The Acute Immune Response in Sheep Following Immunization with Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites or Parasite-Derived Glycoconjugates
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Parasites
2.3. Glycoconjugate Extraction
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. IgM ELISA
2.6. IgG ELISA
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analyses
2.9. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
3.1. Parasite Glycoconjugate Production
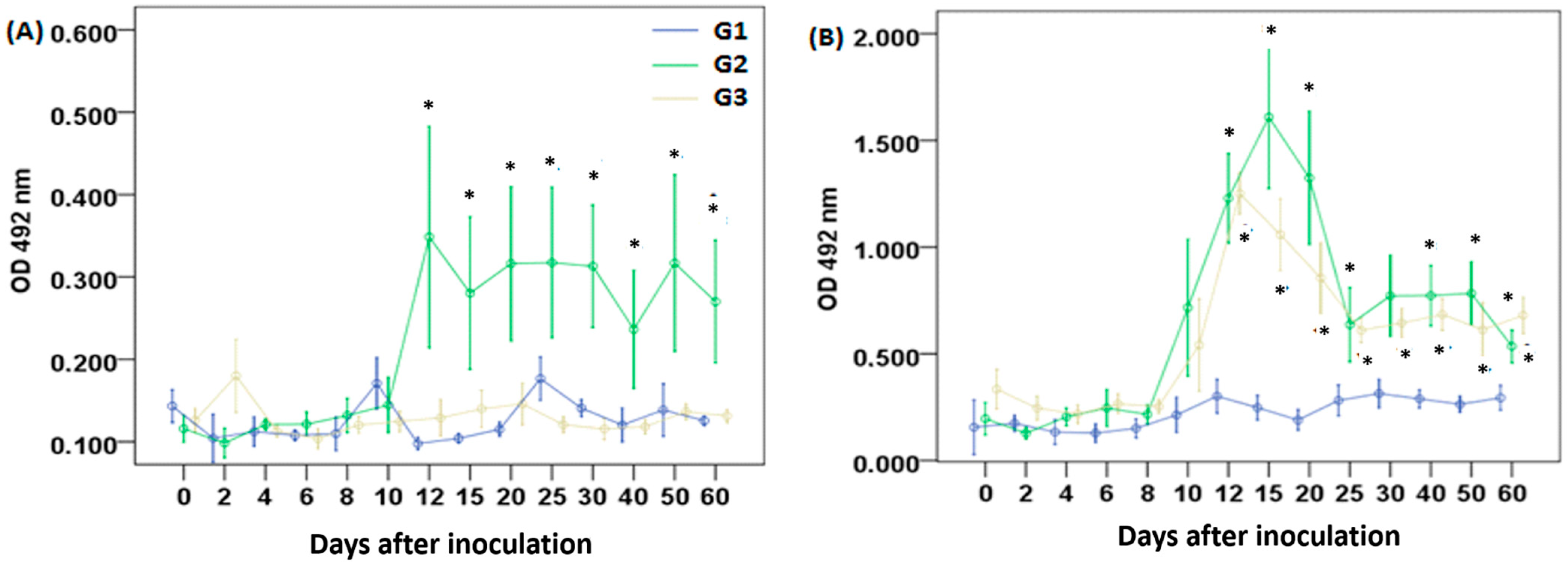
3.2. Clinical Signs and Humoral Immune Response
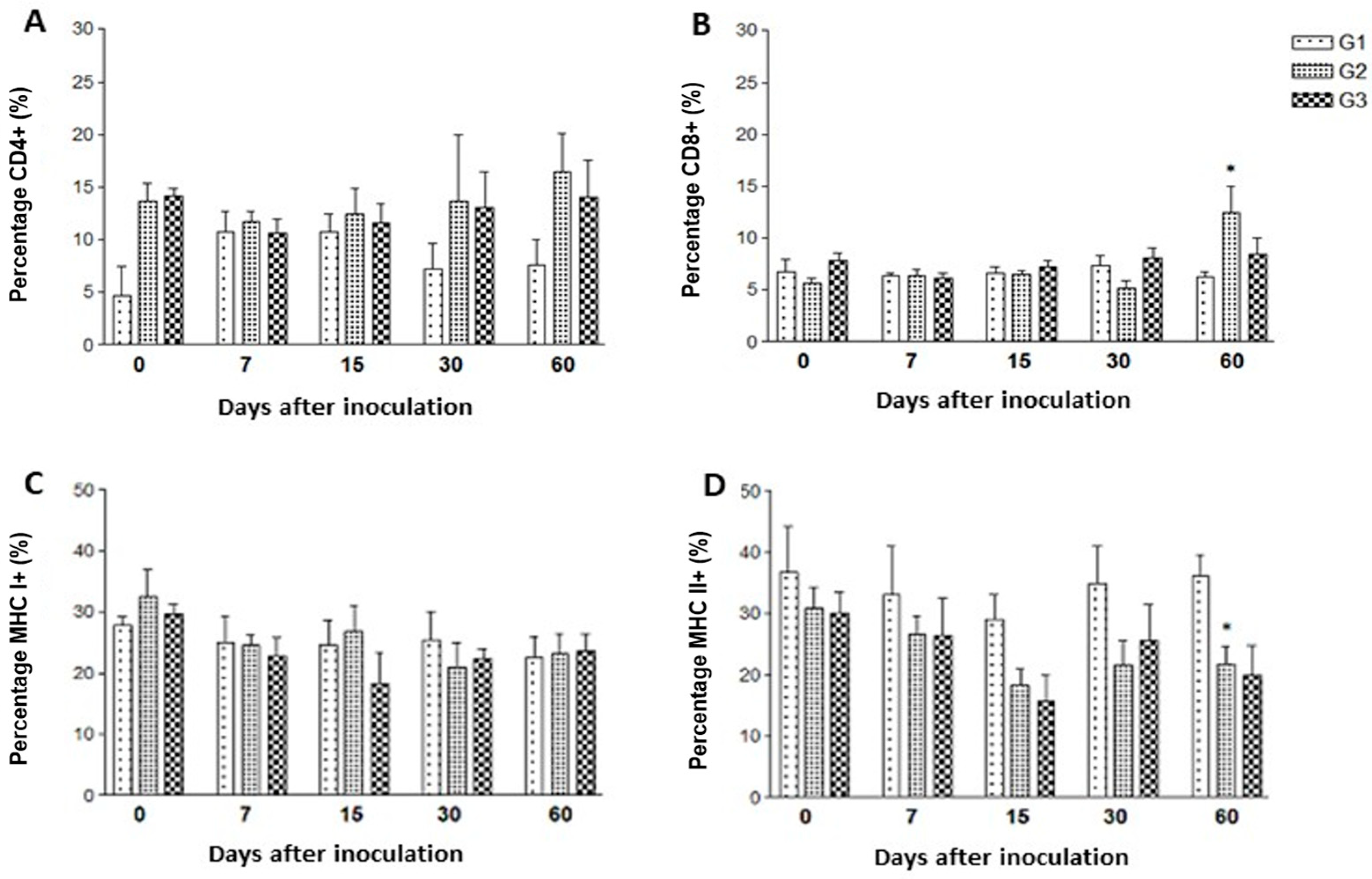
3.3. Cellular Immune Response
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| CD4+ | Cluster of Differentiation 4 positive cells |
| CD8+ | Cluster of Differentiation 8 positive cells |
| CEUA | Ethics Committee on Animal Use in Experimentation |
| CS | Circumsporozoite Protein |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| F3 | Fraction 3 (from glycoconjugate extraction process) |
| FITC | Fluorescein Isothiocyanate |
| GIPLs | Glycosylinositolphospholipids |
| GlyC | Glycoconjugates |
| GPI | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol |
| GRA6 | Dense Granule Antigen 6 |
| IFAT | Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Test |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin E |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LA | Lysate Antigen |
| MAG1 | Matrix Antigen 1 |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| NK cells | Natural Killer Cells |
| OPD | o-Phenylenediamine |
| p.i. | Post-inoculation |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| rpm | Revolutions per Minute |
| SAG1 | Surface Antigen 1 |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| Th1 | T helper type 1 |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
References
- de Barros, R.A.M.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Marciano, M.A.M.; Mazuz, M.L.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Fux, B. Toxoplasmosis in Human and Animals Around the World: Diagnosis and Perspectives in the One Health Approach. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugoch, G.; Noro, M.; Andrade, J. Meta-análise da prevalência de toxoplasmose em gatos e ovinos no Brasil. Rev. Ciênc. Vet. Saúde Pública 2018, 6, 041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, L.P.P.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Fux, B. Involvement of Extracellular Vesicles in the Interaction of Hosts and Toxoplasma gondii. In Extracellular Vesicles from Basic Research to Clinical Applications, 1st ed.; Torrecilhas, A.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 94, pp. 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Abdullah, S.; Othman Dyary, H.; Ismael Dana, O.; Hasanvand, M. Ovine Toxoplasmosis Sero-Status, Risk Factors Analysis, and Estimation of Haematological and Serum Biochemical Alterations. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entrican, G. Immune regulation during pregnancy and host-pathogen interactions in infectious abortion. J. Comp. Pathol. 