Cloud Point Extraction in Beverage Analysis: Innovations and Applications for Trace Elements
Abstract
1. Introduction
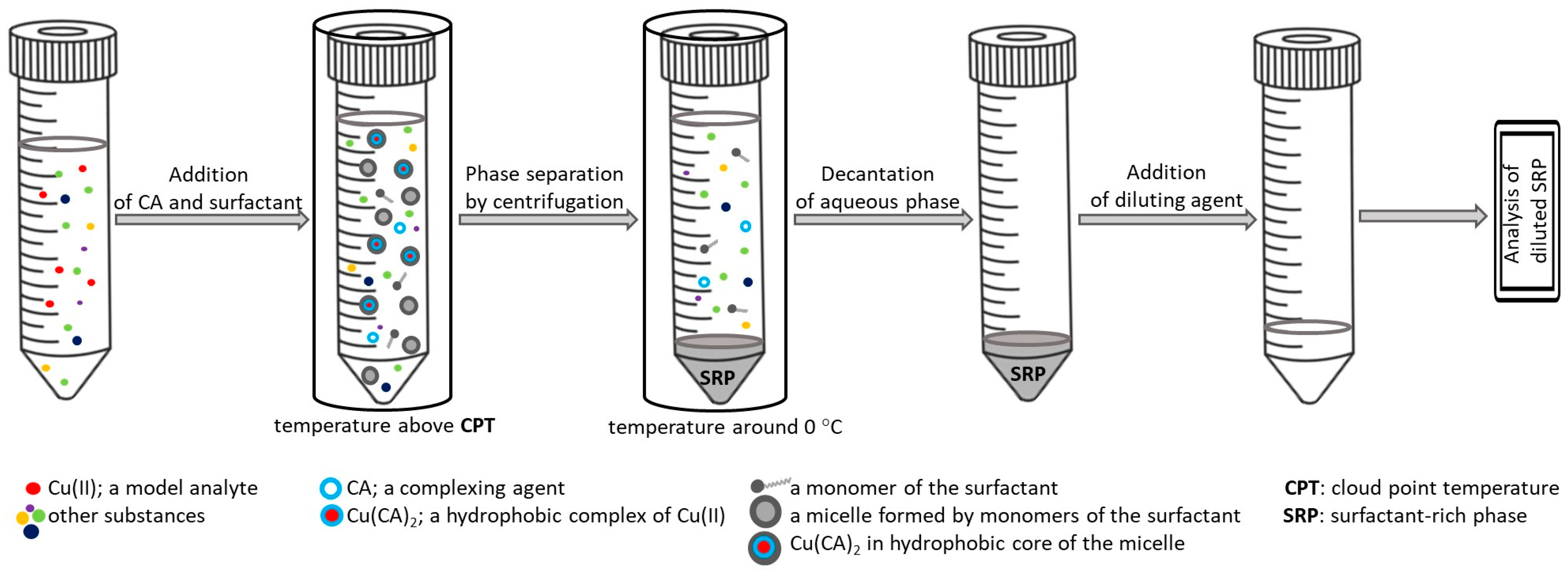
2. Principle of Cloud Point Extraction for Trace Elements Analysis
3. Different Approaches to Sample Preparation Prior CPE Procedure Application
| Sample | Analyte | Complexing Agent | Surfactant | Detection Method | LOD (μg/L) | RSD (%) | Recovs. (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit juices, wine, beer | As(V) | AOH+/TA | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 1.14 | 5.7 | 95–100 | [25] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer | Sb(V) | VPB+ | TX-114 | FAAS | 0.25 | 4.2 | 97–104 | [36] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer, milk | Sb(V) | Pyronin B | TX-114/SDS | FAAS | 4.28 | 6.1 | 97–99 | [38] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer, milk | Sb(III) | Pyronin B | TX-114/SDS | FAAS | 1.68 | 6.0 | 97–99 | [38] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer | Sb(III) | VPB+ | TX-114 | FAAS | 5.15 | 4.5 | 98–103 | [36] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer, milk | Sb(III) | Azomethine-H | TX-114/CPC | FAAS | 0.15 | 5.9 | 95–98 | [30] |
| Fruit juices | Sn(IV) | Celestine blue/TA | TX-114/SDS | UV–Vis | 1.3 | 5.3 | 97–103 | [45] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer | Sn(IV) | GC+/glycine | Tween20/CPC | FAAS | 0.33 | 6.2 | 96–104 | [36] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer | Cu(II) | Sudan II | TX-114/SDS | UV–Vis | 0.085 | 3.9 | 99–101 | [29] |
| Orange juices | Cu(II) | BIYPYBI | TX-114 | FAAS | 1.4 | 1.1 | 104 | [47] |
| Orange juices | Ni(II) | BIYPYBI | TX-114 | FAAS | 1.9 | 1.1 | 103 | [47] |
| Wine, beer | Co(II) | CCA | TX-114/CPC | FAAS | 0.20 | 5.7 | 92–104 | [27] |
| Fruit juices | Cd(II) | VBB+/KI | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.34 | 4.6 | 97–101 | [43] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer | Zn(II) | PBHA | TX-114 | FAAS | 0.42 | 3.2 | 99–100 | [29] |
| Orange juices | Zn(II) | BIYPYBI | TX-114 | FAAS | 1.0 | 1.0 | 103 | [47] |
| Beer | Fe(II) | 5-Br-PADAP/EDTA | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.80 | 1.0 | 100–102 | [48] |
| Orange juices, milk | Fe(III) | Ferron | TX-114 | FAAS | 0.40 | 1.3 | 102–103 | [49] |
| Orange juices | Fe(III) | BIYPYBI | TX-114 | FAAS | 2.2 | 0.8 | 104 | [47] |
| Fruit juices, wine | Mo(VI) | VPB+/KSCN | TX-114/CPC | FAAS | 2.18 | 3.2 | 97–102 | [44] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer, milk | B(III) | Azomethine-H | TX-114/CPC | FAAS | 0.75 | 4.0 | 95–98 | [30] |
4. Innovative CPE Procedures for the Separation and Preconcentration of Trace Elements in Beverage Samples
| Sample | Analyte | CPE Modification | Complexing Agent | Surfactant | Detection Method | LOD (μg/L) | RSD (%) | Recovs. (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drinking water, fruit juices, wine, beer | As(V) | UA-CPE | NRH+/PG | PONPE 7.5 | FAAS | 0.45 | 4.2 | 98–104 | [35] |
| Tap water, pulp fruit juices | Sb(III) | UA-CPE | NRH+ | PONPE 7.5/CTAB | HG-AAS | 0.0036 | 5.3 | 93–107 | [19] |
| Tap water, Nescafe, fruit juices, wine | Sb(III) | UA-CPE | Morin | PONPE 7.5/CTAB | FAAS | 0.03 | 5.2 | 97–104 | [34] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer, milk | Sb(III) | UA-CPE | TAR | Tween 80/SDS | FAAS | 0.13 | 3.2 | 98–103 | [30] |
| Fruit juices, wine, beer, milk | Sb(III) | UA-CPE | TAC | Tween 80/SDS | FAAS | 0.28 | 3.5 | 98–103 | [30] |
| Tap water, mineral water | Se(IV) | UA-CPE | Dithizone | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.30 | 3.2 | 93–102 | [24] |
| Tap water, pulp fruit juices | Se(IV) | UA-CPE | NRH+ | PONPE 7.5/CTAB | HG-AAS | 0.00245 | 5.1 | 93–107 | [19] |
| Tap water, Nescafe, fruit juices, wine | Sn(IV) | UA-CPE | Morin | PONPE 7.5/CTAB | FAAS | 0.03 | 5.4 | 97–104 | [34] |
| Milk | Mo(VI) | UA-CPE | Nile Blue A | PONPE 7.5 | FAAS | 0.86 | 2.4 | 96–102 | [51] |
| Fruit juices, milk, vinegar | V(V) | UA-CPE | Safranin T/PG | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.58 | 4.6 | 95–98 | [41] |
| Milk | V(V) | UA-CPE | Nile Blue A | PONPE 7.5 | FAAS | 1.55 | 2.2 | 96–102 | [51] |
| Fruit juices, milk, vinegar | Cu(II) | UA-CPE | Safranin T/PG | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.60 | 4.4 | 93–98 | [52] |
