Audio-Visual Stress Classification Using Cascaded RNN-LSTM Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Causes of Mental Stress
1.2. Importance of Mental Stress Detection
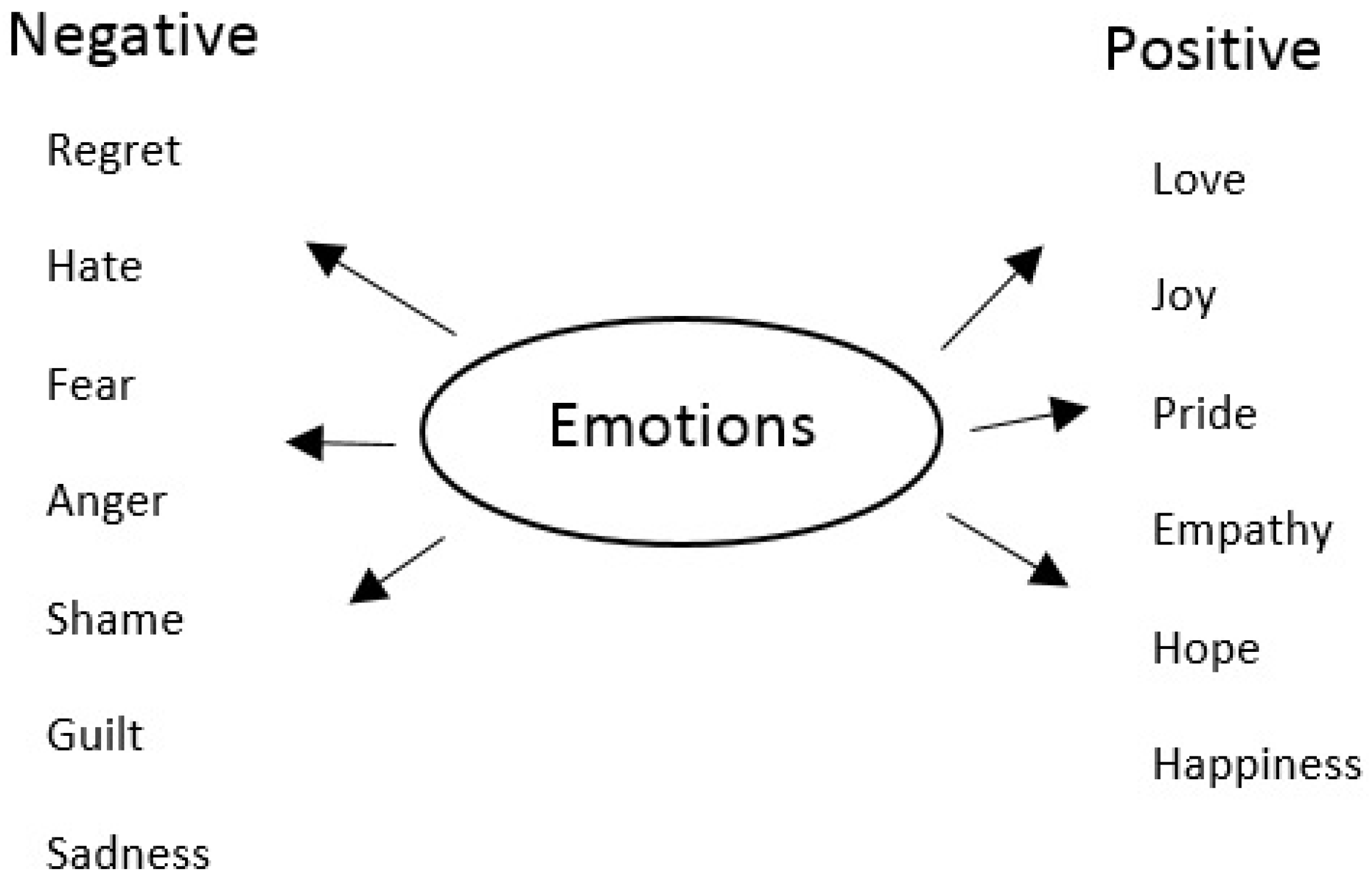
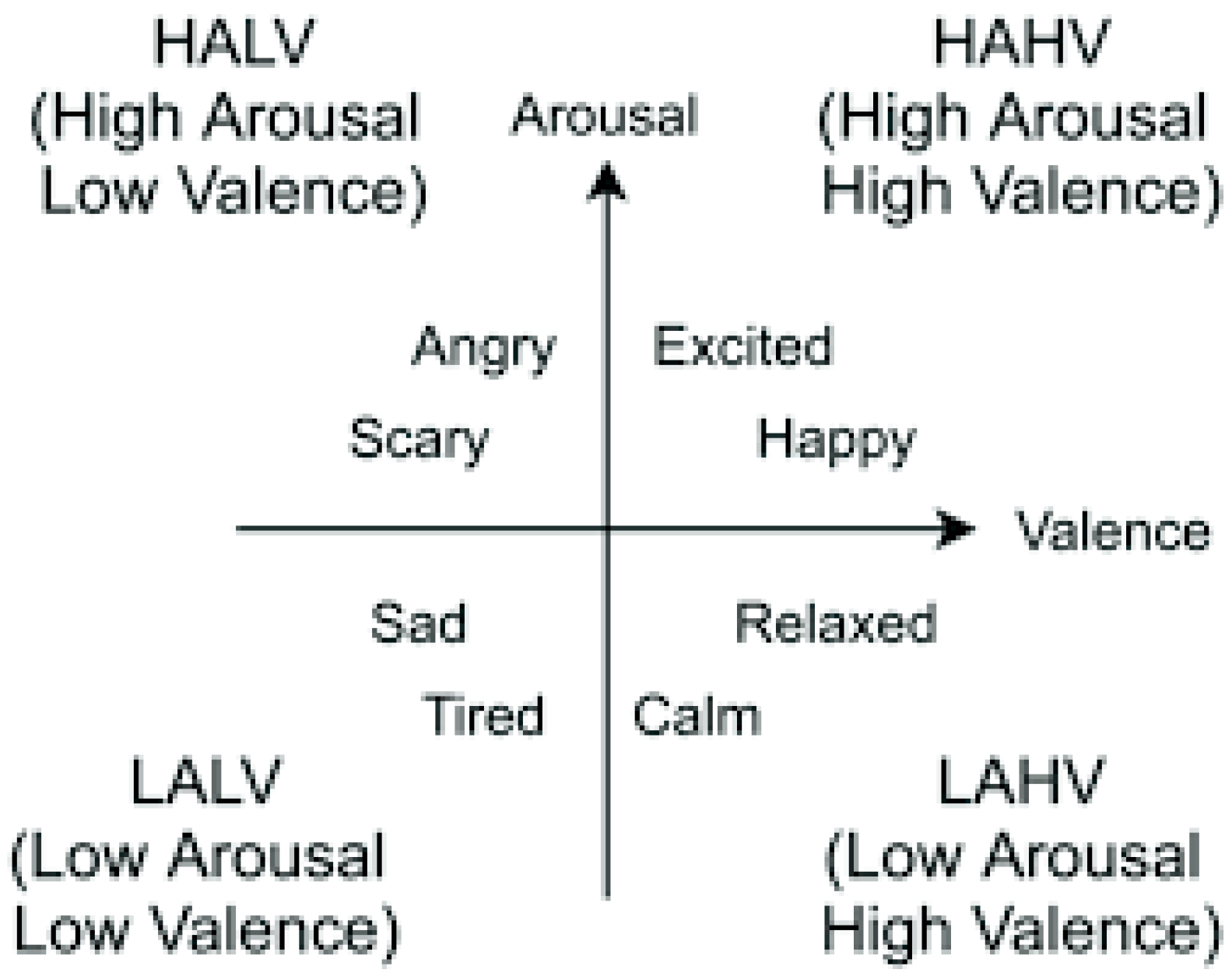
1.3. Role of Emotion in Stress Identification
