Thoracoscopic Assisted PleuralPortTM Application in Seven Dogs Affected by Chronic Pleural Effusion
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
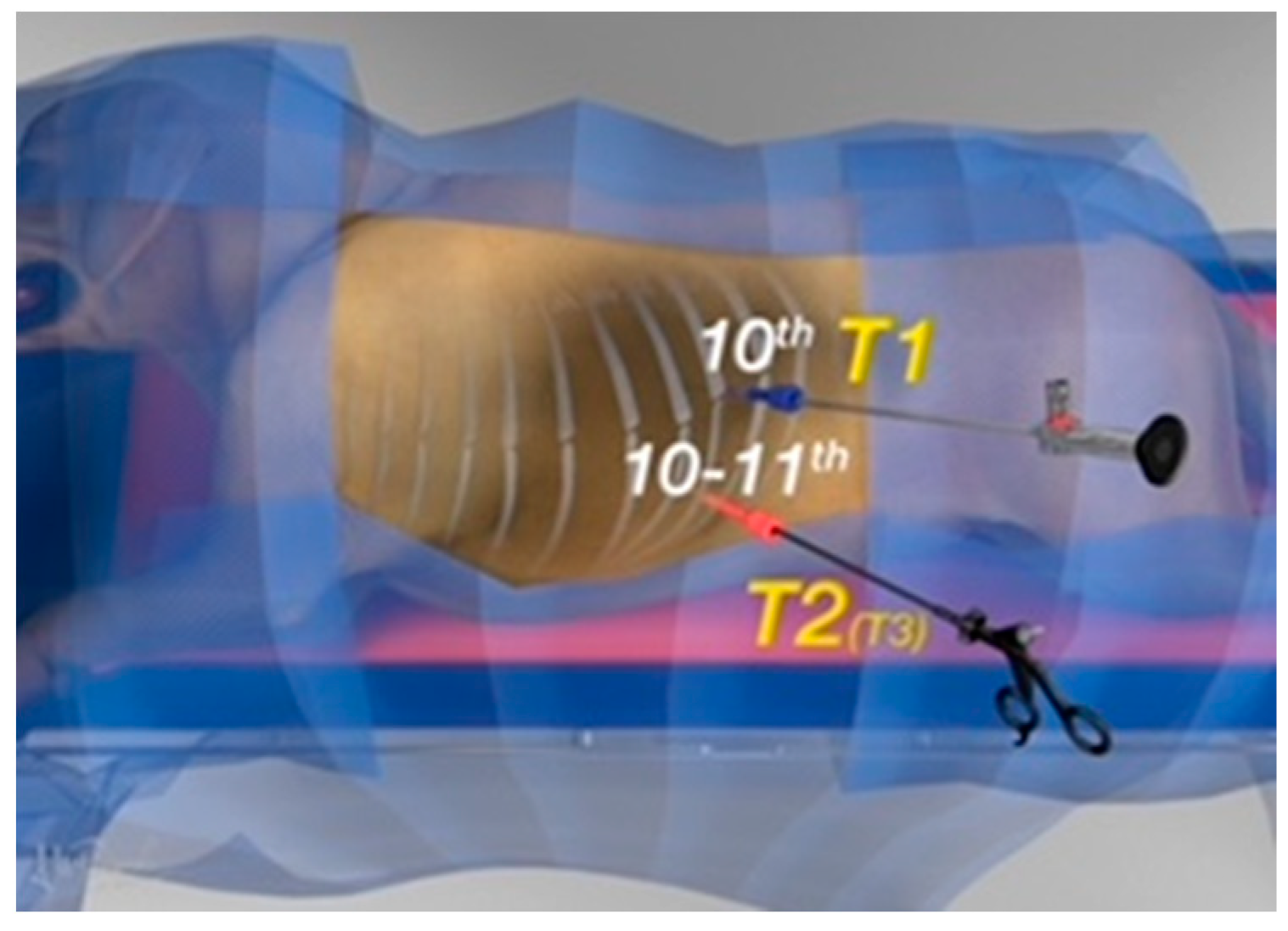
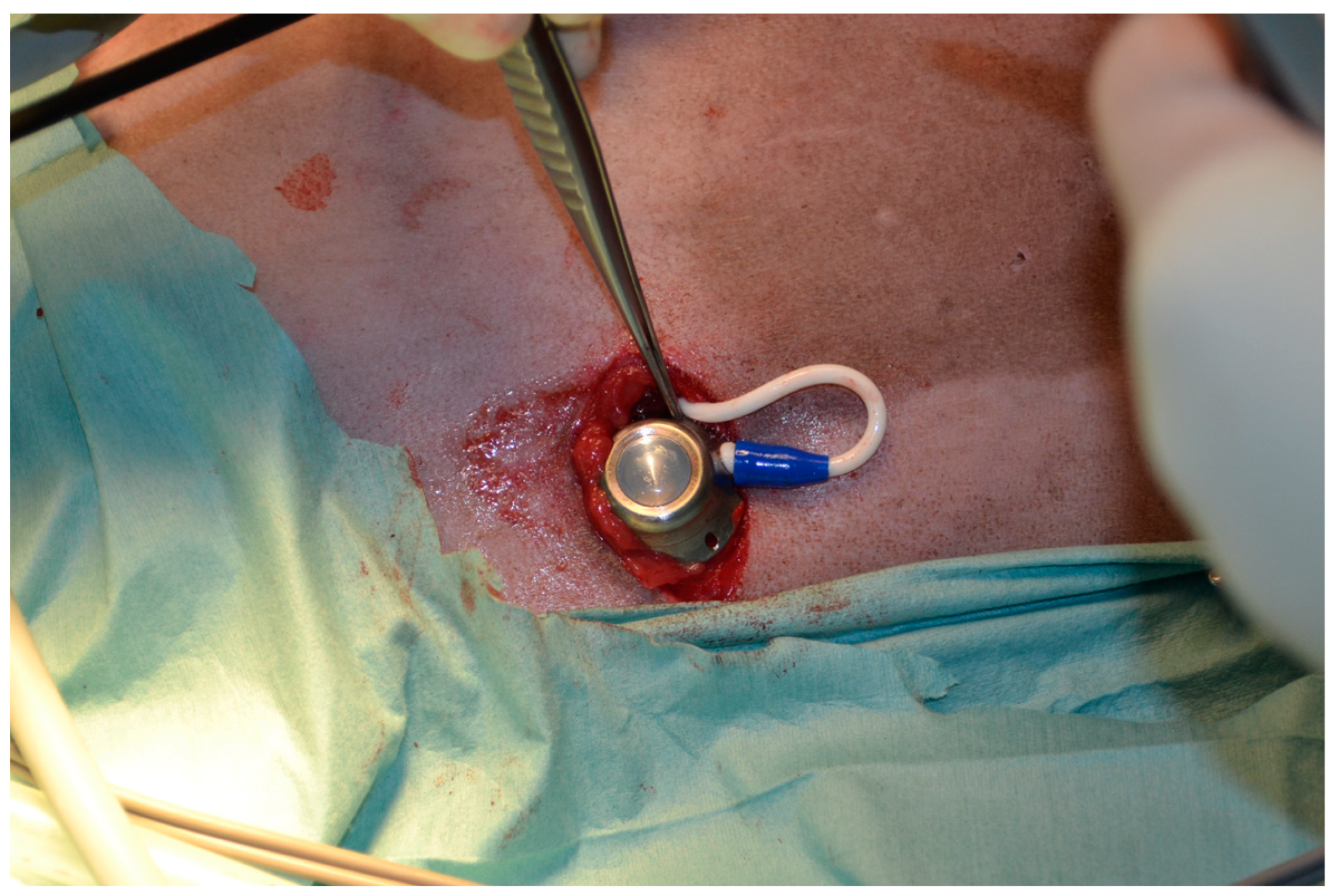
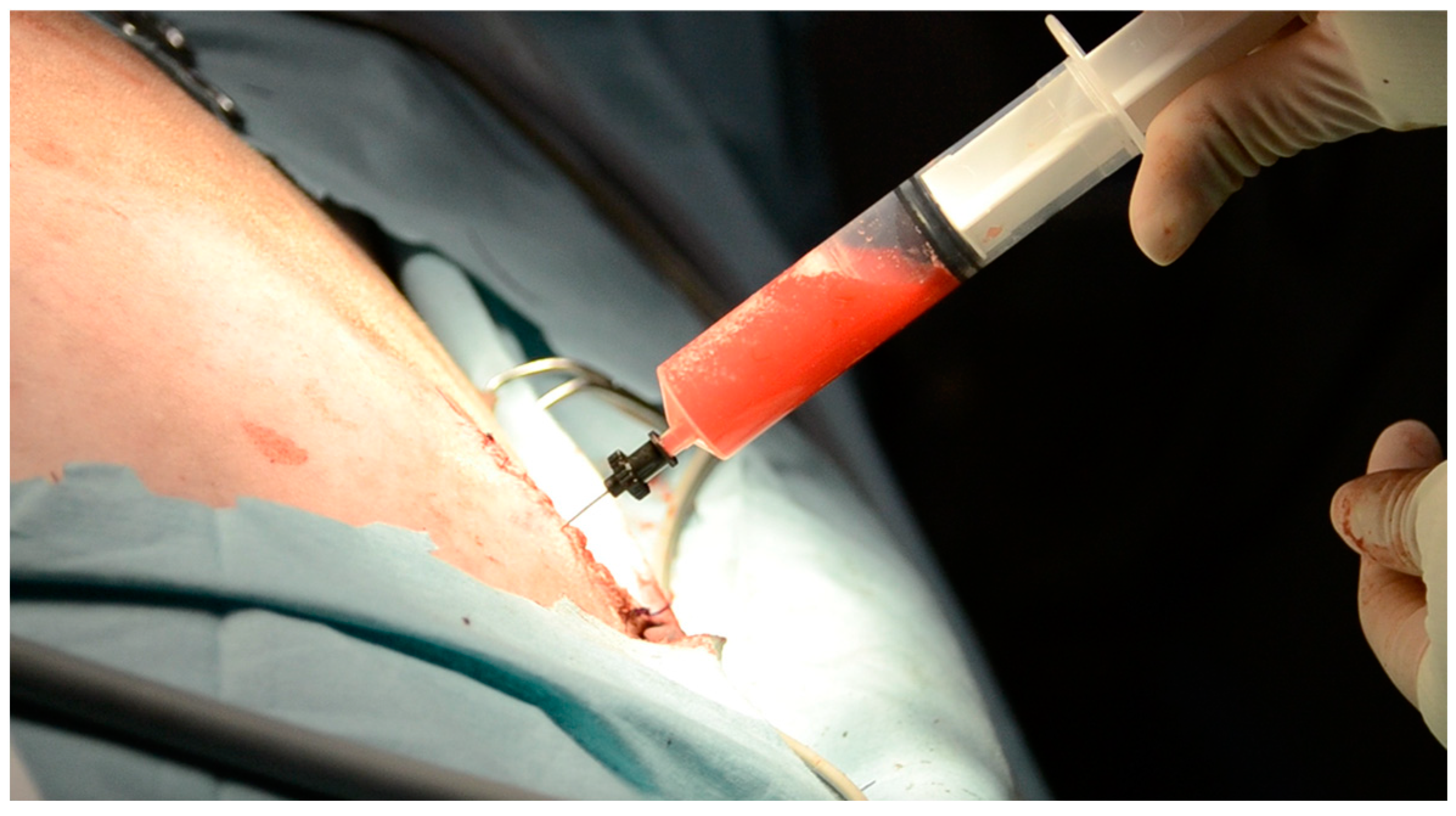
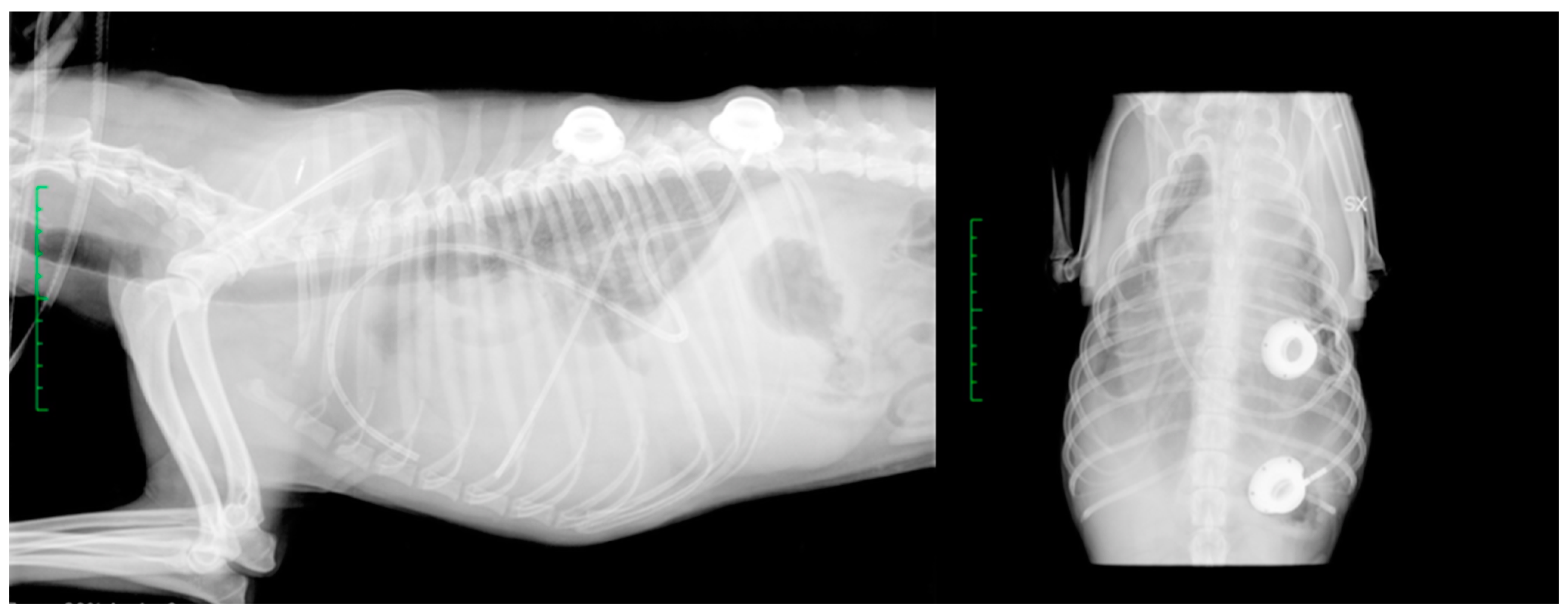
2.1. Surgical Procedure
2.2. Post-Operative Management
2.3. Complications
2.4. Follow-Up Information
2.5. Descriptive Statistics
3. Results
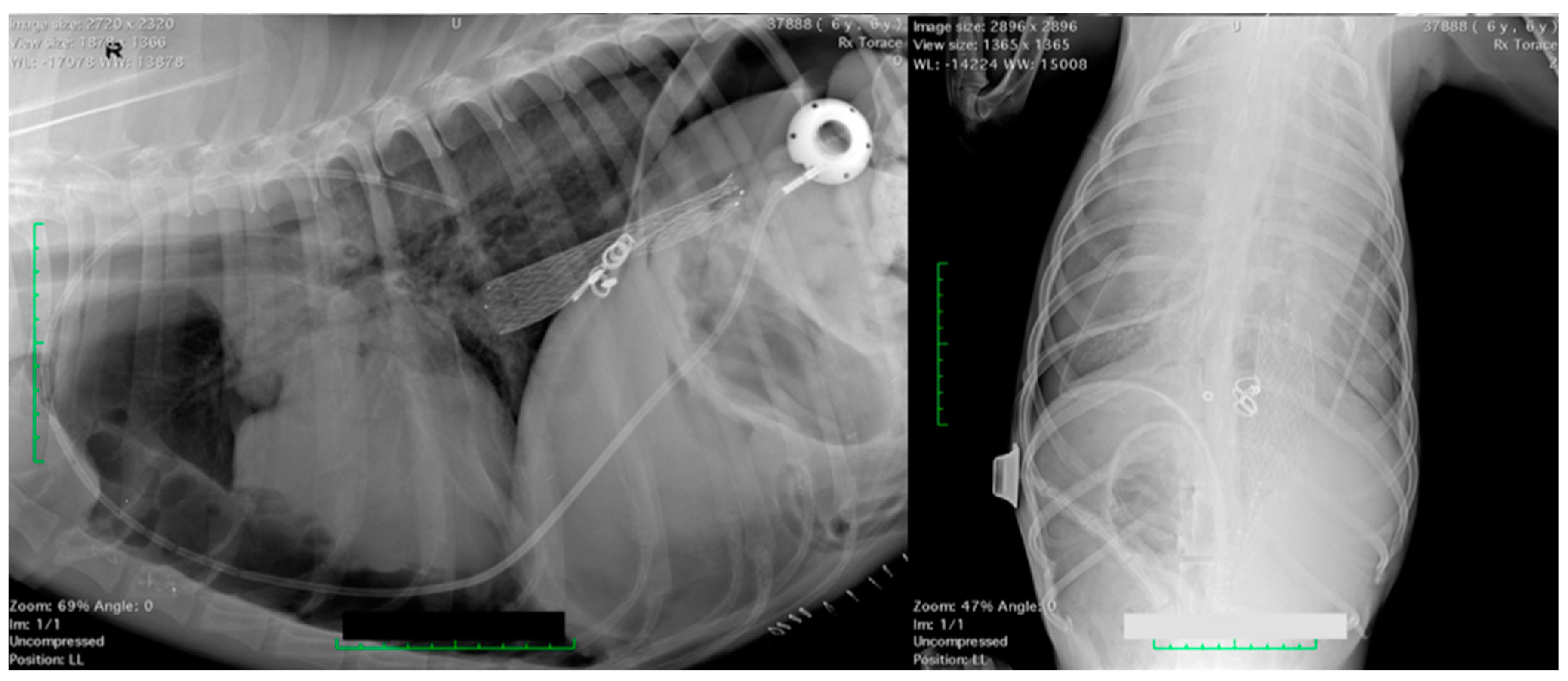
3.1. Complications
3.2. Follow-Up Information
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smeak, D.D.; Birchard, S.J.; McLoughlin, M.A.; Lindsey, M.M.; Holt, D.E.; Caywood, D.D.; Downs, M.O. Treatment of Chronic Pleural Effusion with Pleuroperitoneal Shunts in Dogs: 14 Cases (1985–1999). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, S.M.; Ewing, P.J. A Review of the Pathophysiology, Classification, and Analysis of Canine and Feline Cavitary Effusions. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2011, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, K.M.; Darrow, B.G.; Cavity, M.G.R.T. Veterinary Surgery: Small Animal Expert Consult; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, S.E. Exudative Pleural Diseases in Small Animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 44, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizabeth Rozanski Diseases of the Pleural Space. Veterinary Surgery: Small Animal Expert Consult; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 2819–2834. [Google Scholar]
