The Selective α1 Antagonist Tamsulosin Alters ECM Distributions and Cellular Metabolic Functions of ARPE 19 Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 2D Culture of ARPE 19 Cells
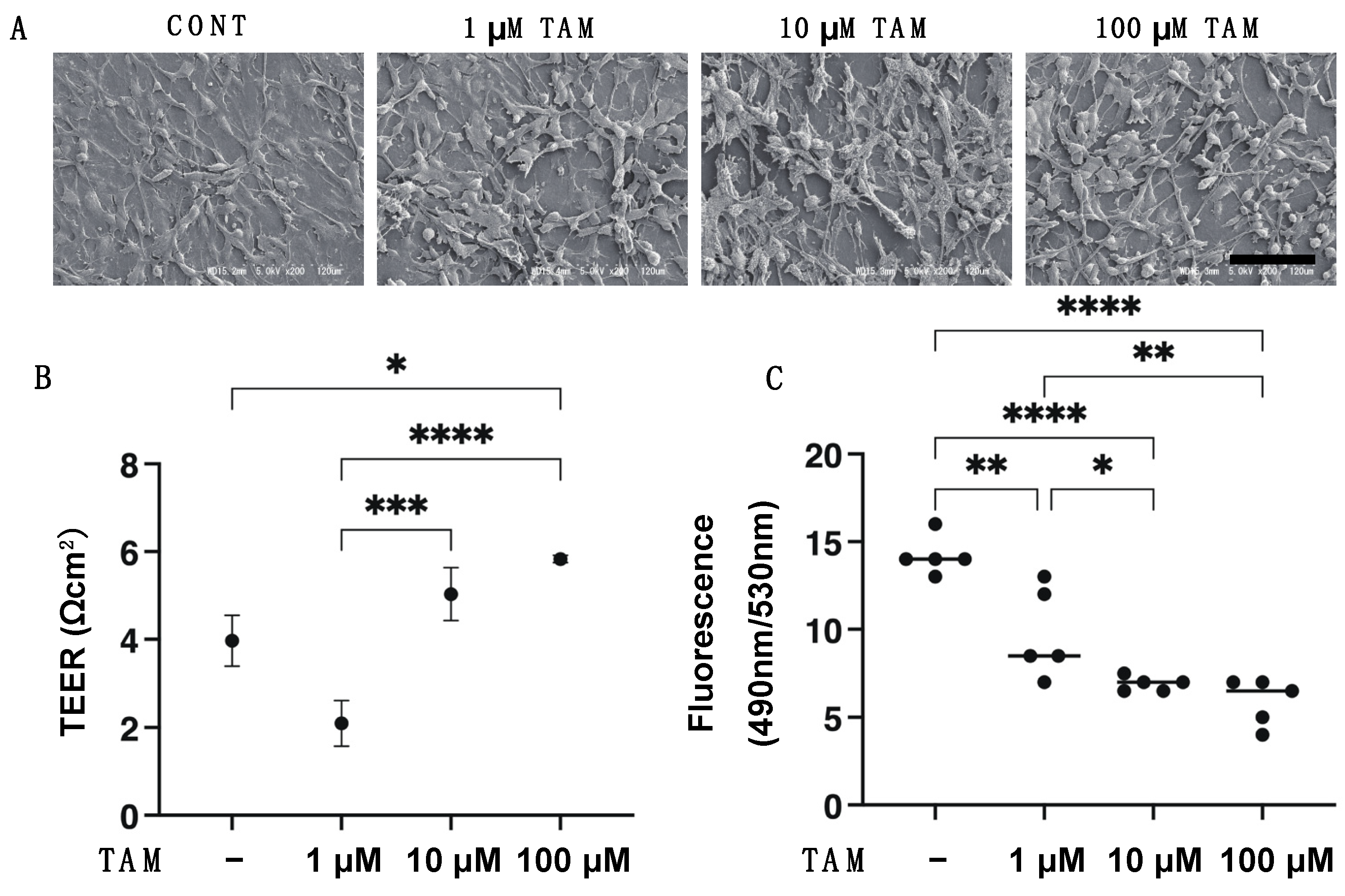
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis, Transepithelial Electron Resistance (TEER) and FITC-Dextran Permeability Measurements of 2D Cultured ARPE 19 Cell Monolayer
2.3. Measurement of Real-Time Cellular Metabolic Functions of 2D ARPE 19 Cells
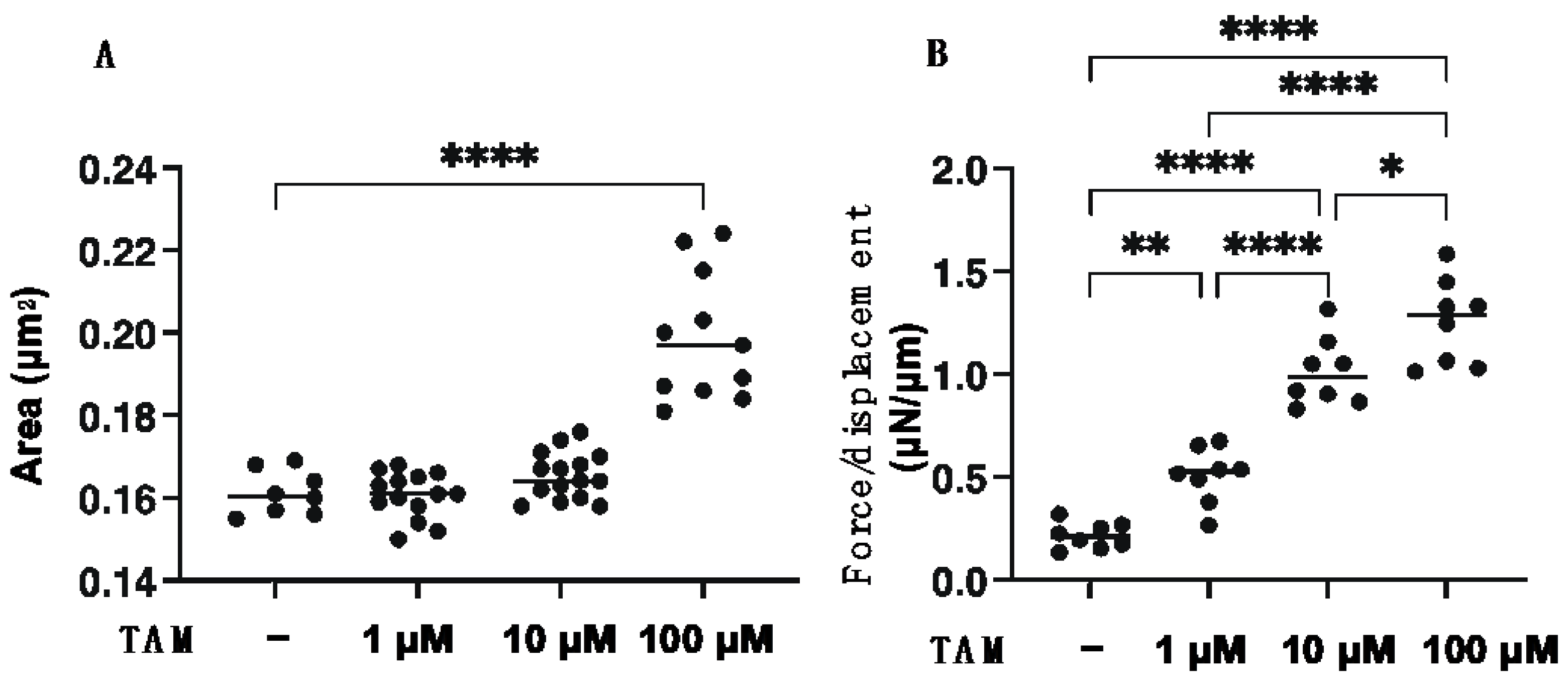
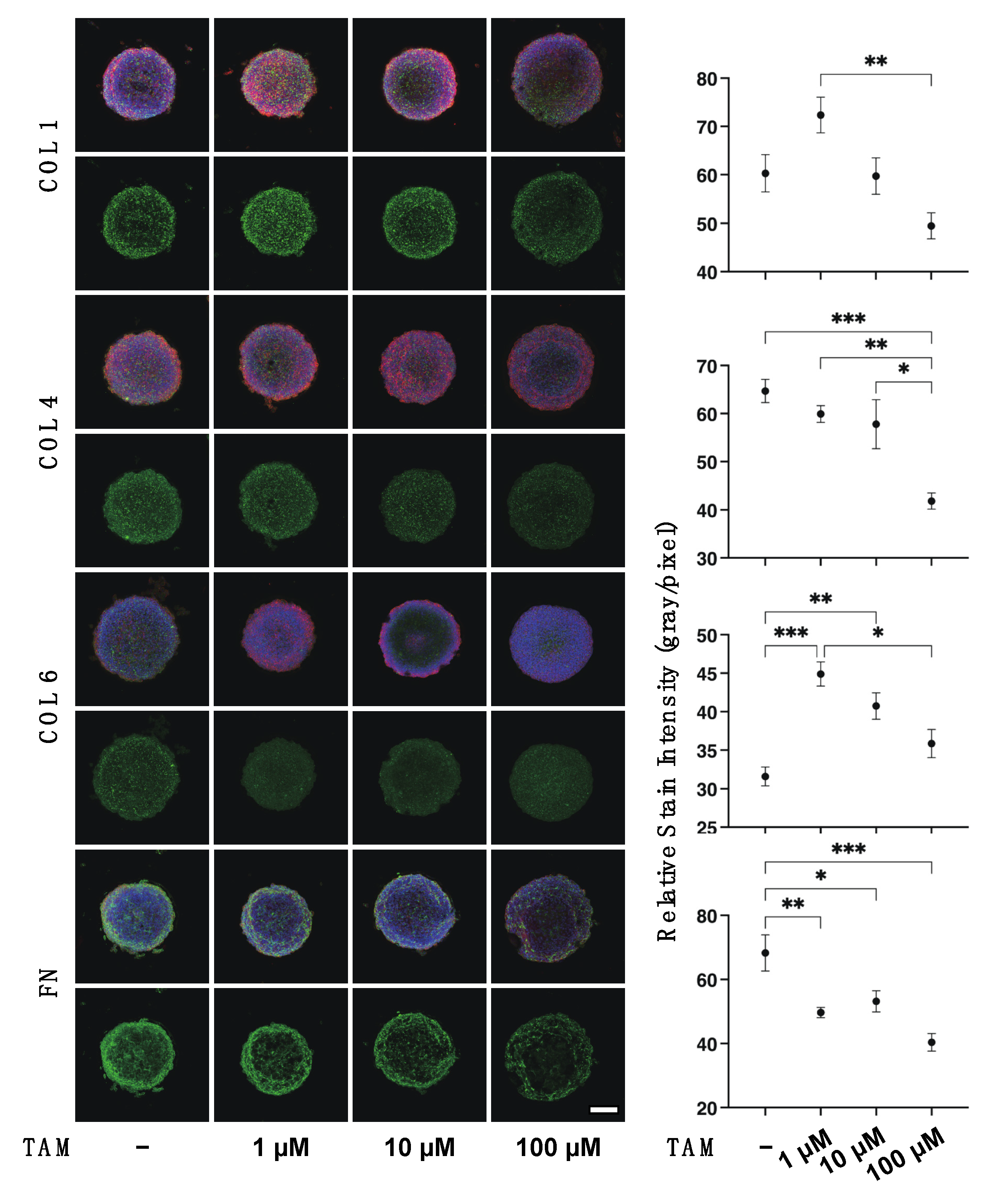
2.4. Preparation of 3D ARPE 19 Spheroids
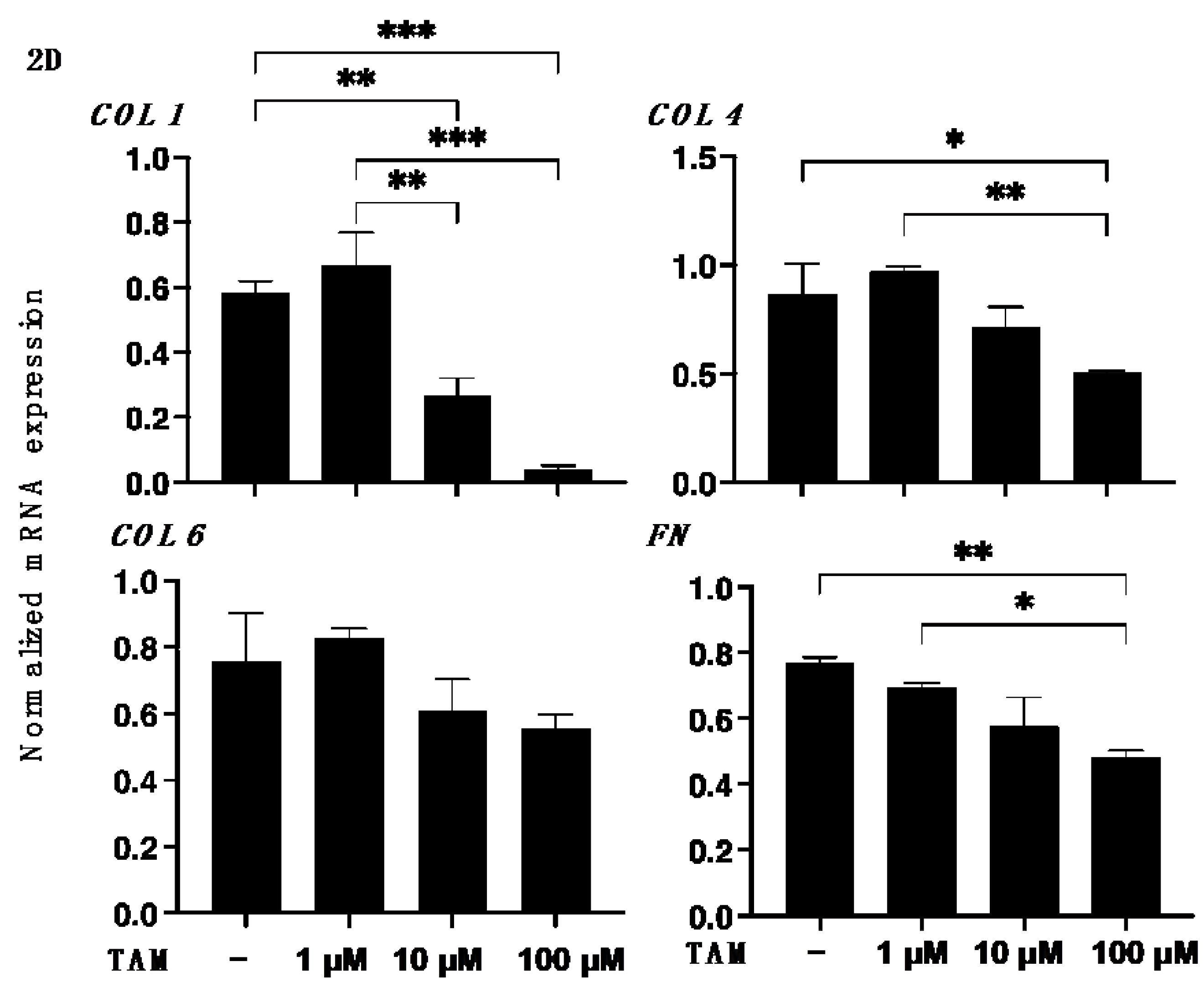
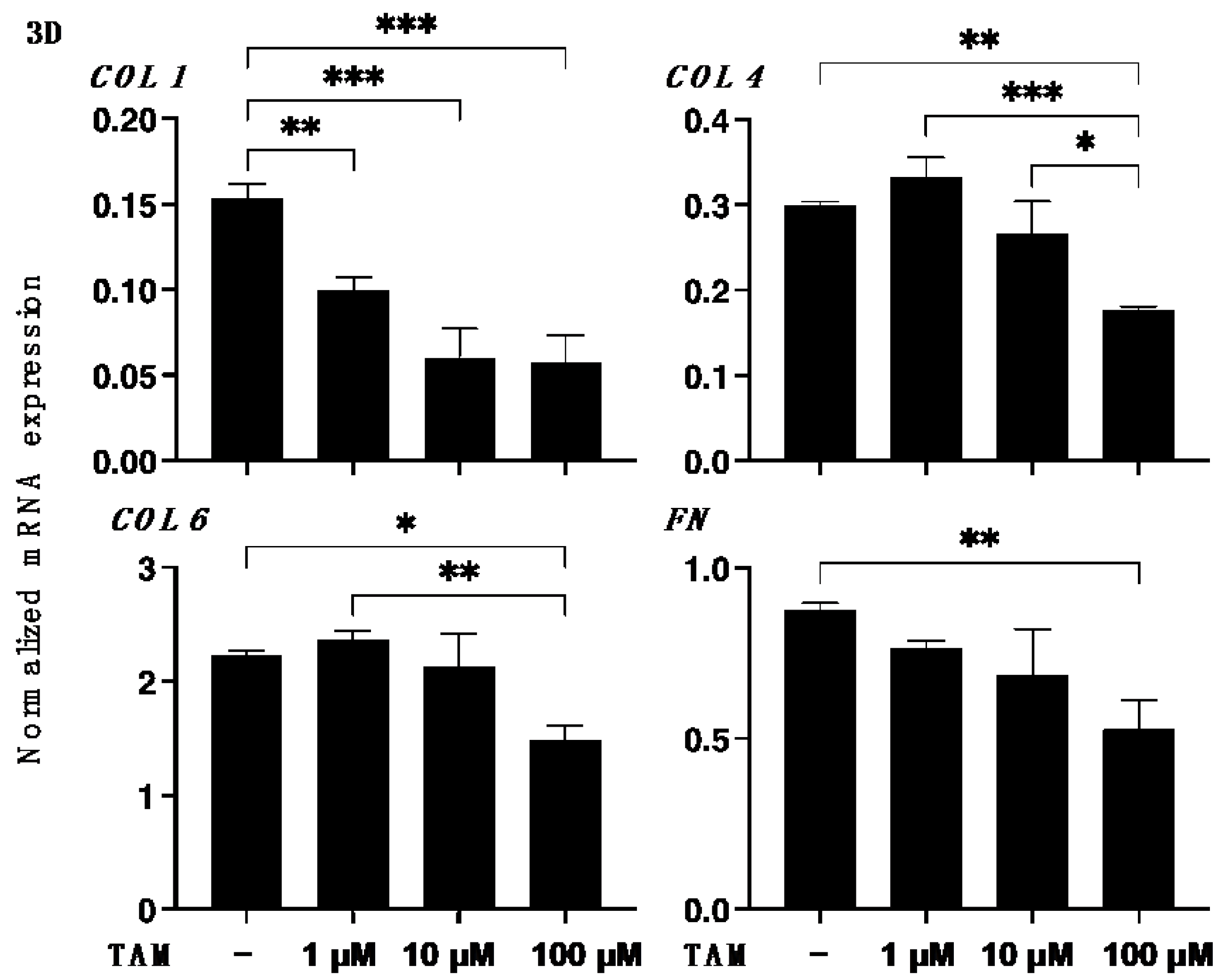
2.5. Immunocytochemistry of 2D ARPE 19 Cells and 3D ARPE 19 Cells Spheroids
2.6. Other Analytical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cotecchia, S.; Schwinn, D.A.; Randall, R.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Caron, M.G.; Kobilka, B.K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7159–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwinn, D.A.; Lomasney, J.W.; Lorenz, W.; Szklut, P.J.; Fremeau, R.T., Jr.; Yang-Feng, T.L.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Cotecchia, S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 8183–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomasney, J.W.; Cotecchia, S.; Lorenz, W.; Leung, W.Y.; Schwinn, D.A.; Yang-Feng, T.L.; Brownstein, M.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Caron, M.G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6365–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.M.; Piascik, M.T.; Graham, R.M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: Isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol. Pharmacol. 1991, 40, 876–883. [Google Scholar]
