Indirect ELISA Using Multi-Antigenic Dominants of 3AB and 3C Recombinant Protein to Detect Antibodies Against Senecavirus A in Pigs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses, Cells, and Serum Samples
2.2. Screening of Dominant Epitopes and Plasmid Construction
2.3. Expression in E. coli and Purification
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.5. Virus Neutralization Test (VNT)
2.6. Development of iELISAs
2.7. Determination of the Cut-Off Values
2.8. Determination of the Sensitivity, Specificity, and Repeatability
2.9. Animal Experiment
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
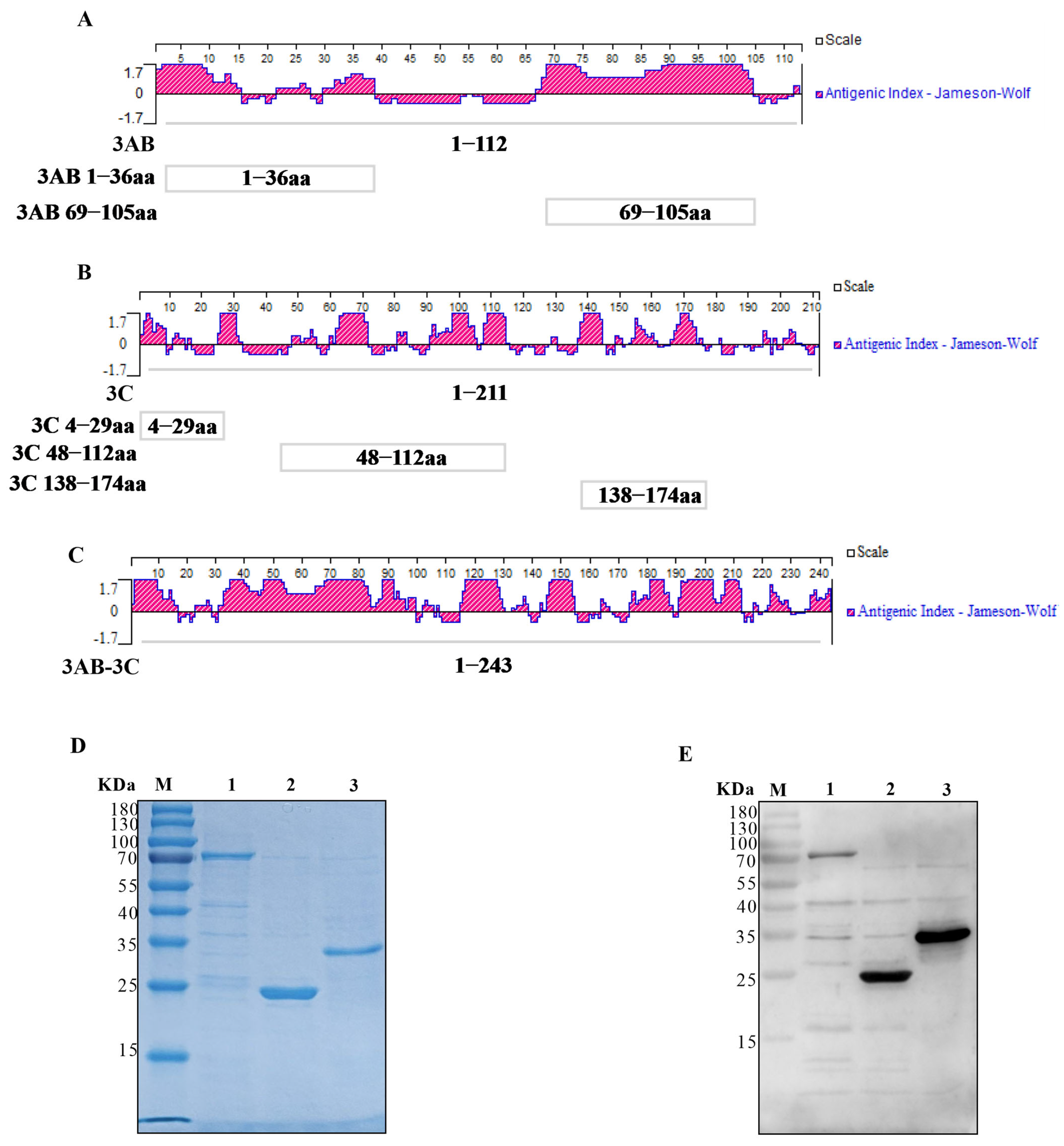
3.1. Epitope Analysis and Recombinant Protein Expression
3.2. Establishment of iELISAs and Immunoreactivity Verification of SVA Proteins
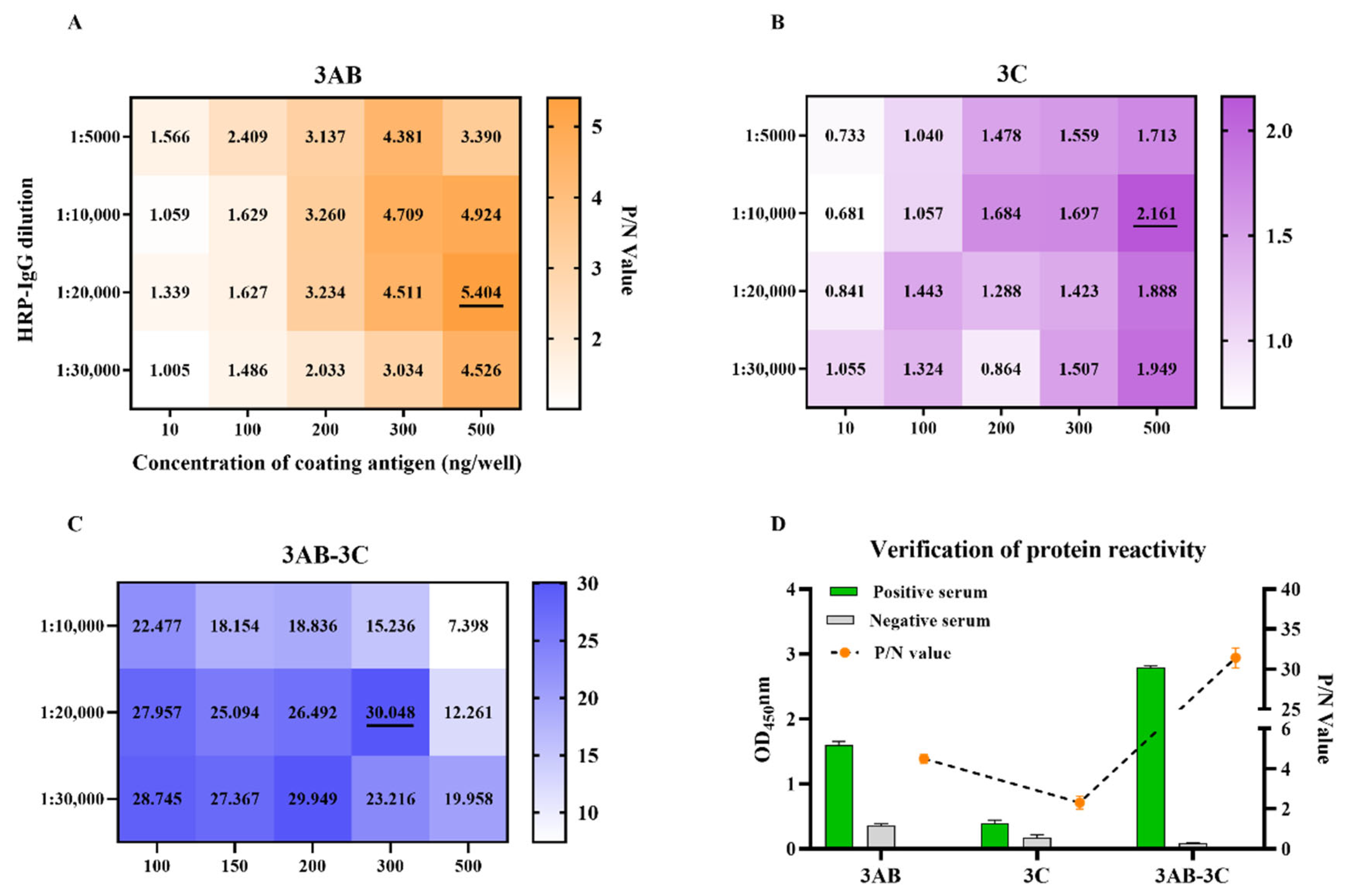
3.3. Assay Optimization and Cut-Off Determination for r3AB and r3AB-3C iELISAs
3.4. Evaluation of the Repeatability and Reproducibility
3.5. Analytical Sensitivity, Specificity, and Diagnostic Performance
3.6. Large-Scale Serological Survey for SVA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| iELISA | indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| NSPs | non-structural proteins |
| S/P | sample-to-positive |
| DIVA | Differentiating Infected from Vaccinated Animals |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| WOAH | World Organisation for Animal Health |
| IBRS-2 | Instituto Biologico-Rim Suino-2 |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CPE | cytopathic effect |
| TCID50 | 50% tissue culture infective dose |
| FMIA | fluorescent microsphere immunoassays |
| IFA | immunofluorescence assay |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry assay |
| VNT | virus neutralization test |
| SVA | Senecavirus A |
| FMDV | foot-and-mouth disease virus |
| SVE | swine vesicular exanthema |
| PRRSV | porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus |
| PRV | pseudorabies virus |
| PCV2 | porcine circovirus 2 |
| PCV3 | porcine circovirus 3 |
| CSFV | classical swine fever virus |
| ASFV | African swine fever virus |
| IPTG | isopropyl-β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside |
| P/N | positive-to-negative control |
| dpi | days post-immunization |
| dpc | days post-challenge |
References
- Hales, L.M.; Knowles, N.J.; Reddy, P.S.; Xu, L.; Hay, C.; Hallenbeck, P.L. Complete genome sequence analysis of Seneca Valley virus-001, a novel oncolytic picornavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, S.; Reddy, S.P.; Loo, J.; Idamakanti, N.; Hallenbeck, P.L.; Reddy, V.S. Structure of Seneca Valley Virus-001: An oncolytic picornavirus representing a new genus. Structure 2008, 16, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segales, J.; Barcellos, D.; Alfieri, A.; Burrough, E.; Marthaler, D. Senecavirus A. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 54, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.H.V.; de Lima, M.; Joshi, L.R.; Diel, D.G. A virulent and pathogenic infectious clone of Senecavirus A. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasma, T.; Davidson, S.; Shaw, S.L. Idiopathic vesicular disease in swine in Manitoba. Can. Vet. J. 2008, 49, 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Pineyro, P.E.; Rademacher, C.J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, G.; Yuan, J.; Hoang, H.; Gauger, P.C.; Madson, D.M.; Schwartz, K.J.; et al. Novel Senecavirus A in Swine with Vesicular Disease, United States, July 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1325–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, R.A.; Zotti, E.; Alcantara, B.K.; Oliveira, M.V.; Freitas, L.A.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Senecavirus A: An Emerging Vesicular Infection in Brazilian Pig Herds. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeng-Chuto, K.; Rodtian, P.; Temeeyasen, G.; Wegner, M.; Nilubol, D. The first detection of Senecavirus A in pigs in Thailand, 2016. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Vannucci, F.; Knutson, T.P.; Corzo, C.; Marthaler, D.G. Emergence and whole-genome sequence of Senecavirus A in Colombia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Bai, Y.; Sun, B.; Xie, Q.; Ma, J. The First Identification and Complete Genome of Senecavirus A Affecting Pig with Idiopathic Vesicular Disease in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhai, Q.; Niu, J.; Li, G.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Kang, H.; Li, C.; Gou, H.; Chu, P.; et al. Pathogenicity of the First Buffalo-origin Senecavirus A in Conventional Piglets and Buffaloes. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2025, 2025, 6222217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, M.; Jayawardena, N.; Sun, E.; Easingwood, R.A.; Burga, L.N.; Bostina, M. Cryo-Electron Microscopy Structure of Seneca Valley Virus Procapsid. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Meng, H.; Ge, D.; Shan, H.; Geri, L.; Liu, F. Structural and nonstructural proteins of Senecavirus A: Recent research advances, and lessons learned from those of other picornaviruses. Virology 2023, 585, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.H.V.; Maggioli, M.F.; Otta, J.; Joshi, L.R.; Lawson, S.; Diel, D.G. Senecavirus A 3C Protease Mediates Host Cell Apoptosis Late in Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, A.; Lager, K. Efficacy of an inactivated Senecavirus A vaccine in weaned pigs and mature sows. Vaccine 2022, 40, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watcharavongtip, P.; Jermsutjarit, P.; Tantituvanont, A.; Nilubol, D. Development of a differentiating of infected from vaccinated animal (DIVA) ELISA to detect antibodies against Senecavirus A in pigs using two expression systems of non-structural proteins. Vet. Q. 2025, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, H.; Wei, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, T.; Hu, X.; Luo, P.