Establishment and Application of a Triplex Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Differentiation of PEDV, TGEV and PKV
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primer and Probe Design
2.2. Viral Strains and Standard Plasmid Construction
2.3. Reagents and Instruments
2.4. Sample Collection and Processing
2.5. Optimization of RT-qPCR Amplification Conditions
2.6. Construction of Standard Curves
2.7. Validation of Specificity, Sensitivity, and Stability
2.8. Comparison between Triplex RT-qPCR and PCR Methods of the Gold Standard in China
2.9. Clinical Application of Triplex RT-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Optimal Reaction Conditions
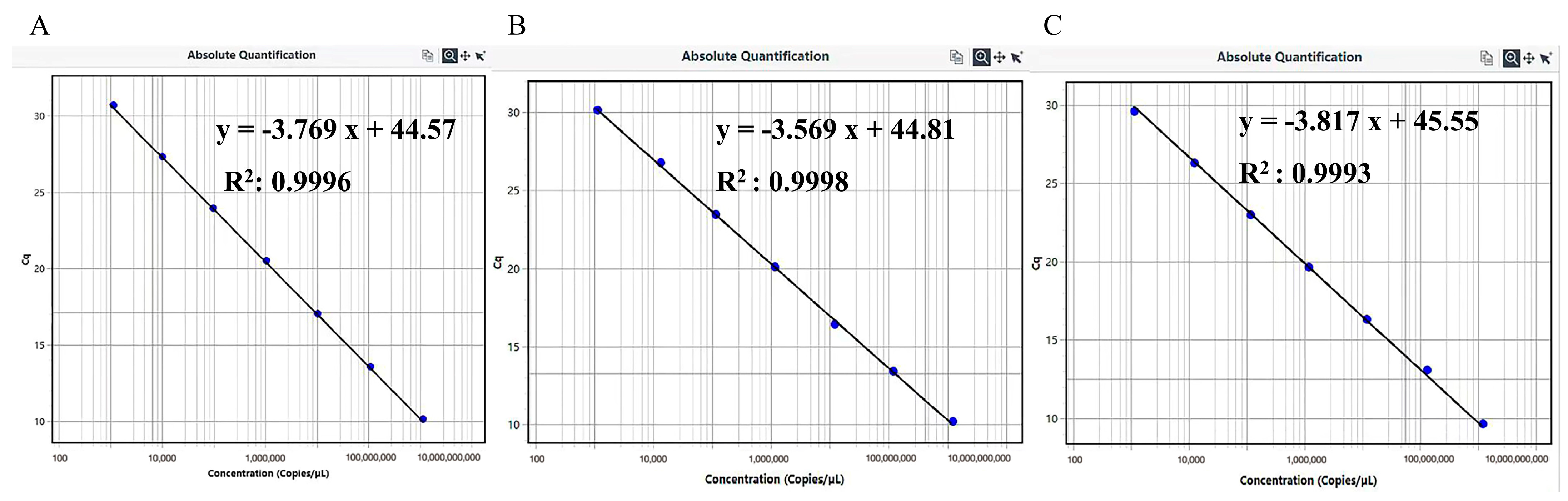
3.2. Establishment of Standard Curves
3.3. Validation of Specificity
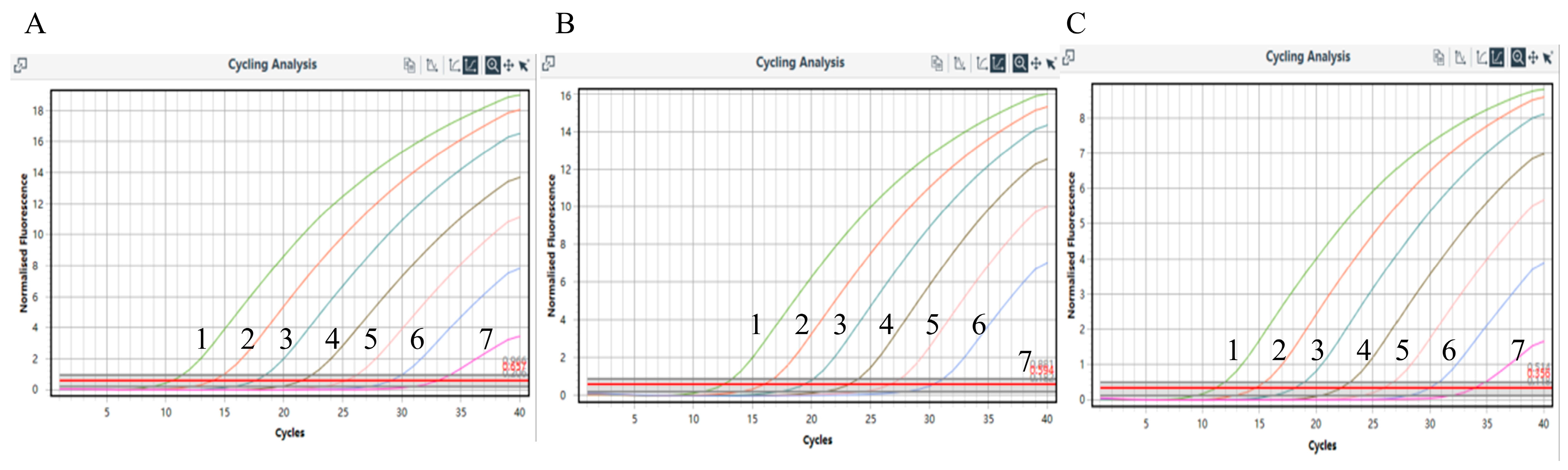
3.4. Validation of Sensitivity
3.5. Validation of Stability
3.6. Comparison with the PCR Methods of the Gold Standard in Clinical Sample Testing
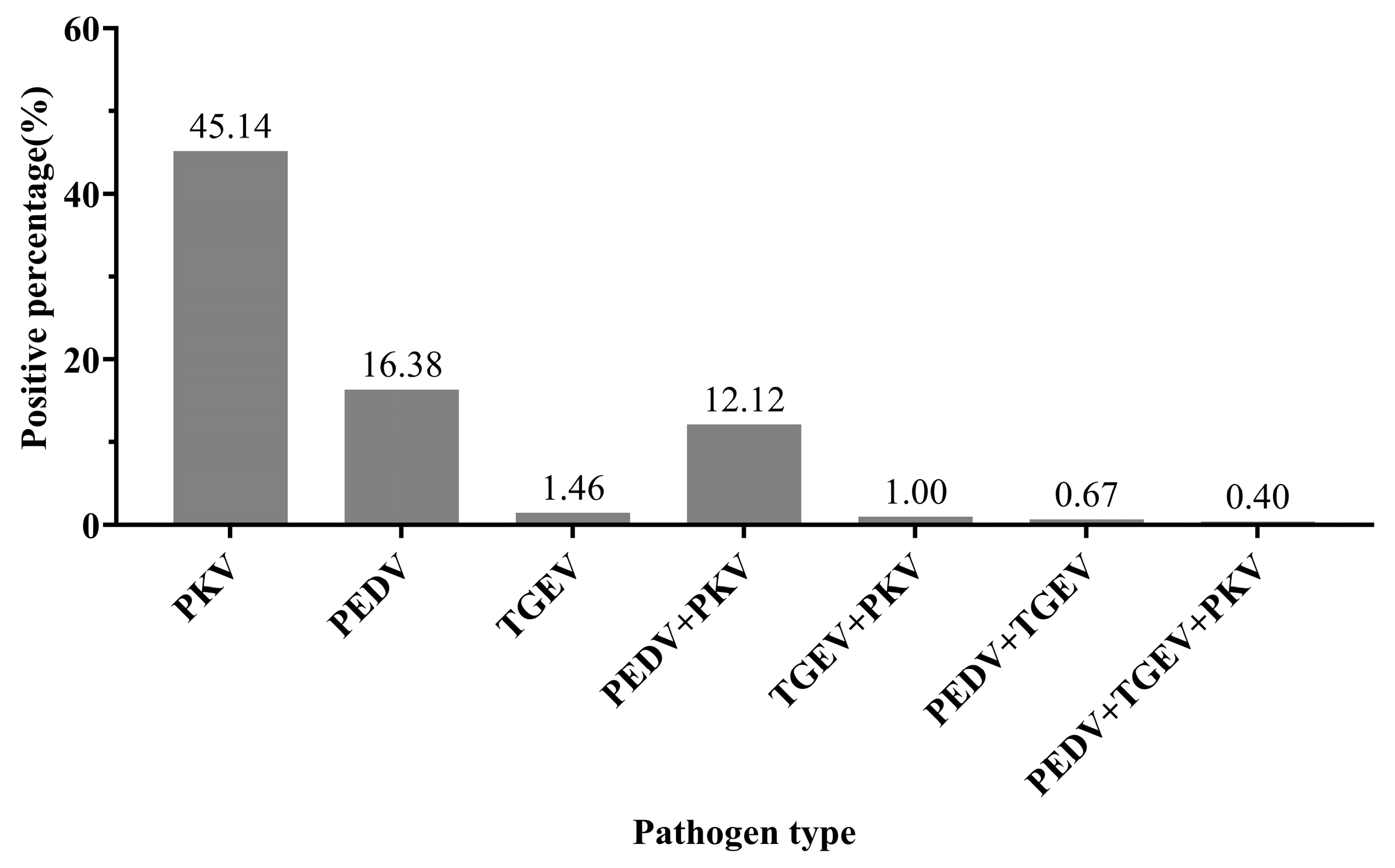
3.7. Clinical Application of Triplex RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, S.; Feng, B.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; Qiao, X.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Dual priming oligonucleotide (DPO)-based real-time RT-PCR assay for accurate differentiation of four major viruses causing porcine viral diarrhea. Mol. Cell Probes 2019, 47, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, R.; Tang, X.; Wu, C.; He, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Wu, B. Occurrence and investigation of enteric viral infections in pigs with diarrhea in China. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Wang, Q. Prevention and Control of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea: The Development of Recombination-Resistant Live Attenuated Vaccines. Viruses 2022, 14, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Nawal Bahoussi, A.; Tariq Shah, P.; Guo, Y.Y.; Wu, C.; Xing, L. Genetic comparison of transmissible gastroenteritis coronaviruses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1146648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, E.M.; Halbur, P.G.; Paul, P.S. Sequence comparison of porcine respiratory coronavirus isolates reveals heterogeneity in the S, 3, and 3-1 genes. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3176–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eléouët, J.F.; Slee, E.A.; Saurini, F.; Castagné, N.; Poncet, D.; Garrido, C.; Solary, E.; Martin, S.J. The viral nucleocapsid protein of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV) is cleaved by caspase-6 and -7 during TGEV-induced apoptosis. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3975–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Lan, D.; Hua, X. Porcine kobuvirus from pig stool specimens in Shanghai, China. Virus Genes. 