Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Matrix (PRP-GM): Description of a New Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
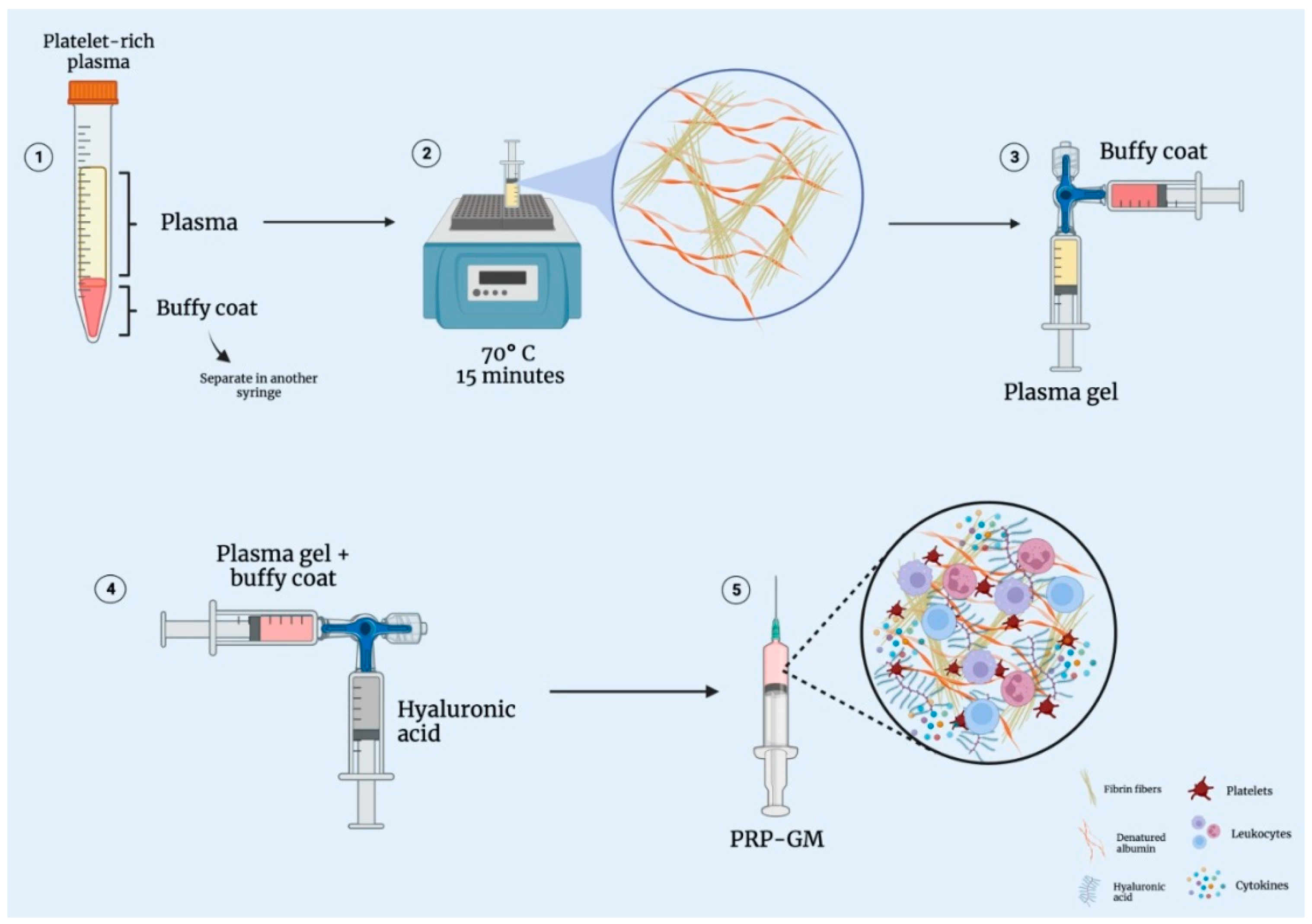
2. Technique and Processing Method
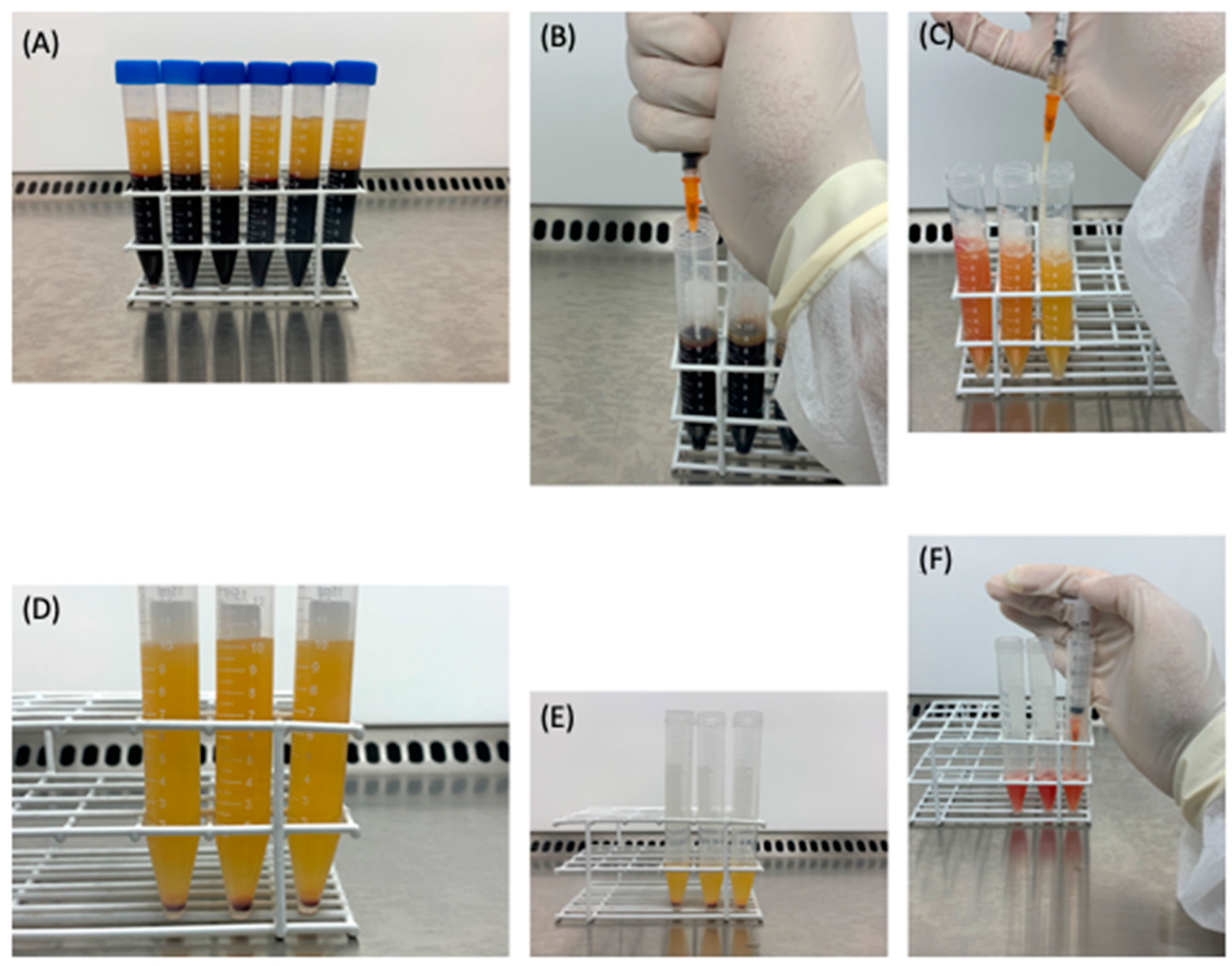
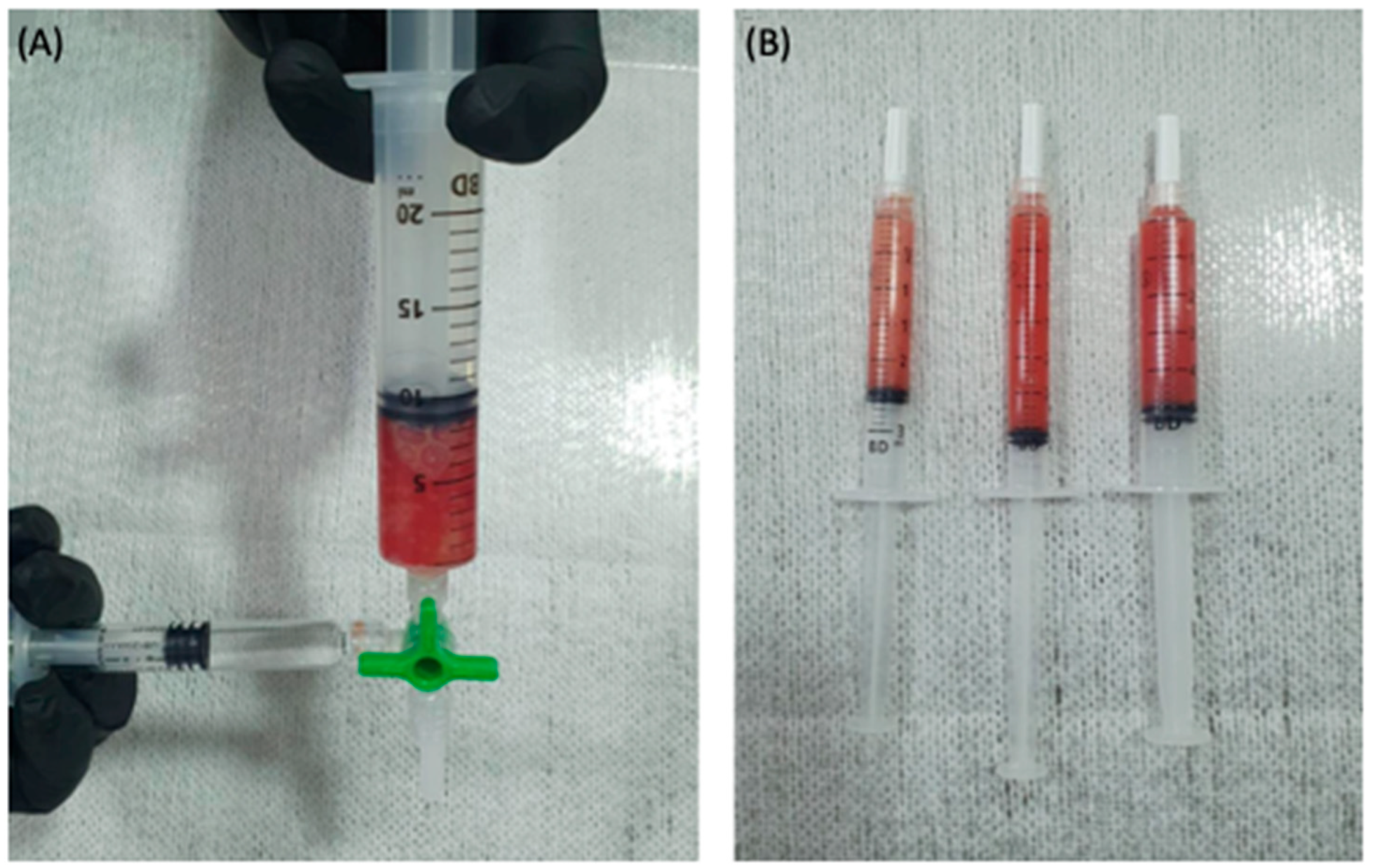
2.1. Obtaining Leukocyte-Rich PRP
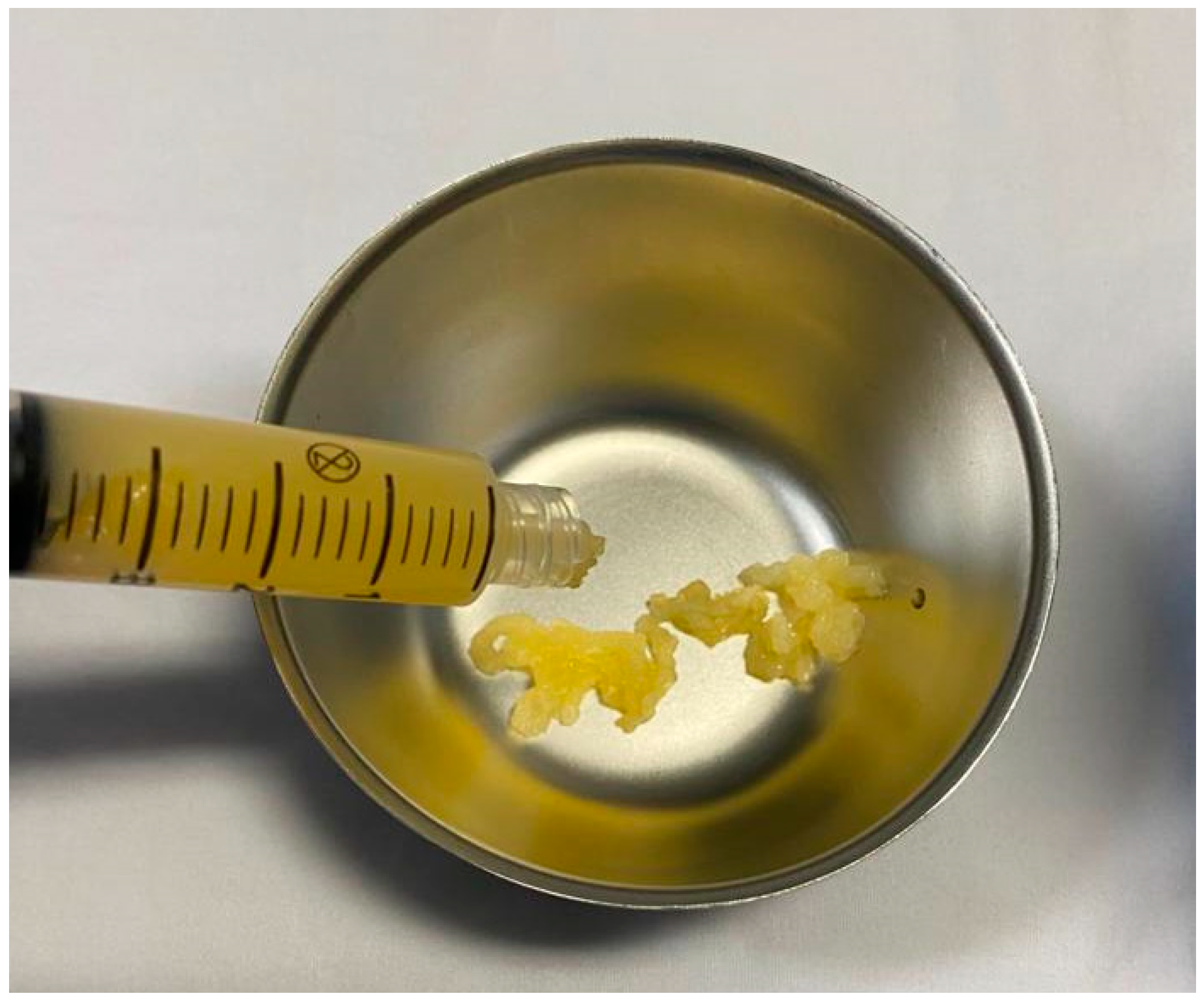
2.2. Obtaining the Plasma Gel
2.3. The PRP Gel Matrix (PRP-GM)
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parrish, W.R. Physiology of Blood Components in Wound Healing: An Appreciation of Cellular Co-Operativity in Platelet Rich Plasma Action. JESO 2017, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.G.; Santos, G.S.; Alkass, N.; Chiesa, T.L.; Azzini, G.O.; da Fonseca, L.F.; dos Santos, A.F.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Mosaner, T.; Lana, J.F. The Regenerative Mechanisms of Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Review. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, A. The Delicate Balance between Fat and Muscle: Adipokines in Metabolic Disease and Musculoskeletal Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Buul, G.M.; Koevoet, W.L.M.; Kops, N.; Bos, P.K.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Weinans, H.; Bernsen, M.R.; van Osch, G.J.V.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Releasate Inhibits Inflammatory Processes in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2011, 39, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo, C.; Filardo, G.; Mariani, E.; Kon, E.; Marcacci, M.; Pereira Ruiz, M.T.; Facchini, A.; Grigolo, B. Comparison of Platelet-Rich Plasma Formulations for Cartilage Healing: An in Vitro Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2014, 96, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, N.; Diamond, R.; Sekyere, E.; Thomas, W. Management of Knee Osteoarthritis by Combined Stromal Vascular Fraction Cell Therapy, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Musculoskeletal Exercises: A Case Series. JPR 2015, 799, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.; Travis, S.; Jewell, D. Ciclosporin Use in Acute Ulcerative Colitis: A Long-Term Experience. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 17, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, J.; Bulsara, M.; Zheng, M.H. The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Am. J. Sport. Med. 2017, 45, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, C.D.; Gardiner, E.E.; Arthur, J.F.; Southey, M.; Andrews, R.K. Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma for Healing Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers: Clinical Efficacy and Potential Mechanisms. Int. Wound J. 2019, 16, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.C.; de Moraes Martinelli, B.; Quintero, M.; de Paula, L.Í.S.; Cataldo, J.L.; de Lima Montalvão, S.A.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. A Case Series of Platelet Rich Plasma in Chronic Venous Ulcers. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, J.W.; Kraeutler, M.J.; Houck, D.A.; Goodrich, J.A.; Dragoo, J.L.; McCarty, E.C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J.Sport. Med. 2021, 49, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.-C.; Sheu, S.-D.; Chung, P.-C.; Yeh, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-W.; Kuo, T.-F. Hyaluronic Acid Supplement as a Chondrogenic Adjuvant in Promoting the Therapeutic Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy in Cartilage Healing. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariel, A.; Lider, O.; Brill, A.; Cahalon, L.; Savion, N.; Varon, D.; Hershkoviz, R. Induction of Interactions between CD44 and Hyaluronic Acid by a Short Exposure of Human T Cells to Diverse Pro-Inflammatory Mediators: T-Cell CD44 Activation by Inflammatory Mediators. Immunology 2000, 100, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, J.; Weglein, A.; Sampson, S.; Vicente, E.; Huber, S.; Souza, C.; Ambach, M.; Vincent, H.; Urban-Paffaro, A.; Santana, M.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Hyaluronic Acid, Platelet-Rich Plasma and the Combination of Both in the Treatment of Mild and Moderate Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J. Stem. Cells Regen. Med. 2016, 12, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martins Shimojo, A.A.; Santos Duarte, A.d.S.; Santos Duarte Lana, J.F.; Malheiros Luzo, Â.C.; Fernandes, A.