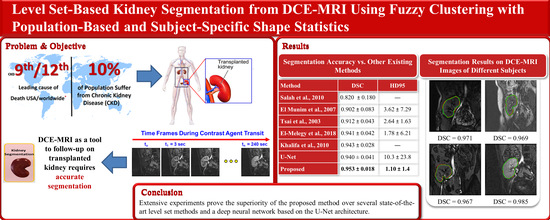
Level-Set-Based Kidney Segmentation from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Population-Based and Subject-Specific Shape Statistics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
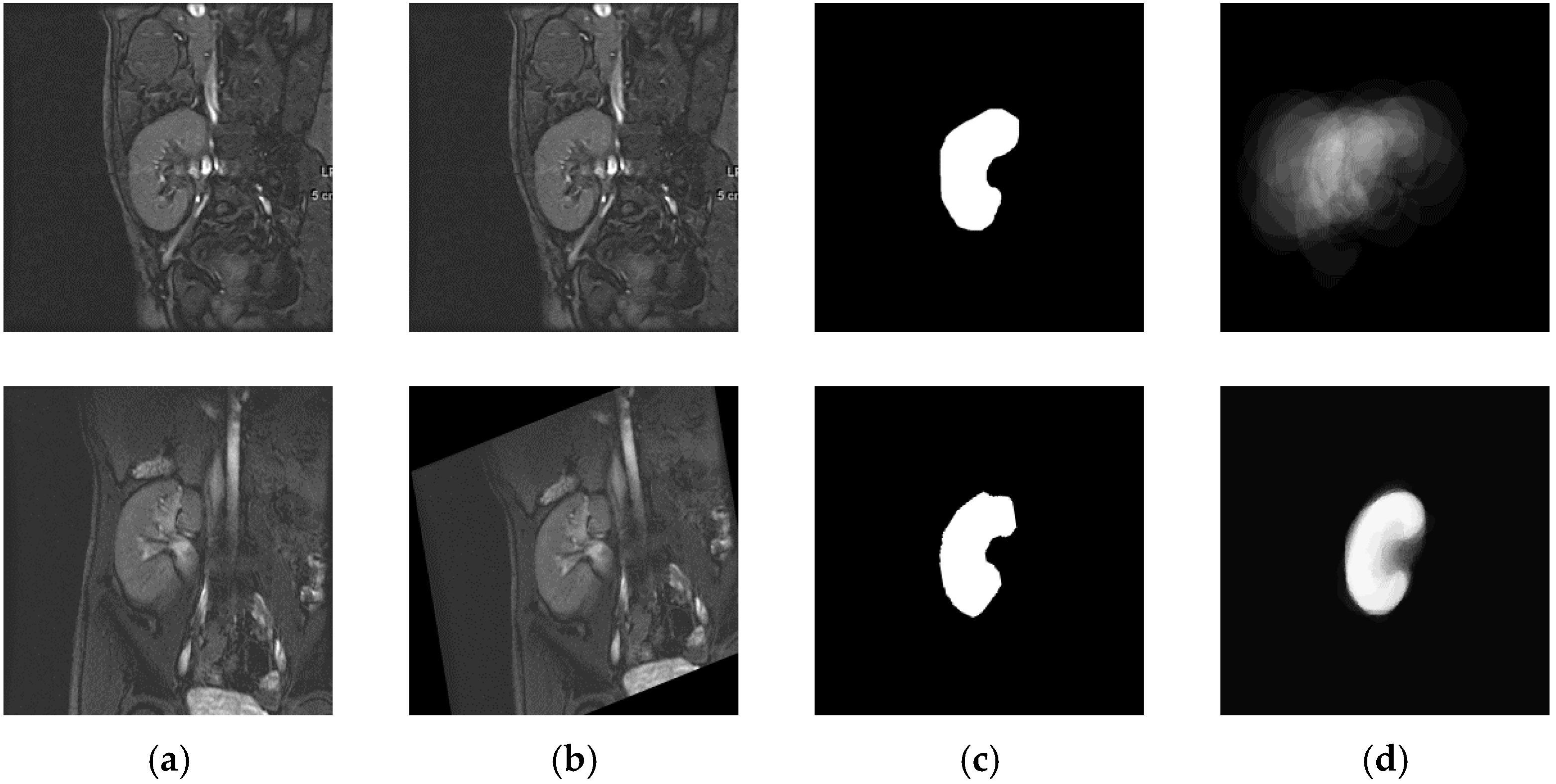
2.1. Materials
2.2. Problem Statement and Notations
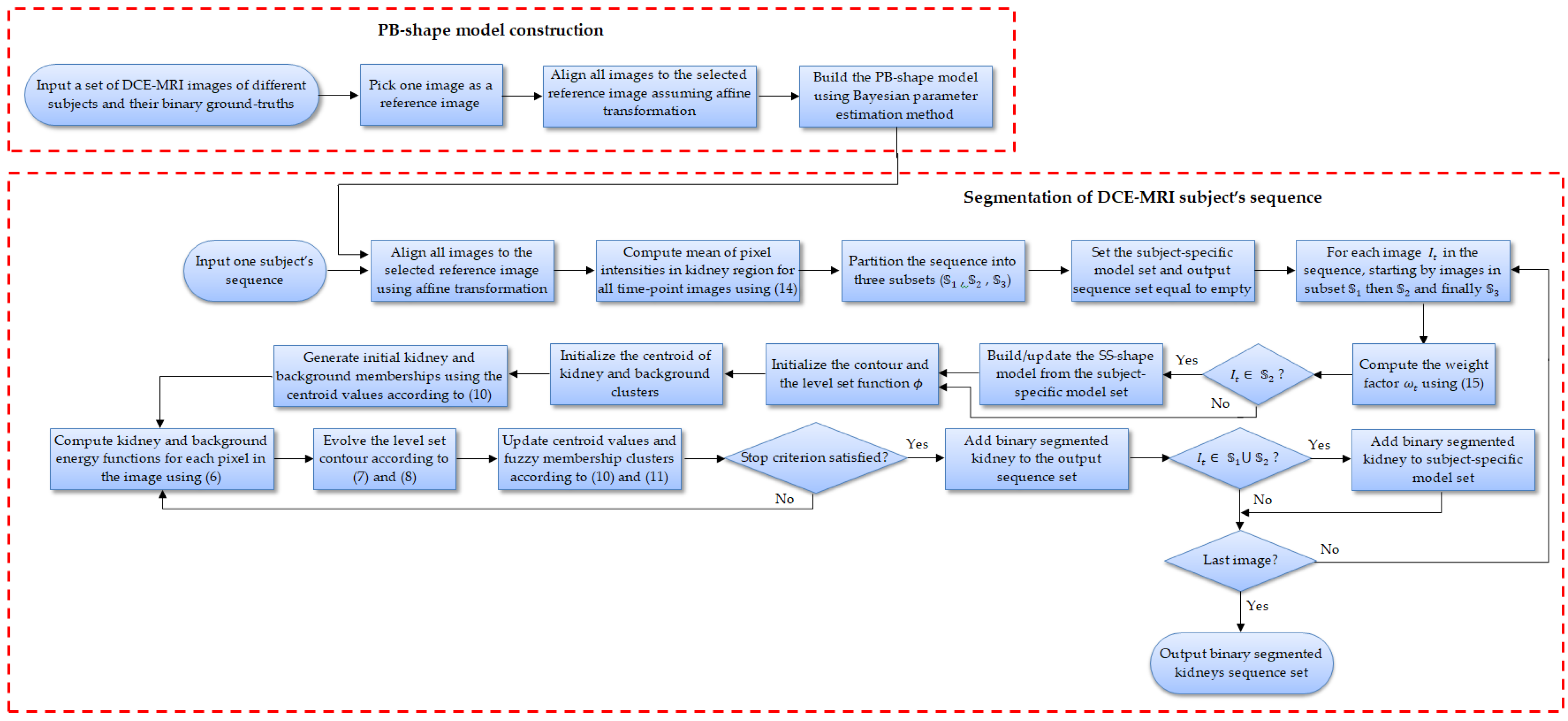
2.3. Level-Set-Based Segmentation Model with Fuzzy Clustering and Shape Statistics
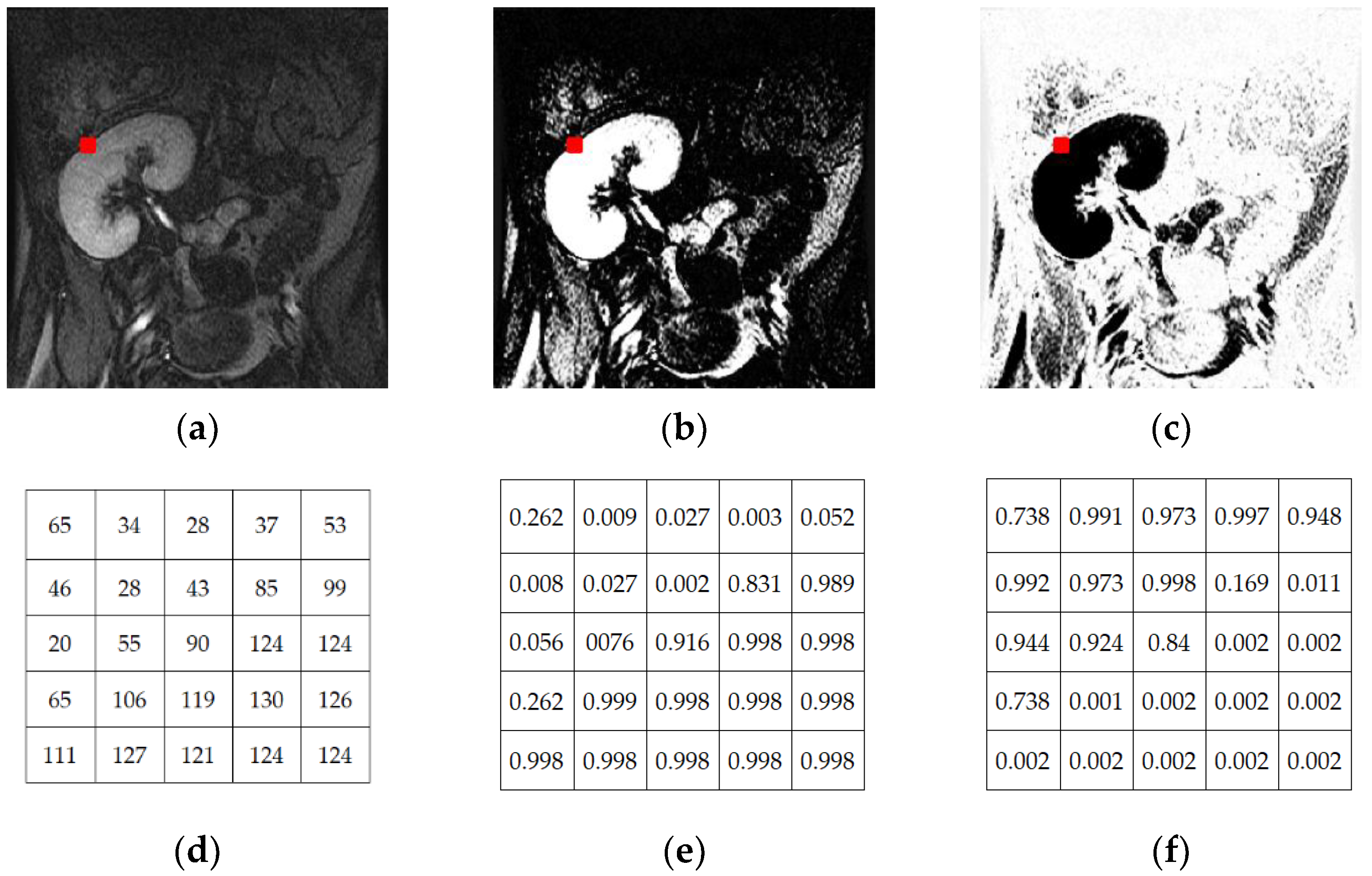
2.4. FCM Membership Function
2.5. Statistical Kidney Shape Model
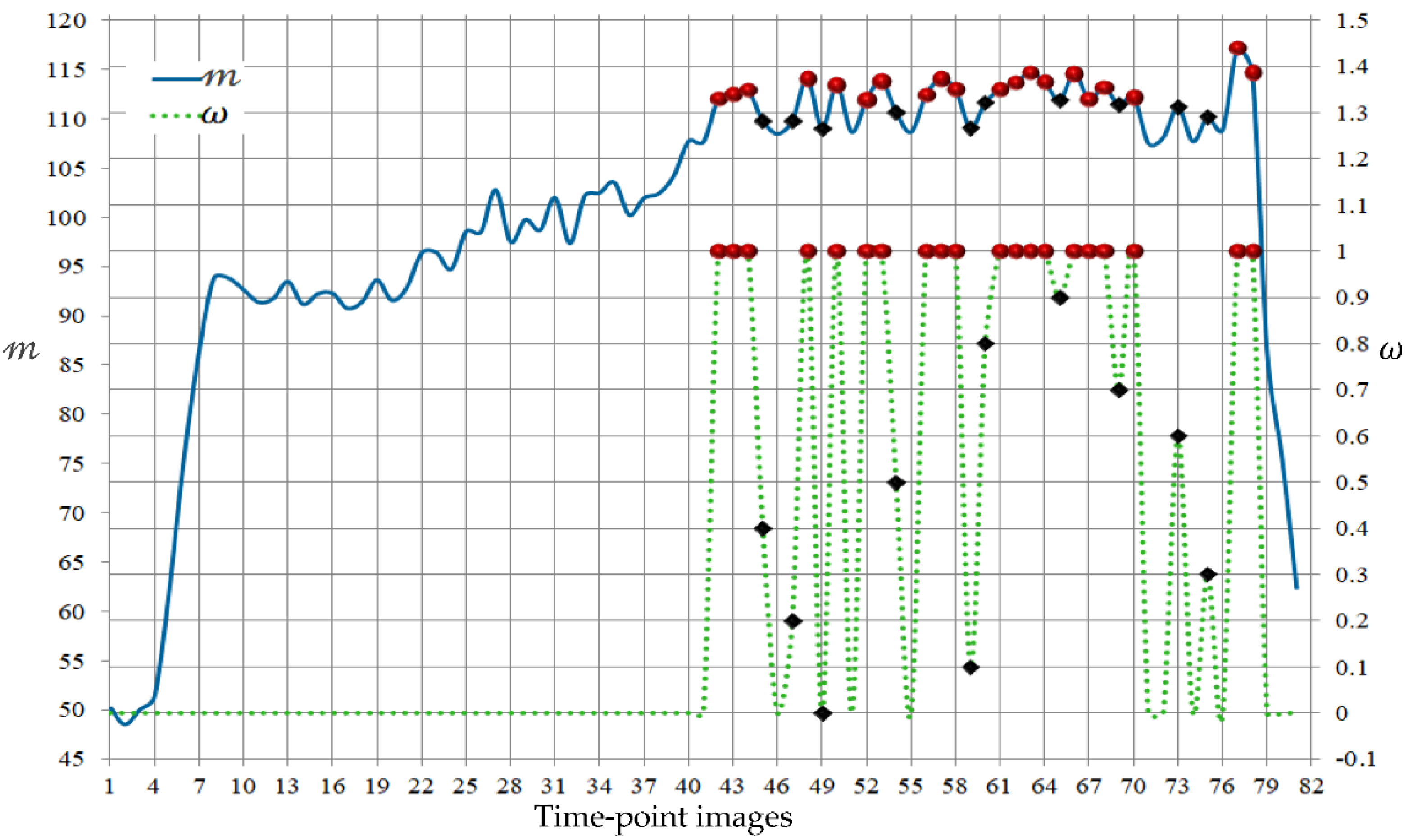
2.6. Sequence Partitioning and the Weight Factor
3. Results
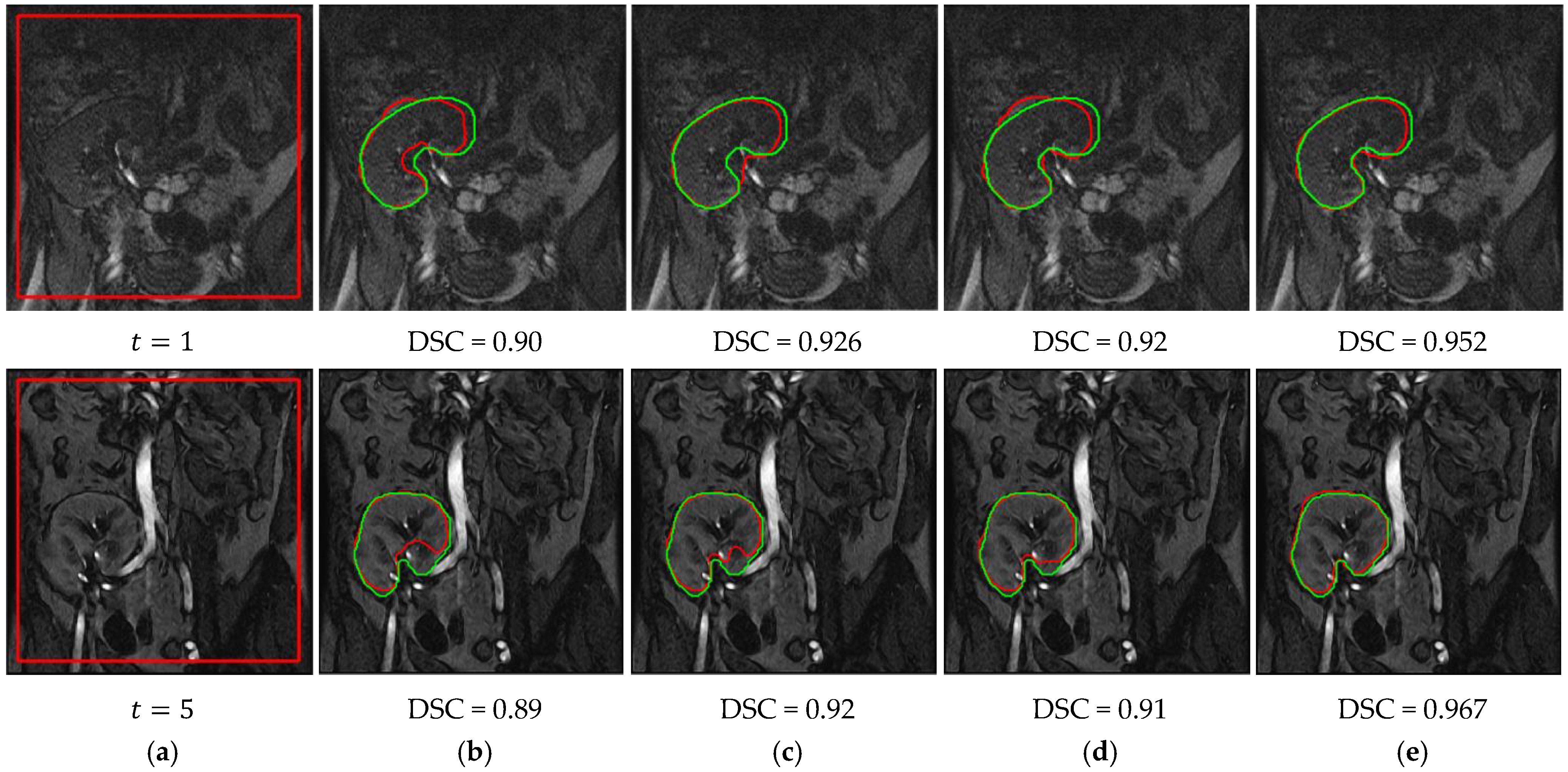
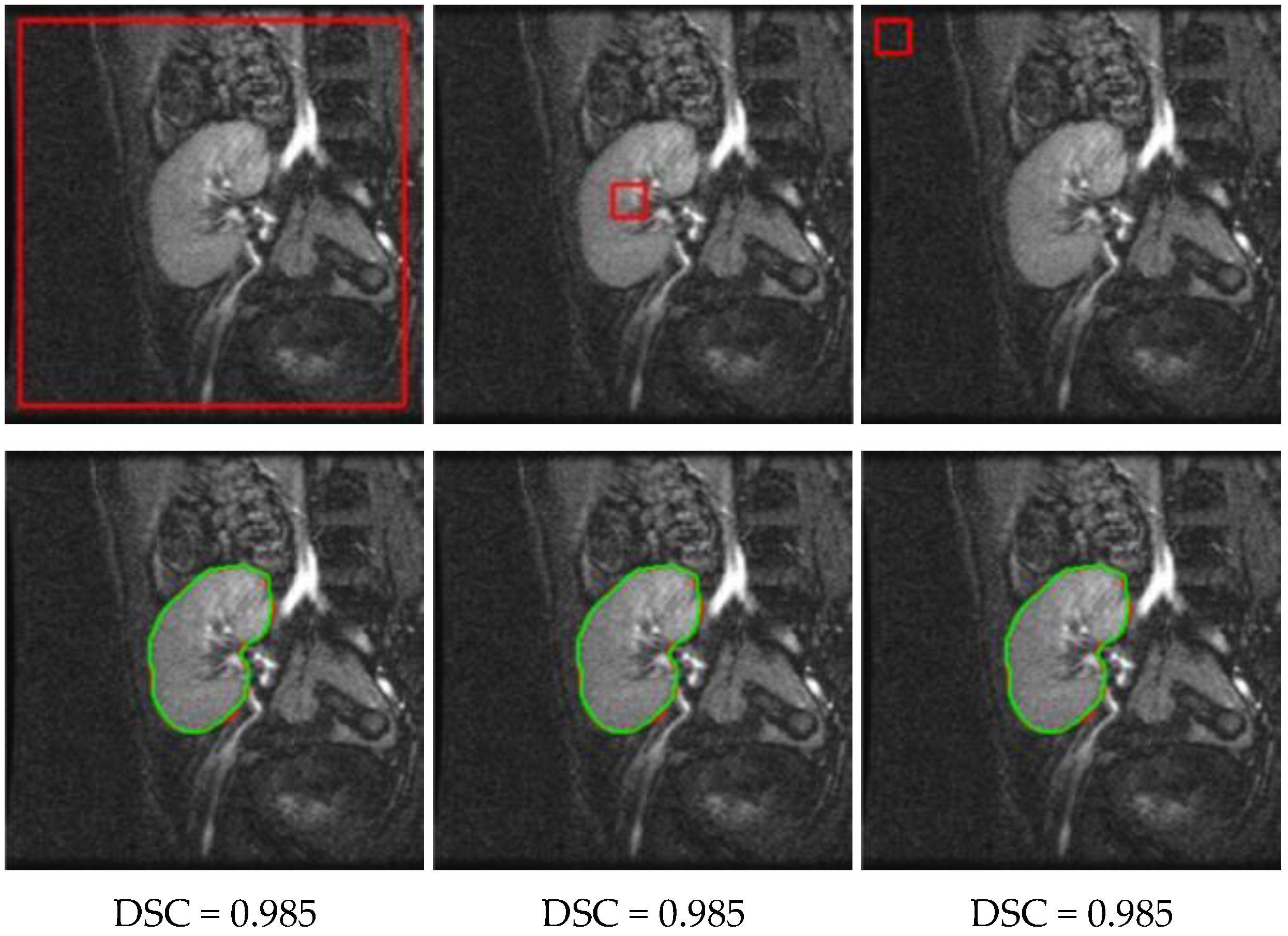
3.1. Method Performance with Comparisons to Other Methods
3.2. Ablation Experiments
3.3. Comparison to U-Net-Based Deep Neural Networks
4. Conclusions
- It integrates the FCM clustering algorithm, the level set method, and both PB-shape and SS-shape statistics for this problem for the first time in literature;
- The FCM clustering algorithm is embedded into the level set method; a pixel’s kidney/background fuzzy memberships are coupled with the level set evolution, considering the image intensities directly, as well as the kidney’s shape indirectly. This allows the proposed method to precisely capture the kidney, even on noisy and low-contrast images;
- The PB-shape and the SS-shape models are built using Bayesian parameter estimation, which statistically accounts for kidney pixels that are possibly not observed in the images that are used for the model building, thus rendering more accurate shape models;
- An automated, simple, and time-efficient strategy is proposed for partitioning the patient’s sequence into three subsets in order to properly determine the blending factor between the PB-shape and the SS-shape models;