2011, 43, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, N.; Kempf, E.; Hotzel, H.; Schubert, E.; Torgerson, P.; Slickers, P.; Ehricht, R.; Tasara, T.; Pospischil, A.; Sachse, K. Direct identification of chlamydiae from clinical samples using a DNA microarray assay: A validation study. Mol. Cell Probes 2008, 22, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.L.; Zhang, H.; Lin, T.; Chen, S.N.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Q.L.; Lv, D.H.; Wen, X.H.; Zhou, X.R.; Jia, C.L.; et al. A novel porcine kobuvirus emerged in piglets with severe diarrhoea in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lan, X.; Yang, B. Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Porcine kobuvirus and Its Coinfection Rate with PEDV and SaV in Northwest China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7590569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L. Molecular characterization of a porcine kobuvirus variant strain in China. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2379–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, K.; Feng, J.; Chen, G.; Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Q.; Ma, J. The detection and phylogenetic analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus from Guangdong Province in Southern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gou, F.; Meng, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, W.; Ding, W.; Xu, W.; Gu, C.; Hu, X.; Cheng, G.; et al. Porcine kobuvirus enhances porcine epidemic diarrhea virus pathogenicity and alters the number of intestinal lymphocytes in piglets. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 293, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Sha, W.; Liu, G. Development of a multiplex RT-PCR for the detection of major diarrhoeal viruses in pig herds in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; D’Anza, E.; Rossi, A.; Improda, E.; Iovane, V.; Pagnini, U.; Iovane, G.; Montagnaro, S. A Serological Investigation of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome and Three Coronaviruses in the Campania Region, Southern Italy. Viruses 2023, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Xia, C.; Gao, C. Development of a triplex quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for the detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus, and porcine rotavirus A. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1390328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Su, W.; Xiao, S.; Fang, L. Coinfection and nonrandom recombination drive the evolution of swine enteric coronaviruses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2332653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fablet, C.; Marois, C.; Dorenlor, V.; Eono, F.; Eveno, E.; Jolly, J.P.; Le Devendec, L.; Kobisch, M.; Madec, F.; Rose, N. Bacterial pathogens associated with lung lesions in slaughter pigs from 125 herds. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opriessnig, T.; Giménez-Lirola, L.G.; Halbur, P.G. Polymicrobial respiratory disease in pigs. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2011, 12, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Amimo, J.O.; Saif, L.J. Porcine Rotaviruses: Epidemiology, Immune Responses and Control Strategies. Viruses 2017, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Fukunari, K.; Suzuki, T. Multiplex RT-qPCR Application in Early Detection of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Healthy Calves. Viruses 2023, 15, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Bivins, A.; Metcalfe, S.; Smith, W.J.M.; Ziels, R.; Korajkic, A.; McMinn, B.; Graber, T.E.; Simpson, S.L. RT-qPCR and ATOPlex sequencing for the sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA for wastewater surveillance. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, C.; Kaisar, M.M.M.; Vasandani, S.R.; Surja, S.S.; Tjoa, E.; Chriestya, F.; Junusmin, K.I.; Widowati, T.A.; Irwanto, A.; Ali, S. Wide Application of Minimally Processed Saliva on Multiple RT-qPCR Kits for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Indonesia. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 691538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Wu, S.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, W. Complete genomic sequence analysis and intestinal tissue localization of a porcine Kobuvirus variant in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 104, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, G. Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) infections in pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, I.; Tsuda, T.; Mori, M.; Ono, M.; Sueyoshi, M.; Uruno, K. Isolation of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in porcine cell cultures and experimental infection of pigs of different ages. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 72, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.Q.; Cai, R.J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liang, P.S.; Chen, D.K.; Song, C.X. Outbreak of porcine epidemic diarrhea in suckling piglets, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayudhya, S.N.; Assavacheep, P.; Thanawongnuwech, R. One world–one health: The threat of emerging swine diseases. An Asian perspective. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59 (Suppl. S1), 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; He, Q. New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: An emerging and re-emerging epizootic swine virus. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, H.; Taira, O.; Hirai, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Nagao, A.; Ishikawa, Y.; Tuchiya, K.; Nunoya, T.; Ueda, S. Multiplex PCR and multiplex RT-PCR for inclusive detection of major swine DNA and RNA viruses in pigs with multiple infections. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 160, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Tao, J.; Cheng, J.; Liu, H. The Complex Co-infections of Multiple Porcine Diarrhea Viruses in Local Area Based on the Luminex xTAG Multiplex Detection Method. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 602866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Luo, Y.; Lin, C.; Tan, M.; Wan, P.; Xie, B.; Xiong, L.; Ji, H. Epidemiological monitoring and genetic variation analysis of pathogens associated with porcine viral diarrhea in southern China from 2021 to 2023. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1303915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, K.; Long, F.; Zhao, K.; Feng, S.; Yin, Y.; Xiong, C.; Qu, S.; Lu, W.; Li, Z. A Quadruplex qRT-PCR for Differential Detection of Four Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, B. Development of a Multiplex Quantitative PCR for Detecting Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus, and Porcine Deltacoronavirus Simultaneously in China. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.P.; Yang, Z.; Lin, W.D.; Wang, W.Y.; Yang, J.; Jin, W.J.; Qin, A.J. The rate of co-infection for piglet diarrhea viruses in China and the genetic characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and porcine kobuvirus. Acta Virol. 2016, 60, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Shang, R.; Cheng, K.; Wang, S.; Yuan, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, Z. Phylogenetic analysis and molecular characterization of the co-infection of the new variant of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and the novel porcine kobuvirus isolated from piglets with diarrhea. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ullman, K.; Chowdry, V.; Reining, M.; Benyeda, Z.; Baule, C.; Juremalm, M.; Wallgren, P.; Schwarz, L.; Zhou, E.; et al. Molecular investigations on the prevalence and viral load of enteric viruses in pigs from five European countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kong, D.; Fan, J.; Zhao, M.; Hua, L.; Xiang, J.; Tang, X.; Xiao, S.; et al. Development of a multiplex reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (qPCR) method for detecting common causative agents of swine viral diarrhea in China. Porc. Health Manag. 2024, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.J.; Pyo, H.M.; Tark, D.S.; Song, J.Y.; Hyun, B.H. Multiplex real-time RT-PCR for the simultaneous detection and quantification of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 146, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimkin, V.; Beer, M.; Blome, S.; Hanke, D.; Höper, D.; Jenckel, M.; Pohlmann, A. New Chimeric Porcine Coronavirus in Swine Feces, Germany, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1314–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belsham, G.J.