Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD): A Database for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Research
Abstract
:1. Summary
2. Data Description
- Retinal images with the signs of DR and/or DME.
- Normal retinal images (without signs of DR and/or DME).
- Pixel level annotations of typical diabetic retinopathy lesions and optic disc.
- Image level disease severity grading of diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic macular edema.
- Optic Disc and Fovea center co-ordinates.
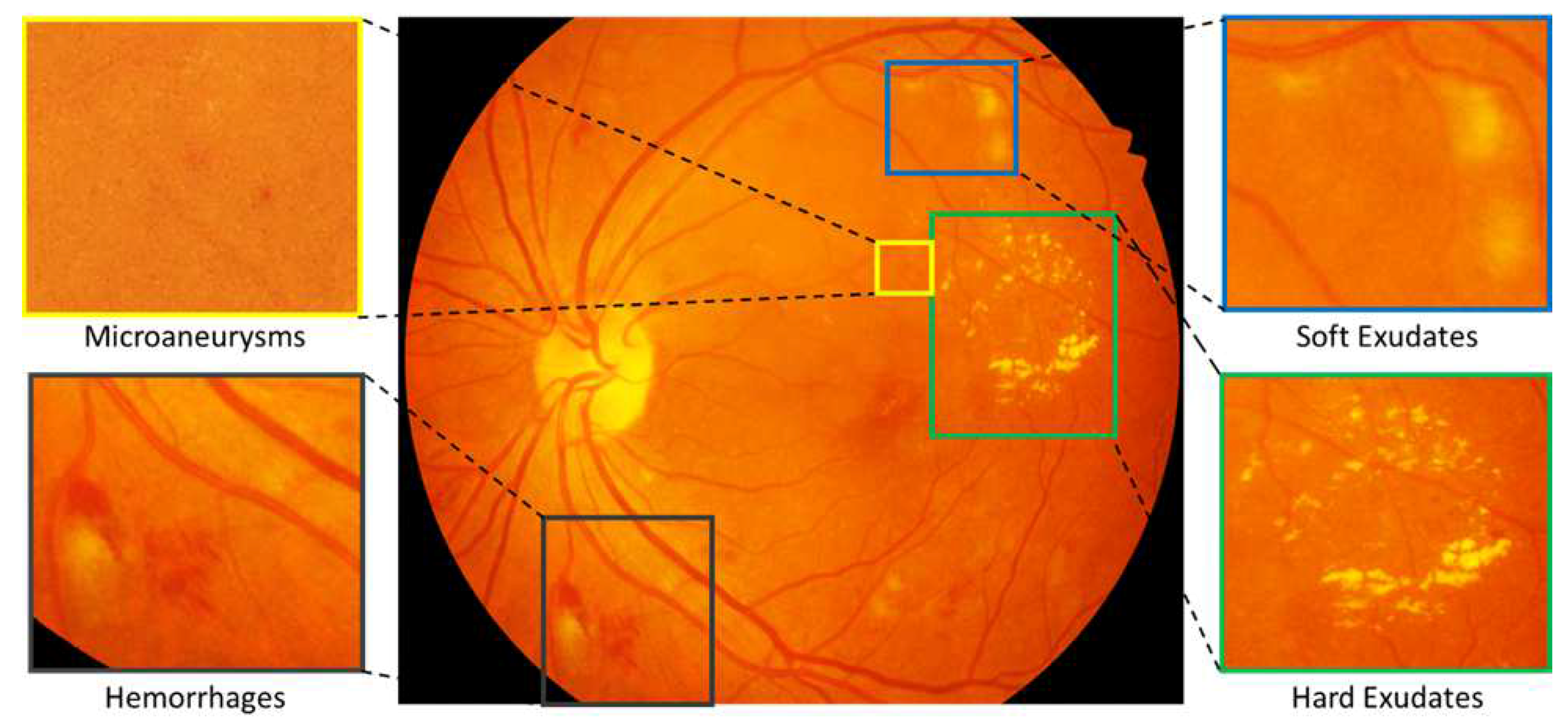
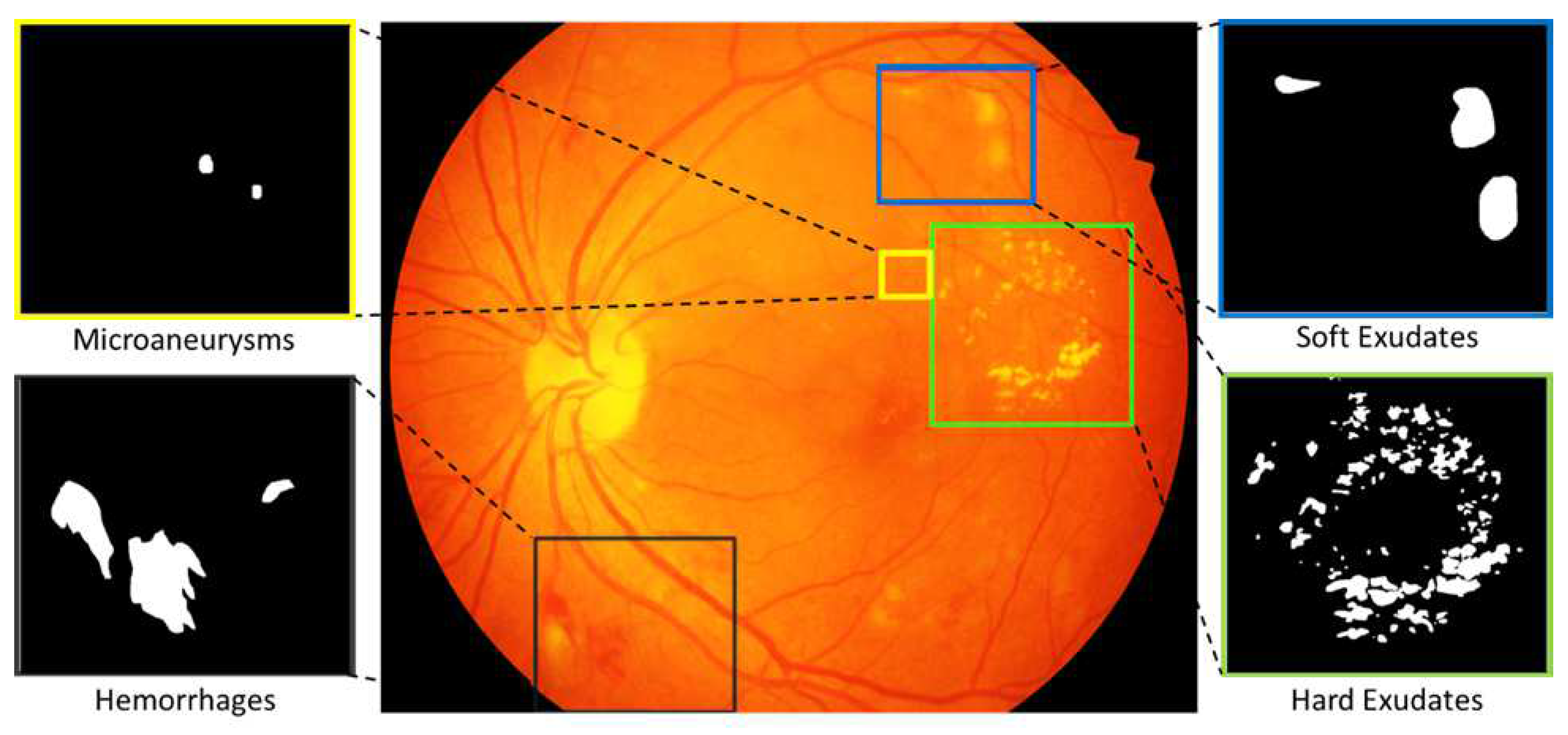
2.1. Pixel Level Annotated Data
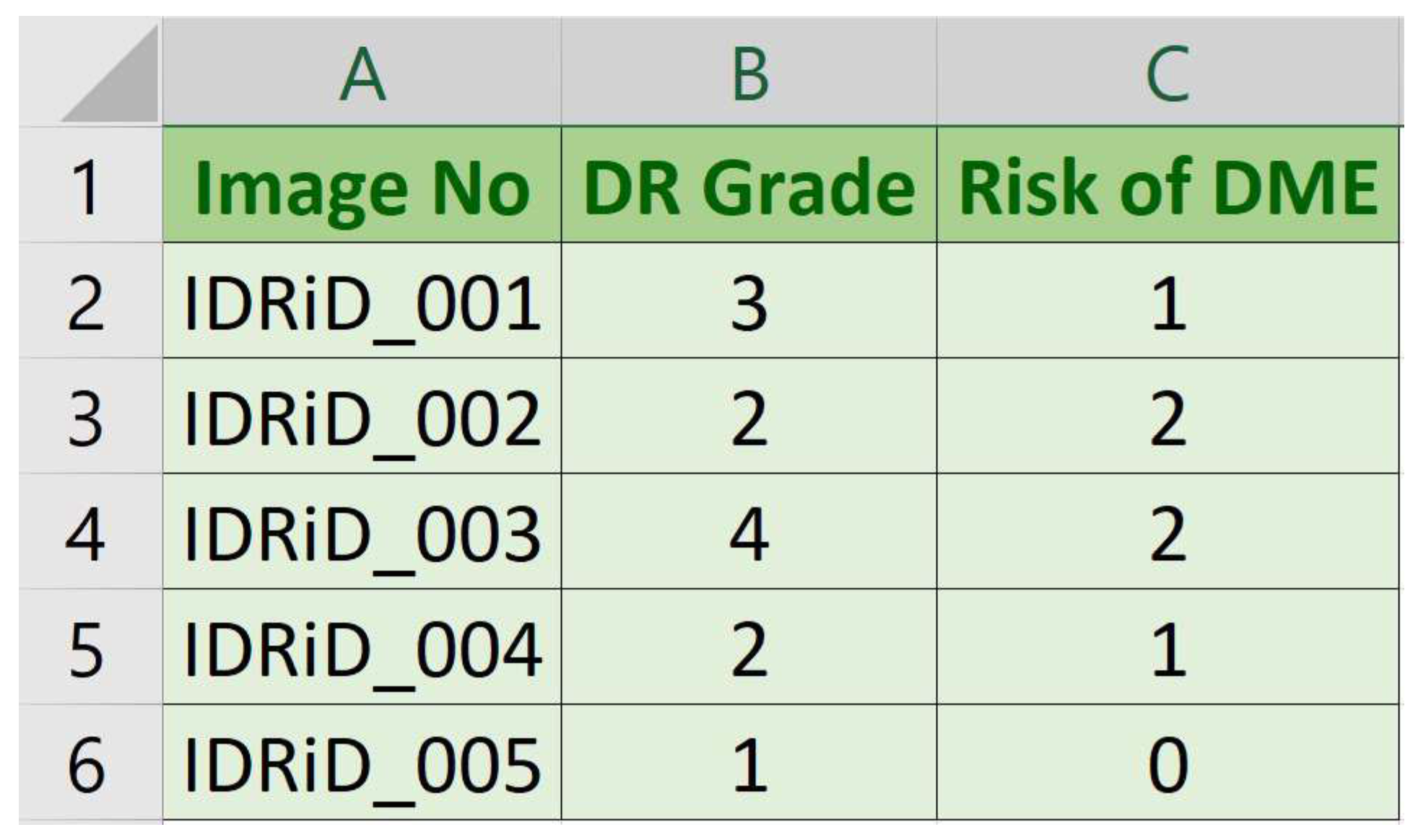
2.2. Image Level Disease Grading
- Image No: Name (serial number) of deidentified and renamed patient image.
