Ultrafast PCR Detection of COVID-19 by Using a Microfluidic Chip-Based System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
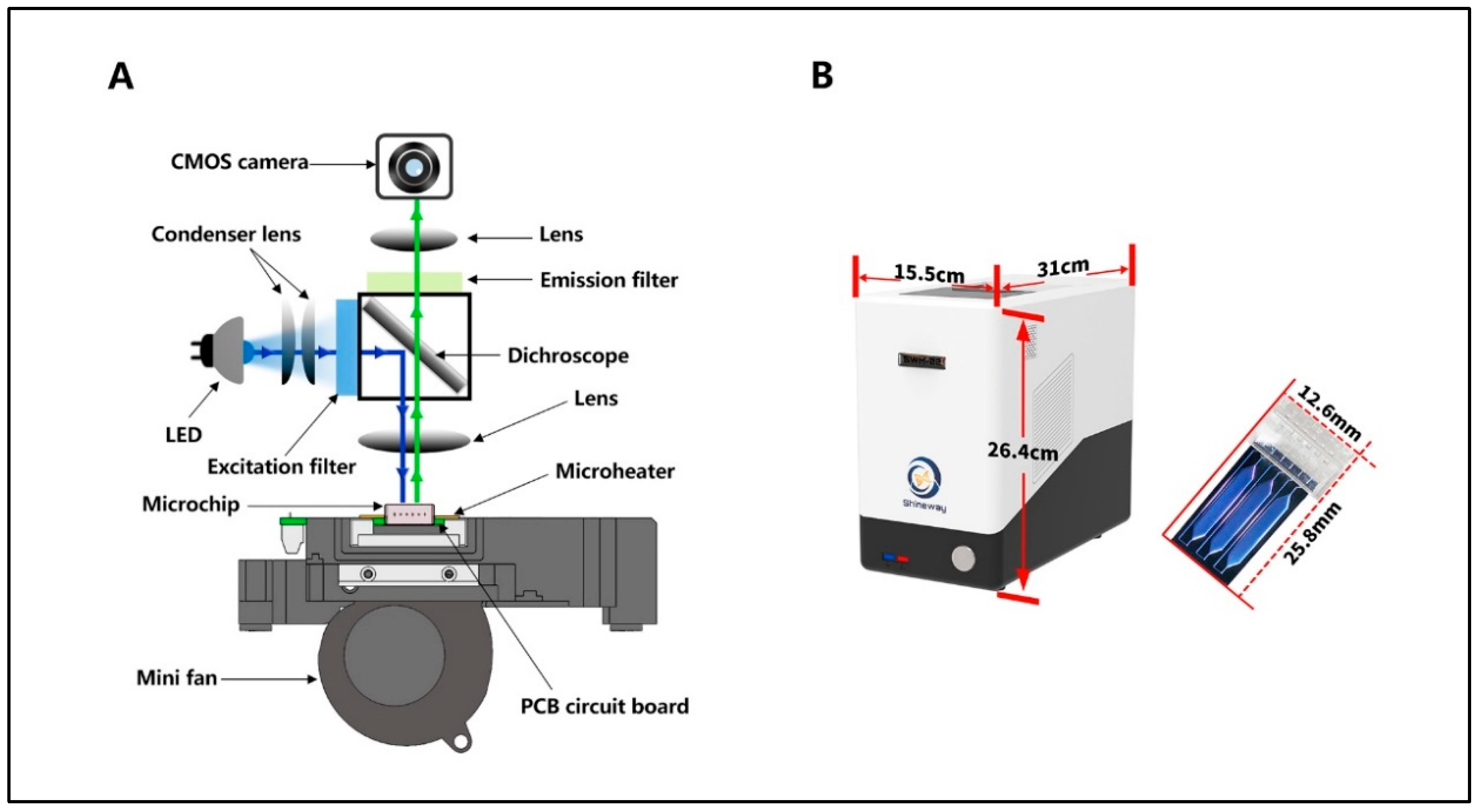
2.1. SWM-02 Unltrafast PCR Microchip-Based Platform
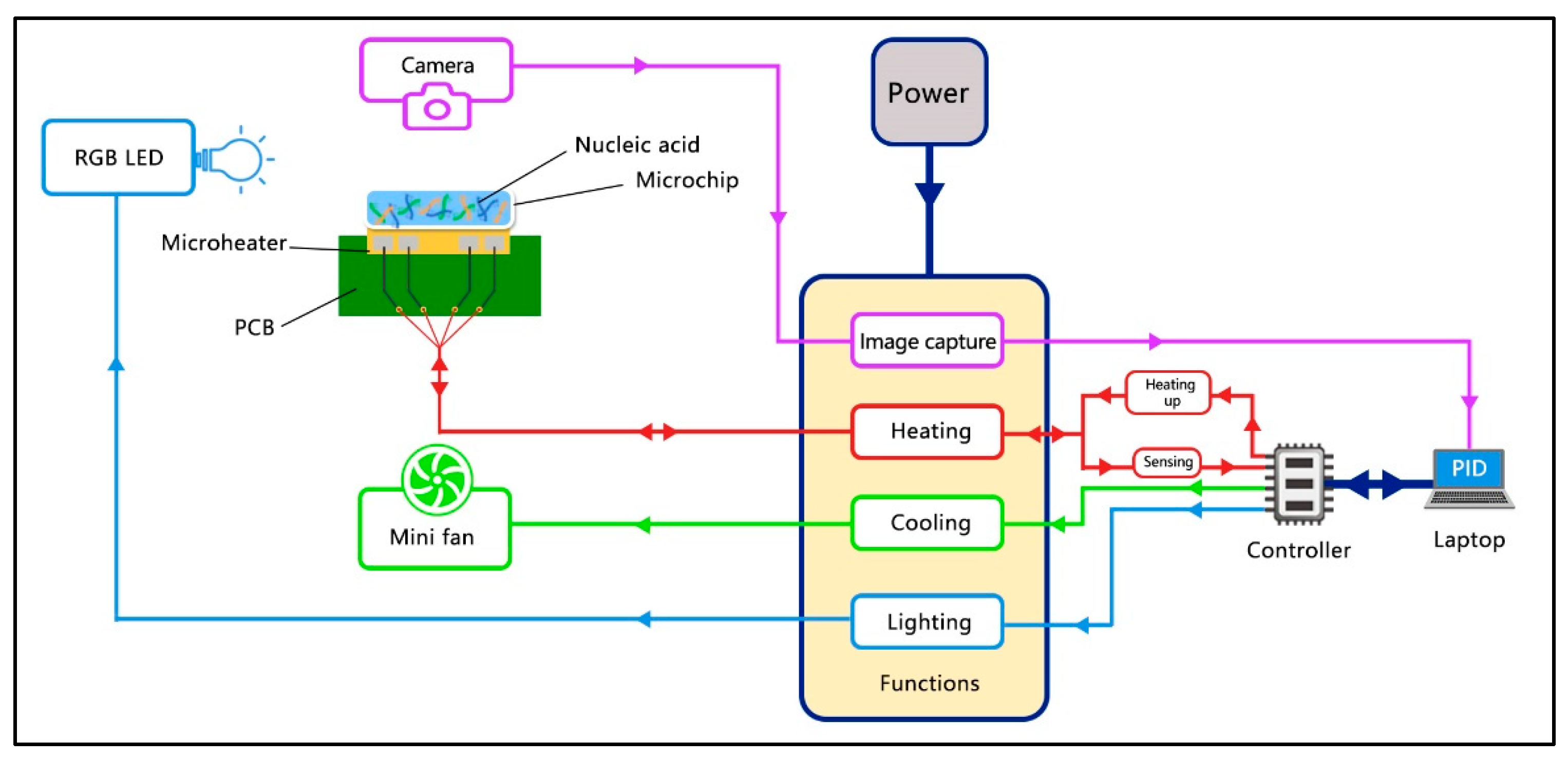
2.2. Control Scheme of the SWM-02
2.3. Materials and Sample Pretreatment
2.4. Reagent Preparation and PCR Condition
3. Results and Discussion
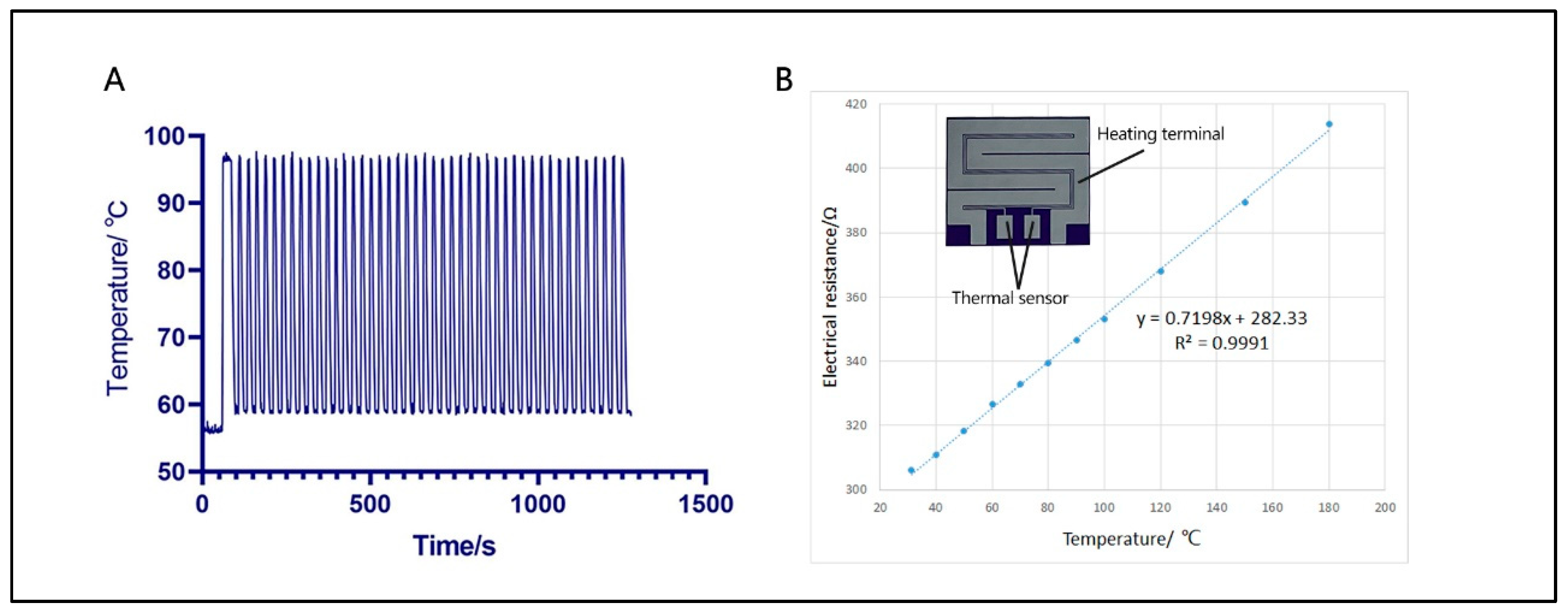
3.1. Thermal Properties of Ultrafast PCR Microdevice
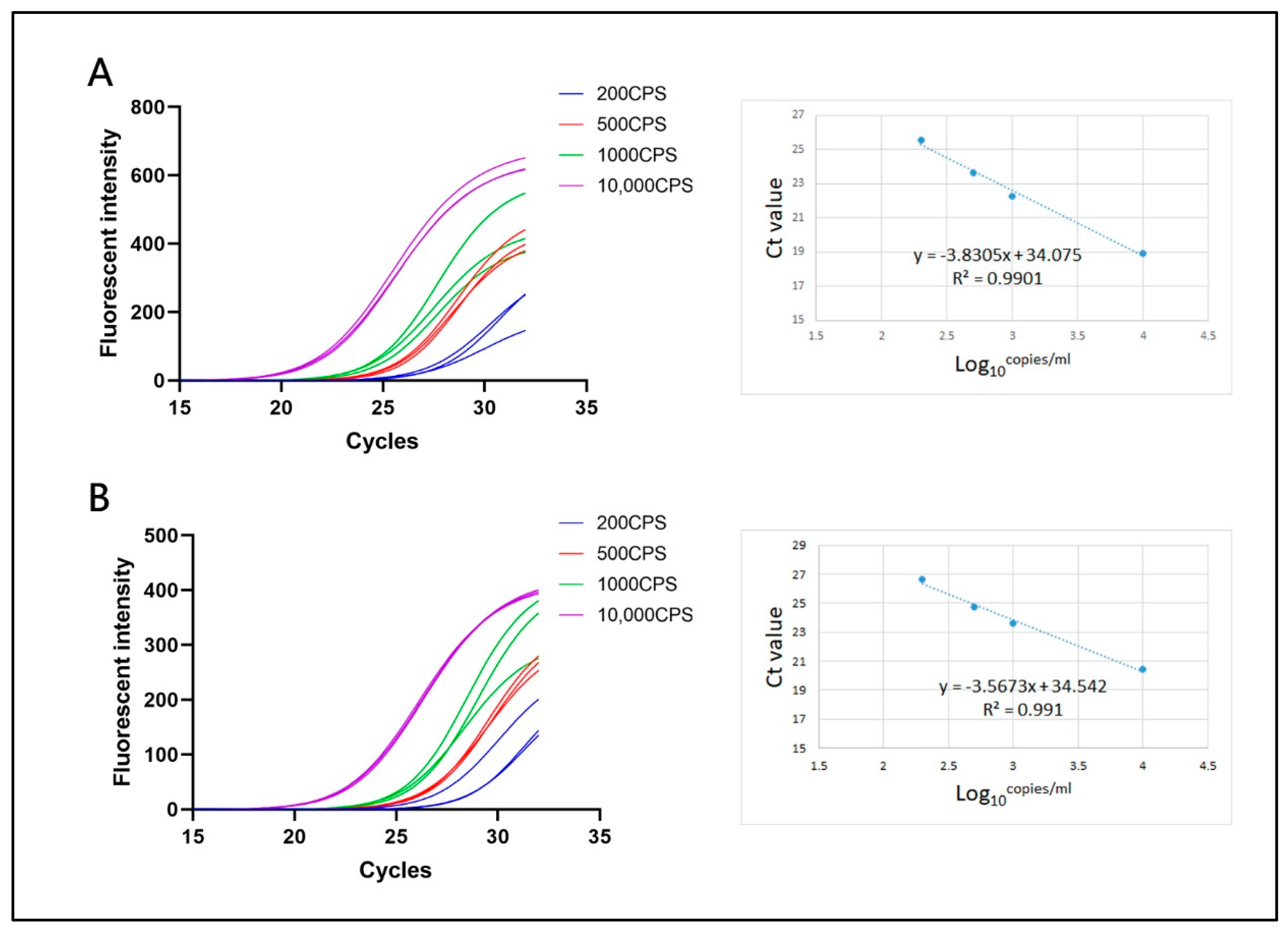
3.2. Limit-of-Detection and Reproducibility
3.3. Linear Correlation
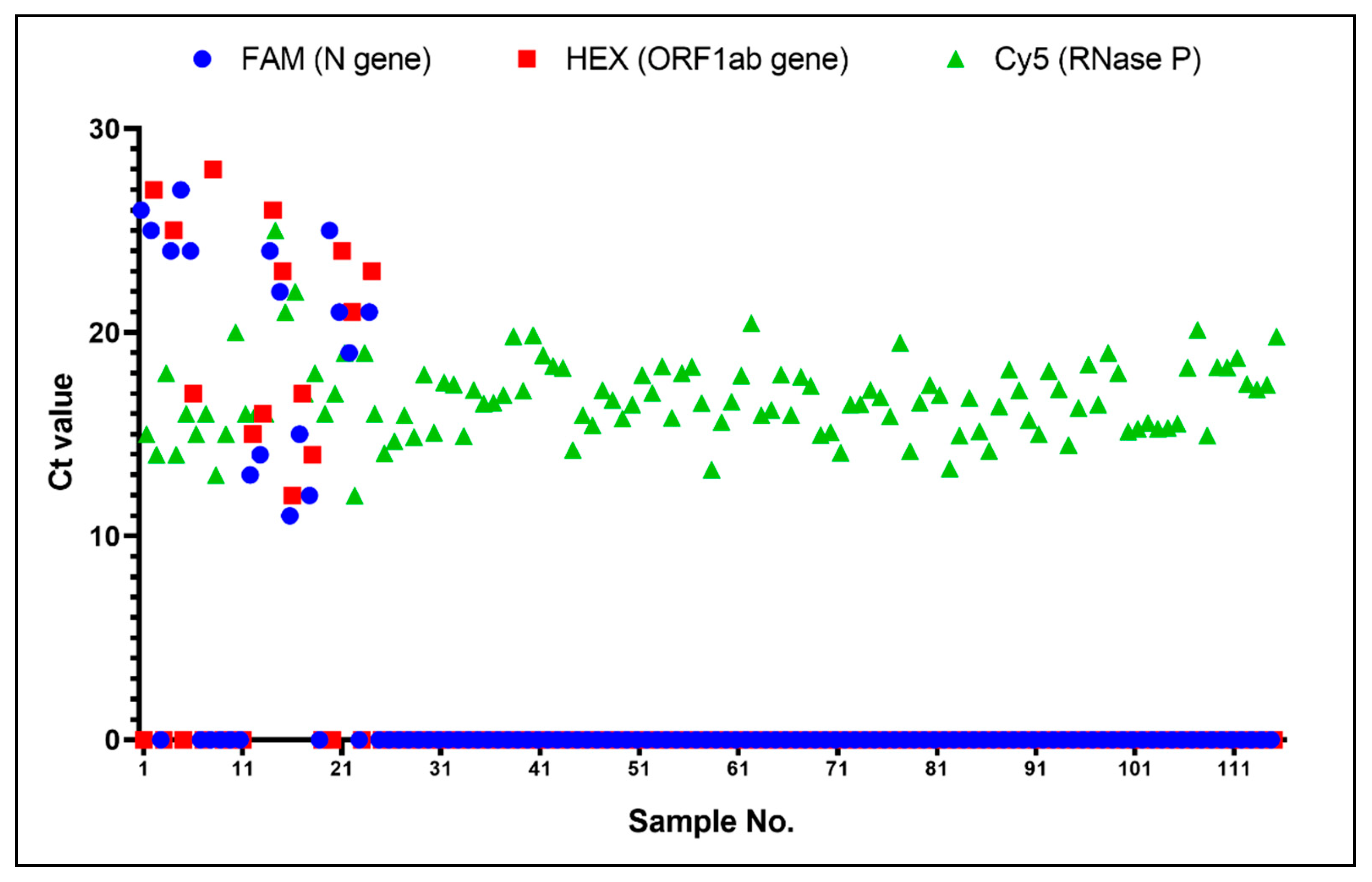
3.4. Clinical Evaluation between On-Chip PCR and Conventional qPCR
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jadhav, S.A.; Biji, P.; Panthalingal, M.K.; Krishna, C.M.; Rajkumar, S.; Joshi, D.S.; Sundaram, N. Development of integrated microfluidic platform coupled with Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for diagnosis of COVID-19. Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, E.; Torres, I.; Bueno, F.; Huntley, D.; Molla, E.; Fernández-Fuentes, M.; Martínez, M.; Poujois, S.; Forqu, L.; Valdivia, A. Field evaluation of a rapid antigen test (Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) for COVID-19 diagnosis in primary healthcare centres. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 472.e7–472.