The Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper Genes Family Regulates the Jinggangmycin Mediated Immune Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, and Laodelphax striatellus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigation of the HDZIP Gene Family Members and Sequence Analysis in Oryza sativa
2.2. Phylogenetic Tree, Motif, and Digital Expression Analysis
2.3. Cis-Elements and Gene Ontology of the OsHDZIP Genes
2.4. Interactive Protein Analysis of the OsHDZIP Genes
2.5. Prediction of Putative MicroRNAs Targeting OsHDZIP Genes
2.6. Insect Rearing and Chemical and Stress Treatment
2.7. Expression Profiling of HDZIP Genes in Oryza sativa
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of OsHDZIP Genes in Oryza sativa
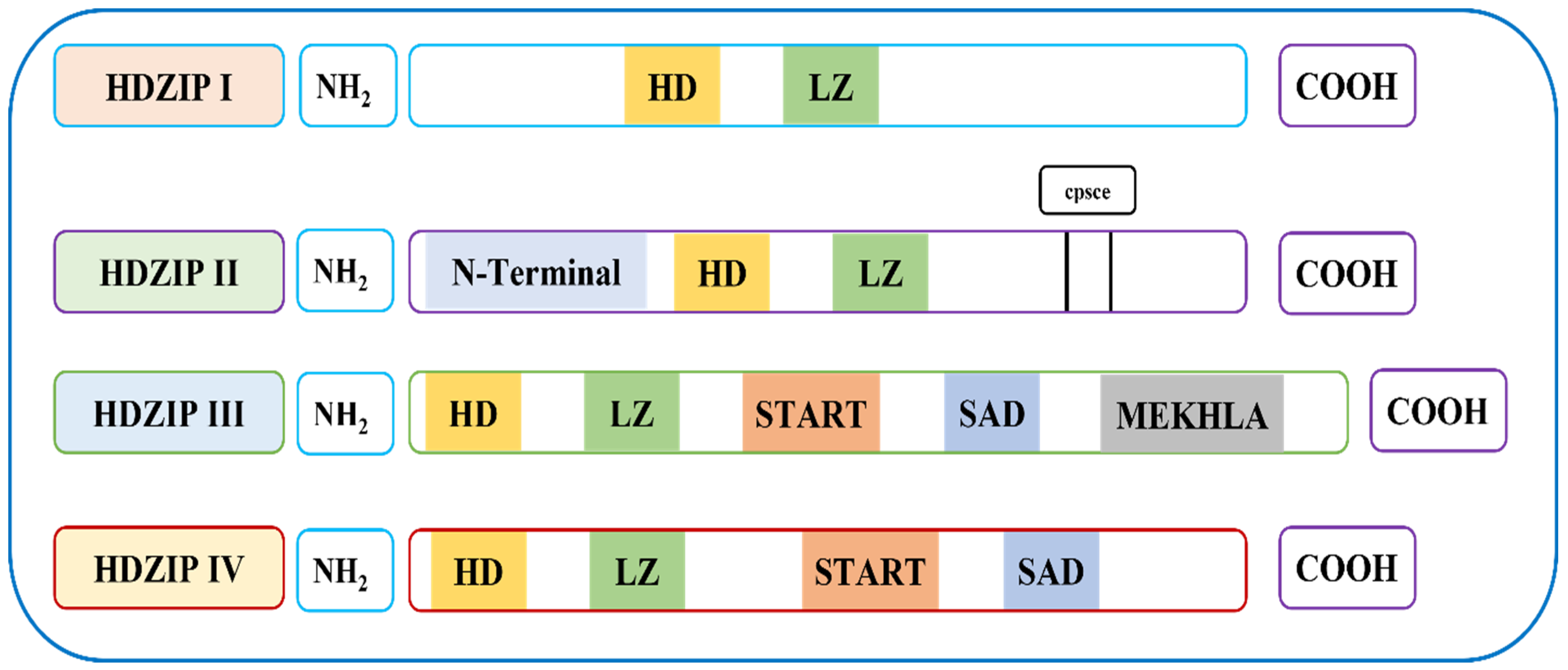
3.2. The OsHDZIP Genes Conservative Domain Analysis
3.3. Evolutionary Relationship of Oryza sativa HDZIP Genes
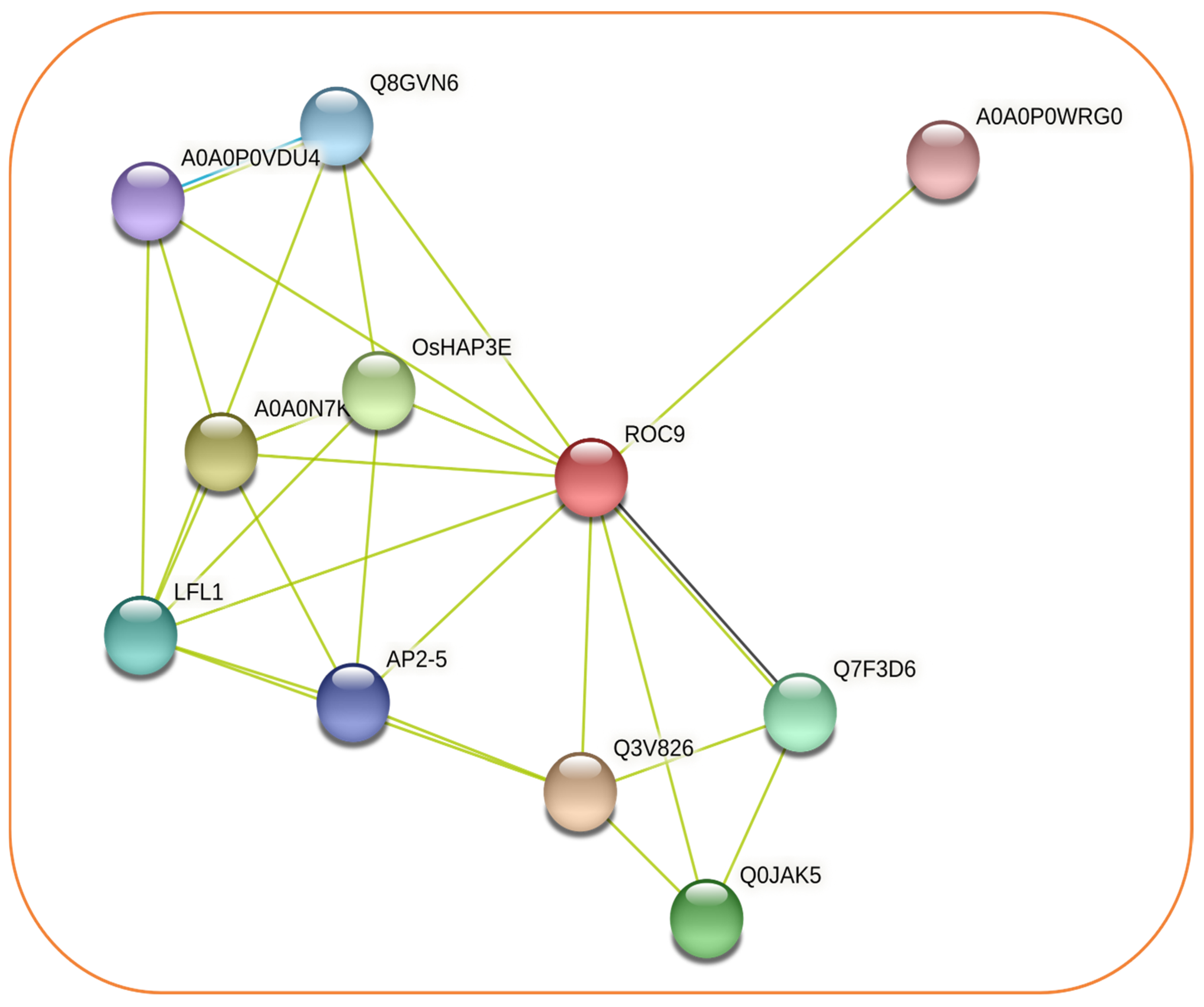
3.4. An Interactive Network of OsHDZIP Protein
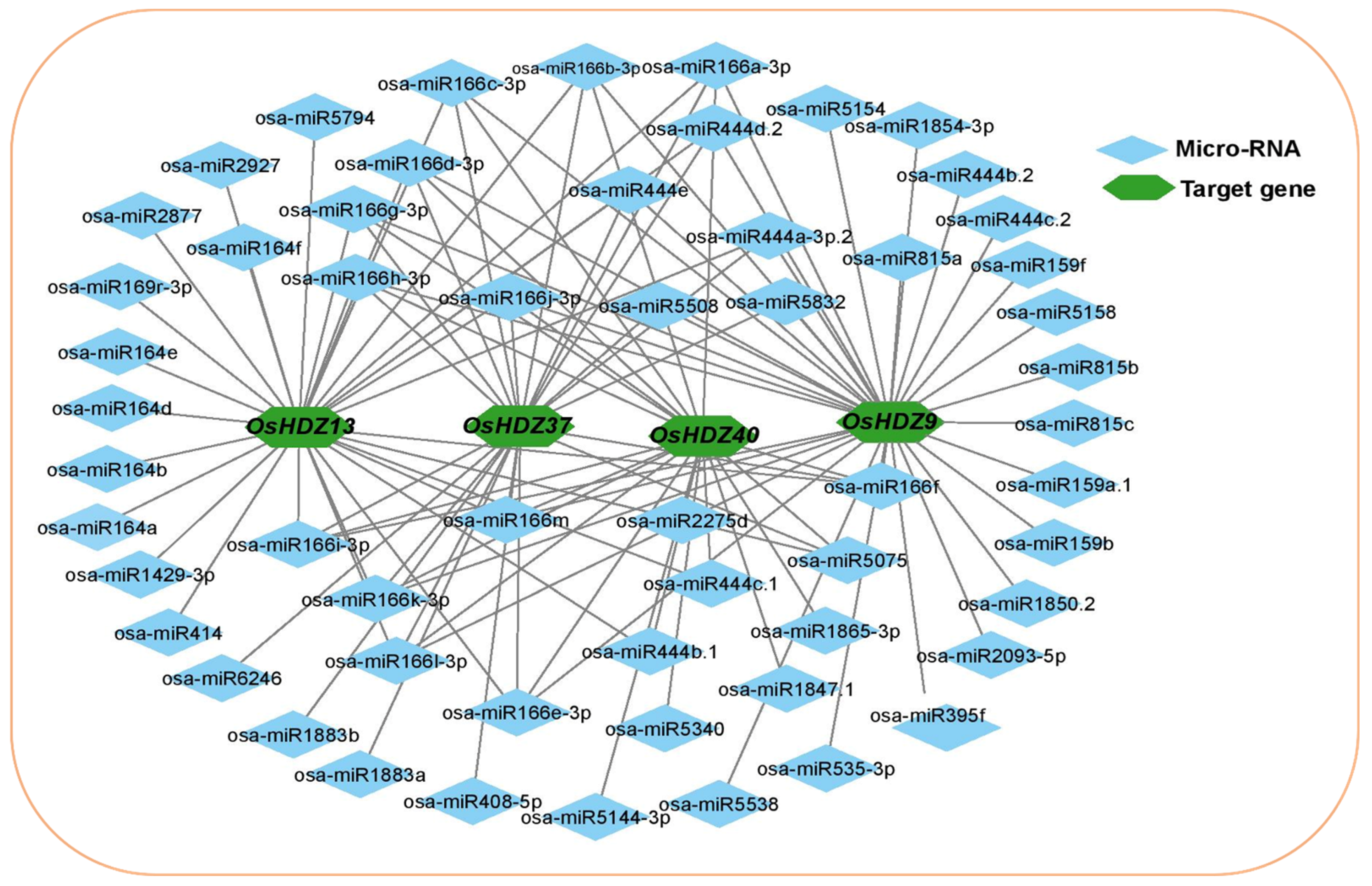
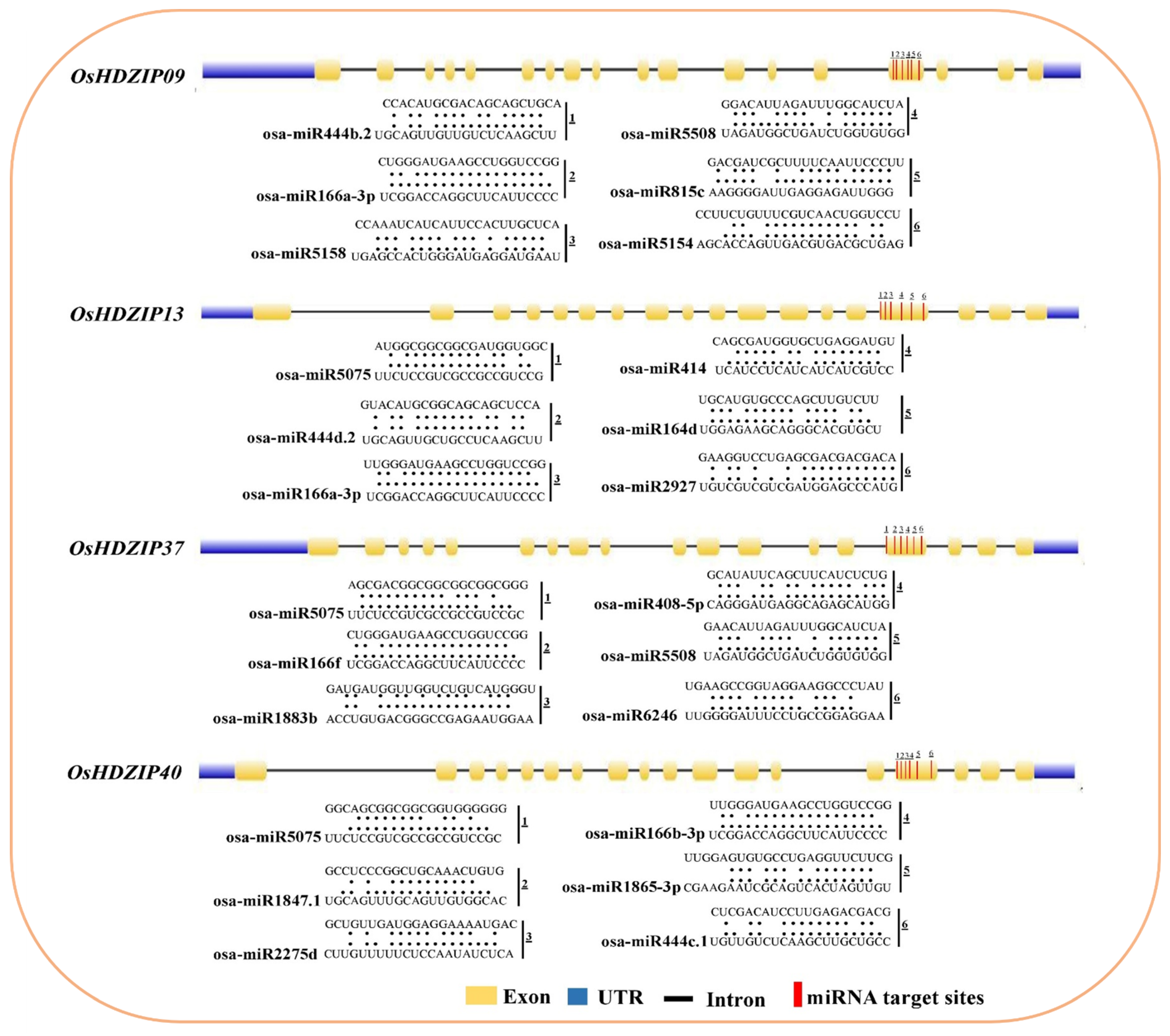
3.5. Prediction of the Potential MicroRNAs Targeting OsHDZIP Genes
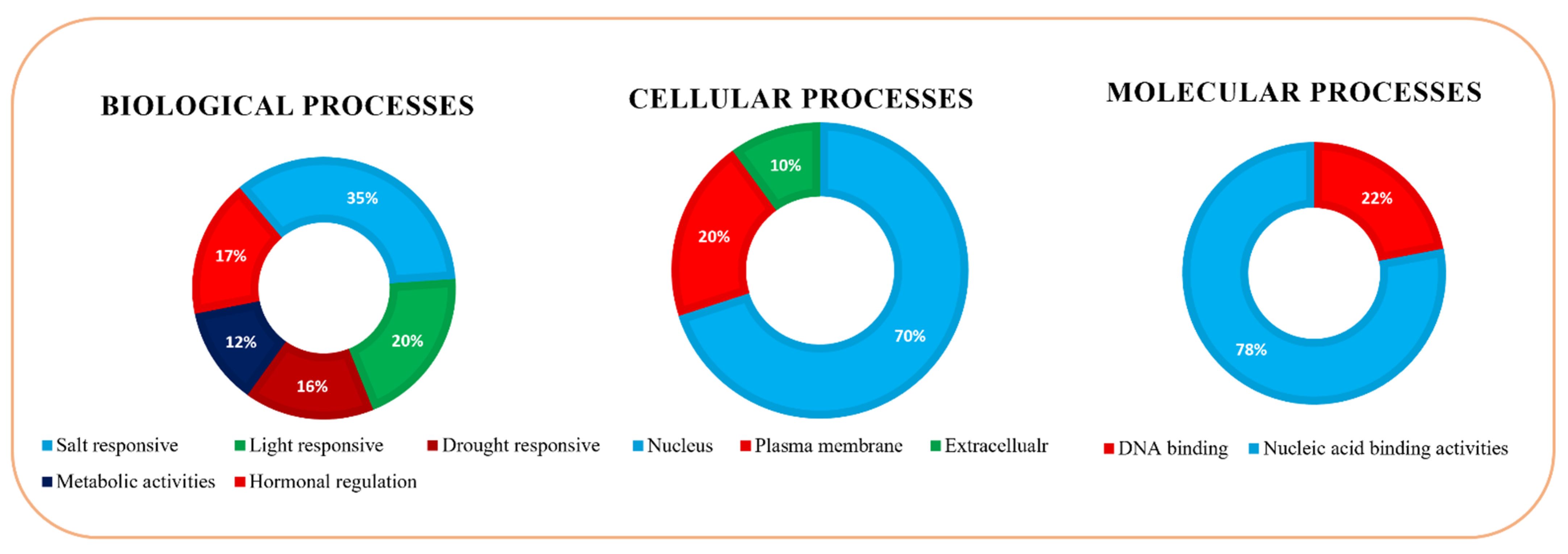
3.6. Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
3.7. Identified cis-Regulatory Elements in OsHDZIP Genes
3.8. Gene Structure, and Motif Patterns of OsHDZIP Genes
3.9. Microarray Expression Analysis of OsHDZIP Genes in Rice Tissues in Developmental Stages under Abiotic/Biotic Stresses and Hormonal Applications
3.9.1. Microarray Expression Analysis of HDZIP Genes in Developmental Stages
3.9.2. Expression Analysis of OsHDZIP Genes under Salinity
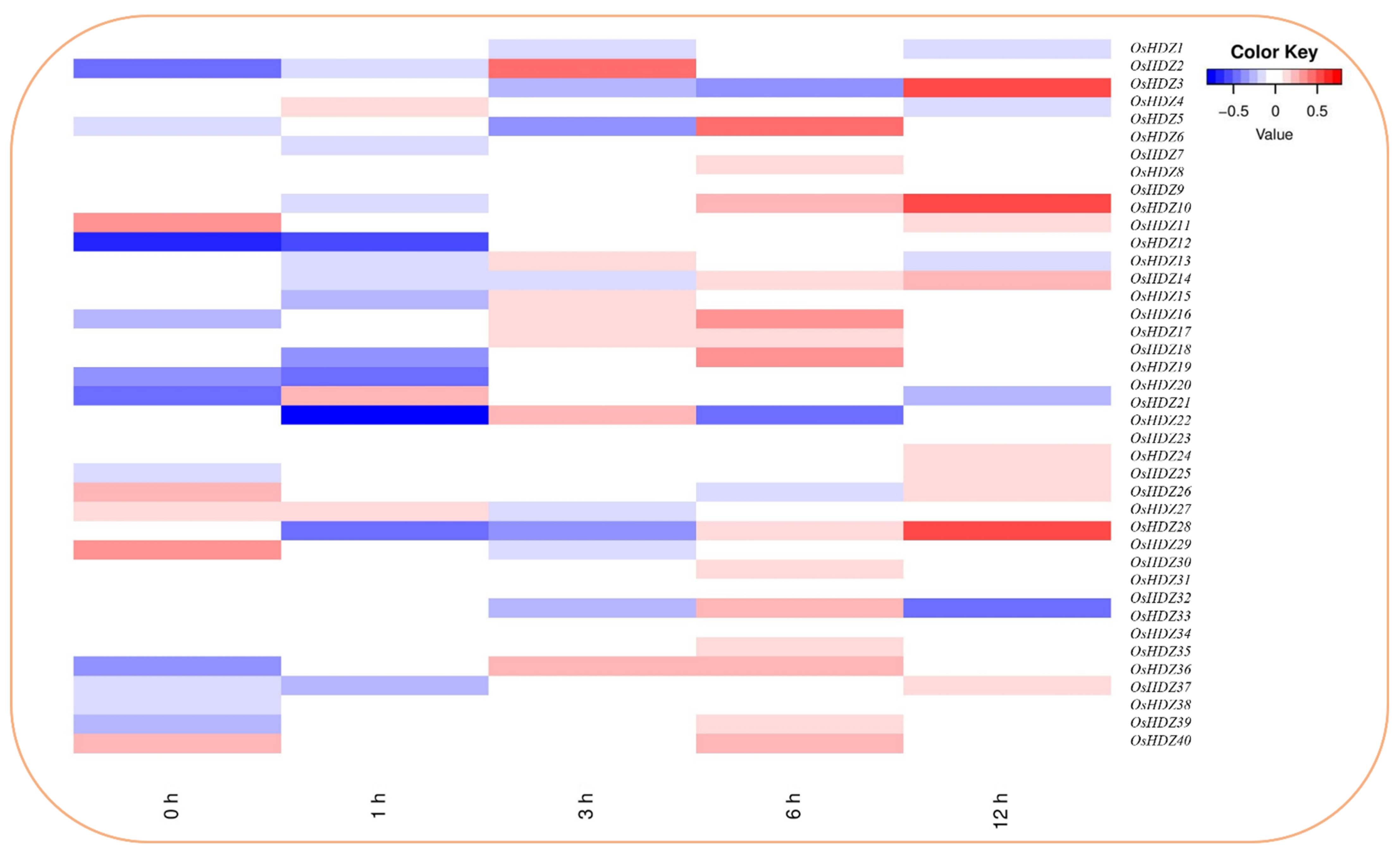
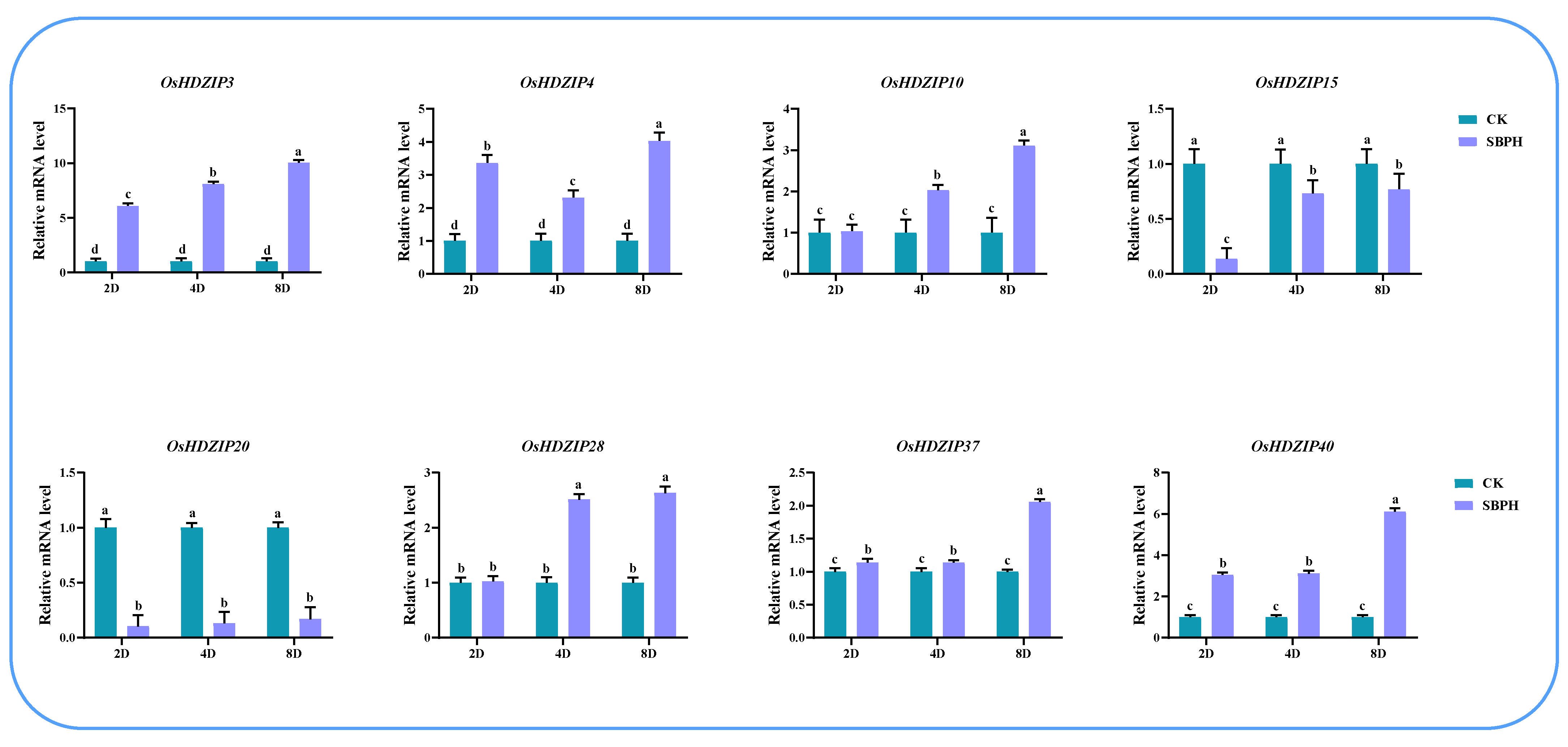
3.9.3. Expression Analysis of OsHDZIP Genes under BPH, SSB, and SSB_BPH
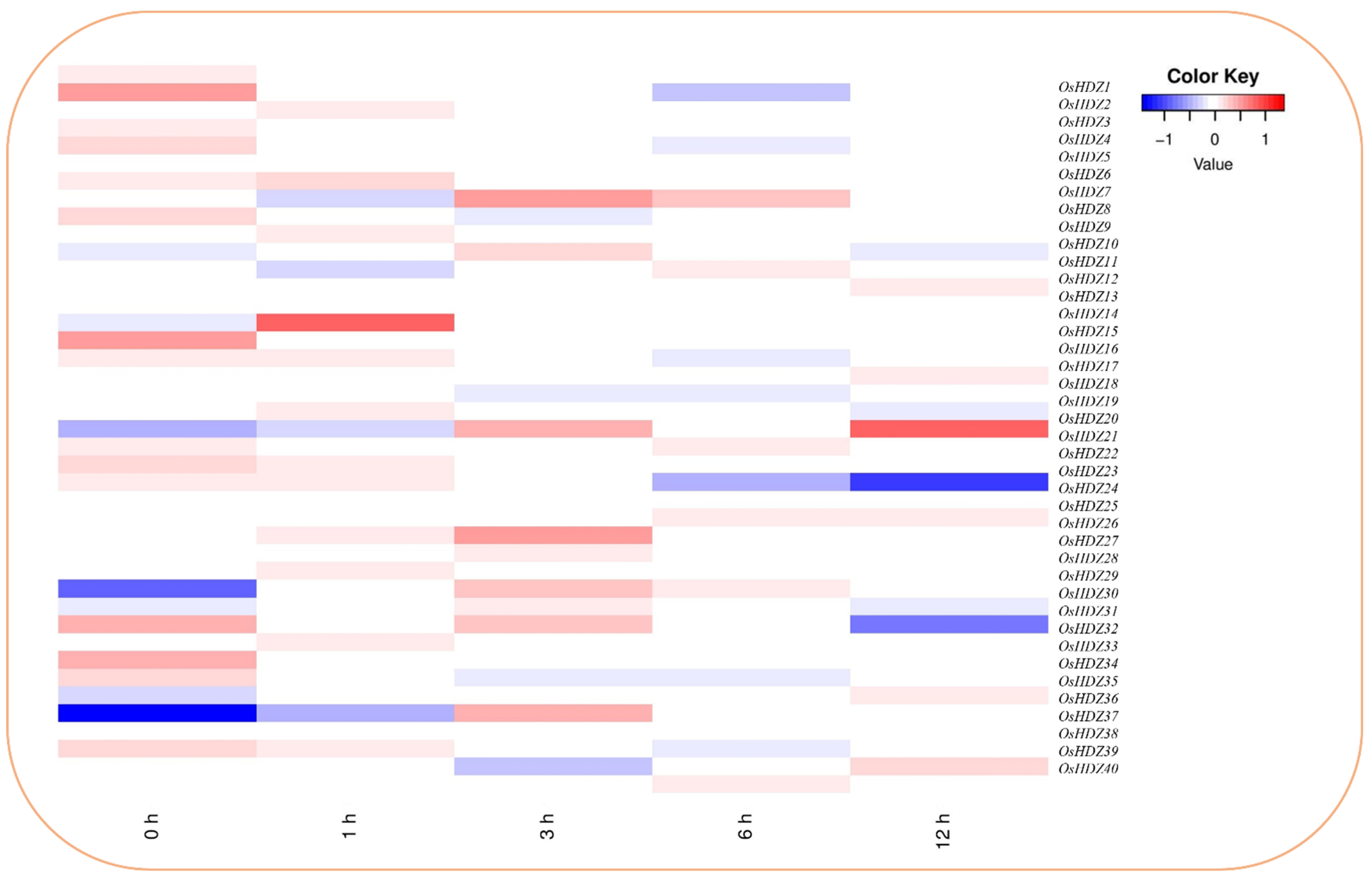
3.9.4. Expression Analysis of OsHDZIP Genes under Cnaphalocrocis medinalis
3.9.5. Expression Analysis of OsHDZIP Genes under Brassinosteroids and Jasmonic Acid
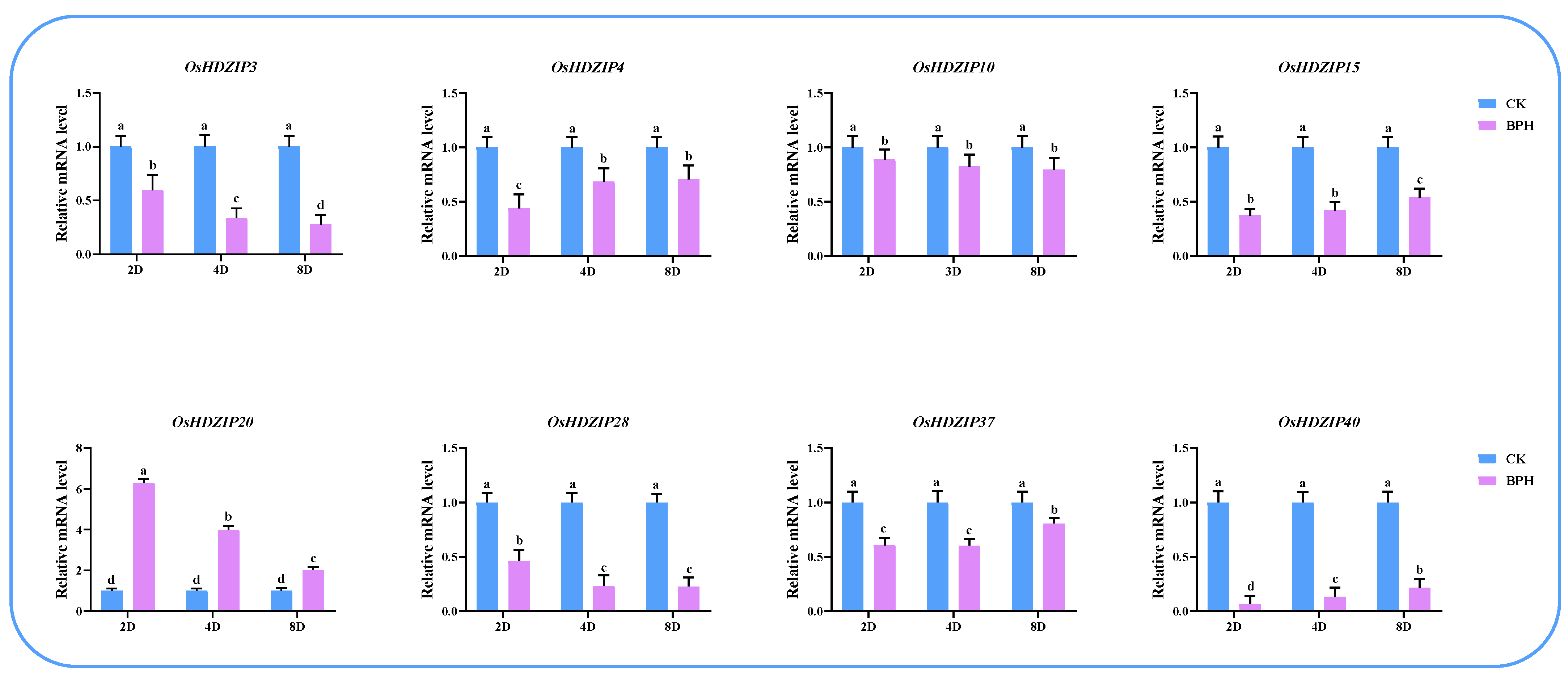
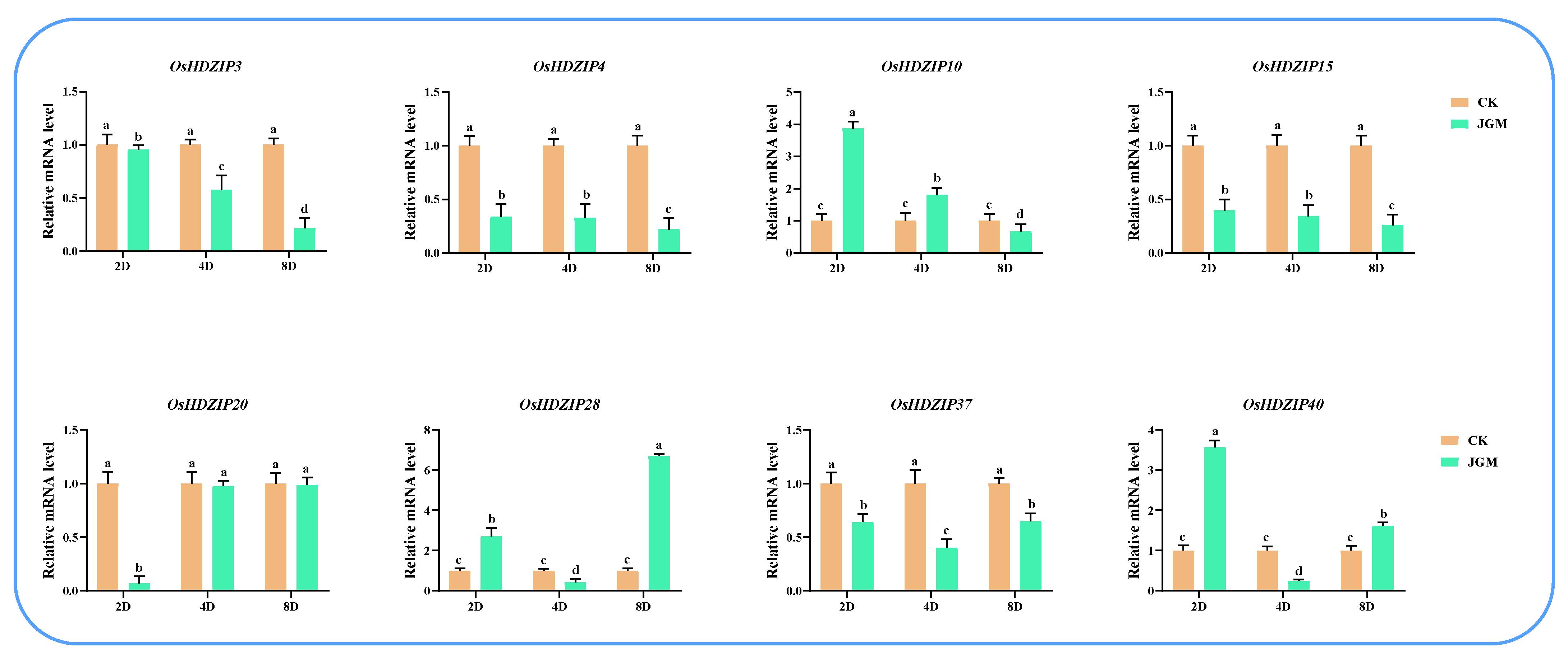
3.10. Differential Expression of OsHDZIP Genes in Response to Nilaparvata lugens, Laodelphax striatellus Infestations, and JGM Spraying
4. Discussion
4.1. OsHDZIP Genes Are Widely Distributed in the Rice Genome
4.2. OsHDZIP Genes Have Tissue Specificity and Play an Integral Role in the Development of Oryza sativa
4.3. OsHDZIP Genes Regulate Plant Response to Chewing Insects and other Abiotic Stresses
4.4. MicroRNAs in Plant–Insect Interaction and Insect Pest Control
4.5. Expression Analysis of HDZIP Gene Family under Hormonal Applications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sultan, S.E. Plant developmental responses to the environment: Eco-devo insights. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Ito, Y.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariel, F.D.; Manavella, P.A.; Dezar, C.A.; Chan, R.L. The true story of the HD-Zip family. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.-X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.-M.; Chai, L.-J.; Guo, W.-W. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of HD-ZIP gene family in citrus, and its potential roles in somatic embryogenesis regulation. Gene 2015, 574, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, M.; Davis, R.W. HD-Zip proteins: Members of an Arabidopsis homeodomain protein superfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3894–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhiti, M.; Stasolla, C. Structure and function of homodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) proteins. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.C.; Hrmova, M.; Lopato, S.; Langridge, P. Modulation of plant growth by HD-Zip class I and II transcription factors in response to environmental stimuli. New Phytol. 2011, 190, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, R.; Xie, C.; Wang, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P.; Li, Y. Genome wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of HD-ZIP gene family in Cucumis sativus L. under biotic and various abiotic stresses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Henriksson, E.; Söderman, E.; Henriksson, K.N.; Sundberg, E.; Engström, P. The Arabidopsis homeobox gene, ATHB16, regulates leaf development and the sensitivity to photoperiod in Arabidopsis. Dev. Biol. 2003, 264, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, A.E.; Övernäs, E.; Johansson, H.; Rada-Iglesias, A.; Engström, P. The homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) class I transcription factors ATHB7 and ATHB12 modulate abscisic acid signalling by regulating protein phosphatase 2C and abscisic acid receptor gene activities. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, F.; Ribone, P.A.; Capella, M.; Miguel, V.N.; Chan, R.L. A matter of quantity: Common features in the drought response of transgenic plants overexpressing HD-Zip I transcription factors. Plant Sci. 2016, 251, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindler, C.; Carabelli, M.; Borello, U.; Morelli, G.; Ruberti, I. Phytochrome A, phytochrome B and other phytochrome(s) regulate ATHB-2 gene expression in etiolated and green Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Environ. 1997, 20, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, C.; Salla-Martret, M.; Bou-Torrent, J.; Roig-Villanova, I.; Martínez-García, J.F. ATHB4, a regulator of shade avoidance, modulates hormone response in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2009, 59, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou-Torrent, J.; Salla-Martret, M.; Brandt, R.; Musielak, T.; Palauqui, J.-C.; Martínez-García, J.F.; Wenkel, S.J. ATHB4 and HAT3, two class II HD-ZIP transcription factors, control leaf development in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Wang, H. The role of HD-ZIP III transcription factors and miR165/166 in vascular development and secondary cell wall formation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1078955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoud, V.; Laigle, G.; Rozier, F.; Meeley, R.B.; Perez, P.; Rogowsky, P.M. The HD-ZIP IV transcription factor OCL4 is necessary for trichome patterning and anther development in maize. Plant J. 2009, 59, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Misra, P.; Alok, A.; Kaur, N.; Sharma, S.; Lakhwani, D.; Asif, M.H.; Tiwari, S.; Trivedi, P.K. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of homeodomain leucine zipper subfamily IV (HDZ IV) gene family from Musa accuminata. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbandeh, M. Total Rice Consumption Worldwide from 2008/2009 to 2020/2021 (in 1000 Metric Tons). Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/255977/total-global-rice-consumption/ (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Yoshida, K.; Matsukura, K.; Sakai, J.; Onuki, M.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Towata, T.; Matsumura, M. Seasonal occurrence of Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in a rice-forage crops mixed cropping area in central Kyushu, Japan. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Lu, F.; Zhai, B.-P.; Lu, M.-H.; Liu, W.-C.; Zhu, F.; Wu, X.-W.; Chen, G.-H.; Zhang, X.-X. Outbreaks of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in the Yangtze River Delta: Immigration or local reproduction? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Fang, R.; Qian, W.; Chen, X. Massively parallel pyrosequencing-based transcriptome analyses of small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus), a vector insect transmitting rice stripe virus (RSV). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Lacombe, S.; Bangratz, M.; Ta, H.A.; Vinh, D.N.; Gantet, P.; Brugidou, C. p2 of Rice grassy stunt virus (RGSV) and p6 and p9 of Rice ragged stunt virus (RRSV) isolates from Vietnam exert suppressor activity on the RNA silencing pathway. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wen, J.; Cai, D.; Li, P.; Xu, D.; Zhang, S. Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: A new proposed Fijivirus species in the family Reoviridae. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.; Jeung, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, H.; Brar, D. High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18 (t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.-B.; Zhao, K.-F.; Wang, D.-J.; Wu, J.-C. Effects of different treatment methods of the fungicide jinggangmycin on reproduction and vitellogenin gene (Nlvg) expression in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 102, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.Q.; Zheng, S.; Gu, H.T.; Zhou, Y.K.; Zhou, Z.; Song, Q.S.; Stanley, D. Jinggangmycin-induced UDP-glycosyltransferase 1-2-like is a positive modulator of fecundity and population growth in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)(Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xi, C.; Shah, A.Z.; Ge, L. Comprehensive Bioinformatics and Expression Analysis of the TLP Gene Family Revealed Its Role in Regulating the Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, Laodelphax striatellus, and Jinggangmycin. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J. The essential role of jasmonic acid in plant–herbivore interactions–using the wild tobacco Nicotiana attenuata as a model. J. Genet. Genom. 2013, 40, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.A.; Fahad, S.; Sharif, R.; Jan, M.F.; Mujtaba, M.; Ali, Q.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, H.; Amin, N.; Ajayo, B.S. Multifunctional role of brassinosteroid and its analogues in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 92, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Gu, X.; Fan, W.; Lucas, W.J.; Wang, X.; Xie, B.; Ni, P. The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; de la Bastide, M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; McCombie, W.R.; Ouyang, S.; Schwartz, D.C.