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. A recombinant truncated FMDV 3AB protein used to better distinguish between infected and vaccinated cattle. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3435–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, K.J.; Madsen, K.G.; Madsen, E.S.; Salt, J.S.; Nqindi, J.; Mackay, D.K. Differentiation of infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease by the detection of antibodies to the non-structural proteins 3D, 3AB and 3ABC in ELISA using antigens expressed in baculovirus. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1461–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.I.; Jin, J.S.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, A.Y.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.; Lee, E.G.; et al. Factors Involved in Removing the Non-Structural Protein of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus by Chloroform and Scale-Up Production of High-Purity Vaccine Antigens. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioli, M.F.; Lawson, S.; de Lima, M.; Joshi, L.R.; Faccin, T.C.; Bauermann, F.V.; Diel, D.G. Adaptive Immune Responses following Senecavirus A Infection in Pigs. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorak, C.M.; Akkutay-Yoldar, Z.; Stone, S.R.; Tousignant, S.J.; Vannucci, F.A.; Murtaugh, M.P. An indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the identification of antibodies to Senecavirus A in swine. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goolia, M.; Vannucci, F.; Yang, M.; Patnayak, D.; Babiuk, S.; Nfon, C.K. Validation of a competitive ELISA and a virus neutralization test for the detection and confirmation of antibodies to Senecavirus A in swine sera. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2017, 29, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; van Bruggen, R.; Xu, W. Generation and diagnostic application of monoclonal antibodies against Seneca Valley virus. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, J.; Li, K.; Ding, K.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, P.; Bai, X.; Li, D.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Based on Swine Monoclonal Antibodies for Detecting Neutralizing Antibodies against Senecavirus A. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0459922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Bai, J.; Jiang, P. The Establishment and Application of Indirect 3AB-ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies against Senecavirus A. Viruses 2023, 15, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watcharavongtip, P.; Jermsutjarit, P.; Tantituvanont, A.; Nilubol, D. Evaluating the performance of VP1 expressed in baculovirus and Escherichia coli expressed from Senecavirus A in pig using an ELISA. Vet. J. 2025, 311, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Chu, X.; Ding, G.