Exposure of Wild Ruminants to Toxoplasma gondii in Alpine Ecosystems, NE Spain
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
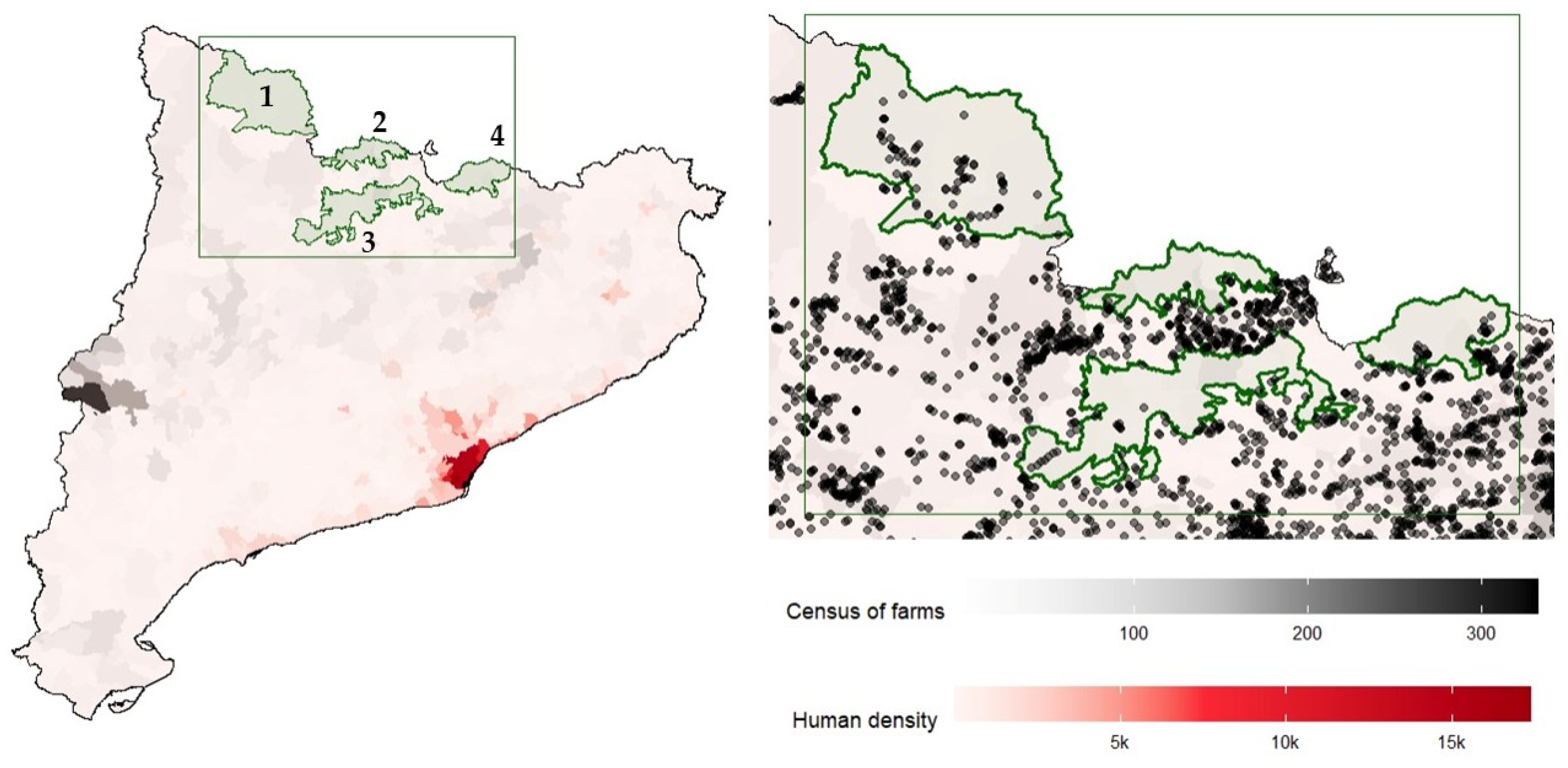
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Animal Samples
2.3. Serological Test
2.4. Molecular Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
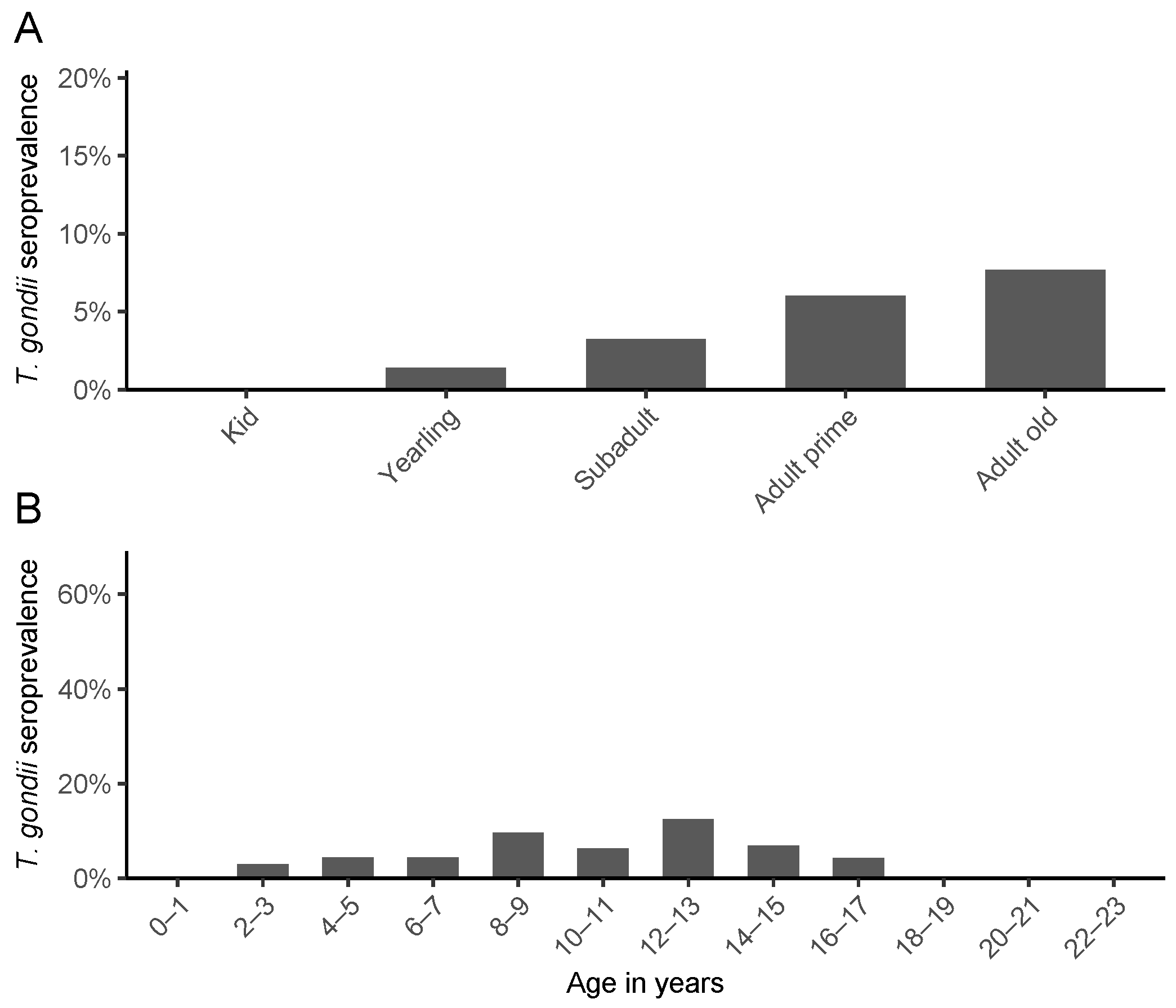
3. Results
4. Discussion
| Species | Prevalence | Test | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wildcat | DNA faeces 2.64% (189) DNA tissues 33.33% (3) | qPCR qPCR | Present study |
| Domestic cat | 14.3% (7) | serology | [48] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 31,8% (88) | IFAT | [49] |
| Iberian lynx Iberian lynx Iberian lynx Wildcat Wildcat Wildcat | IgG 44.9% (69) DNA faeces 0.0% (69) DNA tissues 50.0% (60) IgG 85.0% (20) DNA faeces 5.0% (20) DNA tissues 50.0% (20) | IFAT PCR PCR IFAT PCR PCR | [40] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 13.78% (254) | IFAT | [50] |
| Feral cat | Oocysts 0.7% (290) | coprology | [45] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 42.0% (291) | MAT | [51] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 12.28% (114) | IFAT | [52] |
| Wildcat | IgG 55.5% (9) | NS | [42] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 24.2% (263) Oocysts 0.0% (263) | DAT coprology | [44] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 53.5% (346) Oocysts 0.0% (287) | IFAT coprology | [43] |
| Iberian lynx | IgG 62.8% (129) | MAT | [53] |
| Feral cat | IgG 84.7% (59) | MAT | [54] |
| Iberian lynx Feral cat Feral cat | IgG 80.7% (26) IgG > 50% (25) Oocysts 17,0% | MAT MAT FA | [46] |
| Iberian lynx | IgG 44.0% (48) | IHA test/LA | [55] |
| Wildcat Iberian lynx | IgG 50.0% (3) IgG 81.5% (27) | MAT | [41] |
| Feral cat (urban) Feral cat Domestic cat | IgG 36.9% (317) IgG 33.3% (48) IgG 25.5% (220) | IFAT | [56] |
| Domestic cat | IgG 45.0% (220) | MAT | [57] |
| Feral cat (urban) | IgG 25.5% | IFAT | [58] |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NGR | National Game Reserve |
| IHA | indirect hemagglutination |
| LA | latex agglutination |
| FA | direct immunofluorescence |
| MAT | Modified Agglutination Test |
| DAT | Direct Agglutination Test |
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Samelius, G.; Al-Adhami, B.; Huyvaert, K.P.; Bailey, L.L.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Jenkins, E.J. Estimating Toxoplasma gondii exposure in arctic foxes (Vulpes lagopus) while navigating the imperfect world of wildlife serology. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, S.K.; Nymo, I.H.; Forcada, J.; Godfroid, J.; Hall, A. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in pinnipeds from Antarctica. Vet. Rec. 2012, 171, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, A.; Asbakk, K.; Prestrud, K.W.; Aars, J.; Derocher, A.E.; Tryland, M.; Wiig, O.; Dubey, J.P.; Sonne, C.; Dietz, R.; et al. Prevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in polar bears (Ursus maritimus) from Svalbard and East Greenland. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestrud, K.W.; Asbakk, K.; Fuglei, E.; Mørk, T.; Stien, A.; Ropstad, E.; Tryland, M.; Gabrielsen, G.W.; Lydersen, C.; Kovacs, K.M.; et al. Serosurvey for Toxoplasma gondii in arctic foxes and possible sources of infection in the high Arctic of Svalbard. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 150, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlatti, L.; Cotza, A.; Nelli, L. Linking alternative reproductive tactics and habitat selection in Northern chamois. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 7057–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampe, J.P.; Bon, R.; Gerard, J.F.; Serrano, E.; Caens, P.; Florence, E.; Gonzalez, G. Site fidelity, migratory behaviour, and spatial organization of female isards (Rupicapra pyrenaica) in the Pyrenees National Park, France. Can. J. Zool. 2007, 85, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Olmo, J.; Such-Sanz, A.; Camps, D.; Sayol, F.; Batet, T.; Vilella, M.; Salvador, S. Grans Mamífers de Catalunya i Andorra: Distribució, Biologia, Ecologia i Convervació, 1st ed.; Ruiz-Olmo, J., Camps, D., Eds.; Lynx Nature Books: Barcelona, Spain, 2023; pp. 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Such-Sanz, A.; Ruiz-Olmo, J.; Sayol, F.; Batet, T.; Salvador, S.; Vilella, M.; Federico, P.; Campsolinas, A.; Piñol, C. Felis silvestris. In Grans Mamífers de Catalunya i Andorra: Distribució, Biologia, Ecologia i Convervació, 1st ed.; Ruiz-Olmo, J., Camps, D., Eds.; Lynx Nature Books: Barcelona, Spain, 2023; pp. 238–245. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Scholten, S.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Jiménez-Ruiz, S.; Almería, S.; Risalde, M.A.; Vicente, J.; Acevedo, P.; Arnal, M.C.; Balseiro, A.; Gómez-Guillamón, F.; et al. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in wild ruminants in Spain. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotteland, C.; Aubert, D.; Gibert, P.; Moinet, M.; Klein, F.O.; Game, Y.; Villena, I.; Gilot-Fromont, E. Toxoplasmosis in natural populations of ungulates in France: Prevalence and spatiotemporal variations. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, N.; Trogu, T.; Pedrotti, L.; Gaffuri, A.; Lanfranchi, P.; Ferrari, N. Toxoplasma gondii infection in alpine red deer (Cervus elaphus): Its spread and effects on fertility. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, e0138472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, N.; Gaffuri, A.; Trogu, T.; Viganò, R.; Ferrari, N.; Lanfranchi, P. Spread and genotype of Toxoplasma gondii in naturally infected alpine chamois (Rupicapra r. rupicapra). Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotta, M.; Pellicioli, L.; Gaffuri, A.; Trogu, T.; Formenti, N.; Tranquillo, V.; Luzzago, C.; Ferrari, N.; Lanfranchi, P. Analysis of seroprevalence data on Hepatitis E virus and Toxoplasma gondii in wild ungulates for the assessment of human exposure to zoonotic meat-borne pathogens. Food. Microbiol. 2022, 101, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marreros, N.; Hüssy, D.H.; Albini, S.; Frey, C.F.; Abril, C.; Vogt, H.R.; Holzwarth, N.; Wirz-Dittus, S.; Friess, M.; Engels, M.; et al. Epizootiologic investigations of selected abortive agents in free-ranging alpine ibex (Capra ibex ibex) in Switzerland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffuri, A.; Giacometti, M.; Tranquillo, V.M.; Magnino, S.; Cordioli, P.; Lanfranchi, P. Serosurvey of roe deer, chamois and domestic sheep in the central Italian Alps. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferroglio, E.; Bosio, F.; Trisciuoglio, A.; Zanet, S. Toxoplasma gondii in sympatric wild herbivores and carnivores: Epidemiology of infection in the Western Alps. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vengušt, G.; Kuhar, U.; Jerina, K.; Švara, T.; Gombač, M.; Bandelj, P.; Vengušt, D.Ž. Passive Disease Surveillance of Alpine Chamois (Rupicapra r. rupicapra) in Slovenia between 2000 and 2020. Animals 2022, 12, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Air and Space Administration (NASA) Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Gridded Population of the World. Available online: https://ciesin.columbia.edu/content/data (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Aegerter, J.; Fouracre, D.; Smith, G.C. A First Estimate of the Structure and Density of the Populations of Pet Cats and Dogs across Great Britain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.A.; Kurdzielewicz, S.; Jeanniot, E.; Dupuis, E.; Marnef, F.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Poulle, M.-L. Spatial Distribution of Soil Contaminated with Toxoplasma Gondii Oocysts in Relation to the Distribution and Use of Domestic Cat Defecation Sites on Dairy Farms. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlatti, L.; Gugiatti, A.; Imperio, S. Horn growth patterns in Alpine chamois. Zoology 2015, 118, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavčić, K.; Corlatti, L.; Safner, T.; Budak, N.; Šprem, N. Contrasting patterns of sexually selected traits in Mediterranean and continental populations of European mouflon. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivachelvan, M.N.; Ghali Ali, M.; Chibuzo, G.A. Foetal age estimation in sheep and goats. Small Rumin. Res. 1996, 19, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Desmonts, G. Serological responses of equids fed Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Equine Vet. J. 1987, 19, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzenberg, D.; Lamaury, I.; Demar, M.; Vautrin, C.; Cabié, A.; Simon, S.; Nicolas, M.; Desbois-Nogard, N.; Boukhari, R.; Riahi, H.; et al. Performance Testing of PCR Assay in Blood Samples for the Diagnosis of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis in AIDS Patients from the French Departments of America and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma Gondii: A Prospective and Multicentric Study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, L.; Schares, G.; Stragier, C.; Vignoles, P.; Brouat, C.; Cuny, T.; Dubois, C.; Rohart, T.; Glodas, C.; Dardé, M.L.; et al. Diversity of Toxoplasma Gondii Strains Shaped by Commensal Communities of Small Mammals. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, I.; Kenne Pagui, E.C.; Sartori, N. Mean and median bias reduction in generalized linear models. Stat. Comput. 2020, 30, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Omland, K.S. Model selection in ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version 4.5.