COVID-19 Diagnostic Strategies Part II: Protein-Based Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SARS-COV-2 Virology
3. Serodiagnosis of SARS-COV-2
3.1. Laboratory-Based Non-Isotopic Immunoassay (NIIA) Serological Tests
3.1.1. Chemiluminescence Immunoassays (CLIA)
| Company | Test | Technology | Target | Antigen | Sensitivity (Day 15 after Symptom Onset) | Specificity | Throughput |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. | VITROS Immunodiagnostic Products Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Total Reagent Pack | CLIA | Total Antibody | S | 100% | 100% | 150 tests/h with one result in 48 min |
| Beckman Coulter, Inc. | Access SARS-CoV-2 IgG | Automated CLIA | IgG | S | 96.8% | 99.6% | 50–200 tests/h |
| Babson Diagnostics, Inc. | Babson Diagnostics aC19G1 | Fully Automated CLIA | IgG | S | 100% | 100% | 440 tests/h |
| Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. | VITROS Immunodiagnostic Products Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Reagent Pack | CLIA | IgG | S | 90.0% | 100% | 150 tests/h |
| Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc. | ADVIA Centaur SARS-CoV-2 Total (COV2T) | Automated-Semi-quantitative CMIA | Total Antibody | S | 100% | 99.8% | 240 samples/h with one result in 18 min |
| Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc. | Atellica IM SARS-CoV-2 Total (COV2T) | Automated CMIA | Total Antibody | S | 100% | 99.8% | 440 tests/h with one result in 10 min |
| DiaSorin | LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 IgG | Complex Automated CLIA | IgG | S (S1/S2) | 97.6% | 99.3% | 170 tests/h and 35 min time to first result |
| Vibrant America Clinical Labs | Vibrant COVID-19 Ab Assay | CLIA | IgM and IgG | S and N | 98.1% | 98.6% | 24–36 h |
| SNIBE Diagnostic | MAGLUMI 2019-nCoV IgM/IgG | Automated CLIA | IgM and IgG | S and N | 64.3% | 100% | 30 min for one test |
| Diazyme Laboratories, Inc. | Diazyme SARS-CoV-2 IgM CLIA test | CLIA | IgM | S and N | 94.4% | 98.3% | 50 tests/h |
| Diazyme Laboratories, Inc. | Diazyme DZ-Lite SARS-CoV-2 IgG CLIA Kit | Automated CLIA | IgG | S and N | 100% | 97.4% | 50 tests/h |
| Roche Diagnostics | Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 | ECLIA | Total Antibody | N | 100% | 99.8% | 300 tests/h |
| Abbott Laboratories Inc. | Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG | CMIA | IgG | N | 100% | 99.6% | 100 samples in 70 min |
| Abbott Laboratories Inc. | Alinity i SARS-CoV-2 IgG | CMIA | IgG | N | 100% | 99.0% | 4000 tests in 24 h, with a 29 min time to first result |
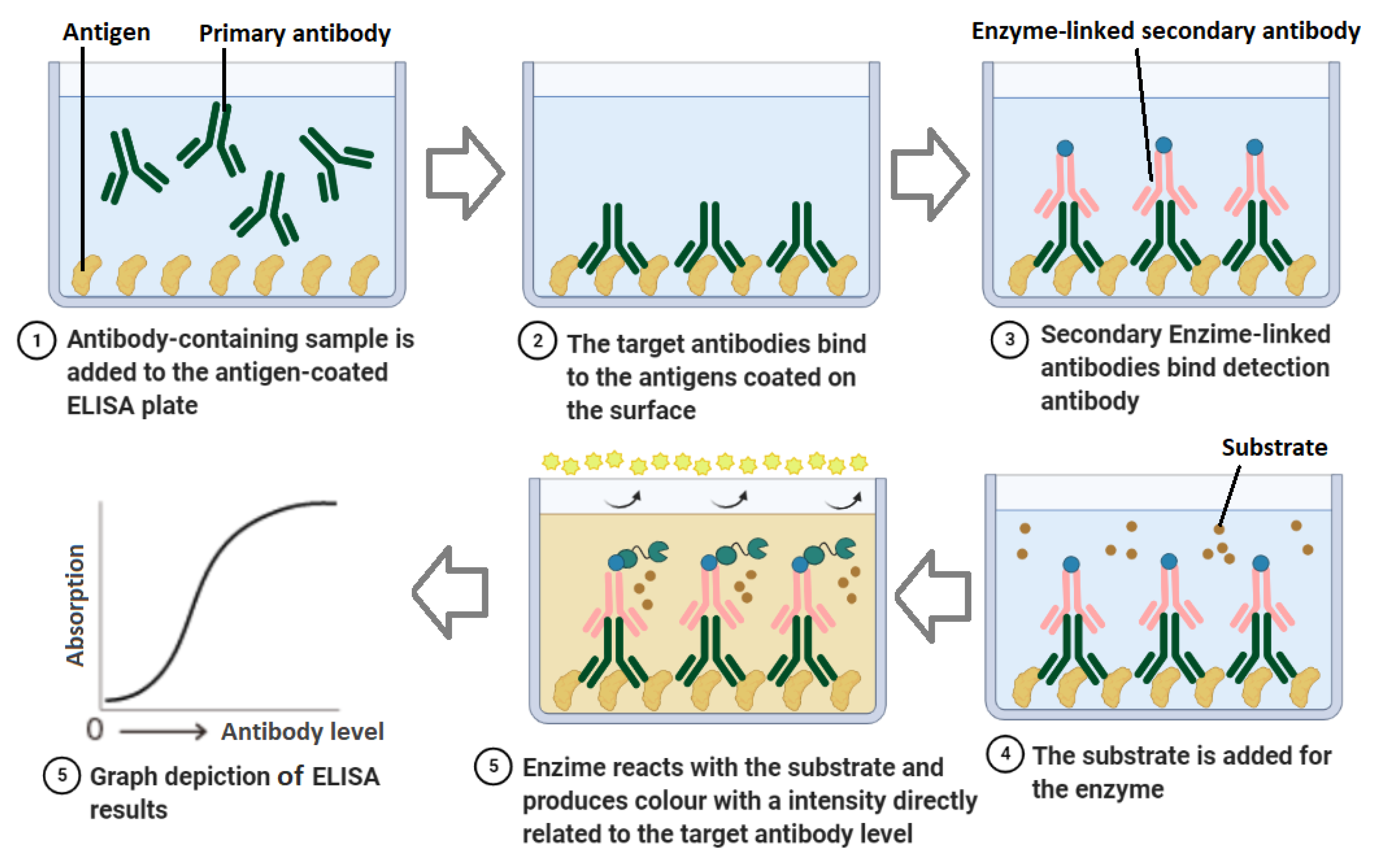
3.1.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
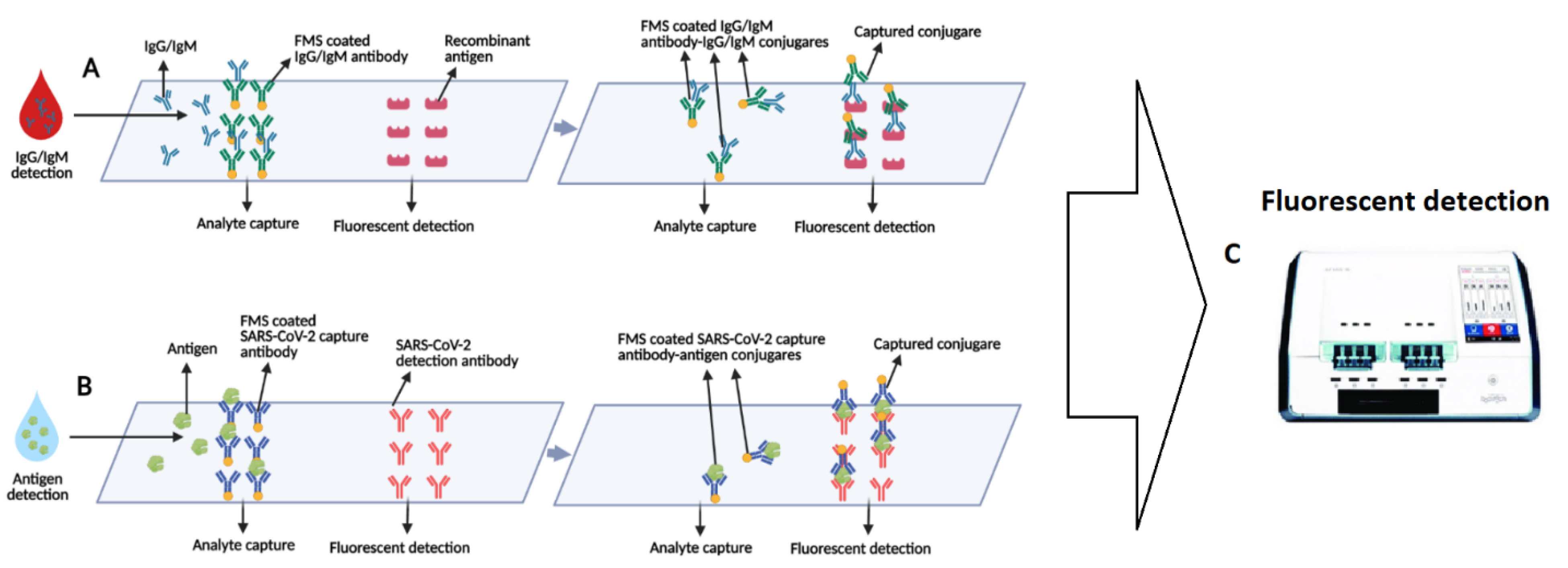
3.2. Lab-Based Fluorescence Immunoassays (FIA)
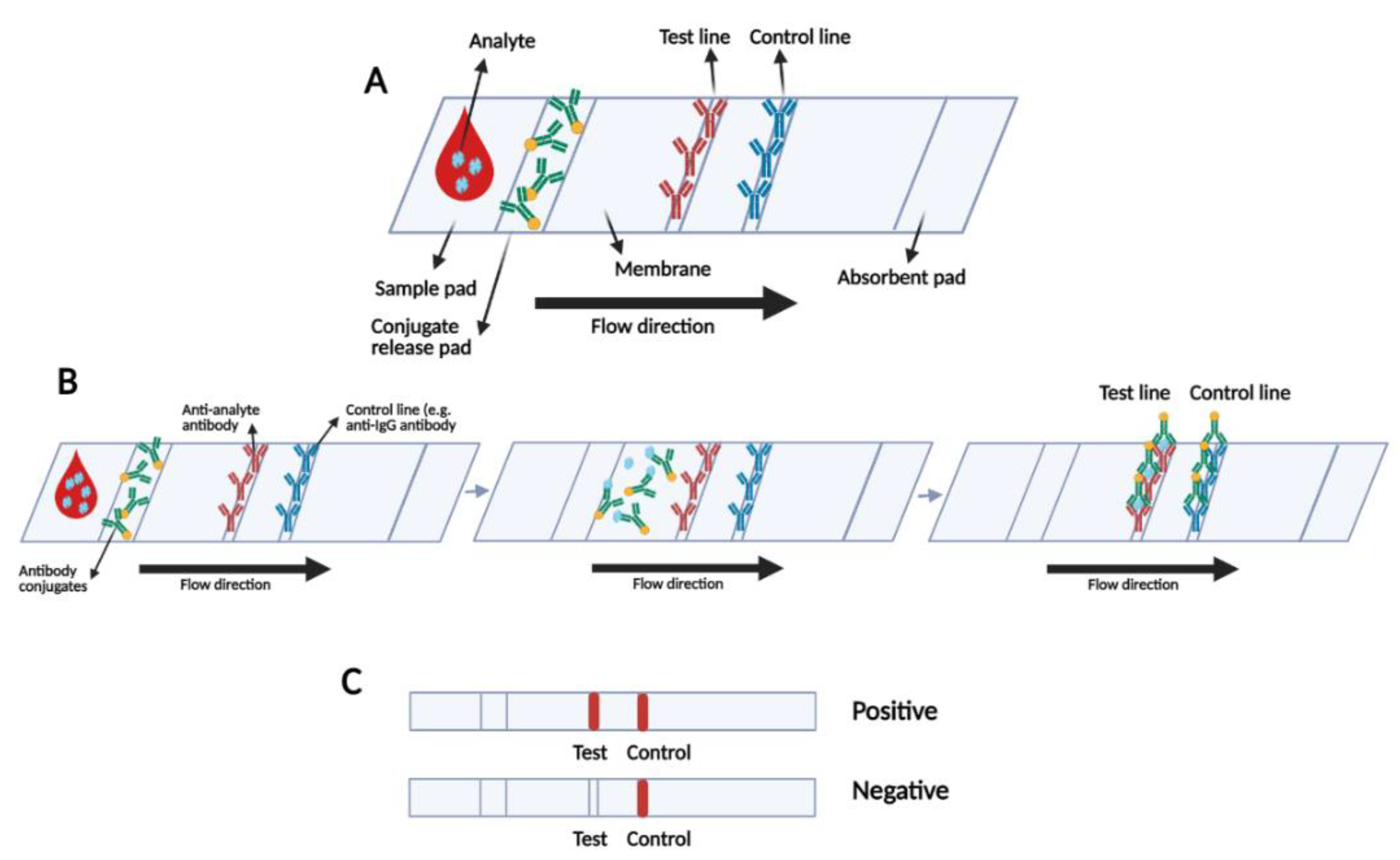
3.3. Rapid Serological Lateral Flow-Based Tests
| Company | Assay | Target | Capture Protein | Technology | Sensitivity (Day 15 after Symptom Onset) | Specificity | Time to Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADVAITE, Inc. [86] | RapCov Rapid COVID-19 Test | IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N antigen | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 90% | 95.2% | Visual Read/ 15 min |
| Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy Enterprise Co., Ltd. [87] | Wantai SARS-CoV-2 Ab Rapid Test | Total Antibody | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S antigen | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 98.8% | 100% | Visual Read/ 10–20 min |
| Salofa Oy [88] | Sienna-Clarity COVIBLOCK COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S antigen | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 93.3% | 98.8% | Visual Read/ 10–20 min |
| Xiamen Biotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd. [89] | BIOTIME SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Rapid Qualitative Test | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S antigen | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 100% | 96.2%—Cross-reactivity with HIV+ | Visual Read/ 15 min |
| Healgen Scientific LLC [90] | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 antigens (S, S1 subunit) | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 100% | 97.5% | Visual Read/ 10–15 min |
| Hangzhou Laihe Biotech Co. [91] | LYHER Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) IgM/IgG Antibody Combo Test Kit | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 antigens (S, S1 subunit) | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 100% | 98.8% | Visual Read/ 10 min |
| Hangzhou Biotest Biotech Co., Ltd. [92] | RightSign COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 antigen (S, RBD Domain) | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 100% | 100% | Visual Read/ 10–20 min |
| Megna Health, Inc. [93] | Rapid COVID-19 IgM/IgG Combo Test Kit | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N antigen | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 100% | 95.0% | Visual Read/ 10–20 min |
| Biohit Healthcare (Hefei) Co., Ltd. [94] | Biohit SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG Antibody Test Kit | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N antigen | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 96.7% | 95.0% | Visual Read/ 10–20 min |
| Assure Tech (Hangzhou) Co., Ltd. [95] | Assure COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Device | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S1 and N antigens | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 100% | 98% | Visual Read/ 20 min |
