Carbon Sequestration Rate Estimates in Delaware Bay and Barnegat Bay Tidal Wetlands Using Interpolation Mapping
Abstract
1. Summary
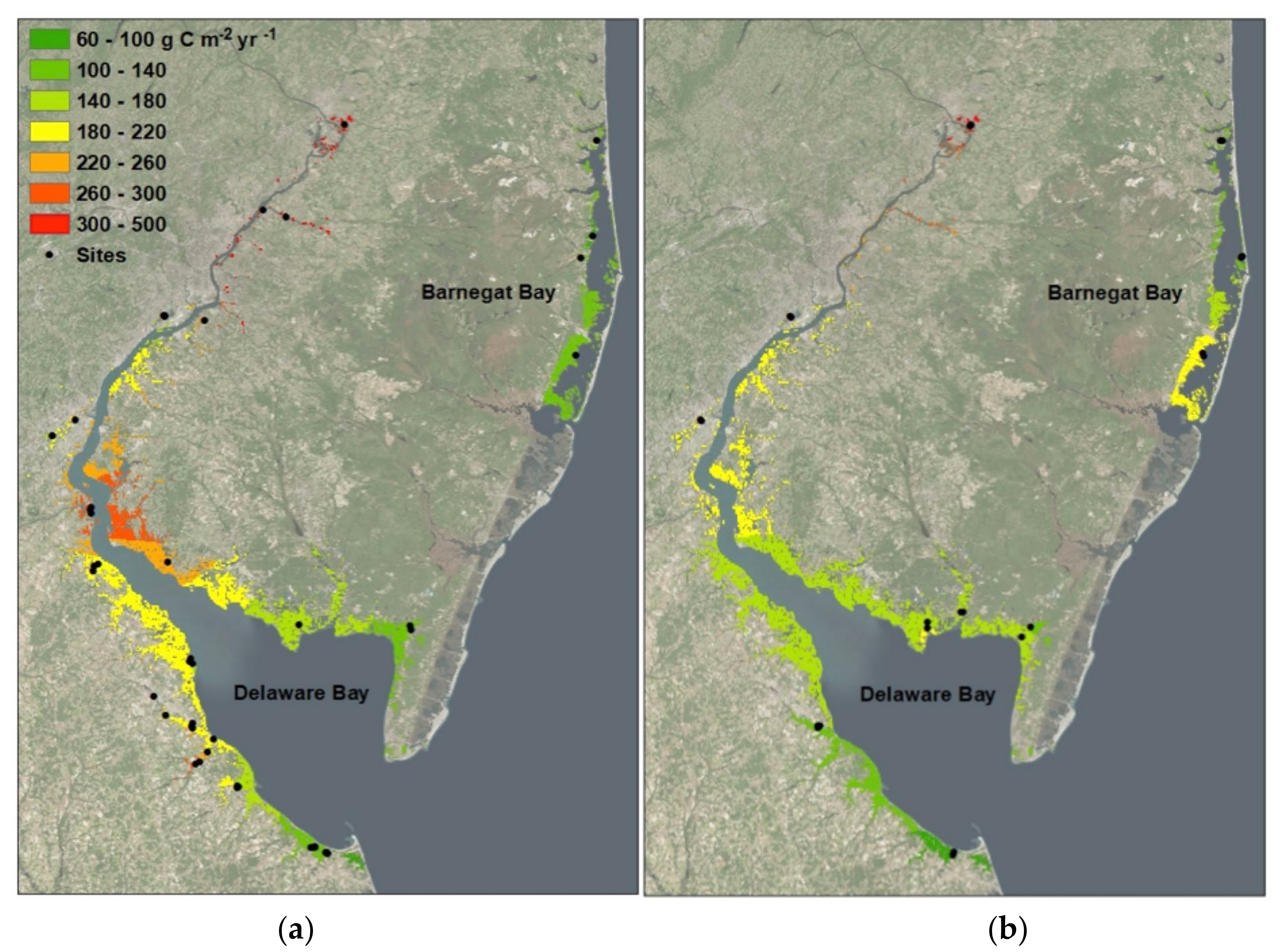
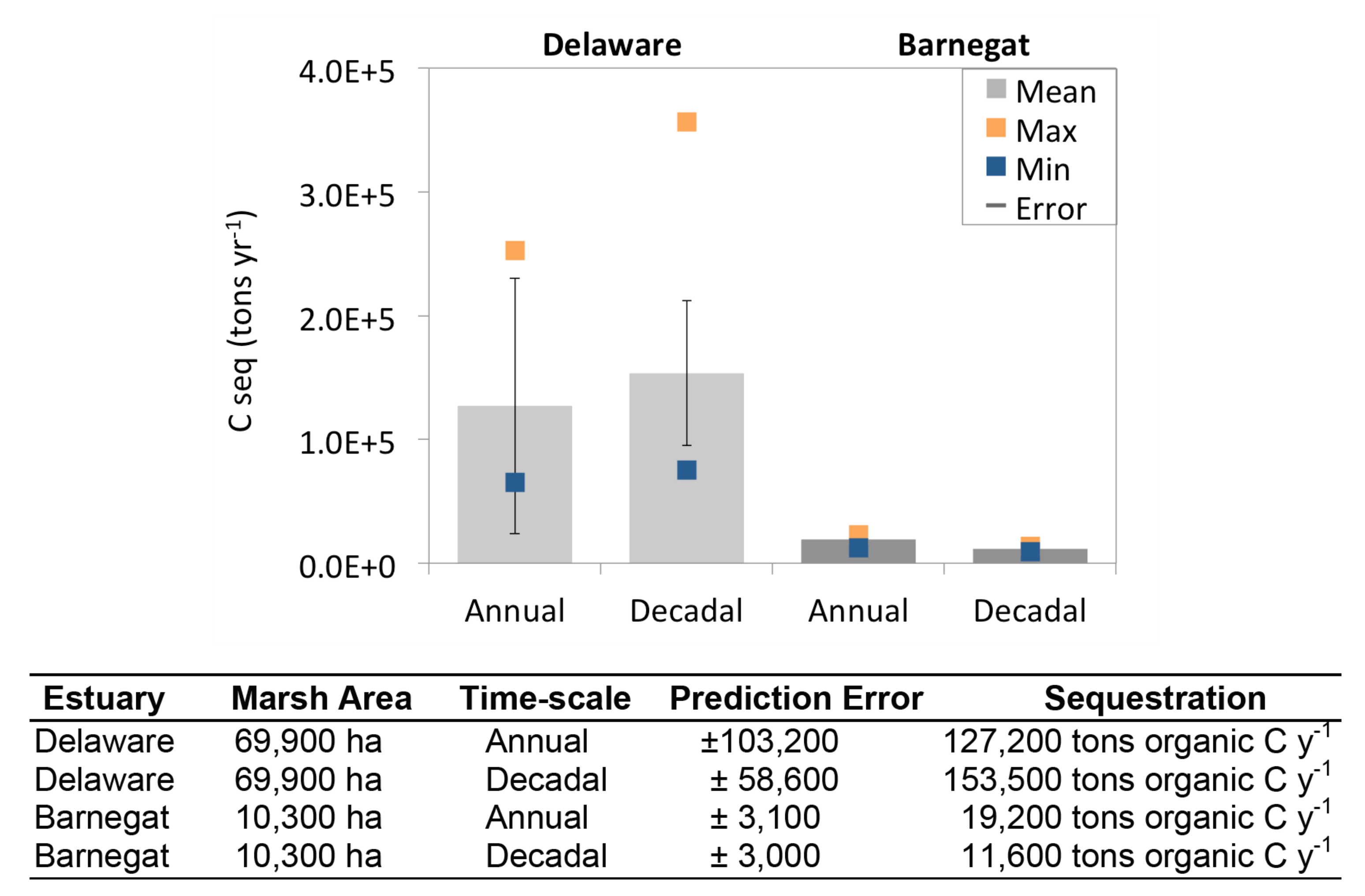
1.1. Spatial Results
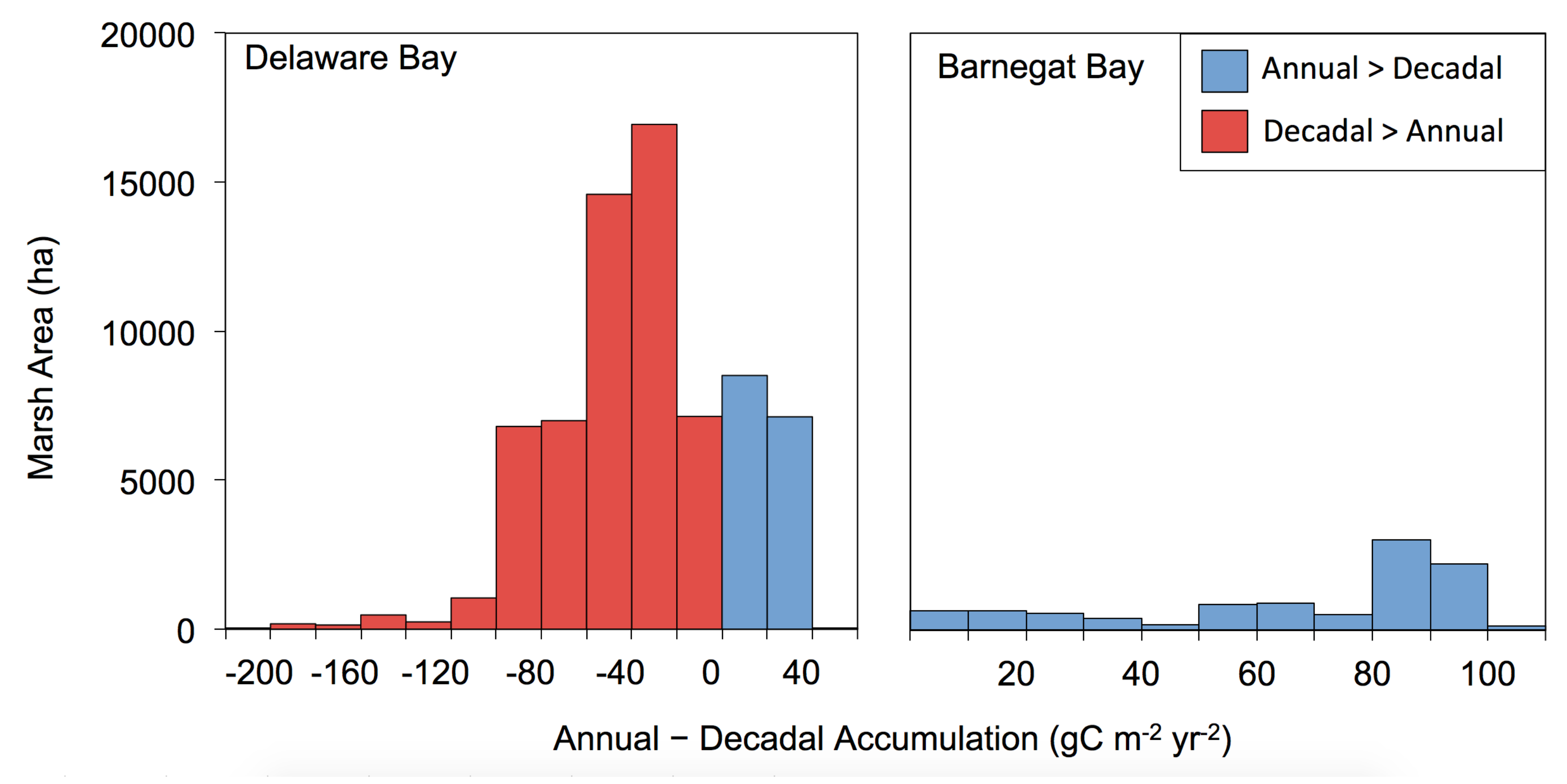
1.2. Temporal Patterns
2. Data Description
2.1. Shapefiles of Carbon Accumulation
2.2. Interpolation Maps of Carbon Accumulation
3. Methods
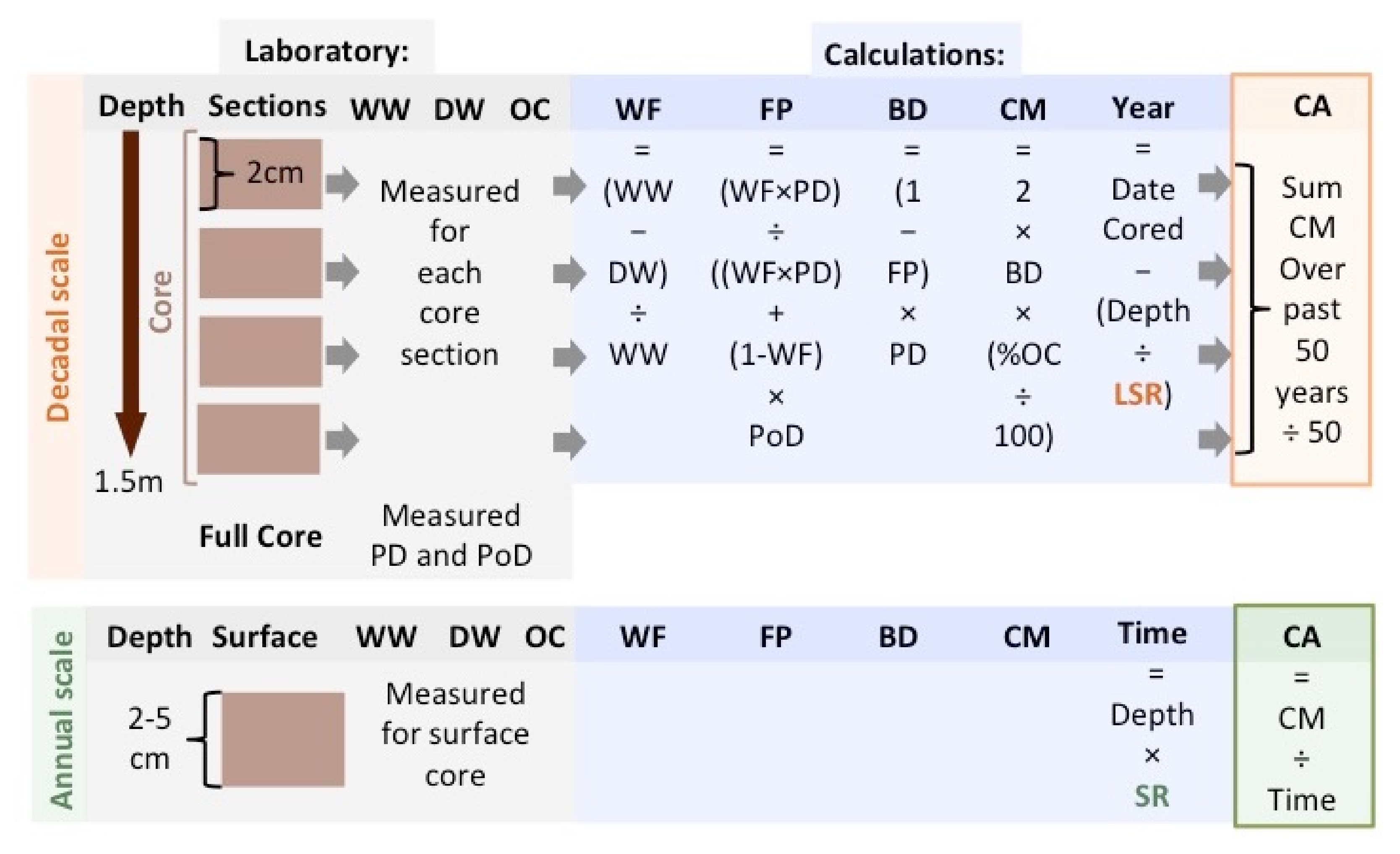
3.1. Annual Accumulation Measurement above Marker Beds
3.2. Decadal Measurement from Sediment Cores
3.3. Interpolation Mapping
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mcleod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A blueprint for blue carbon: Toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Pendleton, L.; Jenkins, A.; Sifleet, S. Green Payments for Blue Carbon: Economic Incentives for Protecting Threatened Coastal Habitats; Nicholas Institute for Environmental Policy Solutions: Durham, NC, USA, 2011; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist, J.R.; Windham-Myers, L.; Bliss, N.; Crooks, S.; Morris, J.T.; Megonigal, J.P.; Troxler, T.; Weller, D.; Callaway, J.; Drexler, J.; et al. Accuracy and Precision of Tidal Wetland Soil Carbon Mapping in the Conterminous United States. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelske, C.L.; Odum, E.P. Mechanisms Maintaining High Productivity in Georgia Estuaries; University of Georgia Marine Institute: Darien, GA, USA, 1961; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, E.B. Changing