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.; Ejmalian, A.; Moghaddam, M.E.; Abin, A.A.; Frangi, A.F.; Mohammadi, M.; Rad, H.S. Medical imaging and computational image analysis in COVID-19 diagnosis: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Geng, M.; Peng, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralik, P.; Ricchi, M. A basic guide to real time PCR in microbial diagnostics: Definitions, parameters, and everything. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascarella, G.; Strumia, A.; Piliego, C.; Bruno, F.; Del Buono, R.; Costa, F.; Scarlata, S.; Agrò, F.E. COVID-19 diagnosis and management: A comprehensive review. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudouris, E.S. Laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watzinger, F.; Ebner, K.; Lion, T. Detection and monitoring of virus infections by real-time PCR. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 254–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.L.; Dempsey, M.H.; Ring, C.J.A.; Kempson, R.E.; Zhang, L.; Gor, D.; Snowden, B.W.; Tisdale, M. Design and performance testing of quantitative real time PCR assays for influenza A and B viral load measurement. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 29, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D. Quantification using real-time PCR technology: Applications and limitations. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yang, S.-M.; Lim, B.; Park, S.H.; Rackerby, B.; Kim, H.-Y. Design of PCR assays to specifically detect and identify 37 Lactobacillus species in a single 96 well plate. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Odiwuor, N.; Xiong, J.; Sun, L.; Nyaruaba, R.O.; Wei, H.; Tanner, N.A. Rapid Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Virus RNA Using Colorimetric LAMP. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Long-Term Care Facilities in the Context of COVID-19: Interim Guidance, 21 March 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Liang, R.; Su, M.; He, C.; Hu, L.; Su, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, F.; et al. Recent advances in the detection of respiratory virus infection in humans. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I.G. Inhibition and facilitation of nucleic acid amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, F.; Najafi, R.; Amini, R.; Khazaei, S.; Bashirian, S. Reducing false negative PCR test for COVID-19. Int. J. Matern. Child Health AIDS 2020, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppa, P.B.; Müller, C.; Schlichtiger, A.; Schlebusch, H. Point-of-care testing (POCT): Current techniques and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.; Rayman, G. Point-of-care blood glucose testing for diabetes care in hospitalized patients: An evidence-based review. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, S.D. Point-of-care detection of lipoarabinomannan (LAM) in urine for diagnosis of HIV-associated tuberculosis: A state of the art review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.-B.; Yang, M.; Pothukuchy, A.; Du, Y. Point-of-care testing of various analytes by means of a one-step competitive displacement reaction and pregnancy test strips. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schot, M.J.C.; Van Delft, S.; Kooijman-Buiting, A.M.J.; De Wit, N.J.; Hopstaken, R.M. Analytical performance, agreement and user-friendliness of six point-of-care testing urine analysers for urinary tract infection in general practice. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Wei, C.; Dai, S.; Li, H.; Li, J. Microfluidics Temperature Compensating and Monitoring Based on Liquid Metal Heat Transfer. Micromachines 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauk, M.G.; Song, J.; Liu, C.; Bau, H.H. Simple Approaches to Minimally-Instrumented, Microfluidic-Based Point-of-Care Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests. Biosensors 2018, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bai, Y.; You, M.; Hu, J.; Yao, C.; Cao, L.; Xu, F. Fully integrated microfluidic devices for qualitative, quantitative and digital nucleic acids testing at point of care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, B.; Lin, L.; Wu, B.; Huang, E.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; He, H.; Lei, X.; Xu, B.; Liu, D. A pocket-sized device automates multiplexed point-of-care RNA testing for rapid screening of infectious pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Dhumpa, R.; Bang, D.D.; Høgberg, J.; Handberg, K.; Wolff, A. A lab-on-a-chip device for rapid identification of avian influenza viral RNA by solid-phase PCR. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kang, J.Y.; Ahn, C.H. A polymer lab-on-a-chip for reverse transcription (RT)-PCR based point-of-care clinical diagnostics. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mauk, M.; Qiu, X.; Liu, C.; Kim, J.; Ramprasad, S.; Ongagna, S.; Abrams, W.R.; Malamud, D.; Corstjens, P.L.A.M.; et al. An integrated, self-contained microfluidic cassette for isolation, amplification, and detection of nucleic acids. Biomed. Microdevices 2010, 12, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chao, S.; Huang, X.; Ge, S.; et al. A High-Throughput, Multi-Index Isothermal Amplification Platform for Rapid Detection of 19 Types of Common Respiratory Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2. Engineering 2020, 6, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolando, J.C.; Jue, E.; Barlow, J.T.; Ismagilov, R.F. Real-time kinetics and high-resolution melt curves in single-molecule digital LAMP to differentiate and study specific and