- Moores, A.L.; Halfacree, Z.J.; Baines, S.J.; Lipscomb, V.J. Indications, Outcomes and Complications Following Lateral Thoracotomy in Dogs and Cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 48, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boullhesen Williams, T.; Fletcher, D.; Fusco, J.; Bichoupan, A.; Weikert, L.; Barenas, M.; Menard, J. Retrospective Evaluation of the Use and Complications of Small-Bore Wire-Guided Thoracostomy Tubes in Dogs and Cats: 156 Cases (2007–2019). Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 818055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willauer, C.C.; Breznock, E.M. Pleurovenous Shunting Technique for Treatment of Chylothorax in Three Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1987, 191, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, S.L. Postcaval Thrombosis and Delayed Shunt Migration After Pleuro-Peritoneal Venous Shunting for Concurrent Chylothorax and Chylous Ascites in a Dog. Vet Surgery 1996, 25, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fildes, J.; Narvaez, G.P.; Baig, K.A.; Pai, N.; Gerst, P.H. Pulmonary Tumor Embolization after Peritoneovenous Shunting for Malignant Ascites. Cancer 1988, 61, 1973–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.C.; Hardie, R.J. Use of the PleuralPort Device for Management of Pleural Effusion in Six Dogs and Four Cats: Use of the PleuralPort Device. Vet. Surg. 2011, 40, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahalane, A.K.; Flanders, J.A.; Steffey, M.A.; Rassnick, K.M. Use of Vascular Access Ports with Intrathoracic Drains for Treatment of Pleural Effusion in Three Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 230, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, J.B. Advances in Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery, Thoracoscopy. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 46, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhew, P.D.; Dunn, M.; Berent, A. Surgical Views: Thoracoscopy: Common Techniques in Small Animals. Compend. Contin. Educ. Vet. 2013, 35, E1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmiedt, C. Small Animal Exploratory Thoracoscopy. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburro, R.; Brunetti, B.; Muscatello, L.V.; Mantovani, C.; De Lorenzi, D. Short-Term Surgical Outcomes and Histomorphological Evaluation of Thermal Injury Following Palatoplasty Performed with Diode Laser or Air Plasma Device in Dogs with Brachycephalic Airway Obstructive Syndrome. Vet. J. 2019, 253, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacitignola, L.; Desantis, S.; Izzo, G.; Staffieri, F.; Rossi, R.; Resta, L.; Crovace, A. Comparative Morphological Effects of Cold-Blade, Electrosurgical, and Plasma Scalpels on Dog Skin. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creation and Validation of the Italian Version of the Glasgow Composite Measure Pain Scale-Short Form (ICMPS-SF). Vet. Ital. 2018, 54, 251–260. [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.S.; Kirk, C.; Cardona, A. Intracavitary Cisplatin Chemotherapy Experience with Six Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1991, 5, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, H.L.; Gramer, I.; Schofield, I.; Blackwood, L.; Killick, D.; Priestnall, S.L.; Guillén, A. Clinical Presentation, Treatment and Outcome of Canine Malignant Mesothelioma: A Retrospective Study of 34 Cases. Vet Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.M.; Niles, J.D. Use of Omentum as a Physiologic Drain for Treatment of Chylothorax in a Dog. Vet. Surg. 1999, 28, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K.; Padgett, S. Chylothorax Treated Via Thoracic Duct Ligation and Omentalization. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2010, 46, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, W.T.N. Pleural Space Disease—Thoracic Drainage and Port Placement. In Veterinary Image-Guided Interventions; Weisse, C., Berent, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 91–99. ISBN 978-1-118-91092-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rehbein, S.; Manchi, G.; Gruber, A.D.; Kohn, B. Successful Treatment of Pneumothorax in a Dog with Sterile Pleural Fibrosis Caused by Chylothorax. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossum, T.W.; Mertens, M.M.; Miller, M.W.; Peacock, J.T.; Saunders, A.; Gordon, S.; Pahl, G.; Makarski, L.A.; Bahr, A.; Hobson, P.H. Thoracic Duct Ligation and Pericardectomy for Treatment of Idiopathic Chylothorax. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2004, 18, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.A.; Monnet, E. Long-Term Outcome of Dogs Treated Surgically for Idiopathic Chylothorax: 11 Cases (1995–2009). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 239, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, L.A.; Anderson, K.M.; Luther, J.K.; Torres, B.T. Treatment of Idiopathic Chylothorax in Dogs and Cats: A Systematic Review. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allman, D.A.; Radlinsky, M.G.; Ralph, A.G.; Rawlings, C.A. Thoracoscopic Thoracic Duct Ligation and Thoracoscopic Pericardectomy for Treatment of Chylothorax in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2010, 39, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhew, P.D.; Balsa, I.M.; Stern, J.A.; Johnson, E.G.; Kaplan, J.; Gonzales, C.; Steffey, M.A.; Gibson, E.; Hagen, B.; Culp, W.T.N.; et al. Resolution, Recurrence, and Chyle Redistribution after Thoracic Duct Ligation with or without Pericardiectomy in Dogs with Naturally Occurring Idiopathic Chylothorax. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 261, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerpsack, S.J.; Smeak, D.D.; Birchard, S.J. Progressive Lymphangiectasis and Recurrent Chylothorax in a Dog after Thoracic Duct Ligation. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1995, 207, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.; Linklater, A.K.J. Complications and Management of a Long-Term Pleural Access Port in a Dog with Chronic Chylothorax Associated with Lung Lobe Torsion. Can. Vet. J. 2021, 62, 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, K.-W.; Choi, U.-S.; Jung, Y.-C.; Hong, S.-J.; Byeun, Y.-E.; Kang, M.-S.; Pachrin, B.; Kim, W.-H.; Hwang, C.-Y.; Kim, D.-Y.; et al. Palliative Intravenous Cisplatin Treatment for Concurrent Peritoneal and Pleural Mesothelioma in a Dog. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2007, 69, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spugnini, E.P.; Crispi, S.; Scarabello, A.; Caruso, G.; Citro, G.; Baldi, A. Piroxicam and Intracavitary Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Advanced Mesothelioma in Pets: Preliminary Observations. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.N.; Colby, T.; Ordonez, N.; Krausz, T.; Attanoos, R.; Beasley, M.B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Butnor, K.; Cagle, P.T.; Chirieac, L.R.; et al. Guidelines for Pathologic Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma: 2012 Update of the Consensus Statement from the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajoinie, M.; Chavalle, T.; Floch, F.; Sayag, D.; Lanore, D.; Ponce, F.; Chamel, G. Outcome of Dogs Treated with Chemotherapy for Mesothelioma: A Retrospective Clinical Study on 40 Cases and a Literature Review. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkes, A.; Murphy, S.; McConnell, F.; Smith, K.; Blunden, A.S.; Papasouliotis, K.; Vanthournout, D. Palliative Intracavitary Carboplatin Therapy in a Cat with Suspected Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2005, 7, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III Study of Pemetrexed in Combination with Cisplatin Versus Cisplatin Alone in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. JCO 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.I.D.C.; Tattersall, J.; Shaw, D.J.; Welsh, E. Retrospective Analysis of the Relationship between Time of Thoracostomy Drain Removal and Discharge Time. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 50, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case | Signalment | PleuralPort | Surgical Time | Diagnosis | Complications | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 yo FN Yorkshire | 2 | 55 min | Malignant mesothelioma | None | Euthanasia after 4 months |
| 2 | 8 yo MN German Shepherd | 1 | 80 min | Malignant mesothelioma | None | Euthanasia after 5 months |
| 3 | 8 yo FN Italian Greyhound | 1 | 35 min | Malignant mesothelioma | None | Euthanasia after 6 months |
| 4 | 10 yo FS Doberman Pincher | 1 | 45 min | Malignant mesothelioma | None | Euthanasia after 5 months |
| 5 | 14 yo ME mixed breed | 1 | 55 min | Malignant mesothelioma | None | Euthanasia after 5 months |
| 6 | 15 yo FN Yorkshire | 1 | 45 min | Pleural carcinomatosis with pulmonary metastasis and neoplastic pleural effusion | Port obstruction after 45 days | Euthanasia after 5 months |
