Exploring the Epiphytic Microbial Community Structure of Forage Crops: Their Adaptation and Contribution to the Fermentation Quality of Forage Sorghum during Ensiling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Forage Cultivation and Preparing the Inoculum
2.2. Silage Making and Treatments
2.3. Silage Fermentation Analysis and Microbial Counts
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.6. Analyzing Statistical Data
3. Results
3.1. Properties of Sterilized and Fresh Forage Sorghum Prior to Ensiling
3.2. Dynamics of Fermentation Products, Chemical and Microbial Composition of Forage Sorghum Silage
3.3. Bacterial Abundance and Diversity of Forage Sorghum Silage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, L.; Kristensen, E.F.; Moset, V.; Ward, A.J.; Møller, H.B. Ensiling of tall fescue for biogas production: Effect of storage time, additives and mechanical pretreatment. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 47, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Rinne, M. Highlights of progress in silage conservation and future perspectives. Grass Forage Sci. 2018, 73, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikmeyer, F.G.; Petra, K.; Andreas, S. Metagenome analyses reveal the influence of the inoculant Lactobacillus buchneri CD034 on the microbial community involved in grass ensiling. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muck, R. Recent advances in silage microbiology. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Ali Kaka, N.; Shao, T. Abundance and diversity of epiphytic microbiota on forage crops and their fermentation characteristic during the ensiling of sterile sudan grass. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Parker, D.; Allen, D.J.; Tsesmetzis, N. Dynamic bacterial and fungal microbiomes during sweet sorghum ensiling impact bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, C.A.; Maeda, R.N.; Santa Anna, L.M.M.; Pereira, N. Sweet sorghum as a whole-crop feedstock for ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 94, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzo, A.F.; Carvalho, G.G.P.; Santos, E.M.; Bezerra, H.F.C.; Silva, T.C.; Pereira, G.A.; Ramos, R.C.S. Agronomic Evaluation of Sorghum Hybrids for Silage Production Cultivated in Semiarid Conditions. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.; Idler, C.; Heiermann, M. Improving aerobic stability and biogas production of maize silage using silage additives. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E. Silage microbiology and its control through additives. Rev. Brasil. Zoot. 2010, 39, 39183–39191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardes, T.; Daniel, J.; Adesogan, A.; McAllister, T.; Drouin, P.; Nussio, L.; Huhtanen, P.; Tremblay, G.; Bélanger, G.; Cai, Y. Silage review: Unique challenges of silages made in hot and cold regions. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4001–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Q.; Xin, G.; Zhang, J. Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their inoculating effects on the silage fermentation at high temperature. Lett. Appl. Microbial. 