- DR Grade: DR severity level in range 0 (No apparent DR) to 4 (Severe DR).
- Risk of DME: Macular edema severity level in range 0 (No DME) to 2 (Severe DME).
2.3. Optic Disc and Fovea Center Location
3. Experimental Design, Materials and Methods
3.1. Ethics Statement
3.2. Data Acquisition
- Pretreatment of Samples: All the subjects in the dataset had undergone mydriasis prior to capturing of images. Mydriasis is process of pupil dilation which was done with one drop of tropicamide at 0.5% concentration.
- Fundus Camera Specifications: Images were acquired using a Kowa VX-10 digital fundus camera with 50 field of view (FOV). The images have resolution of pixels and are stored in jpg file format. The size of each image is about 800 KB.
- Data Quality: The dataset is formed by extracting 516 images from the thousands of examinations done during the period 2009–2017. Experts verified that all images are of adequate quality, clinically relevant, that no image is duplicated and that a reasonable mixture of disease stratification representative of diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME) is present.
3.3. Annotation of Images
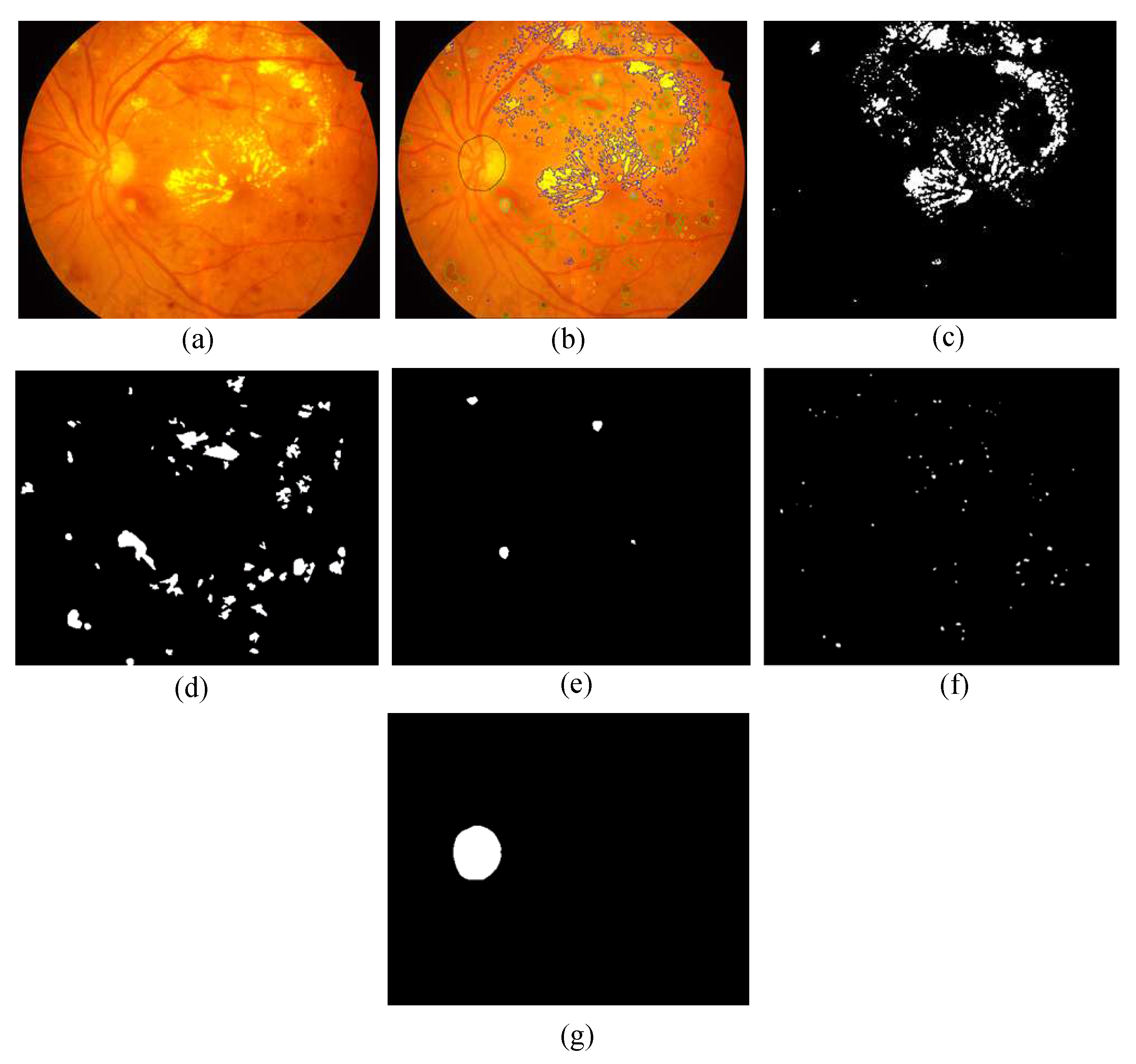
- Pixel Level Annotation: Initially, all observers were trained by expert ophthalmologists for the identification of individual lesion. An image processing expert chose 81 images with contextual data comprising soft exudates, hard exudates, microaneurysms, and hemorrhages. The pixel level annotation is done by a master’s student using special software developed by ADCIS [22] specifically for annotation purposes. Figure 5 shows the sample image from the database and manually drawn contours. Later the markings on each of these images were reviewed by two retinal specialists, and they were finalized when the necessary consensus was reached. The final groundtruth images for all lesions and optic disc are shown in Figure 6. Similar pixel level lesion annotations are available in the E-Optha dataset [23].
- DR and DME Grading: The medical experts graded full set of 516 images with variety of pathological conditions of DR and DME. The diabetic retinal images were classified into separate groups ranging from 0 (No apparent DR) to 4 (Severe DR) according to the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy Scale [24], similar to existing Kaggle DR Dataset [25]. The risk of macular edema can be determined by the presence of exudates [26], severity grading of DME is done based on occurrences of hard exudates near to macula center as per the definitions provided by Messidor database [27].
