High Resistance of a Sludge Enriched with Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria to Ammonium Salts and Its Potential as a Biofertilizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inocula Collection
2.2. Bioreactor Operation
2.2.1. Phase 1. Enrichment of NFB
2.2.2. Phase 2. Inocula Adaptation to Ammonium Salts Conditions
2.2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Survey Bacterial Community
2.3.1. DNA Extraction, PCR, and DGGE
2.3.2. RNA 16S Gene Sequencing and Diversity Analysis
2.4. Evaluation of Biofertilization
3. Results
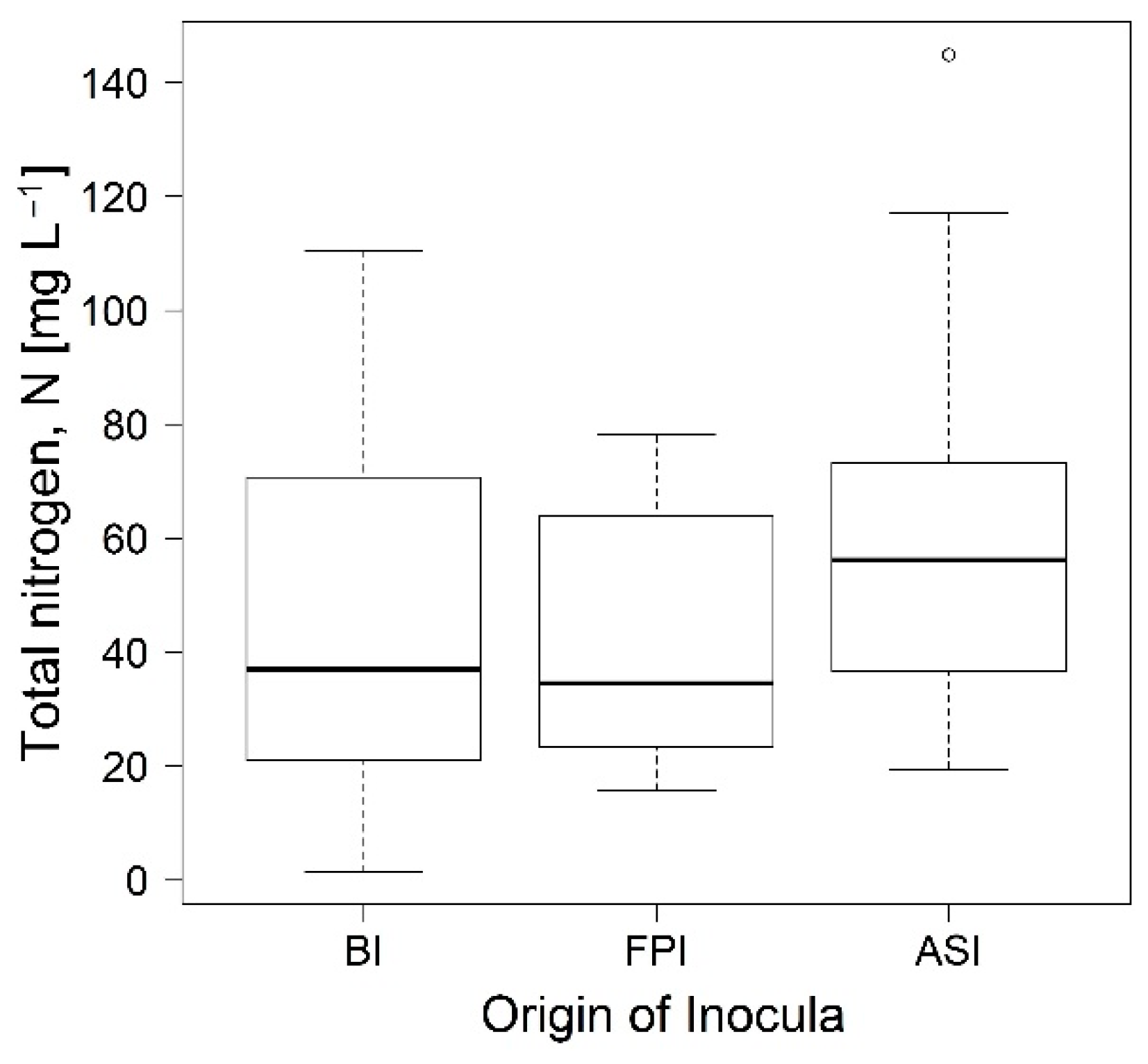
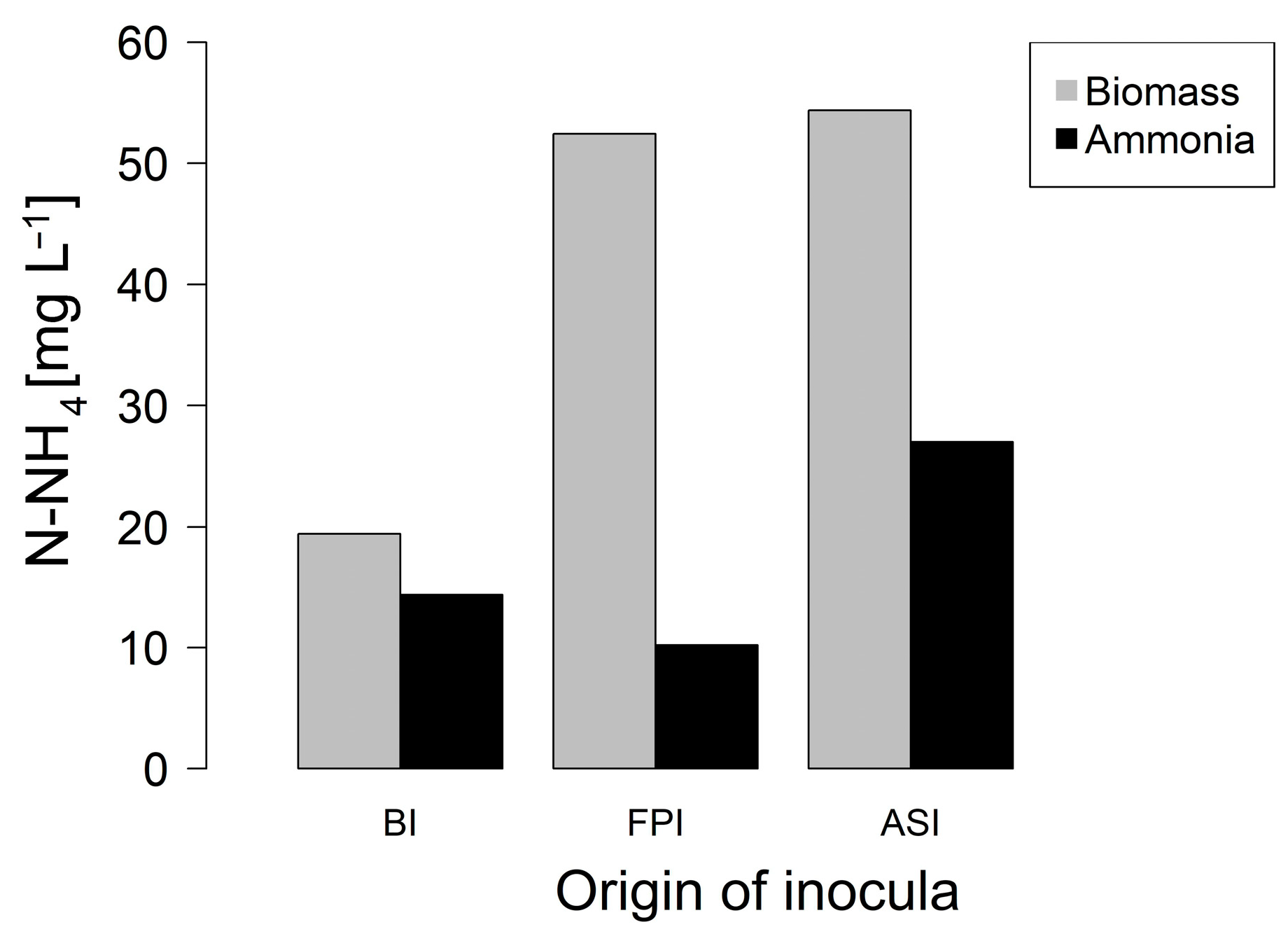
3.1. Phase 1. Enrichment of Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
3.2. Phase 2. Inocula Adaptation to Ammonium Salts Increase
3.3. Microbial Diversity Analysis with DGGE
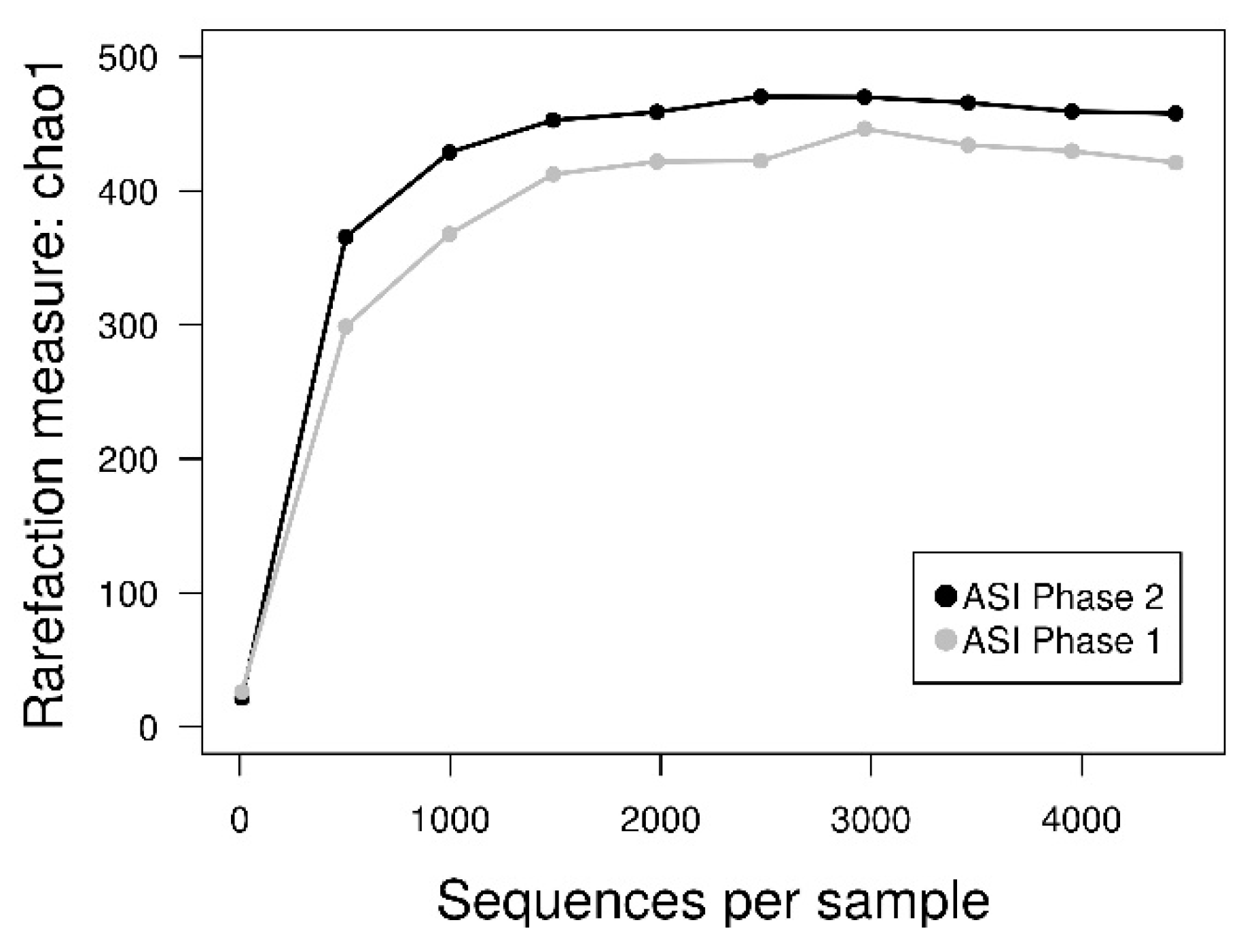
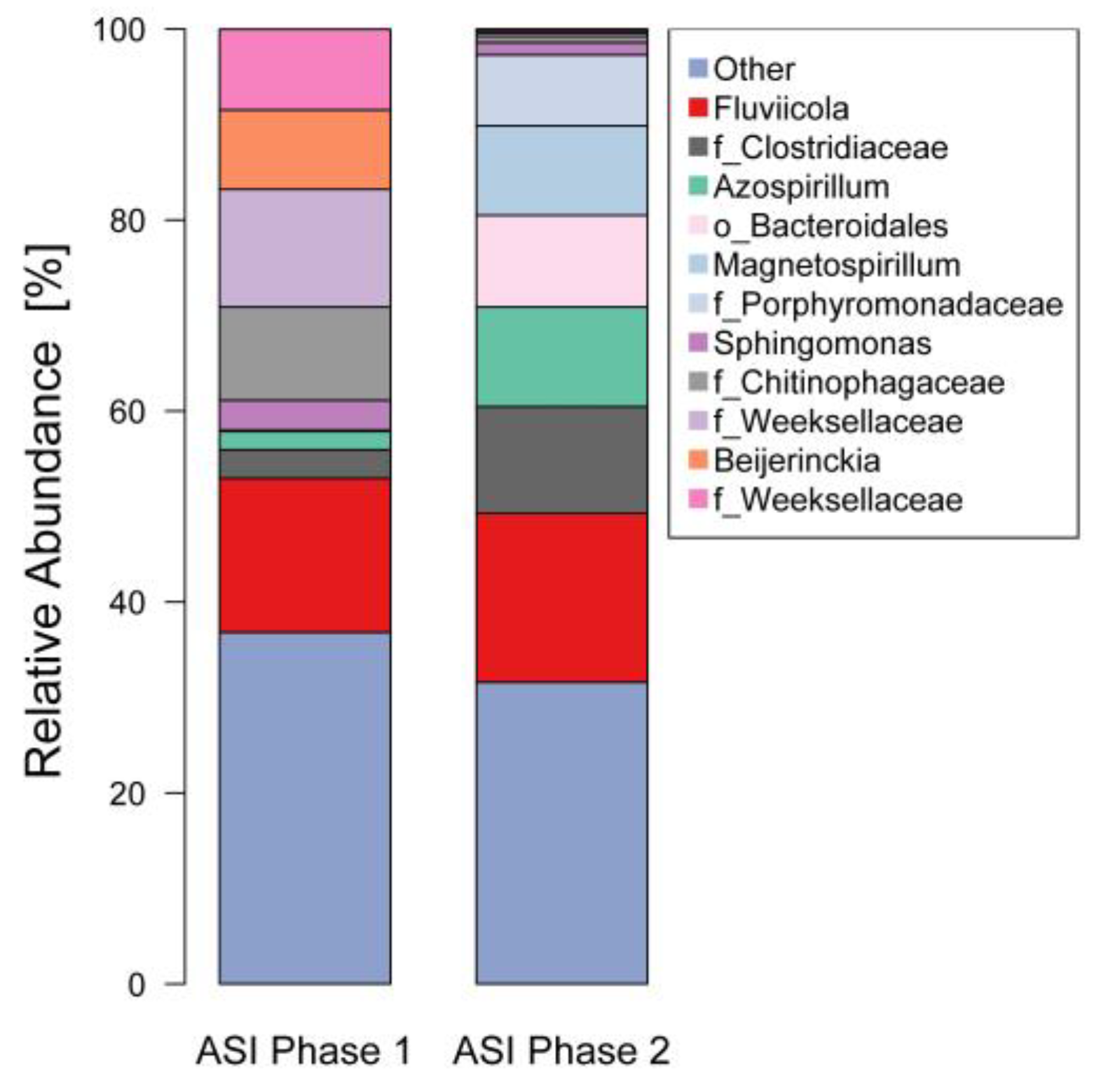
3.4. 16S rDNA Diversity Analysis
3.5. Biofertilizer Effect on Coriandrum Sativum
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Associations in the Bioreactor
4.2. Inoculum Application in Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASI | Activate Sludge Inoculum |
| BI | Biodisc Inoculum |
| DGGE | Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| FPI | Facultative Pound Inoculum |
| H-B | Haber Bosch process |
| NFB | Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria |
| OMC | Organic Matter Content |
| OTUs | Operational Taxonomic Units |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PGPRs | Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria |
| SBR | Sequential Batch Reactor |
| T0 | Treatment with no fertilization |
| T1 | Treatment with commercial Azotobacter chroococcum |
| T2 | Treatment with chemical fertilizer |
| T3 | Treatment with adapted inocula, −10% of dose |
| T4 | Treatment with adapted inocula, 100% of dose |
| T5 | Treatment with adapted inocula, +10% of dose |
| TAE | Tris base, Acetic acid and EDTA solution |
| TKN | Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen |
| TNC | Total Nitrogen Content |
| WWTP | Waste Water Treatment Plant |
References