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S.J.R. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Milpetz, F.; Bork, P.; Ponting, C.P. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: Identification of signaling domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; De Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P. STRING v10: Protein—Protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, H.; Shaozhong, F.; Li, X.; Bilal, M.A.; Yousef, A.; Chenglong, Y.; Shi, M.; Jaber, M.; Anwar, M.; Hu, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of KCS Gene Family in Passion Fruit (Passiflora edulis) Under Fusarium kyushuense and Drought Stress Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 872263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.-Q.; Wang, L.-P.; Zhao, K.-F.; Wu, J.-C.; Huang, L.-J. Mating pair combinations of insecticide-treated male and female Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) planthoppers influence protein content in the male accessory glands (MAGs) and vitellin content in both fat bodies and ovaries of adult females. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2- ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, G.; Carabelli, M.; Ruberti, I.; Lucchetti, S.; Baima, S.; Morelli, G. Identification of distinct families of HD-Zip proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. In Plant Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 411–426. [Google Scholar]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, H.; Shang, C.; Ma, S.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J. The Roles of Auxin Biosynthesis YUCCA Gene Family in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkar, R.; Zhu, J.-K.J.T. Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2001–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Takehisa, H.; Kamatsuki, K.; Minami, H.; Namiki, N.; Ikawa, H.; Ohyanagi, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Antonio, B.A.; Nagamura, Y.J. RiceXPro version 3.0: Expanding the informatics resource for rice transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1206–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Cheng, Y.; Han, S.; Van Handel, B.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Xie, X. Whole genome sequencing and comparative transcriptome analysis of a novel seawater adapted, salt-resistant rice cultivar—Sea rice 86. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hu, X.; Su, S.; Ning, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ye, G.; Lou, Y.; Turlings, T.C.; Li, Y.J. Cooperative herbivory between two important pests of rice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Du, L.; Hallerman, E.M.; Li, Y. Transcriptomic and metabolomic responses of rice plants to Cnaphalocrocis medinalis caterpillar infestation. Insects 2020, 11, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, W.; Hrmova, M.; Lopato, S.J. Role of homeodomain leucine zipper (HD-Zip) IV transcription factors in plant development and plant protection from deleterious environmental factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8122–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cao, C.