Development of a Data Set of Pesticide Dissipation Rates in/on Various Plant Matrices for the Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB)
Abstract
1. Summary
2. Data Description
3. Methods
4. User Notes
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAS RN | Chemical Abstract Service Registry Number |
| RL50 | Half-life (also known as Residual Lifetime) of the pesticide on the specified plant matrix |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organisation |
| IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry |
| PPDB | Pesticide Properties Database |
| US EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
References
- Whitmyre, G.K.; Ross, J.H.; Lunchick, C.; Volger, B.; Singer, S. Biphasic dissipation kinetics for dislodgeable foliar residues in estimating post-application occupational exposures to endosulfan. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, G.L.; Shea, P.J.; Christians, N.; Miller, D.R.; Stuefer-Powell, C.; Starrett, S.K. Pesticide dissipation under golf course fairway conditions. Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, T.W.; Jeffries, M.D. Dislodgeable 2, 4-D from Athletic Field Turfgrass. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 116–122. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24126908 (accessed on 3 August 2017).
- Fantke, P.; Juraske, R.; Jolliet, O. Considering human exposure to pesticides in food products: Importance of dissipation dynamics. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Life Cycle Assessment in the Agri-Food Sector (LCA Food 2014), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–10 October 2014; American Center for Life Cycle Assessment: Tacoma, WA, USA, 2014; pp. 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, R.; Chen, H.P.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, Q.H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X. Dissipation pattern, processing factors, and safety evaluation for dimethoate and its metabolite (Omethoate) in tea (Camellia Sinensis). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwudebe, A.C.; Cox, D.L.; Palmer, S.J.; Morneweck, L.A.; Payne, L.D.; Dunbar, D.M.; Wislocki, P.G. Toxicity of emamectin benzoate foliar dislodgeable residues to two beneficial insects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3689–3693. Available online: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf970375c (accessed on 13 April 2017). [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Qiao, K.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, K. Dissipation rate of thiacloprid and its control effect against Bemisia tabaci in greenhouse tomato after soil application. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; He, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wei, Y.; Mu, W.; Liu, F. Dissipation dynamics of clothianidin and its control efficacy against Bradysia odoriphaga Yang and Zhang in Chinese chive ecosystems. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantke, P.; Wieland, P.; Wannaz, C.; Friedrich, R.; Jolliet, O. Dynamics of pesticide uptake into plants: From system functioning to parsimonious modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 40, 316–324. Available online: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.09.016 (accessed on 13 April 2017). [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, A.; Knisel, W.G. Evaluation of the GLEAMS model for pesticide leaching in Sweden. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 1994, 29, 1167–1182. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10934529409376101 (accessed on 3 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, D.H.; De Haan, M.; Leenheers, L.H.; De Vreede, S.A.F.; Van Hemmen, J.J. Half-lives of pesticides on greenhouse crops. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 58, 976–984. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9136663 (accessed on 3 August 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraske, R.; Antón, A.; Castells, F. Estimating half-lives of pesticides in/on vegetation for use in multimedia fate and exposure models. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1748–1755. Available online: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.047 (accessed on 14 July 2017).
- Fantke, P.; Gillespie, B.W.; Juraske, R.; Jolliet, O. Estimating half-lives for pesticide dissipation from plants. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2014, 48, 8588–8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spynu, E.I. Predicting pesticide residues to reduce crop contamination. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxcol. 1989, 109, 90–107. [Google Scholar]
- Fantke, P.; Juraske, R. Variability of pesticide dissipation half-lives in plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3548–3562. Available online: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/es303525x (accessed on 3 August 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, W.; El-Aty, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Shin, H.C.; Shim, J.H. An overview on common aspects influencing the dissipation pattern of pesticides: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.A. The Pesticide Manual 17th Edition; British Crop Protection Council: Hampshire, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2015.1133242 (accessed on 3 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- NPIC—National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2017. Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/ (accessed on 3 August 2017).
- Kegley, S.E.; Hill, B.R.; Orme, S.; Choi, A.H. PAN Pesticide Database. Pesticide Action Network, North America. 2000. Available online: http://www.pesticideinfo.org/ (accessed on 3 August 2017).
