Fecal Protein Profile in Eight Dogs Suffering from Acute Uncomplicated Diarrhea before and after Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Sampling and Patients’ Management
2.4. 2-DE and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
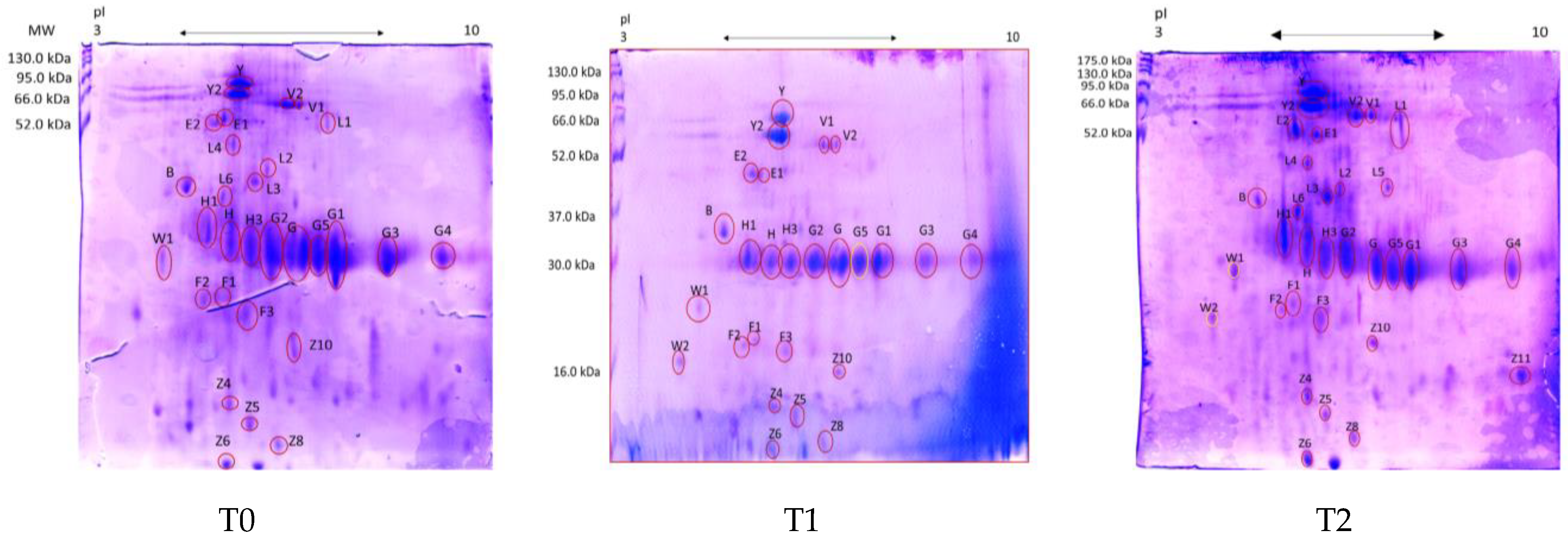
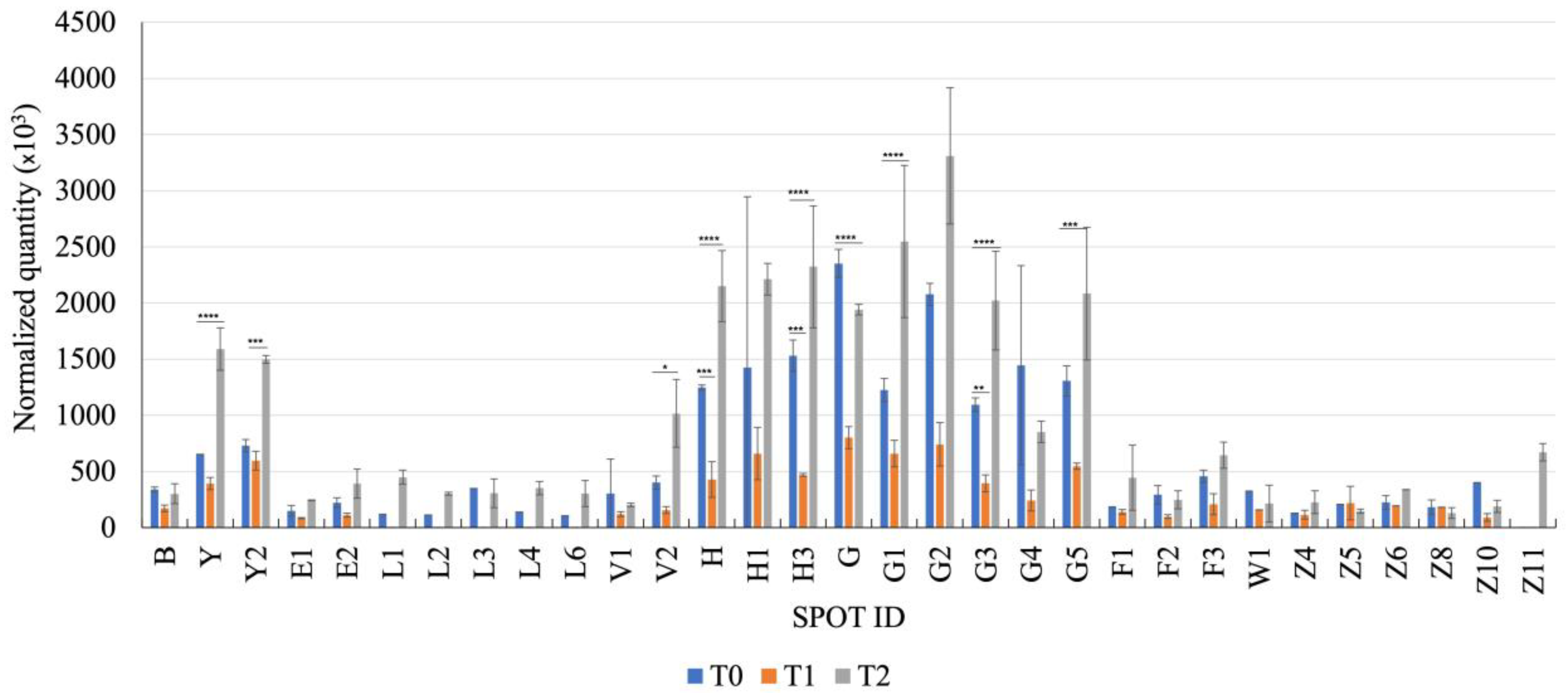
3. Results
Fecal Proteomics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neumann, S.; Steingräber, L.; Herold, L. Investigation of procalcitonin and beta-defensin2 in the serum and feces of dogs with acute diarrhea. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 50 (Suppl. S1), 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berset-Istratescu, C.M.; Glardon, O.J.; Magouras, I.; Frey, C.F.; Gobeli, S.; Burgener, I.A. Follow-up of 100 dogs with acute diarrhoea in a primary care practice. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candellone, A.; Cerquetella., M.; Girolami., F.; Badino, P.; Odore, R. Acute Diarrhea in Dogs: Current Management and Potential Role of Dietary Polyphenols Supplementation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, N.; Jessen, L.R.; Moberg, F.; Zyskind, N.; Lorentzen, C.; Bjørnvad, C.R. A retrospective study of 237 dogs hospitalized with suspected acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome: Disease severity, treatment, and outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Guard, M.M.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Unterer, S. Fecal markers of inflammation, protein loss, and microbial changes in dogs with the acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome (AHDS). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2017, 27, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipig-Rudolph, M.; Busch, K.; Prescott, J.F.; Mehdizadeh Gohari, I.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hermanns, W.; Wolf, G.; Hartmann, K.; Verspohl, J.; Unterer, S. Intestinal lesions in dogs with acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome associated with netF-positive Clostridium perfringens type A. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterer, S.; Busch, K.; Leipig, M.; Hermanns, W.; Wolf, G.; Straubinger, R.K.; Mueller, R.S.; Hartmann, K. Endoscopically visualized lesions, histologic findings, and bacterial invasion in the gastrointestinal mucosa of dogs with acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Spaterna, A.; Tesei, B.; Gavazza, A.; Pengo, G.; Pucciarelli, S.; Scortichini, L.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; et al. Fecal Proteomic Analysis in Healthy Dogs and in Dogs Suffering from Food Responsive Diarrhea. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 2742401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquetella, M.; Marchegiani, A.; Mangiaterra, S.; Rossi, G.; Gavazza, A.; Tesei, B.; Spaterna, A.