2. Literature Review
2.1. Stress Detection Using Speech Signal
2.2. Stress Detection Using Audio-Visual Data
2.3. Analysis
2.4. Transition from Holistic Facial Recognition to Deep Learning Based Recognition
3. Feature Extraction from Facial Expressions
3.1. Facial Action Coding System
3.2. OpenFace
4. Proposed Method to Classify Mental Stress
4.1. The RAVDESS Dataset
4.1.1. Description
4.1.2. Data
4.2. Proposed System
4.2.1. Why RNN?
4.2.2. Speech-Based Stress Detection
4.2.3. Proposed Method for Audio-Visual Based Stress Detection
4.3. Analysis
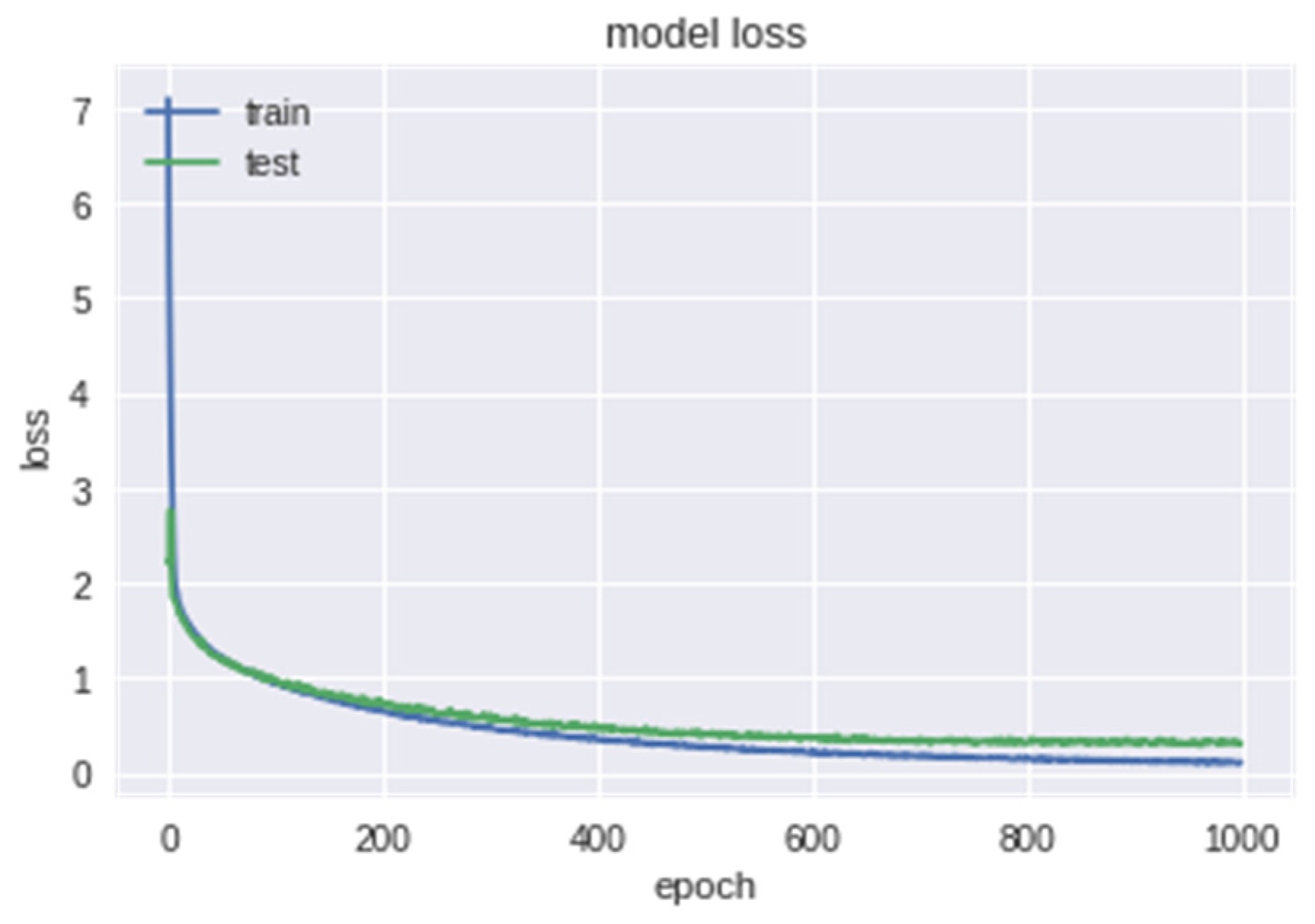