non-specific amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Tong, Z.; Shen, C.; Xu, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Mao, H. Micro-PCR chip-based multifunctional ultrafast SARS-CoV-2 detection platform. Lab Chip 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; You, M.; Gao, B.; Xie, X.; Xue, Z.; Peng, P.; Yao, C.; Xu, F. A digitalized isothermal nucleic acid testing platform based on a pump-free open droplet array microfluidic chip. Analyst 2021, 146, 6960–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Hunter, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, X.; Ma, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Serpe, M.J. Portable point-of-care diagnostic devices: An updated review. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 5418–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Wang, Y.; Yang, N.; Shu, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D. A fully automated microfluidic PCR-array system for rapid detection of multiple respiratory tract infection pathogens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chen, D.; Wen, Y.; Li, Z. Capillarity self-driven DNA hydrogel sensor for visual quantification of microRNA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 313, 128036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, P. Versatile MEMS and mems integration technology platforms for cost effective MEMS development. In Proceedings of the 2009 European Microelectronics and Packaging Conference, Rimini, Italy, 15–18 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, R.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Lou, K.; Gong, X.; Gao, Y.; Wen, W. A fully portable microchip real-time polymerase chain reaction for rapid detection of pathogen. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Lou, K.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W. A Rapid Digital PCR System with a Pressurized Thermal Cycler. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Reports and IFUS for Products Eligible for Procurement. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic, Emergency Use Listing Procedure (EUL) Open for IVDs. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/vitro-diagnostics/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-pandemic-%E2%80%94-emergency-use-listing-procedure-eul-open (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Specification of Coronavirus Test Kit(DA-099X) PDF. Available online: https://en.daangene.com/products/covid-19-saliva-coronavirus-test-kit/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

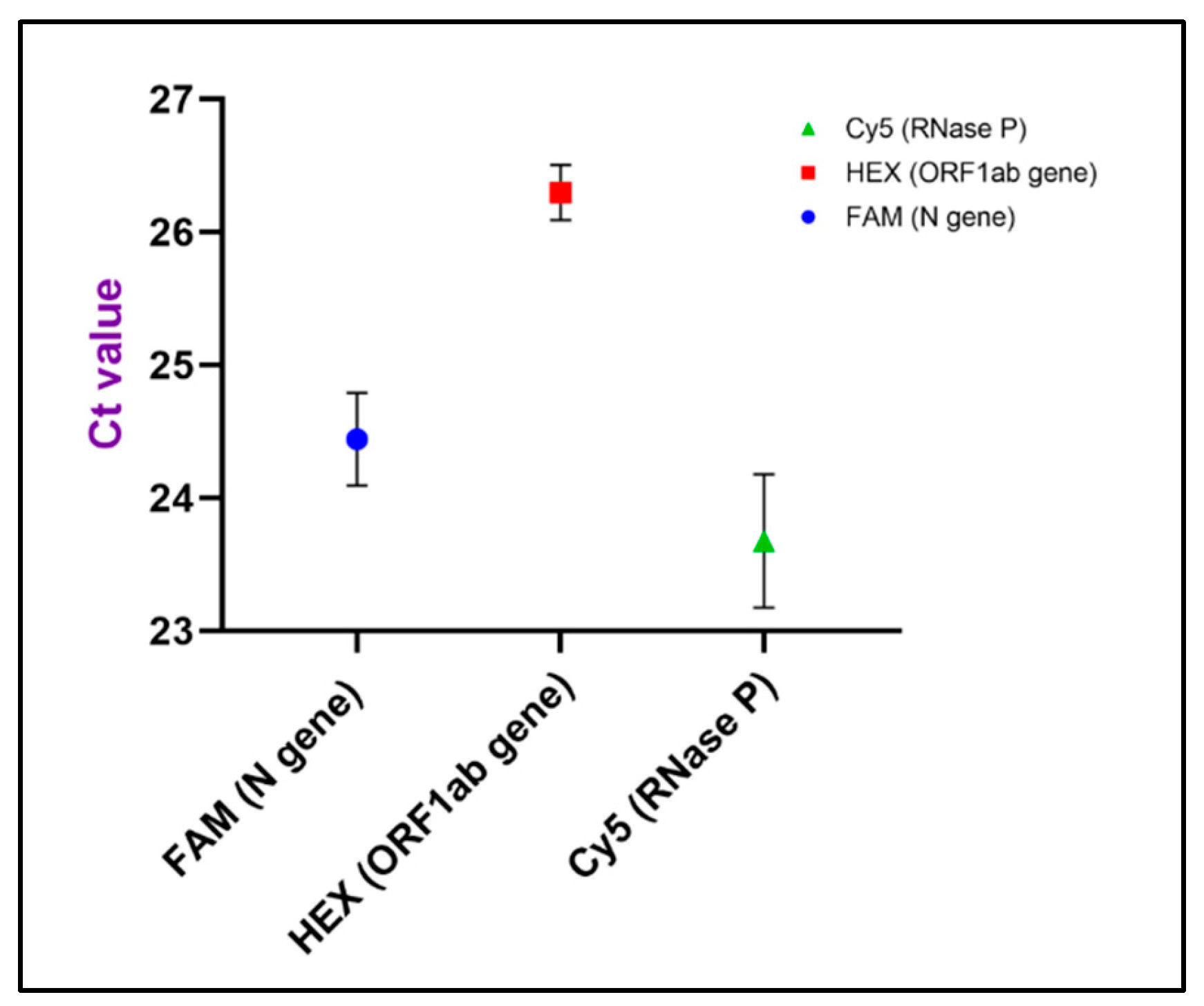
| No | FAM (N Gene) | HEX (ORF1ab Gene) | Cy5 (RNase P) |
| 1 | 24.59 | 26.48 | 23.9 |
| 2 | 24.03 | 26.19 | 23.92 |
| 3 | 24.77 | 26.28 | 23.84 |
| 4 | 24.06 | 26.57 | 22.66 |
| 5 | 24.84 | 25.99 | 23.8 |
