Seroprevalence of Equine Leptospirosis in the State of Goiás, Brazil
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
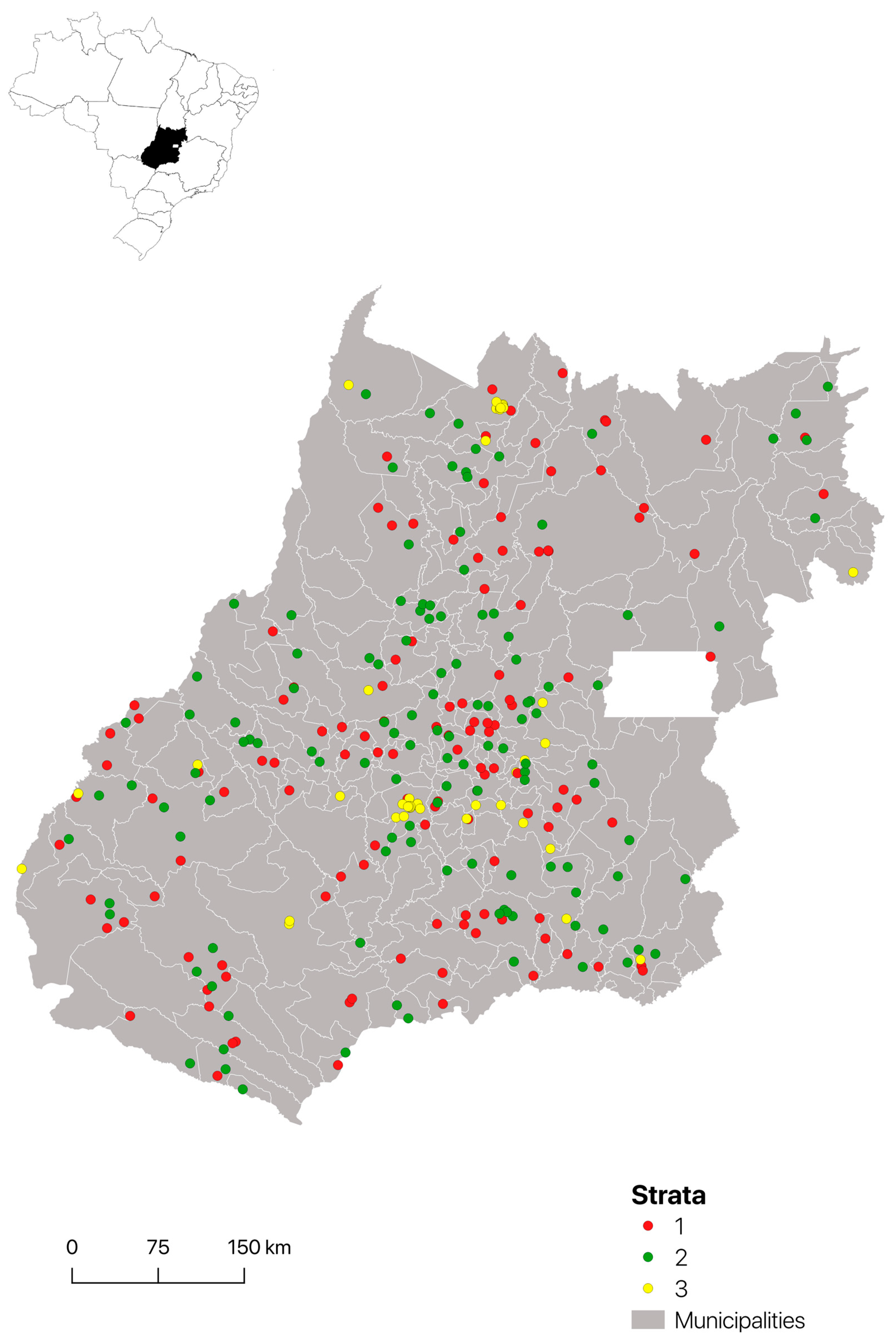
2.1. Study Area and Animals
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
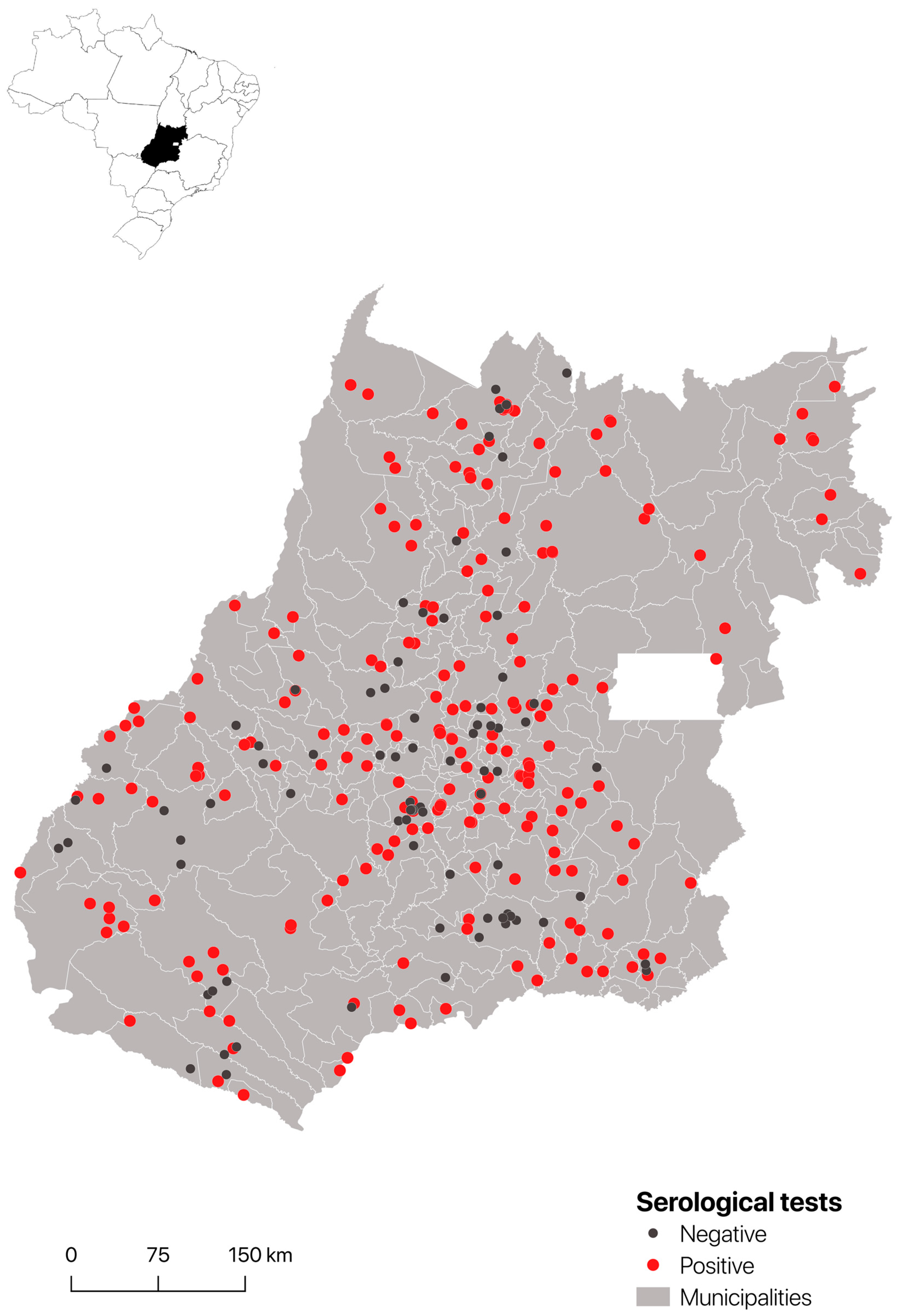
3.1. Seroprevalence
3.2. Serology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellis, W.A. Animal leptospirosis. Curr. Trop. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 99–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, P.S.; Libonati, H.; Lilenbaum, W. A systematic review of leptospirosis on dogs, pigs, and horses in Latin America. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global morbidity and mortality of Leptospirosis: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Ault, S.K.; Periago, M.R. The neglected tropical diseases of Latin America and the Caribbean: A review of disease burden and distribution and a roadmap for control and elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divers, T.J. Acute kidney injury and renal failure in horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 38, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Azevedo, M.I.N.; Lilenbaum, W. Equine genital leptospirosis: Evidence of an important silent chronic reproductive syndrome. Theriogenology 2022, 192, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himebaugh, N.E.; Gilger, B.C. Role of Leptospira spp. testing and ocular examination in horses with equine recurrent uveitis: A retrospective study of 63 horses. Equine Vet. Edu. 2022, 34, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stevenson, B.; Adler, B. Leptospirosis in horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 61e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meny, P.; Menéndez, C.; Ashfield, N.; Quintero, J.; Rios, C.; Iglesias, T.; Schelotto, F.; Varela, G. Seroprevalence of leptospirosis in human groups at risk due to environmental, labor or social conditions. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, B.J.; Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Fuertes, H.; Sheleby-Elías, J.; Múzquiz, J.L.; Jirón, W.; Duttmann, C.; Halaihel, N. A cross-sectional epidemiological study of domestic animals related to human leptospirosis cases in Nicaragua. Acta Trop. 2017, 170, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim, E.C.; Silva, R.L.; Almeida, M.N.R.; Fichtner, S.S.; Candida, M.F. Aglutininas antileptospira em eqüinos no Estado de Goiás State, Brazil. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 1978, 8, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Linhares, G.F.C.; Girio, R.J.S.; Linhares, D.C.L.; Mondeiro, L.C.; Oliveira, A.P.A. Sorovares de Leptospira interrogans e respectivas prevalências em cavalos da microrregião de Goiânia, GO. Cienc. Anim. Bras. 2005, 6, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE (Instituto Brasileiro de geografia e Estatística). Pesquisa da Pecuária Municipal, Efetivo de Rebanho Equino. 