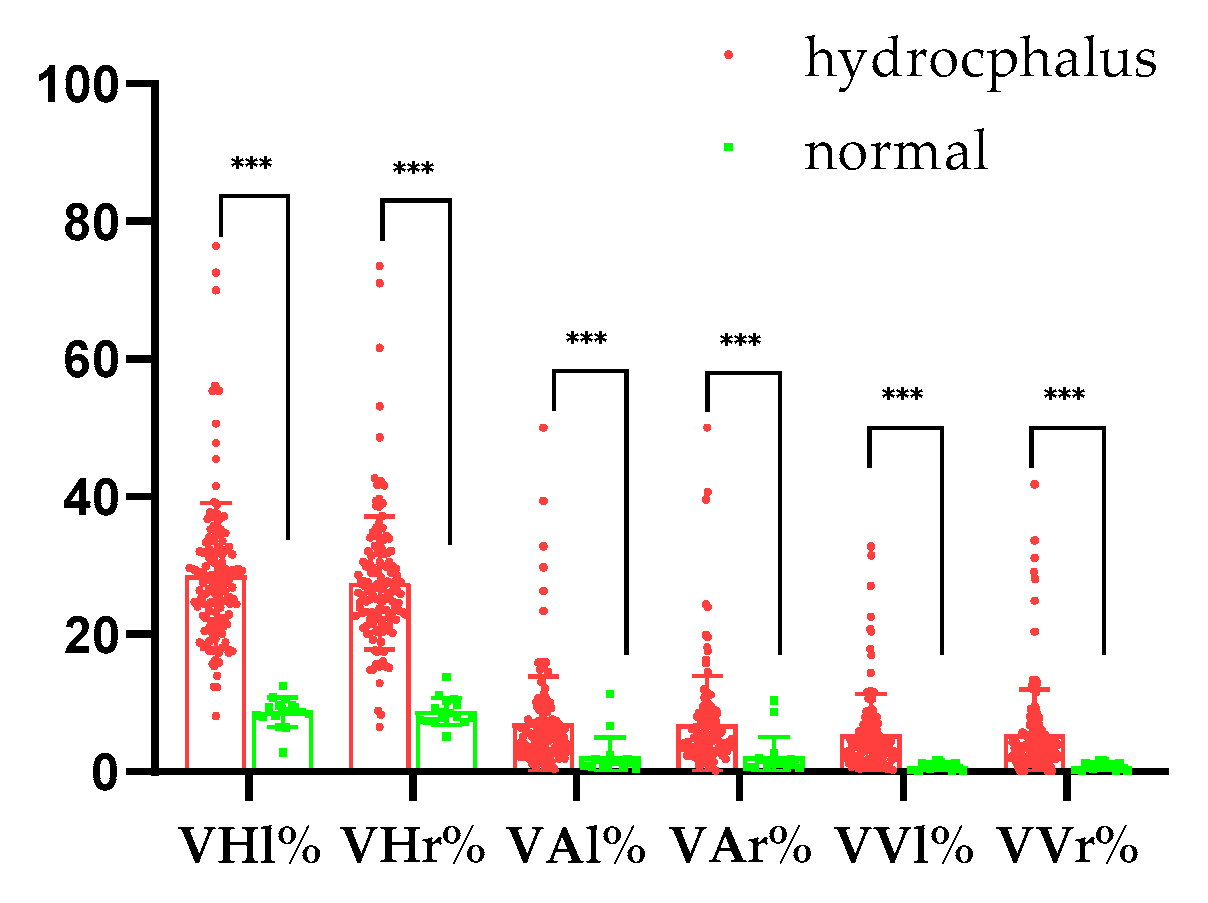
3.2. Left and Right Ventricle and Brain Heights in Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
3.3. Left and Right Ventricles and Brain Areas in Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
3.4. Left and Right Ventricle and Brain Volumes in Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
3.5. Quantitative Analysis Results for Normal and Hydrocephalus Cases
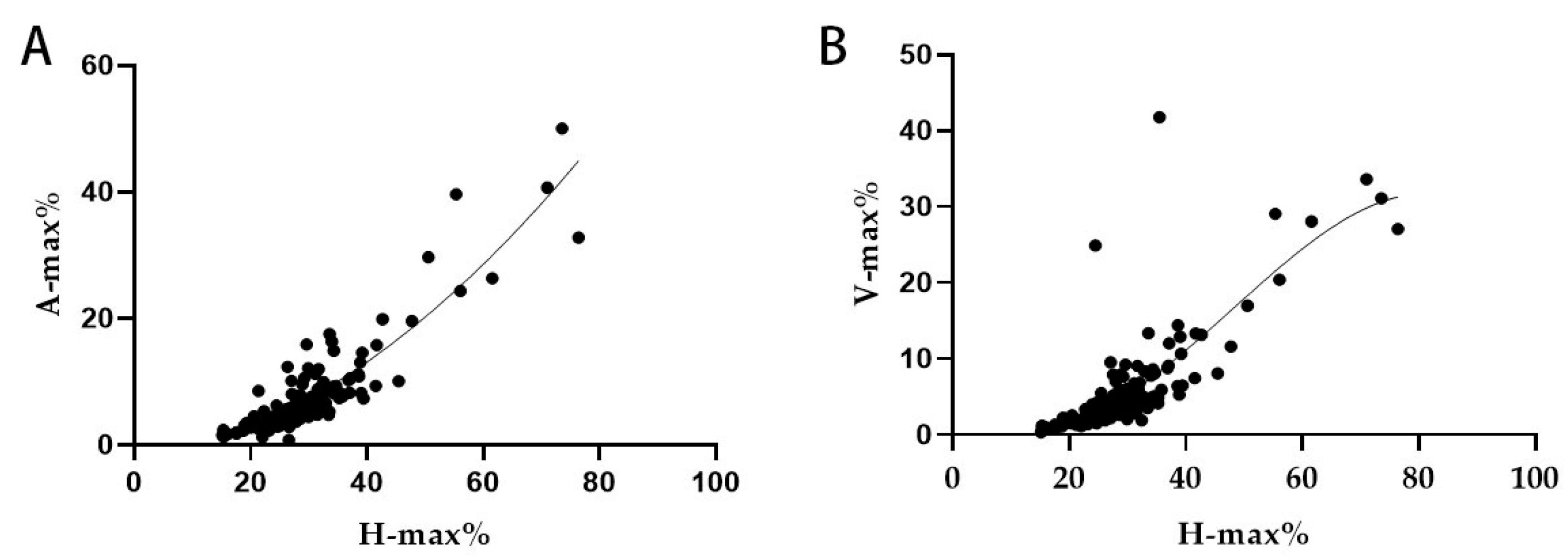
3.6. Regression Analysis Result for the Hydrocephalus Cases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Aiyan, A.; Balan, R.; Ghebrehiwot, E.; Mihreteab, Y.; Zerom, S.; Gebreigziabiher, S.; AlDarwich, A.; Willingham, A.L.; Kishore, U. Mapping of the exterior architecture of the mesocephalic canine brain. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, S.; Gilbert, Z.; De Decker, S. Results of oral prednisolone administration or ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement in dogs with congenital hydrocephalus: 40 cases (2005–2016). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 254, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Ondreka, N. Hydrocephalus in animals. Pediatr. Hydrocephalus 2019, 53–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstetler, A.; Raskin, J.; Blazer-Yost, B.L. Hydrocephalus: Historical analysis and considerations for treatment. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farke, D.; Olszewska, A.; Büttner, K.; Schmidt, M.J. Association among raised intraventricular pressure, clinical signs, and magnetic resonance imaging findings in dogs with congenital internal hydrocephalus. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farke, D.; Siwicka, A.K.; Olszewska, A.; Czerwik, A.; Büttner, K.; Schmidt, M.J. Risk factors, treatment, and outcome in dogs and cats with subdural hematoma and hemispheric collapse after ventriculoperitoneal shunting of congenital internal hydrocephalus. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J.R.; Axlund, T.W.; Dewey, C.; Smith, J. Hydrocephalus in dogs and cats. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. 2006, 28, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwik, A.; Schmidt, M.J.; Olszewska, A.; Hinz, S.; Büttner, K.; Farke, D. Reliability and interobserver variability of a grading system of ventricular distension in dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1271545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, J.; Bernardini, M.; Rusbridge, C.; Boudreau, E.; Santifort, K.; Glass, E.; Shores, A.; Green, L.; Ortega, M.; Dutil, G. Clinical Findings, MRI