Effect of Additional Information on Consumer Acceptance: An Example with Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Panelists
2.2.3. Orientation and Evaluation
2.3. Consumer Research
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Consumers
2.3.3. Test Design and Evaluation
2.4. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) Determination
2.4.1. Samples
2.4.2. Experimental Determination
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Consumer Research
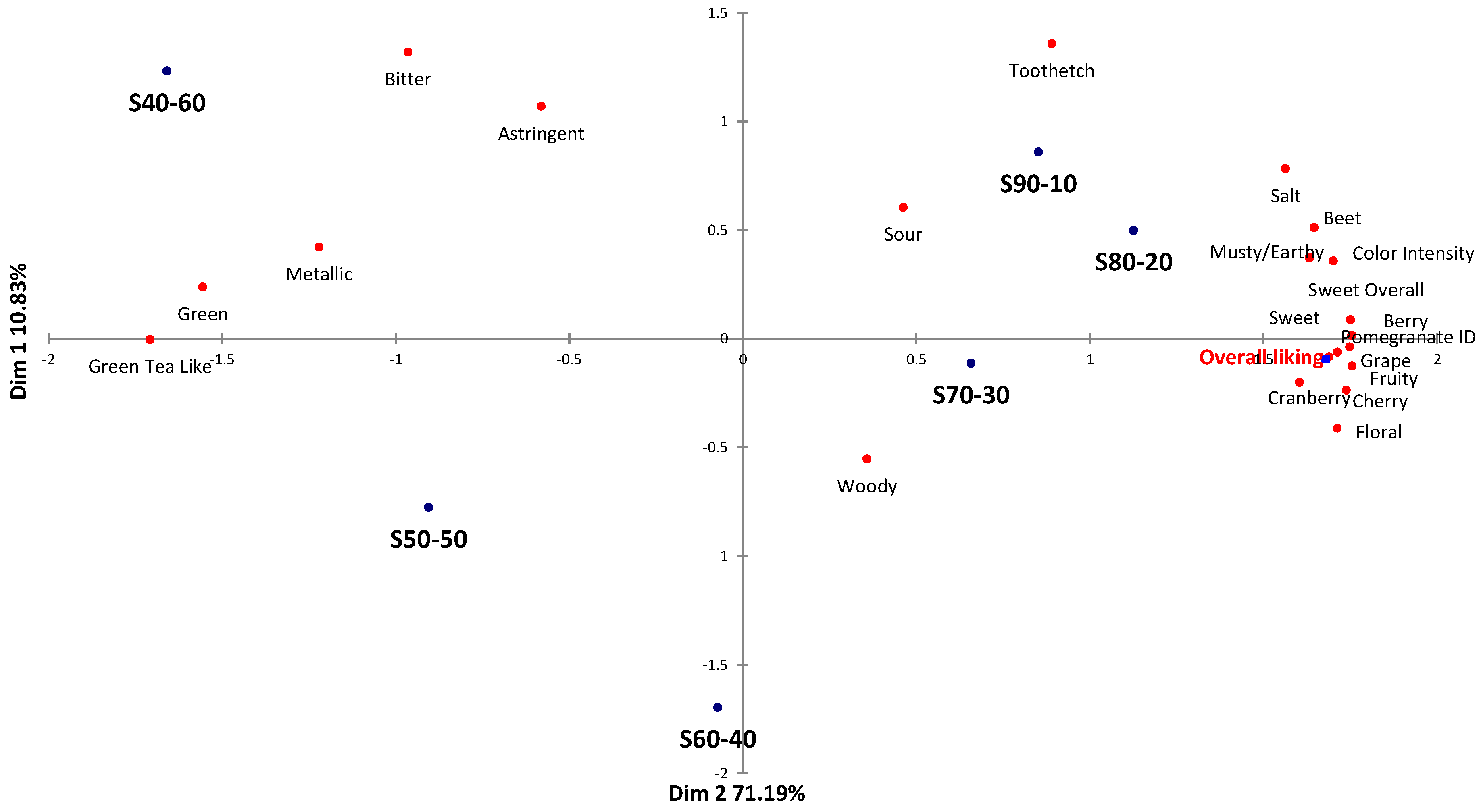
3.2.1. Preference Mapping
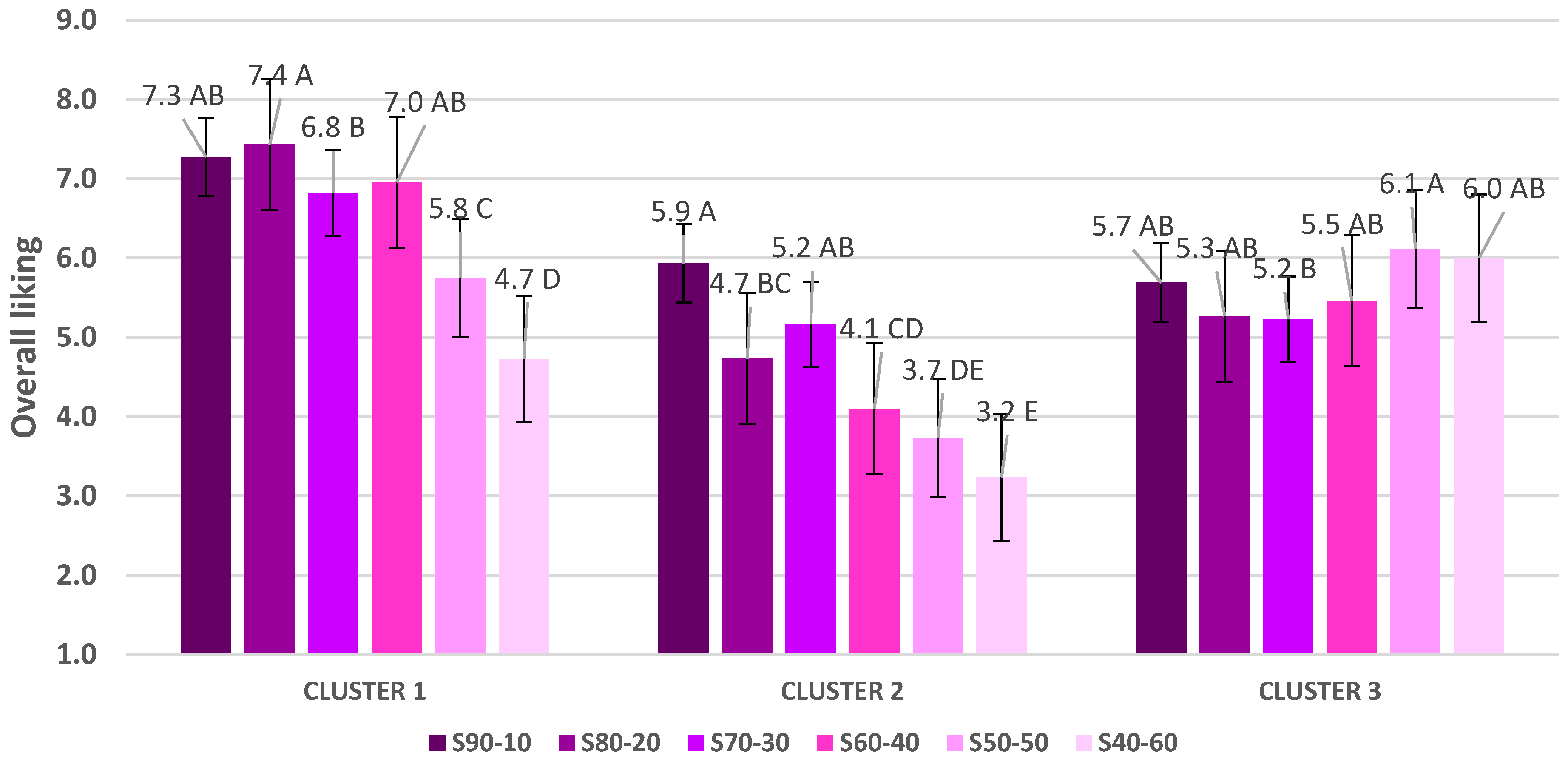
3.2.2. Cluster Analysis
3.3. Total Phenolic Content of Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seeram, N.P.; Aviram, M.; Zhang, G.Y.; Henning, S.; Feng, L.; Dreher, M.; Heber, D. Comparison of Antioxidant Potency of Commonly Consumed Polyphenol-Rich Beverages in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.D.; Mehta, A.R.; Yu, W.; Neeman, I.; Livne, Y.T.; Amichay, A.; Poirier, D.; Nicholls, P.; Kirby, A.; Jinag, W.; et al. Chemopreventive and adjuvant therapeutic potential of pomegranate (Punica Granatum) for human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2002, 71, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.N.; Lansky, E.P.; Varani, J. Pomegranate as a cosmeceutical source: Pomegranate fractions promote proliferation and procollagen synthesis and inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-1 production in human skin cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Siddiqui, R.; Ahmad, S.; Rasool, S.A.; Sayeed, S.A. Antibacterial Activity Directed Isolation of Compounds from Punica Granatum. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichayupakaranant, P.; Tewtrakul, S.; Yuenyongsawad, S. Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of standardized pomegranate rind extract. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, E. A Wonderful World: Pom Wonderful takes Pomegranates to places it has never gone before (cover story). Beverage Ind. 2008, 99, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. The U.S. consumers’ acceptability and emotion measures when consuming novel Korean traditional non-alcoholic beverages. J. Sens. Stud. 2016, 31, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, S.; Flint, S.W. The impact of menu label design on visual attention, food choice and recognition: An eye tracking study. J. Sens. Stud. 2016, 31, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, K.; Chambers, E., IV. Development and Application of a Lexicon to Describe the Flavor of Pomegranate Juice. J. Sens. Stud. 2010, 25, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chambers, D. A Lexicon for Flavor Descriptive Analysis of Green Tea. J. Sens. Stud. 2007, 22, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chambers, D.; Chambers, E., IV. A comparison of the flavor of green teas from around the world. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 94, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Chambers, D. Sensory descriptive evaluation: Brewing methods affect flavor of green tea. Asian J. Food Agro-Ind. 2009, 2, 427–439. [Google Scholar]
- Koppel, K.; Chambers, E., IV; Vazquez-Araujo, L.; Timberg, L.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Suwonsichon, S. Cross Country comparison of pomegranate juice acceptance in Estonia, Spain, Thailand, and United States. Food Qual. Preference 2014, 31, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.; Koppel, K.; Chambers, E., IV. Consumer Evaluation of Processing Variants of Pomegranate Juice. Beverages 2015, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A.; Calin-Sanchez, A.; Bagatar, B.; Hernandez, F.; Legua, P.; Martinez-Font, R.; Melgarejo, P. Potential of Spanish sour-sweet pomegranates (cultivar C25) for the juice industry. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2011, 18, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Chambers, D. Descriptive Analysis and U.S. Consumer Acceptability of 5 Green Tea Samples from China, Japan, and Korea. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Chambers, E., IV; Chambers, D.; Chun, S.S.; Oupadissakoon, G.; Johnson, D.E. Consumer acceptance for green tea by consumers in the United States, Korea and Thailand. J. Sens. Stud. 2010, 25, 109–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, L.J.R.; Threlfall, R.T.; Meullenet, J.F.; Howard, L.R. Applying a Mixture Design for Consumer Optimization of Black Cherry, Concord Grape and Pomegranate Juice Blends. J. Sens. Stud. 2013, 28, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales-Molina, E.; Moreno, D.A.; GarciaViguera, C. A new drink rich in healthy bioactives combining lemon and pomegranate juices. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Araujo, L.; Chambers, E., IV; Adhikari, K.; Carbonell-Barrachina, A.A. Sensory and Physicochemical Characterization of Juices Made with Pomegranate and Blueberries, Blackberries, or Raspberries. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezcan, F.; Gultekin-Ozguven, G.; Diken, T.; Ozcelik, B.; Erim, F.B. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic, organic acid and sugar content in commercial pomegranate juices. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzulker, R.; Glazer, I.; Bar-Ilan, I.; Holland, D.; Aviram, M.; Amir, R. Antioxidant Activity, Polyphenol Content, and Related Compounds in Different Fruit Juices and Homogenates Prepared from 29 Different Pomegranate Accessions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9559–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Araujo, L.; Chambers, E., IV; Adhikari, K.; Carbonell-barrachina, A.A. Physico-chemical and sensory properties of pomegranate juices with pomegranate albedo and carpellar membranes homogenate. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, M.I.; TomasBarberan, F.A.; Hess, B. Antioxidant Activity of Pomegranate Juice and Its Relationship with Phenolic Composition and Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppel, K.; Anderson, E.L.; Chambers, E., IV. Influence of processing on pomegranate (Punicagranatum L.) juice flavor and aroma. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 95, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senanayake, N. Green Tea extracts: Chemistry, antioxidant properties and food applications—A Review. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuorila, H.; Meiselman, H.L.; Bell, R.; Cardello, O.A.V.; Johnson, W. Role of Sensory and Cognitive Information in the Enhancement of Certainty and Liking for Novel and Familiar Foods. Appetite 1994, 23, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkyilmaz, M.; Tagi, S.; Dereli, U.; Ozkan, M. Effects of various pressing programs and yields on the antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, phenolic content and colour of pomegranate juices. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, G.E.; Lewers, K.; Medina, M.; Saftner, R. Comparative analysis of strawberry total phenolics via Fast Blue BB vs. Folin–Ciocalteau: Assay interference by ascorbic acid. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2012, 27, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, J. Interferences during Analysis of Polyphenols in Fruit Juices; Second cycle, A2E; SLU Alnarp, Horticulture: Uppsala, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Liem, D.G.; Miremadi, F.; Zandstra, E.H.; Keast, R.S.J. Health labelling can influence taste perception and use of table salt for reduced sodium products. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbe, S.; Verbeke, W.; Deliza, R.; Matta, V.; Van Damme, P. Effect of a health claim and personal characteristics on consumer acceptance of fruit juices with different concentrations of acai (Euterpeoleracea Mart.). Appetite 2009, 53, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihlberg, I.; Johansson, L.; Langsrud, Ø.; Risvik, E. Effects of Information on liking of bread. Food Qual. Preference 2005, 16, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astill, C.; Birch, M.; Dacombe, C.; Humphrey, P.G.; Martin, P. Factors affecting the Caffeine and Polyphenol Content of Black and Green Tea Infusions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5340–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Chambers, D.; Chambers, E., IV. Sensory and Instrumental Flavor Changes in Green Tea Brewed Multiple Times. Foods 2013, 2, 554–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, M.B.; Hsieh, P.Y.