elevation, accretion, and tidal marsh plant assemblages in a South San Francisco Bay tidal marsh. Estuaries 2004, 27, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couwenberg, J.; Dommain, R.; Joosten, H. Greenhouse gas fluxes from tropical peatlands in south-east Asia. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1715–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Fienberg, K.; Jerolmack, D.J.; Marr, J.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Experimental evidence for statistical scaling and intermittency in sediment transport rates. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, F01025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, P.M. The influence of hiatuses on sediment accumulation rates. GeoRes. Forum. 1999, 5, 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- Schumer, R.; Jerolmack, D.J. Real and apparent changes in sediment deposition rates through time. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, F00A06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, B.M.; Sommerfield, C.K.; Elsey-Quirk, T. Hydrogeomorphic influences on salt marsh sediment accumulation and accretion in two estuaries of the US Mid-Atlantic coast. Mar. Geol. 2017, 383, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, T.M.; Sommerfield, C.K.; Velinsky, D.J.; Point, D.; Benoit, C.; Amouroux, D.; Plaa, D.; Donard, O.F.X. Marsh sediments as records of sedimentation, eutrophication and metal pollution in the urban Delaware Estuary. Mar. Chem. 2006, 102, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velinsky, D.J.; Sommerfield, C.K.; Charles, D. Vertical