Engineered Dutasteride-Lipid Based Nanoparticle (DST-LNP) System Using Oleic and Stearic Acid for Topical Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Dutasteride-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (DST-NLP)
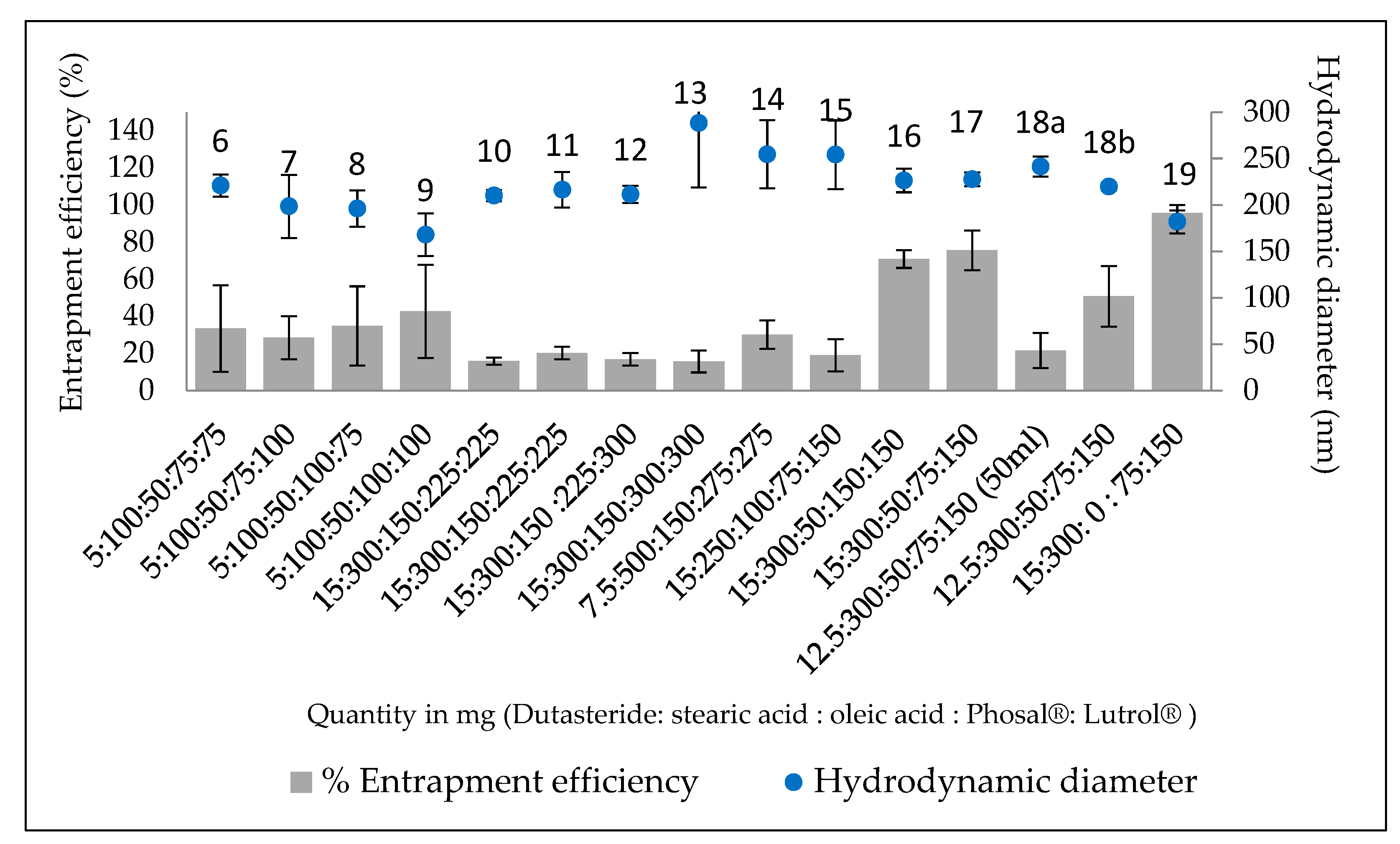
2.3. Experimental Design of Preparation of DST-LNP
2.4. Characterisation of DST-LNP
2.4.1. Measurement of Particle Size Distribution and Zeta Potential
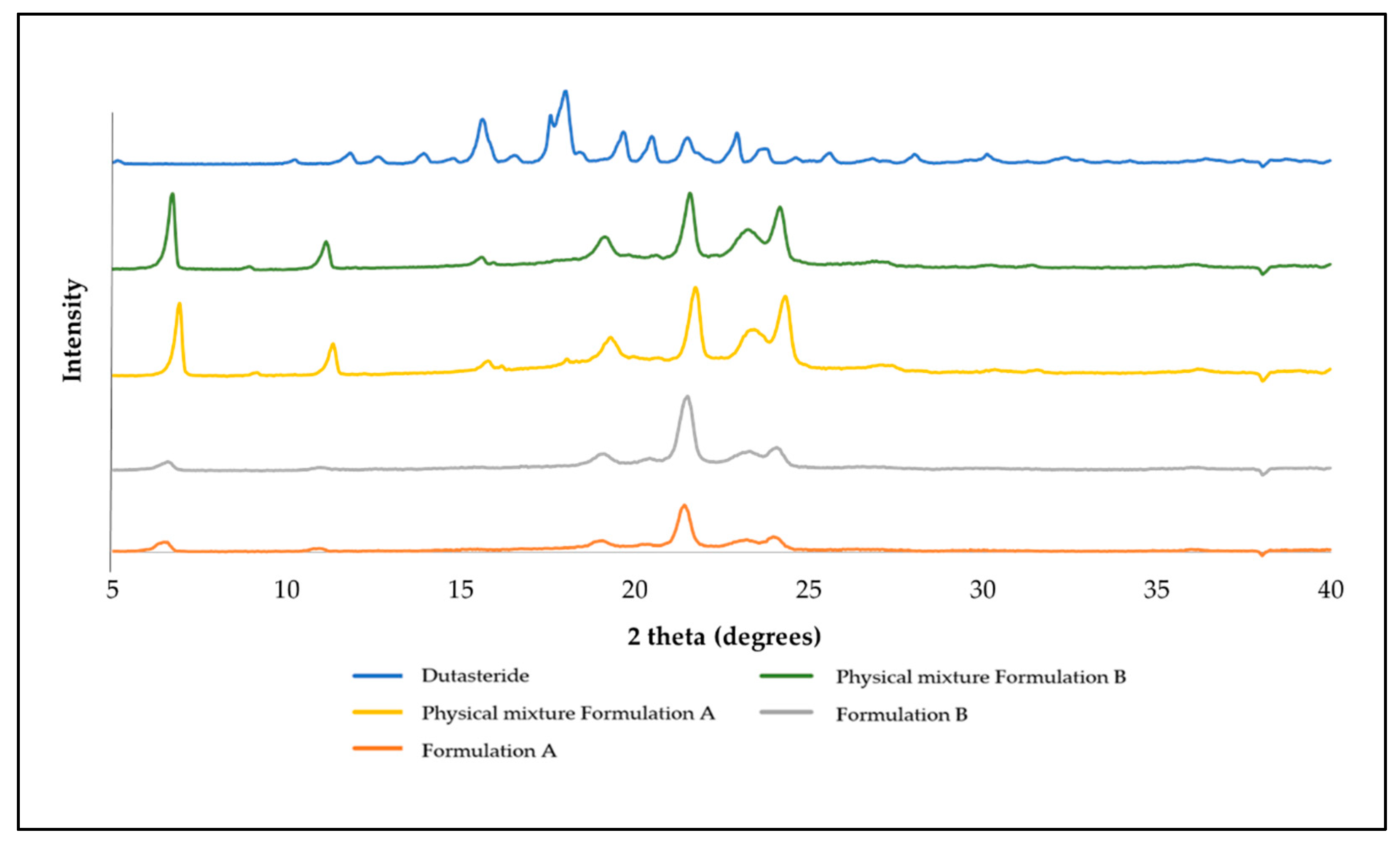
2.4.2. Determination of Nanoparticle Morphology and Crystallinity
2.4.3. Entrapment Efficiency
- n1 = concentration of entrapped dutasteride in DST-LNP
- n2 = total concentration of dutasteride in DST-LNP
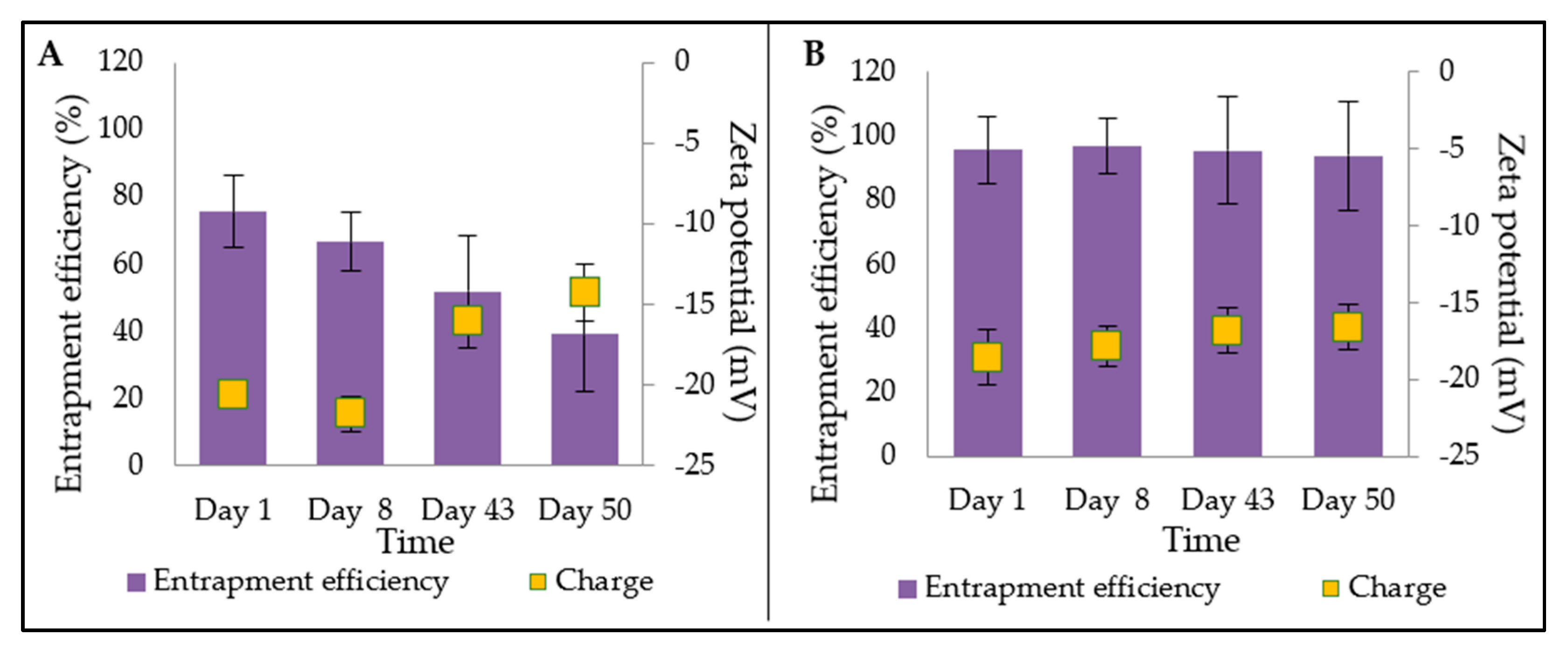
2.5. Physical Stability Study
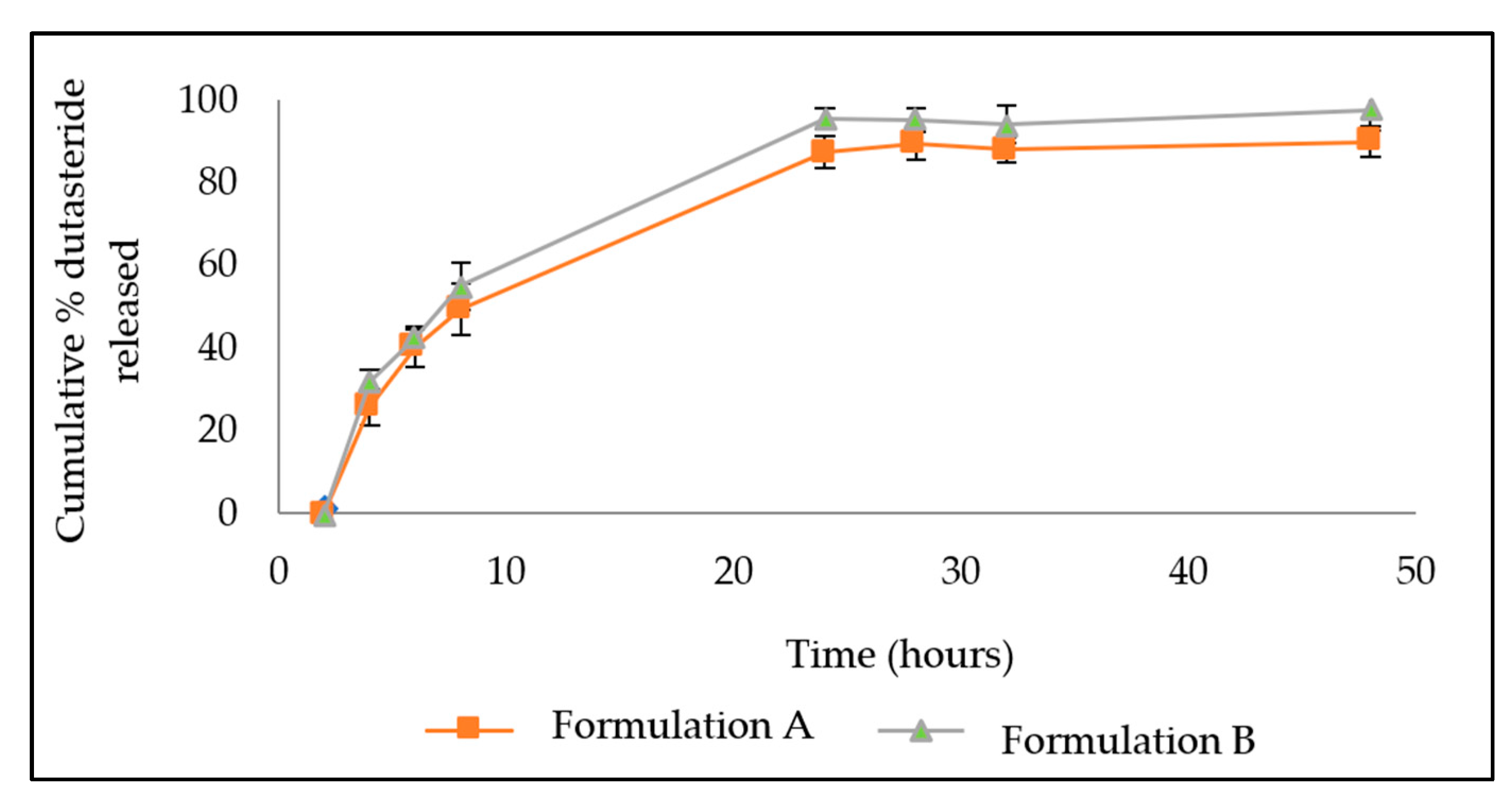
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release
2.7. In Vitro Permeation Study
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterisation of DST-LNP
3.1.1. Determination of Nanoparticle Morphology and Crystallinity
3.1.2. Entrapment Efficiency and Drug Loading
3.2. In Vitro Drug Release
3.3. In Vitro Permeation Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norwood, O.T. Male pattern baldness: Classification and incidence. South. Med. J. 1975, 68, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholt, D.R.; Gillespie, N.A.; Heath, A.C.; Martin, N.G. Genetic basis of male pattern baldness. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Hamer, M.A.; Heilmann, S.; Herold, C.; Moebus, S.; Hofman, A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Nöthen, M.M.; Van Duijn, C.M.