2013, 56, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulfam, A.; Guo, G.; Tajebe, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, X.; Bai, Y.; Saho, T. Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effect on the fermentation quality of Napier grass silage at three high temperatures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureenok, S.; Namihira, T.; Kawamoto, Y.; Nakada, T. Additive effects of fermented juice of epiphytic lactic acid bacteria on the fermentative quality of guinea grass (Panicum maximum Jacq.) silage. Grassl. Sci. 2005, 51, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, N.; Si, B.; Tu, Y.; Ma, T.; Diao, Q. Effects of different source additives and wilt conditions on the pH value, aerobic stability, and carbohydrate and protein fractions of alfalfa silage. Anim. Sci. 2017, 88, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogodiniyai Kasmaei, K.; Dicksved, J.; Spörndly, R.; Udén, P. Separating the effects of forage source and field microbiota on silage fermentation quality and aerobic stability. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 72, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Ali Kaka, N.; Shao, T. Effects of various epiphytic microbiota inoculation on the fermentation quality and microbial community dynamics during the ensiling of sterile Napier grass. J. Appl. Microbial. 2020, 130, 1466–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junges, D.; Morais, G.; Spoto, M.H.F.; Santos, P.S.; Adesogan, A.T.; Nussio, L.G.; Daniel, J.L.P. Short communication: Influence of various proteolytic sources during fermentation of reconstituted corn grain silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9048–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Assessment of inoculating various epiphytic microbiota on fermentative profile and microbial community dynamics in sterile Italian ryegrass. J. Appl. Microbial. 2020, 129, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Microbial diversity and fermentation profile of red clover silage inoculated with reconstituted indigenous and exogenous epiphytic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, G.; Yu, C.; Zhang, J.; Shimojo, M.; Shao, T. The effects of replacement of whole—Plant corn with oat and common vetch on the fermentation quality, chemical composition and aerobic stability of total mixed ration silage in Tibet. Anim. Sci. J. 2015, 86, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Desta, S.T.; Dong, Z.; Mugabe, W.; Shao, T. Characterization of Enterococcus faecalis JF85 and Enterococcus faecium Y83 isolated from Tibetan yak (Bos grunniens) for ensiling Pennisetum sinese. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, U.; Muscato, T.V.; Sniffen, C.J.; Soest, P.J.V. Nitrogen Fractions in Selected Feedstuffs. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.V.; Robertson, J.; Lewis, B. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Microbial community dynamics and their contributions to organic acid production during the early stage of the ensiling of Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum). Grass Forage Sci. 2020, 75, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ni, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, F. Fermentation characteristics, chemical composition and microbial community of tropical forage silage under different temperatures. Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussio, L. Silage Production and Utilisation. In Proceedings of the XIVth International Silage Conference, a Satellite Workshop of the XXth International Grassland Congress, Belfast, Northern Ireland, July 2005; Park, P.S., Stronge, M.D., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shuai, Y.; Feng, G.; Ran, Q.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Microbial communities and natural fermentation of corn silages prepared with farm bunker-silo in Southwest China. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, S.J.; Edwards, R.A.; McDonald, P. Changes in the nitrogenous components of gamma—Irradiated and inoculated ensiled ryegrass. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1986, 37, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted Italian ryegrass silage inoculated with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri. Lett. Appl. Microbial. 2011, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, K.; Ulric, A.; Idler, C.; Klocke, M. Bacterial community dynamics during ensiling of perennial ryegrass at two compaction levels monitored by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Appl. Microbial. 2016, 120, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.; Ávila, C.; Bernardes, T.; Pereira, M.; Santos, C.; Schwan, R. Fermentation profile and identification of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts of rehydrated corn kernel silage. J. Appl. Microbial. 2017, 122, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Danner, H.; Mayrhuber, E.; Braun, R. The aerobic stability of silages influenced by metabolites of lactic acid bacteria. Meded. Rijksuniv. Te Gent. Fak. Van De Landbouwkd. En Toegep. Biol. Wet. 2001, 66, 459–461. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.; Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Franco, D. Chapter 3–Main Groups of Microorganisms of Relevance for Food Safety and Stability: General Aspects and Overall Description. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 53–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, N.B.; Sloth, K.H.; Hjberg, O.; Spliid, N.H.; Jensen, C.; Thgersen, R. Efects of microbial inoculants on corn silage fermentation, microbial contents, aerobic stability, and milk production under feld conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3764–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. Am. Soc. Agron. 2003, 42, 31–94. [Google Scholar]
- Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Holmes, B.J.; Muck, R.E. Silage review: Factors affecting dry matter and quality losses in silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Martinez-Tuppia, C.; Queiroz, O.C.M.; Jiang, Y.; Drouin, P.; Wu, F.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Mycotoxins in silage: Occurrence, effects, prevention, and mitigation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, A.L.; Cockburn, J.E.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Merry, R.J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria in inoculants on changes in amino acid composition during ensilage of sterile and non-sterile ryegrass. J. Appl. Microbial. 