SideCow-VSS: A Video Semantic Segmentation Dataset and Benchmark for Intelligent Monitoring of Dairy Cows Health in Smart Ranch Environments
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
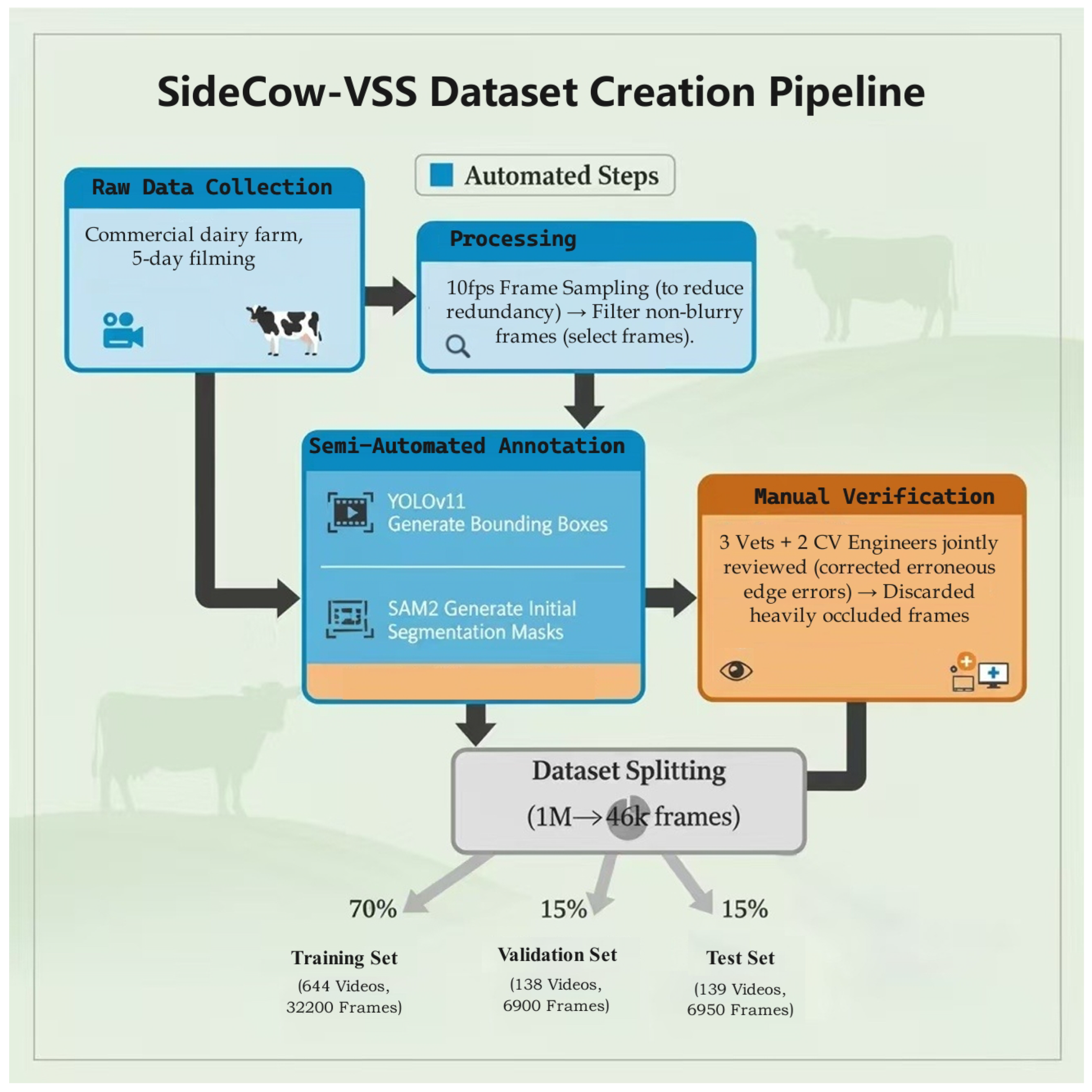
2.1. Dataset Construction
2.2. Benchmark Models
2.3. Implementation Details and Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Comparison
3.2. Accuracy Versus Speed Trade-Off
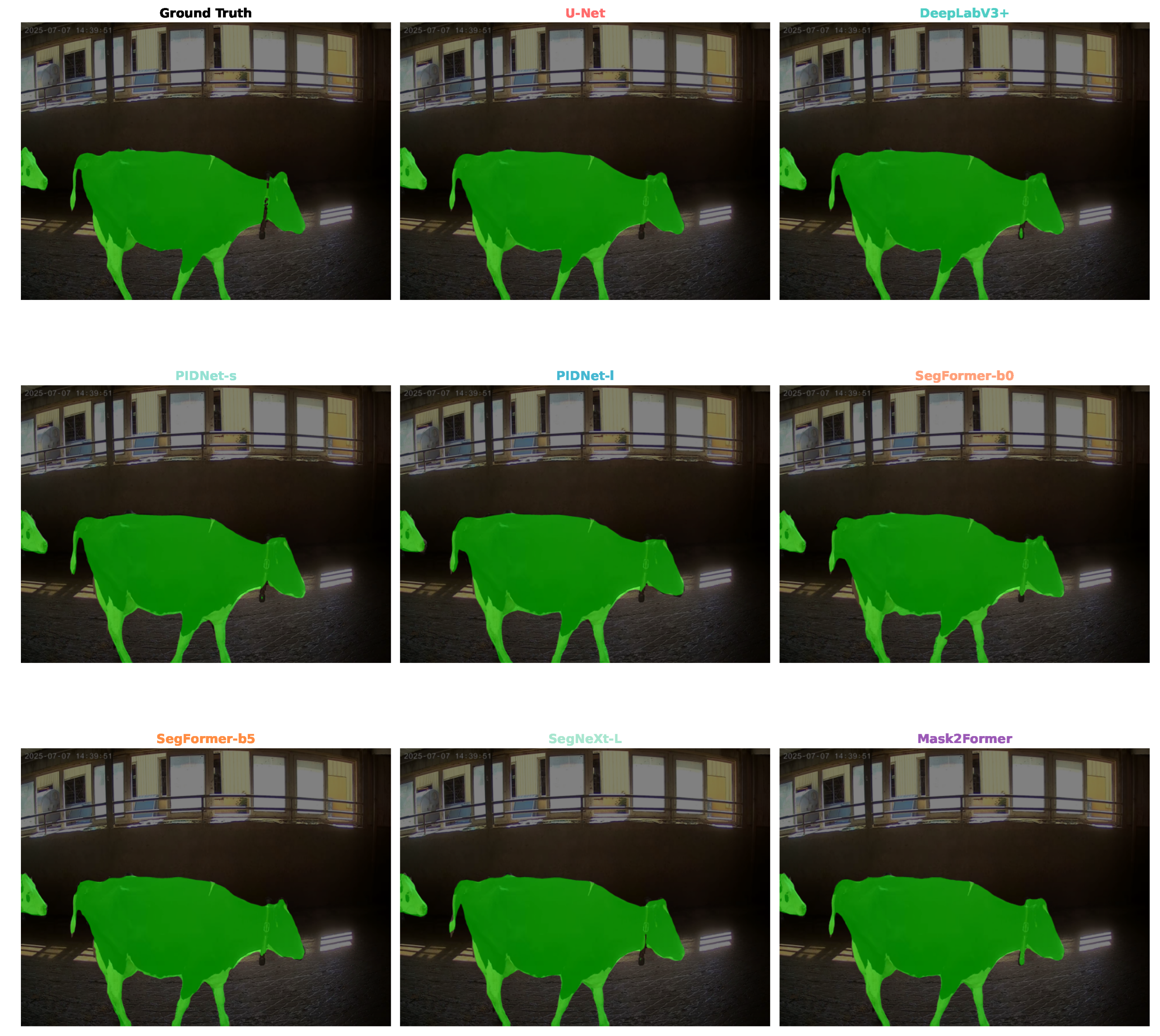
3.3. Qualitative Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BCS | Body Condition Scoring |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| mDice | mean Dice Coefficient |
| mIoU | mean Intersection over Union |
| MOT | Multi-Object Tracking |
| PLF | Precision Livestock Farming |
| SAM2 | Segment Anything Model 2 |
| SOTA | State-of-the-Art |
Appendix A. Model-Specific Hyperparameters
| Model | Backbone | Batch | Optimizer | Base LR | W-Decay | LR Sched. | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | — | 4 | SGD | Poly | Standard Augmentation | ||
| DeepLabV3+ | ResNet-101 | 4 | SGD | Poly | SyncBN enabled | ||
| PIDNet-s | — | 4 | SGD | Poly | — | ||
| PIDNet-l | — | 2 | SGD | Poly | — | ||
| SegFormer-b0 | MiT-b0 | 4 | SGD | Poly | — | ||
| SegFormer-b5 | MiT-b5 | 4 | SGD | Poly | — | ||
| SegNeXt-L | MSCAN-L | 2 | AdamW | Lin. + Poly | Head lr_mult = 10 | ||
| Mask2Former | Swin-L | 1 | AdamW | 0.05 | Poly | Grad. clip (0.01) |
References
- Raboisson, D.; Mounié, M.; Maigné, E. Diseases, reproductive performance, and changes in milk production associated with subclinical ketosis in dairy cows: A meta-analysis and review. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArt, J.A.A.; Nydam, D.V.; Oetzel, G.R. Epidemiology of subclinical ketosis in early lactation dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5056–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, N.; Gabeur, V.; Hu, Y.T.; Hu, R.; Ryali, C.; Ma, T.; Khedr, H.; Rädle, R.