-H.; Bell, L.N. Tea preparation and its influence on methylxanthine concentration. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Attribute | Definition | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pomegranate ID | The sour, sweet, fruity aromatic that may be somewhat dark, musty, earthy, with an astringent mouthfeel. These aromatics are reminiscent of a combination of fruits that may or may not include concord grape, cranberries, blackberries, raspberries, cherries, currants, etc. There are also vegetable notes of beets and carrots. | Fresh pomegranate juice diluted (1:1) = 3.5 1 Preparation: Dilute fresh pomegranate Juice 1 (juice):1 (water). Serve in 1 oz cup. |
| Green tea-like | A somewhat green, dusty, dried plant leaf aromatic associated with green tea. | Lipton Green tea. Preparation: Brew tea following instructions for preparing ice tea. |
| Berry | The sweet, sour, sometimes dark aromatics associated with a variety of berries such as blackberries, cherries, currants, raspberries, etc., excluding cranberries. | Blackwell Red Currant Jelly = 8.5 |
| Cranberry | The sweet, fruity, slightly sour and sharp aromatics commonly associated with cranberries. | Old Orchard’s Frozen Cranberry diluted (1:1) = 3.5 Ocean Spray Dried cranberries = 9.0 Preparation: Reconstitute Cranberry Concentrate according to instructions on the can. Dilute the reconstituted cranberry juice 1 (juice):1 (water) |
| Cherry | The sour, fruity, slightly bitter aromatics commonly associated with cherries. | RW Knudsen Cherry Juice diluted (1:2) = 4.0 Preparation: Dilute the cherry juice 1 (juice):2 (water), serve in 1 oz cup. |
| Grape | The sweet, brown, fruity, musty aromatics commonly associated with grapes. | Welch’s Concord Grape Juice diluted (1:1) = 5.0 Welch’s White Grape Juice diluted (1:1) = 5.0 Dilute grape juices 1 (juice):1 (water), serve in 1 oz. cup |
| Floral | An aromatic blend of a variety of fruits, excluding citrus, cranberry, and concord grape. May include apples, pears, white grapes, etc. | Welch’s White Grape Juice diluted (1:1) = 5.0 Dilute grape juice 1 (juice):1 (water) |
| Fruity | An aromatic blend of a variety of fruits, excluding citrus, cranberry, and concord grape. May include apples, pears, white grapes, etc. | Welch’s white grape juice diluted (1:1) = 5.0 Dilute grape juice 1 (juice):1 (water) |
