Hematology Reference Values for the Iberian Ribbed Newt (Pleurodeles waltl) Under Human Care
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Animals and Environmental Conditions
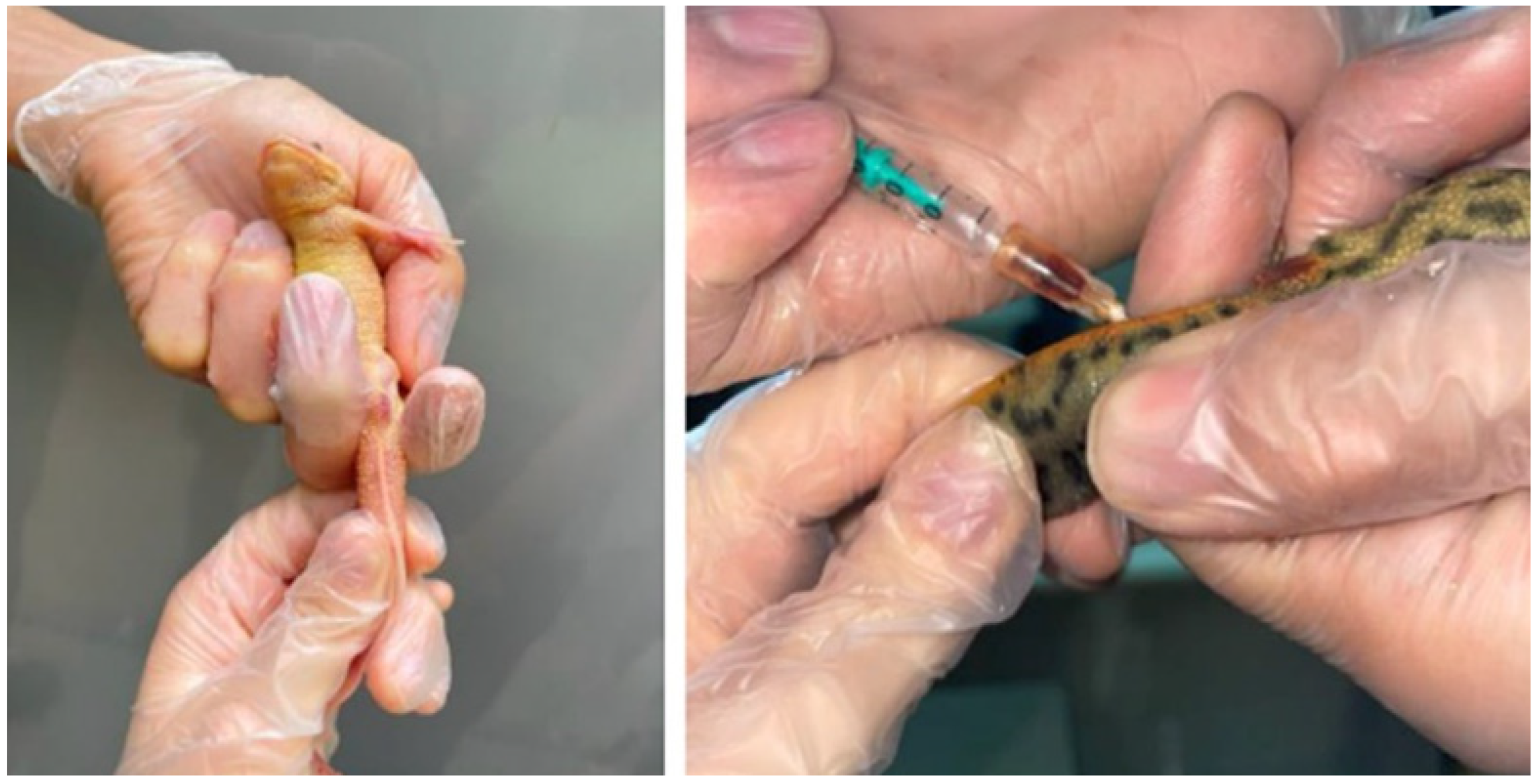
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
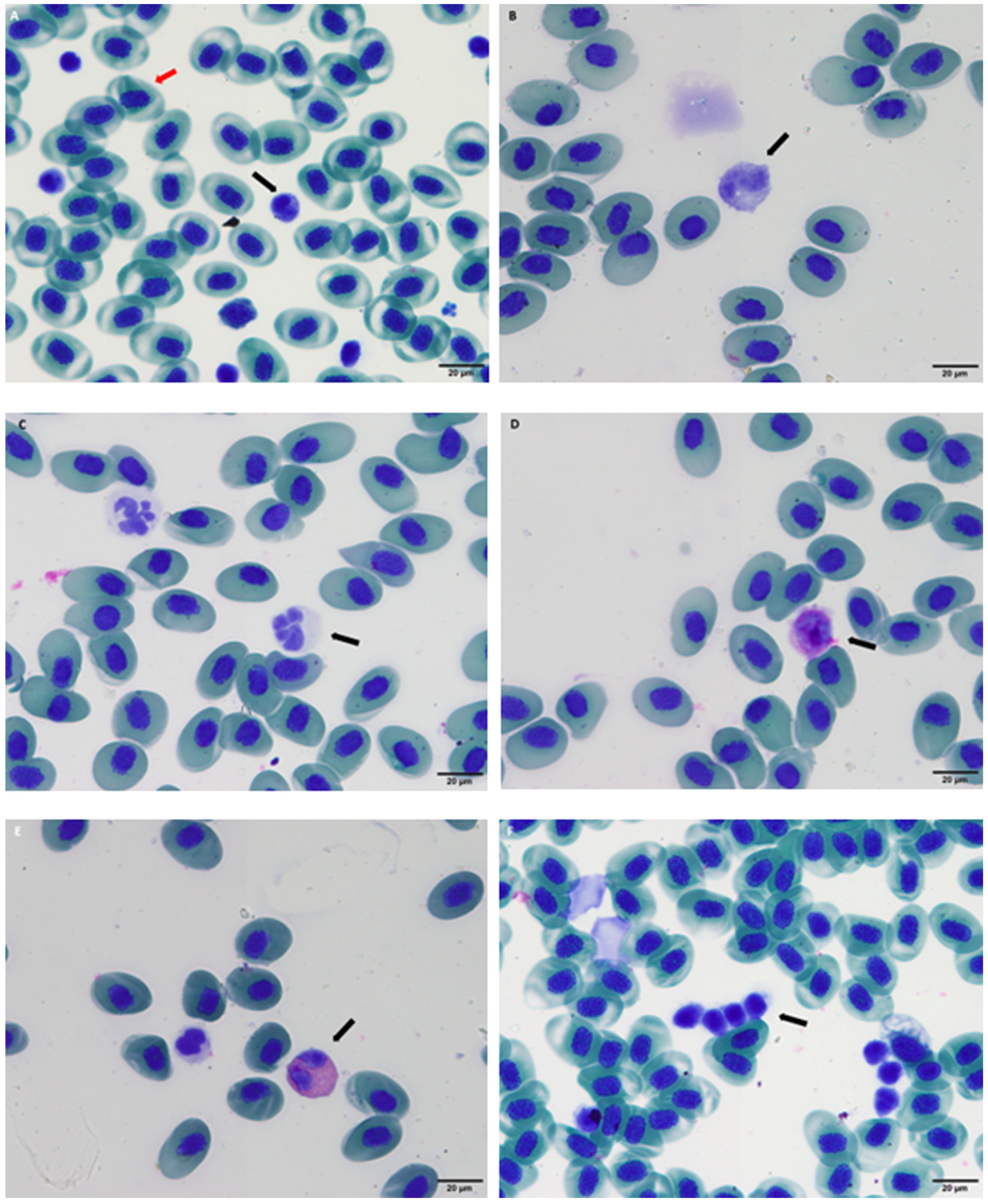
2.4. Hematological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEC | Animal Ethics Committee |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ASVCP | American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology |
| HCT | Hematocrit |
| HCV | Hematocrit value |
| RBC | Red blood cells |
| WBC | White blood cells |
| RI | Reference intervals |
| RV | Reference values |
| LRL | Lower Reference Limit |
| URL | Upper Reference Limit |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SPSS | IBM SPSS Statistics |
| SVL | Snout–vent length |
| IUCN | International Union for Conservation of Nature |
References
- Matheson, A.M.M.; Chua, N.J.; Tosches, M.A. Iberian Ribbed Newts. Curr. Biol. 2025, 35, R49–R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Beja, P.; Bosch, J.; Tejedo, M.; Edgar, P.; Donaire-Barroso, D.; Lizana, M.; Martinez-Solano, I.; Salvador, A.; García-París, M.; Recuero, E.; et al. Pleurodeles waltl; IUCN Red List Threat Species e.T59463A1192633; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listado de Especies Silvestres en Régimen de Protección Especial y Catálogo Español de Especies Amenazadas. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/biodiversidad/temas/conservacion-de-especies/especies-proteccion-especial/ce-proteccion-listado.html (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Gómez-Ramírez, F.; Pérez, M.Á.; Caballero-Díaz, C.; Sánchez-Montes, G.; Martinez-Solano, I. The Importance of Naturalized Quarries as Amphibian Breeding Sites: A Case Study in Central Spain. Basic Appl. Herpetol. 2023, 37, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frippiat, J.-P. Contribution of the Urodele Amphibian Pleurodeles waltl to the Analysis of Spaceflight-Associated Immune System Deregulation. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 56, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siboulet, R.; Grinfeld, S.; Deparis, P.; Jaylet, A. Micronuclei in Red Blood Cells of the Newt Pleurodeles waltl Michah: Induction with X-Rays and Chemicals. Mutat. Res. 1984, 125, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Iida, M.; Hayashi, T.; Suzuki, K.-I.T. CRISPR-Cas9-Based Functional Analysis in Amphibians: Xenopus Laevis, Xenopus Tropicalis, and Pleurodeles waltl. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2637, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, R.; Lizana, M.; Pleguezuelos, J. Atlas Y Libro Rojo de Los Anfíbios Y Reptiles de España; Organismo Autónomo Parques Nacionales: Madrid, Spain, 2002; ISBN 978-84-8014-450-6. [Google Scholar]