2021. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/economicas/agricultura-e-pecuaria/9107-producao-da-pecuaria-municipal.html (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Pádua, B.R.; Dias, R.A.; Fioravanti, M.C.S.; Borsanelli, A.C. Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with equine infectious anemia in the state of Goiás, Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 209, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH. World Organization for Animal Health. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 8th ed.; OIE: Paris, France, 2021; Chapter 3.1.12; Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-manual-online-access/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Silva, A.S.; Jaguezeski, A.M.; Laber, I.F.; Von Laer, A.E.; Lovato, L.T.; Silva, M.O.; Moura, A.B. Leptospira spp. in horses in southern Brazil: Seroprevalence, infection risk factors, and influence on reproduction. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hamond, C.; Martins, G.; Lawson-Ferreira, R.; Medeiros, M.A.; Lilenbaum, W. The role of horses in the transmission of leptospirosis in an urban tropical area. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.S.; Souza, C.F.; Baldissera, M.D.; Von Laer, A.E.; Lovato, L.T.; Sarturi, J.A.; Herrmann, G.P.; Moura, A.B.; Favaretto, J.A.; Frias-De-Diego, A.; et al. Relation of reproductive disturbance in sheep and Leptospira interrogans serovar Icterohaemorrhagiae infection: Impacts on cellular oxidation status. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topazio, J.; Tonin, A.A.; Machado, G.; Noll, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.; Moura, A.B.; Stefani, L.M. Antibodies to Leptospira interrogans in goats and risk factors of the disease in Santa Catarina (West side), Brazil. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 99, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolino, R.R.; Lopes, L.B.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Teixeira, J.F.B.; Haddad, J.P.A. Prevalence and spatial analysis of antileptospiral agglutinins in dairy cattle—Microregion of Sete Lagoas, Minas Gerais, 2009/2010. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2014, 66, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Human Leptospirosis: Guide to Diagnosis, Surveillance and Control; World Health Organization: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008; 127p. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, M.O.; Neto, V.A.; Veronesi, R.; Fabbri, S.O.A. Leptospirosis in horses: Serological survey. Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz 1957, 19, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.S.; Guedes Junior, D.S.; Pereira, R.C.G.; Santos, C.C.A.; Castro, V.; Jesus, V.L.T. Serological survey of the occurrence of leptospirosis in horses from the Itaguaí microregion in the state of Rio de Janeiro-RJ. Rev. Bras. Med. Vet. 2012, 34, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, C.C.G.; Kuroda, R.B.S.; Pinho, A.P.V.B.; Ywasaki, F.; Meneses, A.M.C.; Martins, A.V.; Amaral Junior, J.M.; Dias, H.L.T.; Vasconcellos, S.A. Research of antibodies to pathogenic Leptospira interrogans serovars in horses raised on the island of Algodoal, State of Pará. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Agrar. 2010, 53, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Favero, A.C.M.; Pinheiro, S.R.; Vasconcelhos, S.A.; Morais, Z.M.; Ferreira Neto, J.S. Most frequent serovars of leptospires in serological tests of buffaloes, sheeps, goats, horses, swines and dogs from several Brazilian states. Cienc. Rural 2022, 32, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornazari, F.; Langoni, H.; Marson, P.M.; Nóbrega, D.B.; Teixeira, C.R. Leptospira reservoirs among wildlife in Brazil: Beyond rodents. Acta Trop. 2018, 178, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO/FAO/OIE Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Leptospirosis. Leptospira Serovar Data Sheet. Serovar Djasiman. 2011. Available online: http://www.health.qld.gov.au/qhcss/qhss/lepto/documents/djasiman.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2023).
- Simbizi, V.; Saulez, M.N.; Potts, A.; Lötter, C.; Gummow, B. A study of leptospirosis in South African horses and associated risk factors. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 134, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.F.; Alba, D.A.H.; Jorge, S.; Gindri, P.; Bialves, T.S.; Souza, G.N.; Bruhn, F.R.P.; Pegoraro, L.M.C.; Dellagostin, O.A. Leptospirosis in dairy cattle from Southern Brazil—Risk factors. Acta Sci. Vet. 2022, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.S.; Narduche, L.; Martins, G.; Péres, I.A.H.F.S.; Zimmermann, N.P.; Juliano, R.S.; Pellegrin, A.O.; Lilenbaum, W. Detection of wild animals as carriers of Leptospira by PCR in the Pantanal biome, Brazil. Acta Trop. 2016, 163, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.F.; Wasfy, M.O.; Abdul-Rahman, B.; Murray, C.K.; Hospenthal, D.R.; Abdel-Fadeel, M.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.; Samir, A.; Hatem, M.E.; Klena, J.; et al. Retrospective serosurvey of leptospirosis among patients with acute febrile illness and hepatitis in Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Héry, G.; Letheulle, J.; Flécher, E.; Quentin, C.; Piau, C.; Le Tulzo, Y.; Tattevin, P. Massive intra-alveolar hemorrhage caused by Leptospira serovar Djasiman in a traveler returning from Laos. J. Travel. Med. 2015, 22, 21–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carvalho, O.S.; Gonzaga, L.N.R.; Albuquerque, A.S.; Bezerra, D.C.; Chaves, N.P. Occurrence of Brucella abortus, Leptospira interrogans and bovine herpesvirus type 1 in 31 buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) herd under extensive breeding system. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, G.P.; Lage, A.P.; Moreira, E.C.; Haddad, J.P.A.; Resende, J.R.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Leite, R.C. Seroprevalence of agglutinins anti-Leptospira spp. in sheep from the Southeast and Southwest Mesoregions of the State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Cienc. Rural 2004, 34, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.M.P.; Correia, L.; Spohr, K.A.H.; Aguiar, D.M.; Martins, G.; Jayme, V.S. Risk factors associated with seroreactivity against Leptospira sp. in horses from Brazilian Amazon. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 68, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanazio, D.A.; Silva, E.F.; Santos, C.S.; Rocha, G.M.; Vannier-Santos, M.A.; McBride, A.J.A.; Ko, A.I.; Reis, M.G. Rattus norvegicus as a model for persistent renal colonization by pathogenic Leptospira interrogans. Acta Trop. 2008, 105, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, D.M.; Cavalcante, G.T.; Lara, M.C.C.S.H.; Villalobos, E.M.C.; Cunha, E.M.S.; Okuda, L.H.; Stéfano, E.; Nassar, A.F.C.; Souza, G.O.; Vasconcellos, S.A.; et al. Prevalência de anticorpos contra agentes virais e bacterianos em equídeos do Município de Monte Negro, Rondônia, Amazônia Ocidental Brasileira. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2008, 45, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.J.; Mathias, L.A.; Magajevski, F.S.; Werther, K.; Assis, N.A.; Girio, R.J.S. Anticorpos contra Leptospira spp. em animais domésticos e silvestres presentes no campus universitário da FCAV, UNESP, Jaboticabal/SP. Ars Vet. 2010, 26, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Caselani, K.; Oliveira, P.R.; Ferraudo, A.S.; Lima-Ribeiro, A.M.C.; Girio, R.J.S. Estudo soroepidemiológico de leptospirose em equinos utilizados para tração urbana. Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz 2012, 71, 582–587. [Google Scholar]
- Finger, M.A.P.; Barros Filho, I.V.; Leutenegger, C.; Estrada, M.; Ullmann, L.S.; Langoni, H.; Kikuti, M.; Dornbush, P.T.; Deconto, I.; Biondo, A.W. Serological and molecular survey of Leptospira spp. among cart horses from an endemic area of human leptospirosis in Curitiba, Southern Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2014, 56, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasta, C.S.; Oliveira, S.T.; Merini, L.P.; Dasso, M.G.; Pedralli, V.; González, F.H.D. Pesquisa de aglutininas anti-Leptospira em soros de equinos de tração em Porto Alegre, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Vet. 2013, 20, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Lilenbaum, W. The panorama of animal leptospirosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, regarding the seroepidemiology of the infection in tropical regions. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.A.A.; Leal, E.A.; Correia, M.A.; Serufo Filho, J.C.; Dias, R.S.; Serufo, J.C. Human leptospirosis: Occurrence of serovars of Leptospira spp. In the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, from 2008 to 2012. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, E.C.; Blanco, R.M.; Galloway, R.L. Application of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for the discrimination of leptospiral isolates in Brazil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barocchi, M.A.; Ko, A.I.; Ramos, F.S.; Faria, M.T.; Reis, M.G.; Riley, L.W. Identification of new repetitive element in Leptospira interrogans serovar copenhageni and its application to PCR-based differentiation of Leptospira serogroups. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pescador, C.A.; Corbellini, L.G.; Loretti, A.P.; Wunder Júnior, E.; Frantz, F.J.; Driemeier, D. Aborto equino por Leptospira sp. Cienc. Rural 2004, 34, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baverud, V.; Gunnarsson, A.; Engvall, E.O.; Franzen, P.; Egenvall, A. Leptospira seroprevalence and associations between seropositivity, clinical disease and host factors in horses. Acta Vet. Scand. 2009, 51, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebani, V.V.; Bertelloni, F.; Pinzauti, P.; Cerri, D. Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Italian horses. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolin, C.A. Diagnosis of leptospirosis in swine. J. Swine Health Prod. 1994, 2, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Langoni, H.; Silva, A.V.; Pezerico, S.B.; Lima, V.Y. Anti-Leptospire agglutinins in equine sera, from São Paulo, Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, 1996–2001. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 2004, 10, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, B.; Moctezuma, A.P. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; Bonfanti, L.; Natale, A.; Comin, A.; Ferronato, A.; La Greca, E.; Patregnani, T.; Lucchese, L.; Marangon, S. Application of an integrated outbreak management plan for the control of leptospirosis in dairy cattle herds. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stratum | Farms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Focus * | % | CI95% | |
| 1 | 122 | 85 | 68.3 | 59.6–76.2 |
| 2 | 123 | 94 | 73.7 | 65.3–80.9 |
| 3 | 49 | 34 | 67.7 | 52.9–79.9 |
| Total | 294 | 213 | 72.9 | 71.7–78.9 |
| Stratum | Animals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | MAT (+) | % | CI95% | |
| 1 | 390 | 207 | 65.1 | 50.0–78.4 |
| 2 | 380 | 233 | 61.2 | 53.1–68.9 |
| 3 | 124 | 73 | 58.5 | 49.7–67.0 |
| Total | 894 | 513 | 61.6 | 54.3–69.0 |
| Serogroup | Serovar | Stratum 1 | Stratum 2 | Stratum 3 | Goiás (n/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Djasiman | Djasiman | 37 (18.0) | 39 (17.0) | 8 (10.4) | 84 (16.4) |