| Beet | The damp, musty/earthy, slightly sweet aromatics commonly associated with beets | Diluted Kroger Canned Beet juice (1:2) = 4.0 Preparation: Drain juice from beets. Dilute beet juice 1 (juice):2 (water). |
| Green | Sharp, slightly pungent aromatics associated with green plant/vegetable matter, such as asparagus, Brussels sprouts, celery, green beans, parsley, spinach, etc. | Fresh Parsley water = 9.0 (flavor) Preparation: Weigh 25 g of fresh parsley, rinse, chop, and add 300 mL of water. Let it sit for 15 min. Filter and serve the liquid part. |
| Musty/Earthy | Humus-like aromatics that may or may not include damp soil, decaying vegetation, or cellar-like characteristics. | Raw potatoes = 3.0 (aroma). Diluted Kroger canned beet juice (1:2) = 7.0 (aroma). Preparation: Cut potato into slices, place in medium size snifter. Cover. Drain juice from beets, dilute beet juice 1 (juice):2 (water) Pour half cup in medium snifter, cover |
| Sweet | The fundamental taste factor associated with a sucrose solution. | 2% Sucrose Solution = 2.0 4% Sucrose Solution = 4.0 |
| Sweet Overall | The perception of the combination of sweet taste, sweet aromatics, caramelized, brown sugar, honey, and maple | 3% C&H Golden Brown Sugar solution = 4.0 |
| Woody | The aromatics associated with dry freshly cut wood. | Diamond Shelled Walnuts = 4.0 |
| Salt | Fundamental taste factor of which sodium chloride is typical. | 0.20% NaCl Solution = 2.5 0.25% NaCl Solution = 3.5 |
| Sour | A fundamental taste factor of which citric acid in water is typical. | 0.025% Citric Acid Solution = 2.5 0.050% Citric Acid Solution = 3.5 0.080% Citric Acid Solution = 5.0 |
| Bitter | The fundamental taste factor of which caffeine or quinine is typical. | 0.010% Caffeine Solution = 2.0 0.020% Caffeine Solution = 3.5 0.035% Caffeine Solution = 5.0 |
| Metallic | The impression of slightly oxidized metal, such as iron, copper, and silver spoons. | 0.10% Potassium Chloride solution = 1.5 |
| Astringent | The dry puckering mouthfeel associated with an alum solution. | 0.05% Alum Solution = 2.5 0.1% Alum Solution = 5.0 |
| Toothetch | A sensation of abrasion and drying of the surface of the teeth. | Welch’s Concord Grape Juice diluted (1:1) = 5.0 Dilute concord grape juice 1 (water):1 (juice) and serve in 1 oz. cups |
| Color Intensity | The intensity of strength of the color from light to dark. | Pantone Color Bridge coated 7640 = 6.0 Pantone Color Bridge coated 7641 = 8.0 Pantone Color Bridge coated 7642 = 10.0 |
| Sample Attribute | 90/10 | 80/20 | 70/30 | 60/40 | 50/50 | 40/60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pomegranate ID | 3.61 1 a | 3.75 a | 3.67 a | 3.31 b | 2.81 c | 2.58 c |