- The experiments that were performed on 45 subjects demonstrate the accuracy of the proposed method and its robustness against noise, low contrast, and contour initialization with no need for tuning the method’s parameters. The comparisons with several state-of-the-art level set methods, and two CNN based on the U-Net architecture, confirm the superior and consistent performance of the proposed method.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mostapha, M.; Khalifa, F.; Alansary, A.; Soliman, A.; Suri, J.; El-Baz, A.S. Computer-aided diagnosis systems for acute renal transplant rejection: Challenges and methodologies. In Abdomen And Thoracic Imaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöllner, F.G.; Kociński, M.; Hansen, L.; Golla, A.K.; Trbalić, A.Š.; Lundervold, A.; Materka, A.; Rogelj, P. Kidney segmentation in renal magnetic resonance imaging-current status and prospects. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71577–71605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, S.E.; El-Baz, A.; Farag, A.A.; El-Ghar, M.; Eldiasty, T.; Ghoneim, M.A. A kidney segmentation framework for dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J. Vib. Control. 2007, 13, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; El-Baz, A.; Gimel’farb, G.; El-Ghar, M.A. Non-invasive image-based approach for early detection of acute renal rejection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Beijing, China, 20–24 September 2010; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; Beache, G.M.; El-Ghar, M.A.; El-Diasty, T.; Gimel’farb, G.; Kong, M.; El-Baz, A. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI-based early detection of acute renal transplant rejection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1910–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Soliman, A.; Gimel’farb, G.; El-Baz, A. Segmenting kidney DCE-MRI using 1st-order shape and 5th-order appearance priors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodneland, E.; Hanson, E.A.; Lundervold, A.; Modersitzki, J.; Eikefjord, E.; Munthe-Kaas, A.Z. Segmentation-driven image registration-application to 4D DCE-MRI recordings of the moving kidneys. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltanboly, A.; Ghazal, M.; Hajjdiab, H.; Shalaby, A.; Switala, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Sahoo, P.; El-Azab, M.; El-Baz, A. Level sets-based image segmentation approach using statistical shape priors. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 340, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamasneh, A.R.; Jalab, H.A.; Palaiahnakote, S.; Obaidellah, U.H.; Ibrahim, R.W.; El-Melegy, M.T. A new local fractional entropy-based model for kidney MRI image enhancement. Entropy 2018, 20, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shamasneh, A.R.; Jalab, H.A.; Shivakumara, P.; Ibrahim, R.W.; Obaidellah, U.H. Kidney segmentation in MR images using active contour model driven by fractional-based energy minimization. Signal Image Video Process 2020, 14, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Rørvik, J.; Lundervold, A. Fast semi-supervised segmentation of the kidneys in DCE-MRI using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific Symposium, Functional Renal Imaging: Where Physiology, Nephrology, Radiology and Physics Meet, Berlin, Germany, 11–13 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, M.; Warfield, S.K.; Kurugol, S. Automatic renal segmentation in DCE-MRI using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milecki, L.; Bodard, S.; Correas, J.M.; Timsit, M.O.; Vakalopoulou, M. 3D unsupervised kidney graft segmentation based on deep learning and multi-sequence MRI. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, V.; Brunetti, A.; Cascarano, G.D.; Guerriero, A.; Pesce, F.; Moschetta, M.; Gesualdo, L. A comparison between two semantic deep learning frameworks for the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease segmentation based on magnetic resonance images. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Cascarano, G.D.; Feudis, I.D.; Moschetta, M.; Gesualdo, L.; Bevilacqua, V. Detection and segmentation of kidneys from magnetic resonance images in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Nanchang, China, 3–6 August 2019; pp. 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavur, A.E.; Gezer, N.S.; Barış, M.; Aslan, S.; Conze, P.H.; Groza, V.; Pham, D.D.; Chatterjee, S.; Ernst, P.; Özkan, S.; et al. CHAOS challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Melegy, M.T.; Abd El-karim, R.M.; El-Baz, A.; El-Ghar, M.A. Fuzzy membership-driven level set for automatic kidney segmentation from DCE-MRI. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.; Naik, B.; Behera, H.S. Fuzzy C-means (FCM) clustering algorithm: A decade review from 2000 to 2014. In Computational Intelligence in Data Mining; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedkiw, R.; Osher, S. Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- El-Melegy, M.T.; Abd El-Karim, R.M.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Shehata, M.; Khalifa, F.; El-Baz, A.S. Kidney segmentation from DCE-MRI converging level set methods, fuzzy clustering and Markov random field modeling. Sci. Rep. 2022. In Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, T.; Meinzer, H.P. Statistical shape models for 3D medical image segmentation: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2009, 13, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Qi, F.; Xue, Z.; Chen, L.; Ito, K.; Matsuo, H.; Shen, D. Segmenting lung fields in serial chest radiographs using both population-based and subject-specific shape statistics. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Melegy, M.T.; Abd El-Karim, R.M.; El-Baz, A.S.; Abou El-Ghar, M. A Combined Fuzzy C-means and level set method for automatic DCE-MRI kidney segmentation using both population-based and patient-specific shape statistics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.; Singer, Y. Efficient Bayesian parameter estimation in large discrete domains. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’98), Denver, CO, USA, 30 November–5 December 1998; pp. 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Reinke, A.; Eisenmann, M.; Tizabi, M.D.; Sudre, C.H.; Rädsch, T.; Antonelli, M.; Arbel, T.; Bakas, S.; Cardoso, M.J.; Cheplygina, V.; et al. Common limitations of image processing metrics: A picture story. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M.; Fathy, M.; Escalera, S. Bi-Directional ConvLSTM U-Net with Densley connected convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, N.; Sathianathen, N.; Kalapara, A.; Walczak, E.; Moore, K.; Kaluzniak, H.; Rosenberg, J.; Blake, P.; Rengel, Z.; Oestreich, M.; et al. The kits19 challenge data: 300 kidney tumor cases with clinical context, CT semantic segmentations, and surgical outcomes. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Melegy, M.T.; Mokhtar, H. Tumor segmentation in brain MRI using a fuzzy approach with class center priors. EURASIP J. Image Video Process 2014, 2014, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Wells, W.M., III. Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 24, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, K.A.; Svore, K.M.; Keromytis, A.D.; Stolfo, S.J. One class support vector machines for detecting anomalous windows registry accesses. In Proceedings of the ICDM Workshop on Data Mining for Computer Security, Melbourne, FL, USA, 19 November 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.; Yezzi, A.; Wells, W.; Tempany, C.; Tucker, D.; Fan, A.; Willsky, A. A shape-based approach to the segmentation of medical imagery using level sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Munim, H.E.A.; Farag, A.A. Curve/surface representation and evolution using vector level sets with application to the shape-based segmentation problem. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.B.; Mitiche, A.; Ayed, I.B. Multiregion image segmentation by parametric kernel graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2010, 20, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, B.; Asaturyan, H.; Kurugol, S.; Afacan, O.; Bell, J.D.; Thomas, E.L. 3D Deep learning for anatomical structure segmentation in multiple imaging modalities. In Proceedings of the IEEE 34th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Aveiro, Portugal, 7–9 June 2021; pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Zhang, J.S.; Khan, M.K.; Chen, X.; Alghathbar, K. Dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis: A novel approach for face and palmprint recognition in DCT domain. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar]





| Method | All Images | Low-Contrast Images | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | IoU | HD95 | DSC | IoU | HD95 | |
| FCMLS [19] | 0.941 ± 0.042 | 0.89 ± 0.056 | 1.78 ± 6.21 | 0.88 ± 0.137 | 0.80 ± 0.156 | 8.18 ± 22.8 |
| PBPSFL [25] | 0.952 ± 0.041 | 0.90 ± 0.043 | 1.11 ± 1.7 | 0.923 ± 0.13 | 0.88 ± 0.056 | 1.93 ± 2.32 |
| FML [22] | 0.956 ± 0.019 | 0.91 ± 0.035 | 1.15 ± 1.46 | 0.936 ± 0.024 | 0.88 ± 0.042 | 1.94 ± 1.58 |
| Proposed | 0.953 ± 0.018 | 0.91 ± 0.033 | 1.10 ± 1.4 | 0.942 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.034 | 1.56 ± 1.46 |
