Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of Pseudorabies Virus via Suppressing the Entry and Release Stages in Its Replication Cycle
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
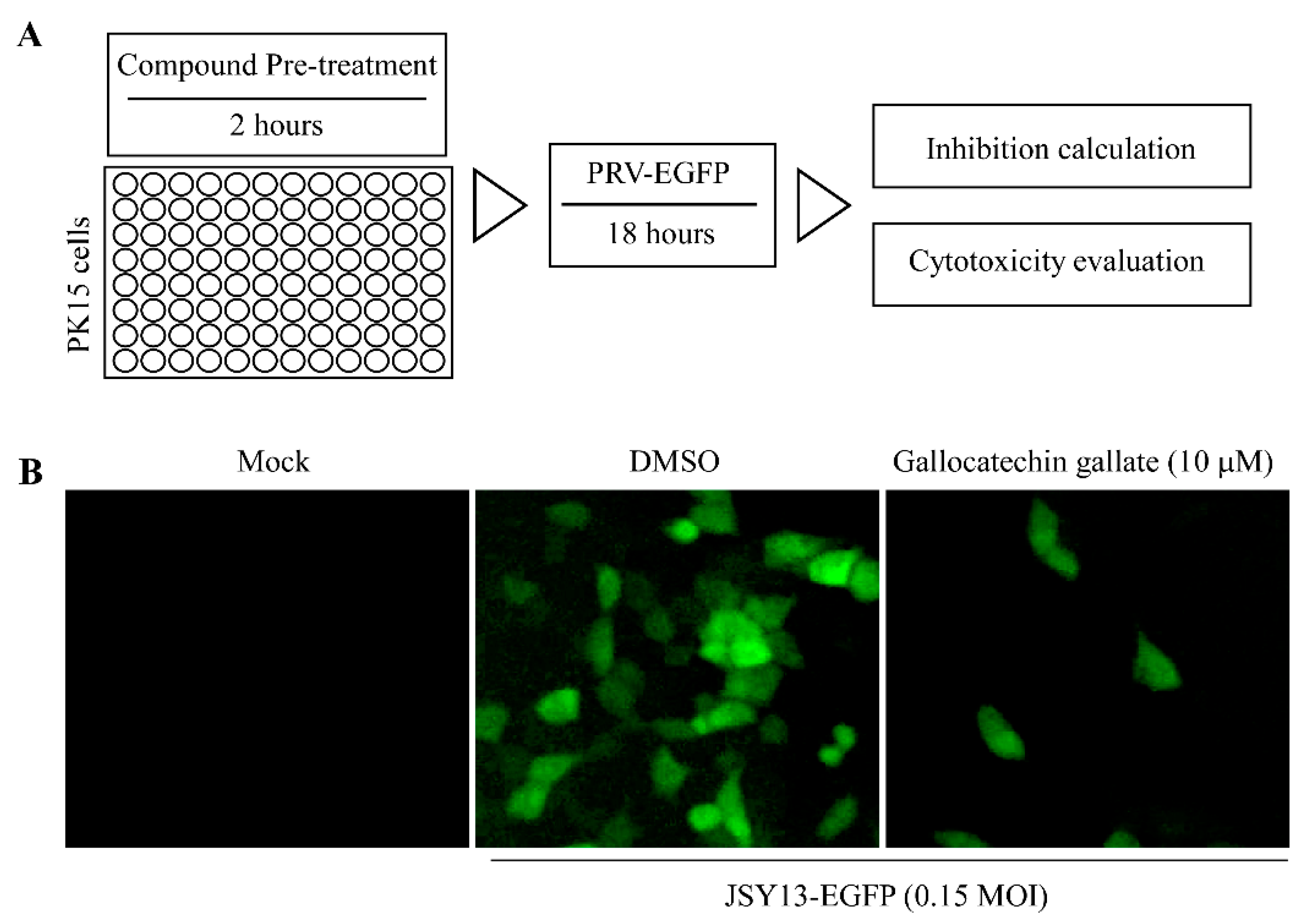
2.3. Anti-PRV-Compound Screening
2.4. Cell-Based ELISA
2.5. Western-Blot
2.6. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay
2.7. The mRNA Level of PRV Genes and GAPDH Was Measured Using qPCR
2.8. Detection of the Effect of Gallocatechin Gallate on the Attachment of PRV
2.9. Detection of the Effect of Gallocatechin Gallate on PRV Entry into Cells
2.10. Assaying the Effect of Drugs on PRV Release
2.11. Assay for Direct Inactivation of PRV by Gallocatechin Gallate
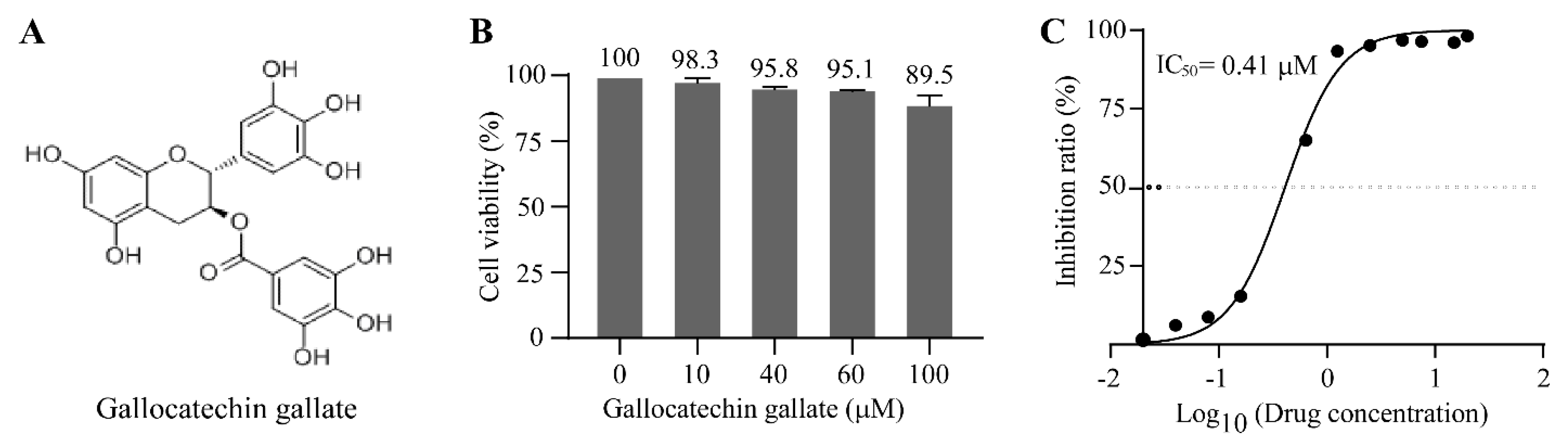
2.12. Cell Viability Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fluorescence-Based Screening of the Anti-PRV Compounds
3.2. Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of PRV with a Low IC50 of 0.41 μM
3.3. Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of PRV in a Dose-Dependent Manner
3.4. Gallocatechin Gallate Suppressed the Entry Stage of PRV
3.5. Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Release Stage in the PRV Replication Cycle
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, T.; Hahn, E.C.; Tottewitz, F.; Kramer, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Freuling, C. Pseudorabies virus in wild swine: A global perspective. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeranz, L.E.; Reynolds, A.E.; Hengartner, C.J. Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: Impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2005, 69, 462–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauwynck, H.; Glorieux, S.; Favoreel, H.; Pensaert, M. Cell biological and molecular characteristics of pseudorabies virus infections in cell cultures and in pigs with emphasis on the respiratory tract. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Wilson, M.R. A review of pseudorabies (Aujeszky’s disease) in pigs. Can. Vet. J. Rev. Vet. Can. 1979, 20, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, E.C.; Fadl-Alla, B.; Lichtensteiger, C.A. Variation of Aujeszky's disease viruses in wild swine in USA. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Bätza, H.J.; Schlüter, H.; Conraths, F.J.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Eradication of Aujeszky’s disease in Germany. J. Vet. Medicine. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2003, 50, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensaert, M.; Morrison, R.B. Challenges of the final stages of the ADV eradication program. Vet. Res. 2000, 31, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamiguchi, K.; Kojima, S.; Sakumoto, K.; Kirisawa, R. Isolation and molecular characterization of a variant of Chinese gC-genotype II pseudorabies virus from a hunting dog infected by biting a wild boar in Japan and its pathogenicity in a mouse model. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhou, C.; Guo, S.; Tan, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. The Epidemiology and Variation in Pseudorabies Virus: A Continuing Challenge to Pigs and Humans. Viruses 2022, 14, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Han, T.; Li, X.; Gu, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; et al. Pathogenic pseudorabies virus, China, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Su, S.; Zhou, J.; Lei, J.; Xing, G.; Sun, H.; et al. Genome Characteristics and Evolution of Pseudorabies Virus Strains in Eastern China from 2017 to 2019. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.Q.; Peng, J.M.; Tian, Z.J.; Zhao, H.Y.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, J.Z.; Leng, C.L.; Sun, Y.; Chang, D.; et al. Pseudorabies virus variant in Bartha-K61-vaccinated pigs, China, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Ma, Z.; Bai, J.; Sun, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Liu, X. Comparison of the protective efficacy between the candidate vaccine ZJ01R carrying gE/gI/TK deletion and three commercial vaccines against an emerging pseudorabies virus variant. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 276, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Wu, X.M.; Che, Y.L.; Chen, R.J.; Hou, B.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, L.B.; Zhou, L.J. The Immune Efficacy of Inactivated Pseudorabies Vaccine Prepared from FJ-2012ΔgE/gI Strain. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, G.R.; Ahmad, A.; Davies, J.A. The infrequency of transmission of herpesviruses between humans and animals; postulation of an unrecognised protective host mechanism. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2001, 24, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, G.F. Pseudorabies virus: A neglected zoonotic pathogen in humans? Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cui, Q.; Fu, Q.; Song, X.; Jia, R.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; He, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Antiviral properties of resveratrol against pseudorabies virus are associated with the inhibition of IκB kinase activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.X.; Wang, T.Y.; Tang, Y.D.; Wei, P. Isobavachalcone inhibits Pseudorabies virus by impairing virus-induced cell-to-cell fusion. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, D.; Yuan, L.; Lian, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Nowotny, N.; Shi, Y.; Li, X. Meclizine Inhibits Pseudorabies Virus Replication by Interfering With Virus Entry and Release. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 795593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Miao, Y.; Xi, R.; Gao, X.; Miao, D.; Chen, H.; Jung, Y.S.; Qian, Y.; Dai, J. Emergence of a novel pathogenic recombinant virus from Bartha vaccine and variant pseudorabies virus in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Yan, F. A 5`-tRNA Derived Fragment NamedtiRNA-Val-CAC-001 Works as a Suppressor in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 2323–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzow, H.; Klupp, B.G.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Entry of pseudorabies virus: An immunogold-labeling study. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3200–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.H.; Fu, P.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Pseudorabies Virus: From Pathogenesis to Prevention Strategies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, N.; Cong, X.; Wang, C.H.; Du, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, D.D.; Li, S.; et al. Pathogenicity and genomic characterization of a pseudorabies virus variant isolated from Bartha-K61-vaccinated swine population in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, Z.; Li, X. A Review of Pseudorabies Virus Variants: Genomics, Vaccination, Transmission, and Zoonotic Potential. Viruses 2022, 14, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liang, L.; Tang, X.; Hou, S.; Yang, W.; Liang, R. Assessing the Risk of Commercial Vaccines Against Pseudorabies Virus in Cats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 857834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, T.; Enquist, L.W. Directional spread of alphaherpesviruses in the nervous system. Viruses 2013, 5, 678–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WuDunn, D.; Spear, P.G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettenleiter, T.C.; Zsak, L.; Zuckermann, F.; Sugg, N.; Kern, H.; Ben-Porat, T. Interaction of glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike substance mediates adsorption of pseudorabies virus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzow, H.; Weiland, F.; Jöns, A.; Klupp, B.G.; Karger, A.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Ultrastructural analysis of the replication cycle of pseudorabies virus in cell culture: A reassessment. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 2072–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, W.; Klupp, B.G.; Granzow, H.; Mettenleiter, T.C. The UL20 gene product of pseudorabies virus functions in virus egress. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5639–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, W.; Klupp, B.G.; Granzow, H.; Rziha, H.J.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Identification and characterization of the pseudorabies virus UL3.5 protein, which is involved in virus egress. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 3517–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Imada, T.; Watanabe, W.; Honda, Y.; Nakajima-Iijima, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Sekikawa, K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the major capsid protein gene of pseudorabies virus. Virology 1991, 185, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, H.M.; Du, Y.M.; Yan, R.A.; Ou, S.Y.; Chen, T.F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.X.; Fu, L. C-geranylated flavanones from YingDe black tea and their antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibition activities. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Amano, F.; Okubo, T.; Aoi, N.; Iwaki, M.; Kumagai, S. Epigallocatechin gallate and gallocatechin gallate in green tea catechins inhibit extracellular release of Vero toxin from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1472, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yu, Y.; Sun, L.M.; Xing, J.Q.; Li, T.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Xue, W.; Xia, T.; et al. GCG inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication by disrupting the liquid phase condensation of its nucleocapsid protein. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Cui, M.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, P.; Ren, S.; Bao, J.; Gao, D.; Sun, R.; Wang, M.; Lin, J.; et al. Both Baicalein and Gallocatechin Gallate Effectively Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication by Targeting M(pro) and Sepsis in Mice. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.Y.; Cheng, M.L.; Weng, S.F.; Leu, Y.L.; Chiu, D.T. Antiviral effect of epigallocatechin gallate on enterovirus 71. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6140–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Peng, J.M.; Zhu, W.; Cheng, B.H.; Li, C.M. Gallocatechin gallate (GCG) inhibits 3T3-L1 differentiation and lipopolysaccharide induced inflammation through MAPK and NF-κB signaling. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 30, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Ye, P.; Zhang, L.; Tan, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. Epigallocatechin gallate protects against oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, Z.; Zhu, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of Pseudorabies Virus via Suppressing the Entry and Release Stages in Its Replication Cycle. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030189
Bo Z, Zhu J, Guo M, Zhang C, Cao Y, Zhang X, Wu Y. Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of Pseudorabies Virus via Suppressing the Entry and Release Stages in Its Replication Cycle. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(3):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030189
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Zongyi, Jinjin Zhu, Mengjiao Guo, Chengcheng Zhang, Yongzhong Cao, Xiaorong Zhang, and Yantao Wu. 2023. "Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of Pseudorabies Virus via Suppressing the Entry and Release Stages in Its Replication Cycle" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 3: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030189
APA StyleBo, Z., Zhu, J., Guo, M., Zhang, C., Cao, Y., Zhang, X., & Wu, Y. (2023). Gallocatechin Gallate Inhibits the Replication of Pseudorabies Virus via Suppressing the Entry and Release Stages in Its Replication Cycle. Veterinary Sciences, 10(3), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10030189