2001, 89, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbial. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A.; Heron, J. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed; Chalcombe Publications: Marlow, UK, 1991; p. 340. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Ogunade, I.M.; Weinberg, Z.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Foodborne pathogens in silage and their mitigation by silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Minh, T.T.; Tu, T.T.M.; Tsuruta, T.; Pang, H.; Nishino, N. Comparative microbiota assessment of wilted Italian ryegrass, whole crop corn, and wilted alfalfa silage using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and next-generation sequencing. Appl. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela, S. Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appl. Microbio. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duniere, L.; Xu, S.; Long, J.; Elekwachi, C.; Mcallister, T.A. Bacterial and fungal core microbiomes associated with small grain silages during ensiling and aerobic spoilage. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J. Factors influencing the distribution of lactic acid bacteria on Pennisetum grasses. Grassl. Sci. 2017, 63, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiumei, X.U.; Chen, G.Y. Occurrence of soluble carbohydrates on the phylloplane of maize (Zea mays L.): Variations in relation to leaf heterogeneity and position on the plant. New Phytol. 1990, 115, 609–615. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, S.; Zimmermann, C. Selection of specific strains of silage bacteria for different environmental niches. Proc. 2nd Forage Symp. 1989, 27, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.M.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an Inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from Forage Crops on Silage Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Terada, F. Natural populations of lactic acid bacteria isolated from vegetable residues and silage fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 3136–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



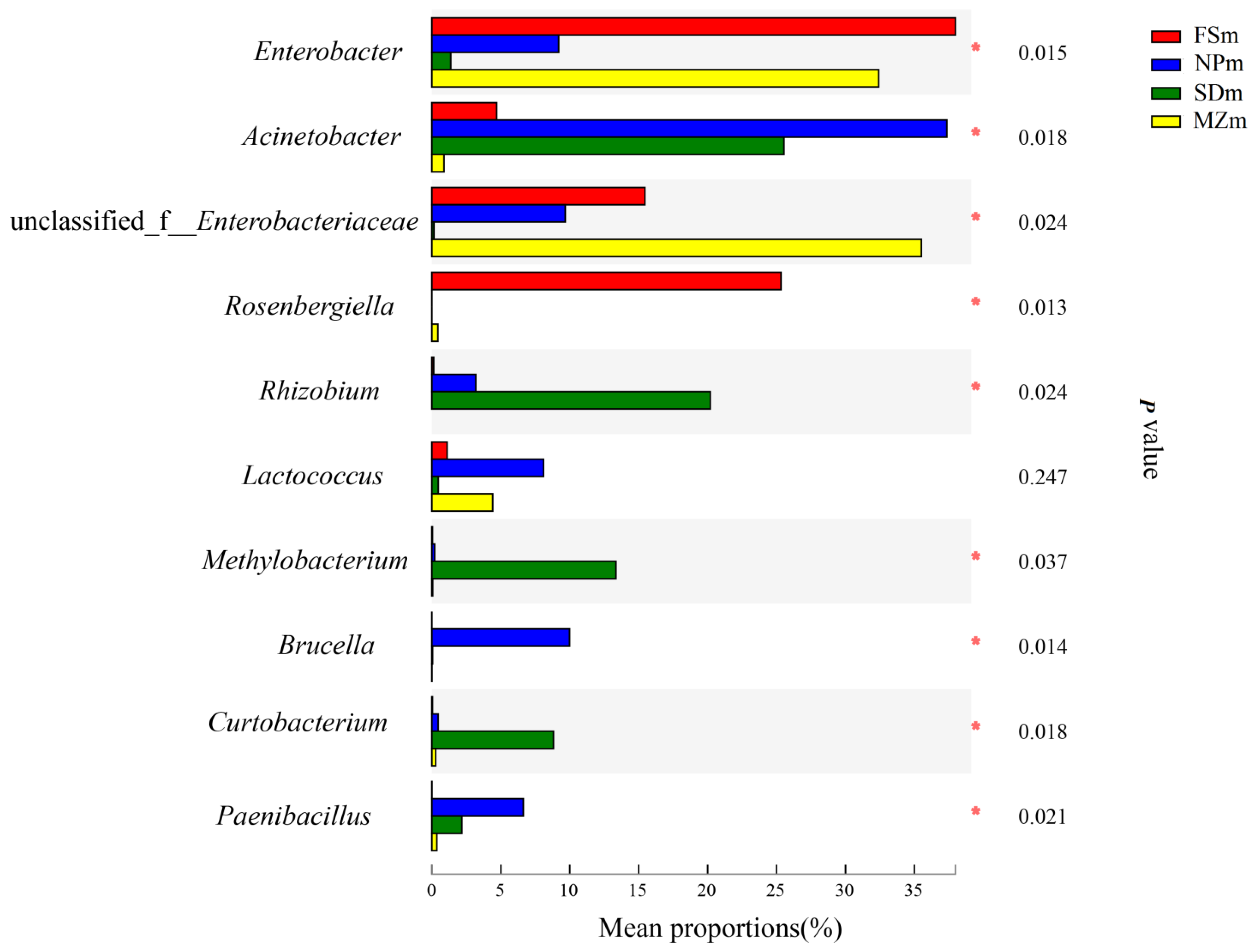

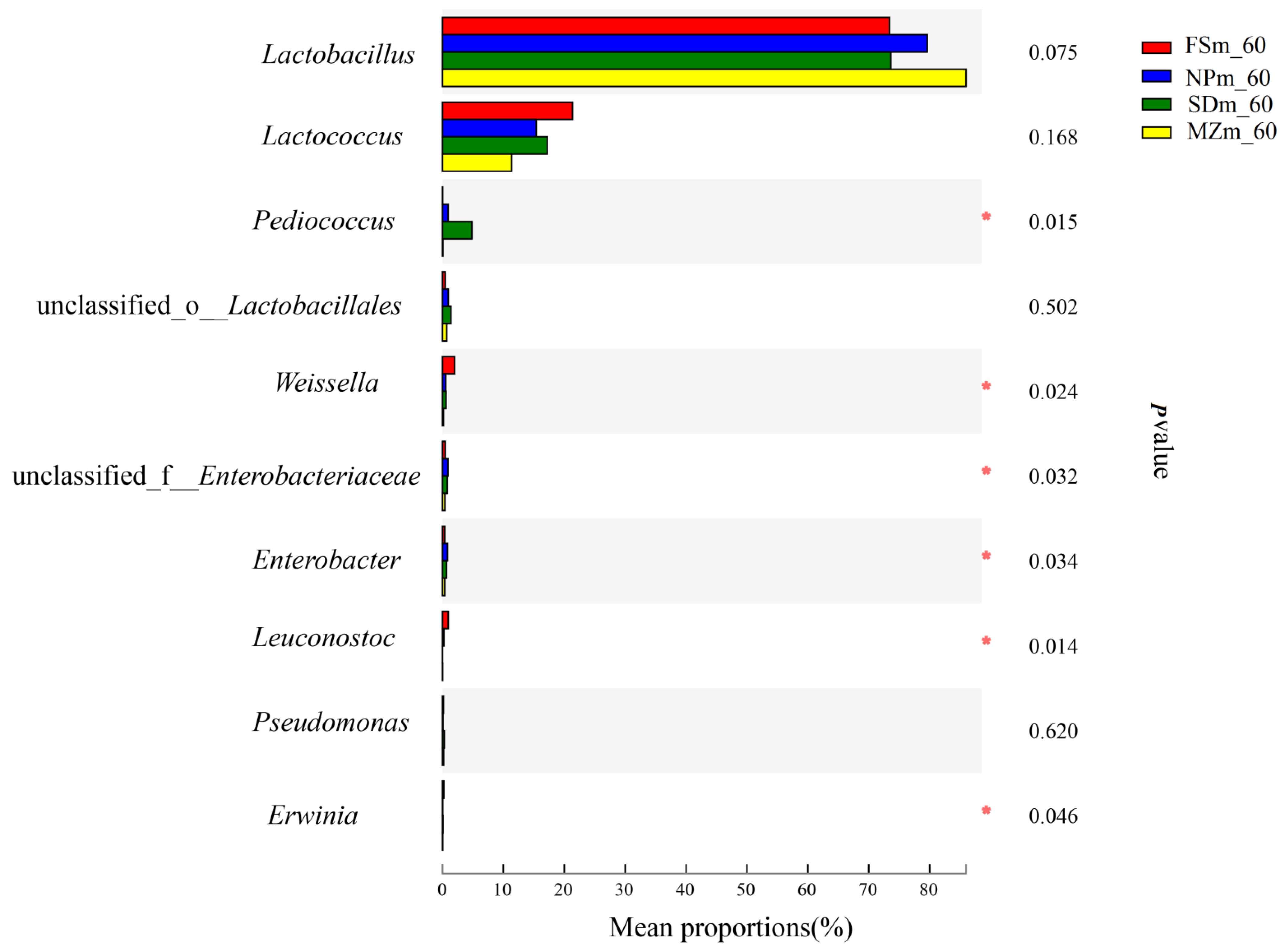
| Parameter | Fresh Forage Sorghum | Sterilized Forage Sorghum | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter (g/kg FW) | 278 | 277 | 0.342 |
| pH | 5.86 | 5.81 | 0.321 |
| Crude protein (g/kg DM) | 36.5 | 36.0 | 0.421 |
| Water soluble carbohydrate (g/kg DM) | 170 | 169 | 0.213 |
| Buffering capacity (mEq/kg DM) | 283 | 282 | 0.235 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | 603 | 602 | 0.211 |
| Acid detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | 281 | 280 | 0.186 |
| Lactic acid bacteria (Log10 CFU/g FW) | 3.33 | ND | - |
| Aerobic bacteria (Log10 CFU/g FW) | 8.98 | ND | - |
| Yeast (Log10 CFU/g FW) | 5.90 | ND | - |
| Enterobacteriaceae (Log10 CFU/g FW) | 8.14 | ND | - |
| Parameter 1 | Treatments 2 | Storage Time (Days) | SEM 3 | p-Values 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | 60 | T | D | T × D | |||