2002, 126, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, D.; De Craeye, S.; Entrican, G.; Dorny, P.; Cox, E. Parasite distribution and associated immune response during the acute phase of Toxoplasma gondii infection in sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, T.; Nishikawa, Y. Advances in vaccine development and the immune response against toxoplasmosis in sheep and goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 951584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, E.A.; Panton, W.R.; Sanderson, A.; Thomson, K.M.; Wastling, J.M.; Maley, S.; Buxton, D. Induction of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in efferent lymph responding to Toxoplasma gondii infection: Analysis of phenotype and function. Parasit. Immunol. 1995, 17, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Park, S.J.; Park, H. Trend in serological and molecular diagnostic methods for Toxoplasma gondii infection. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Sołowińska, K. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Small Ruminants: Old Problems, and Current Solutions. Animals 2023, 13, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, M.; Portela, R.W.; Snege, M.; Leser, P.G.; Camargo, M.E.; Mineo, J.R.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Immunoglobulin M (IgM)-glycoinositolphospholipid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: An immunoenzymatic assay for discrimination between patients with acute toxoplasmosis and those with persistent parasite-specific IgM antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striepen, B.; Zinecker, C.F.; Damm, J.B.; Melgers, P.A.; Gerwig, G.J.; Koolen, M.; Vliegenthart, J.F.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Schwarz, R.T. Molecular structure of the “low molecular weight antigen” of Toxoplasma gondii: A glucose alpha 1-4 N-acetylgalactosamine makes free glycosyl-phosphatidylinositols highly immunogenic. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 266, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeri, T.; Sarvi, S.; Daryani, A. Effective Factors in the Pathogenesis of Toxoplasma gondii. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paing, M.M.; Tolia, N.H. Multimeric Assembly of Host-Pathogen Adhesion Complexes Involved in Apicomplexan Invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debierre-Grockiego, F.; Azzouz, N.; Schmidt, J.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Geyer, H.; Geyer, R.; Weingart, R.; Schmidt, R.R.; Schwarz, R.T. Roles of glycosylphosphatidylinositols of Toxoplasma gondii: Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32987–32993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portela, R.W.D.; Bethony, J.; Costa, M.I.; Gazzinelli, A.; Vitor, R.W.A.; Hermeto, F.M.; Correa-Oliveira, R.; Gazzinelli, R.T. A Multihousehold Study Reveals a Positive Correlation between Age, Severity of Ocular Toxoplasmosis, and Levels of Glycoinositolphospholipid-Specific Immunoglobulin A. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, W.D.; da Costa, A.J.; Santana, L.F.; Dos Santos, R.S.; Rossanese, W.M.; Lopes, W.C.; Costa, G.H.; Sakamoto, C.A.; Dos Santos, T.R. Aspects of Toxoplasma infection on the reproductive system of experimentally infected rams (Ovis aries). J. