Changes in the Microbiome in Yak Mastitis: Insights Based on Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Assessing Clinical Health Status
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Somatic Cell Counts
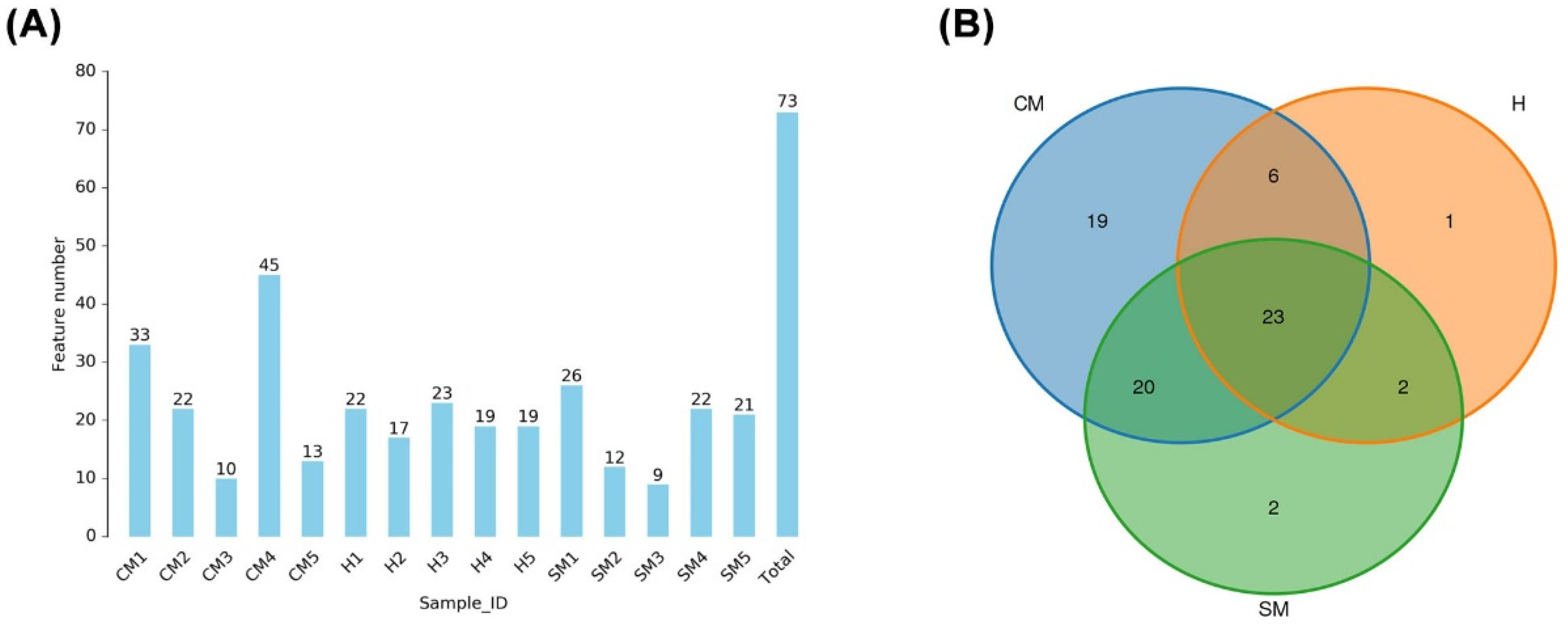
3.2. Taxonomic Identification of Milk Bacterial Community in Yak
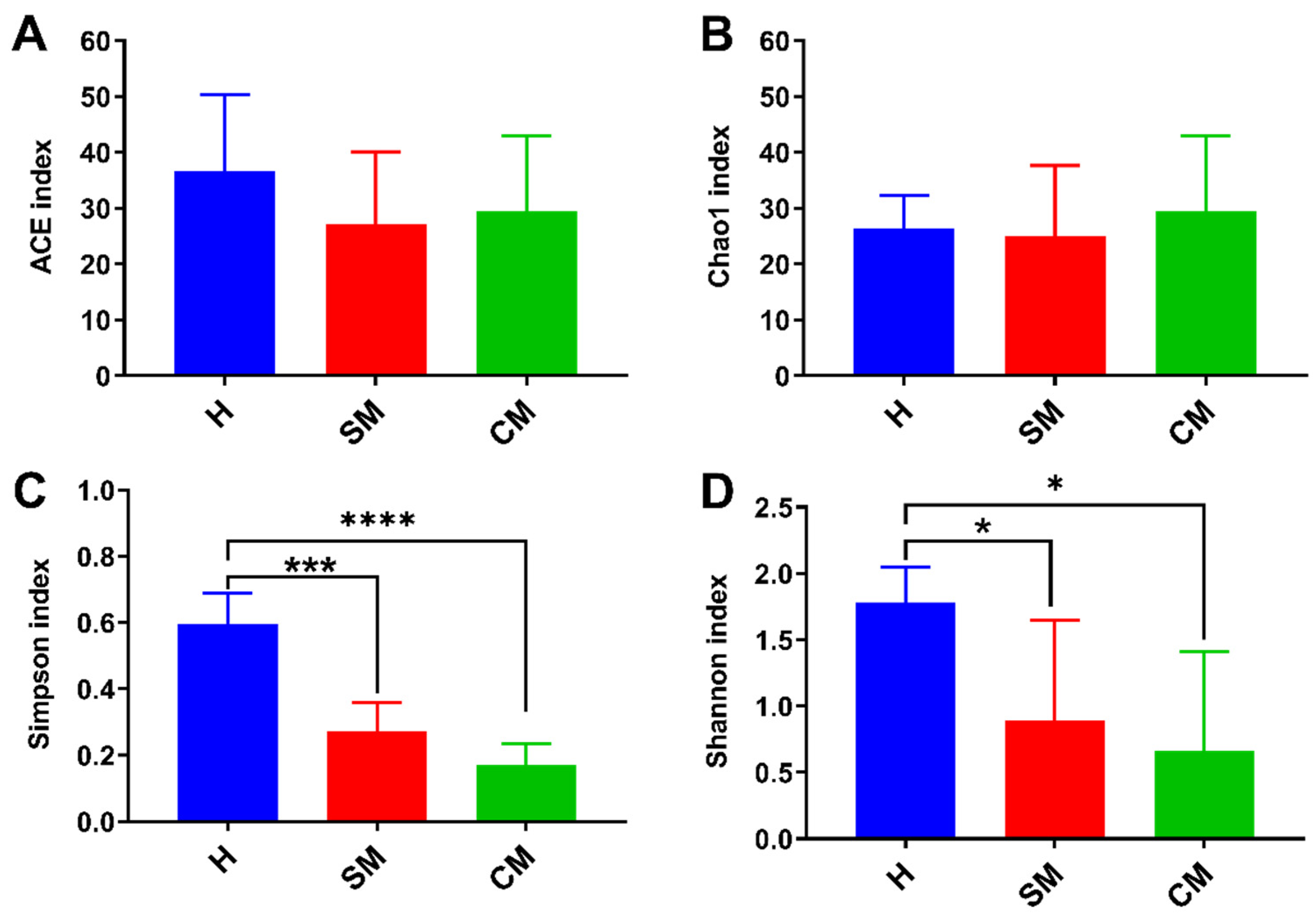
3.3. Characterization of the Bacterial Diversity in Yak Milk Samples
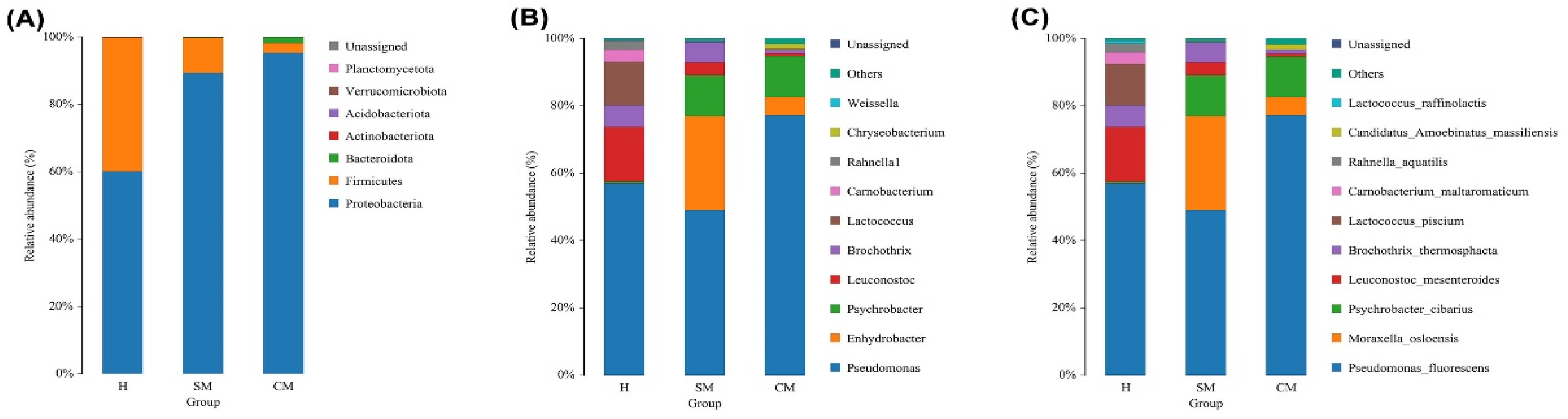
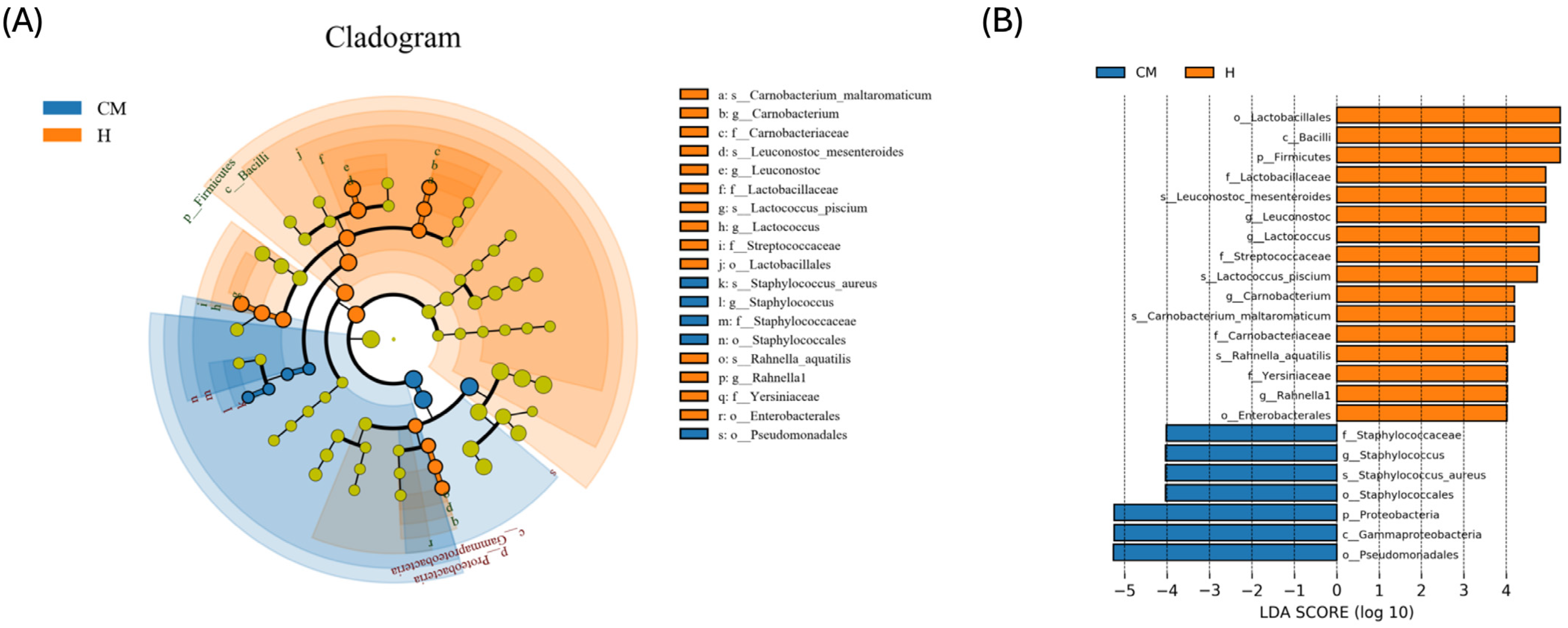
3.4. Taxonomic Bacterial Profiling of Milk Samples from Yak
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruegg, P.L. A 100-Year Review: Mastitis Detection, Management, and Prevention. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10381–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Deng, Z.; Cai, L.; Shan, R.; Zhang, S.; Zou, J.; Kastelic, J.P.; et al. Incidence of Clinical Mastitis and Distribution of Pathogens on Large Chinese Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4797–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Ma, S.; Lei, L.; He, J.; Li, X.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prevalence, Etiology, and Economic Impact of Clinical Mastitis on Large Dairy Farms in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 242, 108570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerto, M.A.; Shepley, E.; Cue, R.I.; Warner, D.; Dubuc, J.; Vasseur, E. The Hidden Cost of Disease: I. Impact of the First Incidence of Mastitis on Production and Economic Indicators of Primiparous Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7932–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshani, H.; Fehr, K.B.; Sepehri, S.; Francoz, D.; De Buck, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Plaizier, J.C.; Khafipour, E. Invited Review: Microbiota of the Bovine Udder: Contributing Factors and Potential Implications for Udder Health and Mastitis Susceptibility. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10605–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, X.; Bao, L.; Wu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, M.; Feng, L.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Induces the Development of Mastitis through a Reduction in Host Anti-Inflammatory Enzyme Activity by Endotoxemia. Microbiome 2022, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oultram, J.W.H.; Ganda, E.K.; Boulding, S.C.; Bicalho, R.C.; Oikonomou, G. A Metataxonomic Approach Could Be Considered for Cattle Clinical Mastitis Diagnostics. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.N.; Istiaq, A.; Clement, R.A.; Sultana, M.; Crandall, K.A.; Siddiki, A.Z.; Hossain, M.A. Metagenomic Deep Sequencing Reveals Association of Microbiome Signature with Functional Biases in Bovine Mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.N.; Istiaq, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Anwar, A.; Siddiki, A.M.A.M.Z.; Sultana, M.; Crandall, K.A.; Hossain, M.A. Microbiome Dynamics and Genomic Determinants of Bovine Mastitis. Genomics 2020, 112, 5188–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonesi, P.; Severgnini, M.; Romanò, A.; Sala, L.; Luini, M.; Castiglioni, B. Bovine Milk Microbiota: Comparison among Three Different DNA Extraction Protocols To Identify a Better Approach for Bacterial Analysis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00374-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Imran, M. Causes, Types, Etiological Agents, Prevalence, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, Effects on Human Health and Future Aspects of Bovine Mastitis. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2020, 21, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Xie, X.; Bao, H.; Sun, L.; He, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wei, R.; et al. Insights into the Bovine Milk Microbiota in Dairy Farms with Different Incidence Rates of Subclinical Mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, G.; Sangalli, E.; Facchi, M.; Fontana, F.; Mancabelli, L.; Donofrio, G.; Ventura, M. Metataxonomic Analysis of Milk Microbiota in the Bovine Subclinical Mastitis. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ma, T.; Qian, W.; Ye, Z.; Cao, C.; Hu, Q.; Kim, J.; Larkin, D.M.; Auvil, L.; et al. The Yak Genome and Adaptation to Life at High Altitude. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, W.; Chu, M.; Liang, C.; Wu, X.; Ping, Y. Adaptation Mechanisms of Yak (Bos grunniens) to High-Altitude Environmental Stress. Animals 2021, 11, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.N.; Hu, H.; Wen, P.C.; Lian, S.; Xie, X.L.; Song, H.L.; Yang, Z.N.; Ren, F.Z. Yak Milk–Derived Exosomes Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Inflammation by Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/C3 Pathway Activation. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8411–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobirka, M.; Tancin, V.; Slama, P. Epidemiology and Classification of Mastitis. Animals 2020, 10, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Duarte, R.; Černáková, L.; Kadam, S.; Kaushik, K.S.; Salehi, B.; Bevilacqua, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Antolak, H.; Dybka-Stępień, K.; Leszczewicz, M.; et al. Advances in Chemical and Biological Methods to Identify Microorganisms—From Past to Present. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Nawaz, M.; Yaqub, T.; Mushtaq, M.H. Investigation of Milk Microbiota of Healthy and Mastitic Sahiwal Cattle. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasapane, N.G.; Khumalo, Z.T.H.; Kwenda, S.; Nkhebenyane, S.J.; Thekisoe, O. Characterisation of Milk Microbiota from Subclinical Mastitis and Apparently Healthy Dairy Cattle in Free State Province, South Africa. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Kushima, H.; Koide, Y.; Kinoshita, Y. Pseudomonas Fluorescens Pneumonia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 140, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, P.; Hall, A.R.; Paterson, S.; Buckling, A. Rapid Decline of Adaptation of Pseudomonas Fluorescens to Soil Biotic Environment. Biol. Lett. 2022, 18, 20210593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridl, J.; Suman, J.; Fraraccio, S.; Hradilova, M.; Strejcek, M.; Cajthaml, T.; Zubrova, A.; Macek, T.; Strnad, H.; Uhlik, O. Complete Genome Sequence of Pseudomonas alcaliphila JAB1 (=DSM 26533), a Versatile Degrader of Organic Pollutants. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chautrand, T.; Depayras, S.; Souak, D.; Bouteiller, M.; Kondakova, T.; Barreau, M.; Ben Mlouka, M.A.; Hardouin, J.; Konto-Ghiorghi, Y.; Chevalier, S.; et al. Detoxification Response of Pseudomonas Fluorescens MFAF76a to Gaseous Pollutants NO2 and NO. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Nagendra, N.P.; Dhananjaya, B.L.; Mohan Kumar, K.; Yallappa, S.; Satish, S. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Endosymbiont Pseudomonas Fluorescens CA 417 and Their Bactericidal Activity. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 95, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Qian, N.; Sun, Y.; Lu, X.; Duan, H.; Qian, L. Pseudomonas Fluorescens DN16 Enhances Cucumber Defense Responses against the Necrotrophic Pathogen Botrytis cinerea by Regulating Thermospermine Catabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 645338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, S.; Fursova, K.; Shulcheva, I.; Nikanova, D.; Artyemieva, O.; Kolodina, E.; Sorokin, A.; Dzhelyadin, T.; Shchannikova, M.; Shepelyakovskaya, A.