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Barbosa Souto, E.; Andrade Santana, M.H. Association of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Auto-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Microparticles: Approach for Orthopedic Application. Polymers 2019, 11, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, B.A.G.; França, C.G.; Dávila, J.L.; Batista, N.A.; Caliari-Oliveira, C.; d’Ávila, M.A.; Luzo, Â.C.M.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Santana, M.H.A. Hyaluronic Acid and Fibrin from L-PRP Form Semi-IPNs with Tunable Properties Suitable for Use in Regenerative Medicine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.A.M.; Knape, J.T.A.; Weibrich, G.; Hoffmann, J.; Overdevest, E.P.; Box, H.A.M.; van Zundert, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet Gel: A Review. J. Extra-Corpor. Technol. 2006, 14, 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Anitua, E.; Pino, A.; Troya, M.; Jaén, P.; Orive, G. A Novel Personalized 3D Injectable Protein Scaffold for Regenerative Medicine. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedyakova, E.; Pino, A.; Kogan, L.; Eganova, C.; Troya, M.; Anitua, E. An Autologous Protein Gel for Soft Tissue Augmentation: In Vitro Characterization and Clinical Evaluation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghaim, N.N.; El-Tatawy, R.A.; Neinaa, Y.M.E. Assessment of the Efficacy and Safety of Platelet Poor Plasma Gel as Autologous Dermal Filler for Facial Rejuvenation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Gui, L.; Xiao, R. The Effect of Anticoagulants on the Quality and Biological Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.G.M.; Lichy, R.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Luzo, Â.C.M.; Belangero, W.D.; Santana, M.H.A. Prediction and Modulation of Platelet Recovery by Discontinuous Centrifugation of Whole Blood for the Preparation of Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma. BioResearch Open Access 2013, 2, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.G.M.