| Cellex, Inc. [96] | Cellex qSARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Cassette Rapid Test | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S and N antigens | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 93.8% | 96.0% | Visual Read/ 15–20 min |
| TBG Biotechnology Corp. [82] | TBG SARS-CoV-2 IgG / IgM Rapid Test Kit | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S and N antigens | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 99.8% | 99.8% | Visual Read/ 15 min |
| Biocan Diagnostics Inc. [97] | Tell Me Fast Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) IgG/IgM Antibody Test | IgM/IgG | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S and N antigens | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | 96.2% | 99.4% | Visual Read/ 10 min |
3.4. Protein Microarray
| Manufacturer | Test | Target | Microarray Content | Sensitivity | Specificity | Format | Regulatory Status | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quotient Limited SAÂ [29] | MosaiQ ™ COVID-19 Antibody Microarray | IgG, IgM directed to SARS-CoV-2 S protein | SARS-CoV-2 S protein antigens | Varies based on the phase of the disease (71–100%) | 99.8% | High-throughput automated Immunoassay-Antibody employing enhancement reagent to enable silver to nucleate on the gold nanoparticles | FDA EUA—CE-IVD | 35 min for the first microarray, 24 s for each next microarray. |
| PEPperPRINT GmbH [114] | PEPperCHIP® SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Microarray | IgG, IgA, and IgM | The whole proteome of SARS-CoV-2 (GenBank ID: MN908947.3) translated into overlapping peptides | (No info) | (No info) | Manual-One single peptide array | CE-IVD | For vaccine development, or screen viral antigens to find and characterize immunodominant epitopes for in-vitro diagnostics research |
| PEPperPRINT GmbH [115] | PEPperCHIP® SARS-CoV Antigen Microarray | SARS-CoV-2 specific Antibodies | S, N, M and E antigens | (No info) | no cross-reactivity | Manual- Containing three array copies per microarray, with 998 antigen specific peptides printed in duplicate | CE-IVD | including a two-day experimental workflow |
| PEPperPRINT GmbH [116] | PEPperCHIP® Pan-Corona Spike Protein Microarray | Antibodies against S antigen | S proteins derived from seven coronaviruses translated into overlapping peptides | (No info) | (No info) | One array with 4564 peptides in duplicate | RUO | For Serum antibody fingerprint analysis, Immune monitoring and Epitope studies |
| Nirmidas Biotech, Inc. [117] | pGOLD™ COVID-19 IgG/IgM Assay Kit | IgG and IgM against S1 subunit and rbd domain of S | Three SARS-CoV-2 specific antigens | Sensitivity > 87% for IgM 5 days post symptom, ~100% for IgG and IgM 15 days post symptom onset | >99.5 | Automated semi-Quantitative Microarray Based High Throughput ELISA-like COVID-19 array | RUO | 48 samples with controls in each run, read by western blot reader or Nirmidas’ MidaScan™instument |
| Sengenics Corporation Pte Ltd. [118] | ImmuSAFE™ Respiratory Virus Protein Microarray | SARS-CoV-2 specific Antibodies | Multiple SARS-CoV-2 proteins, N from 5 other human Coronaviruses as well as Influenza A and B HA antigen subtypes | (No info) | (No info) | Manual or automated single and double-colour fluorescently-labelled antibody assay | RUO | The key application is for research and development purposes |
| Sengenics Corporation Pte Ltd. [119] | ImmuSAFE™ COVID+ Biochip Test | SARS-CoV-2 specific Antibodies | Multiple SARS-CoV-2 specific domains (N and S) including full-length and numerous truncated versions | (No info) | (No info) | Single-colour fluorescently-labelled antibody assay, and Dual-colour fluorescently-labelled antibody assays for quantitative analysis | RUO | 24 arrays per slide (24 samples per slide)—Key applications are vaccine clinical trials and seroprevalence research studies. |
4. Rapid Antigenic Tests
5. Other Biosensors
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.E. Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19). Clin. Exp. Pediatrics 2020, 63, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report, 147. Data as Received by WHO from National Authorities by 10:00 CEST, 15 June 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200615-covid-19-sitrep-147.pdf?sfvrsn=2497a605_4 (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Nishiura, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Miyama, T.; Suzuki, A.; Jung, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kinoshita, R.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R. Estimation of the asymptomatic ratio of novel coronavirus infections (COVID-19). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-COV-2 Diagnostic Pipeline. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/?avance=In+development&type=all&test_target=all&status=all§ion=show-all&action=default#diag_tab (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Kakhki, R.K.; Kakhki, M.K.; Neshani, A. COVID-19 target: A specific target for novel coronavirus detection. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N.E.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2. Handb. Proteolytic Enzym. 2013, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasöksüz, M.; Kiliç, S.; Saraç, F. Coronaviruses and SARS-COV-2. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, S.; Concetta, R.; Francesco, R.; Annalisa, C. SARS-Cov-2 infection: Response of human immune system and possible implications for the rapid test and treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106519. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, D.; Wang, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, D.; Ye, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, W. Clinical Features of COVID-19 Patients with Different Outcomes in Wuhan: A Retrospective Observational Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, J. Clinical features of COVID-19-related liver functional abnormality. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, T.R.; Dhamdhere, G.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Goudy, L.; Zeng, L.; Chemparathy, A.; Chmura, S.; Heaton, N.S.; Debs, R. Development of CRISPR as an antiviral strategy to combat SARS-CoV-2 and influenza. Cell 2020, 181, 865–876.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratory Testing for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Suspected Human Cases: Interim Guidance, 19 March 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331501 (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Xiao, A.T.; Tong, Y.X.; Zhang, S. False negative of RT-PCR and prolonged nucleic acid conversion in COVID-19: Rather than recurrence. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1755–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SARS-CoV-2 Reference Panel Comparative Data. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/sars-cov-2-reference-panel-comparative-data (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Tahmasebi, S.; Khosh, E.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. The outlook for diagnostic purposes of the 2019-novel coronavirus disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9211–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, L. Profile of immunoglobulin G and IgM antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2255–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacofsky, D.; Jacofsky, E.M.; Jacofsky, M. Understanding antibody testing for COVID-19. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, F.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Peng, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, H. Antibody detection and dynamic characteristics in patients with COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Du, R.-H.; Li, B.; Zheng, X.-S.; Yang, X.-L.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Xiao, G.-F.; Yan, B.; Shi, Z.-L. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: Implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Mei, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, F.; Geng, S.; Pan, A. Low-dose corticosteroid therapy does not delay viral clearance in patients with COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 147–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, W.; He, H.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Jin, T. Serum IgA, IgM, and IgG responses in COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontou, P.I.; Braliou, G.G.; Dimou, N.L.; Nikolopoulos, G.; Bagos, P.G. Antibody tests in detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinquanta, L.; Fontana, D.E.; Bizzaro, N. Chemiluminescent immunoassay technology: What does it change in autoantibody detection? Autoimmun. Highlights 2017, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, T.; Li, J. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with novel coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinaud, C.; Hejl, C.; Igert, A.; Bigaillon, C.; Bonnet, C.; Mérens, A.; Wolf, A.; Foissaud, V.; Leparc-Goffart, I. Evaluation of the Quotient® MosaiQ™ COVID-19 antibody microarray for the detection of IgG and IgM antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 virus in humans. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 130, 104571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, N.; Jeremiah, S.S.; Ryo, A. Interpreting diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 323, 2249–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral flow assays: Principles, designs and labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.D.; Patel, K.R. Enzyme immunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Investig. Derm. 2013, 133, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ning, J.; Peng, D.; Chen, T.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, A.; Lei, Z.; Abu bakr Shabbir, M.; Cheng, G.; Yuan, Z. Current advances in immunoassays for the detection of antibiotics residues: A review. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, L.; Chu, X. Chemiluminescence immunoassay. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, A.P.; Akgun, Y.; Al Mana, A.F.; Tjendra, Y.; Millan, N.C.; Gomez-Fernandez, C.; Cray, C. Review of current advances in serologic testing for COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, A.; Pepper, G.; Wener, M.H.; Fink, S.L.; Morishima, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Jerome, K.R.; Mathias, P.C.; Greninger, A.L. Performance characteristics of the Abbott Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG assay and seroprevalence in Boise, Idaho. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Cai, L.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, L.; Lin, Y.; Deng, L. Clinical findings in critical ill patients infected with SARS-Cov-2 in Guangdong Province, China: A multi-center, retrospective, observational study. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K. In Vitro Diagnostic Assays for COVID-19: Recent Advances and Emerging Trends; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Infantino, M.; Grossi, V.; Lari, B.; Bambi, R.; Perri, A.; Manneschi, M.; Terenzi, G.; Liotti, I.; Ciotta, G.; Taddei, C. Diagnostic accuracy of an automated chemiluminescent immunoassay for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibodies: An Italian experience. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Long, Q.; Deng, H.; Fan, K.; Liao, P.; Liu, B.; Wu, G.; Chen, Y. A Peptide-based Magnetic Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay for Serological Diagnosis of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Guo, J.; Dai, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X. Evaluations of serological test in the diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infections during the COVID-19 outbreak. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, M.; Zuo, Z.; Fan, C.; Ye, F.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Pan, K.; Xu, A. Diagnostic value and dynamic variance of serum antibody in coronavirus disease 2019. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUA Authorized Serology Test Performance. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/eua-authorized-serology-test-performance (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Maghsoudlou, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): The basics. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 77, C98–C101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wen, F.; Guo, X.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Meng, L.; Xu, Q. Evaluation of an ELISA-based visualization microarray chip technique for the detection of veterinary antibiotics in milk. Food Control 2019, 106, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlke, C.; Heidepriem, J.; Kobbe, R.; Santer, R.; Koch, T.; Fathi, A.; Ly, M.L.; Schmiedel, S.; Seeberger, P.H.; Addo, M.M. Distinct early IgA profile may determine severity of COVID-19 symptoms: An immunological case series. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang, K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J. A serological assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okba, N.M.; Muller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses in COVID-19 patients. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, Q.; Wang, T.; Ke, Y.; Mo, F.; Jia, R.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of recombinant nucleocapsid and spike proteins for serological diagnosis of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/vitro-diagnostics-euas (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- cPass™ SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Antibody Detection Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/143583/download (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- Lassaunière, R.; Frische, A.; Harboe, Z.B.; Nielsen, A.C.; Fomsgaard, A.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Jørgensen, C.S. Evaluation of nine commercial SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays. Medrxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, L.; Chang, S.P.; Nerurkar, V.R. COVID-19 Special Column: Principles Behind the Technology for Detecting SARS-CoV-2, the Cause of COVID-19. Hawaii J. Health Soc. Welf. 2020, 79, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose, J.H. Evaluation of a microsphere-based immunoassay (MIA) in measuring diagnostic and prognostic markers of dengue virus infection. Evaluation 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.S.; Racine-Brzostek, S.E.; Lee, W.T.; Hunt, D.; Yee, J.; Chen, Z.; Kubiak, J.; Cantu, M.; Hatem, L.; Zhong, E. SARS-CoV-2 antibody characterization in emergency department, hospitalized and convalescent patients by two semi-quantitative immunoassays. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.R.; Anand, R.; Andersson, M.I.; Auckland, K.; Baillie, J.K.; Barnes, E.; Bell, J.; Berry, T.; Bibi, S.; Carroll, M. Evaluation of antibody testing for SARS-Cov-2 using ELISA and lateral flow immunoassays. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.S.; Tesoriero, J.M.; Rosenthal, E.M.; Chung, R.; Barranco, M.A.; Styer, L.M.; Parker, M.M.; Leung, S.-Y.J.; Morne, J.; Greene, D. Cumulative incidence and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in New York. Ann. Epidemiol. 2020, 48, 23–29.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.H.-Y.; Cai, J.-P.; Dissanayake, T.K.; Chen, L.-L.; Choi, C.Y.-K.; Wong, L.-H.; Ng, A.C.-K.; Pang, P.K.; Ho, D.T.-Y.; Poon, R.W.-S. Improved Detection of Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 by Microsphere-Based Antibody Assay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Sheng, Y. An indirect competitive fluorescence immunoassay for determination of dicyclohexyl phthalate in water samples. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, J.M. Fluorescence immunoassay. Hum. Pathol. 1984, 15, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, R.R. Serological Approach for Diagnosis and Surveillance of Multiple Agents in Serum and Oral Fluid Samples. Available online: https://porkcheckoff.org/research/serological-approach-for-diagnosis-and-surveillance-of-multiple-agents-in-serum-and-oral-fluid-samples/ (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Langenhorst, R.J.; Lawson, S.; Kittawornrat, A.; Zimmerman, J.J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.A.; Fang, Y. Development of a fluorescent microsphere immunoassay for detection of antibodies against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus using oral fluid samples as an alternative to serum-based assays. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okda, F.; Liu, X.; Singrey, A.; Clement, T.; Nelson, J.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.A.; Lawson, S. Development of an indirect ELISA, blocking ELISA, fluorescent microsphere immunoassay and fluorescent focus neutralization assay for serologic evaluation of exposure to North American strains of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New York SARS-CoV Microsphere Immunoassay for Antibody Detection. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137540/download (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- xMAP® SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Testing. Available online: https://www.luminexcorp.com/xmap-sars-cov-2-antibody-testing/#overview (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- ichromxTM COVID-19 Ab from Boditech. Available online: http://www.boditech.co.kr/eng/common/asp/download.asp?file=/board/NEWS/ichroma%E2%84%A2_COVID-19_Ab_(with_ichroma%E2%84%A2_II_Reader)_test_system.pdf&target=TB_BOARD_ALL&num=2883 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Serology Test Evaluation Report for “GenBody COVID-19 IgM/IgG” from GenBody Inc. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/presentations/maf/maf3300-a001.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- ichroma COVID-19 Ab by Boditech Med Inc. Available online: https://covid19innovationhub.org/innovation/ichroma-covid-19-ab (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Azman, A.S.; Reich, N.G.; Lessler, J. The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: Estimation and application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldog, P.; Tekeli, T.; Vizi, Z.; Dénes, A.; Bartha, F.A.; Röst, G. Risk assessment of novel coronavirus COVID-19 outbreaks outside China. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, B.A.S.; Hodel, K.V.S.; Barbosa-Júnior, V.G.; Soares, M.B.P.; Badaró, R. The Main Molecular and Serological Methods for Diagnosing COVID-19: An Overview Based on the Literature. Viruses 2021, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Xia, J. Barcode lateral flow immunochromatographic strip for prostate acid phosphatase determination. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboowa, G. Current and emerging diagnostic tests available for the novel COVID-19 global pandemic. AAS Open Res. 2020, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Cavalera, S.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C. Multiplex lateral flow immunoassay: An overview of strategies towards high-throughput point-of-need testing. Biosensors 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Baloda, M.; Gurung, A.S.; Lin, Y.; Liu, G. Multiplex electrochemical immunoassay using gold nanoparticle probes and immunochromatographic strips. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Wang, W.; Du, T.-E. Rapid quantitative immunochromatographic strip for multiple proteins test. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wen, T.; Shi, F.-J.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Jiao, Y.-J. Rapid Detection of IgM Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral-Flow Assay. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12550–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhao, H.; Bian, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, Using Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7226–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TBG SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Kit Cat. No. 20010, Instruction for Use. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141773/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- COVID-19 Assay Kit: COVID 19 IgG/IgM Coronavirus Assay Kit. Available online: https://www.mybiosource.com/covid-19-assay-kits/covid-19-igg-igm-coronavirus/7135927 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- COVID-19 IgM/IgG Rapid Test. Available online: https://www.biomedomics.com/products/infectious-disease/covid-19-rt/ (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Test. Available online: https://www.pharmact.eu/ (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- RapCov™ Rapid COVID-19 Test—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/145080/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- WANTAI SARS-CoV-2 Ab Rapid Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140030/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- SiennaTM-Clarity COVIBLOCK™ COVID-19 lgG/lgM Rapid Test Cassette. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140082/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- BIOTIME SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Rapid Qualitative Test—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140443/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138438/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- IgM/IgG Antibody Combo Test Kit—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139409/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- RightSign COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138660/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Rapid COVID-19 IgM/IgG Combo Test Kit—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140297/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Biohit SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG Antibody Test Kit—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139283/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Assure COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Device—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139792/download#:~:text=The%20Assure%20COVID%2D19%20IgG,EDTA)%20and%20fingerstick%20whole%20blood (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Cellex—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136625/download (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- IgG/IgM Antibody Test—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141550/download#:~:text=The%20Tell%20Me%20Fast%20Novel,whole%20blood%20(Lithium%2DHeparin%2C (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Chembio Announces Launch of DPP COVID-19 Serological Point-of-Care Test. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/fr/news-release/2020/04/01/2009684/0/en/Chembio-Announces-Launch-of-DPP-COVID-19-Serological-Point-of-Care-Test.html (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Kalsi, S.; Valiadi, M.; Tsaloglou, M.-N.; Parry-Jones, L.; Jacobs, A.; Watson, R.; Turner, C.; Amos, R.; Hadwen, B.; Buse, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of antibiotic resistance on a programmable digital microfluidic platform. Lab A Chip 2015, 15, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherlands Becomes Latest Country to Reject China-Made Coronavirus Test Kits, Gear. Available online: https://www.foxnews.com/world/netherlands-becomes-latest-country-to-reject-china-made-coronavirus-test-kits-gear (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- 80% of Rapid COVID-19 Tests the Czech Republic Bought From China are Wrong. Available online: https://praguemorning.cz/80-of-rapid-covid-19-tests-the-czech-republic-bought-from-china-are-wrong/ (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Spain, Europe’sWorst-Hit Country after Italy, Says Coronavirus Tests It Bought from China are Failing to Detect Positive Cases. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.in/science/news/spain-europes-worst-hit-country-after-italy-says-coronavirus-tests-it-bought-from-china-are-failing-to-detect-positive-cases/articleshow/74832667.cms (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- China Supplied Faulty Coronavirus Test Kits to Spain, Czech Republic. Available online: https://news.yahoo.com/china-supplied-faulty-coronavirus-test-162306412.html (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Wingren, C.; Borrebaeck, C.A. Antibody-based microarrays. In Microchip Methods in Diagnostics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 57–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Qi, H.; Li, H.; Men, D.; Zhou, J.; Tao, S. SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray for global profiling of COVID-19 specific IgG and IgM responses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, X.; Wu, X.; Liang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Teng, F.; Dai, J.; Duan, H.; Guo, S. SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray for mapping COVID-19 antibody interactions at amino acid resolution. bioRxiv 2020, 6, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Carbayo, M. Antibody microarrays as tools for biomarker discovery. In Protein Microarrays; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 159–182. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Men, D.; Yang, X.; Qi, H.; Zhou, J.; Tao, S. Global profiling of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG/IgM responses of convalescents using a proteome microarray. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaiq™ by Quotient the Mosaiq Covid-19 Antibody Microarray. Available online: https://quotientbd.com/covid-19#:~:text=The%20MosaiQ%20COVID%2D19%20Antibody%20Microarray%20is%20designed%20as%20a,at%20SARS%2DCoV%2D2. (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Quotient Limited Reports Impressive Results from an Independent SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection Study Conducted in Spain. Quotient Limited Company. 20 July 2020. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2020/07/20/2064203/0/en/Quotient-Limited-Reports-Impressive-Results-from-an-Independent-SARS-CoV-2-Antibody-Detection-Study-Conducted-in-Spain.html (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Kohmer, N.; Westhaus, S.; Rühl, C.; Ciesek, S.; Rabenau, H.F. Brief clinical evaluation of six high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.S.; Hock, K.G.; Logsdon, N.M.; Hayes, J.E.; Gronowski, A.M.; Anderson, N.W.; Farnsworth, C.W. Clinical performance of two SARS-CoV-2 serologic assays. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECDC. An Overview of the Rapid Test Situation for COVID-19 Diagnosis in the EU/EEA; ECDC: Solna, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- PEPperCHIP® SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Microarray. Available online: https://www.pepperprint.com/products/pepperchipr-standard-microarrays/pepperchipr-sars-cov-2-proteome-microarray/#:~:text=PEPperCHIP%C2%AE%20SARS%2DCoV%2D2%20Proteome%20Microarray&text=In%20light%20of%20the%20ongoing,CoV%2D2)%20viral%20genome (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- 1PEPperCHIP® SARS CoV Antigen Microarray. Available online: http://www.biocat.com/bc/pdf/PEPperCHIP_SARS-CoV_Antigen_Microarray.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- PEPperCHIP® Pan-Corona Spike Protein Microarray. Available online: https://www.pepperprint.com/products/pepperchipr-standard-microarrays/pepperchipr-pan-corona-spike-protein-microarray/ (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- pGOLD™ COVID-19 High Accuracy IgG/IgM Assay. Available online: https://www.nirmidas.com/pgold-covid-19-igg-igm-assay-kit (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Immusafe COVID Test Brochure—Sengenics. Available online: https://www.sengenics.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/IMMUSAFE-COVID-TEST-BROCHURE.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- ImmuSAFE Biochip. Available online: https://sengenics.com/immusafe-covid-test/ (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Viral Protein Array—Sino Biological. Available online: https://www.sinobiological.com/research/virus/coronavirus-array (accessed on 19 February 2020).
