Abstract
This review covers three fundamental aspects of alcohol consumption and research efforts around the prevention and mitigation of its toxic effects in the human body. First, the sociocultural aspects of alcohol consumption are analysed, including drinking habits and strategies to combat intoxication. Second, we briefly introduce the biochemical aspects of ethanol metabolism and the biochemical pathways leading to its degradation, particularly the activation of toxic response pathways. Finally, we review current evidence and research efforts for finding compounds and substances able to prevent and mitigate the toxic effects of alcohol when over-indulgence has occurred. The toxic effects appear as a time-evolution process based on the stage of intoxication. We explore different compounds and formulations traditionally used to combat alcohol toxicity, as well as state-of-the-art research in the topic for novel molecules and formulations. Although we aimed to categorise which compounds are more effective for a particular level of alcohol intoxication, it is impossible to fully prevent or mitigate toxicity effects by only the compounds in isolation, further research is required to establish the long-term prevention and mitigation from the clinical point of view.
1. Introduction
Ingestible alcohol, or more specifically ethanol, is an abundant organic compound that constitutes an essential part of the metabolism in many living organisms. Ethanol is an important link in the the most abundant biochemical pathway: glycolysis. Ethanol is the product of sugar degradation via fermentation, and it is naturally present in carbohydrate rich fruits after reaching post-maturity. Yeast and some bacteria accelerate the fermentation processes, and are responsible for favouring ethanol production. Carbohydrate rich fruits were an important constituent in the diet of early humans [1]. It is very likely that ancient humans experienced the taste of alcohol, first from fermented fruits and vegetables, and later from fermented juices or cereals, before knowing the nature of the compound [2,3]. Thus, alcohol consumption and tolerance likely evolved together with humans’ digestive system.
The development of pottery around 10,000 BC could have triggered the first production of purpose-made alcoholic beverages [4]. The earliest evidence of a purpose-made fermentation, comes from a mixture of rice, honey and wild grapes from around 7000 BC [4]. Wine and beer, as we know them today, were probably produced as earlier as 5400 BC and 3500 BC, respectively [3]. Distillation exists from 1 AD, and the earliest modern drinks from distillation appeared around the 13th century [5].
Since alcohol consumption has been part of human culture for millennia, it has not been usually regarded as a dangerous substance. In fact, alcohol has been perceived as integral part of a meal, or in some instances as a cure against infectious diseases, or as a cleaning agent. Only recently, when its consumption increased beyond unprecedented levels, have its toxic effects for the human body been of concern. Alcohol, in fact, is tremendously harmful for human health, particularly at the rates that it is currently consumed. Nowadays, we are able to understand its long-term effects on degenerative diseases, neuro psychiatric conditions, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, cancers, cardiovascular conditions, and immunodeficiency [6]. Furthermore, biochemical and genetic evidence can direct us to the specific pathways revealing its toxicity, its chronic impact in several organs, and the mechanisms for addiction [7]. Nevertheless, there are cultural differences in alcohol consumption habits for which toxic effects are universal. There is no doubt that its increasing consumption and the associated health problems are of great concern for health organizations around the globe [6]. These concerns go beyond just the individual’s health, they affect entire populations and the economic burdens to the healthcare systems are now worth discussing.
Global Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol markets are growing globally (1% CAGR) with over 70 million litres consumed every day [6]. Its consumption varies by geography, but it is steadily growing globally, particularly in emerging economies (Figure 1). Although a great economic opportunity, the health risks associated with it are also growing and pose a burden to the healthcare systems. Large proportions of the population are accustomed to heavy drinking episodes beyond what the body can metabolise (Figure 2). Certain geographies are more susceptible to the adversities of alcohol consumption because of the lack of public policies and regulations and cultural susceptibility to heavy drinking (Figure 3). The implementation of policies are tied to cultural factors, biological susceptibility in local populations, and alcohol tolerance [8]. Nevertheless, there is a common understanding of what an alcoholic drink represents, and the risks associated with elevated blood alcohol contents (see Figure 4).
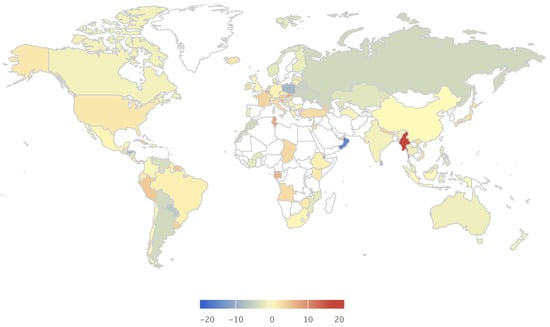
Figure 1.
Consumption per capita growth 2014 (%). Figures assembled with combined data from the Global Information System on Alcohol and Health (http://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.GISAH?lang=en) from the World Health Organization Global Health Observatory Data Repository.
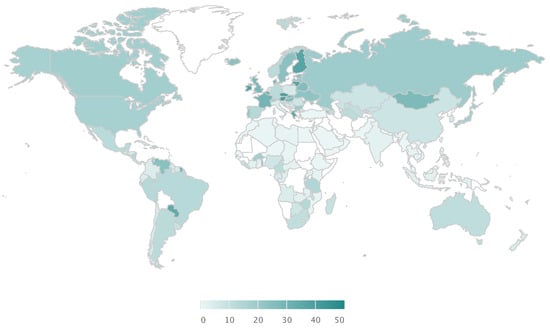
Figure 2.
Percentage of population with one heavy drinking episode in the past 30 days (%). Figures assembled with combined data from the Global Information System on Alcohol and Health (http://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.GISAH?lang=en) from the World Health Organization Global Health Observatory Data Repository.
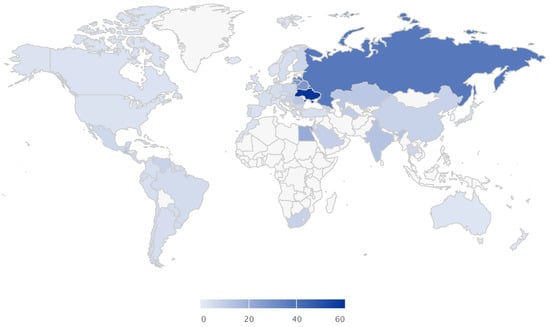
Figure 3.
Total deaths per 100,000 L of alcohol consumed (deaths). Figures assembled with combined data from the Global Information System on Alcohol and Health (http://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.GISAH?lang=en) from the World Health Organization Global Health Observatory Data Repository.
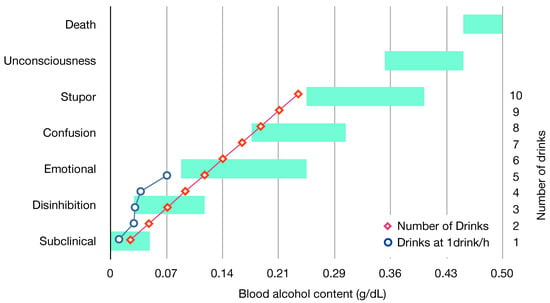
Figure 4.
Clinical status, average number of drinks and blood alcohol content [16,17]. One drink equals one unit, an average unit is 14 mL of pure alcohol. Figures assembled with combined data from the Global Information System on Alcohol and Health (http://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.GISAH?lang=en) from the World Health Organization Global Health Observatory Data Repository.
Alcohol markets are growing globally (1% CAGR) with over 70 million litres are consumed every day [6]. Its consumption varies by geography but it is steadily growing globally, particularly in emerging economies (Figure 1). Although a great economic opportunity, the health risks associated with it are also growing and pose a burden to the healthcare systems. Large proportions of the population are accustomed to heavy drinking episodes beyond what the body can metabolise (Figure 2). Certain geographies are more susceptible to the adversities of alcohol consumption because of the lack of public policies and regulations and cultural susceptibility to heavy drinking (Figure 3). See Supplementary Figures S1–S6 for an overview on the current demographics and impact of alcohol consumption. The implementation of policies are tied to cultural factors, biological susceptibility in local populations, and alcohol tolerance [8]. Nevertheless, there is a common understanding of what an alcoholic drink represents in terms of volume of pure alcohol, and the risks associated with elevated blood alcohol contents (see Figure 4).
Even though fatalities are a reasonable measure for the negative impact of alcohol consumption, the statistics generally include accidents due to intoxication but not the degree of which was solely caused by the blood alcohol content. The scope of this paper is related to the biological aspects of ethanol consumption; therefore, we use these statistics only as a guide. The main problem with documenting the adverse effects of alcohol to human health is that intoxication causes, not only short term damage, but also long-term chronic complications. The adverse effects of alcohol intoxication are widely studied in the medical community; however, there is a need for a holistic understanding of such effects over the whole body, in different organs, and over time. Leaving aside the need for policies to prevent alcohol chronic damage due to repetitive ingestion, there is also a need to understand the biological mechanisms that exist to prevent or mitigate its toxicity. Here, we explore those possibilities and give an extensive review of mitigation strategies from the metabolic point of view, by analysing and organising the state-of-the-art research in the topic.
2. Alcohol Metabolism and Toxicity
In order to tackle the adverse effects of alcohol consumption, it is important to understand at which level of ingestion it becomes toxic for the human body. This, of course, varies from individual to individual, and from organ to organ within the body. Nevertheless, it is paramount to revise pathways involved in the alcohol metabolism present in humans in addition to understanding their localization in different organs, and the extent of their functions over time. The use of alcohol in combination with other drugs or substances has a complex impact in human health and it is not covered by this review. By-products of the distillation of alcoholic spirits such as methanol, tannins, or additives for aroma, color and taste of other alcoholic beverages can also cause toxicity when metabolized; however, this is not covered in this review. It is advised not to drink beverages from dubious origin as the risk of intoxication by unknown undesired by-products is high, nevertheless these substances can be present in drinks of known origin as well. Societal factors, such as malnutrition, personal, or psychological problems can also have an impact on the alcohol consumption. We focus here, however, on the direct physiological adverse effects of ethanol consumption from alcoholic beverages.