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.J. The identification of Cucumis sativus Glabrous 1 (CsGL1) required for the formation of trichomes uncovers a novel function for the homeodomain-leucine zipper I gene. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aso, K.; Kato, M.; Banks, J.A.; Hasebe, M.J. Characterization of homeodomain-leucine zipper genes in the fern Ceratopteris richardii and the evolution of the homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family in vascular plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.K.; Floyd, S.K.; Sakakibara, K.; Bowman, J.L.J. Class III HD-Zip activity coordinates leaf development in Physcomitrella patens. Dev. Biol. 2016, 419, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigge, M.J.; Clark, S.E.J. Evolution of the class III HD-Zip gene family in land plants. Evol. Dev. 2006, 8, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, J.; Cao, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of HD-ZIP genes in potato. Gene 2019, 697, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P.J.T. Genome—Wide identification, classification, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses of homeobox genes in rice. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2845–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, G.; Steindler, C.; Morelli, G.; Ruberti, I.J. The Arabidopsis Athb-8,-9 and genes are members of a small gene family coding for highly related HD-ZIP proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 38, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Niu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Evolution and expression analysis reveal the potential role of the HD-Zip gene family in regulation of embryo abortion in grapes (Vitis vinifera L.). BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ré, D.A.; Capella, M.; Bonaventure, G.; Chan, R.L. Arabidopsis AtHB7 and AtHB12 evolved divergently to fine tune processes associated with growth and responses to water stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.; Carlsbecker, A.; Etchells, J.P. Class III HD-ZIPs govern vascular cell fate: An HD view on patterning and differentiation. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, R.; Weng, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Xiao, H. Domain-specific expression of meristematic genes is defined by the LITTLE ZIPPER protein DTM in tomato. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Katsumata, H.; Abe, M.; Yabe, N.; Komeda, Y.; Yamamoto, K.T.; Takahashi, T. Characterization of the class IV homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Malabanan, P.B.; Abrigo, E. OsHox4 regulates GA signaling by interacting with DELLA-like genes and GA oxidase genes in rice. Euphytica 2015, 201, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Ding, Y.; Hu, S.; Ding, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C. The role of HD-Zip class I transcription factors in plant response to abiotic stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 167, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Jin, X.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, L.; Yan, H.; Sheng, L.