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Polzonetti, V.; et al. Faecal proteome in clinically healthy dogs and cats: Findings in pooled faeces from 10 cats and 10 dogs. Vet. Rec. Open 2021, 8, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Gavazza, A.; Vincenzetti, S.; Mangiaterra, S.; Galosi, L.; Marchegiani, A.; Pengo, G.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Cerquetella, M. Clinicopathological and Fecal Proteome Evaluations in 16 Dogs Presenting Chronic Diarrhea Associated with Lymphangiectasia. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiaterra, S.; Vincenzetti, S.; Rossi, G.; Marchegiani, A.; Gavazza, A.; Petit, T.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Cerquetella, M. Evaluation of the Fecal Proteome in Healthy and Diseased Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) Suffering from Gastrointestinal Disorders. Animals 2022, 12, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, E.L.; Horvatić, A.; Kuleš, J.; Gelemanović, A.; Mrljak, V.; Huang, Y.; Brady, N.; Chadwick, C.C.; Eckersall, P.D.; Ridyard, A. Faecal proteomics in the identification of biomarkers to differentiate canine chronic enteropathies. J. Proteom. 2022, 254, 104452, Erratum in J. Proteom. 2022, 259, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsilio, S.; Dröes, F.C.; Dangott, L.; Chow, B.; Hill, S.; Ackermann, M.; Estep, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Characterization of the intestinal mucosal proteome in cats with inflammatory bowel disease and alimentary small cell lymphoma. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 179–189, Erratum in J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, N.; Stumbles, P.; Mansfield, C.S. Concentrations of interleukin-6, -8, -10 and tumour necrosis factor-α in the faeces of dogs with acute diarrhoea. N. Z. Vet. J. 2019, 67, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinler Ay, C. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker in puppies with acute diarrhea. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2022, 32, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moxham, G. Waltham feces scoring system—A tool for veterinarians and pet owners: How does your pet rate? Walth. Focus 2001, 11, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gianella, P.; Pietra, M.; Cagnasso, F.; Galiazzo, G.; Marchetti, V.; Pierini, A.; Boari, A.; Crisi, P.E.; Furlanello, T.; Marchegiani, A.; et al. Critical review on the usage of antimicrobials and on the restoration of the intestinal environment in canine acute and chronic diarrhea. Veterinaria 2021, 35, 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Karp, N.A.; Lilley, K.S. Investigating sample pooling strategies for DIGE experiments to address biological variability. Proteomics 2009, 9, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Pucciarelli, S.; Huang, Y.; Ricciutelli, M.