Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
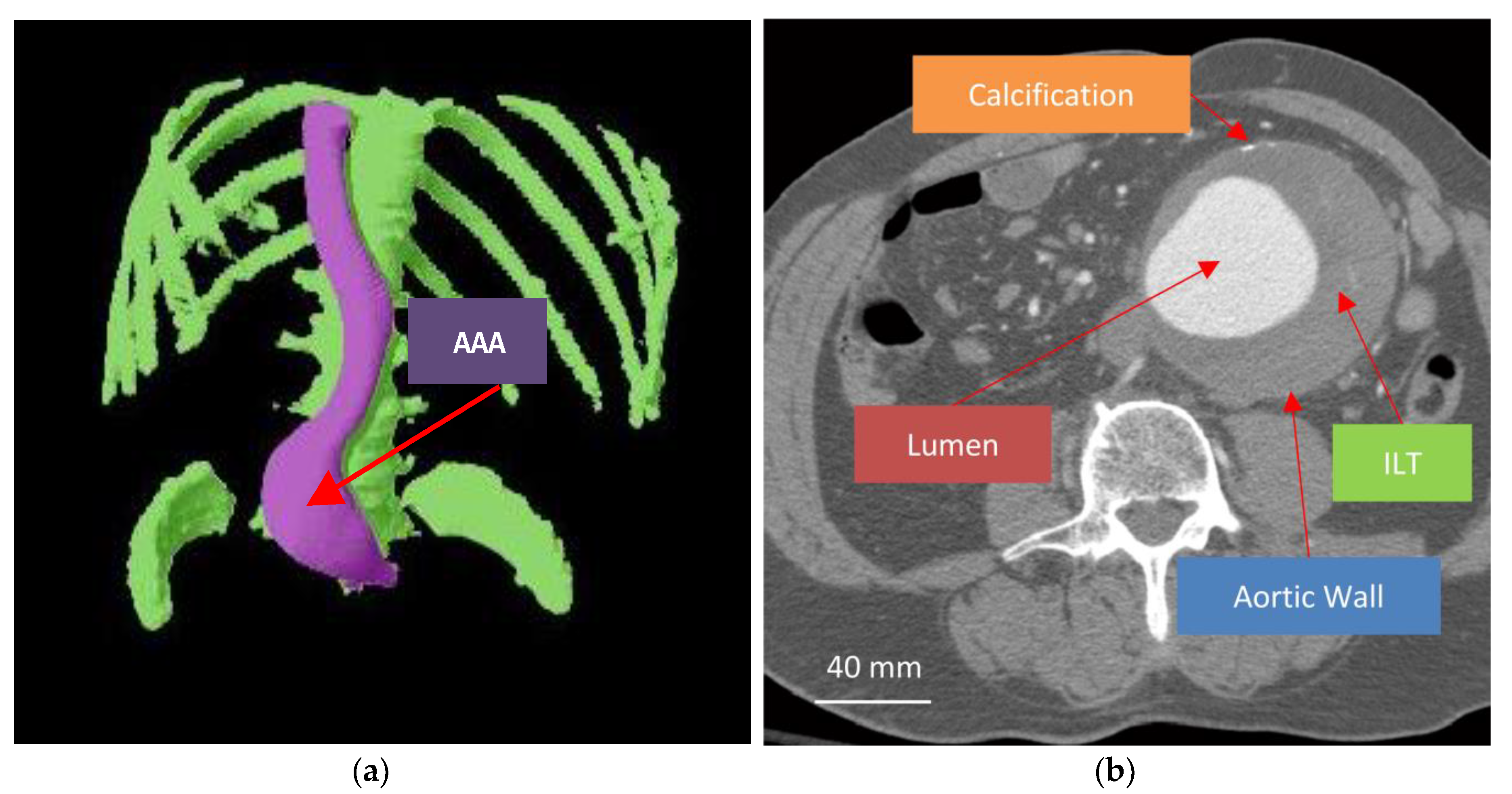
2. Biomechanics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
2.1. Aortic Wall
2.2. Intraluminal Thrombus (ILT)
2.3. Lumen
3. Computational Modeling Techniques
3.1. Basic Biomechanics Concepts and Aortic Wall Stress Quantification
3.2. Quantifying Aortic Wall Stress
3.2.1. Classical Model
3.2.2. Equilibrium Model
3.3. Models of Aortic Wall Strength
4. Studies and Limitations
4.1. Initial Studies
4.2. Studies Accounting for the Intraluminal Thrombus
4.3. Refined Models of AAA and RPI
4.4. Beyond Biomechanical Models
5. Looking Forward
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, J.; Wolff, J.; Rodd, C.; Cooper, D.; Earnshaw, J.J. Outcome in Men with a Screen-detected Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Who are not Fit for Intervention. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 50, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Johnston, K.W.; Rutherford, R.B.; Tilson, M.D.; Shah, D.M.; Hollier, L.; Stanley, J.C. Suggested standards for reporting on arterial aneurysms. Subcommittee on Reporting Standards for Arterial Aneurysms, Ad Hoc Committee on Reporting Standards, Society for Vascular Surgery and North American Chapter, International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery. J. Vasc. Surg. 1991, 13, 452–458. [Google Scholar]
- Liddington, M.I.; Heather, B.P. The relationship between aortic diameter and body habitus. Eur. J. Vasc. Surg. 1992, 6, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geest, J.P.V.; Di Martino, E.S.; Bohra, A.; Makaroun, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. A Biomechanics-Based Rupture Potential Index for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risk Assessment: Demonstrative Application. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1085, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherifova, S.; Holzapfel, G.A. Biomechanics of aortic wall failure with a focus on dissection and aneurysm: A review. Acta Biomater. 2019, 99, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, J.S.; Finch, D.; Carter, P. A study of the mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms in a district community. Eur. J. Vasc. Surg. 1989, 3, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmens, J.B.; Lawrence-Brown, M.; Norman, P.E.; Codde, J.; Holman, C.D.J. The Quality of Surgical Care Project: Benchmark Standards of Open Resection for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Western Australia. ANZ J. Surg. 1998, 68, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermerhorn, M.; Bensley, R.P.; Giles, K.A.; Hurks, R.; O’malley, A.J.; Cotterill, P.; Chaikof, E.; Landon, B.E. Changes in abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture and short-term mortality, 1995–2008: A retrospective observational study. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, M.J.; Ulug, P.; Powell, J.T.; Desgranges, P.; Balm, R.; Ruptured Aneurysm Trialists. Ruptured Aneurysm Trials: The Importance of Longer-term Outcomes and Meta-analysis for 1-year Mortality. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 50, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Qamar, A.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, A. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: A comprehensive review. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2011, 16, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gwon, J.-G.; Kwon, T.-W.; Cho, Y.-P.; Han, Y.J.; Noh, M.S. Analysis of in hospital mortality and long-term survival excluding in hospital mortality after open surgical repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2016, 91, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Kingdom, E.T.I. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, T.S.; Wang, J.G.; Derrow, A.E.; Dame, D.A.; Ozaki, C.; Zelenock, G.B.; Flynn, T.C.; Seeger, J.M. Experience in the United States with intact abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 33, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.T.; Sweeting, M.J.; Ulug, P.