2.1. Key Organs, Pathways, and Metabolic Processes
There are well studied enzymatic reactions and pathways exclusive to alcohol metabolism in humans. The main enzymes involved in ethanol transformation through the body are aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), cytochrome P450 (CYP2E1), and catalase [9]. Increased alcohol consumption results in an increased activity of these enzymes and pathways, and thus in the metabolites and by-products produced by them. Non-oxidative pathways of alcohol metabolism can be activated during high dosages, or during chronic ingestion, mainly driven by inhibition of the other other pathways (oxidative) [9]. The main enzymes involved in these pathways are phospholipase D (PLD) and fatty acid ethyl ester synthase (FAEES). These metabolic pathways can be influenced by several factors: the interconnections in the pathway network, the enzymes responsive of the metabolic gearing, and the expression levels of genes involved in their production. Pathways and gene expression may differ in organisms, organs, tissues, and even individual cells. Alcohol is carried from the stomach to the small intestine, and then to the blood stream. Once in the bloodstream, it is distributed through the body and degraded by the metabolic pathways. During sustained ethanol metabolization, these processes occur mainly in the liver. Although the pathways and degradation mechanisms are also present in the stomach, brain, and other organs, the rate of degradation varies depending on the blood alcohol content (BAC). Several other factors influence this, for example the type of drink, food ingestion, genetics, age, historic consumption, etc. [10,11]. Genetic variations play a key role on the development of alcohol metabolism, toxicity tolerance, and also related diseases [9]. For example, it is well known that a high percentage of Japanese, Chinese and Korean populations express variations in the primary enzymes involved in the transformation of ethanol to acetaldehyde and acetate [12]. This genetic variation causes the so-called ‘flush reaction’ that has caused increased awareness for ethanol toxicity amongst Asian populations. Similarly, genetic factors are associated with high tolerance, for example in Russian and Slavic populations [13]. Tolerance to alcohol consumption, however, may not necessarily be related to tolerance to its toxic effects. In fact, populations that may show higher ethanol processing metabolic rates are more susceptible to long-term health effects [9]. Alcohol tolerance has been also found to have a genetic component, a gene regulating cellular stress, a pathway involving noradrenaline, and a zinc-finger protein suggesting nucleic acid binding [7]. This section discusses the direct effects of alcohol consumption on the degradation pathways, as well as the indirect effects on other related pathways, tissues, and organs from the metabolic point of view.
2.2. Adverse Effects of Alcohol Consumption in Human Health
Typical effects associated as ‘adverse’ due to alcohol ingestion are: first the feeling of drunkenness and losing control, then the hangover, and finally short term and chronic intoxication. Despite hangover and drunkenness being noticeable signs, they are only early warnings for intoxication, the real damage from alcohol consumption comes at a later stage. In this review, we use the word drunkenness as the status of intoxication beyond sustained ethanol metabolisation and before the withdrawal (consumption is stopped). Drunkenness is a complimentary term for the observable signs of the pathophysiological stage of alcohol intoxication; for a more thorough discussion about what is alcohol intoxication, see reference [14].
2.2.1. Drunkenness
It must be clarified that the progression into drunkenness depends greatly on the blood alcohol content and on the individual alcohol tolerance influenced by age, body mass, and gender. In addition, it depends greatly on the rate at which alcohol is consumed, as a quick uptake could lead to the same effects for lower BAC. Exceeding a limit at which BAC causes the body to go beyond sustained metabolization causes the initiation of the intoxication phase. Typically, the BAC level is set in most countries to be 0.08 g/dL [15], but there are initiatives to lower it to 0.05 g/dL [15]. In one single drinking episode, the stages of blood alcohol content influence feelings and personality and can be mapped from physical and mental impairments from the clinical point of view [16]. Blood alcohol content in sobriety or subclinical levels (<0.05 g/dL) renders not noticeable changes, except for thought, judgment, or concentration loss in tests. As the concentration increases (0.03 g/dL–0.12 g/dL), extroversion and disinhibition are typical characteristics, also euphoria and bad reflexes. In a further level (0.09 g/dL–0.25 g/dL), emotional swings and excitement are noticeable together with slightly impaired sensorial and motor coordination, typical drinking episodes reach this stage. Confusion characterises the next level (0.18 g/dL–0.30 g/dL) with memory blackouts and muscular discoordination. In a further level, stupor is typical (0.25 g/dL–0.40 g/dL), accompanied with the inability to move or walk, and, finally, unconsciousness (0.35 g/dL–0.45 g/dL) where heart rate and respiration are impaired and comma is likely. Concentrations above 0.45 g/dL result in death. Figure 4 shows a graphic representation of these levels and the reference values for one drinking episode.
Drunkenness in recurrent episodes could cause not only physiological damage, but also social and psychological problems related to addiction and depression. Neurotransmitters are immediately affected as soon as alcohol is drunk, and the brain can take several months to correct itself for the changes. Brain damage, memory loss, and seizures have been associated with heavy alcohol intake [18]. Preventing drunkenness can be as trivial as drinking abundant water to maintain the BAC required for sustained ethanol metabolization. The problem of preventing drunkenness is that it contradicts the social purpose for alcohol consumption. Ideally, it would be desired to reach the BAC that gives disinhibition or emotional levels, and still undergo a sustained alcohol metabolization to prevent toxicity. We will discuss this possibility in the final remarks.
2.2.2. Hangover
Hangover, or the withdrawal of alcohol from the body, is experienced when the blood alcohol concentration decreases to zero [19]. The symptoms of this withdrawal are well known: thirst, fatigue, headache, nausea, decreased sleep, sensory vertigo, sweating, anxiety, decreased attention, etc. Likewise, the causes are well documented and can be easily identified. During alcohol intake, the production of vasopressin (an antidiuretic hormone) is stimulated, causing a constant need to urinate and therefore the continuous loss of water. Dehydration during hangover results in electrolyte imbalance, which is a common cause of cardiovascular diseases and nervous disorders associated with alcohol consumption [20]. Alcohol is an irritant to the stomach and causes the increased production of gastric acid; it can lead to gastritis and damage to the digestive system. The liver accumulates triglycerides during high alcohol intake, also associated with cardiovascular problems, and a direct consequence of hangover [19]. Liver disturbances cause the alteration of blood sugar levels; this can result in hypoglycemia, which can linked to neural damage [21]. The vasodilative and sedative effects of alcohol, prior and during hangover, disrupt normal sleep patterns and temperature rhythms, causing headache and alteration of hormones released during normal sleeping cycles. The result of these alterations have a negative impact on protein synthesis, carbohydrate synthesis, and stress responses [22]. Furthermore, alcohol is a depressant, its withdrawal experienced during hangover affects the nervous system at the neurotransmitter level, causing nervous stress [19]. The greatest effects from alcohol withdrawal are short-term toxicity caused by by-products of alcohol metabolization. Acetaldehyde, for example, causes sweating, flushing, nausea, and metabolism unbalance.
2.2.3. Intoxication and Metabolic Long-Term Damage
As discussed in the previous section, non-metabolized toxic by-products with toxic effects cause an immediate sensation of unwellness. There are, however, also long-term consequences caused by continuous short-term exposures. The adverse effects of alcohol consumption will be discussed in this section from the biomolecular level up to the organ level and the consequent diseases.
One of the most abundant by-products of ethanol metabolization is acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde has a short life in the organism, but when accumulated in cells and tissues has damaging long-term effects. An excess of acetaldehyde can interact with aromatic amino acids in proteins, generating hybrid compounds and abducts unrecognized by the body [9]. Proteins known to be susceptible to these interactions are hemoglobin and membrane proteins in erythrocytes, albumin in blood plasma, lipoproteins associated with heart disease, tubulin in cell division and cell transport, collagen in connective tissue, and cytochromes, which are key in the metabolism of ethanol [9]. These foreign abducts are recognized by the immune system causing cytotoxic immune responses, particularly in the liver and blood. Acetaldehyde also interacts with amines in neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, thus also responsible for causing chronic emotional imbalances [9].
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are perhaps the most dangerous by-products of the ethanol metabolization. Their damaging effects cascade down onto other important pathways with detrimental and irreversible consequences to human health. Alcohol ingestion increases ROS from the CYP2E1, ADH and ALDH pathways. ROS also form free radicals with other molecules (, , , ); under normal conditions, endogenous antioxidants scavenge these harmful species, keeping balance. Upon alcohol intake, the body spends its antioxidant reservoir in mitigating the excess radicals; this is called oxidative stress. The consequences of oxidative stress are severe; free radicals play a key role in carcinogenesis, diabetes, aging, atherosclerosis, and inflammation [23]. The underlying metabolic processes of these diseases are lipid, protein and DNA peroxidation, and tumor necrotic factor production. As a consequence, cell and mitochondrial membrane permeability are affected, immune response to these abducts leads to inflammation, cellular apoptosis and necrosis, ultimately causing tissue and organ damage.
Other by-products, naturally occurring under normal metabolism, can cause several health adversities when overproduced. For example, ethanol oxidation by CYP2E1 induces synthesis of caspases and apoptosis [24]. Alcohol metabolism via ADH and ALDH produces NADH, which binds oxygen to hydrogen to produce water, and in excess makes hepatocytes close to the veins take oxygen from the blood resulting in hypoxia [25]. Hypoxia triggers other metabolic pathways altering the normal production of essential molecules for other functions. NADH and NAD+ are present in many other pathways, when their ratio is altered, gene expression responses are triggered; for example, caloric restriction, and genes involved in aging, diabetes, cancer, immune and cardiovascular diseases [26]. Other common metabolic disorders caused by alcohol intoxication are: hyperlipidemia, lactic acidosis, ketosis, hyperuricemia, atrophy in brain tissue, and fatty liver [27,28].
In summary, alcohol consumption causes molecular and cellular damage at unprecedented levels, tissue damage and organ damage in the liver, heart, brain, lungs and blood cells. Acute damage propagates through the body by interlinked pathways, and the overall effect is a diminished quality of life. In combination with other health conditions, the damage can be tremendous—for example, medication for hypertension and alcohol may result in death. Alcohol ingested during pregnancy can affect fetal development pathways affecting fetus brain formation [29,30]. Known direct relations exist from alcohol consumption and esophagus, larynx, oral cavity, and liver cancers [31,32].