| Method | All Images | Low-Contrast Images | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | IoU | HD95 | DSC | IoU | HD95 | |
| PBPSFL [25] | 0.944 ± 0.022 | 0.89 ± 0.039 | 1.71 ± 1.7 | 0.93 ± 0.025 | 0.87 ± 0.042 | 2.47 ± 1.85 |
| Proposed | 0.952 ± 0.016 | 0.91 ± 0.029 | 1.20 ± 1.0 | 0.95 ± 0.018 | 0.90 ± 0.033 | 1.41 ± 1.24 |
| Method | DSC | IoU | HD95 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PKGC [35] | 0.820 ± 0.180 | - | - |
| VLS [34] | 0.902 ± 0.083 | 0.84 ± 0.12 | 3.62 ± 7.29 |
| SB [33] | 0.912 ± 0.043 | 0.84 ± 0.07 | 2.64 ± 1.63 |
| FCMLS [19] | 0.941 ± 0.042 | 0.89 ± 0.056 | 1.78 ± 6.21 |
| 2nd-MGRF [4] | 0.943 ± 0.028 | - | - |
| PBPSFL [25] | 0.952 ± 0.041 | 0.90 ± 0.043 | 1.10 ± 1.69 |
| FML [22] | 0.956 ± 0.019 | 0.91 ± 0.035 | 1.15 ± 1.46 |
| Proposed | 0.953 ± 0.018 | 0.91 ± 0.033 | 1.1 ± 1.4 |
| Method | All Images | Low-Contrast Images | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | IoU | HD95 | DSC | IoU | HD95 | |
| PB-shape + Fuzzy memberships | 0.945 ± 0.055 | 0.89 ± 0.056 | 1.63 ± 3.87 | 0.884 ± 0.12 | 0.81 ± 0.128 | 5.61 ± 12.54 |
| PB-shape + Embedded fuzzy memberships | 0.946 ± 0.029 | 0.89 ± 0.048 | 1.63 ± 1.97 | 0.918 ± 0.06 | 0.85 ± 0.096 | 3.18 ± 4.28 |
| PB-shape + Embedded memberships + SS-shape | 0.953 ± 0.018 | 0.91 ± 0.033 | 1.10 ± 1.4 | 0.942 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.034 | 1.56 ± 1.46 |
| Experiment | All Images | Low-Contrast Images | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | IoU | HD95 | DSC | IoU | HD95 | |||
| 1 | 15 | 15 | 0.949 ± 0.021 | 0.90 ± 0.038 | 1.34 ± 1.43 | 0.942 ± 0.022 | 0.89 ± 0.038 | 1.58 ± 1.46 |
| 2 | 20 | 10 | 0.953 ± 0.018 | 0.91 ± 0.033 | 1.10 ±1.4 | 0.942 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.034 | 1.56 ± 1.46 |
| 3 | 10 | 20 | 0.946 ± 0.027 | 0.89 ± 0.038 | 1.41 ± 1.62 | 0.94 ± 0.023 | 0.88 ± 0.041 | 1.61 ± 1.48 |