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 2009, 602803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, I.B.; Droppa-Almeida, D.; Ferreira, C.; Nascimento, R.J.M.; Portela, R.W.; de Oliveira Silva, M.T.; Alves, M.S.D.; Dos Santos, G.S.; Azevedo, V.; Padilha, F.F.; et al. Immunization of mice and goats with Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis-derived rPTS, rRBN, and rCP40 recombinant proteins. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, T.D.; Kalil, M.A.; Mariutti, R.B.; Arni, R.K.; Gismene, C.; Sousa, F.S.; Collares, T.; Seixas, F.K.; Borsuk, S.; Estrela-Lima, A.; et al. Immunoprophylactic properties of the Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis-derived MBP:PLD:CP40 fusion protein. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 8035–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, M.; Cannizzaro, H.; Ferguson, M.A.; Almeida, I.C.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Fractionation of membrane components from tachyzoite forms of Toxoplasma gondii: Differential recognition by immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG present in sera from patients with acute or chronic toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Zhu, B. Polysaccharides and glycolipids of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their induced immune responses. Scand. J. Immunol. 2023, 97, e13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.L.M.; Martins-Teixeira, M.B.; Carvalho, I. Protozoan Parasites Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Anchors: Structures, Functions and Trends for Drug Discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 4301–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, P.R.B.; Ferreira, A.W. High Diagnostic Efficiency of IgM-ELISA with the Use of Multiple Antigen Peptides (MAP1) from T. gondii ESA (SAG-1, GRA-1 and GRA-7), in Acute Toxoplasmosis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2010, 52, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachinel, N.; Buzoni-Gatel, D.; Dutta, C.; Mennechet, F.J.; Luangsay, S.; Minns, L.A.; Grigg, M.E.; Tomavo, S.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Kasper, L.H. The induction of acute ileitis by a single microbial antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sołowińska, K.; Holec-Gąsior, L. IgM Antibody Detection as a Diagnostic Marker for Acute Toxoplasmosis: Current Status of Studies and Main Limitations. Antibodies 2025, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Ai, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, H.; Kang, M.; You, X.; Li, J. Application of Toxoplasma gondii-specific SAG1, GRA7 and BAG1 proteins in serodiagnosis of animal toxoplasmosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1029768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Gurupwar, R.; Mitra, P.; Aswale, K.; Shinde, S.; Chaudhari, S. Toxoplasma gondii Induces Robust Humoral Immune Response against Cyst Wall Antigens in Chronically Infected Animals and Humans. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Oledzka, G.; McFarlane, R.G.; Spellerberg, M.B.; Smith, S.M.; van Gelder, F.B.; Kur, J.; Stankiewicz, M. Immunological Response of Sheep to Injections of Plasmids Encoding Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 and ROP1 Genes. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundén, A. Immune responses in sheep after immunization with Toxoplasma gondii antigens incorporated into iscoms. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 56, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Zhang, M.; Xin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, H.; He, S. Compound DNA vaccine encoding SAG1/ SAG3 with A2/B subunit of cholera toxin as a genetic adjuvant protects BALB/c mice against Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferra, B.; Holec-Gąsior, L.; Kur, J. Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in farm animals (horses, swine, and sheep) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using chimeric antigens. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis in sheep—The last 20 years. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkers, E.Y.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Regulation and function of T-cell-mediated immunity during Toxoplasma gondii infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, F.; Yamamoto, M. The Role of IFN-γ-Mediated Host Immune Responses in Monitoring and the Elimination of Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Int. Immunol. 2024, 36, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklenar, I.; Jones, T.C.; Alkan, S.; Erb, P. Association of symptomatic human infection with Toxoplasma gondii with imbalance of monocytes and antigen-specific T cell subsets. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 153, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, M.; Rashid, M.; Rashid, I.; Akbar, H.; Gomez-Marin, J.E.; Dimier-Poisson, I. Immune Response against Toxoplasmosis—Some Recent Updates: Toxoplasma gondii Immune Response. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2022, 36, 3946320221078436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shallberg, L.A.; Hunter, C.A. T Cell Surveillance of Toxoplasma gondii: Basic Insights into How T Cells Operate in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 77, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierszinski, F.; Pepper, M.; Stumhofer, J.S.; LaRosa, D.F.; Wilson, E.H.; Turka, L.A.; Halonen, S.K.; Hunter, C.A.; Roos, D.S. Presentation of Toxoplasma gondii Antigens via the Endogenous Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Pathway in Nonprofessional and Professional Antigen-Presenting Cells. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5200–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldszmid, R.S.; Coppens, I.; Lev, A.; Caspar, P.; Mellman, I.; Sher, A. Host ER–Parasitophorous Vacuole Interaction Provides a Route of Entry for Antigen Cross-Presentation in Toxoplasma gondii-Infected Dendritic Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, N.; Gonzalez, F.; Schaeffer, M.; Joncker, N.T.; Cheng, T.; Shastri, A.J.; Robey, E.A.; Shastri, N. Immunodominant, protective response to the parasite Toxoplasma gondii