| pH | ST | 5.45 Aa | 5.30 Aa | 5.32 Aa | 5.34 Aa | 5.31 Aa | 5.29 Aa | 0.072 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 5.36 Aa | 4.30 BCb | 3.93 Bc | 3.91 Bc | 3.64 Cc | 3.60 Cd | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 4.99 Ba | 4.18 Cb | 3.92 Bc | 3.94 Bc | 3.62 Cd | 3.74 Bd | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 4.96 Ba | 4.24 Cb | 3.93 Bc | 3.91 Bc | 3.77 Bc | 3.76 Bc | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 5.34 Aa | 4.70 Bb | 4.06 Bc | 3.80 Bdc | 3.57 Cd | 3.59 Cd | - | - | - | - | |
| LA (g/kg DM) | ST | 0.56 Cb | 0.64 Dab | 0.93 aCb | 0.81 Dab | 0.98 Ca | 0.87 Bab | 2.21 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 2.73 BCd | 13.6 Bc | 16.6 Bc | 47.2 Bb | 60.6 Ab | 73.3 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 5.60 Ac | 16.4 Ab | 20.9 Bb | 57.5 Aa | 59.3 Aa | 62.3 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 4.00 ABe | 14.5 ABd | 17.2 Bd | 36.4 Cc | 46.8 Bb | 56.0 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 2.00 BCd | 11.0 Cc | 35.9 Ab | 55.7 Aa | 63.0 Aa | 76.7 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| AA (g/kg DM) | ST | 0.13 Bb | 0.26 Bb | 0.26 Bb | 0.30 Bb | 0.57 Ba | 0.71 Ca | 0.791 | <0.001 | <0.018 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 2.00 Ad | 6.33 Ac | 8.67 Ac | 13.7 Ab | 17.0 Aa | 19.0 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 2.33 Ae | 6.00 Ad | 9.00 Ac | 13.0 Ab | 17.7 Aa | 24.3 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 1.67 ABe | 6.00 Ad | 9.33 Ac | 12.7 Ab | 15.3 Ab | 23.7 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 1.00 ABc | 3.00 Bc | 7.00 Ab | 11.3 Ab | 16.3 Aab | 18.7 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| LA/AA ratio (g/kg DM) | ST | 4.49 Aa | 2.46 ABbc | 3.59 Aab | 3.04 Aabc | 1.75 Bc | 1.30 Cc | 0.693 | <0.001 | <0.019 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 1.56 Bc | 2.05 Bbc | 1.91 Abc | 3.51 Aa | 3.05 Aab | 3.34 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 2.43 ABb | 2.79 ABb | 2.35 Ab | 7.67 Aa | 3.36 Ab | 2.87 Bb | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 2.83 ABa | 2.47 ABa | 1.92 Aa | 2.88 Aa | 3.06 Aa | 2.51 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 2.00 ABa | 3.83 Aa | 30.0 Aa | 10.5 Aa | 3.66 Aa | 3.51 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| Parameter 1 | Treatments 2 | Storage Time (Days) | SEM 3 | p-Values 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | 60 | T | D | T × D | |||
| BA (g/kg DM) | ST | 0.73 Aa | 0.66 Aa | 0.72 Aa | 0.65 Ba | 0.68 Aa | 0.84 Aa | 0.041 | <0.001 | 0.021 | 0.54 |
| FSm | 0.74 Ab | 0.81 Ab | 0.85 Ab | 1.10 Aab | 1.43 Aa | 1.08 Aab | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 0.97 Aa | 0.71 Aa | 1.39 Aa | 1.02 ABa | 1.19 Aa | 1.43 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 0.85 Aa | 1.35 Aa | 1.21 Aa | 1.07 Aa | 1.13 Aa | 1.51 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 0.90 Aa | 1.29 Aa | 1.44 Aa | 0.84 ABa | 1.38 Aa | 1.27 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| Ethanol (g/kg DM) | ST | 4.47 Aa | 5.06 Aa | 4.33 Ba | 4.85 Ca | 4.17 Ba | 4.33 Ca | 0.061 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 