- Kuypers, M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Cape, J.N.; Reis, S.; Sheppard, L.J.; Jenkins, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- YARA Yara Fertilizer Industry Handbook. Available online: https://www.yara.com/siteassets/investors/057-reports-and-presentations/other/2018/fertilizer-industry-handbook-2018-with-notes.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Bicer, Y.; Dincer, I.; Vezina, G.; Raso, F. Impact assessment and environmental evaluation of various ammonia production processes. Environ. Manag. 2017, 59, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Chen, Z.; Figiela, M.; Stepniak, I.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.-J. Emerging alternative for artificial ammonia synthesis through catalytic nitrate reduction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 77, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Luo, S.; Hu, L.; Chen, B.; Xie, Z.; Ma, B.; Ma, W.; Du, G.; Ma, X.; Le Roux, X. Responses of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea diversity to N, P and NP fertilization: Relationships with soil environmental variables and plant community diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 145, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, F.; He, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, K. Increased organic fertilizer application and reduced chemical fertilizer application affect the soil properties and bacterial communities of grape rhizosphere soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring soil quality to mitigate soil degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sathya, A.; Vijayabharathi, R.; Varshney, R.K.; Gowda, C.L.; Krishnamurthy, L. Plant growth promoting rhizobia: Challenges and opportunities. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antar, M.; Lyu, D.; Nazari, M.; Shah, A.; Zhou, X.; Smith, D.L. Biomass for a sustainable bioeconomy: An overview of world biomass production and utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounaffaa, M.; Florio, A.; Le Roux, X.; Jayet, P.-A. Economic and environmental analysis of maize inoculation by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the French Rhône-Alpes region. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 146, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahemad, M.; Kibret, M. Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Current perspective. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jez, J.M.; Lee, S.G.; Sherp, A.M. The next green movement: Plant biology for the environment and sustainability. Science 2016, 353, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiei, Z.; Hosseini, S.J.; Pirdashti, H.; Hazrati, S. Physiological and biochemical traits in coriander affected by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under salt stress. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawarda, P.C.; Le Roux, X.; Van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Deliberate introduction of invisible invaders: A critical appraisal of the impact of microbial inoculants on soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Betancourth, C.; Acharya, K.; Allen, B.; Entwistle, J.; Head, I.M.; Sanabria, J.; Curtis, T.P. Enrichment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in a nitrogen-deficient wastewater treatment system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3539–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, N.M.; Bowers, T.H.; Lloyd-Jones, G. Bacterial community composition of a wastewater treatment system reliant on N2 fixation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Peláez, N.; Peña-Varón, M.; Sanabria, J.S.J. Comunidades bacterianas involucradas en el ciclo del nitrógeno en humedales construidos. Ing. Y Compet. 2011, 13, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.; Larriva, J.; Sánchez, E.; Idrovo, D.; Cisneros, J.F. Assessment of decentralized wastewater treatment systems in the rural area of Cuenca, Ecuador. Water Pract. Technol. 2017, 12, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Betancourth, C.; Acharya, K.; Sanabria, J.; Curtis, T.P. Low inhibitory effect of ammonia on the nitrogen-fixing activity of a sludge enriched with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 14, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvon, G.; Vasel, J.-L.; Wouwer, A.V. Dynamic simulation and optimisation of a SBR wastewater treatment system. In Proceedings of the Conference Dynamic Simulation and Optimisation of a SBR Wastewater Treatment System, Sinaia, Romania, 13–15 October 2016; pp. 