2.3. Molecular and Physiological Pathways on a Time-Scale Basis
As discussed in the previous sections, ethanol is processed by the body via oxidative pathways involving aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), cytochrome P450 (CYP2E1), and catalase. Excessive alcohol intake will result in increased activity of those metabolic pathways, and thus in an excess production of related toxic by-products. Non-oxidative pathways of alcohol metabolism can be activated during high doses or chronic ingestion. In these cases, phospholipase D (PLD) and the fatty acid ethyl esters synthase (FAEES) pathways are involved. A summary of the pathways of ethanol metabolization, by-products, and negative consequences is shown in Figure 5a. It is a simple process, yet many factors will influence its toxicity susceptibility in the human body.
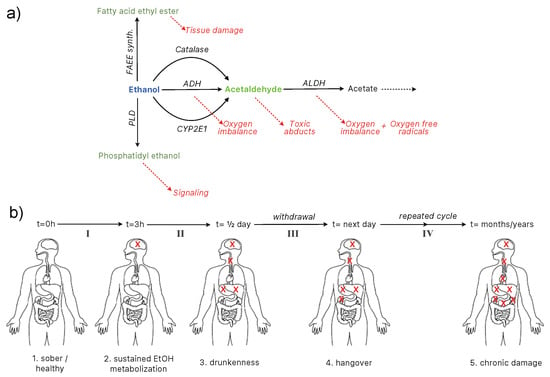
Figure 5.
(a) alcohol ingestion pathways [9,33] and (b) toxicity evolution on a time-scale basis.
One particularity of alcohol consumption is that its distribution through the body is localized to certain organs. Ethanol is carried from the stomach to the small intestine and then to the bloodstream, where it is distributed to different organs and finally degraded. Although degradation pathways are present in several organs including stomach, liver and the brain among others, the rate of degradation varies and affects their physiology differently depending on the blood alcohol content (BAC). When the BAC exceeds the concentration for sustained metabolization, it becomes toxic. There are three stages of alcohol toxicity evolution: drunkenness, hangover, and chronic damage.
The metabolic pathways in Figure 5a are affected differently through the body depending on the organ and the stage of intoxication. Figure 5a shows a more detailed view of all the pathways involved in ethanol metabolization in different organs. Figure 5b represents the alcohol toxicity evolution on a timescale basis and the depth of the damage inflicted overtime. The key message is that different stages involve different organs, and that, once the sustained ethanol metabolization is surpassed, the toxicity starts.
The toxicity mitigation levels are defined as follows:
- Level I: from sober to sustained metabolization (1–2),
- Level II: from sustained metabolization to drunkenness,
- Level III: from drunkenness to hangover (withdrawal),
- Level IV: chronic intoxication.
It is important to note that Level II and III have different effects depending on the intensity of the drinking episode, which, on one occasion, have long-standing effects (see Figure 4). For the purpose of this review, considerably intense drunkenness and its consequential withdrawal (surpassing the stupor stage) are classified as chronic intoxication.
3. Alcohol Toxicity Prevention and Relief
The first section of this review discusses cultural and socio-economic aspects of alcohol consumption. The maxima for prevention also lies on cultural and socio-economic measures and policy implementation. Alcohol in excess is harmful and its consumption should be moderated. This review will focus on the biochemical measures and approaches taken to reduce the harm of alcohol intake. Controlling or determining what is ‘excessive’ is a very challenging task. Solutions to set limits on alcohol consumption vary across cultures and countries. However, one fact prevails: once an individual experiences ‘drunkenness’, alcohol toxicity is already having an impact on the metabolism and health. This section gathers a collection of state-of-the-art research and scientific knowledge to tackle alcohol toxicity at different stages. We aim to set the basis for a comprehensive classification of such solutions, with emphasis on prevention.
3.1. Drunkenness Prevention and Relief
The first stages of alcohol intoxication start with drunkenness. Preventing drunkenness can be achieved by correctly dosing alcohol intake. Popular folk recommendations exist for preventing drunkenness by restrained drinking [34]; this requires the mental capacity that can be inhibited due to its embriagating effects, thus resulting in being challenging. Alcohol tolerance, however, is person-specific and varies across populations. There are standard measures of alcohol recommended by health authorities aiming to englobe most alcohol users. An alcohol unit in is approximately 14 mL of pure alcohol, and the daily recommended intake is three units per day but no more than 10 units per week (in separate occasions). Those standards are set and meant to prevent drunkenness, as alcohol is naturally metabolized by the body under the correct dosage and timing (see Figure 4). Therefore, the most effective drunkenness prevention strategy is to keep the metabolism at peace. Similarly, continuous ingestion of water and moderate physical activity have been found to increase arterial and alveolar oxygenation enhancing the metabolization of alcohol [35]. If drunkenness cannot be avoided, it can be mitigated in a similar fashion: stopping alcohol intake, consuming abundant liquids, and performing moderate physical activity. Some have also suggested the use of alternative substances to alcohol with similar ‘drunkenness’ effects, not in the scope of this review. For example, proposing ‘synthetic alcohol’ chemicals designed to act upon brain receptors for alcohol, which can have the same effects but contain the damage of intoxication [36].
There are a plethora of remedies reported to reduce alcohol in the blood by accelerating alcohol metabolism, which prevents further drinking. For example, concoctions of extracts from Pueraria lobata, Tabernanthe iboga, Panax ginseng, and Salvia miltiorrhiza and Hypericum perforatum have been reported to prevent alcohol consumption by inhibiting the will to drink [37,38,39,40]. The mechanisms behind it are still unclear, but a blockage of absorption at the gastrointestinal tract, on the central nervous system, and on the brain reward pathway have been suggested [38,39,41]. The active compounds on these extracts are isoflavonoids, puerarin, daidzin, daidzein, ibogaine and analogues [39,41]. Extracts from P. lobata, known as kudzu, have also shown inhibition of ALDH2 enzymes, which could result in increased neoplasm risk [42]. Active compounds in kudzu are isoflavones, puerarin, daidzein, daidzin, mirificin, and salvianolic acid [39,41]. Other herbal extracts, popular in Asian countries, that have been tested in animal models showing reduction of blood alcohol sugar contain mixtures of: Artemisia capillaris, Pueraria thunbergiana, Hovenia dulcis, Atractylodes macrocephala, Polyporus umbellatus, Poria cocos, Citrus unshiu, and Lycium chinense [43].
3.2. Hangover Prevention and Relief
Excessive drinking and the type of alcohol ingested influence the severity of hangovers. The presence of bioactive chemicals, which give character to wines and spirits, are associated with a high incidence of hangovers [44,45]. For instance, vodka and gin are known to have less hangover effects than whisky and brandy or red wine [46].
Mitigation of hangover adverse effects is possible, as it is for the drunkenness stage. Ingesting abundant liquids and foods with complex carbohydrates, such as fruits, fruit juices, or bread, can prevent hangover effects [19]. Ingesting foods rich in carbohydrates reduce hypoglycemia preventing nausea [46], while liquids and electrolyte solutions help with dehydration. Using medications to relieve the symptoms (headaches, nausea, muscle pain) is not recommended; for example, ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin are irritants to the stomach that contribute to the acidification caused by alcohol itself. Furthermore, they add to the liver toxicity, the organ responsible for their degradation, and may cause irreversible damage in combination. Medicaments for hangover symptoms have shown no evidence to mitigate hangovers in placebo experiments. Despite the lack of thorough studies, there is a plethora of reported pharmaceutical formulations claiming to alleviate hangover symptoms, and these are undergoing study. Tolfenamic acid, for example, is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis; prostaglandins are responsible for vasodilation and muscle relaxation and a human study showed it contributes to alleviate hangover symptoms when consumed before and after ethanol consumption [47]. Multiple compounds studied in isolation have been found to act over biochemical pathways. Compounds with a proven relief action will be discussed in the following section and further classified in relation to the pathways, organs and stages of toxicity evolution.
4. Known Compounds for Alcohol Toxicity Mitigation
Although previous sections review alcohol consumption and its metabolic implications, it is this section of the review that comprises the core review activity on the topic. An initial search of the literature revealed that there are multiple reviews on alcohol metabolism and reviews on such reviews. There are also reviews on the topic of alcoholism prevention, alcohol toxicity, and hangover. Nevertheless, we have identified a gap in the review literature that addresses the alcohol toxicity problems according to the alcohol metabolism. In other words, there was a lack of consistent reporting on the real consequences of alcohol toxicity in the human body with the research around prevention and mitigation. Following review strategy recommendations published elsewhere [48], we defined the methodology as described next.
4.1. Review Strategy Methodology
Several keywords and keyword combinations were selected as follows: alcohol + secondary keyword + tertiary keyword. The secondary keyword was selected based on the alcohol toxicity evolution from the metabolic perspective, as discussed in the previous sections, whose keywords were: toxicity, drunkenness, and hangover. The tertiary keyword was selected from those that imply favouring a positive outcome on each stage of the alcohol toxicity evolution. The selected tertiary keywords were: prevention, relief, mitigation, protection, alleviation; and variations of such words, for instance protective, and preventive. This strategy rendered other keywords added to the tertiary keyword pool; for instance, hepatoprotective. Having this keyword pool, we used Google Scholar (GS) and Web of Science (WS) to search for a multitude of articles. Legal documents were excluded from GS, patents were also excluded, except those cited by scholarly articles; books and reviews citing individual research studies were excluded if the original article was found. It has been shown that the first result pages in GS provide acceptable results, with ’grey’ literature coming up on average after page 80 [49]. Therefore, we limited our initial literature mining on that search engine to page 40. Only articles that overlapped in search results at WS were considered, with the exception of those found relevant in foreign languages published by national academies of science. Duplicated entries and follow up studies were excluded. Articles citing compounds previously cited along the review timeline were excluded. The criteria for inclusion was the mention of a compound, extract, or concoction; its origin (animal, plants, synthetic, etc.), its active chemical ingredients, and the model on which the research was performed (humans, cell lines, mice, or in vitro). Active ingredients not found in the main source article were looked for in a separate search. Over 100 scholarly entries are cited in this review, even though the search was thorough, the authors cannot guarantee it is exhaustive, the science continues to evolve and the authors hope that future researchers complete and expand this initial task.
4.2. Plant Extracts and Plant Concoctions
Herbal extracts have been known to alleviate common alcohol drinking symptoms, or help with drunkenness, particularly in Asia. Not all have proven real efficacy. Some of these compounds have been characterized and tested in animal and human models, and some demonstrated ameliorating adverse alcohol toxicity.