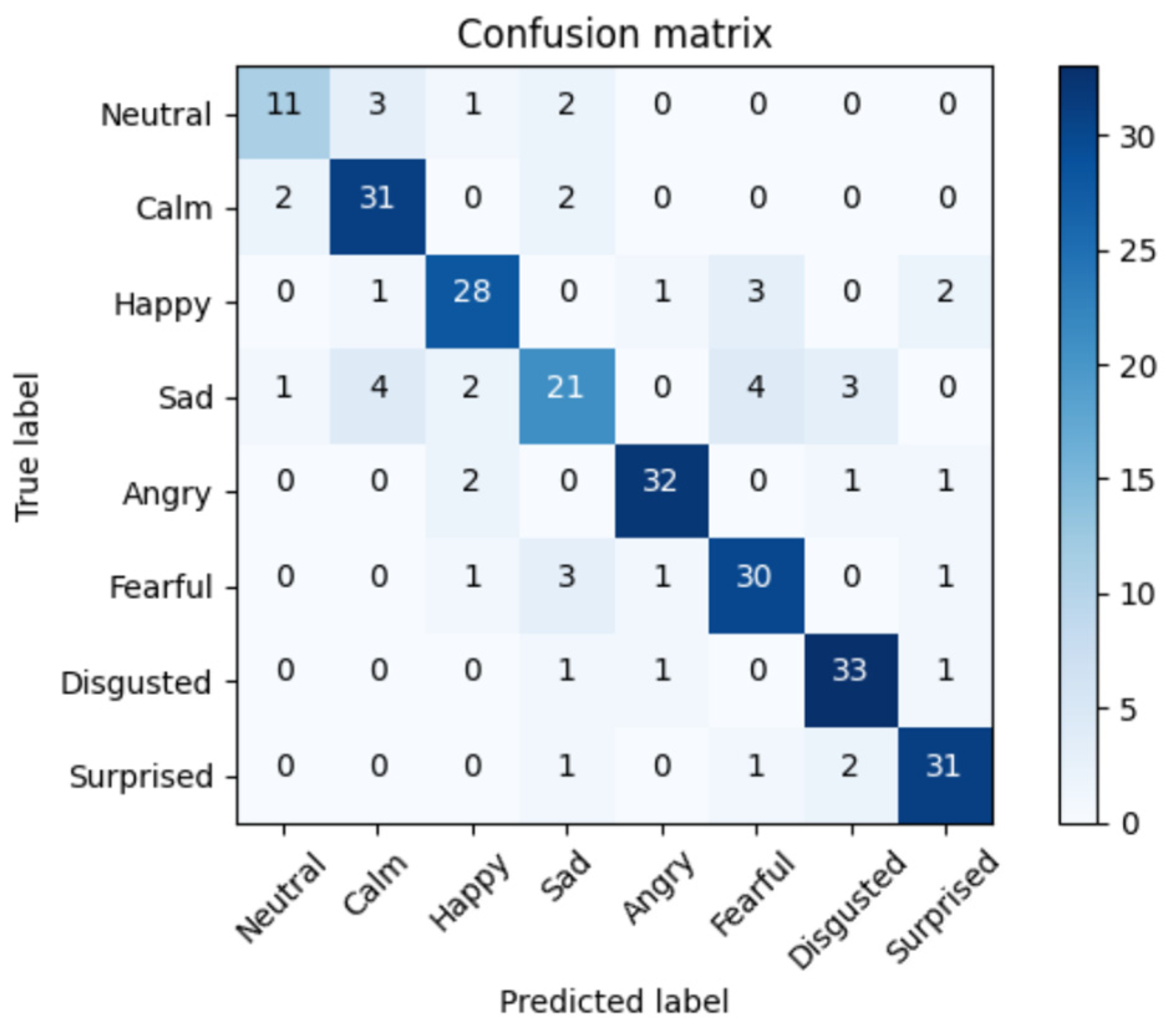
5. Experimental Results
6. Our Contributions
7. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/wealth/personal-finance-news/82-indians-bogged-down-by-stress-cigna-360-well-being-study/articleshow/68615097.cms (accessed on 17 November 2019).