- Optic Disc and Fovea Center Location Markup: The OD and fovea center markups are done by a master’s and PhD student. The final center co-ordinates are obtained by computing average of two locations. The averaged markups were further verified by a retinal expert.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reichel, E.; Salz, D. Diabetic retinopathy screening. In Managing Diabetic Eye Disease in Clinical Practice; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Diabetes Atlas; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bandello, F.; Parodi, M.B.; Lanzetta, P.; Loewenstein, A.; Massin, P.; Menchini, F.; Veritti, D. Diabetic macular edema. In Macular Edema; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 47, pp. 73–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ciulla, T.A.; Amador, A.G.; Zinman, B. Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema: Pathophysiology, screening, and novel therapies. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2653–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council of Ophthalmology (ICO). Guidelines for Diabetic Eye Care, 2nd ed.; International Council of Ophthalmology (ICO): San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, R.R.; Stevens, G.A.; White, R.A.; Smith, J.L.; Flaxman, S.R.; Price, H.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Leasher, J.; Naidoo, K.; et al. Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e339–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Larsen, M.; Sharma, S.; Simó, R. Diabetic Retinopathy. Nat. Rev. Disease Prim. 2016, 2, 16012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Garvin, M.K.; Sonka, M. Retinal imaging and image analysis. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 169–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, H.; Cree, M.J. Automated Image Detection of Retinal Pathology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Edwards, R. Diabetic retinopathy screening: A systematic review of the economic evidence. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Ramulu, P.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Sabanayagam, C. Addressing risk factors, screening, and preventative treatment for diabetic retinopathy in developing countries: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 44, 300–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, R.; Gella, L.; Srinivasan, S.; Sharma, T. Diabetic retinopathy: An epidemic at home and around the world. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 64, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwal, P.; Pachade, S.; Kokare, M.; Deshmukh, G.; Sahasrabuddhe, V. Automatic Retinal Image Analysis for the Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy. In Biomedical Signal and Image Processing in Patient Care; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 146–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, G.C.M.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: global prevalence, major risk factors, screening practices and public health challenges: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 44, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, T.; Klein, J.C.; Massin, P.; Erginay, A. A contribution of image processing to the diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy-detection of exudates in color fundus images of the human retina. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortliffe, E.H.; Blois, M.S. The computer meets medicine and biology: Emergence of a discipline. In Biomedical Informatics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, N.; Aslam, T.M.; MacGillivray, T.; Deary, I.J.; Dhillon, B.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Yogesan, K.; Constable, I.J. Retinal image analysis: Concepts, applications and potential. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2006, 25, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trucco, E.; Ruggeri, A.; Karnowski, T.; Giancardo, L.; Chaum, E.; Hubschman, J.P.; Al-Diri, B.; Cheung, C.Y.; Wong, D.; Abramoff, M.; et al. Validating retinal fundus image analysis algorithms: Issues and a proposal. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 3546–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwal, P.; Pachade, S.; Kamble, R.; Kokare, M.; Deshmukh, G.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.; Meriaudeau, F. Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD). IEEE DataPort 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porwal, P.; Pachade, S.; Kamble, R.; Kokare, M.; Deshmukh, G.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.; MacGillivray, T.; Sidibé, D.; Giancardo, L.; Quellec, G.; et al. Diabetic Retinopathy Segmentation and Grading Challenge. IEEE ISBI Challenge. 2018. Available online: https://idrid.grand-challenge.org/ (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Patton, N.; Aslam, T.; MacGillivray, T.; Pattie, A.; Deary, I.J.; Dhillon, B. Retinal vascular image analysis as a potential screening tool for cerebrovascular disease: A rationale based on homology between cerebral and retinal microvasculatures. J. Anat. 2005, 206, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advanced Concepts in Imaging Software (ADCIS). Aphelion Image Annotator. ADCIS France. 2018. Available online: http://www.adcis.net/en/Image-Processing-And-Analysis-Software-And-Custom-Engineering-Developments.html (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Decencière, E.; Cazuguel, G.; Zhang, X.; Thibault, G.; Klein, J.C.; Meyer, F.; Marcotegui, B.; Quellec, G.; Lamard, M.; Danno, R.; et al. TeleOphta: Machine learning and image processing methods for teleophthalmology. Irbm 2013, 34, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fernandez-Loaiza, P.; Sauma, J.; Hernandez-Bogantes, E.; Masis, M. Classification of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. World J. Diabetes 2013, 4, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuadros, J.; Bresnick, G. EyePACS: an adaptable telemedicine system for diabetic retinopathy screening. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giancardo, L.; Meriaudeau, F.; Karnowski, T.P.; Li, Y.; Garg, S.; Tobin, K.W., Jr.; Chaum, E. Exudate-based diabetic macular edema detection in fundus images using publicly available datasets. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decencière, E.; Zhang, X.; Cazuguel, G.; Lay, B.; Cochener, B.; Trone, C.; Gain, P.; Ordonez, R.; Massin, P.; Erginay, A.; et al. Feedback on a publicly distributed image database: The Messidor database. Image Anal. Stereol. 2014, 33, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