A popular extract in Korea known as JBU contains Artemisia caillaris, Pueraria thunbergiana, Hovenia dulcis, Artractylodes macrocephala, Polyporus umbellatus, Poria cocos, Citrus unshiu, Lycium chinense, Panax ginseng, and Silybum maximum. The anti-ethanol-toxicity from this extract is attributed to flavonoids and antioxidants, as it has been shown to reduce not only alcohol blood concentration, but also acetaldehyde [43]. These herbs have been reported individually to have alleviating effects on alcohol toxicity. For example, P. ginseng, whose active ingredients are ginsenosides, showed reduced toxicity in human and animal models [50]. H. dulcis extracts have shown free radical scavenging, anti hangover properties, and hepatoprotective effects likely due to heteropolysaccharides, rhamnose, arabinose, galactose and galacturonic acid [51].
Some formulations of common use in China for the same purposes consist of ethanolic extracts of herbal combinations. For example, Cinchona oficinalis, Lobelia inflata, Nux vomica, Quercus glandium spiritus, Ranunculus bulbosus, additioned with zinc, and Rhododendron Crysanthum [52]. Cinchona pubescens extracts contain quinidine, which has been shown to help with treating cirrhotic patients [53].
In Japan, herbal formulations known as Kampo, that treat alcoholic intoxication, have been well documented and classified in terms of ingredients and proportions [54]. One concoction (goreisan) includes Aslisma rhizome, A. lancea rhizome, Polyporus sclerotium, Artemisa capilaris flower or Poria sclerotium, and it has been shown to have hepatoprotective effects and to aid in alcohol metabolism, main substances found on those species are cinnamic acid, alisol A, and atractilenolide III. Its mechanism consists of accelerating oxidation of ethanol through the activation of alcohol dehydrogenase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and enzymes involved in the glutathione metabolism [55]. Another formulation (orengedokotu) containing Scutellaria root, Coptis rhizome, Gardenia fruit, and Phellodendron bark has shown reduction of breath alcohol content [56], anti-hangover [57], gastric and hepatic protection by enhancing hepatic enzymes [58]. Its main components are coptisine, baicalin, palmatine, berberine, and wogonoside and are known to react amongst them in the preparation [59]. A formulation (hangeshashinto) known for hangover relief contains Pinellia tuber, Scutellaria root, processed ginger, Glycyrrhiza, Jujube, Ginseng, and Coptis rhizome, whose active compounds in this formulation are glycyrrhizin, liquiritin, baicalin, berberine, and glucuronides [60].
Herbal extracts studied more in depth, for example Gracinia indica (kokum), popular in India, have been shown to prevent depletion of antioxidant free radical scavenging enzymes and reduced glutamate [61]. The main antioxidant constituents from G. indica are hydroxycitric acid (up to 12.7%), garcinol (1.6% direct extract), iso-garcinol, hydroxycitric acid lactone, citric acid, oxalic acid, xanthochymol, iso-xanthochymol, and benzhophenone [62].
Other plants exclusively, sourced for their medicinal properties, have also been reported to mitigate alcohol toxicity. The piper beetle leaf extract is a common masticatory that has been proven effective in the reduction of neurotoxicity of ethanol ingestion in animal models, and it resulted in lower production of free fatty acids and lipids peroxidation, together with an increase of antioxidant substances being intrinsically produced [63]. Main active compounds in Piper beetle extracts are benzoic acid, hydroxychavicol, eugenol, and chavibetol [64,65]. Cudrania tricuspidata root extracts, which have been found to modulate positively enzyme activities and blood gas levels [66], and hepatoprotection from xantones and prenyl-flavones [67]. Sapindus mukorossi and Rheum emodi extracts showed reduction of free-radical activity in hepatic tissue in mice, mainly containing saponins and anthraquinones [68]. Cassia occidentalis L. (kasondi), used in Unani medicine contains various bioactive compounds including achrosin, emodin, anthraquinones, anthrones, apigenin, aurantiobtusin, campesterol, and cassiollin [69]. It has shown lower transaminases and phosphatases production in liver in mice [70]. Peumus boldus extracts have shown hepatoprotective effects by reducing the lipid peroxidation and the enzymatic leakage of LDH. Boldine is the main alkaloid present in the extract to which the hepatoprotection has been associated [71]. The antioxidant activity from phyllanthin, hypophyllanthin, triacontanal and tricontanol of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. et. Thonn has been shown to reduce ethanol induced levels of transaminases, enhanced liver cell recovery of triglycerides and tumor necrotic factor [72]. Fenugreek seed extracts, Trigonella foenum graecum has been shown to reduce glutathione after 24 h ethanol dosage on liver cells; and reduced apoptosis and enzymatic leakages in brain and liver tissues [73,74]; fenugreek main compounds are apigenin, kaempferol, and luteolin [75]. Curcumins from the rhizome of Curcuma longa have shown a favorable effect in inflammatory processes including ethanol-caused hepatic injury and lipid peroxidation [76]. Cardiospermum halicacabum L. extracts with luteloin, myo-inositol, chrysoeriol, epidermin, and quebrachitol have shown hydroxyl radical scavenging, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, and most notably inhibition of gastric ulcers by oral administration [77]. Taraxacum officinale (dandelion) root has shown protective action in the liver by elevating antioxidative potentials and decreasing lipid peroxidation [78], and its main active compounds are taraxinic acid, cycloartenol, taraxasterol, inulin, eudesmanolides, tetrahydroridentin, guaianolides, dihydrolactucin, ixerin, taraxinic acid, glucopyranoside, and various triterpenes [79]. Similarly, Hygrophila auriculata root extracts have shown antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effects via reduction of transaminases in vivo [80], and its main compounds are lupeol, betulin, sitosterol, and stigmasterol [81]. Some plant formulations target the carbohydrate depletion by using polysaccharide-rich concoctions. For example, extracts of Acanthopanax senticosus have shown inhibition of alcohol-induced hypoglycemia and inflammatory responses [82].
Other herbal extracts or concoctions from around the world are derived from commonly available plants and fruits. For example, volatile oil from Origanum majorana L. contains potent antioxidants, phenolic terpenoids, flavonoids, tannins, phenolic glycosides, sitosterol, and pro-anthocyanidins oligomers. These extracts’ protective effects are known to act at the oxidative stress level and at the lipid peroxidation level. Furthermore, they are known to increase intrinsic vitamin C production and lower membrane permeability in brain, liver and testis tissue [83]. Grape juice has also shown to protect against alcohol intoxication by inhibiting production of ethanol-induced free radicals [84]. The active components present in grape juice and grape seed extract Vitis vinifera L. are flavonoids, such as catechins, epicatechins, anthocyanidins, proanthocyanidins, and resveratrol [85,86].
Coffee drinking has also been associated with hepatoprotective effects, likely due to its antioxidant properties from polyphenols and melanoidins acting on reactive oxygen species [87]. Caffeic acid found in modest quantities in coffee but abundant in other plant species has also been found to protect against liver injury in animal models [88]. Cooked vegetables are also known to produce hepatoprotective effects—for example, black garlic, a slow-cooked product of Allium sativum, which undergoes Maillard reaction. Its active compounds are allyl sulfides, allyl cysteines, fructosyl aminoacids, allixin, selenium, and tetrahydro-beta-carbolines; it provides suppression of lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage [89]. Opuntia ficus indica (tuna), an edible cactus fruit, has shown not only to be beneficial in reducing the negative effects of ethanol consumption withdrawal [90], but also hepatoprotective by reducing free-radical chain reactions [91]. The active ingredients of Optunia are vitamin C and E, polyphenols, carotenoids, flavonoids such as kaempherol, quercetin, and isorhamnetin, taurine, and betalains: betacyanin and betaxanthine [92,93,94].
Characterised Plant Bioactive Compounds
Carotenoids have been shown to mitigate alcohol toxicity, and a well characterized example is astaxanthin, which is extracted as a rich complex from green algae Haematococcus pluvialis [95]. Astaxanthin has been found to inhibit acetaldehyde-induced cytotoxicity [96], and to protect maternal ethanol induced embryonic deficiency [97]. Astaxanthin is an antioxidant and its action mechanisms are upon oxidative stress maintaining the redox balance and modulating apoptotic and survival signals [97]. Other sources of astaxanthin are flowers of Tagetes erecta, yeasts Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous, and shrimp.
Flavonoids such as rutin, hesperidin, and hesperidin–methyl–chalcone from citrus fruits have also been used to mitigate alcohol damage in combination with vitamins and antioxidants [98]. One well studied flavonoid from herbal medicine that has proven effectivity against ethanol toxicity is dihydromyricetin extracted from Hovenia dulcis. One of its main actions is aiding prior to ethanol binding to GABA receptors directly in the central nervous system and brain, thus counteracting not only intoxication but chronic dependence [99].
Sesamin, a lignan obtained from sesame seeds has been shown to have multiple alcohol protective effects—for example by inducing activity of microsomal ethanol oxidizing system enzymes, acting within hours of consumption [100]. Furthermore, sesamin has shown to be transformed by the liver into catechol metabolites, which are very effective oxygen free radical scavengers with ethanol hepatoprotective effects [101].
Silybum marianum extracts contain the active ingredient Silymarin and it is used as a reference hepatoprotective substance for ethanol ingestion. Its action mechanism lies in the protection against hepatic lipid peroxidation usually carried out by reduced glutathione inhibited by ethanol consumption, and resulting in tumor necrotic factor production [102,103]. Silymarin has been found to also have a membrane stabilizing function [104], to reduce reactive oxygen species, and to aid in a clinically proven reduction of liver transaminases in alcoholic liver disease patients [105].
Crocetin, a component of fruits of Gardenia jaminoides Ellis used in traditional medicine has been studied and proven to quench superoxide anion free radicals, protecting against oxidative damage [106].
Magnolol and honokiol are active compounds from bark of Magnolia officinalis, used against hangovers [54], have also proven to be effective neuroprotective agents with anti-oxidative against excitatory amino acids in neurons [107]. Picrorhiza kurroa (kutaki) active ingredients picroside I and II have shown not only peroxide scavenging activities, but also hepatoprotective effects in clinical trials [108]. Rubiadin from Rubia cordifolia Linn. has shown to have hepatoprotective effects by reduction and restoration of transaminases in liver cells [109]. Apigenin and alpha-bisabolol from chamomile Matricaria recutita and have been shown to inhibit the development of gastric ulcers induced by alcohol in animal models [110]. Dioscin is a natural steroid saponin found in several plant species, particularly in rhizomes of Tamus communis and Dioscorea communis and has been found to ameliorate ethanol-induced oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, and inflammatory cytokine production [111].
