L-Malic Acid Descaler for Drinking Water—Physicochemical Analysis and Biological Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. L-Malic Acid Descaler
2.2. Standards for Drinking Water
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.4. Yeast-Cell-Based Analyses
2.4.1. Strains
2.4.2. Treatment with Malic Acid Granules
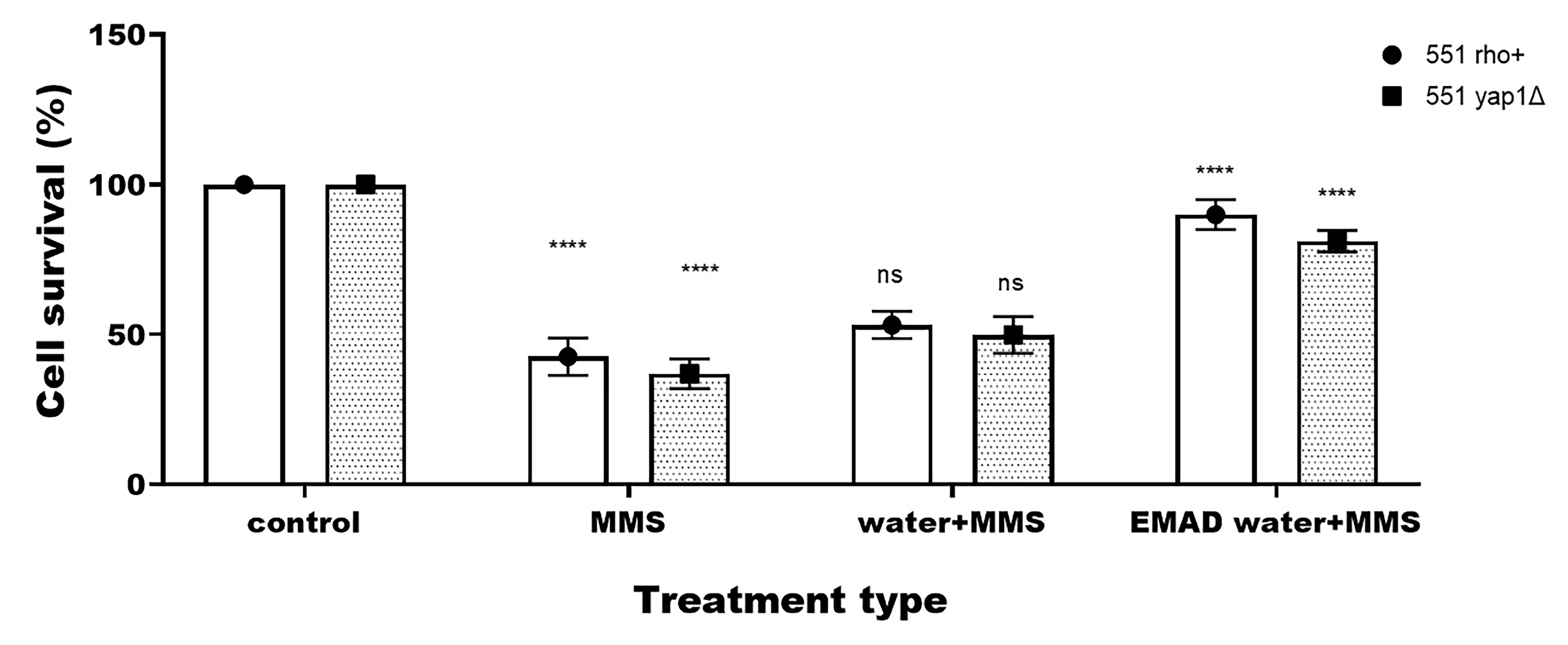
2.4.3. Cell Survival
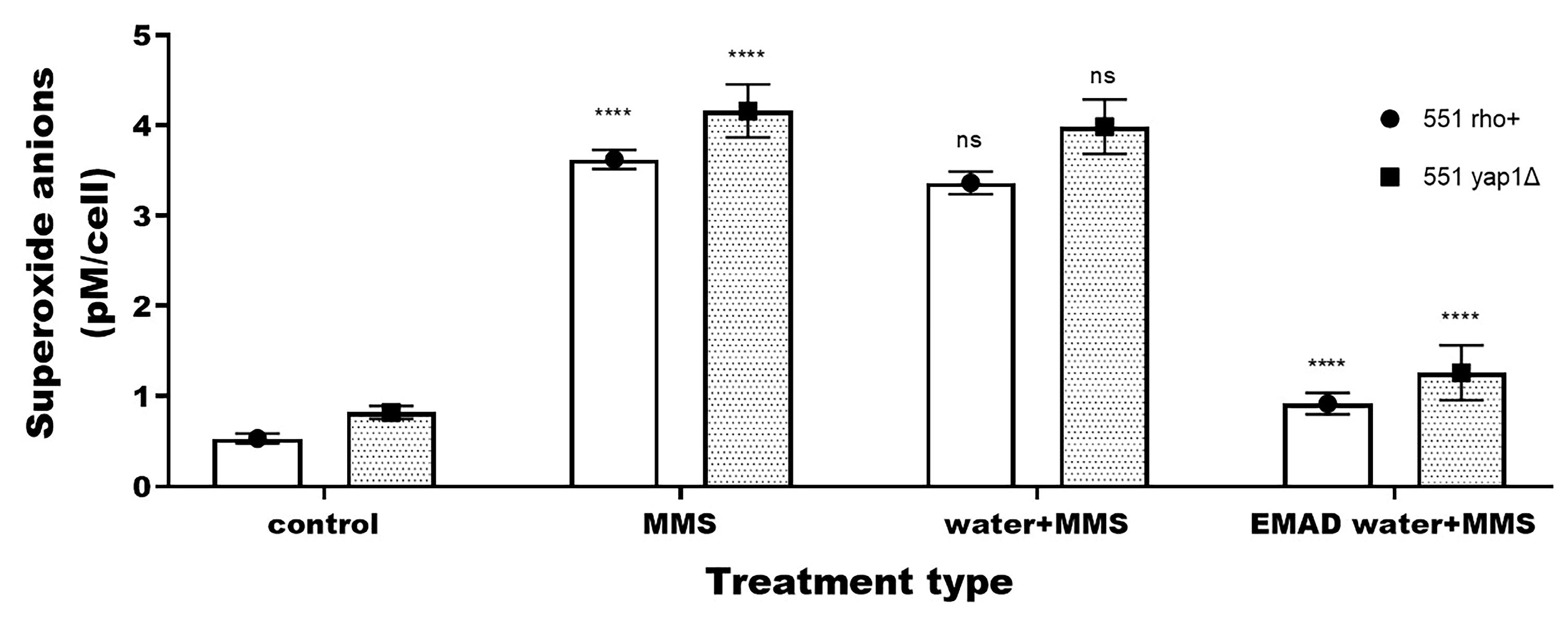
2.4.4. Quantitative Measurement of Physiologically Active Superoxide Anions in Living Cells
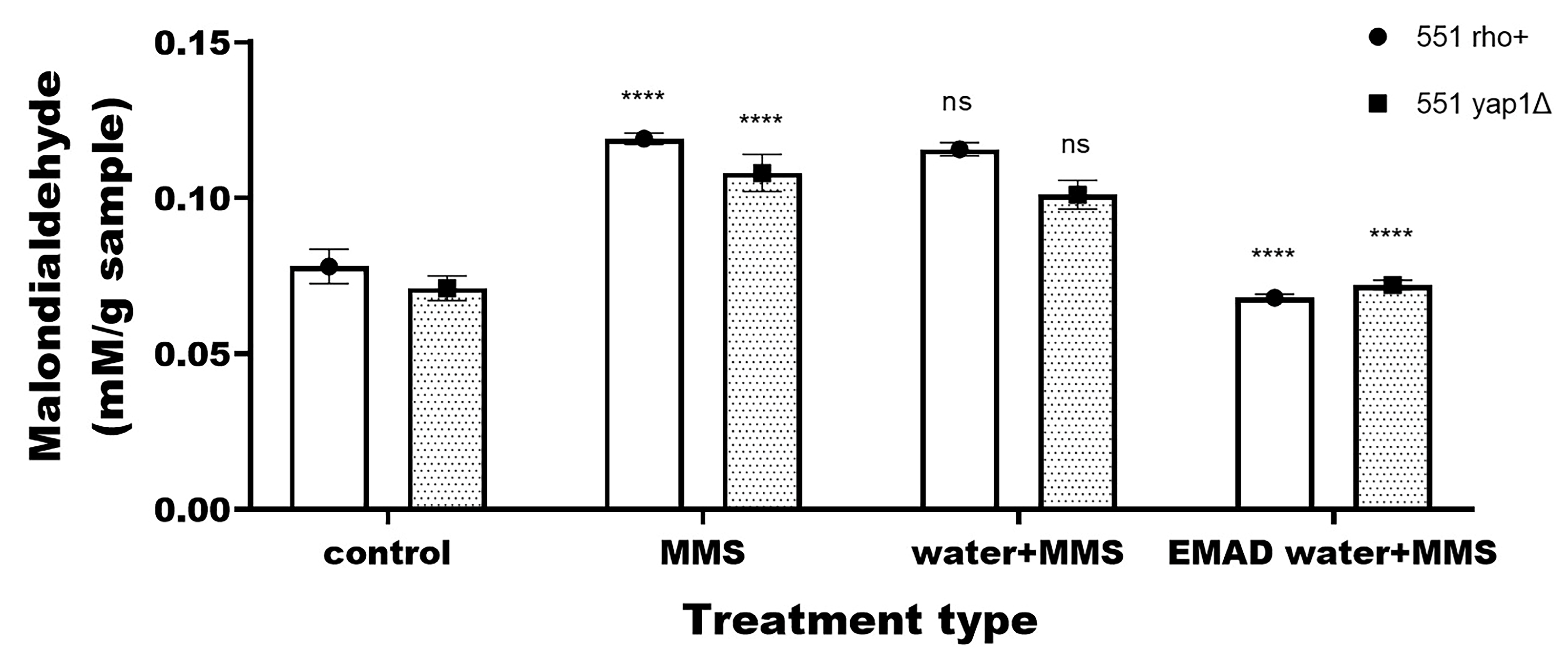
2.4.5. Lipid Peroxidation Measured by the TBARS Method-Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Species
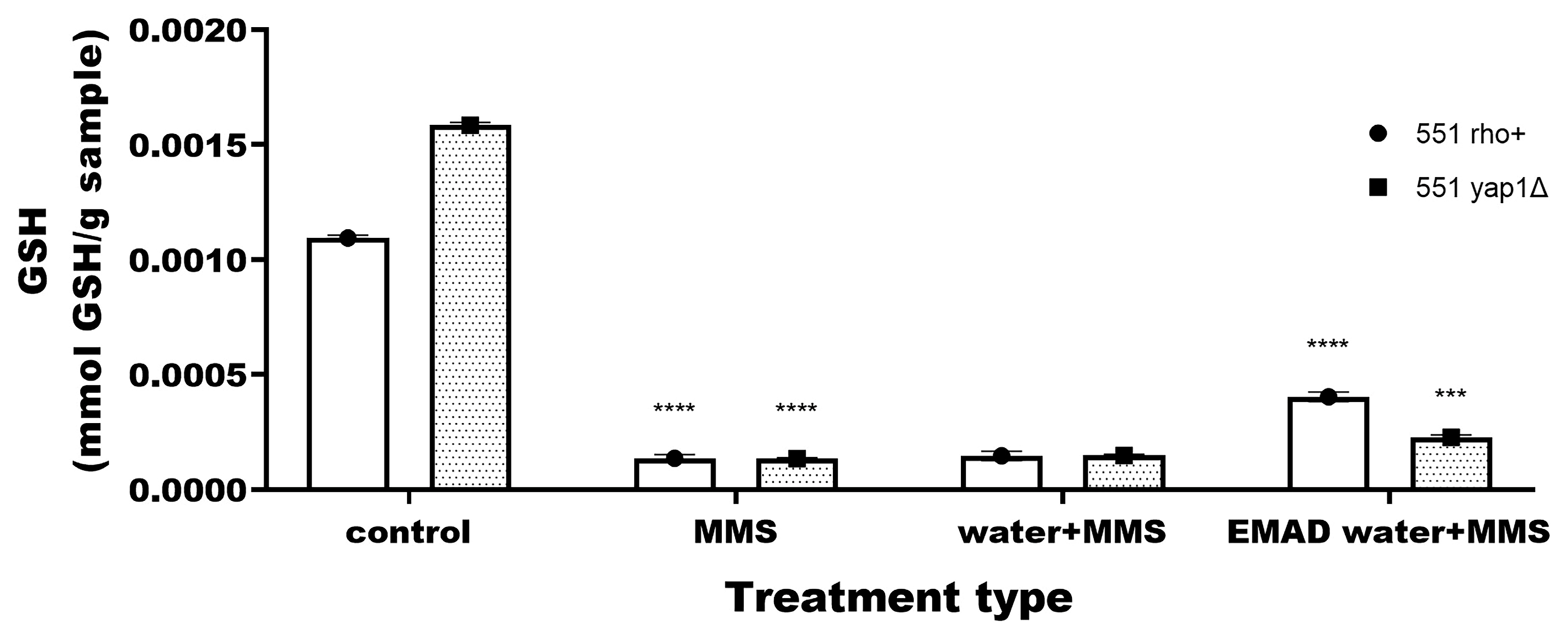
2.4.6. Total Glutathione (GSH)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Method
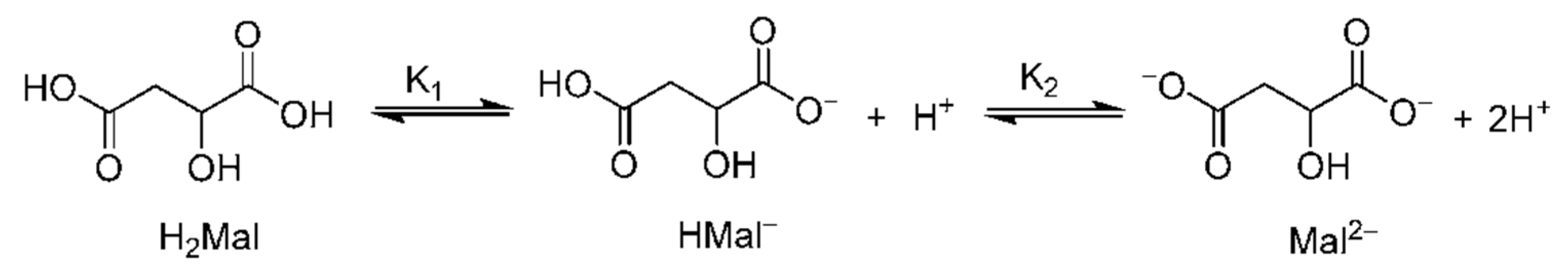
3.2. Reactions of Malic Acid in Water
3.3. Yeast-Cell-Based Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Nahas, S.; Khodari, M.; Hamam, A.A.; Gad El Rab, A.N.; Toghan, A. Descaling of Evaporator Tubes in Sugarcane Factories Using Molasses as a Green and Effective Technology. Sugar Tech. 2024, 26, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayunigari, M.K.; Maity, A.; Agarwal, S.; Vinod Kumar Gupta, V.K. Curcumin-malic acid based green copolymers for control of scale and microbiological growth applications in industrial cooling water treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, G.Y.; Khan, I.; Chi, Z.M. Microbial biosynthesis and secretion of l-malic acid and its applications. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 36, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Q. Metabolic engineering of Aspergillus niger for accelerated malic acid biosynthesis by improving NADPH availability. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, 2400014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevas, E.; Karamelidou, A.; Hatzidimitriou, A.; Mateescu, C.; Salifoglou, A. pH-specific halide-dependent materials from ZrIV/hydroxycarboxylic acid/aromatic chelator reactivity: Architecture–lattice dimensionality and spectroscopic fingerprint relations. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, M.; Li, C.; Ogutu, C.; Li, M.; Ma, F. Determination of Predominant Organic Acid Components in Malus Species: Correlation with Apple Domestication. Metabolites 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovilein, A.; Kubisch, C.; Cai, L.; Ochsenreither, K. Malic acid production from renewables: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Scientific Opinion on the safety and efficacy of malic acid and a mixture of sodium and calcium malate when used as technological additives for all animal species. EFSA Panel on Additive and Products or Substances Used in Animal Feed. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3563. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, K.; He, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Qi, G.; Guo, N.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S. Bio-Fermented Malic Acid Facilitates the Production of High-Quality Chicken via Enhancing Muscle Antioxidant Capacity of Broilers. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Xia, C.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Y. Effects of malic acid and citric acid on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, haematology, and immune response of Carassius auratus gibelio. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 2766–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Raissy, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Vatnikov, Y.A.; Kulikov, E.V. Effects of dietary malic acid supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant and immunological parameters, and intestinal gene expressions in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Maternal malic acid may ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in sows through modulating gut microbiota and host metabolic profiles during late pregnancy. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yan, M.; Guo, R.; Liu, Z. The research progress of water treatment technology on recirculated cooling water. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 508, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabansis, S.E.; Leenheer, J.A.; McVey, I.F. Aqueous infrared carboxylate absorbances: Aliphatic di-acids. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol Biomol. Spectrosc. 