| Green Tea-like | 2.19 d | 2.25 d | 2.53 c | 2.58 c | 2.83 b | 3.14 a |
| Berry | 2.86 ab | 2.92 a | 2.67 bc | 2.50 c | 2.19 d | 1.92 e |
| 2.36 a | 2.47 a | 2.36 a | 2.39 a | 1.97 b | 2.00 b | |
| Cranberry | 2.17 ab | 2.25 a | 2.11 ab | 1.94 bc | 1.75 c | 1.36 d |
| Cherry | 1.86 ab | 2.03 a | 2.03 a | 1.69 bc | 1.50 cd | 1.31 d |
| Grape | 2.42 a | 2.47 a | 2.44 a | 2.36 a | 2.14 b | 1.92 c |
| Floral | 2.81 ab | 2.89 a | 2.75 ab | 2.64 b | 2.36 c | 2.17 c |
| Fruity | 1.47 | 1.50 | 1.36 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.14 |
| Beet | 1.86 | 1.944 | 2.06 | 2.03 | 2.08 | 2.31 |
| Green | 1.97 | 2.03 | 2.00 | 1.92 | 1.83 | 1.86 |
| Musty/Earthy | 3.61 a | 3.75 a | 3.67 a | 3.31 b | 2.81 c | 2.58 c |
| Woody | 1.83 | 1.86 | 1.92 | 1.89 | 1.83 | 1.86 |
| Sweet Overall | 3.08 a | 3.11 a | 2.92 ab | 2.78 bc | 2.56 cd | 2.38 d |
| Sweet | 2.58 a | 2.50 a | 2.39 ab | 2.28 b | 2.19 b | 1.88 c |
| Salt | 1.86 | 1.89 | 1.83 | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.72 |
| Sour | 2.56 | 2.64 | 2.56 | 2.53 | 2.56 | 2.58 |
| Bitter | 3.00 | 2.89 | 2.81 | 2.83 | 2.89 | 3.14 |
| Metallic | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 1.00 |
| Astringent | 2.92 | 2.86 | 3.00 | 2.81 | 2.92 | 3.00 |
| Toothetch | 2.31 | 2.25 | 2.29 | 2.06 | 2.06 | 2.22 |
| Color Intensity | 12.06 a | 11.58 b | 10.86 c | 9.75 d | 8.72 e | 8.25 f |
| Sample | TPC (mg Gallic Acid Equivalents/L ± Stdev) |
|---|---|
| Tea | 697.436 ± 0.003 |
| 40:60 | 1312.821 ± 0.003 |
| 50:50 | 1564.569 ± 0.008 |
| 60:40 | 1802.331 ± 0.003 |
| 70:30 | 1960.839 ± 0.005 |
| 80:20 | 2091.375 ± 0.009 |
| 90:10 | 2310.490 ± 0.013 |
| Juice | 2450.350 ± 0.009 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higa, F.; Koppel, K.; Chambers, E. Effect of Additional Information on Consumer Acceptance: An Example with Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends. Beverages 2017, 3, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3030030
Higa F, Koppel K, Chambers E. Effect of Additional Information on Consumer Acceptance: An Example with Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends. Beverages. 2017; 3(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiga, Federica, Kadri Koppel, and Edgar Chambers. 2017. "Effect of Additional Information on Consumer Acceptance: An Example with Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends" Beverages 3, no. 3: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3030030
APA StyleHiga, F., Koppel, K., & Chambers, E. (2017). Effect of Additional Information on Consumer Acceptance: An Example with Pomegranate Juice and Green Tea Blends. Beverages, 3(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3030030