Features, and Short-Term Outcome of Medium-to-Large Breed Dogs with Hydrocephalus. In Proceedings of the 34th Symposium of the European Society of Veterinary Neurology—Spinal Cord Injury, Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 23–24 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, C.; Tanaka, N.; Sekiguchi, N.; Kitagawa, M.; Ito, D. Cerebrospinal fluid flow in small-breed dogs with idiopathic epilepsy observed using time-spatial labeling inversion pulse images: A preliminary study. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 86, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, K.A.; Sharp, N.J. Ultrasonographic imaging of the lateral cerebral ventricles in the dog. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 1990, 31, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Ratsch, B.; Kneissl, S.; Gabler, C. Comparative evaluation of the ventricles in the Yorkshire Terrier and the German Shepherd dog using low-field MRI. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2001, 42, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, D.; Choi, C.; Nam, J.; Ryu, K.; Jahng, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Ahn, K. Quantitative analysis of hydrocephalic ventricular alterations in Yorkshire terriers using magnetic resonance imaging. Vet. Med. 2010, 55, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubner, S.; Ondreka, N.; Failing, K.; Kramer, M.; Schmidt, M.J. Magnetic resonance imaging signs of high intraventricular pressure-comparison of findings in dogs with clinically relevant internal hydrocephalus and asymptomatic dogs with ventriculomegaly. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, A.K.; Holl, E.; Kitchen, N.D.; Watkins, L.D. Evans’ Index Revisited: The Need for an Alternative in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estey, C.M. Congenital hydrocephalus. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 46, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramall, A.N.; Anton, E.S.; Kahle, K.T.; Fecci, P.E. Navigating the ventricles: Novel insights into the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus. EBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekate, H.L. A consensus on the classification of hydrocephalus: Its utility in the assessment of abnormalities of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2011, 27, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.B. Hydrocephalus in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, S.; Fleck, S.; Baldauf, J.; Mensel, B.; Kühn, J.P.; Kirsch, M. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Hydrocephalus in Adults. Rofo 2017, 189, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missori, P.; Rughetti, A.; Peschillo, S.; Gualdi, G.; Di Biasi, C.; Nofroni, I.; Marinelli, L.; Fattapposta, F.; Currà, A. In normal aging ventricular system never attains pathological values of Evans’ index. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Yamada, S.; Miyajima, M.; Ishii, K.; Kuriyama, N.; Kazui, H.; Kanemoto, H.; Suehiro, T.; Yoshiyama, K.; Kameda, M.; et al. Guidelines for Management of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (Third Edition): Endorsed by the Japanese Society of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2021, 61, 63–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarı, E.; Sarı, S.; Akgün, V.; Özcan, E.; Ìnce, S.; Babacan, O.; Saldır, M.; Açıkel, C.; Başbozkurt, G.; Yeşilkaya, Ş.; et al. Measures of Ventricles and Evans’ Index: From Neonate to Adolescent. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2015, 50, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, B.P. Neuroimaging in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2015, 9, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyborowska, P.; Adamiak, Z.; Zhalniarovich, Y. Quantification of cerebral lateral ventricular volume in cats by low- and high-field MRI. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.j.; Lee, K.J.; Ahn, S.J.; Kwon, Y.H.; Jung, K.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, Y.W. Comparative evaluation of the lateral ventricles with computed tomography in Yorkshire Terrier, Maltese, and Shih-Tzu dogs. J. Vet. Clin. 2011, 28, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kii, S.; Uzuka, Y.; Taura, Y.; Nakaichi, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Inokuma, H.; Onishi, T. Magnetic resonance imaging of the lateral ventricles in beagle-type dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 1997, 38, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellathurai, A.; Subbiah, K.; Abdul Ajis, B.N.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Gnanasigamani, S. Role of 3D SPACE sequence and susceptibility weighted imaging in the evaluation of hydrocephalus and treatment-oriented refined classification of hydrocephalus. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2018, 28, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guil-Ibáñez, J.J.; García-Pérez, F.; Gomar-Alba, M.; Huete-Allut, A.; Narro-Donate, J.M.; Masegosa-González, J. ETV as treatment for obstructive hydrocephalus in an aneurysmal malformation of the vein of Galen in infants: Case report and review of literature. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Normal (n = 17) | Hydrocephalus (n = 137) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 6.24 ± 4.41 | 5.85 ± 4.77 | 0.751340 |