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ni, S.; Korabečná, M.; Yobas, L.; Neuzil, P. The vision of point-of-care PCR tests for the COVID-19 pandemic and beyond. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azkur, A.K.; Akdis, M.; Azkur, D.; Sokolowska, M.; van de Veen, W.; Brüggen, M.C.; O’Mahony, L.; Gao, Y.; Nadeau, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID-19. Allergy 2020, 75, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.-W.; Tsang, O.T.-Y.; Leung, W.-S.; Tam, A.R.; Wu, T.-C.; Lung, D.C.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Cai, J.-P.; Chan, J.M.-C.; Chik, T.S.-H. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: An observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing Basics. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/coronavirus-disease-2019-testing-basics (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Goudouris, E.S. Laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19. J. De Pediatr. 2021, 97, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes First Antigen Test to Help in the Rapid Detection of the Virus that Causes COVID-19 in Patients. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-first-antigen-test-help-rapid-detection-virus-causes (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Lukić, V. Laboratory information system—where are we today? J. Med. Biochem. 2017, 36, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia SARS Antigen FIA|Quidel. Available online: https://www.quidel.com/immunoassays/rapid-sars-tests/sofia-sars-antigen-fia (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Sofia 2 Flu + SARS Antigen FIA. Available online: https://www.quidel.com/immunoassays/sofia-2-flu-sars-antigen-fia#:~:text=The%20Sofia%202%20Flu%20%2B%20SARS,and%20SARS%2DCoV%2D2 (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- BD Veritor™ Plus System for Rapid COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Testing. Available online: https://www.bd.com/en-us/offerings/capabilities/microbiology-solutions/point-of-care-testing/bd-veritor-plus-system-for-rapid-covid-19-sars-cov-2-testing (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- BD Veritor System for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139755/download (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- BinaxNOWTM COVID-19 Ag CARD HOME TEST—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/144574/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Antigen Test as First Over-the-Counter Fully At-Home Diagnostic Test for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-antigen-test-first-over-counter-fully-home-diagnostic (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- CareStart COVID-19 Antigen test—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142919/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Status™ COVID-19/Flu—Princeton BioMeditech Corporation. Available online: http://www.pbmc.com/downloads/Status_Cov_Flu_EUA210015_IFU_P-5382.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Sampinute™ COVID-19 Antigen MIA—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/143270/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- SimoaTM SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Antigen Test—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/144929/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/144256/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- BinaxNOW™ COVID-19 Ag Card—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141570/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141304/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Sofia 2 Flu + SARS Antigen FIA—FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142704/download (accessed on 5 April 2021).
- Lin, Q.; Wen, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Microfluidic immunoassays for sensitive and simultaneous detection of IgG/IgM/antigen of SARS-CoV-2 within 15 min. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9454–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test. Available online: https://www.lumiradx.com/us-en/what-we-do/diagnostics/test-technology/antigen-test (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Abbott’s Fast, $5, 15-Minute, Easy-to-Use COVID-19 Antigen Test Receives FDA Emergency Use Authorization; Mobile App Displays Test Results To Help Our Return to Daily Life; Ramping Production to 50 Million Tests a Month. Abbot: 2020. Available online: https://abbott.mediaroom.com/2020-08-26-Abbotts-Fast-5-15-Minute-Easy-to-Use-COVID-19-Antigen-Test-Receives-FDA-Emergency-Use-Authorization-Mobile-App-Displays-Test-Results-to-Help-Our-Return-to-Daily-Life-Ramping-Production-to-50-Million-Tests-a-Month (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Navica™ Mobile App and Binaxnow™ COVID-19 Ag Card. Available online: https://www.globalpointofcare.abbott/en/product-details/navica-binaxnow-covid-19-us.html (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- PCL COVID-19 Rapid FIA. Available online: http://pclchip.com/eng/sub_n4/4_6.php?mode=view&number=813&b_name=eng_notice&page=1 (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.-H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.-S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G. Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoa SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Antigen Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/144925/download (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- ELLUME COVID-19 Home Test. Product Overview for Healthcare Professionals. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/144592/download (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Choi, J.R. Development of Point-of-Care Biosensors for COVID-19. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Tiwari, J.N.; Kemp, K.C.; Perman, J.A.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Kim, K.S.; Zboril, R. Noncovalent functionalization of graphene and graphene oxide for energy materials, biosensing, catalytic, and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5464–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, G. CRISPR/Cas multiplexed biosensing: A challenge or an insurmountable obstacle? Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, D.; Bhatia, H.; Sai, V.; Satija, J. P-FAB: A fiber-optic biosensor device for rapid detection of COVID-19. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, T.H.; Petrovick, M.S.; Nargi, F.E.; Harper, J.D.; Schwoebel, E.D.; Mathews, R.H.; Blanchard, D.J.; Bortolin, L.T.; Young, A.M.; Chen, J. AB cell-based sensor for rapid identification of pathogens. Science 2003, 301, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- athSensors, Inc. Announced the Development of a SARS-CoV-2 Biosensor. Available online: https://pathsensors.com/psi-sars-cov-2-biosensor/ (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Combating 2019-nCoV: Advanced Nanobiosensing Platforms for POC Global Diagnostics and Surveillance. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101003544 (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Hochreiter, B.; Pardo-Garcia, A.; Schmid, J.A. Fluorescent proteins as genetically encoded FRET biosensors in life sciences. Sensors 2015, 15, 26281–26314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, V. Probes: FRET sensor design and optimization. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.-H.; Chang, T.-J.; Wang, M.-L.; Tsai, P.-H.; Lin, T.-H.; Wang, C.-T.; Yang, D.-M. Novel biosensor platforms for the detection of coronavirus infection and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, S.-K.; Yoo, S.M.; Yang, S.-M.; Lee, S.Y. Development of reflective biosensor using fabrication of functionalized photonic nanocrystals. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Manufacture | Test | Target Antigen | Antibody | Technique | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount Sinai Laboratory | Mt. Sinai Laboratory COVID-19 ELISA Antibody Test | Full length S antigen | IgG | High Throughput 2-Step direct ELISA | 92.5% | 100% |
| InBios International, Inc. | SCoV-2 Detect IgG ELISA | SARS-CoV-2 S antigen | IgG | High Throughput ELISA | 100% | 100% |
| InBios International, Inc. | SCoV-2 Detect IgM ELISA | S antigen | IgM | High Throughput ELISA | 96.7% | 98.8% |
| Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics | Dimension Vista SARS-CoV-2 Total antibody assay (COV2T) | S antigen | Total Antibody | Fully automated, fvfRapid High Throughput ELISA (10 min for one result, 440 assays per hour) | 100% | 99.8% |
| Quanterix Corporation | Simoa Semi-Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibody Test | S antigen | IgG | High Throughput, Automated Paramagnetic Microbead-based Sandwich ELISA. 96 tests in 2 h and 45 min | 100% (LoD: 0.77 µg/mL) | 99.2% |
| Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy Enterprise Co., Ltd. | WANTAI SARS-CoV-2 Ab ELISA | S antigen (RBD domain) | IgG | High Throughput ELISA | 96.7% | 97.5% |
| Emory Medical Laboratories | SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG test | S antigen (RBD domain) | IgG | High Throughput ELISA | 100% | 96.4% |
| Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics | Dimension EXL SARS-CoV-2 Total antibody assay (CV2T) | S antigen (RBD domain) | Total Antibody | High Throughput ELISA | 100% | 99.9% |
| GenScript USA Inc. | cPass SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Antibody Detection Kit | S antigen (RBD domain) | Total Neutralizing Antibodies | High Throughput Blocking ELISA (92 samples in 1 h) | 100% | 100% |
| EUROIMMUN US Inc. | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA | S antigen (S1 subunit) | IgG | High Throughput ELISA | 90.0% | 100% |
| Luminex Corporation | xMAP SARS-CoV-2 Multi-Antigen IgG Assay | S antigen (S1 subunit and RBD domain) and N antigen | IgG | Multiplex, microsphere-based and high-throughput FMIA (96 samples per run in each 3 h) | 100% | 99.2% |
| Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. | Platelia SARS-CoV-2 Total Ab assay | Recombinant N antigen | Total Antibody | High Throughput Semi-quantitative ELISA | 92.2% | 99.6% |
| Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health | New York SARS-CoV Microsphere Immunoassay for Antibody Detection | N antigen | Total Antibody | High Throughput MIA (FMIA) | 88.0% | 98.8% |
| Manufacturer Name | Test Name | Technology | Target Antigen | Sensitivity in Symptomatic Patients | Specificity | Detection | Test Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbott Diagnostics Scarborough, Inc. [132] | BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card Home Test | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA, Prescription Home Testing | N antigen | 97.1% | 98.5% | Visual read + submitting the result via the NAVICA mobile application | 15 min |
| Ellume Limited [133] | Ellume COVID-19 Home Test | Fluorescent LF, Over the Counter (OTC) Home Testing, Screening | N antigen | 95% | 97% | Instrument Read (smartphone-based) | 15 min |
| Access Bio, Inc. [134] | CareStart COVID-19 Antigen test | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | N antigen | 88% | 100% | Visual read | 10 min |
| Princeton BioMeditech Corp [135] | Status COVID-19/Flu | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA, Multi-analyte | N antigen | 93.9% (LoD: 2.7 × 103 TCID50/mL) | 93.9% | Visual Read | 15 min |
| Celltrion USA, Inc. [136] | COVID-19 Antigen MIA | Magnetic Force-assisted Electrochemical Sandwich Immunoassay (MESIA) | S antigen (RBD domain) | 94.4% (LoD: 3.0 × 101 TCID50/mL) | 100% | Instrument Read | 10 min |
| Quanterix Corporation [137] | Simoa SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Antigen Test | High throughput Paramagnetic Microbead-based Immunoassay | N antigen | 97.70% (LoD: 0.31 TCID50/mL) | Cross-reaction with SARS-CoV | Instrument Read | 80 min |
| Luminostics, Inc. [138] | Clip COVID Rapid Antigen Test | LF immunoluminescent assay | N antigen | (LoD: 0.88 × 102 TCID50/mL) | Cross-reaction with SARS-CoV | Instrument Read (smartphone-based) | 30 min |
| Abbott Diagnostics Scarborough, Inc. [139] | BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card | Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based LFIA | N antigen | 97.1%/22.5 TCID50/mL | 98.5% | Visual Read + submitting the result via the NAVICA mobile application | 15 min |
| LumiraDx UK Ltd. [140] | LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 Ag Test | FIA | N antigen | 97.6% /32 TCID50/mL | 96.6% | Instrument Read | 12 min |
| Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD) [131] | BD Veritor System for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 | Chromatographic digital immunoassay | N antigen | 84% | No cross-reaction | Instrument Read | 15 min |
| Quidel Corporation [128] | Sofia SARS Antigen FIA | FIA | N antigen | 87.5% | Cross-reaction with SARS-CoV | Instrument Read | 15 min |
| Quidel Corporation [141] | Sofia 2 Flu + SARS Antigen FIA | FIA | N antigen | (No info) | Cross-reaction with SARS-CoV | Instrument Read | 15 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaffaf, T.; Ghafar-Zadeh, E. COVID-19 Diagnostic Strategies Part II: Protein-Based Technologies. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050054
Shaffaf T, Ghafar-Zadeh E. COVID-19 Diagnostic Strategies Part II: Protein-Based Technologies. Bioengineering. 2021; 8(5):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050054
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaffaf, Tina, and Ebrahim Ghafar-Zadeh. 2021. "COVID-19 Diagnostic Strategies Part II: Protein-Based Technologies" Bioengineering 8, no. 5: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050054
APA StyleShaffaf, T., & Ghafar-Zadeh, E. (2021). COVID-19 Diagnostic Strategies Part II: Protein-Based Technologies. Bioengineering, 8(5), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8050054