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Scuppa, G.; Soverchia, L.; Ubaldi, M.; Polzonetti, V. Biomarkers mapping of neuropathic pain in a nerve chronic constriction injury mice model. Biochimie 2019, 158, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, T.M.; Myklebust, R.; Whybrow, A.; Jenkins, R. Epithelial integrity, cell death and cell loss in mammalian small intestine. Histol. Histopathol. 1999, 14, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.M.; Duckworth, C.A.; Burkitt, M.D.; Watson, A.J.; Campbell, B.J.; Pritchard, D.M. Epithelial cell shedding and barrier function: A matter of life and death at the small intestinal villus tip. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G. New Acquisitions Regarding Structure and Function of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier. In Immunology of the GI Tract—Recent Advances; Rodrigo, L., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, K.; Kato, K.; Sawa, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Takizawa, R.; Nishifuji, K. Comparison of the expression, activity, and fecal concentration of intestinal alkaline phosphatase between healthy dogs and dogs with chronic enteropathy. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 77, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celi, P.; Verlhac, V.; Pérez Calvo, E.; Schmeisser, J.; Kluenter, A.-M. Biomarkers of gastrointestinal functionality in animal nutrition and health. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, A.; Ludwig, M.; Hegyi, E.; Szépeová, R.; Witt, H.; Sahin-Tóth, M. Mesotrypsin Signature Mutation in a Chymotrypsin C (CTRC) Variant Associated with Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 17282–17292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girodon, E.; Rebours, V.; Chen, J.M.; Pagin, A.; Levy, P.; Ferec, C.; Bienvenu, T. Clinical interpretation of SPINK1 and CTRC variants in pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, R.; Palone, F.; Armuzzi, A.; Fulci, V.; Negroni, A.; Carissimi, C.; Cucchiara, S.; Stronati, L. Proteomic analysis identifies three reliable biomarkers of intestinal inflammation in the stools of patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 17, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.; Kim, J.; Ganesan, L.P.; Phillips, G.S.; Robinson, J.M.; Anderson, C.L. Abundant intracellular IgG in enterocytes and endoderm lacking FcRn. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.H.; Niels-Christiansen, L.L.; Immerdal, L.; Danielsen, E.M. Antibodies in the small intestine: Mucosal synthesis and deposition of anti-glycosyl IgA, IgM, and IgG in the enterocyte brush border. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G82–G90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U.; Minchiotti, L.; Galliano, M.; Peters, T., Jr. Human serum albumin isoforms: Genetic and molecular aspects and functional consequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5405–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMichael, M.A. Oxidative stress, antioxidants, and assessment of oxidative stress in dogs and cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 231, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, A.M.; Kohn, C.W.; Ramberg, C.F.; Cimprich, R.E.; Reid, C.F.; Bolton, J.R. Plasma clearance of [51Cr] albumin into the intestinal tract of normal and chronically diarrheal horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1977, 38, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unterer, S.; Busch, K. Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome in Dogs. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, F.; Strohmeyer, K.; Hartmann, K.; Unterer, S. Acute haemorrhagic diarrhoea syndrome in dogs: 108 cases. Vet. Rec. 2015, 176, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziese, A.L.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Hartmann, K.; Busch, K.; Anderson, A.; Sarwar, F.; Sindern, N.; Unterer, S. Effect of probiotic treatment on the clinical course, intestinal microbiome, and toxigenic Clostridium perfringens in dogs with acute hemorrhagic diarrhea. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.L.; Minikhiem, D.; Kiely, B.; O’Mahony, L.; O’Sullivan, D.; Boileau, T.; Park, J.S. Clinical benefits of probiotic canine-derived Bifidobacterium animalis strain AHC7 in dogs with acute idiopathic diarrhea. Vet. Ther. 2009, 10, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Herstad, H.K.; Nesheim, B.B.; L’Abée-Lund, T.; Larsen, S.; Skancke, E. Effects of a probiotic intervention in acute canine gastroenteritis—A controlled clinical trial. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 51, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmalberg, J.; Montalbano, C.; Morelli, G.; Buckley, G.J. A Randomized Double Blinded Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of a Probiotic or Metronidazole for Acute Canine Diarrhea. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Schmitz, S.S.; Allenspach, K.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Furlanello, T.; Gavazza, A.; Marchegiani, A.; Unterer, S.; et al. Proposal for rational antibacterial use in the diagnosis and treatment of dogs with chronic diarrhoea. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 61, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N. | Breed | Age (Years) | Sex | Therapy Undertaken | FS § T0 | FS § T1 | FS § T2 | * Serum Albumin (g/dL) [Reference Value 2.60–3.30] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | English Setter | 2 | M | Diet ** + probiotics | 4.5 | 5 | 2 | 2.55 |
| 2 | Pinscher | 4 | M | Diet ** + probiotics + ranitidine + maropitant + complementary feed to support liver function | 3.5 | 4 | 2.5 | 3.56 |
| 3 | Cocker Spaniel | 3 | M | Probiotics + fluids + ranitidine + maropitant | 3 | - | - | 2.67 |