- Thumsová, B.; Alarcos, G.; Ayres, C.; Rosa, G.M.; Bosch, J. Relationship between Two Pathogens in an Amphibian Community That Experienced Mass Mortalities. Conserv. Biol. 2024, 38, e14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, B.R.; Wright, K.M. Amphibian Medicine. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery; Mader, D.R., Divers, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 992–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichs, K.R.; Harr, K.E.; Freeman, K.P.; Szladovits, B.; Walton, R.M.; Barnhart, K.F.; Blanco-Chavez, J.; American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology. ASVCP Reference Interval Guidelines: Determination of de Novo Reference Intervals in Veterinary Species and Other Related Topics. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 41, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffré, A.; Friedrichs, K.; Harr, K.; Concordet, D.; Trumel, C.; Braun, J.-P. Reference Values: A Review. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 38, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.E.; Camus, M.S.; Freeman, K.P.; Giori, L.; Hooijberg, E.H.; Jeffery, U.; Korchia, J.; Meindel, M.J.; Moore, A.R.; Sisson, S.C.; et al. ASVCP Guidelines: Principles of Quality Assurance and Standards for Veterinary Clinical Pathology (Version 3.0): Developed by the American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology’s (ASVCP) Quality Assurance and Laboratory Standards (QALS) Committee. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 48, 542–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.W.; Grant, K.R. Exotic Animal Hematology and Cytology, 5th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Divers, S.J. Diagnostic Techniques and Sample Collection. In Mader’s Reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery, 3rd ed.; Divers, S.J., Stahl, S.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Long, S.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Muhammad-Farooq, T.; Shen, Y. Reference Intervals for Hematology, Plasma Biochemistry, and Bone Mineral Density in Captive Ceratophrys cranwelli (Anura: Ceratophryidae). Anim. Dis. 2023, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, Z.; Popgeorgiev, G.; Mehterov, N.H. Haematological Parameters of Pelophylax ridibundus (amphibia: Ranidae) from the Region of the Lead and Zinc Plant “Kardzhali” (South Bulgaria) and Their Use in the Environmental Quality Assessment. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2015, 67, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Carotenuto, R.; Pallotta, M.M.; Tussellino, M.; Fogliano, C. Xenopus laevis (Daudin, 1802) as a Model Organism for Bioscience: A Historic Review and Perspective. Biology 2023, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzán, M.J.; Heatley, J.; Russell, K.E.; Horney, B. Clinical Pathology of Amphibians: A Review. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 46, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.; Felt, S.; Torreilles, S.; Howard, A.; Behan, C.; Moorhead, R.; Green, S. Serum Clinical Biochemical and Hematologic Reference Ranges of Laboratory-Reared and Wild-Caught Xenopus Laevis. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, S.; Warner, J.; Speare, R.; Berger, L.; Skerratt, L.F.; Muller, R. Hematologic and Plasma Biochemical Reference Intervals for Health Monitoring of Wild Australian Tree Frogs. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 41, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.; Burgdorf-Moisuk, A.; Kass, P.H.; Brady, J.; Wack, R.F. Hematology and plasma biochemistry intervals for captive-born california tiger salamanders (Ambystoma californiense). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2016, 47, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, M.E.; Bandeff, J.M.; Huang, Y. Hematology and serum chemistry of ozark and eastern hellbenders (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis). Herpetologica 2007, 63, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, Y.; Une, Y. Blood Clinical Biochemistries and Packed Cell Volumes for the Mexican axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum). J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2017, 27, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekhova, T.; Sof’in, A.; Kobelkova, T.; Marco, R.; Dournon, C. Sex-Linked Differences in Activity of Enzymes in the Blood of the Urodele Amphibian Pleurodeles waltl. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 130, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekhova, T.; Sof’in, A.V.; Kobel’kova, T.G.; Novozhilova, T.I.; Durnon, K. Activities of certain enzymes in blood of the Pleurodeles waltl newt. Aerosp. Environ. Med. 2001, 35, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jaylet, A.; Deparis, P.; Ferrier, V.; Grinfeld, S.; Siboulet, R. A New Micronucleus Test Using Peripheral Blood Erythrocytes of the Newt Pleurodeles waltl to Detect Mutagens in Fresh-Water Pollution. Mutat. Res. 1986, 164, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.J. Processing Data for Outliers. Biometrics 1953, 9, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn-Christie, R.G.; Flatland, B.; Friedrichs, K.R.; Szladovits, B.; Harr, K.E.; Ruotsalo, K.; Knoll, J.S.; Wamsley, H.L.; Freeman, K.P.; American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology (ASVCP). ASVCP Quality Assurance Guidelines: Control of Preanalytical, Analytical, and Postanalytical Factors for Urinalysis, Cytology, and Clinical Chemistry in Veterinary Laboratories. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 41, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZIMS—Species360. Available online: https://species360.org/zims/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Sobrino-Yacobi, J.; Fuertes-Recuero, M.; De La Riva-Fraga, M.; Encinas Cerezo, T.; Montesinos Barceló, A.; Camina Vega, Á.; Morón-Elorza, P. Hematology and Plasma Biochemistry Reference Values of the Subgenus Hapturosaurus (Varanus macraei, Varanus prasinus, Varanus beccarii) Under Human Care. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morón-Elorza, P.; Rojo-Solis, C.; Steyrer, C.; Álvaro-Álvarez, T.; Valls-Torres, M.; Encinas, T.; García-Párraga, D. Hematology and Plasma Chemistry Reference Values in Nursehound Shark (Scyliorhinus stellaris) Maintained Under Human Care. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 909834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, V.M.; Jarchow, J.L.; Trueblood, M.H. Hematology and Plasma Biochemistry Reference Range Values for Free-Ranging Desert Tortoises in Arizona. J. Wildl. Dis. 2002, 38, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamirande, E.W.; Bratthauer, A.D.; Fischer, D.C.; Nichols, D.K. Reference Hematologic and Plasma Chemistry Values of Brown Tree Snakes (Boiga irregularis). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1999, 30, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, C.J. Clinical Differentiation of Chinese water dragon, Physignathus spp., Leukocytes. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2001, 11, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, A.K.; Thapliyal, J.P. Erythropoietin, Testosterone, and Thyroxine in the Erythropoietic Response of the Snake, Xenochrophis piscator. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1984, 53, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrigth, K.M.; DeVoe, R.S. Amphibians. In Exotic Animal Formulary; Carpenter, J.W., Ed.; Saunders/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 53–82. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | n | Mean | Median | SD | Minimum | Maximum | RI | LRL | URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT (%) | 29 | 36.40 | 34.20 | 7.80 | 25.00 | 56.30 | 20.10–52.60 | 16.30–24.20 | 48.30–56.70 |
| RBC (×106/μL) | 30 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.36 | 0.07–0.37 | 0.05–0.10 | 0.31–0.44 |
| WBC (×103/μL) | 30 | 3.53 | 3.50 | 1.78 | 1.00 | 7.25 | 0.50–8.00 | 0.20–1.08 | 6.63–9.55 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 30 | 46.80 | 48.50 | 12.10 | 15.00 | 68.00 | 18.10–69.00 | 16.00–28.00 | 65.40–78.10 |
| Eosinophils (%) | 30 | 13.20 | 13.50 | 4.80 | 3.00 | 24.00 | 3.20–23.20 | 0.90–5.70 | 20.60–25.70 |
| Monocytes (%) | 28 | 2.20 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 0.00 | 5.00 | < 5.30 | - | 4.50–6.20 |