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Xie, Z. Plant growth promotion properties of bacterial strains isolated from the rhizosphere of the Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) adapted to saline–alkaline soils and their effect on wheat growth. Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA. WEF 4500-N NITROGEN. In Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Poly, F.; Monrozier, L.J.; Bally, R. Improvement in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SequentiX-Digital DNA Processing. GelQuest Software for Analysis of DNA Fingerprint Data; SequentiX-Digital DNA Processing: Klein Raden, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- SequentiX-Digital DNA Processing. ClusterVis Software for Analysis and Visualisation of Phylogenetic Data; SequentiX-Digital DNA Processing: Klein Raden, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Z.; Li, Q.; Lv, T.; Misselbrook, T.; Liu, X. Response of ammonia volatilization to biochar addition: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Koslicki, D.; McClelland, J.; Reeve, N.; Xu, Z.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. Striped UniFrac: Enabling microbiome analysis at unprecedented scale. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 847–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, S.; Tan, M.; Gapes, D.; Shilton, A. Development and examination of a granular nitrogen-fixing wastewater treatment system. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, P.J.; Ramond, J.-B.; Braun, L.; Vikram, S.; Le Roes-Hill, M. Bacterial nitrogen fixation in sand bioreactors treating winery wastewater with a high carbon to nitrogen ratio. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Ekama, G.A.; Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Ødegaard, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.M. Influence of carbon to nitrogen ratio on nitrous oxide emission in an Integrated Fixed Film Activated Sludge Membrane BioReactor plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, W.L.; Calgaro, M.; Coelho, D.S.; Santos, D.B.D.; Souza, M.A.D. Growth of sugar cane varieties under salinity. Rev. Ceres 2016, 63, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ward, B.B.; Sigman, D.M. Global nitrogen cycle: Critical enzymes, organisms, and processes for nitrogen budgets and dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5308–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Kamakura, Y.; Suzuki, K.