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; Lederle, F.A.; Becquemin, J.; Greenhalgh, R.M. Meta-analysis of individual-patient data from EVAR-1, DREAM, OVER and ACE trials comparing outcomes of endovascular or open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm over 5 years. BJS 2017, 104, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruin, J.L.; Baas, A.F.; Buth, J.; Prinssen, M.; Verhoeven, E.L.; Cuypers, P.W.; van Sambeek, M.R.; Balm, R.; Grobbee, D.E.; Blankensteijn, J.D. Long-Term Outcome of Open or Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaik, T.G.; Yeung, K.K.; Verhagen, H.J.; De Bruin, J.L.; Van Sambeek, M.R.H.M.; Balm, R.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Van Herwaarden, J.A.; Blankensteijn, J.D.; Bak, A.; et al. Long-term survival and secondary procedures after open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 66, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.B.; Ultee, K.H.; Hoeks, S.E.; Stolker, R.J.; Verhagen, H.J. Life expectancy and causes of death after repair of intact and ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, W.W. Learning from the last ultrasound. A population-based study of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Arch. Intern. Med. 1997, 157, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merali, F.S.; Anand, S.S. Immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar]
- United Kingdom Small Aneurysm Trial Participants. Long-term outcomes of immediate repair compared with surveillance of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, P.; Powell, J.T. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Circulation 2007, 115, 2865–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortality results for randomised controlled trial of early elective surgery or ultrasonographic surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Lancet 1998, 352, 1649–1655. [CrossRef]
- Darling, R.C.; Messina, C.R.; Brewster, D.C.; Ottinger, L.W. Autopsy study of unoperated abdominal aortic aneurysms. The case for early resection. Circulation 1977, 56, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Cronenwett, J.L.; Murphy, T.F.; Zelenock, G.B.; Whitehouse, W.M.; Lindenauer, S.M.; Graham, L.M.; E Quint, L.; Silver, T.M.; Stanley, J.C. Actuarial analysis of variables associated with rupture of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Surgery 1985, 98, 472–483. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, S.C.; Gardner, J.B.; Meissner, M.H.; Johansen, K.H. Rupture in small abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 1998, 28, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Powell, J.T. Risk Factors for Aneurysm Rupture in Patients Kept Under Ultrasound Surveillance. Ann. Surg. 1999, 230, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, G.; Powell, J.T.; Martinez, M.A.-M.; Ballard, D.J. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD001835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulug, P. Surgery for small asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysms. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.V.; Haas, K.; Phillips, S.; Comerota, A.J. Adventitial elastolysis is a primary event in aneurysm formation. J. Vasc. Surg. 1993, 17, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, E.F.; Buckley, C.; Thompson, R.W. Prospects for the Medical Management of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2003, 37, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholt, J.S. Aneurysmal wall calcification predicts natural history of small abdominal aortic aneurysms. Atherosclerosis 2008, 197, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, S.A.; Mulvihill, J.J.; Barrett, H.; Kavanagh, E.; Walsh, M.; McGloughlin, T.; Doyle, B.J. Determining the influence of calcification on the failure properties of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) tissue. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 42, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; U-King-Im, J.; Tang, T.Y.; Soh, E.; See, T.C.; Gillard, J.H. Impact of calcification and intraluminal thrombus on the computed wall stresses of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speelman, L.; Bohra, A.; Bosboom, E.M.H.; Schurink, G.W.H.; Van De Vosse, F.; Makaroun, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. Effects of Wall Calcifications in Patient-Specific Wall Stress Analyses of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. J. Biomech. Eng. 2006, 129, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, A.; Gee, M.W.; Reeps, C.