| Drinking water, fruit juices, tea samples | As(V) | VA-CPE | ARH+/PG | TX-45 | UV–Vis | 0.25 | 3.7 | 96–103 | [42] |
| Tap water, milk | Mo(VI) | RT-CPE | DHDPhB | TX-100 | UV–Vis | 2.3 | 4.5 | 97–106 | [16] |
| Tap water, mineral water | Se(IV) | RS-CPE | Dithizone | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.20 | 4.3 | 95–105 | [24] |
| Tap water | Hg(II) | M-CPE | PAR | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 13.1 | 6.4 | 108–115 | [54] |
| Tap water | Zn(II) | M-CPE | PAR | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 51.7 | 4.7 | 93–113 | [54] |
| Tap water | Cu(II) | M-CPE | PAR | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 9.8 | 5.9 | 93–98 | [54] |
| Tap water, mineral water | Hg(II) | IL-CPE | TPPP | TEGII | Fluorimetry | 80 | 2.4 | 100–101 | [55] |
| Tap water | Hg(II) | IL-CPE | HECAT | TX-114 | UV–Vis | 0.5 | 1.5 | 95–96 | [56] |
| Drinking water, mineral water, fruit juices | Hg(II) | MA-CPE-DSPE | CdFe2O4NPs/ DBH | TX-114 | FS-FAAS | 5.0 | 4.2 | 91–100 | [46] |
| Tap water, mineral water, wine, beer | Cu(II) | CPE-DSPE | AgNPs/ MESNA | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.0024 | 4.3 | 95–105 | [39] |
| Tap water, well water, mineral water | Cu(II) | CPE-DSPE | Al2O3NPs * | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.0026 | 4.9 | 96–106 | [57] |
| Tap water, mineral water, wine, beer | Ni(II) | CPE-DSPE | AgNPs/ MESNA | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.0021 | 4.3 | 95–106 | [39] |
| Tap water, well water, mineral water | Ni(II) | CPE-DSPE | Al2O3NPs * | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.0028 | 5.6 | 96–104 | [57] |
| Tap water, well water, mineral water | Co(II) | CPE-DSPE | Al2O3NPs * | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.0025 | 6.5 | 96–104 | [57] |
| Tap water | Zn(II) | CPE-DSPE | TiO2NPs * | TX-100 | Colorimetry | 0.33 | 1.8 | 100–102 | [58] |
| Tap water, well water | Pb(II) | CPE-DSPE | ZrNO2NPs/ cadion | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.0022 | 3.5 | 95–99 | [59] |
| Tap water, mineral water | Cr(III) | CPE-DSPE | GONPs * | TX-45 | ETAAS | 0.005 | 5.2 | 98–103 | [60] |
| Tap water, mineral water, wine, beer | Cr(III) | CPE-DSPE | AgNPs * | TX-114 | ETAAS | 0.002 | 4.3 | 95–105 | [31] |
| Tap water, mineral water, beer | V(IV+V) | CPE-DSPE | GONPs * | TX-114 | ETAAS | 20 | 4.7 | 96–105 | [61] |
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Hosry, L.; Sok, N.; Richa, R.; Al Mashtoub, L.; Cayot, P.; Bou-Maroun, E. Sample preparation and analytical techniques in the determination of trace elements in food: A review. Foods 2023, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luján, C.E.; Lemos, A.A.; Oviedo, M.N.; Llaver, M.; Wuilloud, R.G. Deep eutectic solvents as a green alternative for trace element analysis in food and beverage samples: Recent advances and challenges. Talanta 2024, 269, 125451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogwasi, R.; Onyancha, M.E.; Mobegi, E.; Nyabaro, O. Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry versus flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry for the analysis of Fe, Cu, Zn, Mn and Cr in medicinal plants: A comparison study. Adv. Transl. Med. 2023, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagarová, I.; Urík, M. New approaches to the cloud point extraction: Utilizable for separation and preconcentration of trace metals. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2016, 12, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghambarian, M.; Yamini, Y.; Saleh, A.; Shariati, S.; Yazdanfar, N. Taguchi OA16 orthogonal array design for the optimization of cloud point extraction for selenium determination in environmental and biological samples by tungsten-modified tube electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2009, 78, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Qin, J.P.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, S.; Yang, B.Y. Determination of total selenium in food samples by d-CPE and HG-AFS. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagarová, I.; Nemček, L. Recent advances in speciation analysis of trace antimony in environmental and biological samples based on cloud point extraction and spectrometric methods. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 52, pp. 49–77. [Google Scholar]