- Bylund, D.B.; Eikenberg, D.C.; Hieble, J.P.; Langer, S.Z.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Minneman, K.P.; Molinoff, P.B.; Ruffolo, R.R., Jr.; Trendelenburg, U. International Union of Pharmacology nomenclature of adrenoceptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1994, 46, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hieble, J.P.; Bylund, D.B.; Clarke, D.E.; Eikenburg, D.C.; Langer, S.Z.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Minneman, K.P.; Ruffolo, R.R., Jr. International Union of Pharmacology. X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: Consensus update. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995, 47, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa, A.; Horie, K.; Tanaka, T.; Takagaki, K.; Murai, M.; Yano, J.; Tsujimoto, G. Cloning, functional expression and tissue distribution of human cDNA for the alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 195, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.J.; Chang, T.K.; Yamanishi, S.S.; Salazar, F.H.; Kosaka, A.H.; Khare, R.; Bhakta, S.; Jasper, J.R.; Shieh, I.S.; Lesnick, J.D.; et al. Molecular cloning, genomic characterization and expression of novel human alpha1A-adrenoceptor isoforms. FEBS Lett. 1998, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, F.; Taniguchi, T.; Takauji, R.; Murata, S.; Muramatsu, I. Splice isoforms of alpha(1a)-adrenoceptor in rabbit. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suzuki, F.; Taniguchi, T.; Nakamura, S.; Akagi, Y.; Kubota, C.; Satoh, M.; Muramatsu, I. Distribution of alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtypes in RNA and protein in rabbit eyes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, F.; Takayanagi, I. Characterization of postsynaptic alpha 1-adrenoceptors in the rabbit iris dilator smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1986, 333, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Suzuki, F.; Akagi, Y.; Muramatsu, I. Evaluation of alpha1-adrenoceptors in the rabbit iris: Pharmacological characterization and expression of mRNA. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuchi, Y.; Yoshitomi, T.; Gregory, D.S. Do alpha-adrenergic receptors participate in control of the circadian rhythm of IOP? Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 3186–3194. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, K.; Kuwayama, Y.; Matsugi, T.; Sun, N.; Shirasawa, E. Selective suppression by bunazosin of alpha-adrenergic agonist evoked elevation of intraocular pressure in sympathectomized rabbit eyes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1993, 34, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.F.; Lee, P.Y.; Mittag, T.W.; Podos, S.M.; Serle, J.B. Effect of 5-methylurapidil, an alpha 1a-adrenergic antagonist and 5-hydroxytryptamine1a agonist, on aqueous humor dynamics in monkeys and rabbits. Curr. Eye Res. 1997, 16, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.L.; Toris, C.B.; Camras, C.B.; Wang, Y.L.; Yablonski, M.E. Bunazosin reduces intraocular pressure in rabbits by increasing uveoscleral outflow. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 14, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Gregory, D.S. Hydroxyamphetamine increases intraocular pressure in rabbits. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2001, 119, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Walkenbach, R.J.; Ye, G.S.; Reinach, P.S.; Boney, F. Alpha 1-adrenoceptors in the corneal endothelium. Exp. Eye Res. 1992, 55, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.J.; Matheson, A.; Faulds, D.M. Tamsulosin: A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the management of lower urinary tract symptoms. Drugs Aging 2002, 19, 135–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Grzybowski, A.; Wang, N. A narrative review of intraoperative floppy iris syndrome: An update 2020. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.J.; El-Defrawy, S.R.; Gill, S.S.; Whitehead, M.; Campbell, E.L.P.; Hooper, P.L.; Bell, C.M.; Ten Hove, M.W. Evolution in the Risk of Cataract Surgical Complications among Patients Exposed to Tamsulosin: A Population-Based Study. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pärssinen, O.; Leppänen, E.; Keski-Rahkonen, P.; Mauriala, T.; Dugué, B.; Lehtonen, M. Influence of tamsulosin on the iris and its implications for cataract surgery. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3766–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.F.; Campbell, J.R. Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome associated with tamsulosin. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2005, 31, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.M.; Hatch, W.V.; Fischer, H.D.; Cernat, G.; Paterson, J.M.; Gruneir, A.; Gill, S.S.; Bronskill, S.E.; Anderson, G.M.; Rochon, P.A. Association between tamsulosin and serious ophthalmic adverse events in older men following cataract surgery. Jama 2009, 301, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroi-Fetters, S.E.; Earley, O.; Hirakata, A.; Caron, M.G.; Jaffe, G.J. Binding, coupling, and mRNA subtype heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in cultured human RPE. Exp. Eye Res. 1995, 60, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uta, D.; Hattori, T.; Yoshimura, M. Effect of Alpha 1-Adrnoceptor Antagonists on Postsynaptic Sensitivity in Substantia Gelatinosa Neurons From Lumbosacral Spinal Cord in Rats Using Slice Patch-Clamp Technique for mEPSC. Int. Neurourol. J. 2020, 24, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oouchi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Ida, Y.; Ohguro, H.; Hikage, F. Rosiglitasone and ROCK Inhibitors Modulate Fibrogenetic Changes in TGF-β2 Treated Human Conjunctival Fibroblasts (HconF) in Different Manners. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, Y.; Ohta, M.; Inoue, T.; Mizuno, K.; Isobe, T.; Tanabe, S.; Tanihara, H. Effects of K-115 (Ripasudil), a novel ROCK inhibitor, on trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Shao, F. Sitagliptin protects renal glomerular endothelial cells against high glucose-induced dysfunction and injury. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikage, F.; Atkins, S.; Kahana, A.; Smith, T.J.; Chun, T.H. HIF2A-LOX Pathway Promotes Fibrotic Tissue Remodeling in Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, Y.; Hikage, F.; Itoh, K.; Ida, H.; Ohguro, H. Prostaglandin F2α agonist-induced suppression of 3T3-L1 cell adipogenesis affects spatial formation of extra-cellular matrix. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Hikage, F.; Ida, Y.; Ohguro, H. Prostaglandin F2α Agonists Negatively Modulate the Size of 3D Organoids from Primary Human Orbital Fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Posadas, L.; Diebold, Y. Three-Dimensional Human Cell Culture Models to Study the Pathophysiology of the Anterior Eye. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Eliott, D. Molecular Targets for Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 36, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Josset, E.; Noel, G. Three-dimensional cell culture: A breakthrough in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5517–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund-Bau, H.; Edéll-Gustafsson, U.; Spångberg, A. Bothersome urinary symptoms and disease-specific quality of life in patients with benign prostatic obstruction. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2007, 41, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, E.D.; Wilson, S.S.; McConnell, J.D.; Slawin, K.M.; Lieber, M.C.; Smith, J.A.; Meehan, A.G.; Bautista, O.M.; Noble, W.R.; Kusek, J.W.; et al. Baseline factors as predictors of clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia in men treated with placebo. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 1422–1426, discussion 1426–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, F.C. Role of the newer alpha, -adrenergic-receptor antagonists in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia-related lower urinary tract symptoms. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.C.; Blouin, J.; Perreault, S.; Lapointe, A.; Dragomir, A. Intraoperative floppy-iris syndrome associated with alpha1-adrenoreceptors: Comparison of tamsulosin and alfuzosin. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2007, 33, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Radomski, S.; Chung, J.; Plazker, T.; Singer, S.; Slomovic, A.R. Intraoperative floppy-iris syndrome during cataract surgery in men using alpha-blockers for benign prostatic hypertrophy. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2007, 33, 1826–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.F.; Osher, R.H.; Wang, L.; Koch, D.D. Prospective multicenter evaluation of cataract surgery in patients taking tamsulosin (Flomax). Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwinn, D.A.; Afshari, N.A. Alpha(1)-Adrenergic receptor antagonists and the iris: New mechanistic insights into floppy iris syndrome. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2006, 51, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Sun, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W. Tamsulosin attenuates high glucose- induced injury in glomerular endothelial cells. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 5184–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, T.S.; Du, Y.; Tang, J.; Lee, C.A.; Liu, H.; Dreffs, A.; Leinonen, H.; Antonetti, D.A.; Palczewski, K. Regulation of Adrenergic, Serotonin, and Dopamine Receptors to Inhibit Diabetic Retinopathy: Monotherapies versus Combination Therapies. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, T.; Leinonen, H.; Getter, T.; Dong, Z.; Sun, W.; Gao, S.; Veenstra, A.; Heidari-Torkabadi, H.; Kern, T.S.; Kiser, P.D.; et al. A Combination of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Modulators Protects Photoreceptors from Degeneration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, H.; Choi, E.H.; Gardella, A.; Kefalov, V.J.; Palczewski, K. A Mixture of U.S. Food and Drug Administration-Approved Monoaminergic Drugs Protects the Retina From Light Damage in Diverse Models of Night Blindness. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, E.; Sari, E.S.; Yazici, A.; Koç, A.; Bulbul, E.; Koytak, A.; Ermis, S.S.; Erol, M.K. The Effect of Systemic Tamsulosin Hydrochloride on Choroidal Thickness Measured by Enhanced Depth Imaging Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.L.; Petrovic, V.; Lee, S.E.; Flach, A.; McCaffery, S.; O’Brien, J.M. Choroidal detachment following the use of tamsulosin (Flomax). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takmaz, T.; Can, I. Intraoperative floppy-iris syndrome: Do we know everything about it? J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2007, 33, 1110–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masket, S.; Belani, S. Combined preoperative topical atropine sulfate 1% and intracameral nonpreserved epinephrine hydrochloride 1:4000 [corrected] for management of intraoperative floppy-iris syndrome. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2007, 33, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Koss, M.C. Functional characterization of alpha-adrenoceptors mediating pupillary dilation in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 471, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Koss, M.C. Studies of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists on sympathetic mydriasis in rabbits. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 19, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goseki, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Ogasawara, S.; Mashimo, K.; Nemoto, N.; Taguchi, Y.; Yago, K.; Shimizu, K. Effects of tamsulosin and silodosin on isolated albino and pigmented rabbit iris dilators: Possible mechanism of intraoperative floppy-iris syndrome. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2012, 38, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantrell, M.A.; Bream-Rouwenhorst, H.R.; Steffensmeier, A.; Hemerson, P.; Rogers, M.; Stamper, B. Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome associated with alpha1-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Ann. Pharmacother. 2008, 42, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrás, T. The cellular and molecular biology of the iris, an overlooked tissue: The iris and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2014, 23 (Suppl. 1), S39–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keski-Rahkonen, P.; Pärssinen, O.; Leppänen, E.; Mauriala, T.; Lehtonen, M.; Auriola, S. Determination of tamsulosin in human aqueous humor and serum by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, Y.; Tomomatsu, T.; Matsumura, T.; Takihara, Y.; Kozai, S.; Arimura, S.; Yokota, S.; Inatani, M. Vitreous and aqueous concentrations of brimonidine following topical application of brimonidine tartrate 0.1% ophthalmic solution in humans. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 31, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariprasad, S.M.; Mieler, W.F.; Holz, E.R. Vitreous penetration of orally administered gatifloxacin in humans. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2002, 100, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukuda, M.; Shibata, N.; Osada, H.; Yamashiro, Y.; Sasaki, H. Vitreous and aqueous penetration of orally and topically administered moxifloxacin. Ophthalmic Res. 2011, 46, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.P.; Loo, A.V.; Khaw, K.W.; Sthaneshwar, P.; Khang, T.F.; Hassan, M.; Subrayan, V. Plasma, aqueous and vitreous homocysteine levels in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ida, Y.; Sato, T.; Watanabe, M.; Umetsu, A.; Tsugeno, Y.; Furuhashi, M.; Hikage, F.; Ohguro, H. The Selective α1 Antagonist Tamsulosin Alters ECM Distributions and Cellular Metabolic Functions of ARPE 19 Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100556
Ida Y, Sato T, Watanabe M, Umetsu A, Tsugeno Y, Furuhashi M, Hikage F, Ohguro H. The Selective α1 Antagonist Tamsulosin Alters ECM Distributions and Cellular Metabolic Functions of ARPE 19 Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100556
Chicago/Turabian StyleIda, Yosuke, Tatsuya Sato, Megumi Watanabe, Araya Umetsu, Yuri Tsugeno, Masato Furuhashi, Fumihito Hikage, and Hiroshi Ohguro. 2022. "The Selective α1 Antagonist Tamsulosin Alters ECM Distributions and Cellular Metabolic Functions of ARPE 19 Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100556
APA StyleIda, Y., Sato, T., Watanabe, M., Umetsu, A., Tsugeno, Y., Furuhashi, M., Hikage, F., & Ohguro, H. (2022). The Selective α1 Antagonist Tamsulosin Alters ECM Distributions and Cellular Metabolic Functions of ARPE 19 Cells in a Concentration-Dependent Manner. Bioengineering, 9(10), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100556