| Method | All Images | Low-Contrast Images | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | IoU | HD95 | DSC | IoU | HD95 | |
| U-Net [13] | 0.940 ± 0.041 | 0.89 ± 0.069 | 10.30 ± 23.8 | 0.88 ± 0.071 | 0.77 ± 0.13 | 19.9 ± 28.8 |
| BCDU-Net [28] | 0.942 ± 0.038 | 0.89 ± 0.062 | 4.62 ± 12.35 | 0.90 ± 0.057 | 0.82 ± 0.089 | 7.89 ± 12.27 |
| Proposed | 0.957 ± 0.016 | 0.93 ± 0.019 | 0.80 ± 1.03 | 0.952 ± 0.014 | 0.90 ± 0.026 | 0.85 ± 0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Melegy, M.; Kamel, R.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; Alghamdi, N.S.; El-Baz, A. Level-Set-Based Kidney Segmentation from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Population-Based and Subject-Specific Shape Statistics. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110654
El-Melegy M, Kamel R, Abou El-Ghar M, Alghamdi NS, El-Baz A. Level-Set-Based Kidney Segmentation from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Population-Based and Subject-Specific Shape Statistics. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(11):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110654
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Melegy, Moumen, Rasha Kamel, Mohamed Abou El-Ghar, Norah S. Alghamdi, and Ayman El-Baz. 2022. "Level-Set-Based Kidney Segmentation from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Population-Based and Subject-Specific Shape Statistics" Bioengineering 9, no. 11: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110654
APA StyleEl-Melegy, M., Kamel, R., Abou El-Ghar, M., Alghamdi, N. S., & El-Baz, A. (2022). Level-Set-Based Kidney Segmentation from DCE-MRI Using Fuzzy Clustering with Population-Based and Subject-Specific Shape Statistics. Bioengineering, 9(11), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110654