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; et al. Sam 2: Segment anything in images and videos. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.00714. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willshire, J.A.; Bell, N.J. An economic review of cattle lameness. Cattle Pract. 2009, 17, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Banhazi, T.M.; Lehr, H.; Black, J.L.; Crabtree, H.; Schofield, P.; Tscharke, M.; Berckmans, D. Precision livestock farming: An international review of scientific and commercial aspects. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabucci, G.; Evangelista, C.; Girotti, P.; Viola, P.; Spina, R.; Ronchi, B.; Bernabucci, U.; Basiricò, L.; Turini, L.; Mantino, A.; et al. Precision livestock farming: An overview on the application in extensive systems. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 24, 859–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognoli, V.; Presutti, L.; Bovo, M.; Torreggiani, D.; Tassinari, P. Computer Vision in Dairy Farm Management: A Literature Review of Current Applications and Future Perspectives. Animals 2025, 15, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.R.; Arroqui, M.; Manqude, P.; Toloz, J. Advances in automatic detection of body condition score of cows. A. mini review. J. Dairy Vet. Anim. Res. 2017, 5, 00149. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; Van Mourik, S.; Koerkamp, P.W.G.G.; Van Der Tol, P.P.J. Automated body condition scoring of dairy cows using 3-dimensional feature extraction from multiple body regions. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4294–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, J.D.; Galligan, D.T.; Thomsen, N. Principal descriptors of body condition score in Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’leary, N.W.; Byrne, D.T.; O’Connor, A.H.; Shalloo, L. Invited review: Cattle lameness detection with accelerometers. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3895–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Liang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, G. Accuracy of Detecting Degrees of Lameness in Individual Dairy Cattle Within a Herd Using Single and Multiple Changes in Behavior and Gait. Animals 2025, 15, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, G. Accurate Detection of Lameness in Dairy Cattle with Computer Vision: A New and Individualized Detection Strategy Based on the Analysis of the Supporting Phase. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10628–10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezen, R.; Edan, Y.; Halachmi, I. Computer vision system for measuring individual cow feed intake using RGB-D camera and deep learning algorithms. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 172, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, D. Cattle body detection based on YOLOv5-ASFF for precision livestock farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbálek, R.; Ufitikirezi, J.d.D.M.; Zoubek, T.; Umurungi, S.N.; Stehlík, R.; Havelka, Z.; Kuneš, R.; Bartoš, P. Computer vision-based approaches to cattle identification: A comparative evaluation of body texture, QR code, and numerical labelling. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 70, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Bytetrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Qin, L. YOLO-BYTE: An efficient multi-object tracking algorithm for automatic monitoring of dairy cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ren, H.; Xie, X.; Cao, Y. A Review of Multi-Object Tracking in Recent Times. IET Comput. Vis. 2025, 19, e70010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xing, J.; Milan, A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Kim, T.K. Multiple object tracking: A literature review. Artif. Intell. 2021, 293, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Janga, K.R.; Ramesh, R. IoT-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion Framework for Livestock Health Monitoring, Prediction, and Decision-Making Operations. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 11, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Xiao, Z.; Fan, H. Animaltrack: A benchmark for multi-animal tracking in the wild. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.; Prabhune, O.C.; Raskar, U.; Panditharatne, D.; Chung, H.; Choi, C.; Kim, Y. MmCows: A Multimodal Dataset for Dairy Cattle Monitoring. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 59451–59467. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. PIDNet: A real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19529–19539. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Rother, C.; Dollár, P. Panoptic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9404–9413. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zeng, P.; Yue, S.; Zheng, Z.; Qin, L.; Song, H. Automatic body condition scoring system for dairy cows in group state based on improved YOLOv5 and video analysis. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025, 15, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.; Kostermans, T.; Brovold, J.W.; Laique, T.; Ocepek, M. Automated Body Condition Scoring in Dairy Cows Using 2D Imaging and Deep Learning. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]