4.3. Fungi, Bacterial, and Animal Extracts
Enriched yeast and bacteria extracts have also shown to be beneficial against the effects of alcohol toxicity. For example, Bacillus subtilis natto fermented vegetable broth also known as Biozyme has been shown to have alleviation effects, reducing alcohol blood concentration in humans, and decreasing acetaldehyde toxicity in mice [112]. Glutathione enriched yeast and rice embryo extracts, which have been found to be useful in preventing alcohol toxicity by directly influencing the expression of ADH and ALDH [113], also by eliminating free radicals and lipid accumulation in fatty liver [113]. A glutathione precursor, S-adenosyl-l-methionine, and vitamin E analogs have also shown to attenuate liver damage [24]. Phycocyanobilin, an abundant compound in spirulina, the biomass of cyanobacteria, has been shown to inhibit certain NADPH oxidase complexes and is seen as having the potential for ameliorating alcohol toxicity [114].
Certain types of propolis (cuban red propolis, brazilian red propolis) have shown protection against alcohol induced liver injury and reduced activity of acetyl transferases [115,116]. The composition of propolis varies by region; the main constituents come from the propolis coloration: flavonoids, chalcones and terpenoids such as acacetin, apigenin, quercetin, naringenin, or pinobanksin [117].
Oil extracts from krill, a small crustacean, have been found to increase alcohol metabolism and provide protective effects; their main components are phospholipids, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid [118]. Similar effects were found from these components in fish oil [119].
Recombinant human cytoglobin expressed in E. coli has been specifically designed for protective effects against chronic alcohol liver injury. The mechanisms of cytoglobin involve blockage of oxygen free radicals, reactive oxygen and nitrous species, as well as inflammatory cytokines [120].
4.4. Synthetic Drugs and Other Chemicals
There are chemical formulations that focus on specific deficiencies contributing to sub-optimal alcohol metabolism. For example, ingestion of minerals such as selenium, zinc, copper, vanadium, iron, and magnesium are suspected to influence the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory system [121]. Soft carbonated drinks, particularly weak alkali soda drinks containing sodium citrate, flavour additives and sugar have shown increased activities of ALDH and ADH [122]. Taurine, which is also added to such drinks, has demonstrated such ethanol detoxification activities [123]. Other ingestible substances or nutraceuticals, such as taurine, have shown potential for ameliorating toxic effects of alcohol—for example, pantethine, and lipoic acid, which may boost activity of mitochondrial ALDH-2 [114]. Supplements such as pyritinol and vitamin B6 have been shown to be effective in reducing hangover symptoms, due to their action on the aldehyde metabolization [124].
Other drugs have been found to act directly on ethanol toxicity pathways. For example, tolfenamic acid, an inhibitor of prostaglandin activity and biosynthesis, has been shown to reduce effects of alcohol intoxication [47]. Rosiglitazone is a synthetic drug, initially targeting diabetes and then withdrawn due to adverse effects, which has proven to induce ALDH2 expression and alleviate symptoms of ethanol hangover in animal models [125]. Trolox or 4-methylpyrazole has shown mitigation of ethanol apoptosis by specifically inhibiting CYP2E1 in cell-line models [24]. Other formulations have been designed to lower causes of intoxication by targeting a multitude of symptoms. For example, formulations containing aspirin or acetaminophen as analgesics, dextrose as quick energy source, caffeine as stimulant, and magnesium trisilicate, and calcium carbonate to prevent acidity have proven effective [126]. A formulation including a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, naproxen sodium, and antihistamines loratadine, cetrizine, ranitidine or famotidine has been proposed to reduce alcohol induced inflammatory responses, and used in addition with B complex vitamins and magnesium salts (citrate, aspartate, hydroxide) [127]. Mesna (sodium 2-mercaptoethane sulfonate) and dimesna or (disodium 2,2-dithio bis-ethane sulfonate) have also shown to mitigate cytotoxic effects in other cases and are proposed for hangover mitigation [128]. Other formulations include vitamins from the B complex, aminoacids, and glycerophospholipid extracts from lecithin [129]. Sucralfate is a drug used in the treatment of gastric ulcers. It has also been shown to repair alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury after 6 h of treatment in mice action from 15 min to 24 h of alcohol ingestion [130].
Formulations that help with chronic damage are, for example, bicyclol, an anti-hepatitis drug with anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties, which has proven effective against alcohol liver injury in mice inhibiting reactive oxygen species [131]. Artemisinin is a semi-synthetic drug produced from extracts of Artemisia annua and has shown to be protective against liver damage and chronic alcohol poisoning. It acts against the activation of necrotic factor and the expression of inflammatory cytokines [132]. Diallyl sulfide is a chemical compound, which, despite being synthesized, is commonly obtained from Allium sp plants, and has been shown to reduce damage to adipose tissue in ethanol induced oxidative stress in mice, also reducing proinflammatory and lipogenic gene expression levels [133]. Carnitine esters propionyl l-carnitine and acetyl l-carnitine have been proven to be protective against alcohol-induced gastric lesions in rats by an increased gastric content of reduced glutathione and a decrease in the ulceration of the mucosa, partly through antioxidant mechanisms [134].
4.5. Complex Formulations
Combination of herbal extracts and prescription drugs have also shown efficacy against alcohol intoxication. For instance, Salvia miltiorrhiza extract combined with Naloxene have shown effectiveness over acute alcoholism and rapid consciousness recovery [135]. Zinc combined with plant extracts has also been shown to have an effect on alcohol toxicity at the stomach level [52]. Liver disease is associated with a decrease in zinc and its binding protein metallothionein, supplementation of Zn prevents intestinal damage, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) production in the liver [136]. Other formulations include aminoacids and antioxidants such as L-glutamine, L-cysteine, fumaric acid, succinic acid, vitamin B12, Vitamin B1 and young barley grass juice powder [137]; such complex formulations have proven to have some effect in alleviating toxicity at least on a symptomatic level [138].
Plant and fungi extracts that have been shown to help with alcohol degradation and toxicity include Viscum album L., Inonotus obliquus and Acanthopanax senticosus H. [139]. The main compounds extracted from these formulations that could be responsible for the protective actions are viscotoxins, flavonoids, triterpene acids, mistletoe lectins, melanins (lanoline alkane triterpenes), polyphenols, lignans, and coumarins, syringic acid, chlorogenic acid, eleutheroside, syringaresinol-di-glucoside, and isofraxidin [140,141,142,143]. The same composition in combination with Lycium chinense L., has also shown alcohol degradation, protection of the gastric mucous membrane, and reduction in nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor production [139]. Rutin, chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid, and citric acid are its main extractions [144].
Enzyme-rich extracts have also shown to be beneficial—for example from soybeans with microbial synthesized alcohol dehydrogenase. These formulations are enriched with amylase, lipase, proteases and antioxidants, and have proven to reduce, not only ethanol concentrations, but also acetaldehyde by increasing aldehyde dehydrogenase in humans [145,146]. Enzymes have also been used in pure form bundled and encapsulated in polymers to exclusively target alcohol blood content. For example alcohol oxidase and catalase in nanocapsules have been proven effective with digesting ethanol in mouse [147].
Many more substances and mechanisms or mitigating alcohol toxicity are yet to be discovered. The literature provides clues on where to explore, and how to identify novel formulations. For example, even in non-clinical fields, electrolyzed reduced water (containing molecular hydrogen and Pt nanoparticles) has shown to increase lifespan of nematodes by scavenging ROS [148]. Its potential for alcohol toxicity is possible, and reactive oxygen species are the major damaging agents in the human body.
5. Key Substances and Key Blockage Points for Mitigation
It is important to understand the effects over alcohol tolerance and toxicity, in the short and long term, to learn how to tackle them, find alleviation of the symptoms, and design toxicity prevention strategies. In order to make a comprehensive list of the available compounds in the current literature, we have categorized the different levels of action for such compounds on the time evolution of alcohol toxicity from Figure 5b. It is important to note that we are seeking to categorize substances that mitigate or prevent alcohol toxicity. Nevertheless, we also include here those that are used to treat the symptoms. Using Figure 5b as a guide, we have classified our findings by toxicity mitigation level based on the stages of the alcohol toxicity evolution over time in Table 1. References for each substance and main findings are discussed in the sections above; where main components of the tested formulations were not reported, they were sourced from other references. Most studies relating to toxicity at the cellular level (in human or animal models) are only relevant for chronic toxicity (Stage IV); they are setup to ‘cure’ the conditions and prevent further damage. Although we are focusing on prevention, we include them here for completion.

Table 1.
Active components for the mitigation of alcohol toxicity evolution.
The summary presented in the table above shows substances grouped on a time evolution basis related to which process of the intoxication they may help or intervene. As it can be noticed, some substances act specifically on certain organs. The literature tends to focus on liver damage as most of the alcohol by-products are processed there and animal models exist for reference. Another classification of said substances worth studying is their incidence on different organs. Focusing on liver damage when studying mitigation of alcohol toxicity, which tends to correspond to chronic damage, yielded abundant substances that could help with chronic damage mitigation. However, the provision of medicine is changing from focusing on the already present effects towards a more preventive approach. We hope this review contributes and encourages future research with preventive scope.
Most of the substances identified regardless of the mitigation level belong to certain chemical families, antioxidants, flavonoids, terpenoids, and vitamins, amongst the frequently identified or named. Most of these chemicals are known to provide support human metabolism and were usually identified in combination with others for toxicity mitigation. Most of these compounds are important for oxidative balance, which governs most enzymatic reactions in the metabolism.