- Halko, R.; Hagarová, I.; Andruch, V. Innovative approaches in cloud-point extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1701, 464053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quina, F.H.; Hinze, W.L. Surfactant-mediated cloud point extractions: An environmentally benign alternative separation approach. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 4150–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Xu, H.H.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhuang, B.H.; Qi, H.S. Cloud point of nonionic surfactant Triton X-45 in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2008, 61, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, W.L.; Pramauro, E. A critical review of surfactant-mediated phase separations (Cloud-point extractions)—Theory and applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1993, 24, 133–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.S.C.; Lee, P.F.S. CMC of Polysorbates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1974, 63, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagarová, I.; Nemček, L. Reliable quantification of ultratrace selenium in food, beverages, and water samples by cloud point extraction and spectrometric analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depoi, F.D.; Pozebon, D. The use of cloud point extraction and hydride generation for improving the Sb and Se limits of detection in ICP OES. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biata, N.R.; Mashile, G.P.; Ramontja, J.; Mketo, N.; Nomngongo, P.N. Application of ultrasound-assisted cloud point extraction for preconcentration of antimony, tin and thallium in food and water samples prior to ICP-OES determination. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 76, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigur, D.; Barbalat, D.; Chebotarev, A.; Synievyd, A.; Bevziuk, K. A rapid cloud point extraction of Molybdenum(VI) with 6,7-dihydroxy-2,4-diphenylbenzopyrylium perchlorate prior to its spectrophotometric determination. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsaw, A.; Sananmuang, R.; Udnan, Y.; Ross, G.M.; Chaiyasith, W.C. Dual-cloud point extraction for speciation of mercury in water and fish samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B-At. Spectrosc. 2019, 160, 105685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.B.; Hu, B.; He, M. Cloud point extraction combined with electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the speciation of inorganic selenium in environmental water samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2894–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R. Separation/preconcentration of ultra-trace levels of inorganic Sb and Se from different sample matrices by charge transfer sensitized ion-pairing using ultrasonic-assisted cloud point extraction prior to their speciation and determination by hydride generation AAS. Talanta 2016, 159, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, H.I.; Gürkan, R.; Ulusoy, S. Cloud point extraction and spectrophotometric determination of mercury species at trace levels in environmental samples. Talanta 2012, 88, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, A.; Momeni-Isfahani, T.; Ahmari, Z. Spectrophotometric determination of mercury in water samples after cloud point extraction using nonionic surfactant Triton X-114. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Madrakian, T.; Siampour, H. Highly selective determination of trace quantities of mercury in water samples after preconcentration by the cloud-point extraction method. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2006, 86, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wuilloud, J.C.A.; Wuilloud, R.G.; Silva, M.F.; Olsina, R.A.; Martinez, L.D. Sensitive determination of mercury in tap water by cloud point extraction pre-concentration and flow injection-cold vapor-inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B-At. Spectrosc. 2002, 57, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X.C. Comparison of rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction and ultrasound-assisted cloud point extraction for trace selenium coupled with spectrophotometric determination. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 123, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürkan, R.; Mr, U.; Altunay, N. Development of a simple, sensitive and inexpensive ion-pairing cloud point extraction approach for the determination of trace inorganic arsenic species in spring water, beverage and rice samples by UV-Vis spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Han, Q.; Hu, E.Y.; Yang, C.; Yin, M.M. Determination of trace mercury in water samples by cloud point extraction coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 78, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, H.I.; Gürkan, R.; Demir, Ö.; Ulusoy, S. Micelle-mediated extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometric method for determination of trace cobalt ions in beverage samples. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, P. Determination and fractionation of metals in beer: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurkan, R.; Altunay, N. A reliable method of quantification of trace copper in beverages with and without alcohol by spectrophotometry after cloud point extraction. Quim. Nova 2013, 36, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R. Simultaneous determination of antimony and boron in beverage and dairy products by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after separation and pre-concentration by cloud-point extraction. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Non-chromatographic speciation of chromium at sub-ppb levels using cloud point extraction in the presence of unmodified silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 132, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindlay, G.; Mora, J.; Gras, L.; de Loos-Vollebregt, M.T.C. Atomic spectrometry methods for wine analysis: A critical evaluation and discussion of recent applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 691, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, P. What do metals tell us about wine? Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R.; Yildirim, E. A new ultrasound assisted-cloud point extraction method for the determination of trace levels of tin and antimony in food and beverages by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2960–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R.; Kir, U. Ultrasound assisted-cloud point extraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for selective preconcentration and determination of As(v) in selected water and beverage samples. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6629–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, R.; Altunay, N. Determination of total Sn in some canned beverages by FAAS after separation and preconcentration. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filik, H.; Aksu, D. Determination of vanadium in food samples by cloud point extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R. A simple, inexpensive and convenient procedure for determination of inorganic Sb species in milk and beverage samples in PET containers by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 9850–9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Vicente-Martínez, Y.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Determination of very low amounts of free copper and nickel ions in beverages and water samples using cloud point extraction assisted by silver nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3786–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczycha-Madeja, A.; Welna, M.; Jedryczko, D.; Pohl, P. Developments and strategies in the spectrochemical elemental analysis of fruit juices. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 55, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, N.K.; Gürkan, R. Preconcentration and determination of trace vanadium(V) in beverages by combination of ultrasound assisted-cloud point extraction with spectrophotometry. Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R.; Kir, U. Spectrophotometric determination of low levels arsenic species in beverages after ion-pairing vortex-assisted cloud-point extraction with acridine red. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürkan, R.; Altunay, N. Determination of trace cadmium in nonalcoholic beverages by coupling cloud point extraction with spectrophotometry. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 63, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gürkan, R.; Aksoy, Ü.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Akçay, M. Determination of low levels of molybdenum (VI) in food samples and beverages by cloud point extraction coupled with flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 32, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Gürkan, R. An inexpensive and sensitive method for speciative determination of Sn(IV), Sn(II), and total Sn as Sn(IV) in selected beverages by micellar improved spectrophotometry. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmohammadi, P.; Taheri, A.; Rezayatizad, Z. Extraction and determination of mercury from spring water, beverage and rice samples using combined microwave-assisted cloud point and dispersive-solid phase extraction in micellar media. Water Environ. J. 2023, 37, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Niknam, K.; Niknam, E.; Soylak, M. Application of cloud point extraction for copper, nickel, zinc and iron ions in environmental samples. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2009, 56, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, H.; Giray, D. Cloud point extraction for speciation of iron in beer samples by spectrophotometry. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Shokrollahi, A.; Mehrnoosh, R.; Hossaini, O.; Soylak, M. Combination of cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry for preconcentration and determination of trace iron in environmental and biological samples. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2008, 6, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Moraes, L.M.B.; Rocha, F.R.P.; Virgilio, A. Sample preparation and spectrometric methods for elemental analysis of milk and dairy products—A review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, R.; Korkmaz, S.; Altunay, N. Preconcentration and determination of vanadium and molybdenum in milk, vegetables and foodstuffs by ultrasonic-thermostatic-assisted cloud point extraction coupled to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 155, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, N.K.; Gürkan, R. Application of ultrasound-assisted cloud-point extraction and spectrophotometry for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of copper(II) in beverages. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.P.; Zhu, X.S.; Wei, Y.X.; Wu, S.B. Cloud point extraction-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for separation/analysis of aqueous-exchangeable and unaqueous-exchangeable selenium in tea samples. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, E.; Kaykhaii, M. Determination of zinc, copper, and mercury in water samples by using novel micro cloud point extraction and UV-Vis spectrophotometry. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 12, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, S.S.; Ocakoglu, K.; Merdivan, M. Separation and preconcentration of mercury in water samples by ionic liquid supported cloud point extraction and fluorimetric determination. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garoub, M.M.; Gouda, A.A. An efficient ionic liquid-based cloud point extraction to preconcentrate mercury in environmental samples and hair of occupational workers before spectrophotometric detection. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2022, 36, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfarnia, S.; Shakerian, F.; Shabani, A.M.H. Suspended nanoparticles in surfactant media as a microextraction technique for simultaneous separation and preconcentration of cobalt, nickel and copper ions for electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry determination. Talanta 2013, 106, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourreza, N.; Naghdi, T. Combined cloud point-solid phase extraction by dispersion of TiO2 nanoparticles in micellar media followed by semi-microvolume UV-vis spectrophotometric detection of zinc. Talanta 2014, 128, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakerian, F.