-I.; Nakagawa, Y. Salinirepens amamiensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Cryomorphaceae isolated from seawater, and emended descriptions of the genera Fluviicola and Wandonia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.-W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.Q.; Lau, K.W.; Li, S.P.; Jiang, J.D. Fluviicola hefeinensis sp. nov., isolated from the wastewater of a chemical factory. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, J.; Cerezini, P.; Hungria, M. Azospirillum: Benefits that go far beyond biological nitrogen fixation. AMB Express 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubki, R.; Tabassum, H.; Abudawood, M.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alsobaie, S.F.; Ansar, S. Green synthesis, characterization, enhanced functionality and biological evaluation of silver nanoparticles based on Coriander sativum. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Moustakas, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Bio-based fertilizers: A practical approach towards circular economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigua, G.; Adjei, M.; Rechcigl, J. Cumulative and residual effects of repeated sewage sludge applications: Forage productivity and soil quality implications in South Florida, USA (9 pp). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2005, 12, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Gal, L.; Garmyn, D.; Bisaria, V.; Sharma, S.; Piveteau, P. Evidence of biocontrol activity of bioinoculants against a human pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, K.; Perzon, M.; Fröling, M.; Mossakowska, A.; Svanström, M. Sewage sludge handling with phosphorus utilization–life cycle assessment of four alternatives. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Inocula | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI | FPI | ASI | ||||
| To | Tf | To | Tf | To | Tf | |
| DOR | 2.93–3.44 | 2.92–2.93 | 2.99–3.04 | |||