- Severinsen, M.; Jager, T. Modelling the influence of terrestrial vegetation on the environmental fate of xenobiotics. Chemosphere 1998, 37, 41–62. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(98)80002-7 (accessed on 3 August 2017). [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.J.; Mineau, P.; Juraske, R. Determining pesticide foliar half-lives from soil half-life value: Not so “cut-and-dry”. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1531–1533. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21664644 (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Willis, G.H.; McDowell, L.L. Pesticide persistence on foliage. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 23–73. [Google Scholar]
- Katagi, T. Photodegradation of Pesticides on Plant and Soil Surfaces. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 182, 1–195. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15217019 (accessed on 24 July 2017). [PubMed]
- Hoskins, W.M. Mathematical treatment of loss of pesticide residues. Plant Prot. Bull. (FAO) 1961, 9, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
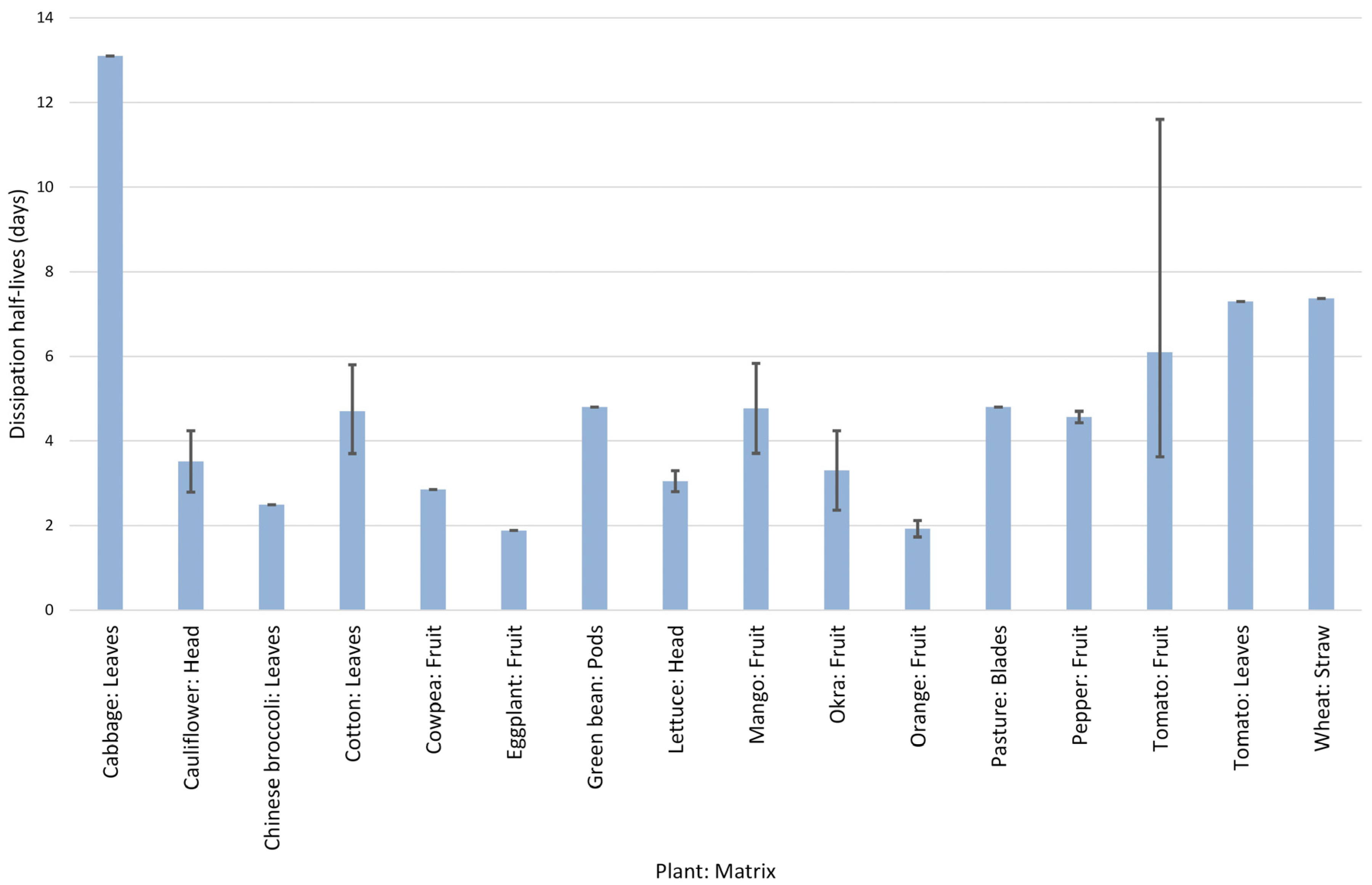
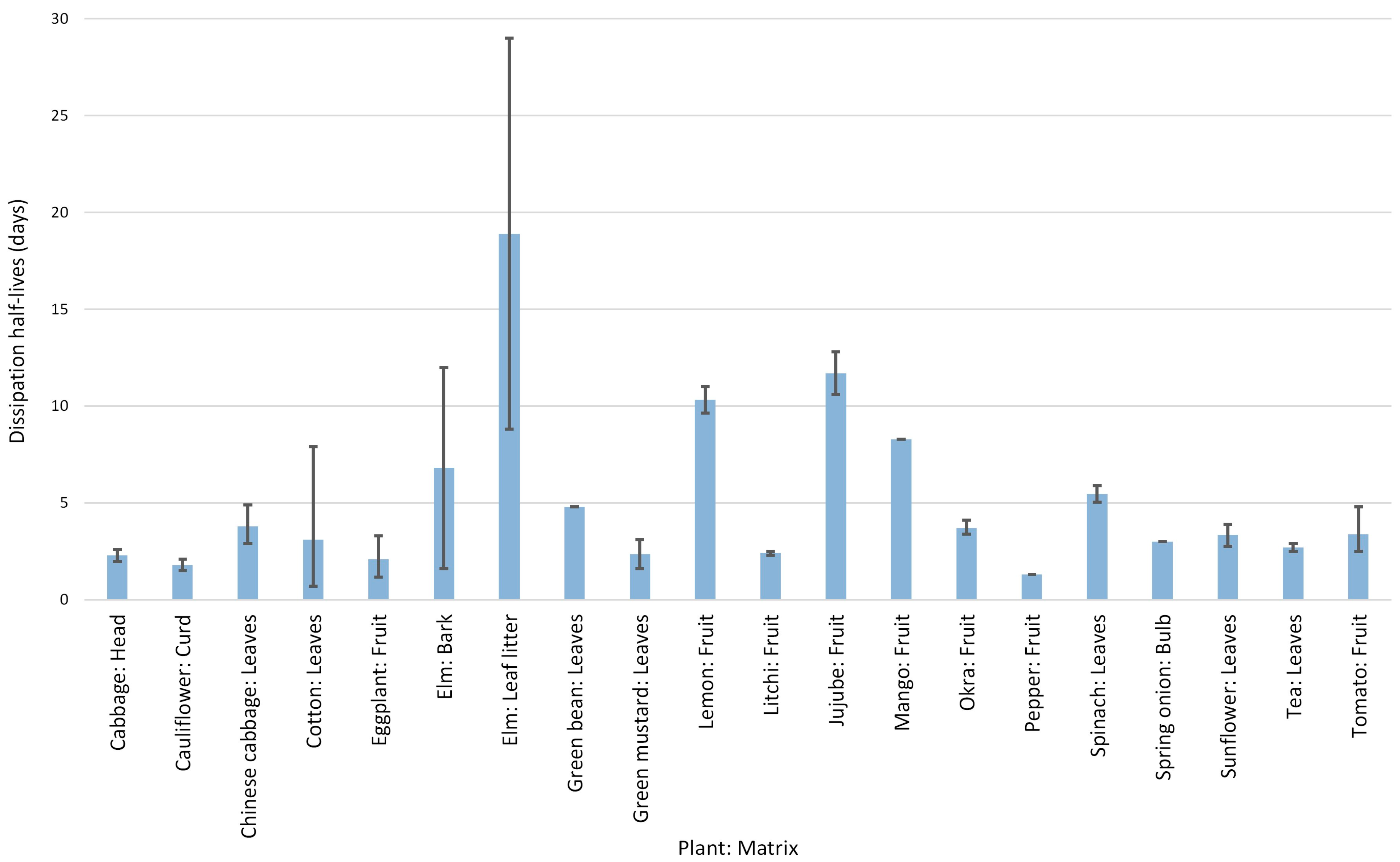
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Pesticide common name | The name by which the pesticide active substance is commonly known. Data in this column are listed alphabetically. |
| Pesticide chemical name | Chemical name of the pesticide using the Chemical Abstract Services (CAS) nomenclature. |
| CAS registry number | The Chemical Abstract Services' unique identifying number (RN) assigned to the pesticide. |
| Plant | Common name of the plant/crop the data relates to. |
| Plant scientific name | Scientific name including cultivar or variety where known |
| Matrix | The part of the plant tested. |
| On/In | Whether the residue was measured on (O—as a surface residue) on in (I—as total residue in and on) the sample. |