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. Indirect ELISA Using Multi-Antigenic Dominants of p30, p54 and p72 Recombinant Proteins to Detect Antibodies against African Swine Fever Virus in Pigs. Viruses 2022, 14, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Tian, X.X.; Xiang, X.Y.; Qi, X.Y.; Zhou, H.R.; Xiao, P.Y.; An, T.Q.; Meng, F.D.; Wang, H.W. Epitope Mapping of Senecavirus A 3A Protein Using Monoclonal Antibodies. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2025, 2025, 3398924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.H.; Zhang, B.; Ren, H.J.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, S.D.; Luo, M.R.; Guo, K.W.; Han, S.C.; He, W.R.; Zhang, G.P.; et al. Preparation and epitope identification of a novel monoclonal antibody against 3A protein of Senecavirus A. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 303, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schisterman, E.F.; Perkins, N.J.; Liu, A.; Bondell, H. Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden Index to discriminate individuals using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, E.; Temeeyasen, G.; Pineyro, P.E. Comprehensive review on immunopathogenesis, diagnostic and epidemiology of Senecavirus A. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, S.; Sun, S.; Dong, H.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, Z.; Ren, M.; Yin, S.; Guo, H. Potent Protective Immune Responses to Senecavirus Induced by Virus-Like Particle Vaccine in Pigs. Vaccines 2020, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, M.; Hu, Z.; Tian, L.; Li, X.; Qian, P. A nanoparticle vaccine based on the VP1(21-26) and VP2 structural proteins of Senecavirus A induces robust protective immune responses. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 296, 110198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Fan, W.; Liu, T.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Cui, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Wei, S.; Chen, H.; et al. Seneca Valley Virus Suppresses Host Type I Interferon Production by Targeting Adaptor Proteins MAVS, TRIF, and TANK for Cleavage. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Shao, J.; Chang, H.; Gao, S.; Cong, G.; Du, J. Generation of monoclonal antibodies against non-structural protein 3AB of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virol. Sin. 2012, 27, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, A.; Wilkie, B.N. Porcine Ig isotypes: Function and molecular characteristics. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Constructs | Primer (5′–3′) | Vector |
|---|---|---|
| pCold-I/pCold-TF | F: GAGCTCGGTACCCTCGAGGG | |
| R: CATATGCCTACCTTCGATATGATGA | ||
| 3AB | F: 1 atatcgaaggtaggcatatgATGAGCCCTAATGAGAACGACGACA | pCold-TF |
| R: ccctcgagggtaccgagctcTTATTGCATTTCCATAAGAGAGAGC | ||
| 3C | F: atatcgaaggtaggcatatgATGCAGCCCAACGTGGACATGGGCT | pCold-I |
| R: ccctcgagggtaccgagctcTTATTGCATTGTAGTCAGAGGCTCA | ||
| 3AB-3C | 2 / | pCold-I |