1998, 54, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosin, O.V.; Shvets, V.I.; Skladnev, D.A.; Ignatov, I. Microbial synthesis of 2H-labelled L-phenylalanine with different levels in isotopic enrichment by a facultative methylotrophic Brevibacterium Methylicum with RuMP assimilation of Carbon. Biochem. Suppl. B Biomed. Chem. 2013, 7, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tran, H.; Van, L.T.M.; Vuu, M.N.; Mai, P.T. Separation performance of polyvinyl alcohol) based nanofiltration membranes crosslinked by malic acid for salt solutions. Sci. Technol. Dev. J. 2016, 19, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telegdi, J.; Trif, L.; Mihaly, J.; Nagy, E.; Nyikos, L. Controlled synthesis and characterization of biodegradable, stereomer co-polycondensates of l-malic acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.; Schwab, S.T.; Nelson, T.F.; Wurst, K.; Iberl, S.; Schleheck, D.; Link, C.; Battagliarin, G.; Mecking, S. Biodegradable high-density polyethylene-like material. Angew. Chem. 2022, 135, e202213438. [Google Scholar]
- Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eudr/2020/2184 (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- Todorova, T.; Pesheva, M.; Gregan, F.; Chankova, S. Antioxidant, antimutagenic, and anticarcinogenic effects of Papaver rhoeas L. extract on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikner, A.; Shiozaki, K. Yeast signaling pathways in the oxidative stress response. Mutat. Res. 2005, 569, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, M.D.; Perrone, G.G.; Dawes, I.W. Complex cellular responses to reactive oxygen species. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorova, T.; Boyadzhiev, K.; Dimitrov, M.; Parvanova, P. Bee venom genotoxicity on Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells–The role of mitochondria and YAP1 transcription factor. Toxicology 2024, 503, 153768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalova, A.V.; Tomova, A.A.; Kujumdzieva, A.V.; Velkova, L.G.; Dolashka, P.A.; Petrova, V.Y. Menadione and hydrogen peroxide trigger specific alterations in RNA polymerases profiles in quiescent Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvanyan, A.; Trchounian, K. Sodium transport and redox regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae under osmotic stress depending on oxygen availability. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Liu, H. Enhanced recombinant protein production under special environmental stress. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 630814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbieralski, K.; Staszewski, J.; Konczak, J.; Lazarewicz, N.; Nowicka-Kazmierczak, M.; Wawrzycka, D.; Maciaszczyk-Dziubinska, E. Multilevel regulation of membrane proteins in response to metal and metalloid stress: A Lesson from Yeast. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, D.W.; Rivers, S.L.; Jamieson, D.J. The role of the YAP1 and YAP2 genes in the regulation of the adaptive oxidative stress responses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 16, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboughaly, M.; Babaei-Ghazvini, A.; Dhar, P.; Patel, R.; Acharya, B. Enhancing the potential of polymer composites using biochar as a filler: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaković, N.; Karahmet, E.; Varešić, B. Assessment of Activated Charcoal Efficiency with Filter Paper in the Water Purification Process. In New Technologies, Development and Application II. NT 2019. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Karabegović, I., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 76. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatov, I. Review of different types of mountain springs and mineral waters from Bulgaria based on their natural origin and health benefits. Med. Perspekt. 2023, 51, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, H.; Elkatatny, S.; Al-Afnan, S.; Bahdat, M. Development of a unique organic acid solution for removing composite field Scales. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1205–1215, Erratum in Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 33, 101131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enchev, P.; Zarev, Y.; Dakovska, A.; Todorova, T.; Dimitrov, M.; Rivera-Mondragón, A.; Ionkova, I. Pentacyclic triterpenoids from the leaves of Cecropia longipes. Pharmacia 2024, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesheva, M.; Krastanova, O.; Staleva, L.; Dentcheva, V.; Hadzhitodorov, M.; Venkov, P. The Ty1 transposition assay: A new short-term test for detection of carcinogens. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesheva, M.; Krastanova, O.; Stamenova, R.; Todorova, I.; Shoevska, R.; Venkov, P.; Tsvetkov, T. The Ty1 transposition assay: A short–term test for selective detection of carcinogenic pollutants in environmental samples. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 14, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Stoycheva, T.; Pesheva, M.; Venkov, P. The role of reactive oxygen species in the induction of Ty1 retrotransposition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2010, 27, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenova, R.; Dimitrov, M.; Stoycheva, T.; Pesheva, M.; Venkov, P.; Tsvetkov, T.S. Transposition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ty1 retrotransposon is activated by improper cryopreservation. Cryobiology 2008, 56, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, T.; Pesheva, M.; Stamenova, R.; Dimitrov, M.; Venkov, P. Mutagenic effect of freezing on nuclear DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2012, 29, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steels, E.L.; Learmonth, R.P.; Watson, K. Stress tolerance and membrane lipid unsaturation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown aerobically or anaerobically. Microbiology 1994, 140, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnik, P.; Medved, P.; Raspor, P. Increased glutathione content in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae exposed to NaCl. Ann. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, O.; Kuhnert, F.; Weber, A.P.N.; Peltier, G.; Li-Besson, Y. Physiological functions in malate shuttles in plants and algae. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhu, H.; Lv, C.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, H.; Fan, Z.; Sun, J.; Huang, Z.; Shi, P. Clioquinol rescues yeast cells from Aβ42 toxicity via the inhibition of oxidative damage. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, 2300662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. Fundamentals of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4200-6930-3. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, N.C.; Mastyugin, M.; Török, B.; Török, M. Structural Features of Small Molecule Antioxidants and Strategic Modifications to Improve Potential Bioactivity. Molecules 2023, 28, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Max, J.-J.; Chapados, C. Infrared scpctroscopy of aquous carboxylic acids: Malic acid. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 27, 6452–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Antitumor activity of protons and molecular hydrogen: Underlying mechanisms. Cancers 2021, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igamberdiev, A.V.; Bykova, N.V. Role of organic acids in the integration of cellular redox metabolism and mediation of redox signalling in photosynthetic tissues of higher plants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 122, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, I. Hydronium ion transport across the liquid/liquid interface assisted by a phase-transfer catalyst: Structure and thermodynamics using molecular dynamics simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 9613–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, N.; Ignatov, I.; Popova, T.P.; Huether, F.; Ignatov, A.I.; Iliev, M.T.; Marinov, Y. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Density Functional Theory (DFT) Study of Water Clusters of Hydrogen-Rich Water (HRW). Water 2024, 16, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, K.W.; Salkowski, A.N. Density functional theory (DFT) study of water autoionization in solvated clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartsch, P.C.; Huether, F. Beneficial health effects of malic acid water treatment on cultured intestinal epithelial cells and functional neutrophils. Appl. Cell. Biol. 2024, 12, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysan, K.; Lou, M.F. Regulation of human thioltransferase (hTTase) gene by AP-1 transcription factor under oxidative stress. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Stoycheva, T.; Pesheva, M.; Dimitrov, M.; Venkov, P. The Ty1 Retrotransposition Short-Term Test for Selective Detection of Carcinogenic Genotoxins; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 83–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoycheva, T. Methylmethane sulfonate increases the level of superoxide anions in yeast cells. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2009, 23, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Composition of L-Malic Acid Descaler | ||
|---|---|---|
| CAS: 617-48-1 EINECS: 210-514-9 | L-malic acid | 45% |
| CAS: 9002-88-4 | Polyethylene | 30% |
| CAS: 64365-11-3 EINECS: 264-846-4 | Charcoal, activated | 25% |
| Absorption Bands | ||
|---|---|---|
| Wave Number (cm−1) | Wavelength (µm) | Type |
| 3601 | 2.78 | medium |
| 3432 | 2.91 | medium |
| 2952 | 3.39 | weak |
| 2919 | 3.43 | medium |
| 2849 | 3.51 | weak |
| 1792 | 5.58 | weak |
| 1714 | 5.83 | strong |
| 1531 | 6.53 | weak |
| 1397 | 7.16 | medium |
| 1362 | 7.34 | medium |