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, B.; et al. A novel maize homeodomain–leucine zipper (HD-Zip) I gene, Zmhdz10, positively regulates drought and salt tolerance in both rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribichich, K.F.; Chiozza, M.; Ávalos-Britez, S.; Cabello, J.V.; Arce, A.L.; Watson, G.; Arias, C.; Portapila, M.; Trucco, F.; Otegui, M.E. Successful field performance in warm and dry environments of soybean expressing the sunflower transcription factor HB4. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 3142–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-P.; Li, C.-P.; Liang, W.-W.; Guo, P.; Yang, L.-T.; Chen, L.-S. Identification of manganese-toxicity-responsive genes in roots of two citrus species differing in manganese tolerance using cDNA-AFLP. Trees 2017, 31, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, J.V.; Giacomelli, J.I.; Piattoni, C.V.; Iglesias, A.A.; Chan, R.L. The sunflower transcription factor HaHB11 improves yield, biomass and tolerance to flooding in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 222, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, R.; Raza, A.; Chen, P.; Li, Y.; El-Ballat, E.M.; Rauf, A.; Hano, C.; El-Esawi, M.A. HD-ZIP gene family: Potential roles in improving plant growth and regulating stress-responsive mechanisms in plants. Genes 2021, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Wei, Z.; Shi, Z.; He, R.; Zhu, L.; Chen, R.; Han, B. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22163–22168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabauatan, P.Q.; Cabunagan, R.C.; Choi, I.-R. Rice viruses transmitted by the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål. In Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2009; pp. 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Raza, A.; Chu, W.; Zou, X.; Cheng, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wenliang, W. Comprehensive in silico characterization and expression profiling of TCP gene family in rapeseed. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, J.; Rinku, S.; Pooja, B.; Shikha, M.; Kaliyugam, S.; Mallikarjuna, M.G.; Kumar, A.; Rao, A.R.; Nepolean, T. Identification, characterization, and functional validation of drought-responsive microRNAs in subtropical maize inbreds. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Figueroa, B.E.; Gao, L.; Diop, N.N.; Wu, Z.; Ehlers, J.D.; Roberts, P.A.; Close, T.J.; Zhu, J.-K.; Liu, R. Identification and comparative analysis of drought-associated microRNAs in two cowpea genotypes. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.-X.; Liu, Y.-F.; Hu, X.-Y.; Zhang, W.-K.; Ma, B.; Chen, S.-Y.; Zhang, J.-S. Identification of miRNAs and their target genes in developing soybean seeds by deep sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Xia, H.; Cao, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Small RNA and degradome deep sequencing reveals peanut microRNA roles in response to pathogen infection. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macovei, A.; Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. microRNAs as promising tools for improving stress tolerance in rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkonyi-Gasic, E.; Gould, N.; Sandanayaka, M.; Sutherland, P.; MacDiarmid, R.M. Characterisation of microRNAs from apple (Malus domestica ‘Royal Gala’) vascular tissue and phloem sap. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, C. Microarray-based analysis of cadmium-responsive microRNAs in rice (Oryza sativa). J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3563–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macovei, A.; Tuteja, N. microRNAs targeting DEAD-box helicases are involved in salinity stress response in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Hause, B. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in Annals of Botany. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 1021–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, R.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Dong, X.; Qi, M.; Jiang, C.-Z.; Xu, T. The HD-Zip transcription factor SlHB15A regulates abscission by modulating jasmonoyl-isoleucine biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 2396–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manghwar, H.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Liu, F. Brassinosteroids (BRs) Role in Plant Development and Coping with Different Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Name | Locus ID | Subgroups | Chr | Start | End | AA | Mw (kDa) | PI | SL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsHDZ1 | LOC_Os01g45570 | II | 1 | 25,883,718 | 25,880,204 | 229 | 229 | 9.00 | N |
| OsHDZ2 | LOC_Os01g55549 | IV | 1 | 32,009,784 | 32,006,374 | 816 | 88,638.79 | 6.43 | N |
| OsHDZ3 | LOC_Os01g57890 | IV | 1 | 33,471,900 | 33,478,535 | 709 | 78,179.26 | 6.97 | P |
| OsHDZ4 | LOC_Os02g05640 | II | 2 | 2,757,693 | 2,758,714 | 237 | 25,593.73 | 9.34 | N |
| OsHDZ5 | LOC_Os02g35770 | II | 2 | 21,489,894 | 21,487,595 | 349 | 37,437.65 | 5.65 | N |
| OsHDZ6 | LOC_Os02g43330 | I | 2 | 26,143,309 | 26,144,731 | 261 | 28,537.38 | 4.84 | N |
| OsHDZ7 | LOC_Os02g45250 | IV | 2 | 27,494,914 | 27,487,865 | 804 | 86,047.24 | 5.55 | P |
| OsHDZ8 | LOC_Os02g49700 | I | 2 | 30,381,303 | 30,383,661 | 343 | 37,614.24 | 4.70 | N |
| OsHDZ9 | LOC_Os03g01890 | III | 3 | 549,823 | 557,909 | 839 | 91,828.58 | 5.74 | N |
| OsHDZ10 | LOC_Os03g07450 | I | 3 | 3,786,933 | 3,784,283 | 366 | 39,623.72 | 6.40 | N |
| OsHDZ11 | LOC_Os03g08960 | I | 3 | 4,652,927 | 4,654,824 | 311 | 33,612.78 | 4.68 | N |
| OsHDZ12 | LOC_Os03g12860 | II | 3 | 6,931,709 | 6,933,328 | 292 | 30,516.17 | 8.64 | N |
| OsHDZ13 | LOC_Os03g43930 | III | 3 | 24,657,650 | 24,651,800 | 862 | 93,747.56 | 6.19 | P |
| OsHDZ14 | LOC_Os04g45810 | I | 4 | 27,124,166 | 27,125,512 | 276 | 30,653.13 | 5.19 | N |
| OsHDZ15 | LOC_Os04g46350 | II | 4 | 27,479,717 | 27,477,579 | 247 | 27,291.10 | 9.06 | N |
| OsHDZ16 | LOC_Os04g48070 | IV | 4 | 28,607,038 | 28,600,698 | 813 | 86,758.01 | 5.59 | N |
| OsHDZ17 | LOC_Os04g53540 | IV | 4 | 31,907,122 | 31,899,718 | 784 | 85,259.35 | 5.59 | N |
| OsHDZ18 | LOC_Os06g04850 | II | 6 | 2,123,398 | 2,124,787 | 256 | 27,016.66 | 9.12 | N |
| OsHDZ19 | LOC_Os06g04870 | II | 6 | 2,137,450 | 2,139,101 | 308 | 32,084.86 | 9.14 | N |
| OsHDZ20 | LOC_Os06g10600 | IV | 6 | 5,502,411 | 5,499,342 | 697 | 75,491.69 | 6.19 | N |
| OsHDZ21 | LOC_Os06g48290 | II | 6 | 29,199,356 | 29,198,270 | 256 | 27,590.97 | 9.13 | N |