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Normann, P.; Vaclavek, P.; Strandbygaard, B.; Bøtner, A. Characterization of a Novel Chimeric Swine Enteric Coronavirus from Diseased Pigs in Central Eastern Europe in 2016. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniotti, M.B.; Papetti, A.; Lavazza, A.; Alborali, G.; Sozzi, E.; Chiapponi, C.; Faccini, S.; Bonilauri, P.; Cordioli, P.; Marthaler, D. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Discovery of a Recombinant Swine Enteric Coronavirus, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Cheng, G.; Wei, L.; Ni, L.; et al. Establishment and application of a quadruplex real-time RT-qPCR assay for differentiation of TGEV, PEDV, PDCoV, and PoRVA. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 191, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) of Primer/Probe | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEDV | PEDV-N-F | ATTCCCAAGGGCGAAAAT | 96 |
| PEDV-N-R | ATCAACACCTTTTTCGACA | ||
| PEDV-N-P | FAM-TAGCAGCTTGCTTCGGACCC-BHQ1 | ||
| TGEV | TGEV-M-F | GTGCATTAGGAAGAAGCTATG | 115 |
| TGEV-M-R | TTCATACCACCTGCAATTTTG | ||
| TGEV-M-P | Cy5-TTCCTCTCGAAGGTGTGCCAAC-BHQ2 | ||
| PKV | PKV-3D-F | TAGGAGACGAACGGGTGAC | 124 |
| PKV-3D-R | TTGATGATGGAAGTGCCCA | ||
| PKV-3D-P | VIC-CTATATCGAAACCATACGCCACTCGC-BHQ1 |
| Plasmid Name | 10-Fold Gradient Dilutions | 106 | 105 | 104 | 103 | 102 | 101 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMD-PEDV-N | concentrations(copies/µL) Ct value | 1.142 × 106 | 1.142 × 105 | 1.142 × 104 | 1.142 × 103 | 1.142 × 102 | 1.142 × 101 | 1.142 |
| 10.70 | 14.16 | 17.74 | 21.66 | 25.43 | 29.36 | 33.24 | ||
| pMD-TGEV-M | concentrations(copies/µL) Ct value | 1.142 × 106 | 1.142 × 105 | 1.142 × 104 | 1.142 × 103 | 1.142 × 102 | 1.142 × 101 | 1.142 |
| 12.57 | 16.06 | 19.42 | 23.23 | 26.75 | 30.38 | N/A | ||
| pMD-PKV-3D | concentrations(copies/µL) Ct value | 1.142 × 106 | 1.142 × 105 | 1.142 × 104 | 1.142 × 103 | 1.142 × 102 | 1.142 × 101 | 1.142 |
| 11.29 | 14.18 | 18.26 | 22.32 | 26.11 | 30.11 | 34.10 |
| Pathogens | DNA/cDNA (Positive Samples) | Within-Group Test | Between-Group Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ct a (Mean ± S.D.) | C.V. b | Ct a (Mean ± S.D.) | C.V. b | ||
| PEDV | 1 | 24.29 ± 0.45 | 1.86% | 24.37 ± 0.06 | 0.26% |
| 2 | 27.95 ± 0.34 | 1.21% | 28.27 ± 0.16 | 0.58% | |
| 3 | 32.27 ± 0.51 | 1.58% | 32.53 ± 0.25 | 0.76% | |
| TGEV | 1 | 24.91 ± 0.44 | 1.76% | 25.09 ± 0.07 | 0.30% |
| 2 | 28.79 ± 0.28 | 0.96% | 29.03 ± 0.18 | 0.60% | |
| 3 | 32.96 ± 0.51 | 1.55% | 33.23 ± 0.34 | 1.03% | |
| PKV | 1 | 24.12 ± 0.44 | 1.76% | 25.05 ± 0.06 | 0.25% |
| 2 | 29.60 ± 0.31 | 1.05% | 29.04 ± 0.14 | 0.48% | |
| 3 | 32.96 ± 0.51 | 1.55% | 33.33 ± 0.34 | 1.02% | |
| Samples | Types | PEDV | TGEV | PKV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tr-PCR b | gb-PCR a | tr-PCR b | gb-PCR a | tr-PCR b | LDTs | ||