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Milk Microbiomes and Their Association with Bovine Mastitis in Two Farms in Central Russia. Animals 2021, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, G.R.; Gupta, N. Dilemma in Identifying Chryseobacterium Species. Infect. Dis. 2018, 50, 878–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbuso, T.; Defourny, L.; Lali, S.E.; Pasdermadjian, S.; Gilliaux, O. Moraxella Osloensis Infection among Adults and Children: A Pediatric Case and Literature Review. Arch. Pediatr. 2021, 28, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Kasahara, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Samejima, K.; Eriguchi, M.; Yano, H.; Mikasa, K.; Tsuruya, K. Peritonitis Due to Moraxella Osloensis: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, P.K.; Herschend, J.; Røder, H.L.; Sørensen, S.J.; Burmølle, M. Genome Sequence of Psychrobacter cibarius Strain W1. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00078-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catozzi, C.; Sanchez Bonastre, A.; Francino, O.; Lecchi, C.; De Carlo, E.; Vecchio, D.; Martucciello, A.; Fraulo, P.; Bronzo, V.; Cuscó, A.; et al. The microbiota of water buffalo milk during mastitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Chen, Q.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Yun, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, W. Antimicrobial activity and proposed action mechanism of linalool against Pseudomonas fluorescens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 562094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, K.C.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 1300–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Leijon, M.; Atkins, E.; Persson Waller, K.; Artursson, K. Longitudinal Study of Staphylococcus aureus Genotypes Isolated from Bovine Clinical Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 11945–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar]
- Howden, B.P.; Giulieri, S.G.; Wong Fok Lung, T.; Baines, S.L.; Sharkey, L.K.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Hachani, A.; Monk, I.R.; Stinear, T.P. Staphylococcus aureus Host Interactions and Adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, A.F.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penadés, J.R. Staphylococcus aureus in Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudu, P.; Yamamoto, Y.; Jensen, P.R.; Hammer, K.; Lechardeur, D.; Gruss, A. Genetics of Lactococci. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, H.C. Identification of the Agent from Lactobacillus plantarum KFRI464 That Enhances Bacteriocin Production by Leuconostoc citreum GJ7. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 2504–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; HuangFu, H.P.