- Mental Health and COVID-19: Early Evidence of the Pandemic’s Impact, Scientific Brief by World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Sci_Brief-Mental_health-2022.1 (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Bhargava, D.; Trivedi, H. A Study of Causes of Stress and Stress Management among Youth. IRA-Int. J. Manag. Soc. Sci. 2018, 11, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrousos, G.P. Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Buwalda, B.; de Boer, S.F.; Flügge, G.; Korte, S.M.; Meerlo, P.; Murison, R.; Olivier, B.; Palanza, P.; et al. Stress revisited: A critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R. Stress and Emotion: A New Synthesis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlidis, I.; Levine, J. Thermal image analysis for polygraph testing. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2002, 21, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefter, L.; Rothkrantz, L.J.M.; Leeuwen, D.A.V.; Wiggers, P. Automatic stress detection in emergency (telephone) calls. Int. J. Intell. Def. Support Syst. 2011, 4, 148–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Barreto, A.; Chin, C.; Li, C. Realization of stress detection using psychophysiological signals for improvement of human-computer interactions. In Proceedings of the IEEE SoutheastCon, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 8–10 April 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.; Eisenberg, D. Mental Health Problems and Help-Seeking Behavior Among College Students. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 46, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Pechenizkiy, M.; Sidorova, N. What’s your current stress level? Detection of stress patterns from GSR sensor data. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11 December 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Colligan, T.W.; Higgins, E.M. Workplace Stress. J. Work. Behav. Health 2006, 21, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Dhall, A.; Gedeon, T.; Goecke, R. Thermal spatio-temporal data for stress recognition. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2014, 2014, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhole, N.P.; Kale, S.N. Study of Recurrent Neural Network Classification of Stress Types in Speech Identification. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 2347–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Jiménez, C.; Griol, D.; Callejas, Z.; Kleinlein, R.; Montero, J.M.; Fernández-Martínez, F. Multimodal Emotion Recognition on RAVDESS Dataset Using Transfer Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutchik, R. Emotion, a Psychoevolutionary Synthesis; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis; Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Patil, S. Speech under stress: Analysis, modeling and recognition. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Müller, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paulmann, S.; Furnes, D.; Bøkenes, A.M.; Cozzolino, P. How Psychological Stress Affects Emotional Prosody. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, K.R.; Moors, A. The Emotion Process: Event Appraisal and Component Differentiation. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 719–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikwad, P.G.; Paithane, A. Novel Approach for Stress Recognition using EEG Signal by SVM Classifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2017 International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication, Erode, India, 18–19 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lahane, P.; Thirugnanam, M. A novel approach for analyzing human emotions based on electroencephalography (EEG). In Proceedings of the 2017 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Vellore, India, 21–22 April 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Thejaswini, S.; Kumar, K.M.R.; Vijayendra, A.; Shyam, R.; Anchan, P.D.; Gowda, E. An Algorithm to Detect Emotion States and Stress Levels Using EEG Signals. Int. J. Latest Res. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Frauendorfer, D.; Rabbi, M.; Mast, M.S. StressSense: Detecting Stress in Unconstrained Acoustic Environments Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tomba, K.; Dumoulin, J.; Mugellini, E.; Khaled, O.A.; Hawila, S. Stress Detection Through Speech Analysis. In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2018), Porto, Portugal, 26–28 July 2018; Volume 1, pp. 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, B.Z.; Mirvaziri, H.; Sadeghi, F. Designing and Implementing of Intelligent Emotional Speech Recognition with Wavelet and Neural Network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2016, 7, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G.; Song, B.; Hassan, M.M.; Alelaiwi, A.; Alamri, A. Audio–visual emotion-aware cloud gaming framework. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 2105–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Malandrakis, N.; Xiao, B.; Guha, T.; Van Segbroeck, M.; Black, M.; Potamianos, A.; Narayanan, S. Multimodal prediction of affective dimensions and depression in human-computer interactions. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge (AVEC), Orlando, FL, USA, 7 November 2014; pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakakis, G.; Pediaditis, M.; Manousos, D.; Kazantzakis, E.; Chiarugi, F.; Simos, P.G.; Marias, K.; Tsiknakis, M. Stress and anxiety detection using facial cues from videos. Biomed. Signal Processing Control 2017, 31, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, K.P.; Ang, L.-M.; Ooi, C.S. A Combined Rule-Based & Machine Learning Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition Approach. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.; Mishra, N.K. Fusion based Emotion Recognition System. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–17 December 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Noroozi, F.; Marjanovic, M.; Njegus, A.; Escalera, S.; Anbarjafari, G. Audio-visual emotion recognition in video clips. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; He, G.; Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Fan, F. Semi-supervised classification-aware cross-modal deep adversarial data augmentation. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 125, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://viso.ai/deep-learning/deep-face-recognition/ (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Moret-Tatay, C.; Fortea, I.B.; Sevilla, M.D.G. Challenges and insights for the visual system: Are face and word recognition two sides of the same coin? J. Neurolinguistics 2020, 56, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Facial Action Coding System: Investigator’s Guide; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]