| 6 | 24.37 | 26.28 | 23.94 |
| Mean | 24.44 | 26.3 | 23.68 |
| SD | 0.3489 | 0.207 | 0.5008 |
| CV | 1.427% | 0.7872% | 2.115% |
| Count | LightCycler480 | Total | |||
| Negative | Positive | ||||
| SWM-02 | Negative | 98 | 1 | 99 | |
| Positive | 0 | 16 | 16 | ||
| Total | 98 | 17 | 115 | ||
| Value | Asymptotic Standard Error 1 | Approximate T 2 | Approximate Significance | ||
| Measure of AgreementKappa | 0.965 | 0.035 | 10.351 | 0 | |
| N of Valid Cases | 115 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wen, W.; Zheng, W. Ultrafast PCR Detection of COVID-19 by Using a Microfluidic Chip-Based System. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100548
Chen X, Liu Y, Zhan X, Gao Y, Sun Z, Wen W, Zheng W. Ultrafast PCR Detection of COVID-19 by Using a Microfluidic Chip-Based System. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100548
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaojing, Yiteng Liu, Xuan Zhan, Yibo Gao, Zhongyi Sun, Weijia Wen, and Weidong Zheng. 2022. "Ultrafast PCR Detection of COVID-19 by Using a Microfluidic Chip-Based System" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100548
APA StyleChen, X., Liu, Y., Zhan, X., Gao, Y., Sun, Z., Wen, W., & Zheng, W. (2022). Ultrafast PCR Detection of COVID-19 by Using a Microfluidic Chip-Based System. Bioengineering, 9(10), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100548