Profiles of Radioisotopes, Nutrients and Diatoms in Sediment Cores from the Tidal Murderkill River Basin: A Historical Analysis of Ecological Change and Sediment Accretion. Final Report submitted to Dr. Mirsajadi Hassan (DNREC, Watershed Assessment Section, Division of Water Resources, Dover, DE). Available online: http://www.dnrec.delaware.gov/swc/wa/Documents/WAS/Murderkill%20River%20Reports/New%20Murderkill%20Page/5.%20%20Study%20of%20Sediment%20Nutrients%20and%20Ecological%20History.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Tucker, K.J. Variability of Organic Carbon Accumulation on a Tidal Wetland Coast. Master’s Thesis, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Velinsky, D.J.; Paudel, B.; Belton, T.J.; Sommerfield, C.K. Tidal marsh record of nutrient loadings in Barnegat Bay, New Jersey. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 78, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmura, G.L.; Anisfeld, S.C.; Cahoon, D.R.; Lynch, J.C. Global Carbon Sequestration in Tidal, Saline Wetland Soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycle. 2003, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, V.; Elsey-Quirk, T.; Sommerfield, C.; Velinsky, D.J. Stability of organic carbon accumulating in Spartina alterniflora-dominated salt marshes of the Mid-Atlantic US. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 182, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, P.G.; Oldfield, F. Applications of lead-210 to sedimentation studies. In Uranium-Series Disequilibrium: Applications to Earth, Marine, and Environmental Sciences, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Office for Coastal Management. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Office for Coastal Management. “Pennsylvania 2010”, “New Jersey 2010”, “Delaware 2010.” Coastal Change Analysis Program (C-CAP) Regional Land Cover. Charleston, SC: NOAA Office for Coastal Management. Available online: https://www.coast.noaa.gov/ccapftp/#/ (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Grunwald, S.; Reddy, K.R.; Newman, S.; DeBusk, W.F. Spatial variability, distribution and uncertainty assessment of soil phosphorus in a south Florida wetland. Environmetrics 2004, 15, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, U.; Lal, R.; Slater, B.; Calhoun, F.; Liu, D.; Van Meirvenne, M. Predicting Soil Organic Carbon Stock Using Profile Depth Distribution Functions and Ordinary Kriging. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, F.; Corstanje, R.; White, J.R.; Veronesi, F. A Geostatistical Analysis of Soil Properties in the Davis Pond Mississippi Freshwater Diversion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.; Boufassa, A. Comparing the robustness of ordinary kriging and lognormal kriging: Outlier resistance. Math. Geol. 1988, 20, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Site | Estuary | Location (Coordinates) | Site ID | C Seq (g C m−2y−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crosswicks Creeks | Delaware Bay | Bordentown, NJ (40°9.76′ N, 74°42.51′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 479 164 |