| 4 | Labrador Retriever | 2 | F | Probiotics + ranitidine + metoclopramide | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3.7 |
| 5 | Labrador Retriever | 7 | F | Diet ** + fluids + probiotics + ranitidine | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2.7 |
| 6 | Australian Shepherd | 5 | M | Diet ** + probiotics | 5 | 4.5 | 2 | - |
| 7 | Border Collie | 9 | F | Diet ** + probiotics | 4 | 3 | 2 | - |
| 8 | Mixed breed | 10 | M | Diet ** + probiotics | 4 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 9 | Mestizo Pinscher | 2 | F | Diet ** + probiotics | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2.86 |
| Mean values | 3.8 | 3.2 | 1.9 | 3.00 | ||||
| Spot ID a Healthy | Spot ID b AUD | Protein c | Score d | Mr (kDa)/pI e | Mr (kDa)/pI f | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n.d. | B | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 39 | 68.5/5.52 | 35.7/4.8 | DFAEISK |
| present | Y | Serum albumin isoform X1 [Canis lupus familiaris] | 56 | 68.6/5.51 | 72/5.8 | LVAAAQAALV |
| present | Y2 | Serum albumin isoform X1 [Canis lupus familiaris] | 41 | 68.6/5.51 | 63/5.8 | ADFAEISK |
| n.d. | E1 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 216 | 68.5/5.52 | 53.3/5.3 | DFAEISKVVTDLTK |
| n.d. | E2 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 104 | 68.5/5.52 | 50.7/5.2 | KLGEYGFQNALLVR |
| n.d. | L1 | Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase [Mus musculus] | 103 | 60.2/6.24 | 52.3/7.2 | NLIIFLGDGMGVPT |
| n.d. | L2 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 131 | 68.5/5.52 | 36.1/6.1 | LVAAAQAALV |
| n.d. | L3 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 332 | 68.5/5.52 | 33.8/5.8 | LVAAAQAALV |
| n.d. | L4 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 131 | 68.5/5.52 | 43.8/5.5 | LVAAAQAALV |
| n.d. | L6 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 100 | 68.5/5.52 | 29.9/5.3 | DFAEISKVVT |
| present | V1 | Alkaline phosphatase [Canis lupus familiaris] | 125 | 68.6/6,47 | 59/6.6 | ANYQTIGVSAAAR |
| present | V2 | Alkaline phosphatase [Canis lupus familiaris] | 117 | 48.3/6.15 | 58/6.6 | ANYQTIGVSAAAR |
| present | H | Chymotrypsin-C-like [Canis lupus dingo] | 49 | 29.1/5.33 | 29/5.6 | LAEPVQLSDTIK |
| present | H1 | Elastase-3B, Proteinase E [Canis lupus familiaris] | 40 | 28.8/5.27 | 29/5.2 | VSAFNDWIEEVMSS |
| present | H3 | Immunoglobulin kappa light chain [Felis catus] | 41 | 26.7/6.10 | 29/6.3 | FSGSGSGTDFTLR |
| present | G | Immunoglobulin λ-1 light chain [Canis lupus familiaris] | 34 | 25.2/6.88 | 29/7.1 | KGTHVTVLGQPK |
| present | G1 | Immunoglobulin λ-1 light chain [Felis catus] | 39 | 27.8/8.17 | 29/7.6 | QSNNKYAASSYL |
| present | G2 | Immunoglobulin λ-light chain VLJ region [Homo sapiens] | 42 | 29.0/8.14 | 29/6.6 | EFGGGTKLTVLGQP |
| present | G3 | Immunoglobulin λ-light chain VLJ region [Homo sapiens] | 30 | 29.0/8.14 | 27/8.4 | EFGGGTKLTVLGQP |