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Esfahani, G.S. Preconcentration and determination of lead(II) by microextraction based on suspended cadion covered zirconia nanoparticles in a surfactant media. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Muñoz-Sandoval, M.J.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Cloud point microextraction involving graphene oxide for the speciation of very low amounts of chromium in waters. Talanta 2017, 172, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Marín-Hernández, J.J.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometric determination of vanadium after cloud point extraction in the presence of graphene oxide. Spectrochim. Acta Part B-At. Spectrosc. 2018, 143, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussein, N.M.; Muslim, N.M.; Hussien, M.A.; Azooz, E.A.; Al-Mulla, E.A.J. Green preconcentration procedures for the determination of aluminium in bottled beverages prior to electrothermal atomic absorption spectroscopy: A comparative study with environmental assessment tools. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2024, 21, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; He, M.; Chen, B.B. Nanometer-sized materials for solid-phase extraction of trace elements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2685–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekouei, S.; Nekouei, F.; Ulusoy, H.I.; Noorizadeh, H. Simultaneous application of cloud point and solid-phase extraction for determination of Fe(III) and Cu(II) ions by using SnO2 nanopowder in micellar medium. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 12653–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| - uses small volumes of nonionic surfactants (instead of high volumes of more harmful organic solvents) | - uses relatively high energy consumption (mainly in conventional CPE procedures) |
| - high extraction efficiency achieved (even with highly complex matrices) | - optimization is time-consuming and labor-intensive (in conventional as well as innovative CPE procedures) |
| - significant preconcentration factors achieved (due to the small volumes of surfactant-rich phase obtained) | - requires the use of a solvent to dilute the final extract (which, inter al., leads to a decrease in the PF) |
| - availability of surfactants in high-purity grades, their stability, non-volatility, low toxicity, and low flammability | - the phases must be separated with utmost precision (in order to achieve reproducible results) |
| - relatively low cost | - developing a flow-based arrangement is not easy |
| - easy of instrumentation | - even greener variants need further improvement |
| Surfactant | Molecular Formula | Type | CPT (°C) | CMC (mmol/L) | ρ (g/mL) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triton X-114 | (C2H4O)nC14H22O, n = 7–8 | Polyoxyethylene octyl phenyl ether | 23–24 | 0.20–0.35 | 1.058 | [9] |
| Triton X-100 | (C2H4O)nC14H22O, n = 9–10 | Polyoxyethylene octyl phenyl ether | 64–65 | 0.17–0.30 | 1.070 | [9] |
| Triton X-45 | (C2H4O)nC14H22O, n = 4–5 | Polyoxyethylene octyl phenyl ether | Disp. | 136 * | 1.031 | [10] |
| PONPE 5.0 | (C2H4O)nC15H24O, n = 5 | Polyoxyethylene nonyl phenyl ether | 15–17 | 0.57 | 1.040 | [11] |
| PONPE 7.5 | (C2H4O)nC15H24O, n = 7.5 | Polyoxyethylene nonyl phenyl ether | 5–20 | 0.085 | 1.060 | [9] |
| Tween 20 | C58H114O26 | Polyoxyethylene sorbitol ester | 76 | 0.06 | 1.095 | [12] |
| Tween 80 | C64H124O26 | Polyoxyethylene sorbitol ester | 65 | 0.015 | 1.121 | [12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hagarová, I.; Urík, M. Cloud Point Extraction in Beverage Analysis: Innovations and Applications for Trace Elements. Beverages 2024, 10, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10030067
Hagarová I, Urík M. Cloud Point Extraction in Beverage Analysis: Innovations and Applications for Trace Elements. Beverages. 2024; 10(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagarová, Ingrid, and Martin Urík. 2024. "Cloud Point Extraction in Beverage Analysis: Innovations and Applications for Trace Elements" Beverages 10, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10030067
APA StyleHagarová, I., & Urík, M. (2024). Cloud Point Extraction in Beverage Analysis: Innovations and Applications for Trace Elements. Beverages, 10(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages10030067