| / |
| SVA Antisera | Intra-Assay | Inter-Assay | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3AB-3C | 3AB | 3AB-3C | 3AB | |||||||||
| Mean | SD | CV | Mean | SD | CV | Mean | SD | CV | Mean | SD | CV | |
| Strongly positive | 2.476 | 0.034 | 1.4% | 2.101 | 0.042 | 2.0% | 2.355 | 0.182 | 7.7% | 2.196 | 0.112 | 5.1% |
| Moderately positive | 0.915 | 0.042 | 4.6% | 1.226 | 0.049 | 4.0% | 0.911 | 0.038 | 4.1% | 1.135 | 0.104 | 9.2% |
| Weakly positive | 0.513 | 0.037 | 7.2% | 0.844 | 0.045 | 5.3% | 0.496 | 0.041 | 8.3% | 0.885 | 0.062 | 7.0% |
| Province | a Positive | a Negative | a Total | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anhui | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100.0% |
| Fujian | 4 | 3 | 7 | 57.1% |
| Gansu | 1 | 1 | 2 | 50.0% |
| Guangdong | 1 | 2 | 3 | 33.3% |
| Guangxi | 3 | 1 | 4 | 75.0% |
| Hebei | 3 | 1 | 4 | 75.0% |
| Henan | 47 | 55 | 102 | 46.1% |
| Heilongjiang | 1 | 1 | 2 | 50.0% |
| Hubei | 3 | 1 | 4 | 75.0% |
| Hunan | 2 | 0 | 2 | 100.0% |
| Jilin | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.0% |
| Jiangsu | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100.0% |
| Jiangxi | 3 | 1 | 4 | 75.0% |
| Inner Mongolia | 32 | 17 | 49 | 65.3% |
| Shandong | 3 | 4 | 7 | 42.9% |
| Shanxi | 12 | 3 | 15 | 80.0% |
| Shaanxi | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100.0% |
| Sichuan | 4 | 1 | 5 | 80.0% |
| Yunnan | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100.0% |
| Zhejiang | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100.0% |
| Total | 124 | 92 | 216 | 57.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, K.; Li, X. Indirect ELISA Using Multi-Antigenic Dominants of 3AB and 3C Recombinant Protein to Detect Antibodies Against Senecavirus A in Pigs. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111046
Li D, Deng J, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Li Y, Hao L, Zhu Z, Tian K, Li X. Indirect ELISA Using Multi-Antigenic Dominants of 3AB and 3C Recombinant Protein to Detect Antibodies Against Senecavirus A in Pigs. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(11):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111046
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dexin, Junhua Deng, Zenglin Wang, Yunjing Zhang, Yufang Li, Liying Hao, Zhenbang Zhu, Kegong Tian, and Xiangdong Li. 2025. "Indirect ELISA Using Multi-Antigenic Dominants of 3AB and 3C Recombinant Protein to Detect Antibodies Against Senecavirus A in Pigs" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 11: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111046
APA StyleLi, D., Deng, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Hao, L., Zhu, Z., Tian, K., & Li, X. (2025). Indirect ELISA Using Multi-Antigenic Dominants of 3AB and 3C Recombinant Protein to Detect Antibodies Against Senecavirus A in Pigs. Veterinary Sciences, 12(11), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111046








