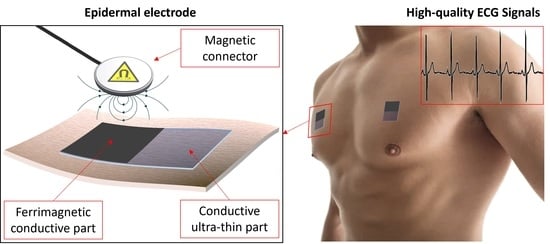
Epidermal Electrodes with Ferrimagnetic/Conductive Properties for Biopotential Recordings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composite Film Materials
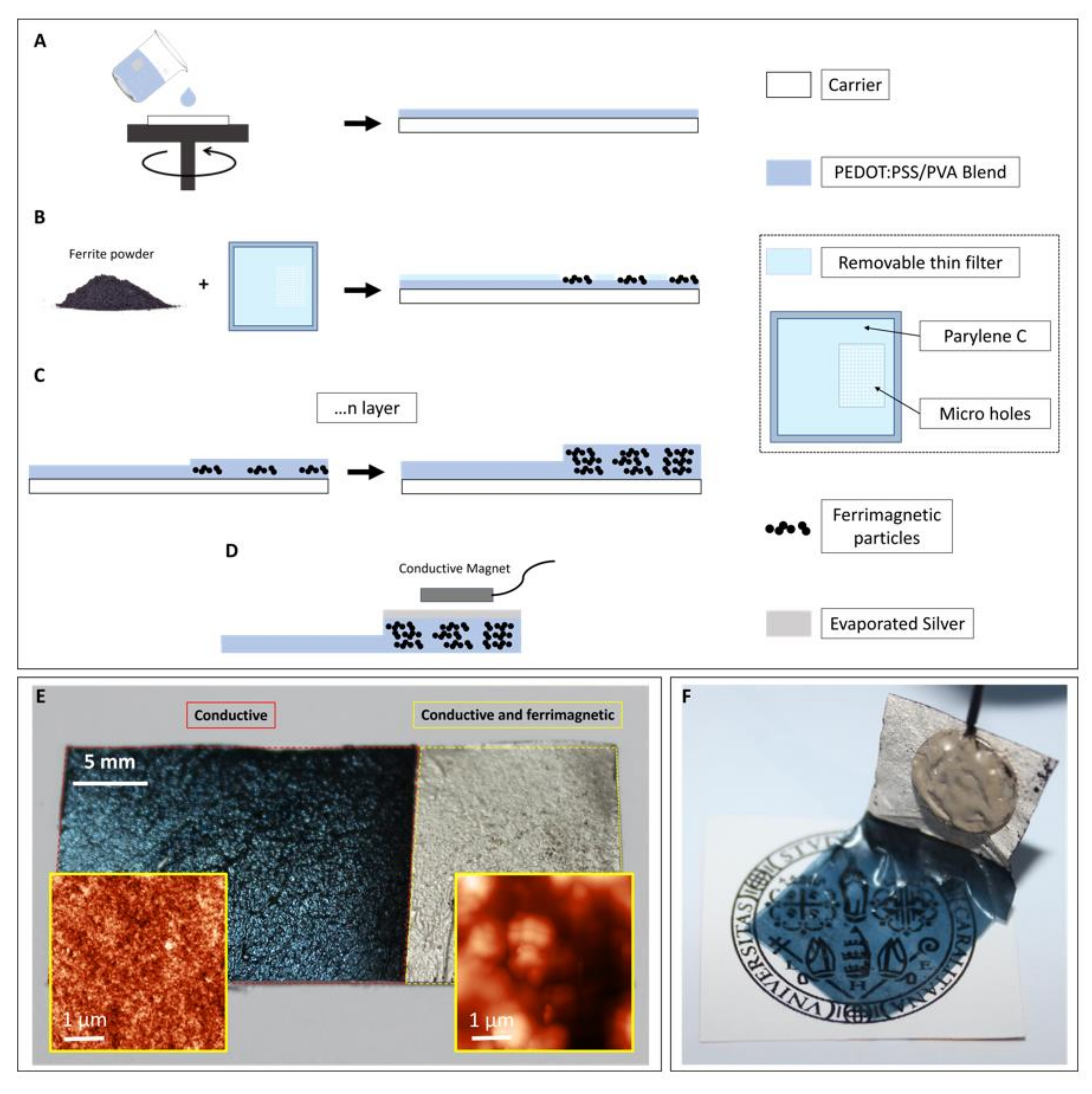
2.2. Fabrication Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Film Characterization
3.1.1. Thickness Characterization
3.1.2. Magnetic Force of Interaction
3.1.3. Conductivity Characterization
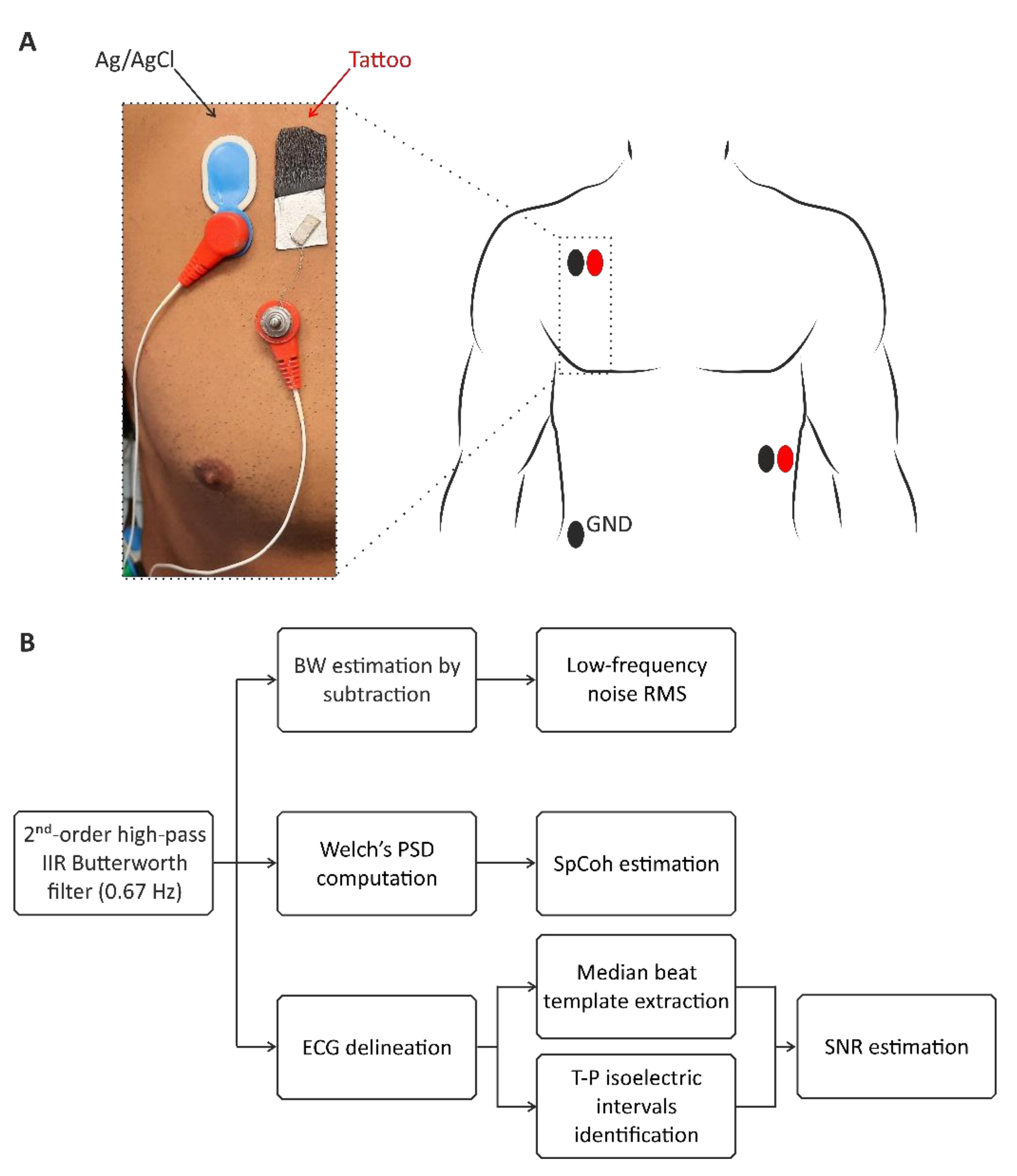
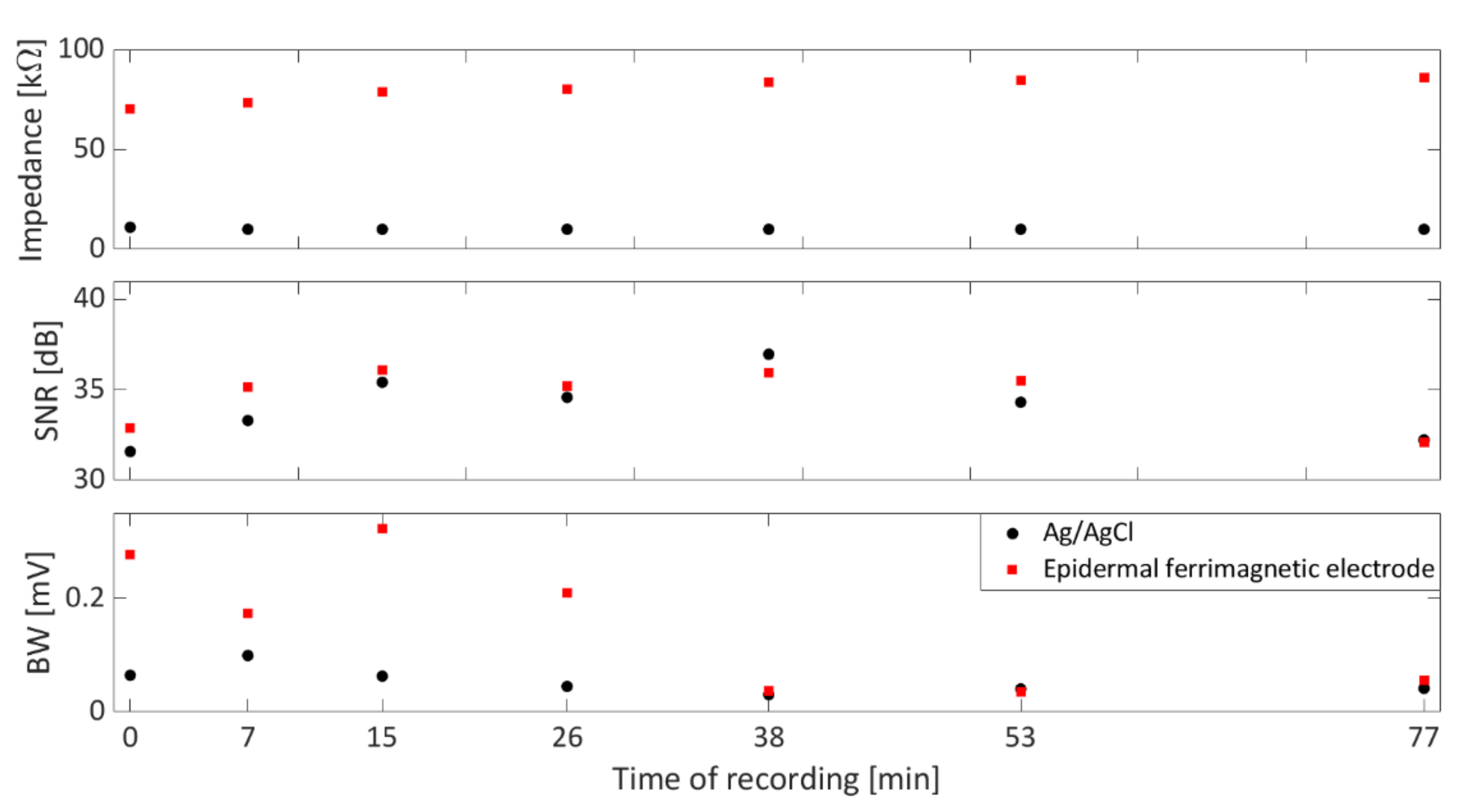
3.2. ECG Measurement Setup and Validation Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.H.; Lu, N.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, R.H.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Won, S.M.; Tao, H.; Islam, A.; et al. Epidermal Electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hua, Q.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, C. Flexible, Stretchable and Wearable Multifunctional Sensor Array as Artificial Electronic Skin for Static and Dynamic Strain Mapping. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, F.A.; Spanu, A.; Ricci, P.C.; Bonfiglio, A.; Cosseddu, P. Ultrathin, flexible and multimodal tactile sensors based on organic field-effect transistors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodagholy, D.; Doublet, T.; Gurfinkel, M.; Quilichini, P.; Ismailova, E.; Leleux, P.; Herve, T.; Sanaur, S.; Bernard, C.; Malliaras, G.G. Highly conformable conducting polymer electrodes for in vivo recordings. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H268–H272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattoli, V.; Greco, F.; Fujie, T.; Taccola, S.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P. Freestanding Functionalized Nanofilms for Biomedical Applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 7, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsukawa, R.; Miyamoto, A.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. Skin Impedance Measurements with Nanomesh Electrodes for Monitoring Skin Hydration. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2001322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Windmiller, J.R.; Yang, Z.; Ramírez, J.; Chan, G.; Wang, J. Electrochemical Tattoo Biosensors for Real-Time Noninvasive Lactate Monitoring in Human Perspiration. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6553–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanshu, L.; Ameri, S.K.; Ha, T.; Nicolini, L.; Stier, A.; Wang, P. Epidermal electronic systems for sensing and therapy. In Proceedings Volume 10167, Nanosensors, Biosensors, Info-Tech Sensors and 3D Systems, 17 April 2017; 101670J. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/10167/101670J/Epidermal-electronic-systems-for-sensing-and-therapy/10.1117/12.2261755.full (accessed on 17 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, S.; Lonjaret, T.; Ismailova, E.; Masuda, A.; Itoh, T.; Malliaras, G.G. Wearable Keyboard Using Conducting Polymer Electrodes on Textiles. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4485–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drack, M.; Graz, I.; Sekitani, T.; Someya, T.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Bauer, S. An Imperceptible Plastic Electronic Wrap. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lee, H.; Ghaffari, R.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Recent Advances in Flexible and Stretchable Bio-Electronic Devices Integrated with Nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4203–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.; Jung, H.N.; Lee, J.W.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Ma, Y.; Jeong, J.W.; Song, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.H.; et al. Ferromagnetic, Folded Electrode Composite as a Soft Interface to the Skin for Long-Term Electrophysilogical Recording. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7281–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taccola, S.; Poliziani, A.; Santonocito, D.; Mondini, A.; Denk, C.; Ide, A.N.; Oberparleiter, M.; Greco, F.; Mattoli, V. Toward the Use of Temporary Tattoo Electrodes for Impedancemetric Respiration Monitoring and Other Electrophysiological Recordings on Skin. Sensors 2021, 21, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Jimbo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Md Nayeem, O.G.; Nishinaka, M.; Someya, T. Nanomesh Organic Electrochemical Transistor for Comfortable On-Skin Electrodes with Local Amplifying Function. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 3601–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.M.; Ismailov, U.; Badier, J.M.; Greco, F.; Ismailova, E. Conducting polymer tattoo electrodes in clinical electro- and magneto-encephalography. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, H.; Wang, H.; Wei, G.; Huang, X. Flexible Magnetoelectrical Devices with Intrinsic Magnetism and Electrical Conductivity. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1900111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Jo, T.; Okuzaki, H. Highly Conductive and Transparent Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Poly(4-styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT/PSS) Thin Films. Polym. J. 2009, 41, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichan, C.; Saikrajang, T.; Lomas, T.; Jomphoak, A.; Maturos, T.; Phokaratkul, D.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Tuantranont, A. Inkjet printing PEDOT: PSS using desktop inkjet printer. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Chonburi, Thailand, 6–9 May 2009; pp. 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.K.; Noh, Y.; Reljin, N.; Treich, G.M.; Mohammadalipour, S.H.; Guo, Y.; Chon, K.H.; Sotzing, G.A. Screen Printed PEDOT:PSS Electrodes on Commercial Finished Textiles for Electrocardiography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37524–37528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellot, G.; Lagonegro, P.; Tarabella, G.; Scaini, D.; Fabbri, F.; Iannotta, S.; Prato, M.; Salviati, G.; Ballerini, L. PEDOT:PSS Interfaces Support the Development of Neuronal Synaptic Networks with Reduced Neuroglia Response In Vitro. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, D.; Achilli, A.; Spanu, A.; Bonfiglio, A.; Gazzoni, M.; Botter, A. Validation of Polymer-Based Screen-Printed Textile Electrodes for Surface EMG Detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Textiles and Their Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Botter, A.; Zedda, A.; Cerone, G.L.; Bonfiglio, A.; Pani, D. Dynamic Surface Electromyography Using Stretchable Screen-Printed Textile Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucca, A.; Cipriani, C.; Sudha; Tarantino, S.; Ricci, D.; Mattoli, V.; Greco, F. Tattoo Conductive Polymer Nanosheets for Skin-Contact Applications. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2015, 4, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, C.A. Some properties of polyvinyl alcohol and their possible applications. In Chemistry and Technology of Water-Soluble Polymers; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1983; pp. 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.Y.; Paknikar, K.M.; Bodas, D.; Gajbhiye, V. Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Run-Wei, L. Magnetic nanoparticle for biomedicine applications. J. Nanotechnol. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 2, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, J.; Aifantis, K.E.; Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Watari, F. Current investigations into magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Koroush, N. Synthesis and magnetic properties evaluation of monosized FeCo alloy nanoparticles through microemulsion method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2017, 30, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soscia, D.A.; Lam, D.; Tooker, A.C.; Enright, H.A.; Triplett, M.; Karande, P.; Peters SK, G.; Sales, A.P.; Wheeler, E.K.; Fischer, N.O. A flexible 3-dimensional microelectrode array for in vitro brain models. Lab A Chip 2020, 20, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Colistra, N.; Farisello, P.; Friz, A.; Arellano, N.; Rettner, C.T.; Bonfiglio, A.; Bozano, L.; Martinoia, S. A three-dimensional micro-electrode array for in-vitro neuronal interfacing. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 036033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Park, Y.; Luan, H.; Dalgin, G.; Jeffris, K.; Yoon, H.-J.; Chung, T.S.; Kim, J.U.; Kwak, S.S.; Lee, G.; et al. Transparent, compliant 3D mesostructures for precise evaluation of mechanical characteristics of organoids. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Kine, A.; Nelson, R.D.; LaRue, J.C. Impedance spectroscopy study of conducting polymer blends of PEDOT: PSS and PVA. Synth. Met. 2015, 206, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, F.; Zucca, A.; Taccola, S.; Menciassi, A.; Fujie, T.; Haniuda, H.; Takeoka, S.; Dario, P.; Mattoli, V. Ultra-thin conductive free-standing PEDOT/PSS nanofilms. Soft Matter. 2011, 7, 10642–10650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligfield, P.; Gettes, L.S.; Bailey, J.J.; Childers, R.; Deal, B.J.; Hancock, E.W.; van Herpen, G.; Hors, J.A.; Macfarlane, P.; Mirvis, D.M.; et al. Recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: Part I: The electrocardiogram and its technology a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1109–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.P.; Almeida, R.; Olmos, S.; Rocha, A.P.; Laguna, P. A wavelet-based ECG delineator: Evaluation on standard databases. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, G.D.; Azuaje, F. Advanced Methods and Tools for ECG Data Analysis; McSharry, P., Ed.; Artech House: Boston, FL, USA, 2006; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, P. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, D.; Cavallari, I.; Creta, A.; Di Giovanni, G.; Calabrese, V.; Di Belardino, N.; Mega, S.; Colaiori, I.; Ragni, L.; Proscia, C.; et al. Impact of the high-frequency cutoff of bandpass filtering on ECG quality and clinical interpretation: A comparison between 40 Hz and 150 Hz cutoff in a surgical preoperative adult outpatient population. J. Electrocardiol. 2016, 49, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Mascia, A.; Baldazzi, G.; Benji, F.S.; Felice, T.; Graziana, V.; Bonfiglio, A.; Cosseddu, P.; Pani, D. Parylene C-Based, Breathable Tattoo Electrodes for High-Quality Bio-Potential Measurements. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 820217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldazzi, G.; Spanu, A.; Mascia, A.; Viola, G.; Bonfiglio, A.; Cosseddu, P.; Pani, D. Validation of a Novel Tattoo Electrode for ECG Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2021 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Brno, Czech Republic, 13–15 September 2021; Volume 48, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, N.V.; Webster, J.G.; Tompkins, W.J. Estimation of QRS Complex Power Spectra for Design of a QRS Filter. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1984, 31, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spanu, A.; Taki, M.; Baldazzi, G.; Mascia, A.; Cosseddu, P.; Pani, D.; Bonfiglio, A. Epidermal Electrodes with Ferrimagnetic/Conductive Properties for Biopotential Recordings. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050205
Spanu A, Taki M, Baldazzi G, Mascia A, Cosseddu P, Pani D, Bonfiglio A. Epidermal Electrodes with Ferrimagnetic/Conductive Properties for Biopotential Recordings. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(5):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050205
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpanu, Andrea, Mohamad Taki, Giulia Baldazzi, Antonello Mascia, Piero Cosseddu, Danilo Pani, and Annalisa Bonfiglio. 2022. "Epidermal Electrodes with Ferrimagnetic/Conductive Properties for Biopotential Recordings" Bioengineering 9, no. 5: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050205
APA StyleSpanu, A., Taki, M., Baldazzi, G., Mascia, A., Cosseddu, P., Pani, D., & Bonfiglio, A. (2022). Epidermal Electrodes with Ferrimagnetic/Conductive Properties for Biopotential Recordings. Bioengineering, 9(5), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9050205