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Wall, W.A. Impact of calcifications on patient-specific wall stress analysis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2010, 9, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Holzapfel, G.A. Structure, Mechanics, and Histology of Intraluminal Thrombi in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, L.P.; Gross, B.H.; Callen, P.W.; A Barth, R. Ultrasonic evaluation of abdominal aortic thrombus. J. Ultrasound Med. 1982, 1, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorp, D.A.; Lee, P.C.; Wang, D.H.; Makaroun, M.S.; Nemoto, E.M.; Ogawa, S.; Webster, M.W. Association of intraluminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysm with local hypoxia and wall weakening. J. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 34, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Leung, J.; Wood, N.B.; Hughes, A.; A Thom, S.; Cheshire, N.J.; Xu, X.Y. Computational analysis of oxygen transport in a patient-specific model of abdominal aortic aneurysm with intraluminal thrombus. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.J.; Kuhn, D.C.S.; Lozowy, R.J.; Kulbisky, G.P. Low Wall Shear Stress Predominates at Sites of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, M.; Thyberg, J.; Religa, P.; Roy, J.; Eriksson, P.; Hedin, U.; Swedenborg, J. Influence of intraluminal thrombus on structural and cellular composition of abdominal aortic aneurysm wall. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 38, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, T.; Auer, M.; Labruto, F.; Swedenborg, J.; Roy, J. Biomechanical Rupture Risk Assessment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Model Complexity versus Predictability of Finite Element Simulations. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2010, 40, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speelman, L.; Schurink, G.W.H.; Bosboom, E.M.H.; Buth, J.; Breeuwer, M.; Van De Vosse, F.; Jacobs, M.H. The mechanical role of thrombus on the growth rate of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 51, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluestein, D.; Dumont, K.; De Beule, M.; Ricotta, J.; Impellizzeri, P.; Verhegghe, B.; Verdonck, P.R. Intraluminal thrombus and risk of rupture in patient specific abdominal aortic aneurysm—FSI modelling. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, E.S.; Vorp, D.A. Effect of variation in intraluminal thrombus constitutive properties on abdominal aortic aneurysm wall stress. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 31, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.H.; Makaroun, M.S.; Webster, M.W.; Vorp, D.A. Effect of intraluminal thrombus on wall stress in patient-specific models of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 36, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.; Wright, A.R.; Cheshire, N.; Crane, J.S.; Thom, S.; Hughes, A.; Xu, X.Y. Fluid structure interaction of patient specific abdominal aortic aneurysms: A comparison with solid stress models. Biomed. Eng. Online 2006, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geest, J.P.V.; Sacks, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. The effects of aneurysm on the biaxial mechanical behavior of human abdominal aorta. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geest, J.P.V.; Wang, D.H.J.