| Tinicum Marsh | Delaware Bay | Philadelphia, PA (39°52.91′ N, 75°16.64′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 206 204 |
| Dividing Creek | Delaware Bay | Dividing Creek, NJ (39°14.14′ N, 75°6.76′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 230 104 |
| Dennis Creek | Delaware Bay | South Dennis, NJ (39°10.58′ N, 74°51.74′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 186 104 |
| Christina River | Delaware Bay | Wilmington, DE (39°43.21′ N, 75°33.74′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 272 150 |
| Broadkill Creek | Delaware Bay | Lewes, DE (39°47.24′ N, 75°9.96′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 116 60 |
| St. Jones Creek | Delaware Bay | Bowers, DE (39°5.01′ N, 75°26.30′ W) | Boardwalk 1 Reverse Ditch 4 Trail 20 | 88 30 269 |
| Maurice River | Delaware Bay | Bilvalve, NJ (39°15.95′ N, 74°59.72′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 207 151 |
| Reedy Creek | Barnegat Bay | Brick, NJ (40°1.74′ N, 74°5.07′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 124 92 |
| Island Beach | Barnegat Bay | Seaside Park, NJ (39°47.96′ N, 74°6.10′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 141 101 |
| Horse Point | Barnegat Bay | West Creek, NJ (39°37.59′ N, 74°15.43′ W) | SET 1 SET 3 | 211 198 |
| Site | Estuary | Location (Coordinates) | Site ID | C Seq (g C m−2y−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canary Creek | Delaware Bay | Lewes, DE (38°46.97′ N, 75°10.25′ W) | CC-1 CC-2 CC-3 CC-5 CC-6 | 28 68 268 106 136 |