| present | G4 | Immunoglobulin λ-light chain VLJ region [Homo sapiens] | 40 | 29.0/8.14 | 27.7/8.9 | QSNNKYAASSYL |
| n.d. | G5 | Immunoglobulin kappa chain V region [Canis lupus familiaris] | 84 | 12.0/6.4 | 25/7 | FSGSGSGTDFTLR |
| present | F1 | Nuclear pore membrane glycoprotein 210 [Canis lupus familiaris] | 29 | 192.4/6.30 | 19.6 ± 1.5/5.8 ± 0.14 | TALLVTASISGSHAPR |
| present | F2 | Cytosol aminopeptidase [Canis lupus familiaris] | 29 | 56.2/8.03 | 21.0 ± 1.3/5.7 ± 0.07 | EILNISGPPLK |
| n.d. | F3 | Immunoglobulin lambda variable 4–60 [Homo sapiens] | 69 | 12.9/5.8 | 16.3 ± 1.6/6 ± 0.1 | FSGSSSGADR |
| n.d. | W1 | Immunoglobulin J chain [Homo sapiens] | 43 | 18.1/5.12 | 21 ± 0.07/4.1 ± 0.05 | IIVPLNNR |
| n.d. | Z4 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 152 | 68.5/5.52 | 8.8 ± 0.5/4.1 ± 0.03 | LVAAAQAALV |
| n.d. | Z5 | Fatty acid-binding protein, intestinal [Homo sapiens] | 69 | 15.2/6.6 | 8.3 ± 3.4/5.9 ± 0.07 | LTITQEGNK |
| n.d. | Z6 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 76 | 68.5/5.52 | 7.1 ± 3.1/5.5 ± 0.2 | EAYKSEIAHRYNDLGE |
| n.d. | Z8 | Albumin [Canis lupus familiaris] | 80 | 68.5/5.52 | 8.1 ± 0.1/6 ± 0.1 | EAYKSEIAHRYNDLGE |
| n.d. | Z10 | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] [Canis lupus familiaris] | 233 | 15.9/5.7 | 8.8 ± 0.5/6.2 ± 0.1 | EKRDDLGKGDNEEST |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerquetella, M.; Mangiaterra, S.; Rossi, G.; Gavazza, A.; Marchegiani, A.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Angeloni, S.; Fioretti, L.; Marini, C.; et al. Fecal Protein Profile in Eight Dogs Suffering from Acute Uncomplicated Diarrhea before and after Treatment. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030233
Cerquetella M, Mangiaterra S, Rossi G, Gavazza A, Marchegiani A, Sagratini G, Ricciutelli M, Angeloni S, Fioretti L, Marini C, et al. Fecal Protein Profile in Eight Dogs Suffering from Acute Uncomplicated Diarrhea before and after Treatment. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(3):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030233
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerquetella, Matteo, Sara Mangiaterra, Giacomo Rossi, Alessandra Gavazza, Andrea Marchegiani, Gianni Sagratini, Massimo Ricciutelli, Simone Angeloni, Licia Fioretti, Carlotta Marini, and et al. 2023. "Fecal Protein Profile in Eight Dogs Suffering from Acute Uncomplicated Diarrhea before and after Treatment" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 3: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030233
APA StyleCerquetella, M., Mangiaterra, S., Rossi, G., Gavazza, A., Marchegiani, A., Sagratini, G., Ricciutelli, M., Angeloni, S., Fioretti, L., Marini, C., Pucciarelli, S., & Vincenzetti, S. (2023). Fecal Protein Profile in Eight Dogs Suffering from Acute Uncomplicated Diarrhea before and after Treatment. Veterinary Sciences, 10(3), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030233