requires antigen processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, D.G.; Johnson, J.J.; Roberts, F.; Roberts, C.W.; Estes, R.G.; David, C.; Grumet, F.C.; McLeod, R. HLA-Class II Genes Modify Outcome of Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüder, C.G.K.; Lang, C.; Giraldo-Velasquez, M.; Algner, M.; Gerdes, J.; Gross, U. Toxoplasma gondii Inhibits MHC Class II Expression in Neural Antigen-Presenting Cells by Down-Regulating the Class II Transactivator CIITA. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 134, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, A.S.; Dzierszinski, F.; Boes, M.; Roos, D.S.; Pearce, E.J. Functional Inactivation of Immature Dendritic Cells by the Intracellular Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophorst, O.; Radošević, K.; Ouwehand, K.; van Beem, W.; Mintardjo, R.; Sijtsma, J.; Kaspers, J.; Companjen, A.; Holterman, L.; Goudsmit, J.; et al. Expression and Immunogenicity of the Plasmodium falciparum Circumsporozoite Protein: The Role of GPI Signal Sequence. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.P.; Pinheiro, C.S.; Figueiredo, B.C.P.; Assis, N.R.G.; Morais, S.B.; Caliari, M.V.; Azevedo, V.; Castro-Borges, W.; Wilson, R.A.; Oliveira, S.C. Vaccination with Enzymatically Cleaved GPI-Anchored Proteins from Schistosoma mansoni Induces Protection against Challenge Infection. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 962538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meira-Santos, P.O.; Piedade, G.C.; Guedes, M.T.; Loureiro, D.; Raynal, J.T.; Meyer, R.; Vicentini, L.; Soares, L.; Fux, B.; Portela, R.W. The Acute Immune Response in Sheep Following Immunization with Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites or Parasite-Derived Glycoconjugates. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100928
Meira-Santos PO, Piedade GC, Guedes MT, Loureiro D, Raynal JT, Meyer R, Vicentini L, Soares L, Fux B, Portela RW. The Acute Immune Response in Sheep Following Immunization with Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites or Parasite-Derived Glycoconjugates. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(10):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100928
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeira-Santos, Patrícia Oliveira, Gabriela Cruz Piedade, Maria Tereza Guedes, Dan Loureiro, José Tadeu Raynal, Roberto Meyer, Letícia Vicentini, Luiz Soares, Blima Fux, and Ricardo Wagner Portela. 2025. "The Acute Immune Response in Sheep Following Immunization with Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites or Parasite-Derived Glycoconjugates" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 10: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100928
APA StyleMeira-Santos, P. O., Piedade, G. C., Guedes, M. T., Loureiro, D., Raynal, J. T., Meyer, R., Vicentini, L., Soares, L., Fux, B., & Portela, R. W. (2025). The Acute Immune Response in Sheep Following Immunization with Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites or Parasite-Derived Glycoconjugates. Veterinary Sciences, 12(10), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100928