4.42 Ae | 6.94 Aed | 8.67 Acd | 11.1 ABbc | 12.5 Ab | 18.3 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 4.70 Ad | 7.33 Ac | 9.00 Ac | 12.3 Ab | 14.2 Aab | 15.0 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 5.04 Ad | 7.53 Acd | 6.20 ABd | 11.5 ABbc | 12.4 Ab | 14.7 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 5.33 Ae | 6.22 Ade | 9.00 Acd | 10.7 Bbc | 13.3 Aab | 17.3 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| Parameter 1 | Treatments 2 | Storage Time (Days) | SEM 3 | p-Values 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | 60 | T | D | T × D | |||
| DM (g/kg FW) | ST | 274 Aa | 274 ABa | 274 ABa | 273 Aa | 272 Aa | 271 Aa | 1.89 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 275 Aa | 274 Ba | 273 Ba | 272 Aab | 272 Aab | 271 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 276 Aa | 275 ABa | 274 ABab | 272 Aabc | 270 Bbc | 266 Bc | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 278 Aa | 278 Aa | 277 Aab | 275 Aab | 273 Abc | 267 Bc | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 277 Aa | 276 ABa | 276 Aa | 274 Aab | 273 Aab | 272 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| NH3–N (g/kg TN) | ST | 6.55 Cd | 8.88 Cd | 15.5 Bc | 19.0 Bc | 24.4 Cb | 30.9 Ca | 1.93 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 19.9 ABd | 32.7 Ac | 45.5 Ab | 48.5 Ab | 51.5 Bb | 68.0 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 18.5 Be | 31.5 Ad | 42.1 Ac | 49.0 Ab | 53.8 ABb | 66.7 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 24.6 Af | 36.0 Ae | 44.0 Ad | 50.3 Ac | 57.0 ABb | 72.3 Aa | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 15.6 Bd | 21.8 Bd | 41.3 Ac | 50.2 Ab | 59.5 Aa | 60.2 Ba | - | - | - | - | |
| WSC (g/kg DM) | ST | 186 Aa | 185 Aab | 183 Aabc | 181 Abc | 181 Abc | 180 Ac | 2.12 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 187 Aa | 170 Bb | 122 Cc | 110 Dd | 97.0 CDe | 89.5 Bf | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 174 Ba | 158 Cb | 139 Bc | 125 Bd | 112 Be | 91.0 Bf | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 170 Ba | 151 Cb | 135 Bc | 119 BCd | 102 Ce | 88.0 Bf | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 189 Aa | 153 Cb | 136 Bc | 115 CDd | 95.7 De | 80.2 Cf | - | - | - | - | |
| Parameter 1 | Treatments 2 | Storage Time (Days) | SEM 3 | p-Values 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 7 | 15 | 30 | 60 | T | D | T × D | |||
| LAB (Log 10 CFU/g FW) | ST | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.313 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 4.31 Ad | 7.19 ABb | 8.45 Aa | 8.57 Aa | 6.45 Bbc | 5.78 Ac | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 5.06 Ac | 7.35 Ab | 8.86 Aa | 8.67 Aa | 8.25 Aab | 5.40 Ac | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 5.06 Ac | 7.31 Ab | 8.65 Aa | 8.99 Aa | 8.60 Aa | 5.33 Ac | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 3.93 Ac | 6.80 Bb | 7.87 Aab | 8.65 Aa | 8.08 Aab | 5.10 Ac | - | - | - | - | |