| OsHDZ22 | LOC_Os08g04190 | IV | 8 | 2,037,504 | 2,034,454 | 749 | 80,854.03 | 5.97 | N |
| OsHDZ23 | LOC_Os08g08820 | IV | 8 | 5,109,238 | 5,116,781 | 784 | 84,615.36 | 5.50 | N |
| OsHDZ24 | LOC_Os08g19590 | IV | 8 | 11,702,603 | 11,711,044 | 786 | 86,649.10 | 8.34 | N |
| OsHDZ25 | LOC_Os08g32080 | I | 8 | 19,888,358 | 19,884,012 | 349 | 37,386.74 | 4.59 | N |
| OsHDZ26 | LOC_Os08g32085 | I | 8 | 19,888,358 | 19,884,012 | 349 | 37,386.74 | 4.59 | N |
| OsHDZ27 | LOC_Os08g36220 | II | 8 | 22,831,125 | 22,829,282 | 354 | 36,889.29 | 7.02 | N |
| OsHDZ28 | LOC_Os08g37580 | I | 8 | 23,805,452 | 23,803,380 | 269 | 28,928.92 | 4.64 | C |
| OsHDZ29 | LOC_Os09g21180 | I | 9 | 12,783,649 | 12,780,659 | 333 | 35,698.53 | 5.08 | N |
| OsHDZ30 | LOC_Os09g27450 | II | 9 | 16,676,359 | 16,674,571 | 362 | 37,833.06 | 6.22 | N |
| OsHDZ31 | LOC_Os09g29460 | I | 9 | 17,903,164 | 17,905,338 | 277 | 29,392.27 | 4.62 | N |
| OsHDZ32 | LOC_Os09g35760 | IV | 9 | 20,574,897 | 20,567,982 | 872 | 91,720.25 | 5.75 | N |
| OsHDZ33 | LOC_Os09g35910 | I | 9 | 20,671,754 | 20,673,282 | 249 | 27,300.31 | 5.62 | N |
| OsHDZ34 | LOC_Os10g01470 | II | 10 | 286,941 | 284,701 | 247 | 27,178.62 | 8.15 | N |
| OsHDZ35 | LOC_Os10g23090 | I | 10 | 12,041,604 | 12,043,235 | 305 | 32,734.71 | 5.05 | N |
| OsHDZ36 | LOC_Os10g26500 | I | 10 | 13,804,811 | 13,806,732 | 355 | 36,848.13 | 6.05 | N |
| OsHDZ37 | LOC_Os10g33960 | III | 10 | 18,085,536 | 18,092,500 | 840 | 92,132.16 | 5.58 | C |
| OsHDZ38 | LOC_Os10g41230 | II | 10 | 22,152,631 | 22,154,163 | 311 | 33,143.22 | 9.09 | N |
| OsHDZ39 | LOC_Os10g42490 | IV | 10 | 22,916,203 | 22,910,460 | 882 | 94,667.18 | 5.63 | N |
| OsHDZ40 | LOC_Os12g41860 | III | 12 | 25,927,353 | 25,920,639 | 855 | 93,109.96 | 5.97 | P |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, S.; Chen, Y.; Shah, A.Z.; Wang, H.; Xi, C.; Zhu, H.; Ge, L. The Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper Genes Family Regulates the Jinggangmycin Mediated Immune Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, and Laodelphax striatellus. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080398
Ahmad S, Chen Y, Shah AZ, Wang H, Xi C, Zhu H, Ge L. The Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper Genes Family Regulates the Jinggangmycin Mediated Immune Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, and Laodelphax striatellus. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(8):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080398
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Sheraz, Yu Chen, Amir Zaman Shah, Huaiqi Wang, Chuanyuan Xi, Haowen Zhu, and Linquan Ge. 2022. "The Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper Genes Family Regulates the Jinggangmycin Mediated Immune Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, and Laodelphax striatellus" Bioengineering 9, no. 8: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080398
APA StyleAhmad, S., Chen, Y., Shah, A. Z., Wang, H., Xi, C., Zhu, H., & Ge, L. (2022). The Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper Genes Family Regulates the Jinggangmycin Mediated Immune Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, and Laodelphax striatellus. Bioengineering, 9(8), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080398