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Stevenson, M.; Nunes, T.; Sanchez, J.; Thornton, R.; Reiczigel, J.; Robison-Cox, J.; Sebastiani, P.; Solymos, P.; Yoshida, K.; Firestone, S. epiR: Tools for the Analysis of Epidemiological Data, R package version 2.0.65; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=epiR (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Bartoń, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference, R package version 1.47.5; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Kosmidis, I. brglm2: Bias Reduction in Generalized Linear Models, R package version 1.0.0; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=brglm2 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Basso, W.; Holenweger, F.; Schares, G.; Müller, N.; Campero, L.M.; Ardüser, F.; Moore-Jones, G.; Frey, C.F.; Zanolari, P. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum infections in sheep and goats in Switzerland: Seroprevalence and occurrence in aborted foetuses. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2022, 28, e00176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, I.; Velarde, R.; López-Olvera, J.R.; Cabezón, O.; Pumarola, M.; Lavín, S. Systemic toxoplasmosis and Gram-negative sepsis in a southern chamois (Rupicapra pyrenaica) from the Pyrenees in northeast Spain. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2009, 21, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dámek, F.; Swart, A.; Waap, H.; Jokelainen, P.; Le Roux, D.; Deksne, G.; Deng, H.; Schares, G.; Lundén, A.; Álvarez-García, G.; et al. Systematic Review and Modelling of Age-Dependent Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Livestock, Wildlife and Felids in Europe. Pathogens 2023, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Shapiro, K.; VanWormer, E. Dynamics and epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii oocyst shedding in domestic and wild felids. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2412–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; VanWormer, E.; Shapiro, K. More people, more cats, more parasites: Human Population Density and Temperature Variation Predict Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Shedding in Free-ranging Domestic and Wild Felids. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; deWit, L.A.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Oocysts in water, soil and food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matas Méndez, P.; Fuentes Corripio, I.; Montoya Matute, A.; Bailo Barroso, B.; Grande Gómez, R.; Apruzzese Rubio, A.; Ponce Gordo, F.; Mateo Barrientos, M. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in endangered wild felines (Felis silvestris and Lynx pardinus) in Spain. Animals 2023, 13, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, R.; Cabezón, O.; Millán, J.; Pabón, M.; Arnal, M.C.; Luco, D.F.; Gortázar, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Almeria, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild carnivores from Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.G.; Pardavila, X.; Ortega, N.; Lamosa, A.; Mangas, J.G.; Martínez-Carrasco, C. Canine distemper virus may affect European wild cat populations in Central Spain. Mamm. Biol. 2019, 97, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, G.; Rupérez, C.; Checa, R.; Gálvez, R.; Hernández, L.; García, M.; Canorea, I.; Marino, V.; Montoya, A. Current status of L. infantum infection in stray cats in the Madrid region (Spain): Implications for the recent outbreak of human leishmaniosis? Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, A.; García, M.; Gálvez, R.; Checa, R.; Marino, V.; Sarquis, J.; Barrera, J.P.; Rupérez, C.; Caballero, L.; Chicharro, C.; et al. Implications of zoonotic and vector-borne parasites to free-roaming cats in central Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 251, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbella, D.; Santana-Hernández, K.M.; Rodríguez-Ponce, E. Small islands as potential model ecosystems for parasitology: Climatic influence on parasites of feral cats. J. Helminthol. 2022, 96, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Candela, M.G.; Palomares, F.; Cubero, M.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Barral, M.; de la Fuente, J.; Almería, S.; León-Vizcaíno, L. Disease threats to the endangered Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus). Vet. J. 2009, 182, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rahimi, M.T.; Pagheh, A.S.; Zarean, M.; Dezhkam, A.; Ahmadpour, E. Toxoplasma gondii infection in domestic and wild felids as public health concerns: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanchez, P.; Romero-Trancón, D.; Falces-Romero, I.; Navarro Carrera, P.; Ruiz-Carrascoso, G.; Carmena, D.; Casares Jiménez, M.; Rivero-Juárez, A.; Moya, L.; Rodón, J.; et al. Zoonosis screening in Spanish immunocompromised children and their pets. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1425870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, M.P.; Planas, S.; Langa, J.; Laborda, A.; Castillo, J.A.; Gracia, M.J. Seroprevalence of zoonotic pathogens in stray cats in an urban area of northeast Spain. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2024, 53, 101052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Martínez, M.; Giner, J.; González, A.; Tobajas, A.P.; Pérez, M.D.; Lira-Navarrete, E.; González-Ramírez, A.M.; Macías-León, J.; Verde, M.; et al. A cross-sectional serosurvey of SARS-CoV-2 and co-infections in stray cats from the second wave to the sixth wave of COVID-19 outbreaks in Spain. Vet. Res. Commun. 2023, 47, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.G.; Fanelli, A.; Carvalho, J.; Serrano, E.; Domenech, G.; Alonso, F.; Martínez-Carrasco, C. Urban landscape and infection risk in free-roaming cats. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Giner, J.; Tobajas, A.P.; Pérez, M.D.; González-Ramírez, A.M.; Macías-León, J.; González, A.; Verde, M.; Yzuel, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; et al. Serological evidence of SARS-CoV-2 and co-infections in stray cats in Spain. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bocanegra, I.; Dubey, J.P.; Martínez, F.; Vargas, A.; Cabezón, O.; Zorrilla, I.; Arenas, A.; Almería, S. Factors affecting seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in the endangered Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus). Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.; Cabezón, O.; Pabón, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in feral cats (Felis silvestris catus) in Majorca, Balearic Islands, Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelke, M.E.; Johnson, W.E.; Millán, J.; Palomares, F.; Revilla, E.; Rodríguez, A.; Calzada, J.; Ferreras, P.; León-Vizcaíno, L.; Delibes, M.; et al. Exposure to disease agents in the endangered Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus). Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, G.; Montoya, A.; Jiménez, S.; Frisuelos, C.; Mateo, M.; Fuentes, I. Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii and intestinal parasites in stray, farm and household cats in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauss, C.B.; Almería, S.; Ortuño, A.; Garcia, F.; Dubey, J.P. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in domestic cats from Barcelona, Spain. J. Parasitol. 2003, 89, 1067–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio Garrido, J.; Cour Boveda, L.; Berzosa Aguilar, M.; Pareja Miralles, J. Study on the epidemiology of toxoplasmosis. Infection in the domestic cat in suburbs of Madrid. Serological and copro-parasitological study. Med. Trop. 1972, 48, 24–39. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jenkins, E.J.; Huyvaert, K.P.; Polley, L.; Root, J.J.; Moore, C.G. Toxoplasma gondii in circumpolar people and wildlife. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species/Year | NGR APA | NGR CM | NGR Ce-AU | NGR Fre-Set | Total | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rupicapra pyrenaica | 12.09% (91) | 7.90% (217) | 12.24% (49) | 4.12% (688) | 5.93% (1045) | |
| 2001 | 0.00% (4) | 0.00% (4) | ELISA a | |||
| 2002 | 0.00% (8) | 0.00% (8) | ELISA a | |||
| 2005 | 0.00% (3) | 0.00% (9) | 0.00% (2) | 0.00% (14) | ELISA a | |
| 2006 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (25) | 0.00% (26) | ELISA a | ||
| 2007 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (53) | 0.00% (54) | ELISA a | ||
| 2008 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (87) | 0.00% (88) | ELISA a | ||
| 2010 | 0.00% (1) | 8.33% (36) | 8.11% (37) | MAT | ||
| 2011 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (34) | 16.67% (6) | 6.59% (91) | 5.30% (132) | MAT |
| 2012 | 14.81% (27) | 0.00% (1) | 1.78% (56) | 7.14% (84) | MAT | |
| 2013 | 17.39% (23) | 15.00% (40) | 20.00% (5) | 3.33% (30) | 12.24% (98) | MAT |
| 2014 | 0.00% (6) | 0.00% (7) | 5.77% (52) | 4.61% (65) | MAT | |
| 2015 | 11.11% (9) | 12.50% (32) | 13.33% (15) | 14.28% (28) | 13.09% (84) | MAT |
| 2016 | 20.00% (15) | 3.85% (26) | 5.88% (17) | 6.60% (106) | 7.31% (164) | MAT |
| 2017 | 16.67% (12) | 13.33% (15) | 14.81% (27) | ELISA b | ||
| 2018 | 0.00% (14) | 0.00% (14) | ELISA b | |||
| 2019 | 0.00% (2) | 0.00% (22) | 0.00% (24) | ELISA b | ||
| 2020 | 0.00% (2) | 4.54% (44) | 4.35% (46) | ELISA b | ||
| 2021 | 7.69% (13) | 7.69% (13) | ELISA b | |||
| 2022 | 0.00% (20) | 0.00% (20) | ELISA b | |||
| 2023 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (22) | 0.00% (23) | ELISA b | ||
| 2024 | 16.67% (6) | 0.00% (14) | 5.00% (20) | ELISA b | ||