| pHR | 6.70–7.33 | 6.84–7.70 | 5.67–7.67 | |||
| NH4+ | 4.00 | 13.05 | 3.50 | 11.25 | 2.70 | 13.2 |
| NO2− | 0.22 | 1.07 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 0.23 | 0.62 |
| NO3− | 3.24 | 9.73 | 3.91 | 11.74 | 3.03 | 9.10 |
| Parameters | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (units) | 7.9 | 8.0 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.9 |
| OMC (%) | 4.03 | 4.41 | 4.32 | 4.70 | 4.65 | 4.41 |
| TNC (%) | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.45 |
| C/N | 13.00 | 11.60 | 12.71 | 13.43 | 11.08 | 9.80 |
| NH3 (mg kg−1) | 35.0 | 35.9 | 35.9 | 39.7 | 76.1 | 52.7 |
| Parameters | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of plants | 16 | 16 | 21 | 19 | 17 | 19 |
| Plant height (cm) | 23.85 | 21.65 | 23.69 | 21.28 | 21.48 | 23.18 |
| No. of flowers | 52 | 27 | 62 | 42 | 34 | 44 |
| No. of leafs | 73 | 73 | 136 | 123 | 59 | 88 |
| Dry matter (g) | 1.04 | 1.12 | 1.96 | 1.56 | 0.74 | 1.22 |
| Foliar nitrogen (%) | 1.03 | 1.62 | 2.05 | 1.92 | 1.74 | 2.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Gonzalez, C.; Ospina-Betancourth, C.; Sanabria, J. High Resistance of a Sludge Enriched with Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria to Ammonium Salts and Its Potential as a Biofertilizer. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050055
Rodriguez-Gonzalez C, Ospina-Betancourth C, Sanabria J. High Resistance of a Sludge Enriched with Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria to Ammonium Salts and Its Potential as a Biofertilizer. Bioengineering. 2021; 8(5):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Gonzalez, Claudia, Carolina Ospina-Betancourth, and Janeth Sanabria. 2021. "High Resistance of a Sludge Enriched with Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria to Ammonium Salts and Its Potential as a Biofertilizer" Bioengineering 8, no. 5: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050055
APA StyleRodriguez-Gonzalez, C., Ospina-Betancourth, C., & Sanabria, J. (2021). High Resistance of a Sludge Enriched with Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria to Ammonium Salts and Its Potential as a Biofertilizer. Bioengineering, 8(5), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050055