| 7 | 13 yo ME Dachshund | 1 | 45 min | Chronic chylothorax | Pneumothorax immediately after port placement and for 12 h | Resolution after 355 days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchi, A.; Collivignarelli, F.; Paolini, A.; Vignoli, M.; Niebauer, G.W.; Dolce, G.; Canal, S.; De Bonis, A.; Rosto, M.; Del Signore, F.; et al. Thoracoscopic Assisted PleuralPortTM Application in Seven Dogs Affected by Chronic Pleural Effusion. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050324
Bianchi A, Collivignarelli F, Paolini A, Vignoli M, Niebauer GW, Dolce G, Canal S, De Bonis A, Rosto M, Del Signore F, et al. Thoracoscopic Assisted PleuralPortTM Application in Seven Dogs Affected by Chronic Pleural Effusion. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(5):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050324
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchi, Amanda, Francesco Collivignarelli, Andrea Paolini, Massimo Vignoli, Gert W. Niebauer, Giulia Dolce, Sara Canal, Andrea De Bonis, Martina Rosto, Francesca Del Signore, and et al. 2023. "Thoracoscopic Assisted PleuralPortTM Application in Seven Dogs Affected by Chronic Pleural Effusion" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 5: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050324
APA StyleBianchi, A., Collivignarelli, F., Paolini, A., Vignoli, M., Niebauer, G. W., Dolce, G., Canal, S., De Bonis, A., Rosto, M., Del Signore, F., & Tamburro, R. (2023). Thoracoscopic Assisted PleuralPortTM Application in Seven Dogs Affected by Chronic Pleural Effusion. Veterinary Sciences, 10(5), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050324