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Luzo, A.C.M.; Belangero, W.D.; Santana, M.H.A. Relevant Aspects of Centrifugation Step in the Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma. ISRN Hematol. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, B.A.G.; Martins Shimojo, A.A.; Marcelino Perez, A.G.; Duarte Lana, J.F.S.; Andrade Santana, M.H. Distribution, Recovery and Concentration of Platelets and Leukocytes in L-PRP Prepared by Centrifugation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 161, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Kuang, M.; Zhao, J.; Sun, L.; Lu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ma, X. Efficacy and Safety of Intraarticular Hyaluronic Acid and Corticosteroid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 39, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.; Grimalt, R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Ski. Appendage Disord 2018, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles-de-Sá, L.; Gontijo-de-Amorim, N.F.; Takiya, C.M.; Borojevic, R.; Benati, D.; Bernardi, P.; Sbarbati, A.; Rigotti, G. Effect of Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Skin with Intrinsic Aging Process. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2018, 38, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.L.; Montalvão, S.A.L.; Cancela, R.B.B.; Silva, F.A.R.; Urban, A.; Huber, S.C.; Júnior, J.L.R.C.; Lana, J.F.S.D.; Annichinno-Bizzacchi, J.M. Treatment of Male Pattern Alopecia with Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Double-Blind Controlled Study with Analysis of Platelet Number and Growth Factor Levels. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, H.; Aalders-Bouhuijs, S.S.F.; Steinfelder-Visscher, J.; van der Heide, S.M.; Morshuis, W.J. Platelet-Leukocyte Rich Gel Application in the Prevention of Deep Sternal Wound Problems after Cardiac Surgery in Obese Diabetic Patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammoto, T.; Jiang, A.; Jiang, E.; Mammoto, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Extract Prevents Pulmonary Edema through Angiopoietin-Tie2 Signaling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol.Biol. 2015, 52, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-X.; Fan, Z.