| Sentot | 14 (6.8) | 13 (5.7) | 2 (2.6) | 29 (5.7) | |
| Icterohaemorrhagiae | Icterohaemorrhagiae | 26 (12.7) | 15 (6.5) | 21 (27.3) | 62 (12.1) |
| Copenhageni | 3 (1.5) | 2 (0.9) | 1 (1.3) | 6 (1.2) | |
| Australis | Bratislava | 10 (4.9) | 15 (6.5) | 3 (3.9) | 28 (5.5) |
| Australis | 3 (1.5) | 3 (1.3) | 1 (1.3) | 7 (1.4) | |
| Pomona | Pomona | 14 (6.8) | 13 (5.7) | 1 (1.3) | 28 (5.5) |
| Pomona GR6 | 1 (0.5) | 2 (0.9) | 0 | 3 (0.6) | |
| Ballum | Castellonis | 8 (3.9) | 9 (3.9) | 3 (3.9) | 20 (3.9) |
| Sjeroe | Hardjobovis | 7 (3.4) | 3 (1.3) | 2 (2.6) | 12 (2.3) |
| Hardjo (CTG) | 0 | 1 (0.4) | 1 (1.3) | 2 (0.4) | |
| Hardjo-prajitno | 0 | 1 (0.4) | 0 | 1 (0.2) | |
| Wolffi | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.2) | |
| Autumnalis | Autumnalis | 3 (1.5) | 6 (2.6) | 0 | 9 (1.8) |
| Butembo | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.3) | 1 (0.2) | |
| Grypphotyphosa | Grypphotyphosa | 2 (1.0) | 6 (2.6) | 0 | 8 (1.6) |
| Shermani | Tarassovi | 0 | 2 (0.9) | 0 | 2 (0.4) |
| Andamana | Andamana | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
| Seramanga | Patoc | 22 (10.7) | 37 (16.2) | 12 (15.6) | 71 (13.9) |
| Without more prevalent serovar * | 53 (25.8) | 62 (27.1) | 21 (27.2) | 136 (26.5) | |
| Total | 205 (100) | 229 (100) | 77 (100) | 513 (100) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanowski, T.N.d.A.; Dias, R.A.; Heinemann, M.B.; Carvalho, S.F.; Silva, T.A.; Martins, A.d.S.; Caetano, G.D.d.C.; Ferreira Júnior, Á.; Santos, J.P.d.; Borsanelli, A.C. Seroprevalence of Equine Leptospirosis in the State of Goiás, Brazil. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100590
Romanowski TNdA, Dias RA, Heinemann MB, Carvalho SF, Silva TA, Martins AdS, Caetano GDdC, Ferreira Júnior Á, Santos JPd, Borsanelli AC. Seroprevalence of Equine Leptospirosis in the State of Goiás, Brazil. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(10):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100590
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanowski, Tatiana Nunes de Azevedo, Ricardo Augusto Dias, Marcos Bryan Heinemann, Stephani Félix Carvalho, Tamires Ataides Silva, Andressa da Silva Martins, Geovanna Domingues da Cunha Caetano, Álvaro Ferreira Júnior, Jandra Pacheco dos Santos, and Ana Carolina Borsanelli. 2023. "Seroprevalence of Equine Leptospirosis in the State of Goiás, Brazil" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 10: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100590
APA StyleRomanowski, T. N. d. A., Dias, R. A., Heinemann, M. B., Carvalho, S. F., Silva, T. A., Martins, A. d. S., Caetano, G. D. d. C., Ferreira Júnior, Á., Santos, J. P. d., & Borsanelli, A. C. (2023). Seroprevalence of Equine Leptospirosis in the State of Goiás, Brazil. Veterinary Sciences, 10(10), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100590