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; et al. Prediction of male-pattern baldness from genotypes. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hibberts, N.; Howell, A.; Randall, V. Balding hair follicle dermal papilla cells contain higher levels of androgen receptors than those from non-balding scalp. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 156, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, M.; Richter-Appelt, H.; Tosti, A.; Viera, M.S.; García, M. The psychosocial impact of hair loss among men: A multinational European study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2005, 21, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, D.; Himmelberger, D.; Rhodes, T.; Cash, T.F.; Girman, C.J. The effects of hair loss in European men: A survey in four countries. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2000, 10, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, N.M.; Nazri, N.Z.; Mohamad-Salam, N.A.; Abdul-Rasid, Z.I.; Hasham, R.; Abdul-Aziz, A. The potential of androgenic alopecia management from plant derivatives. Food Res. 2020, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamashiro, F.L.; Yukuyama, M.N.; Velasco, M.V.R.; De Araújo, G.L.B.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Nanoemulsions containing plant oils: How do they influence hair treatment? Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 43, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, G.; Akram, S.; Westgate, G.E.; Tamburic, S. Can plant-derived phytochemicals provide symptom relief for hair loss ? A critical review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranwell, W.; Sinclair, R. Male androgenetic alopecia. In Endotext [Internet]; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, E.; Hordinsky, M.; Whiting, D.; Stough, D.; Hobbs, S.; Ellis, M.L.; Wilson, T.; Rittmaster, R.S. The importance of dual 5α-reductase inhibition in the treatment of male pattern hair loss: Results of a randomized placebo-controlled study of dutasteride versus finasteride. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Charrette, A. The efficacy and safety of 5α-reductase inhibitors in androgenetic alopecia : A network meta-analysis and benefit—risk assessment of finasteride and dutasteride. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2014, 25, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, S.; Kadowitz, P.J.; Hellstorm, W.J. Effects of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors on erectile function, sexual desire and ejaculation. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2013, 12, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, R.; Ganem-Rondero, A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Occlusive efect and penetration enhancement ability. J. Cosmet. Dermatological Sci. Appl. 2015, 05, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, N.M.; Sheikh, K.; Somavarapu, S.; Taylor, K.M. Preparation and characterization of dutasteride-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers coated with stearic acid-chitosan oligomer for topical delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shimizu, K.; Kondo, R. Anti-androgenic activity of fatty acids. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.M.; Shallan, M.; Mohamed, D.A.; Fouda, K.; Hanna, L.M. Biological evaluation of anti-androgenic effect of some plant foods. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 2, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, N.M.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; Sheikh, K.; Somavarapu, S.; Taylor, K.M.G. In vitro performance of dutasteride-nanostructured lipid carriers coated with lauric acid-chitosan oligomer for dermal delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Dey, S.; Ramani, Y.R.; Ray, S.; Mazumder, B. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC)-based gel for the topical delivery of aceclofenac: Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, M.J.; Martins, S.; Ferreira, D.; Segundo, M.A.; Reis, S. Lipid nanoparticles for topical and transdermal application for alopecia treatment: Development, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro release and penetration studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, K.S.; Sung, K.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Fang, J.Y. Skin permeation of buprenorphine and its ester prodrugs from lipid nanoparticles: Lipid emulsion, nanostructured lipid carriers and solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Microencapsul. 2009, 26, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamma, R.N.; Aburahma, M.H. Follicular delivery of spironolactone via nanostructured lipid carriers for management of alopecia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 5449–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Teichmann, A.; Otberg, N.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Luengo, J.; Weiss, B.; Schaefer, U.F.; Lehr, C.-M.; Wepf, R.; et al. Nanoparticles—An efficient carrier for drug delivery into the hair follicles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noor, N.M.; Umar, S.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; Sheikh, K.; Somavarapu, S. Engineered Dutasteride-Lipid Based Nanoparticle (DST-LNP) System Using Oleic and Stearic Acid for Topical Delivery. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9010011
Noor NM, Umar S, Abdul-Aziz A, Sheikh K, Somavarapu S. Engineered Dutasteride-Lipid Based Nanoparticle (DST-LNP) System Using Oleic and Stearic Acid for Topical Delivery. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoor, Norhayati Mohamed, Sana Umar, Azila Abdul-Aziz, Khalid Sheikh, and Satyanarayana Somavarapu. 2022. "Engineered Dutasteride-Lipid Based Nanoparticle (DST-LNP) System Using Oleic and Stearic Acid for Topical Delivery" Bioengineering 9, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9010011
APA StyleNoor, N. M., Umar, S., Abdul-Aziz, A., Sheikh, K., & Somavarapu, S. (2022). Engineered Dutasteride-Lipid Based Nanoparticle (DST-LNP) System Using Oleic and Stearic Acid for Topical Delivery. Bioengineering, 9(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9010011