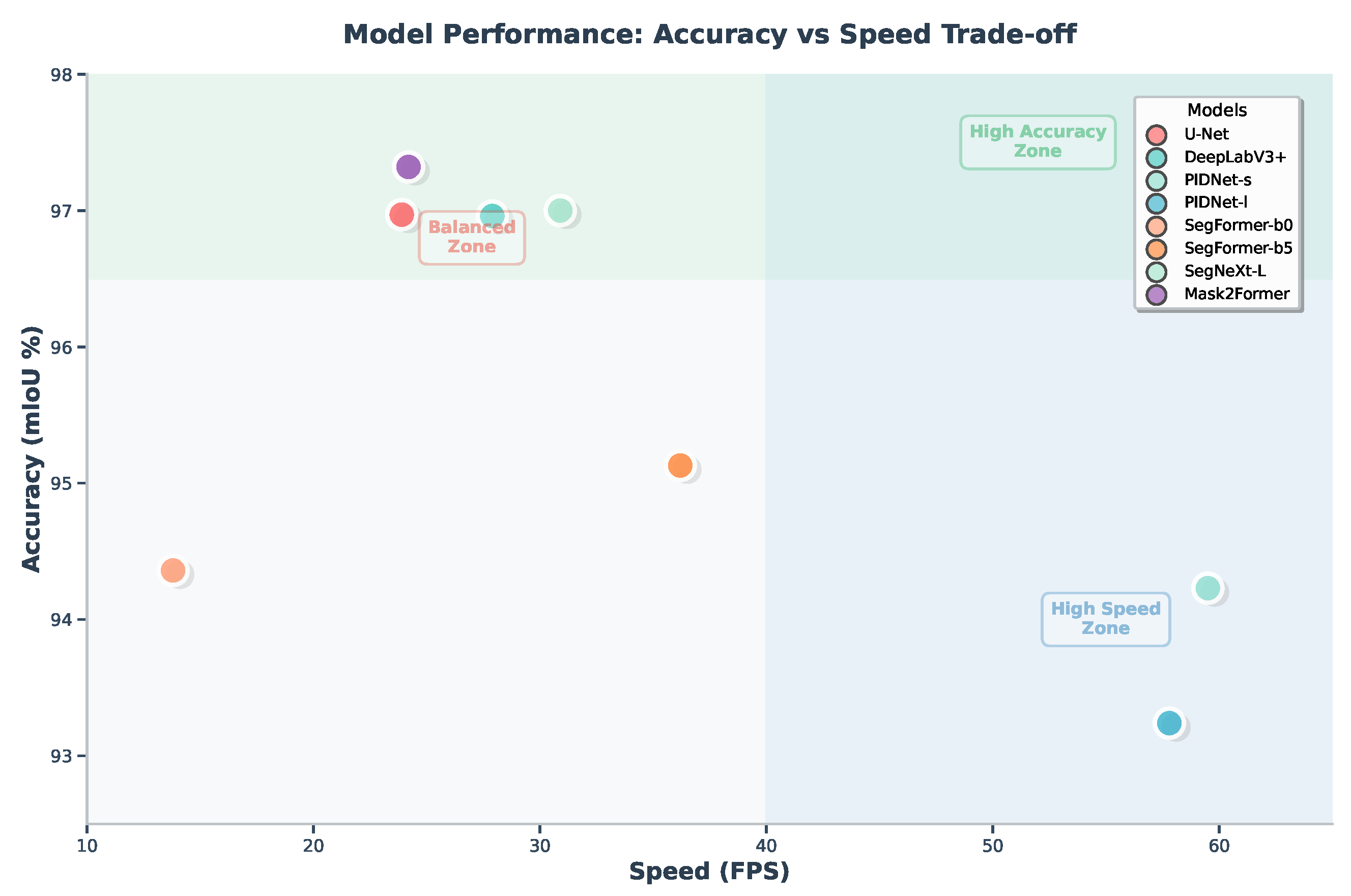

| Model | Backbone | mIoU (%) | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | - | 96.97 | 23.9 |
| DeepLabV3+ | ResNet-101 | 96.96 | 27.9 |
| PIDNet-s | - | 94.23 | 59.5 |
| PIDNet-l | - | 93.24 | 57.8 |
| SegFormer-b0 | MiT-b0 | 94.36 | 13.8 |
| SegFormer-b5 | MiT-b5 | 95.13 | 36.2 |
| SegNeXt-L | MSCAN-L | 97.00 | 30.9 |
| Mask2Former | Swin-L | 97.32 | 24.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, L.; Liu, J.; Hong, W.; Kong, F.; Fan, Z.; Lei, L.; Li, X. SideCow-VSS: A Video Semantic Segmentation Dataset and Benchmark for Intelligent Monitoring of Dairy Cows Health in Smart Ranch Environments. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111104
Yao L, Liu J, Hong W, Kong F, Fan Z, Lei L, Li X. SideCow-VSS: A Video Semantic Segmentation Dataset and Benchmark for Intelligent Monitoring of Dairy Cows Health in Smart Ranch Environments. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(11):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111104
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Lei, Jin Liu, Weinan Hong, Fanrong Kong, Zipei Fan, Lin Lei, and Xinwei Li. 2025. "SideCow-VSS: A Video Semantic Segmentation Dataset and Benchmark for Intelligent Monitoring of Dairy Cows Health in Smart Ranch Environments" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 11: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111104
APA StyleYao, L., Liu, J., Hong, W., Kong, F., Fan, Z., Lei, L., & Li, X. (2025). SideCow-VSS: A Video Semantic Segmentation Dataset and Benchmark for Intelligent Monitoring of Dairy Cows Health in Smart Ranch Environments. Veterinary Sciences, 12(11), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111104