| Basophils (%) | 30 | 2.60 | 2.00 | 2.70 | 0.00 | 10.00 | < 8.20 | - | 5.90–10.00 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 30 | 34.50 | 36.00 | 9.90 | 12.00 | 54.00 | 14.00–55.00 | 9.20–19.00 | 49.70–60.10 |
| Parameter | HCV (%) | RBC (×106/mm3) | WBC (×103/mm3) | Neutrophils (%) | Eosinophils (%) | Monocytes (%) | Basophiles (%) | Lymphocytes (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) | 23.3–47.0 | 0.8–1.5 | 0.6–9.6 | 6.9–9.1 | 0.0–0.5 | - | 62.6–68 | 58.3–72.3 | [11] |
| American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) | 19.3–40.9 | 0.0–1.8 | 11.3–29.7 | 36.1–85.7 | 0.7–5.1 | 2.6–9 | 1.1–5.9 | 17.0–36.6 | [11] |
| Australian green tree frog (Ranoidea caerulea) | 34–40.8 | 0.6–0.8 | 12.4–22.1 | 14.0–27.0 | 5.0–10.0 | 1.0–5.0 | 0.0–0.0 | - | [22] |
| White-lipped tree frog (Nyctimystes infrafrenatus) | 26.0–34.0 | 0.6–0.8 | 14.2–29.1 | 15.0–32.0 | 4.0–8.0 | 0.0–1.3 | 0.0–1.0 | 57.0–78.3 | |
| Hellbender salamander (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis) | 33.0–43.0 | - | - | 15.0–49.0 | 0–1.8 | 5.0–17.0 | 0.5–8.3 | 33.0–69.0 | [24] |
| 26.0–40.0 | - | - | 25.0–43.0 | 0–1.6 | 5.0–19.0 | 0.4–11.2 | 35.0–61.0 | ||
| California tiger salamander (Ambystoma californiense) | 33.0–64.0 | 0.0–1.1 | 0–1.3 | 0.0–58.0 | 0.0–47.0 | 0.0–47.0 | 0.0–14.0 | 17.0–81.0 | [23] |
| Axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) | 28.0–32.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | [25] |
| Iberian ribbed newt (Pleurodeles waltl) | 20.1–52.6 | 0.07–0.37 | 0.5–8.0 | 18.1–69.0 | 3.2–23.2 | < 5.3 | < 8.2 | 14.0–55.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peñas Rodríguez, C.; Fuertes-Recuero, M.; Encinas Cerezo, T.; de la Riva-Fraga, M.; Montesinos Barceló, A.; Morón-Elorza, P. Hematology Reference Values for the Iberian Ribbed Newt (Pleurodeles waltl) Under Human Care. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111103
Peñas Rodríguez C, Fuertes-Recuero M, Encinas Cerezo T, de la Riva-Fraga M, Montesinos Barceló A, Morón-Elorza P. Hematology Reference Values for the Iberian Ribbed Newt (Pleurodeles waltl) Under Human Care. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(11):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111103
Chicago/Turabian StylePeñas Rodríguez, Carmen, Manuel Fuertes-Recuero, Teresa Encinas Cerezo, Manuel de la Riva-Fraga, Andrés Montesinos Barceló, and Pablo Morón-Elorza. 2025. "Hematology Reference Values for the Iberian Ribbed Newt (Pleurodeles waltl) Under Human Care" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 11: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111103
APA StylePeñas Rodríguez, C., Fuertes-Recuero, M., Encinas Cerezo, T., de la Riva-Fraga, M., Montesinos Barceló, A., & Morón-Elorza, P. (2025). Hematology Reference Values for the Iberian Ribbed Newt (Pleurodeles waltl) Under Human Care. Veterinary Sciences, 12(11), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111103