| 1 | fecal swab | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| 2 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 3 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 5 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 6 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 7 | fecal swab | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 8 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 9 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 10 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 12 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 13 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 14 | fecal swab | - | - | + | + | - | - |
| 15 | fecal swab | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| 16 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 17 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 18 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 20 | fecal swab | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| 21 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 23 | fecal swab | + | + | - | - | + | + |
| 24 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | fecal swab | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 26 | intestinal tract | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 27 | intestinal tract | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 28 | intestinal tract | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| 29 | intestinal tract | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | intestinal tract | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, J.; Lin, Z.; Sun, E.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qian, P.; Cheng, G. Establishment and Application of a Triplex Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Differentiation of PEDV, TGEV and PKV. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090413
Tu J, Lin Z, Sun E, Yu T, Zhang W, Sun Y, Zhu H, Qian P, Cheng G. Establishment and Application of a Triplex Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Differentiation of PEDV, TGEV and PKV. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(9):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090413
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Jun, Zhengdan Lin, Erchao Sun, Teng Yu, Weichao Zhang, Yumei Sun, Hechao Zhu, Pin Qian, and Guofu Cheng. 2024. "Establishment and Application of a Triplex Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Differentiation of PEDV, TGEV and PKV" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 9: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090413
APA StyleTu, J., Lin, Z., Sun, E., Yu, T., Zhang, W., Sun, Y., Zhu, H., Qian, P., & Cheng, G. (2024). Establishment and Application of a Triplex Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Differentiation of PEDV, TGEV and PKV. Veterinary Sciences, 11(9), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11090413