| 1289 | 7.76 | weak |
| 1258 | 7.95 | weak |
| 1217 | 8.22 | weak |
| 1166 | 8.58 | medium |
| 1058 | 9.45 | weak |
| 1034 | 9.67 | weak |
| 719 | 13.91 | weak |
| 640 | 15.63 | weak |
| Endpoint | Type of Treatment | 551 rho+ 1 | 551 yap1Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell survival (%) | Untreated | 100 | 100 |
| Treated with water | 101 ± 2.65 ns | 99.67 ± 1.27 ns | |
| Treated with EMAD water | 98.24 ± 3.29 ns | 97.23 ± 4.21 ns | |
| Superoxide anions | Untreated | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 0.82 ± 0.07 |
| Treated with water | 0.57 ± 0.09 ns | 0.85 ± 0.1 ns | |
| Treated with EMAD water | 0.52 ± 0.05 ns | 0.80 ± 0.06 ns | |
| MDA | Untreated | 0.08 ± 0.005 | 0.07 ± 0.004 |
| Treated with water | 0.1 ± 0.002 ns | 0.09 ± 0.005 ns | |
| Treated with EMAD water | 0.06 ± 0.005 ns | 0.06 ± 0.006 ns | |
| GSH | Untreated | 0.0011 ± 0.00001 | 0.0016 ± 0.00001 |
| Treated with water | 0.0013 ± 0.00001 ns | 0.0015 ± 0.00001 ns | |
| Treated with EMAD water | 0.0011 ± 0.00001 ns | 0.0014 ± 0.00001 ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todorova, T.; Boydzhiev, K.; Ignatov, I.; Petrova Popova, T.; Dimitrov, Z.; Gotova, I.; Huether, F.; Ignat Ignatov, A.; Georgiev Marinov, Y. L-Malic Acid Descaler for Drinking Water—Physicochemical Analysis and Biological Activity. Beverages 2025, 11, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11030062
Todorova T, Boydzhiev K, Ignatov I, Petrova Popova T, Dimitrov Z, Gotova I, Huether F, Ignat Ignatov A, Georgiev Marinov Y. L-Malic Acid Descaler for Drinking Water—Physicochemical Analysis and Biological Activity. Beverages. 2025; 11(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodorova, Teodora, Krassimir Boydzhiev, Ignat Ignatov, Teodora Petrova Popova, Zhechko Dimitrov, Irina Gotova, Fabio Huether, Alexander Ignat Ignatov, and Yordan Georgiev Marinov. 2025. "L-Malic Acid Descaler for Drinking Water—Physicochemical Analysis and Biological Activity" Beverages 11, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11030062
APA StyleTodorova, T., Boydzhiev, K., Ignatov, I., Petrova Popova, T., Dimitrov, Z., Gotova, I., Huether, F., Ignat Ignatov, A., & Georgiev Marinov, Y. (2025). L-Malic Acid Descaler for Drinking Water—Physicochemical Analysis and Biological Activity. Beverages, 11(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11030062