| Enterobacteriaceae (Log 10 CFU/g FW) | ST | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.142 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 4.64 Aa | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 5.39 Aa | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.01 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 3.66 Aa | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.02 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 4.70 Aa | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.00 Ab | <2.03 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| Yeast (Log 10 CFU/g FW) | ST | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.172 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| FSm | 4.08 Ba | 3.50 Bab | 3.22 Bb | 3.07 Ab | 3.03 Ab | 2.92 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| NPm | 4.29 Ba | 3.49 Bab | 3.76 ABab | 3.49 Aab | 3.07 Ab | 2.78 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| SDm | 4.70 Ba | 4.29 ABab | 3.75 ABab | 3.66 Aab | 3.66 Aab | 2.80 Ab | - | - | - | - | |
| MZm | 5.69 Aa | 4.70 Ab | 4.29 Ab | 3.99 Abc | 3.49 Acd | 2.87 Ad | - | - | - | - | |
| Treatments | Storage Time (Days) | Sequence Number | OTU Numbers | Shannon | Chao 1 | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSm | 0 | 46443 | 188 | 1.901 | 190.01 | 0.99852 |
| NPm | 0 | 41117 | 299 | 2.641 | 276.56 | 0.9980 |
| SDm | 0 | 39641 | 290 | 2.994 | 252.20 | 0.9985 |
| MZm | 0 | 46514 | 251 | 1.674 | 257.06 | 0.9982 |
| FSm | 3 | 52526 | 74.5 | 1.205 | 90.23 | 0.9993 |
| NPm | 3 | 56792 | 95.3 | 1.175 | 114.49 | 0.9990 |
| SDm | 3 | 33525 | 97.1 | 1.135 | 155.90 | 0.9988 |
| MZm | 3 | 60105 | 309 | 2.003 | 360.74 | 0.9973 |
| FSm | 60 | 61625 | 134 | 1.133 | 185.96 | 0.9986 |
| NPm | 60 | 53776 | 152 | 1.326 | 195.60 | 0.9984 |
| SDm | 60 | 59316 | 138 | 1.328 | 147.92 | 0.9987 |
| MZm | 60 | 58854 | 140 | 0.601 | 181.90 | 0.9985 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazar, M.; Ullah, M.W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Kaka, N.A.; Shao, T. Exploring the Epiphytic Microbial Community Structure of Forage Crops: Their Adaptation and Contribution to the Fermentation Quality of Forage Sorghum during Ensiling. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090428
Nazar M, Ullah MW, Wang S, Zhao J, Dong Z, Li J, Kaka NA, Shao T. Exploring the Epiphytic Microbial Community Structure of Forage Crops: Their Adaptation and Contribution to the Fermentation Quality of Forage Sorghum during Ensiling. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(9):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090428
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazar, Mudasir, Muhammad Wajid Ullah, Siran Wang, Jie Zhao, Zhihao Dong, Junfeng Li, Niaz Ali Kaka, and Tao Shao. 2022. "Exploring the Epiphytic Microbial Community Structure of Forage Crops: Their Adaptation and Contribution to the Fermentation Quality of Forage Sorghum during Ensiling" Bioengineering 9, no. 9: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090428
APA StyleNazar, M., Ullah, M. W., Wang, S., Zhao, J., Dong, Z., Li, J., Kaka, N. A., & Shao, T. (2022). Exploring the Epiphytic Microbial Community Structure of Forage Crops: Their Adaptation and Contribution to the Fermentation Quality of Forage Sorghum during Ensiling. Bioengineering, 9(9), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090428