-H.; Zhao, J.-G.; Zhang, P. The Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma May Be a Novel Treatment for Central Nervous System Diseases. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, M.S.A.; Sazlina, S.G. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Cheng, C.; Sun, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Guo, W. Efficacy and Safety of Intra-Articular Platelet-Rich Plasma in Osteoarthritis Knee: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Bio. Med Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessio-Mazzola, M.; Felli, L.; Trentini, R.; Formica, M.; Capello, A.G.; Lovisolo, S.; Maffulli, N. Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Grade 3 Symptomatic Degenerative Meniscal Lesions: A 1-Year Follow-up Prospective Study. Sport. Health 2021, 10, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, J.F.; Huber, S.C.; Purita, J.; Tambeli, C.H.; Santos, G.S.; Paulus, C.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Leukocyte-Rich PRP versus Leukocyte-Poor PRP-The Role of Monocyte/Macrophage Function in the Healing Cascade. J. Clin. Orthop. and Trauma 2019, 10, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, N.; Koolwijk, P.; De Maat, M.P.M. Fibrin Structure and Wound Healing. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opneja, A.; Kapoor, S.; Stavrou, E.X. Contribution of Platelets, the Coagulation and Fibrinolytic Systems to Cutaneous Wound Healing. Thromb. Res. 2019, 179, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heissig, B.; Dhahri, D.; Eiamboonsert, S.; Salama, Y.; Shimazu, H.; Munakata, S.; Hattori, K. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Fibrinolytic Factor in Tissue Regeneration and Cancer Progression. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4759–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.H.; Molavi, B.; Mohammadi, S.; Nikbakht, M.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Mostafaei, S.; Norooznezhad, A.H.; Ghorbani Abdegah, A.; Ghavamzadeh, A. Evaluation of Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Using Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel: A Single-Arm Clinical Trial. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainys, D.; Cepas, A.; Dambrauskaite, K.; Nedzelskiene, I.; Rimdeika, R. Effectiveness of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel in the Treatment of Hard-to-Heal Leg Ulcers: A Randomised Control Trial. J. Wound Care 2019, 28, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçar, Ö.; Çelik, S. Comparison of Platelet-rich Plasma Gel in the Care of the Pressure Ulcers with the Dressing with Serum Physiology in Terms of Healing Process and Dressing Costs. Int. Wound. J. 2020, 17, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.N.; Birkinshaw, C. Hyaluronic Acid Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering—A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-H.; Lo, W.-C.; Hsu, W.-C.; Wei, H.-J.; Liu, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Tina Chen, S.-Y.; Shieh, Y.-H.; Williams, D.F.; Deng, W.-P. Synergistic Anabolic Actions of Hyaluronic Acid and Platelet-Rich Plasma on Cartilage Regeneration in Osteoarthritis Therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9599–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; D’Este, M.; Vadalà, G.; Cattani, C.; Papalia, R.; Alini, M.; Denaro, V. Platelet Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid Blend for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Rheological and Biological Evaluation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasavvidis, T.; Totlis, T.; Gilat, R.; Cole, B.J. Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined With Hyaluronic Acid Improves Pain and Function Compared With Hyaluronic Acid Alone in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthroscopy J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2021, 37, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, S.A.; Hossain, M.J.; Arefin, M.S.; Islam, M.I.; Begum, S.A.; Shompa, S.S.; Akhtaruzzaman, A. Effects of Platelet Rich Plasma in Combination with Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Primary Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Natl. Inst. Neurosci. Bangladesh 2019, 5, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Procedure | |
|---|---|
| LR-PRP | Harvest peripheral blood in ACD tubes |
