Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Dogs and Humans
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Neuroendocrine Cells
3. Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Nomenclature and Grading
4. Epidemiology and Anatomic Distribution of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
5. Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
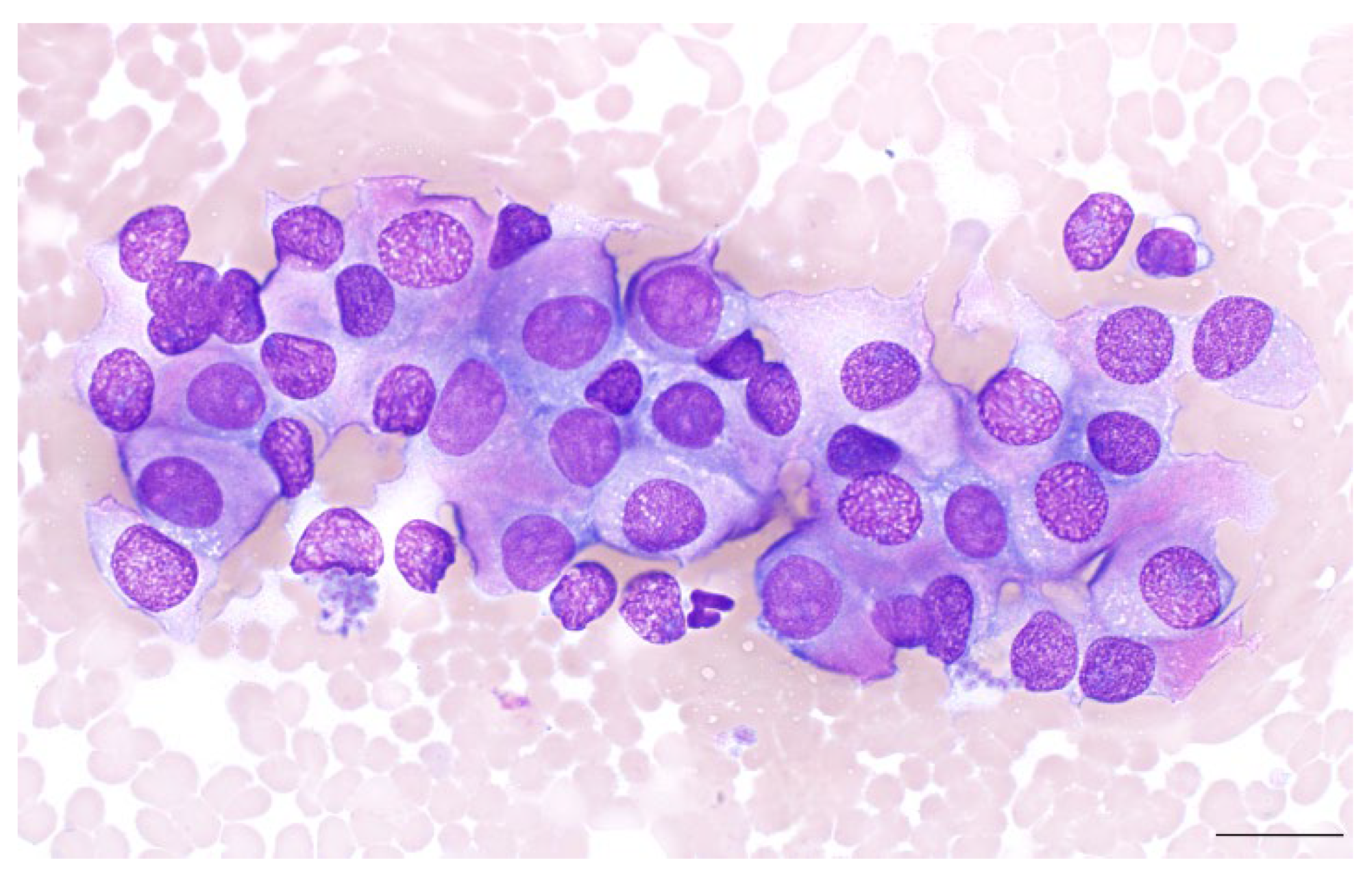
5.1. Diagnosis of Gallbladder NENs: Cytopathology
5.2. Diagnosis of Gallbladder NENs: Histopathology
5.3. Diagnosis of Gallbladder NENs: Immunohistochemistry
6. Gallbladder NENs in Humans
7. Gallbladder NENs in Dogs
7.1. Canine Patient Demographics
7.2. Presenting Complaints and Physical Exam Findings
7.3. Hematological and Biochemical Profiles
7.4. Grading and Mitotic Index
7.5. Immunohistochemical Profile
7.6. Canine Survival Data
7.7. Canine Therapy
7.8. Summary Canine GB NENs
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kloppel, G. Oberndorfer and his successors: From carcinoid to neuroendocrine carcinoma. Endocr. Pathol. 2007, 18, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oronsky, B.; Ma, P.C.; Morgensztern, D.; Carter, C.A. Nothing but net: A review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berruti, A.; Amoroso, V.; Fazio, N. Endocrine and neuroendocrine tumors: A special issue. Cancers 2022, 14, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berruti, A.; Vignani, F.; Russo, L.; Bertaglia, V.; Tullio, M.; Tucci, M.; Poggio, M.; Dogliotti, L. Prognostic role of neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer, putting together the pieces of the puzzle. Open Access J. Urol. 2010, 2, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppel, G. Tumour biology and histopathology of neuroendocrine tumours. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikusoka, M.N.; Kidd, M.; Eick, G.; Latich, I.; Modlin, I.M. The molecular genetics of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer 2005, 104, 2292–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, O. Special issue on the 2022 who classification of endocrine and neuroendocrine tumors: A new primer for endocrine pathology practice. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 who classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr Pathol 2022, 33, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Lieberman, P.H.; Erlandson, R.A.; Antonescu, C. Hepatobiliary neuroendocrine carcinoma in cats: A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of 17 cases. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, K.M.; Bankoff, B.J.; Rosenstein, P.K.; Clendaniel, D.C.; Sánchez, M.D.; Durham, A.C. Clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical features of 13 cases of canine gallbladder neuroendocrine carcinoma. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birettoni, F.; Porciello, F.; Caivano, D.; Arcelli, R.; Sforna, M.; Antognoni, M. Primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the gallbladder in a dog. Vet. Res. Commun. 2008, 32 (Suppl. 1), S239–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimata, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Matsuyama, F.; Fukazawa, E.; Harada, K.; Katayama, R.; Toshima, A.; Kagawa, Y.; Yamagami, T.; Kobayashi, T. Long-term survival in a dog with primary hepatic neuroendocrine tumor treated with toceranib phosphate. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; O’connell, K.; Thomson, M.; Boyd, S.; Sandy, J. Primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide in a dog. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2019, 55, e55305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahira, R.; Michishita, M.; Yoshimura, H.; Hatakeyama, H.; Takahashi, K. Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the mammary gland in a dog. J. Comp. Pathol. 2015, 152, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robat, C.; Houseright, R.; Murphey, J.; Sample, S.; Pinkerton, M. Paraganglioma, pituitary adenoma, and osteosarcoma in a dog. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 45, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegusa, S.; Yamamura, H.; Morita, T.; Hasegawa, A. Pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma in a four-month-old dog. J. Comp. Pathol. 1994, 111, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozmen, M.; Devrim, T.; Kuruca, N.; Inal, S.; Karaca, E.; Gulbahar, M. Primary unilateral small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the kidney in a dog. J. Comp. Pathol. 2020, 176, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, M.D.; Dunstan, R.W.; Faulkner, J. Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the gallbladder in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1988, 192, 926–928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montuenga, L.M.; Guembe, L.; Burrell, M.A.; Bodegas, M.E.; Calvo, A.; Sola, J.J.; Sesma, P.; Villaro, A.C. The diffuse endocrine system: From embryogenesis to carcinogenesis. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 38, 155–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasajima, A.; Klöppel, G. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of lung, pancreas and gut: A morphology-based comparison. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, R417–R432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A.; the WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. The 2019 who classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmack, S.; Svejda, B.; Lawrence, B.; Kidd, M.; Modlin, I.M. The diversity and commonalities of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2011, 396, 273–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloppel, G. Neuroendocrine neoplasms: Dichotomy, origin and classifications. Visc. Med. 2017, 33, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the united states. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, A.; Mehta, K.; Byers, L.A.; Sorbye, H.; Yao, J.C. Comparative study of lung and extrapulmonary poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas: A seer database analysis of 162,983 cases. Cancer 2018, 124, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dasari, A. Epidemiology, incidence, and prevalence of neuroendocrine neoplasms: Are there global differences? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modlin, I.M.; Lye, K.D.; Kidd, M. Carcinoid tumors of the stomach. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 12, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modlin, I.; Kidd, M.; Hinoue, T.; Lye, K.; Murren, J.; Argiris, A. Molecular strategies and 111in-labelled somatostatin analogues in defining the management of neuroendocrine tumour disease: A new paradigm for surgical management. Surgeon 2003, 1, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.S.; Alleman, A.R.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Youn, H.-J.; Lee, C.W. Cytologic and immunohistochemical characterization of a lung carcinoid in a dog. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 37, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, K.S.; Smith, A.N.; Henderson, R.A.; Brawner, W.R.; Spangler, E.A.; Sartin, E.A. Multicentric cutaneous neuroendocrine (merkel cell) carcinoma in a dog. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, J.M.; Vieson, M.D.; Bailey, K.; Rudmann, D.; Baumgartner, W.A.; Selting, K.A. Canine thyroid carcinomas: A review with emphasis on comparing the compact subtype of follicular thyroid carcinomas and medullary thyroid carcinomas. Vet. Pathol. 2024, 61, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galac, S.; Korpershoek, E. Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas in humans and dogs. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, K.; Galac, S.; Meij, B. Pituitary tumour types in dogs and cats. Vet. J. 2021, 270, 105623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enache, D.; Ferro, L.; Morello, E.M.; Massari, F.; Romanelli, G.; Nicoli, S.; Guazzetti, S.; Porporato, F.; Zini, E. Thyroidectomy in dogs with thyroid tumors: Survival analysis in 144 cases (1994–2018). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, C.; Konukiewitz, B.; Weichert, W.; Klöppel, G.; Aupperle-Lellbach, H.; Steiger, K. Do canine pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms resemble human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours? A comparative morphological and immunohistochemical investigation. J. Comp. Pathol. 2020, 181, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieczarka, E.M.; Russell, D.S.; Santangelo, K.S.; Aeffner, F.; Burkhard, M.J. Osseous metaplasia within a canine insulinoma. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 43, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qvigstad, G.; Kolbjørnsen, Ø.; Skancke, E.; Waldum, H. Gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma associated with atrophic gastritis in the norwegian lundehund. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 139, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Newman, S.J.; Scase, T.; Erlandson, R.A.; Antonescu, C.; Craft, D.; Bergman, P.J. Canine hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma: An immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, C.N.; Volk, M.V.; Mankowski, J.L. A carcinoid tumor in the gallbladder of a dog. Vet. Pathol. 2002, 39, 756–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, C.; Kunk, P.; Rahma, O. Small cell carcinoma of the gallbladder: Case report and comprehensive analysis of published cases. J. Oncol. 2015, 2015, 304909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanetkar, A.V.; Patkar, S.; Khobragade, K.H.; Ostwal, V.; Ramaswamy, A.; Goel, M. Ramaswamy and M. Goel. Neuroendocrine carcinoma of gallbladder: A step beyond palliative therapy, experience of 25 cases. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2019, 50, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, C.; Pang, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, X. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the gallbladder: A clinicopathological analysis of 13 patients and a review of the literature. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 5592525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, G.; Klimstra, D.S.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Asa, S.L.; Bosman, F.T.; Brambilla, E.; Busam, K.J.; De Krijger, R.R.; Dietel, M.; El-Naggar, A.K.; et al. A common classification framework for neuroendocrine neoplasms: An international agency for research on cancer (iarc) and world health organization (who) expert consensus proposal. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 1770–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batts, T.L.; Sasaki, E.; Miller, M.; Sparago, J.; Bauer, R.W.; Paulsen, D.; Boudreaux, B.; Liu, C.-C.; Byrum, S.D.; Johnston, A.N. Neoplastic signatures: Comparative proteomics of canine hepatobiliary neuroendocrine tumors to normal niche tissue. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, T. Significance of chromogranin a and synaptophysin in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Bosn. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloppel, G. [Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Two families with distinct features unified in one classification] Neuroendokrine Neoplasien: Zwei Familien mit sehr unterschiedlichen Charakteristika vereint in einer Klassifikation. Pathologe 2019, 40, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooper, L.M.; Sharma, R.; Li, Q.K.; Illei, P.B.; Westra, W.H. Insm1 demonstrates superior performance to the individual and combined use of synaptophysin, chromogranin and cd56 for diagnosing neuroendocrine tumors of the thoracic cavity. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, J.N.; Guo, Z.; Baus, R.M.; Werner, H.; Rehrauer, W.M.; Lloyd, R.V. Insm1: A novel immunohistochemical and molecular marker for neuroendocrine and neuroepithelial neoplasms. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 144, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uccella, S.; La Rosa, S.; Volante, M.; Papotti, M. Immunohistochemical biomarkers of gastrointestinal, pancreatic, pulmonary, and thymic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2018, 29, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mjønes, P.; Sagatun, L.; Nordrum, I.S.; Waldum, H.L. Neuron-specific enolase as an immunohistochemical marker is better than its reputation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2017, 65, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babkina, A.S.; Lyubomudrov, M.A.; Golubev, M.A.; Pisarev, M.V.; Golubev, A.M. Neuron-specific enolase-what are we measuring? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöppel, G.; Rindi, G.; Anlauf, M.; Perren, A.; Komminoth, P. Site-specific biology and pathology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Virchows Arch. 2007, 451 (Suppl. 1), S9–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, B.; Hong, T.; Liu, W.; He, X.; Zheng, C. Neuroendocrine neoplasm of the gallbladder: Clinical features, surgical efficacy, and prognosis. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11344–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, Y.; Sakata, J.; Endo, K.; Takahashi, M.; Saito, R.; Imano, H.; Kido, T.; Yoshino, K.; Sasaki, T.; Wakai, T. A 0.8-cm clear cell neuroendocrine tumor g1 of the gallbladder with lymph node metastasis: A case report. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippo, N.; Williams, J.; Brawer, R.; Sobel, K. Acute hemobilia and hemocholecyst in 2 dogs with gallbladder carcinoid. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandal, J.; Head, L.L.; Francis, D.A.; Foster, R.A.; Berrington, A. Use of color flow doppler ultrasonography to diagnose a bleeding neuroendocrine tumor in the gallbladder of a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 235, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.G.; Mayhew, P.D.; Mehler, S.J. Choledochotomy and primary repair of extrahepatic biliary duct rupture in seven dogs and two cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 52, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argenta, F.F.; Pereira, P.R.; Bertolini, M.; Fratini, L.M.; Saccaro, R.d.O.; Sonne, L.; Driemeier, D.; Pavarini, S.P. Carcinoid of the gallbladder in two dogs. Cienc. Rural. 2020, 50, e20190445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, E.M.; Lim, C.K.; Heng, H.G.; Grosso, F.V.; Hanlon, J.; Jones-Hall, Y. Computed tomographic features of confirmed gallbladder pathology in 34 dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2020, 61, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.N.; Reichle, J.K.; Szabo, D.; Cohen, E.B.; Artiles, C.; Fulkerson, C.V.; Kurihara, M.; Mattoon, J. Ultrasonographic appearance of gallbladder neoplasia in 14 dogs and 1 cat. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2023, 64, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.L.; Seehusen, F.; Nolff, M.C. [Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the gallbladder as a rare cause for melena and hematemesis in dogs] Neuroendokrines Karzinom der Gallenblase als seltene Ursache fur Melana und Hamatemesis beim Hund. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K. Kleintiere Heimtiere 2023, 51, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Akiyoshi, H.; Hirata, S.; Shimada, D.; Nishida, H. Ct findings of bleeding from a canine gall bladder carcinoid tumour. Vet. Rec. 2022, 10, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dog | Breed | Age (Years) | Sex | Grade | Mitotic Index | Survival (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 [18] | Bull Mastiff | 9 | M | — | 1–2 per 400× field | 300+ |
| 2 [39] | Mixed breed | 10 | FS | — | <1 per 400× field | 240 |
| 3 [11] | Mixed breed | 10 | M | — | High (number unspecified) | 120+ |
| 4 [55] | Rhodesian Ridgeback | 10 | MC | — | 1–3 per 1 HPF | 5+ |
| 5 [55] | Beagle mix | 12 | FS | — | Scattered (number unspecified) | 3+ |
| 6 [56] | Keeshond Cross | 13 | FS | — | <1 per 10 HPFs | 365+ |
| 7 [57] | Bull Mastiff | 8.5 | FS | — | — | 930 |
| 8 [58] | Shih Tzu | 10 | F | — | — | 540+ |
| 9 [58] | Cocker Spaniel | 10 | M | — | 1 per 1 HPF | 300+ |
| 10 [59] | Irish Wolfhound | 7.4 | MC | Low-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma (carcinoid) | — | — |
| 11 [62] | Boston Terrier | 10 | M | — | High (number unspecified) | 1350 |
| 12 [44] | Boston Terrier | 5 | MC | NET G1 | — | 730+ |
| 13 [44] | Doberman Pinscher | 7 | MC | NET G1 | — | 730+ |