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Makaroun, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. Towards A Noninvasive Method for Determination of Patient-Specific Wall Strength Distribution in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 34, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mower, W.R.; Quiñones, W.J.; Gambhir, S.S. Effect of intraluminal thrombus on abdominal aortic aneurysm wall stress. J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorp, D.A.; Raghavan, M.; Webster, M.W. Mechanical wall stress in abdominal aortic aneurysm: Influence of diameter and asymmetry. J. Vasc. Surg. 1998, 27, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringfellow, M.M.; Lawrence, P.F.; Stringfellow, R.G. The influence of aorta-aneurysm geometry upon stress in the aneurysm wall. J. Surg. Res. 1987, 42, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzoli, F.; Boschetti, F.; Zappa, M.; Longo, T.; Fumero, R. Biomechanical factors in abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture. Eur. J. Vasc. Surg. 1993, 7, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillinger, M.F.; Raghavan, M.; Marra, S.P.; Cronenwett, J.L.; Kennedy, F.E. In vivo analysis of mechanical wall stress and abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture risk. J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 36, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillinger, M.F.; Marra, S.P.; Raghavan, M.; Kennedy, F.E. Prediction of rupture risk in abdominal aortic aneurysm during observation: Wall stress versus diameter. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 37, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasubramaniam, A.K.; Fagan, M.J.; Mehta, T.; Mylankal, K.J.; Ray, B.; Kuhan, G.; Chetter, I.C.; McCollum, P.T. A comparative study of aortic wall stress using finite element analysis for ruptured and non-ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2004, 28, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Truijers, M.; Pol, J.; SchultzeKool, L.; Van Sterkenburg, S.; Fillinger, M.; Blankensteijn, J.D. Wall Stress Analysis in Small Asymptomatic, Symptomatic and Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2007, 33, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, M.S.; Fagan, M.J.; Collier, J.W.; Desai, G.; Mccollum, P.T.; Chetter, I. Peak wall stress measurement in elective and acute abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geest, J.P.V.; Schmidt, D.E.; Sacks, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. The Effects of Anisotropy on the Stress Analyses of Patient-Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, M.L.; Kratzberg, J.; De Tolosa, E.M.C.; Hanaoka, M.M.; Walker, P.; Da Silva, E.S. Regional distribution of wall thickness and failure properties of human abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 3010–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.K.; Nathan, D.P.; Woo, E.Y.; Fairman, R.M.; Wang, G.J.; Gorman, R.C.; Gorman, J.H.; Jackson, B.M. Local wall thickness in finite element models improves prediction of abdominal aortic aneurysm growth. J. Vasc. Surg. 2013, 61, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, M.; Vorp, D.A. Toward a biomechanical tool to evaluate rupture potential of abdominal aortic aneurysm: Identification of a finite strain constitutive model and evaluation of its applicability. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geest, J.P.V.; Sacks, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. Age Dependency of the Biaxial Biomechanical Behavior of Human Abdominal Aorta. J. Biomech. Eng. 2004, 126, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.J.; Makaroun, M.; Webster, M.W.; Vorp, D.A. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Intraluminal Thrombus From Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. J. Biomech. Eng. 2001, 123, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geest, J.P.V.; Sacks, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. A planar biaxial constitutive relation for the luminal layer of intra-luminal thrombus in abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niestrawska, J.A.; Regitnig, P.; Viertler, C.; Cohnert, T.U.; Babu, A.R.; Holzapfel, G. The role of tissue remodeling in mechanics and pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Acta Biomater. 2019, 88, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.M.; Maier, F.; Weisbecker, H.; Viertler, C.; Verbrugghe, P.; Famaey, N.; Fourneau, I.; Herijgers, P.; Holzapfel, G.A. Human thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysmal tissues: Damage experiments, statistical analysis and constitutive modeling. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 41, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niestrawska, J.A.; Viertler, C.; Regitnig, P.; Cohnert, T.U.; Sommer, G.; Holzapfel, G.A. Microstructure and mechanics of healthy and aneurysmatic abdominal aortas: Experimental analysis and modelling. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20160620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.F.; Ruiz, C.; Doblaré, M.; Holzapfel, G.A. Mechanical Stresses in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Influence of Diameter, Asymmetry, and Material Anisotropy. J. Biomech. Eng. 2008, 130, 021023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, F.; Chandra, S.; Finol, E.A.; Gasser, T.C.; Rodriguez, J.F. A Pull-Back Algorithm to Determine the Unloaded Vascular Geometry in Anisotropic Hyperelastic AAA Passive Mechanics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 41, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speelman, L.; Bosboom, E.M.H.; Schurink, G.W.H.; Buth, J.; Breeuwer, M.; Jacobs, M.J.; van de Vosse, F.N. Initial stress and nonlinear material behavior in patient-specific AAA wall stress analysis. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelaya, J.E.; Goenezen, S.; Dargon, P.T.; Azarbal, A.-F.; Rugonyi, S. Improving the Efficiency of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Wall Stress Computations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joldes, G.R.; Miller, K.; Wittek, A.; Doyle, B.J. A simple, effective and clinically applicable method to compute abdominal aortic aneurysm wall stress. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 58, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joldes, G.R.; Miller, K.; Wittek, A.; Forsythe, R.O.; Newby, D.E.; Doyle, B.J. BioPARR: A software system for estimating the rupture potential index for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, A.; Gee, M.W.; Reeps, C.; Pongratz, J.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Wall, W.A. A Comparison of Diameter, Wall Stress, and Rupture Potential Index for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture Risk Prediction. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 3124–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhart, P.; Hyhlik-Dürr, A.; Geisbüsch, P.; Kotelis, D.; Müller-Eschner, M.; Gasser, T.; Von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Böckler, D. Finite Element Analysis in Asymptomatic, Symptomatic, and Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: In Search of New Rupture Risk Predictors. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 49, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.D.; Barkley, P.L.; Broadbent, K.C.; Huynh, T.T.T.; Hall, A.D. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Screening. Semin. Roentgenol. 2015, 50, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schurink, G.W.; Van Baalen, J.M.; Visser, M.J.; Van Bockel, J.H. Thrombus within an aortic aneurysm does not reduce pressure on the aneurysmal wall. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, E.S.; Mantero, S.; Inzoli, F.; Melissano, G.; Astore, D.; Chiesa, R.; Fumero, R. Biomechanics of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the presence of endoluminal thrombus: Experimental characterisation and structural static computational analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1998, 15, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.G.; Thomas, W.S.; Brennan, F.J.; Goff, W.G.; Sise, M.J.; Bernstein, E.F. Computed tomography scanning findings associated with rapid expansion of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 1994, 20, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vorp, D.A.; Wang, D.H.J.; Webster, M.W.; Federspiel, W.J. Effect of intraluminal thrombus thickness and bulge diameter on the oxygen diffusion in abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Biomech. Eng. 1998, 120, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, E.S.; Bohra, A.; Geest, J.P.V.; Gupta, N.; Makaroun, M.S.; Vorp, D.A. Biomechanical properties of ruptured versus electively repaired abdominal aortic aneurysm wall tissue. J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 43, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, D.