| First spin at 300× g for 5 min (RT) | |
| Collect plasma and buffy coat | |
| Second spin at 700× g for 17 min (RT) | |
| Collect 80% of the supernatant for plasma gel in a syringe | |
| Homogenize and separate the remaining 20% (LR-PRP) | |
| Plasma gel | Place the syringes containing the plasma in a heating device |
| Heat up to 70 °C for 15 min | |
| Hyaluronic acid | Use commercial hyaluronic acid |
| PRP-GM | Mix LR-PRP, plasma gel and hyaluronic acid into a single syringe |
| Inject into the target point using an ultrasound guidance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godoi, T.T.F.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Huber, S.C.; Santana, M.H.A.; da Fonseca, L.F.; Santos, G.S.; Azzini, G.O.M.; Mosaner, T.; Paulus-Romero, C.; Lana, J.F.S.D. Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Matrix (PRP-GM): Description of a New Technique. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120817
Godoi TTF, Rodrigues BL, Huber SC, Santana MHA, da Fonseca LF, Santos GS, Azzini GOM, Mosaner T, Paulus-Romero C, Lana JFSD. Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Matrix (PRP-GM): Description of a New Technique. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(12):817. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120817
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodoi, Thales Thiago Ferreira, Bruno Lima Rodrigues, Stephany Cares Huber, Maria Helena Andrade Santana, Lucas Furtado da Fonseca, Gabriel Silva Santos, Gabriel Ohana Marques Azzini, Tomas Mosaner, Chris Paulus-Romero, and José Fábio Santos Duarte Lana. 2022. "Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Matrix (PRP-GM): Description of a New Technique" Bioengineering 9, no. 12: 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120817
APA StyleGodoi, T. T. F., Rodrigues, B. L., Huber, S. C., Santana, M. H. A., da Fonseca, L. F., Santos, G. S., Azzini, G. O. M., Mosaner, T., Paulus-Romero, C., & Lana, J. F. S. D. (2022). Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Matrix (PRP-GM): Description of a New Technique. Bioengineering, 9(12), 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9120817