| Cause of Stress | Interpersonal conflict |
| Role conflict | |
| Career concern | |
| Occupational demands | |
| Work overload | |
| Poor working condition | |
| Lack of social support | |
| Lack of participation in decision making |
| Title | Datasets Used | Technique | Pros of Technique | Scope for Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stress Detection Through Speech Analysis Kevin Tomba et al. (ICETE 2018) [25] | Berlin Emotional Database (EMO-DB), the Keio University Japanese Emotional Speech Database (KeioESD), and the Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS) | SVMs and ANNs were chosen. | MFCCs, mean energy, and the mean intensity were all demonstrated to be effective speech analysis features. | Only audio input was considered and not audio-visual data |
| Study of Recurrent Neural Network Classification of Stress Types in Speech Identification N.P. Dhole, S.N. Kale (IJCSE 2018) [14] | BERLIN and HUMAINE Datasets | RNN | Real time dataset was created | Efficiency percentage not calculated. Works only on audio and not audio-visual data |
| Designing and Implementing of Intelligent Emotional Speech Recognition with Wavelet and Neural Network Mansouri et al. (IJACSA 2016) [26] | Datasets: EMO-DB and SAVEE | Artificial neural network | Accuracy is good | Time-consuming method. Stress detection was not considered |
| Stress and anxiety detection using facial cues from videos G. Giannakakis et al. (Elsevier 2017) [29] | Recorded using camera | Using facial cues from the videos | Achieves good classification accuracy | 1 min video duration could yield more reliable estimates |
| A Combined Rule-Based & Machine Learning Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition Approach Kah Phooi et al. (IEEE 2016) [30] | eNTERFACE and RML(RAVDESS) | Emotion recognition using rule-based and machine learning | Fusion of audio and visual data | Worked only on emotion using audio-visual data, stress was not detected |
| Fusion-based Emotion Recognition System Anupam Agrawal, Nayaneesh Kumar Mishra (IEEE 2016) [31] | SAVEE and also created own dataset | SVM for emotion classification | Fusion of audio and visual data | Results can be improved using deep learning techniques |
| Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition in Video Clips Noroozi, F et al. (IEEE 2016) [32] | SAVEE eNTERFACE’05 and RML | Fusion at the decision level | Comparison of results based on all 3 datasets | Stress detection was not considered |
| 1 | Inner Brow Raiser | 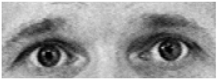 |
| 2 | Outer Brow Raiser |  |
| 4 | Brow Lowerer |  |
| 5 | Upper Lid Raiser |  |
| 6 | Cheek Raiser |  |
| 7 | Lid Tightener |  |
| 9 | Nose Wrinkler |  |
| 10 | Upper Lip Raiser | 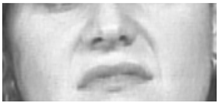 |