-J.; Slump, C.H.; Maal, T.J.J. Optimized Anisotropic Rotational Invariant Diffusion Scheme on Cone-Beam CT. Comput. Vis. 2010, 13, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.E.; Ramazanli, B.; Yavuz, M.M.; Yalcin, H.C. Biomechanical Investigation of Disturbed Hemodynamics-Induced Tissue Degeneration in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Using Computational and Experimental Techniques. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyun, E.; Kwon, S.T.; Acar, A.C.; Lee, W.; Baek, S. Predicting abdominal aortic aneurysm growth using patient-oriented growth models with two-step Bayesian inference. Comput. Boil. Med. 2020, 117, 103620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Galarreta, S.R.; Cazon, A.; Antón, R.; Finol, E. The Relationship Between Surface Curvature and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Wall Stress. J. Biomech. Eng. 2017, 139, 081006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.S.; Chandra, S.; Shum, J.; Finol, E. The role of geometric and biomechanical factors in abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture risk assessment. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 1459–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, J.; Roy, A.; Raut, S.; Antón, R.; Muluk, S.C.; Finol, E.A. Geometric surrogates of abdominal aortic aneurysm wall mechanics. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 59, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchi, T.; Patnaik, S.S.; Nguyen, H.N.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Narayanan, S.; Muluk, S.C.; De Oliveira, V.; Finol, E.A. A Comparative Study of Biomechanical and Geometrical Attributes of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in the Asian and Caucasian Populations. J. Biomech. Eng. 2020, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, E.; Willems, T.P.; Slump, C.H.; Van Der Laan, M.J.; Zeebregts, C. Additional value of biomechanical indices based on CTa for rupture risk assessment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalzadeh, H.; Leemans, E.L.; Indrakusuma, R.; Planken, R.N.; Koelemay, M.J.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Marquering, H.A.; van der Laan, M.J.; Balm, R. Estimation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture Risk with Biomechanical Imaging Markers. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, T.C.; Nchimi, A.; Swedenborg, J.; Roy, J.; Sakalihasan, N.; Böckler, D.; Hyhlik-Dürr, A. A Novel Strategy to Translate the Biomechanical Rupture Risk of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms to their Equivalent Diameter Risk: Method and Retrospective Validation. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2014, 47, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, L.M.; Carlson, E.J.; O’Malley, J.; Snyder, C.K.; Charbonneau, N.L.; Hayflick, S.J.; Coselli, J.S.; Lemaire, S.A.; Sakai, L.Y. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Frequency and Dissection Are Associated With Fibrillin-1 Fragment Concentrations in Circulation. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcic, S.; Hassan, S.M.A.; Rival, D.E.; Bisleri, G. Characterizing the mechanical properties of the aortic wall. Vessel. Plus 2019, 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeps, C.; Maier, A.; Pelisek, J.; Härtl, F.; Grabher-Meier, V.; Wall, W.A.; Essler, M.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Gee, M.W. Measuring and modeling patient-specific distributions of material properties in abdominal aortic aneurysm wall. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2012, 12, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, N.; Virag, L.; Holzapfel, G.A.; Sorić, J.; Karšaj, I. A finite element implementation of a growth and remodeling model for soft biological tissues: Verification and application to abdominal aortic aneurysms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 352, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytsan, A.; Watton, P.; Holzapfel, G.A. A Thick-Walled Fluid–Solid-Growth Model of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Evolution: Application to a Patient-Specific Geometry. J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 031008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.; Holzapfel, G. Mechanics, mechanobiology, and modeling of human abdominal aorta and aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.D.; Chivukula, V.K.; Haller, S.; Vatankhah, N.; Bohannan, C.J.; Moneta, G.L.; Rugonyi, S.; Azarbal, A.F. Aortic outflow occlusion predicts rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.A.; Nichols, W.K.; Silver, D. Is thrombosis of the infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm an acceptable alternative? J. Vasc. Surg. 1986, 3, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmar, J.F.; Paes, E.H.; Pauschinger, P.; Gross, P. Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta and leg amputation. A chance coincidence or a pathogenetic correlation? Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1988, 113, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, S.J.; Crawford, J.D.; Courchaine, K.M.; Bohannan, C.J.; Landry, G.J.; Moneta, G.L.; Azarbal, A.; Rugonyi, S. Intraluminal thrombus is associated with early rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 1051–1058.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Paeng, J.C.; Kim, K.H.; Cheon, G.J.; Lee, D.-J.; Chung, J.-K.; Kang, K.W. Correlation of FDG PET/CT Findings with Long-Term Growth and Clinical Course of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 52, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, A.; Essler, M.; Gee, M.W.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Wall, W.A.; Reeps, C. Correlation of biomechanics to tissue reaction in aortic aneurysms assessed by finite elements and [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2011, 28, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalzadeh, H.; Indrakusuma, R.; Planken, R.; Legemate, D.A.; Koelemay, M.; Balm, R. Inflammation as a Predictor of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth and Rupture: A Systematic Review of Imaging Biomarkers. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2016, 52, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, X.; Mou, X. Machine Learning for Tomographic Imaging; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Erhart, P.; Schiele, S.; Ginsbach, P.; Grond-Ginsbach, C.; Hakimi, M.; Böckler, D.; Lorenzo-Bermejo, J.; Dihlmann, S. Gene Expression Profiling in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms After Finite Element Rupture Risk Assessment. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2017, 24, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffort, J.; Adam, C.; Carrier, M.; Ballaith, A.; Coscas, R.; Jean-Baptiste, E.; Hassen-Khodja, R.; Chakfé, N.; Lareyre, F. Artificial intelligence in abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | AAA Patients (n) | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Fillinger 2002 | 48 (30 electively repaired; 8 symptomatic; 10 ruptured AAAs) | PWS correlates with AAA rupture; patient-specific SBP needed |
| Fillinger 2003 | 103 (42 observed AAAs without intervention; 39 electively repaired; 8 symptomatic; 14 ruptured AAAs) | Location of PWS correlated with location of rupture |
| Venkatasubramaniam 2004 | 27 (12 ruptured) | PWS inversely related to wall thickness |
| Truijers 2007 | 30 (10 asymptomatic; 10 symptomatic; 10 ruptured AAAs) | PWS correlated with AAA rupture; patient-specific SBP needed |
| Heng 2008 | 70 (40 electively repaired; 30 acutely repaired AAAs) | PWS significantly higher for patients undergoing acute repair |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haller, S.J.; Azarbal, A.F.; Rugonyi, S. Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risks. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030079
Haller SJ, Azarbal AF, Rugonyi S. Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risks. Bioengineering. 2020; 7(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaller, Stephen J., Amir F. Azarbal, and Sandra Rugonyi. 2020. "Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risks" Bioengineering 7, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030079
APA StyleHaller, S. J., Azarbal, A. F., & Rugonyi, S. (2020). Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risks. Bioengineering, 7(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030079