| 14 [60] | French Bulldog | * | * | — | — | — |
| 15 [60] | French Bulldog | * | * | — | — | — |
| 16 [60] | Boxer | * | * | — | — | — |
| 17 [60] | American Eskimo | * | * | — | — | — |
| 18 [60] | Boston Terrier | * | * | — | — | — |
| 19 [60] | Golden Retriever | * | * | — | — | — |
| 20 [60] | Bulldog | * | * | — | — | — |
| 21 [60] | Australian Shepherd | * | * | — | — | — |
| 22 [10] | * | * | * | — | 10 per 10 HPFs | 1926 |
| 23 [10] | * | * | * | — | 6 per 10 HPFs | 2191 |
| 24 [10] | * | * | * | — | 3 per 10 HPFs | 1021 |
| 25 [10] | * | * | * | — | 4 per 10 HPFs | 432 |
| 26 [10] | * | * | * | — | 9 per 10 HPFs | 1537 |
| 27 [10] | * | * | * | — | 4 per 10 HPFs | 1785 |
| 28 [10] | * | * | * | — | 8 per 10 HPFs | 1174 |
| 29 [10] | * | * | * | — | 2 per 10 HPFs | 1178 |
| 30 [10] | * | * | * | — | 12 per 10 HPFs | 1834 |
| 31 [10] | * | * | * | — | 13 per 10 HPFs | 1151 |
| 32 [10] | * | * | * | — | 11 per 10 HPFs | 989 |
| 33 [10] | * | * | * | — | 10 per 10 HPFs | 518 |
| 34 [10] | * | * | * | — | 12 per 10 HPFs | 507 |
| 35 [12] | Malinois | 9 | M | — | 4 per 10 HPFs | 390 |
| Dog | Chromogranin A+ | NSE | Synaptophysin | Ki-67 | CK7 | Gastrin | S100 | PGP 9.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 [18] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 [39] | Y a | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 3 [11] | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 4 [55] | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y |
| 5 [55] | Y | — | — | — | — | — | — | Y |
| 6 [56] | 3+ | 2+ | 1+ | — | N | — | — | — |
| 7 [57] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 8 [58] | N | 3+ a | 3+ a | — | N | — | N | — |
| 9 [58] | 2+ a | N | 3+ a | — | N | — | N | — |
| 10 [59] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 11 [62] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12 [44] | Y | Y | Y | 0.04% | N | N | — | — |
| 13 [44] | Y | Y | Y | 0.05% | N | N | — | — |
| 14 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 16 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 17 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 18 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 19 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 20 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 21 [60] | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 22 [10] | 1+ | 2+ | 3+ | — | — | 2+ | — | — |
| 23 [10] | 1+ | 1+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 24 [10] | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 25 [10] | 1+ | 1+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 26 [10] | 1+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 27 [10] | 1+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 28 [10] | 1+ | 2+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 29 [10] | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 30 [10] | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 31 [10] | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 32 [10] | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 33 [10] | 2+ | 3+ | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 34 [10] | 3+ | - | 3+ | — | — | 3+ | — | — |
| 35 [12] | — | 3+ a | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelly, N.; Wu, Y.-T.; Johnston, A.N. Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Dogs and Humans. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080371
Kelly N, Wu Y-T, Johnston AN. Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Dogs and Humans. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(8):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080371
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelly, Nadia, Yen-Tse Wu, and Andrea N. Johnston. 2024. "Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Dogs and Humans" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 8: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080371
APA StyleKelly, N., Wu, Y.-T., & Johnston, A. N. (2024). Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Dogs and Humans. Veterinary Sciences, 11(8), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080371