| 11 | Nasolabial Deepener | 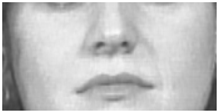 |
| 12 | Lip Corner Puller | 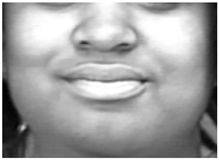 |
| 13 | Cheek Puffer | 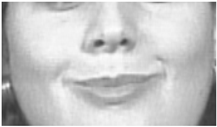 |
| 14 | Dimpler | 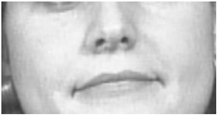 |
| 15 | Lip Corner Depressor | 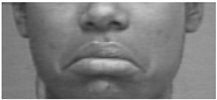 |
| 16 | Lower Lip Depressor | 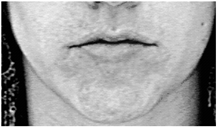 |
| 17 | Chin Raiser |  |
| 18 | Lip Puckerer | 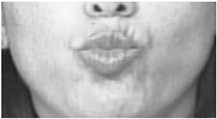 |
| 20 | Lip stretcher |  |
| 22 | Lip Funneler | 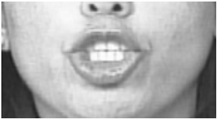 |
| 23 | Lip Tightener |  |
| 24 | Lip Pressor |  |
| 25 | Lips part |  |
| 26 | Jaw Drop | 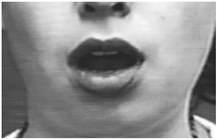 |
| 27 | Mouth Stretch |  |
| 28 | Lip Suck |  |
| 41 | Lid droop |  |
| 42 | Slit |  |
| 43 | Eyes Closed |  |
| 44 | Squint |  |
| 45 | Blink |
| Basic Expressions | Involved Action Units |
|---|---|
| Surprise | AU 1, 2, 5, 15, 16, 20, 26 |
| Fear | AU 1, 2, 4, 5, 15, 20, 26 |
| Disgust | AU 2, 4, 9, 15, 17 |
| Anger | AU 2, 4, 7, 9, 10, 20, 26 |
| Happiness | AU 1, 6, 12, 14 |
| Sadness | AU 1, 4, 15, 23 |
| Identifier | Coding Description of Factor Levels |
|---|---|
| Modality | 01 = Audio-video, 02 = Video-only, 03 = Audio-only |
| Channel | 01 = Speech, 02 = Song |
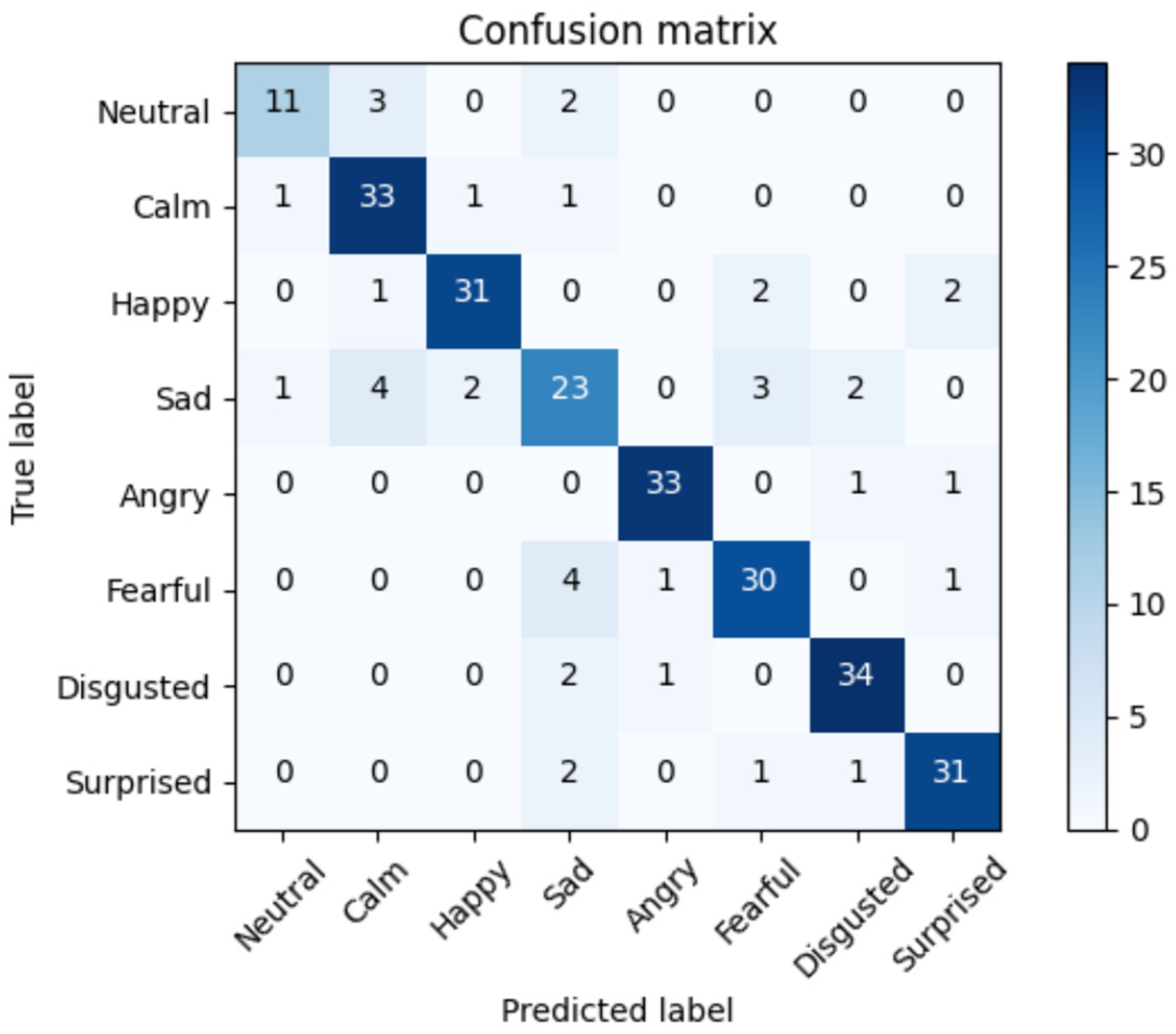
| Emotion | 01 = Neutral, 02 = Calm, 03 = Happy, 04 = Sad, 05 = Angry, 06 = Fearful, 07 = Disgust, 08 = Surprised |
| Intensity | 01 = Normal, 02 = Strong |
| Statement | 01 = “Kids are talking by the door”, 02 = “Dogs are sitting by the door” |
| Repetition | 01 = First repetition, 02 = Second repetition |
| Actor | 01 = First actor, …… 24 = Twenty-fourth actor |
| Classification Accuracy % | SVM | RNN | MFCC (LSTM) | MFCC(LSTM+RNN) Proposed Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | 100 | 70 | 90 | 100 |
| Calm | 66 | 85 | 86 | 98 |
| Happy | 86 | 83 | 84 | 93 |
| Sad | 81 | 75 | 78 | 86 |
| Angry | 89 | 84 | 91 | 98 |
| Fearful | 70 | 72 | 74 | 87 |
| Disgust | 73 | 70 | 75 | 82 |
| Surprise | 60 | 75 | 78 | 84 |
| Overall Accuracy | 76 | 78 | 82 | 91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, M.V.; Vaikole, S.; Oza, A.D.; Patel, A.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.P.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.D. Audio-Visual Stress Classification Using Cascaded RNN-LSTM Networks. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100510
Gupta MV, Vaikole S, Oza AD, Patel A, Burduhos-Nergis DP, Burduhos-Nergis DD. Audio-Visual Stress Classification Using Cascaded RNN-LSTM Networks. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100510
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Megha V., Shubhangi Vaikole, Ankit D. Oza, Amisha Patel, Diana Petronela Burduhos-Nergis, and Dumitru Doru Burduhos-Nergis. 2022. "Audio-Visual Stress Classification Using Cascaded RNN-LSTM Networks" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100510
APA StyleGupta, M. V., Vaikole, S., Oza, A. D., Patel, A., Burduhos-Nergis, D. P., & Burduhos-Nergis, D. D. (2022). Audio-Visual Stress Classification Using Cascaded RNN-LSTM Networks. Bioengineering, 9(10), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100510