| Dennis Creek | Delaware Bay | Dennisville, NJ (39°10.92′ N, 74°10.25′ W) | DEN-1 DEN-3 | 154 117 |
| Crosswicks | Delaware Bay | Bordentown, NJ (40°9.76′ N, 74°42.51′ W) | CCR-3 | 348 |
| Rancocas Marsh | Delaware Bay | Delran, NJ (40°2.54′ N, 74°58.11′ W) | RAN-1 RAN-2 | 419 503 |
| Tinicum Marsh | Delaware Bay | Philadelphia, PA (39°52.91′ N, 75°16.64′ W) | 1B 2A 3B | 139 195 95 |
| Woodbury Creek | Delaware Bay | Thorofare, NJ (39°51.41′ N, 75°10.73′ W) | WC-1 | 254 |
| Dravo Creek | Delaware Bay | Wilmington, DE (39°43.22′ N, 75°33.72′ W) | DM-2 | 256 |
| Churchman | Delaware Bay | Wilmington, DE (39°42.02′ N, 75°37.81′ W) | CM-1 | 135 |
| St. Georges | Delaware Bay | Port Penn, DE (39°32.77′ N, 75°34.20′ W) | SG-1 SG-2 SG-3 | 223 212 440 |
| Blackbird Creek | Delaware Bay | Townsend, DE (39°25.40′ N, 75°36.11′ W) | BC-1 BC-2 BC-3 | 194 203 183 |
| Stow Creek | Delaware Bay | Greenwich, NJ (39°24.56′ N, 75°24.54′ W) | SC-1 | 260 |
| Kelly Island | Delaware Bay | Dover, DE (39°12.76′ N, 75°24.25′ W) | KI-1 KI-2 KI-3 | 204 144 179 |
| St. Jones River | Delaware Bay | Bowers, DE (39°5.01′ N, 75°26.30′ W) | H2 WC1-2 SJBM-1 SJBM-2 SJBM-3 | 240 156 116 337 209 |
| Mispillion River | Delaware Bay | Milford, DE (38°56.87′ N, 75°21.23′ W) | MR-1 MR-2 MR-3 | 146 153 188 |
| Great Marsh | Delaware Bay | Milton, DE (38°47.99′ N, 75°11.74′ W) | GM-1 GM-2 GM-3 GM-4 | 103 99 141 142 |
| Dividing Creek | Delaware Bay | Dividing Creek, NJ (39°14.14′ N, 75°6.76′ W) | DC-2 | 148 |