Timely Mitigation and Preventive Formulations
Even though alcohol toxicity mitigation compounds may exist, the level of alcohol ingestion will always determine the effects of its damage. Moderate alcohol consumption to the level of drunkenness (levels I and II) cannot usually be avoided by individuals; therefore, the last resort for timely mitigation is the transition from drunkenness to withdrawal (levels II and III). As drunkenness itself may consist of different stages varying in intensity (Figure 4), mitigation at level II seems to be of more importance. Substances that fall into II and more categories will be discussed here. Particularly those substances that have been found preventive or mitigative in chronic damage (level IV), suggesting that some may be more effective than others in the long and short term. Some of the substances and formulations from Table 1 are commonly used in practice, or represent commercial formulations used with the sole purpose of alleviating symptoms of toxicity. Aiming towards a more preventive approach, it is necessary to identify those compounds which in combination or isolation could bring this preventive benefit at different levels.
Substances at mitigation levels II and III are: flavonoids, antioxidants, triterpenes, flavones, organic acids, saccharide conjugates, vegetable oils, and phospholipids. Most notably: artemisin, capillarisin, puerarin, hoventins, laricetrin, coptisine, baicalin, palmatine, berberine, wogonoside, cinnamic acid, alisol A, atractyloside III, dihydromyricetin, magnolol, honokiol, apigenin, vitamin E, astaxanthin, and rutin.
Substances at mitigation levels II or III and others include also: isoflavonoids, isoflavones, amino acids, polyphenols, chalcones, complex carbohydrates, small proteins, and minerals—among which are: viscotoxins, lectins, melanins, lignans, coumarin, chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid, syringic acid, syringaresinol glucoside, isofraxidin, sesamin, apigenin, rhamnose, arabinose, galactose, galacturonic acid, vitamin C, kaempferol, quercetin, magnesium, allyl sulfides, hydroxycitric acid lactone, taraxinic acid, inulin, cycloartenol, eudesmanolides, tetrahydroridentin, guaianolides, dihydrolactucin, ixerin, glucopyranoside, and citric acid.
Compounds from these lists commonly used in commercial formulations for hangover relief and prevention are dihydromyricetin and taurine. However, there are several others identified that could bring potential benefits, particularly those with research completed in humans—for instance, coptisine, baicalin, palmatine, berberine, wogonoside, vitamin C, kaempferol, quercetin, and apigenin.
The source of the compounds may also allow for further classification, which could allow an easy path for testing in humans. Such classification can be into natural extracts, synthetic, bio-active characterized, etc. In addition, the type of extraction and availability of the source for extraction can determine further classification. This is important in order to design a timely mitigation and the delivery method for the compounds, therefore, their compatibility as active substances (i.e., ethanolic, extract, oil, water extract, etc.). Those classifications escape the scope of this review; nevertheless, for envisioning a preventive formulation on which one or several compounds are present, the following must be considered:
Origin: plants, bacteria, fungi, animal, synthetic; extraction type: for compatibility in mixed formulation preparations (oil, water, ethanolic); ingestion: from source, from extracts, synthetic pharmaceutical or nutraceutical.
As most of these substances have demonstrated intervention in alcohol metabolism during, or immediately after, a drinking episode, it becomes feasible to suggest ingesting them before, or simultaneously with, alcohol consumption in order to observe prevent or ameliorate toxic effects. Little evidence exists on the literature for the preventive capabilities of the compounds listed in this review and further research efforts must be directed towards evaluating preventive strategies. Even though we aimed at categorising which of these compounds are more effective for a particular level of alcohol intoxication, it is impossible to fully prevent or mitigate toxicity effects by only the compounds in isolation, further research is required to establish the long-term prevention and mitigation from the clinical point of view.
6. Conclusions
Section 1 showed us that alcohol consumption varies over time and across regions. The market demands for alcohol have stayed constant in some countries and been driven forward in others. However, the susceptibility map of Figure 3 allows us to conclude that alcohol intoxication greatly affects certain regions on which drinking alcohol has turned to unprecedented levels. In some other regions, alcohol drinking is a cultural component, but smarter societies may demand smarter drinking strategies to avoid deleterious damage. Alcohol drinking is associated with a feeling of joy (level I), followed by moderate intoxication (level II) and unfortunately by damaging intoxication (level III, IV). Alcohol consumption is expected to remain as a key socialising habit across all different cultures, but society will start demanding a reduction to the damage created to our own bodies by permanent intoxication. Alcohol related diseases are a cost burden for the healthcare system. Even though some preventive strategies may result in being challenging to implement during drinking episodes (moderate exercise, constant hydration), others are fairly well accepted (accompany drinks with food, ingest electrolyte solutions and sugary drinks). We envision and recommend looking at the current scientific evidence to design and study not only mitigation, but also preventive effects of naturally occurring molecules. Alcohol is introduced in excess in an individual diet. By introducing preventive compounds into the drinking habits, it may be possible to counteract its toxic effects and protect the unbalanced metabolism. However, the authors do not recommend that these mitigation agents should be used while being unsupervised by consumers. Mitigation of the effects of alcohol are presented that could be used for further study, as some of these compounds may also have toxic effects when used incorrectly.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2306-5710/4/2/39/s1. Figure S1. Alcohol expenditure as percentage of total household expenditure (%); Figure S2. Household expenditure in alcoholic drinks per capita ($US dollars); Figure S3. Per capita consumption of alcohol (in L of pure alcohol); Figure S4. Five-year growth of alcohol consumption per capita (%, 2010–2015); Figure S5. Alcohol attributable deaths as percentage of total deaths (%); Figure S6. Alcohol use disorders prevalence percentage per year in adult population (%); Figure S7. Suceptibility map expected alcohol related deaths change per year.
Author Contributions
J.L.M.N. wrote the manuscript; B.C.F. edited the manuscript; J.V.P. edited the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Amy Shang for her input and discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Teaford, M.F.; Ungar, P.S. Diet and the evolution of the earliest human ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13506–13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R. Alcohol: A History; UNC Press Books: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McGovern, P.E. Uncorking the Past: The Quest for Wine, Beer, and Other Alcoholic Beverages; Univ of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McGovern, P.E.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hall, G.R.; Moreau, R.A.; Nuñez, A.; Butrym, E.D.; Richards, M.P.; Wang, C.S.; et al. Fermented beverages of pre-and proto-historic China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17593–17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, R.J. A Short History of the Art of Distillation: From the Beginnings up to the Death of Cellier Blumenthal; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, H.; Franz, M.; Heberlein, U. The hangover gene defines a stress pathway required for ethanol tolerance development. Nature 2005, 436, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomasson, H.R.; Crabb, D.W.; Edenberg, H.J.; Li, T.K. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase polymorphisms and alcoholism. Behav. Genet. 1993, 23, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhari, S. Overview: How is alcohol metabolized by the body? Alcoh. Res. Health 2006, 29, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, L.J.; Li, T.K. Alcohol metabolism in American Indians and whites: Lack of racial differences in metabolic rate and liver alcohol dehydrogenase. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 294, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopun, M.; Propping, P. The kinetics of ethanol absorption and elimination in twins and supplementary repetitive experiments in singleton subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1977, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabb, D.W.; Edenberg, H.J.; Bosron, W.F.; Li, T.K. Genotypes for aldehyde dehydrogenase deficiency and alcohol sensitivity. The inactive ALDH2 (2) allele is dominant. J. Clin.l Investig. 1989, 83, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borinskaya, S.; Gasemianrodsari, F.; Kalyina, N.; Sokolova, M.; Yankovsky, N. Polymorphism of alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH1B in Eastern Slavic and Iranian-speaking populations. Russ. J. Genet. 2005, 41, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, J.B.; Stockley, C. The Biology of Intoxication. In Expressions of Drunkenness (Four Hundred Rabbits); Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2011; pp. 31–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sleet, D.A.; Mercer, S.L.; Hopkins Cole, K.; Shults, R.A.; Elder, R.W.; Nichols, J.L. Scientific evidence and policy change: Lowering the legal blood alcohol limit for drivers to 0.08% in the USA. Glob. Health Promot. 2011, 18, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubowski, K.M. Stages of Acute Alcoholic Influence/intoxication; The University of Oklahoma, Department of Medicine: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.; Munoz, R. How to Control Your Drinking: A Practical Guide to Responsible Drinking, Revised Edition; University of New Mexico Press: Albuquerque, New Mexico, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hunt, W.A. The Drunken Synapse: Studies of Alcohol-Related Disorders; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, R.; Davidson, D. Alcohol hangover. Alcohol. Health Res. World 1998, 22, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Surawicz, B. Relationship between electrocardiogram and electrolytes. Am. Heart J. 1967, 73, 814–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieloch, T. Hypoglycemia-induced neuronal damage prevented by an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Science 1985, 230, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauvin, D.V.; Briscoe, R.J.; Baird, T.J.; Vallett, M.; Carl, K.L.; Holloway, F.A. Cross-generalization of an EtOH "hangover" cue to endogenously and exogenously induced stimuli. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 57, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Becker, P. Alcohol metabolism and cancer risk. Alcohol. Res. Health 2007, 30, 38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Cederbaum, A.I. Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis to Stable HepG2 Cell Lines Expressing Human Cytochrome P-4502E1. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteel, G.E.; Raleigh, J.A.; Bradford, B.U.; Thurman, R.G. Acute alcohol produces hypoxia directly in rat liver tissue in vivo: Role of Kupffer cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, G494–G500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordone, L.; Guarente, L. Calorie restriction, SIRT1 and metabolism: Understanding longevity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, L.E. Molecular aspects of alcohol metabolism: Transcription factors involved in early ethanol-induced liver injury. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2004, 24, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleich, S.; Degner, D.; Sperling, W.; Bönsch, D.; Thürauf, N.; Kornhuber, J. Homocysteine as a neurotoxin in chronic alcoholism. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 28, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, G.I.; Chen, J.; Schenker, S. Ethanol, oxidative stress, reactive aldehydes, and the fetus. Front. Biosci. 1999, 4, D541–D550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Kerem, R.; Koren, G. Antioxidants and fetal protection against ethanol teratogenicity: I. Review of the experimental data and implications to humans. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2003, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Stickel, F.; Homann, N. Pathogenetic mechanisms of upper aerodigestive tract cancer in alcoholics. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickel, F.; Schuppan, D.; Hahn, E.; Seitz, H. Cocarcinogenic effects of alcohol in hepatocarcinogenesis. Gut 2002, 51, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñiz-Hernández, S.; Velázquez-Fernández, J.; Díaz-Chávez, J.; López-Sánchez, R.; Hernández, J. Alcoholism: Common and oxidative damage biomarkers. J. Clin. Toxicol. S 2014, 7, S7-006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sean, O. A Unified Theory of Optimal Booze Drinking. Journapocalypse 2011, 32, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, M.S.; Ali, N.; Ali, Z.E.S. Interaction between alcohol and exercise. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, D.J. Alcohol alternatives–a goal for psychopharmacology? J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 20, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penetar, D.M.; Toto, L.H.; Lee, D.Y.W.; Lukas, S.E. A single dose of kudzu extract reduces alcohol consumption in a binge drinking paradigm. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2015, 153, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carai, M.A.; Agabio, R.; Bombardelli, E.; Bourov, I.; Gessa, G.L.; Lobina, C.; Morazzoni, P.; Pani, M.; Reali, R.; Vacca, G.; et al. Potential use of medicinal plants in the treatment of alcoholism. Fitoterapia 2000, 71, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, A.H.; Overstreet, D.H.; Perfumi, M.; Massi, M. Plant derivatives in the treatment of alcohol dependency. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, S.E.; Penetar, D.; Berko, J.; Vicens, L.; Palmer, C.; Mallya, G.; Macklin, E.A.; Lee, D.Y.W. An extract of the Chinese herbal root kudzu reduces alcohol drinking by heavy drinkers in a naturalistic setting. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.C.; Li, T.K. Effects of isoflavones on alcohol pharmacokinetics and alcohol-drinking behavior in rats. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1512S–1515S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, N.R. Pueraria lobata (Kudzu root) hangover remedies and acetaldehyde-associated neoplasm risk. Alcohol 2007, 41, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.S.; Hong, S.G.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, B.N.; Sung, H.J. Effect of an Oriental Herbal Composition, Jang Baek Union (JBU), on Alcohol-Induced Hangover and CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Rats. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 33, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, L.F. Experimental induction of hangover. Q. J. Stud. Alcohol. Suppl. 1970, 5, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Pawan, G. Alcoholic drinks and hangover effects. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1973, 32, 15A. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seppälä, T.; Leino, T.; Linnoila, M.; Huttunen, M.; YIikahri, R. Effects of hangover on psychomotor skills related to driving: Modification by fructose and glucose. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1976, 38, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaivola, S.; Parantainen, J.; Österman, T.; Timonen, H. Hangover headache and prostaglandins: Prophylactic treatment with tolfenamic acid. Cephalalgia 1983, 3, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pautasso, M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Collins, A.M.; Coughlin, D.; Kirk, S. The role of Google Scholar in evidence reviews and its applicability to grey literature searching. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Jeon, G.; Lee, J.W.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.H. Red ginseng relieves the effects of alcohol consumption and hangover symptoms in healthy men: A randomized crossover study. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, X. Preliminary characterization, antioxidant activity in vitro and hepatoprotective effect on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice of polysaccharides from the peduncles of Hovenia dulcis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2964–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxman, E. Hangover Relief Composition. U.S. Patent 7,037,532, 2 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, F.Y.; Lee, S.D.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lai, K.H.; Chao, Y.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, S.S.; Lo, K.J. A randomized controlled trial of quinidine in the treatment of cirrhotic patients with muscle cramps. J. Hepatol. 1991, 12, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Watanabe, K. Japanese Kampo Medicines for the Treatment of Common Diseases: Focus on Inflammation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haranaka, R.; Okada, N.; Kosoto, H.; Ohwada, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Kobayashi, M. Effects of Goreisan and Inchingoreisan on Alcohol Metabolism in Mice Liver. Jpn. J. Pharmacogn. 1984, 38, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, S.; Ojima, T.; Takayama, S.; Nakano, Y.; Nawa, D.; Saito, N.; Arita, R.; Kaneko, S.; Kamiya, T.; Mikami, N.; et al. Preliminary study of the effects of orengedokuto on breath alcohol concentration. Tradit. Kampo Med. 2016, 3, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, H.; Miyamoto, K. Effects of Oren-gedoku-to and its constituents on the cardiovascular system: Investigation of its efficacy in hotflush. J. Tradit. Med. 2002, 19, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, K.; Iijima, K.; Nohmi, M.; Nakayama, S.; Oguchi, K. Effects of Byakushi and Ogon on the hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes in rats. Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 1994, 104, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, T.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Fang, K.; Wu, G.; Yan, M.; Xue, N.; Chen, M.; Xie, T.; et al. Origin and Formation Mechanism Investigation of Compound Precipitation from the Traditional Chinese Prescription Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Molecules 2017, 22, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, J.I.; Motoo, Y.; Moriya, J.; Ogawa, M.; Uenishi, H.; Akazawa, S.; Sasagawa, T.; Nishio, M.; Kobayashi, J. Significance of Kampo, traditional Japanese medicine, in supportive care of cancer patients. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, V.; Ashar, H.; Srinath, S. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of Garcinia indica fruit rind in ethanolinduced hepatic damage in rodents. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2012, 5, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhye, S.; Ahmad, A.; Oswal, N.; Sarkar, F.H. Emerging role of Garcinol, the antioxidant chalcone from Garcinia indica Choisy and its synthetic analogs. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, R.; Rajendra Prasad, N.; Pugalendi, K. Effect of Piper beetle leaf extract on alcoholic toxicity in the rat brain. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimando, A.M.; Han, B.H.; Park, J.H.; Cantoria, M.C. Studies on the constituents of PhilippinePiper beetle leaves. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1986, 9, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, L.W.; Salleh, E.; Mamat, S.N.H. Extraction and qualitative analysis of piper betle leaves for antimicrobial Activities. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, N.E.; Ro, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Cho, H.J. Effects of Cudrania tricuspidata Root Extract (CTE) on Ethanol-Induced Hangover via Modulating Alcohol Metabolizing Enzyme Activities and Blood Gas Levels in Rats. J. Korea Acad.-Ind. 2017, 18, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- An, R.B.; Sohn, D.H.; Kim, Y.C. Hepatoprotective compounds of the roots of Cudrania tricuspidata on tacrine-induced cytotoxicity in Hep G2 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.; Khaja, M.N.; Aara, A.; Khan, A.A.; Habeeb, M.A.; Devi, Y.P.; Narasu, M.L.; Habibullah, C.M. Hepatoprotective activity of Sapindus mukorossi and Rheum emodi extracts: In vitro and in vivo studies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.; Arya, V.; Yadav, S.; Panghal, M.; Kumar, S.; Dhankhar, S. Cassia occidentalis L.: A review on its ethnobotany, phytochemical and pharmacological profile. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, M.; Subhani, M.J.; Javed, K.; Singh, S. Hepatoprotective activity of leaves of Cassia occidentalis against paracetamol and ethyl alcohol intoxication in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanhers, M.C.; Joyeux, M.; Soulimani, R.; Fleurentin, J.; Sayag, M.; Mortier, F.; Younos, C.; Pelt, J.M. Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of a traditional medicinal plant of Chile, Peumus boldus. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramyothin, P.; Ngamtin, C.; Poungshompoo, S.; Chaichantipyuth, C. Hepatoprotective activity of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. et. Thonn. extract in ethanol treated rats: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviarasan, S.; Ramamurty, N.; Gunasekaran, P.; Varalakshmi, E.; Anuradha, C.V. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seed extract prevents ethanol-induced toxicity and apoptosis in Chang liver cells. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006, 41, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirunavukkarasu, V.; Anuradha, C.; Viswanathan, P. Protective effect of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seeds in experimental ethanol toxicity. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benayad, Z.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Es-Safi, N.E. Characterization of flavonoid glycosides from fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) crude seeds by HPLC–DAD–ESI/MS analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20668–20685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, J.; Bernd, A.; Sempere, J.; Dıaz-Alperi, J.; Ramırez, A. The curcuma antioxidants: Pharmacological effects and prospects for future clinical use. A review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2002, 34, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeba, M.; Asha, V. Effect of Cardiospermum halicacabum on ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Yoo, S.; Yoon, H.G.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Oh, K.T.; Lee, J.; Cho, H.Y.; Jun, W. In vitro and in vivo hepatoprotective effects of the aqueous extract from Taraxacum officinale (dandelion) root against alcohol-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, N.; Mora, C.; Muñoz, K.; Díaz, J.; Serna, R.; Castro, D.; Osorio, E. Microscopical descriptions and chemical analysis by HPTLC of Taraxacum officinale in comparison to Hypochaeris radicata: A solution for mis-identification. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, P.; Venkataraman, S. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Hygrophila auriculata (K. Schum) Heine Acanthaceae root extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, A.; Ingale, K.; Vyawahare, N.; Thorve, V. Hygrophila spinosa: A comprehensive review. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.S.; Chung, Y.H.; Chung, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Song, E.H.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.C.; Nam, Y.; Yeong, J.H. Clinical effect of a polysaccharide-rich extract of Acanthopanax senticosus on alcohol hangover. Die Pharm. 2015, 70, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ashmawy, I.M.; Saleh, A.; Salama, O.M. Effects of marjoram volatile oil and grape seed extract on ethanol toxicity in male rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 101, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, A.; Celik, I. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of grapeseeds against ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katalinic, V.; Mozina, S.S.; Generalic, I.; Skroza, D.; Ljubenkov, I.; Klancnik, A. Phenolic profile, antioxidant capacity, and antimicrobial activity of leaf extracts from six Vitis vinifera L. varieties. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, M.; Lazarte, K.; Arnao, I. Hepatoprotección Antioxidante de la Cáscara y Semilla de Vitis vinifera L.(uva); Anales de la Facultad de Medicina; UNMSM, Facultad de Medicina: Lima, Peru, 2008; Volume 69, pp. 250–259. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Teoh, N.C.; Chitturi, S.; Farrell, G.C. Coffee and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Brewing evidence for hepatoprotection? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pari, L.; Karthikesan, K. Protective role of caffeic acid against alcohol-induced biochemical changes in rats. Fund. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 21, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Son, C.W.; Cheong, S.H.; Kim, M.R. Effect of black garlic on acute alcohol-induced hangover and chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wiese, J.; McPherson, S.; Odden, M.C.; Shlipak, M.G. Effect of Opuntia ficus indica on symptoms of the alcohol hangover. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimi, H.; Hfaeidh, N.; Mbarki, S.; Bouoni, Z.; Sakly, M.; Ben, R.K. Evaluation of Opuntia ficus indica f. inermis fruit juice hepatoprotective effect upon ethanol toxicity in rats. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2012, 31, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal-Santillán, E.; García-Melo, F.; Morales-González, J.A.; Vázquez-Alvarado, P.; Muñoz-Juárez, S.; Zuñiga-Pérez, C.; Sumaya-Martínez, M.T.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E.; Hernández-Ceruelos, A. Antioxidant and anticlastogenic capacity of prickly pear juice. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4145–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, J.A.; Almela, L.; Obón, J.M.; Castellar, R. Determination of antioxidant constituents in cactus pear fruits. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuti, J.O. Antioxidant compounds from four Opuntia cactus pear fruit varieties. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, E.A.; Yoo, G.J.; Yoo, J.M.; Son, S.M.; In, M.J.; Kim, D.C.; Chae, H.J. Physiological activity of astaxanthin and its inclusion complex with cyclodextrin. KSBB J. 2009, 24, 570–578. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X. Astaxanthin Inhibits Acetaldehyde-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells by Modulating Akt/CREB and p38MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.; Yin, D.; Peng, Y. The protective effect of astaxanthin on fetal alcohol spectrum disorder in mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 84, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldowan, M.J.; Moldowan, C. Composition and Method for Reducing Hangover. U.S. Patent 4,496,548, 29 January 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Lindemeyer, A.K.; Gonzalez, C.; Shao, X.M.; Spigelman, I.; Olsen, R.W.; Liang, J. Dihydromyricetin as a novel anti-alcohol intoxication medication. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiso, Y.; Ishikawa, T. The Liver Protective Effect of Sesamin. In Novel Compounds from Natural Products in the New Millennium: Potential and Challenges; World Scientific Publisher: Singapore, 2004; p. 139. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, M.; Harada, M.; Nakahara, K.; Akimoto, K.; Shibata, H.; Miki, W.; Kiso, Y. Novel antioxidative metabolites in rat liver with ingested sesamin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, A.; Lagos, C.; Schmidt, K.; Videla, L.A. Silymarin protection against hepatic lipid peroxidation induced by acute ethanol intoxication in the rat. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 34, 2209–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Deaciuc, I.; Song, M.; Lee, D.Y.W.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; McClain, C. Silymarin Protects Against Acute Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönfeld, J.v.; Weisbrod, B.; Müller, M. Silibinin, a plant extract with antioxidant and membrane stabilizing properties, protects exocrine pancreas from cyclosporin A toxicity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saller, R.; Meier, R.; Brignoli, R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 2001, 61, 2035–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.H.; Chu, C.Y.; Huang, J.M.; Shiow, S.J.; Wang, C.J. Crocetin protects against oxidative damage in rat primary hepatocytes. Cancer Lett. 1995, 97, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.R.; Chen, H.H.; Ko, C.H.; Chan, M.H. Neuroprotective activity of honokiol and magnolol in cerebellar granule cell damage. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 537, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, A.; Antarkar, D.; Doshi, J.; Bhatt, A.; Ramesh, V.; Vora, P.; Perissond, D.; Baxi, A.; Kale, P. Picrorhiza kurroa (Kutaki) Royle ex Benth as a hepatoprotective agent—Experimental & clinical studies. J. Postgrad. Med. 1996, 42, 105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, G.M.M.; Rao, C.V.; Pushpangadan, P.; Shirwaikar, A. Hepatoprotective effects of rubiadin, a major constituent of Rubia cordifolia Linn. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, D.L.; Blumberg, J.B. A review of the bioactivity and potential health benefits of peppermint tea (Mentha piperita L.). Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Peng, J. Protective effects of dioscin against alcohol-induced liver injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, H.; Yatagai, C.; Wada, H.; Yoshida, E.; Maruyama, M. Effect of Bacillus natto-fermented product (BIOZYME) on blood alcohol, aldehyde concentrations after whisky drinking in human volunteers, and acute toxicity of acetaldehyde in mice. Jpn. J. Alcohol Stud. Drug Depend. 1995, 30, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Song, J.; Kim, T.M.; Joo, S.S.; Park, D.; Jeon, J.H.; Shin, S.; Park, H.K.; Lee, W.K.; Ly, S.Y.; et al. Effects of a preparation of combined glutathione-enriched yeast and rice embryo/soybean extracts on ethanol hangover. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, M.F. Nutraceutical strategies for ameliorating the toxic effects of alcohol. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 80, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Pillai, K.; Husain, S.; Giri, D.K. Protective role of propolis against alcohol carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 1997, 29, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, C.F.; Chung, C.Y.; Hsu, S.H. The hepatoprotective and therapeutic effects of propolis ethanol extract on chronic alcohol-induced liver injuries. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1997, 25, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucci, M.C. Propolis: Chemical composition, biological properties and therapeutic activity. Apidologie 1995, 26, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, J.; Tsuji, T.; Yanagimoto, K. Alcoholic Injury Mitigating Agent. U.S. Patent 9,061,035, 8 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ulven, S.M.; Kirkhus, B.; Lamglait, A.; Basu, S.; Elind, E.; Haider, T.; Berge, K.; Vik, H.; Pedersen, J.I. Metabolic effects of krill oil are essentially similar to those of fish oil but at lower dose of EPA and DHA, in healthy volunteers. Lipids 2011, 46, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhu, S.; Dong, W. Protective effects of recombinant human cytoglobin against chronic alcohol-induced liver disease in vivo and in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.A.; Lee, K.; Kim, D.J. The application of minerals in managing alcohol hangover: A preliminary review. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 2010, 3, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gan, L.Q.; Li, S.K.; Zheng, J.C.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Effects of herbal infusions, tea and carbonated beverages on alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, S.L.; Viswanathan, P.; Anuradha, C.V. Taurine enhances the metabolism and detoxification of ethanol and prevents hepatic fibrosis in rats treated with iron and alcohol. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 27, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Jensen, K.; Krogh, H. Alcohol-induced hangover: A double-blind comparison of pyritinol and placebo in preventing hangover symptoms. Q. J. Stud. Alcohol 1973, 34, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Shim, W.S.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, S.K.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, B.S. Rosiglitazone relieves acute ethanol-induced hangover in Sprague—Dawley rats. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006, 41, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimberg, B.J.; Kamath, B.L. Therapeutic Composition and Method of Using Same for Treatment of Hangover. U.S. Patent 5,296,241, 22 March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, M.M. Compositions and Methods for the Prevention and Treatment of Alcohol-Induced Hangover Syndrome. U.S. Patent 14,539,776, 14 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hausheer, F.H. Method of Treating Hangover. U.S. Patent 6,077,838, 20 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Halamicek, W.A., III. Compositions for Treating Alcohol Hangover. U.S. Patent 8,377,907, 19 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, D.; Tarnawski, A.; Krause, W.J.; Gergely, H. Protective effect of sucralfate against alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury in the rat: Macroscopic, histologic, ultrastructural, and functional time sequence analysis. Gastroenterology 1985, 88, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Protective effect of bicyclol on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 586, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Protective effect of artemisinin on chronic alcohol induced-liver damage in mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 52, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kema, V.H.; Khan, I.; Jamal, R.; Vishwakarma, S.K.; Lakki Reddy, C.; Parwani, K.; Patel, F.; Patel, D.; Khan, A.A.; Mandal, P. Protective effects of diallyl sulphide against ethanol-induced injury in rat adipose tissue and primary human adipocytes. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, H.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M. Protective role of carnitine esters against alcohol-induced gastric lesions in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Q.; Gao, J.J.; Ou, Y.X.; Zou, Y.G. Observation on therapeutic efficacy of composite Salvia miltiorrhiza injection and Naloxone in acute severe alcoholism. Pract. Clin. Med. 2001, 10, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J.; Zhou, Z. Zinc prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 2005, 26, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, P. Composition for Prevention or Treatment of an Alcohol Hangover. U.S. Patent 11,146,747, 8 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sreeraj, G.; George, R.; Thankachen, R.; Sriraam, V.; Shakthi, A.; et al. Studies on the effectiveness and safety of anti hangover drink (Oh! K) in reducing cocktail (alcohol) induced hangover symptoms in adult male social drinkers. Int. J. Herb. Med. 2014, 2, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, T.J.; Jo, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Shin, K.S.; Suh, H.J. Effect of herbal composition, DTS20 on alcohol degradation and anti-inflammatory activity. KSBB J. 2011, 26, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Miao, K.; Wei, Z. Accumulation of antioxidant phenolic constituents in submerged cultures of Inonotus obliquus. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twardziok, M.; Kleinsimon, S.; Rolff, J.; Jäger, S.; Eggert, A.; Seifert, G.; Delebinski, C.I. Multiple active compounds from Viscum album L. synergistically converge to promote apoptosis in Ewing sarcoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.h.; Ren, K.; Lu, S.j.; Yang, S.y.; Sun, D.z. Progress of research on Inonotus obliquus. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2009, 15, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Murai, R.; Kuribayashi, K.; Kobayashi, D.; Yanagihara, N.; Watanabe, N. Prophylactic and Therapeutic Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms Extract on Murine Collagen-induced Arthritis. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, A.G. The efficiency of flavonoids in polar extracts of Lycium chinense Mill fruits as free radical scavenger. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Bang, C.Y.; Choung, S.Y.; Choi, K. Oral Intake of Anti-Hangover Substance Increases Metabolizing Capacity of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 in Rat Model: New Therapeutic Potentials for Chronic Itch? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, AB254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, C.Y.; Kang, B.; Choung, S.Y.; Choi, K. Oral intake of anti-hangover substance increases aldehyde dehydrogenase activity: New preventive and therapeutic potentials for oxidative neuronal injury? Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 22, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Yan, M.; Lau, M.Y.; Hu, J.; Han, H.; Yang, O.O.; Liang, S.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Biomimetic enzyme nanocomplexes and their use as antidotes and preventive measures for alcohol intoxication. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Kinjo, T.; Tian, H.; Hamasaki, T.; Teruya, K.; Kabayama, S.; Shirahata, S. Mechanism of the lifespan extension of Caenorhabditis elegans by electrolyzed reduced water?participation of PT nanoparticles. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).