| Body Weight | 7.71 ± 2.82 | 6.13 ± 6.49 | 0.325334 |
| Sex | Female: 8 Male: 9 | Female: 73 Male: 64 | |
| Clinical Symptoms | Disorientation: 27.74% (Dogs: 38) Ataxia: 14.60% (Dogs: 20) Head tilt: 9.49% (Dogs: 13) |
| Normal (n = 17) | Hydrocephalus (n = 137) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VHl (mm) | 3.17 ± 0.96 | 8.99 ± 5.42 | 0.000020 |
| VHr (mm) | 3.21 ± 0.92 | 8.59 ± 5.08 | 0.000026 |
| BH (mm) | 36.35 ± 5.20 | 31.81 ± 12.48 | 0.140816 |
| Normal (n = 17) | Hydrocephalus (n = 137) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VAl (mm2) | 18.13 ± 8.31 | 123.10 ± 215.00 | 0.046458 |
| VAr (mm2) | 17.52 ± 8.59 | 119.80 ± 211.70 | 0.048792 |
| BA (mm2) | 1279.00 ± 482.00 | 1747.00 ± 985.30 | 0.055857 |
| Normal (n = 17) | Hydrocephalus (n = 137) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VVl (mm3) | 506.50 ± 386.20 | 2755.00 ± 6247.00 | 0.141055 |
| VVr (mm3) | 493.10 ± 370.30 | 2646.00 ± 6194.00 | 0.155121 |
| BV (mm3) | 61,134.00 ± 21,383.00 | 50,906.00 ± 31,346.00 | 0.193463 |
| Correlation | H-Max% | A-Max% | V-Max% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman | H-max% | Correlation coefficient | 1 | 0.894 ** | 0.792 ** |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 137 | 137 | 137 | ||
| A-max% | Correlation coefficient | 0.883 ** | 1 | 0.777 ** | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 137 | 137 | 137 | ||
| V-max% | Correlation coefficient | 0.792 ** | 0.796 ** | 1 | |
| Sig. (two-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 137 | 137 | 137 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, X.; Geng, D.; Xie, Q.; Hu, C. Quantitative Analysis of 137 MRI Images in Hydrocephalic Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030221
Zhuang H, Yang Q, Zhang L, Xiang X, Geng D, Xie Q, Hu C. Quantitative Analysis of 137 MRI Images in Hydrocephalic Dogs. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030221
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Hao, Qiqing Yang, Lin Zhang, Xiaosong Xiang, Dandan Geng, Qiyun Xie, and Changmin Hu. 2025. "Quantitative Analysis of 137 MRI Images in Hydrocephalic Dogs" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030221
APA StyleZhuang, H., Yang, Q., Zhang, L., Xiang, X., Geng, D., Xie, Q., & Hu, C. (2025). Quantitative Analysis of 137 MRI Images in Hydrocephalic Dogs. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030221