| Murderkill River | Delaware Bay | Frederica, DE (39°14.14′ N, 75°6.76′ W) | MK-1 MK-2 MK-3 MK-4 | 302 307 209 161 |
| Mantololking | Barnegat Bay | Brick, NJ (40°1.79′ N, 74°4.79′ W) | BB-1 | 109 |
| Mid-Bay | Barnegat Bay | Lacey, NJ (39°50.86′ N, 74°8.84′ W) | BB-2 | 81 |
| Oyster Creek | Barnegat Bay | Lacey, NJ (39°48.65′ N, 74°11.41′ W) | BB-3 | 122 |
| West Creek | Barnegat Bay | Eagleswood, NJ (39°37.64′ N, 74°15.61′ W)) | BB-4 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Champlin, L.; Velinsky, D.; Tucker, K.; Sommerfield, C.; Laurent, K.S.; Watson, E. Carbon Sequestration Rate Estimates in Delaware Bay and Barnegat Bay Tidal Wetlands Using Interpolation Mapping. Data 2020, 5, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5010011
Champlin L, Velinsky D, Tucker K, Sommerfield C, Laurent KS, Watson E. Carbon Sequestration Rate Estimates in Delaware Bay and Barnegat Bay Tidal Wetlands Using Interpolation Mapping. Data. 2020; 5(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamplin, Lena, David Velinsky, Kaitlin Tucker, Christopher Sommerfield, Kari St. Laurent, and Elizabeth Watson. 2020. "Carbon Sequestration Rate Estimates in Delaware Bay and Barnegat Bay Tidal Wetlands Using Interpolation Mapping" Data 5, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5010011
APA StyleChamplin, L., Velinsky, D., Tucker, K., Sommerfield, C., Laurent, K. S., & Watson, E. (2020). Carbon Sequestration Rate Estimates in Delaware Bay and Barnegat Bay Tidal Wetlands Using Interpolation Mapping. Data, 5(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/data5010011