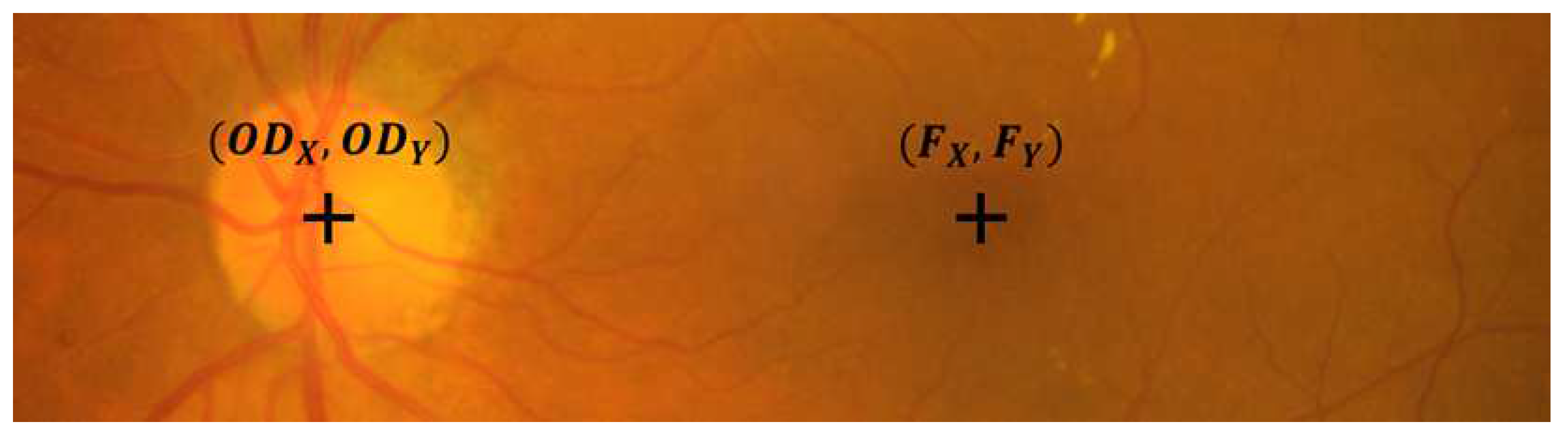

| Subject area | Biomedical Imaging, Ophthalmology |
| More specific subject area | Retinal image analysis for detection of DR and DME |
| Type of data | Image, CSV |
| How data was acquired | Retinal Fundus Camera. Model: Kowa VX-10 |
| Data format | Raw and Manual Annotations |
| Experimental factors | Mydriasis with one drop of tropicamide at 0.5% concentration |
| Experimental features | Retinal image of humans affected by diabetes was captured with 39 mm distance between lenses and examined eye using non-invasive fundus camera having xenon flash lamp. |
| Data source location | Eye Clinic, Sushrusha Hospital Building, Nanded, (M.S.), India |
| Data accessibility | https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/indian-diabetic-retinopathy-image-dataset-idrid |
| Data | Description | Quantity | Data Type | File Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color Fundus Images of Retina | Raw Data | 516 | Image | jpg |
| Disease Severity Grading of DR and DME | Image level grading | 516 | Tabular | CSV |
| Center co-ordinates of OD and Fovea | Manual center co-ordinates | 516 | Tabular | CSV |
| Binary Masks of different lesions | Precise pixel level manual annotation | 81 | Image | tif |
| Binary Masks of optic disc | Precise pixel level manual annotation | 81 | Image | tif |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porwal, P.; Pachade, S.; Kamble, R.; Kokare, M.; Deshmukh, G.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.; Meriaudeau, F. Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD): A Database for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Research. Data 2018, 3, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3030025
Porwal P, Pachade S, Kamble R, Kokare M, Deshmukh G, Sahasrabuddhe V, Meriaudeau F. Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD): A Database for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Research. Data. 2018; 3(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3030025
Chicago/Turabian StylePorwal, Prasanna, Samiksha Pachade, Ravi Kamble, Manesh Kokare, Girish Deshmukh, Vivek Sahasrabuddhe, and Fabrice Meriaudeau. 2018. "Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD): A Database for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Research" Data 3, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3030025
APA StylePorwal, P., Pachade, S., Kamble, R., Kokare, M., Deshmukh, G., Sahasrabuddhe, V., & Meriaudeau, F. (2018). Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD): A Database for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Research. Data, 3(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3030025