| Country | The country (and in some instances region) where the study was undertaken. |
| Study conditions | Whether the study was undertaken in the open field (F), undercover (U) or under special conditions (X). In the latter case the data is accompanied by short qualifying text. |
| Min DT50 (days) | Minimum experimental value for the plant dissipation rate expressed as the half-life (RL50) in days. |
| Max DT50 (days) | Maximum experimental value for the plant dissipation rate expressed as the half-life (RL50) in days. |
| Mean DT50 (days) | Arithmetic mean experimental value for the plant dissipation rate expressed as the half-life (RL50) in days. |
| Reference | Full bibliographical reference for the publication from which the data was extracted. |
| PPDB code | Unique identifier linking the record to the PPDB (see User Notes below). |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewis, K.; Tzilivakis, J. Development of a Data Set of Pesticide Dissipation Rates in/on Various Plant Matrices for the Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB). Data 2017, 2, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/data2030028
Lewis K, Tzilivakis J. Development of a Data Set of Pesticide Dissipation Rates in/on Various Plant Matrices for the Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB). Data. 2017; 2(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/data2030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewis, Kathleen, and John Tzilivakis. 2017. "Development of a Data Set of Pesticide Dissipation Rates in/on Various Plant Matrices for the Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB)" Data 2, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/data2030028
APA StyleLewis, K., & Tzilivakis, J. (2017). Development of a Data Set of Pesticide Dissipation Rates in/on Various Plant Matrices for the Pesticide Properties Database (PPDB). Data, 2(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/data2030028