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Qin, G.Y.; Tan, Z. Antibacterial Activity of Lactic Acid Producing Leuconostoc mesenteroides QZ1178 against Pathogenic Gallibacterium anatis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 630294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogier, J.C.; Casalta, E.; Farrokh, C.; Saïhi, A. Safety Assessment of Dairy Microorganisms: The Leuconostoc Genus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, R.; Wu, J. Extraction and Biological Activity of Exopolysaccharide Produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides SN-8. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Cavalari, C.M.; Imazaki, P.H.; Pirard, B.; Lebrun, S.; Vanleyssem, R.; Gemmi, C.; Antoine, C.; Crevecoeur, S.; Daube, G.; Clinquart, A.; et al. Carnobacterium maltaromaticum as Bioprotective Culture against Spoilage Bacteria in Ground Meat and Cooked Ham. Meat Sci. 2024, 211, 109441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, C.F.; Borges, F.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Zagorec, M.; Remenant, B.; Leisner, J.J.; Hansen, M.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Mangavel, C.; et al. Comparative Genomic Analysis Reveals Ecological Differentiation in the Genus Carnobacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chan, H.; Liu, W.X.; Liu, C.A.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xie, C.; Liu, W.Y.Z.; et al. Carnobacterium maltaromaticum Boosts Intestinal Vitamin D Production to Suppress Colorectal Cancer in Female Mice. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1450–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraoui, T.; Leroi, F.; Björkroth, J.; Pilet, M.F. Lactococcus piscium: A Psychrotrophic Lactic Acid Bacterium with Bioprotective or Spoilage Activity in Food—A Review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahkila, R.; Nieminen, T.; Johansson, P.; Säde, E.; Björkroth, J. Characterization and Evaluation of the Spoilage Potential of Lactococcus piscium Isolates from Modified Atmosphere Packaged Meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, S.; Chaulot-Talmon, A.; Caekebeke, H.; Cardinal, M.; Christieans, S.; Denis, C.; Hélène Desmonts, M.; Dousset, X.; Feurer, C.; Hamon, E.; et al. Origin and Ecological Selection of Core and Food-Specific Bacterial Communities Associated with Meat and Seafood Spoilage. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraoui, T.; Fall, P.A.; Leroi, F.; Antignac, J.P.; Chéreau, S.; Pilet, M.F. Inhibition Mechanism of Listeria monocytogenes by a Bioprotective Bacteria Lactococcus piscium CNCM I-4031. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, S.; Pilet, M.F.; Gigout, F.; Prévost, H.; Leroi, F. Selection and Evaluation of Seafood-Borne Psychrotrophic Lactic Acid Bacteria as Inhibitors of Pathogenic and Spoilage Bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, P.A.; Leroi, F.; Cardinal, M.; Chevalier, F.; Pilet, M.F. Inhibition of Brochothrix thermosphacta and Sensory Improvement of Tropical Peeled Cooked Shrimp by Lactococcus piscium CNCM I-4031. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraoui, T.; Leroi, F.; Chevalier, F.; Cappelier, J.M.; Passerini, D.; Pilet, M.F. Bioprotective Effect of Lactococcus piscium CNCM I-4031 against Listeria monocytogenes Growth and Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.Y.; Lee, C.; Seo, M.J.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, S.H. Characterization of a Potential Probiotic Bacterium Lactococcus raffinolactis WiKim0068 Isolated from Fermented Vegetable Using Genomic and in Vitro Analyses. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, I.; Vadeboncoeur, C.; Moineau, S. Characterization of Genes Involved in the Metabolism of α-Galactosides by Lactococcus raffinolactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4049–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto-Nira, H.; Aoki, R.; Mizumachi, K.; Sasaki, K.; Naito, H.; Sawada, T.; Suzuki, C. Interaction between Lactococcus lactis and Lactococcus raffinolactis during Growth in Milk: Development of a New Starter Culture. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Tang, W.; Zeng, J.; Kulyar, M.F.; Hu, J. Changes in the Microbiome in Yak Mastitis: Insights Based on Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080335
Zhang L, Ma H, Tang W, Zeng J, Kulyar MF, Hu J. Changes in the Microbiome in Yak Mastitis: Insights Based on Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(8):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080335
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lihong, Hongcai Ma, Wenqiang Tang, Jiangyong Zeng, Md. F. Kulyar, and Junjie Hu. 2024. "Changes in the Microbiome in Yak Mastitis: Insights Based on Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 8: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080335
APA StyleZhang, L., Ma, H., Tang, W., Zeng, J., Kulyar, M. F., & Hu, J. (2024). Changes in the Microbiome in Yak Mastitis: Insights Based on Full-Length 16S rRNA Sequencing. Veterinary Sciences, 11(8), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080335