| Ovis aries musimon | 0.00% (11) | 1.92% (104) | 1.74% (115) | |||
| 2008 | 6.45% (31) | 6.45% (31) | ELISA a | |||
| 2020 | 0.00% (30) | 0.00% (30) | ELISA b | |||
| 2021 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (1) | ELISA b | |||
| 2022 | 0.00% (9) | 0.00% (9) | ELISA b | |||
| 2023 | 0.00% (10) | 0.00% (32) | 0.00% (42) | ELISA b | ||
| 2024 | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (1) | 0.00% (2) | ELISA b |
| Species | % T. gondii | Technique | Tissue | Alpine Area/Country | Sampling Period | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrenean chamois | clinical case | HE/IHC | CNS, lung, liver | Pyrenees/Spain | 2002 | [35] |
| Pyrenean chamois | 5.6% (n = 89) | MAT | Serum | Pyrenees/Spain | ND (1999–2020) | [10] |
| Pyrenean chamois Mouflon | 5.99% (n = 1035) 1.74% (n = 115) | ELISA/MAT ELISA | Serum | Pyrenees/Spain | 2001–2024 | Present study |
| Alpine chamois | 16.8% (n = 101) 9.27% (n = 97) | MAT ELISA | Serum | Pyrenees/France | ND | [11] |
| Red deer | 39.5% (n = 81) | ELISA | Serum | Alps/Italy | 2012 | [12] |
| Alpine chamois | 3.2% (n = 93) 2.0% (n = 50) | ELISA PCR | Serum CNS | Alps/Italy | 2011–2013 | [13] |
| Alpine chamois Roe deer Red deer Mouflon | 4.0% (n = 100) 18.2% (n = 55) 18.0% (n = 50) 20.0% (n = 15) | ELISA | Serum | Alps/Italy | 2017–2018 | [14] |
| Alpine ibex | 1.8% (n = 562) | ELISA | Serum | Alps/Switzerland | 2006–2008 | [15] |
| Alpine chamois Roe deer | 5.0% (n = 108) 13% (n = 207) | LAT | Serum | Alps/Italy | 1998–2001 | [16] |
| Alpine chamois Red deer Roe deer | 0.0% (n = 22) 0.0% (n = 13) 2.48% (n = 121) | PCR | Skel. Ms, CNS | Alps/Italy | 2009–2012 | [17] |
| Alpine chamois Mouflon Alpine Ibex | 20.7% (n = 53) 30.0% (n = 10) 0.0% (n = 2) | ELISA | Serum | Alps/Slovenia | 2017–2018 | [18] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escudero, A.; Ribas, M.P.; Almería, S.; Gholipour, H.; Pailler-García, L.; Sastre, N.; Ruiz-Olmo, J.; Palazón, S.; Sayol, F.; Espunyes, J.; et al. Exposure of Wild Ruminants to Toxoplasma gondii in Alpine Ecosystems, NE Spain. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111101
Escudero A, Ribas MP, Almería S, Gholipour H, Pailler-García L, Sastre N, Ruiz-Olmo J, Palazón S, Sayol F, Espunyes J, et al. Exposure of Wild Ruminants to Toxoplasma gondii in Alpine Ecosystems, NE Spain. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(11):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111101
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscudero, Alejandra, Maria Puig Ribas, Sonia Almería, Hojjat Gholipour, Lola Pailler-García, Natalia Sastre, Jordi Ruiz-Olmo, Santiago Palazón, Ferran Sayol, Johan Espunyes, and et al. 2025. "Exposure of Wild Ruminants to Toxoplasma gondii in Alpine Ecosystems, NE Spain" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 11: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111101
APA StyleEscudero, A., Ribas, M. P., Almería, S., Gholipour, H., Pailler-García, L., Sastre, N., Ruiz-Olmo, J., Palazón, S., Sayol, F., Espunyes, J., Aguilar, X. F., & Cabezón, O. (2025). Exposure of Wild Ruminants to Toxoplasma gondii in Alpine Ecosystems, NE Spain. Veterinary Sciences, 12(11), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111101








