Biomimetic Nanocarriers for Cancer Target Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
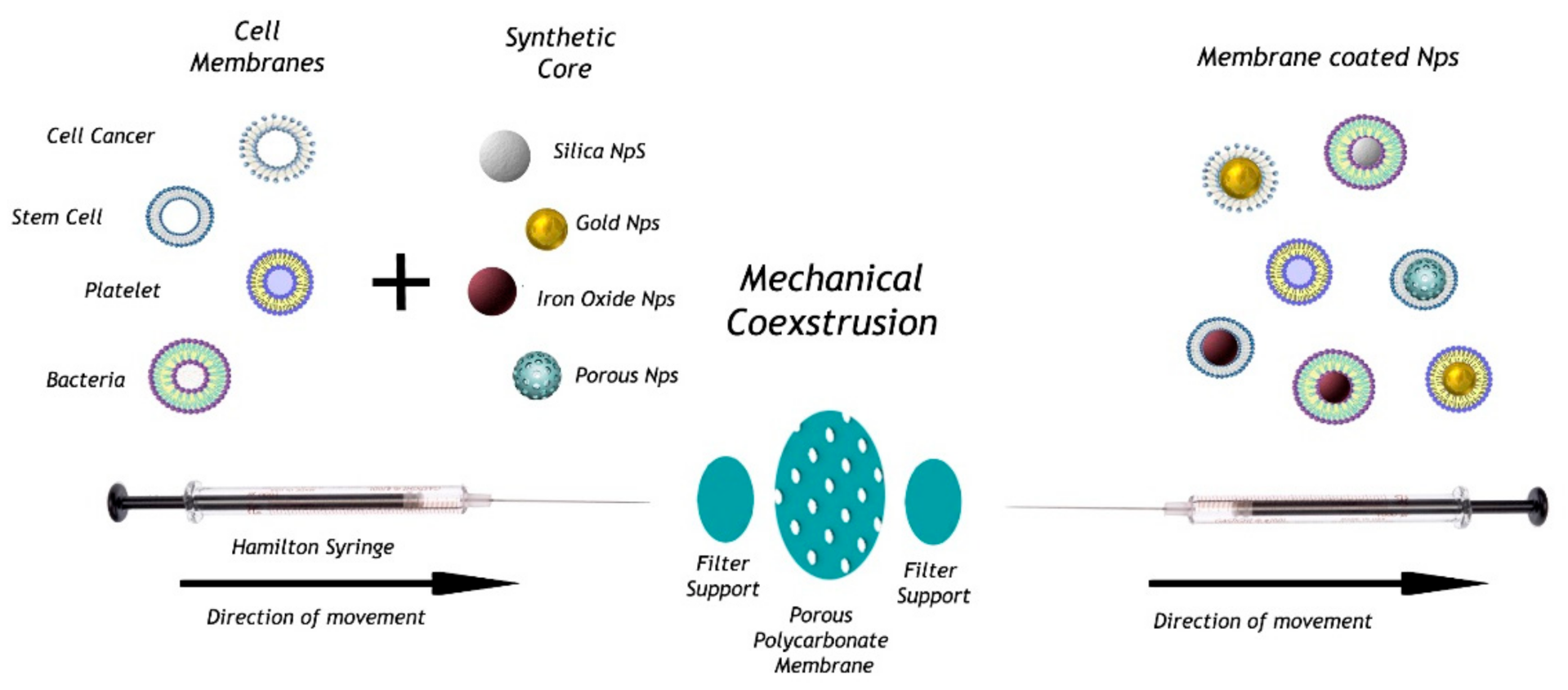
Methods of Production of CMC-NPs
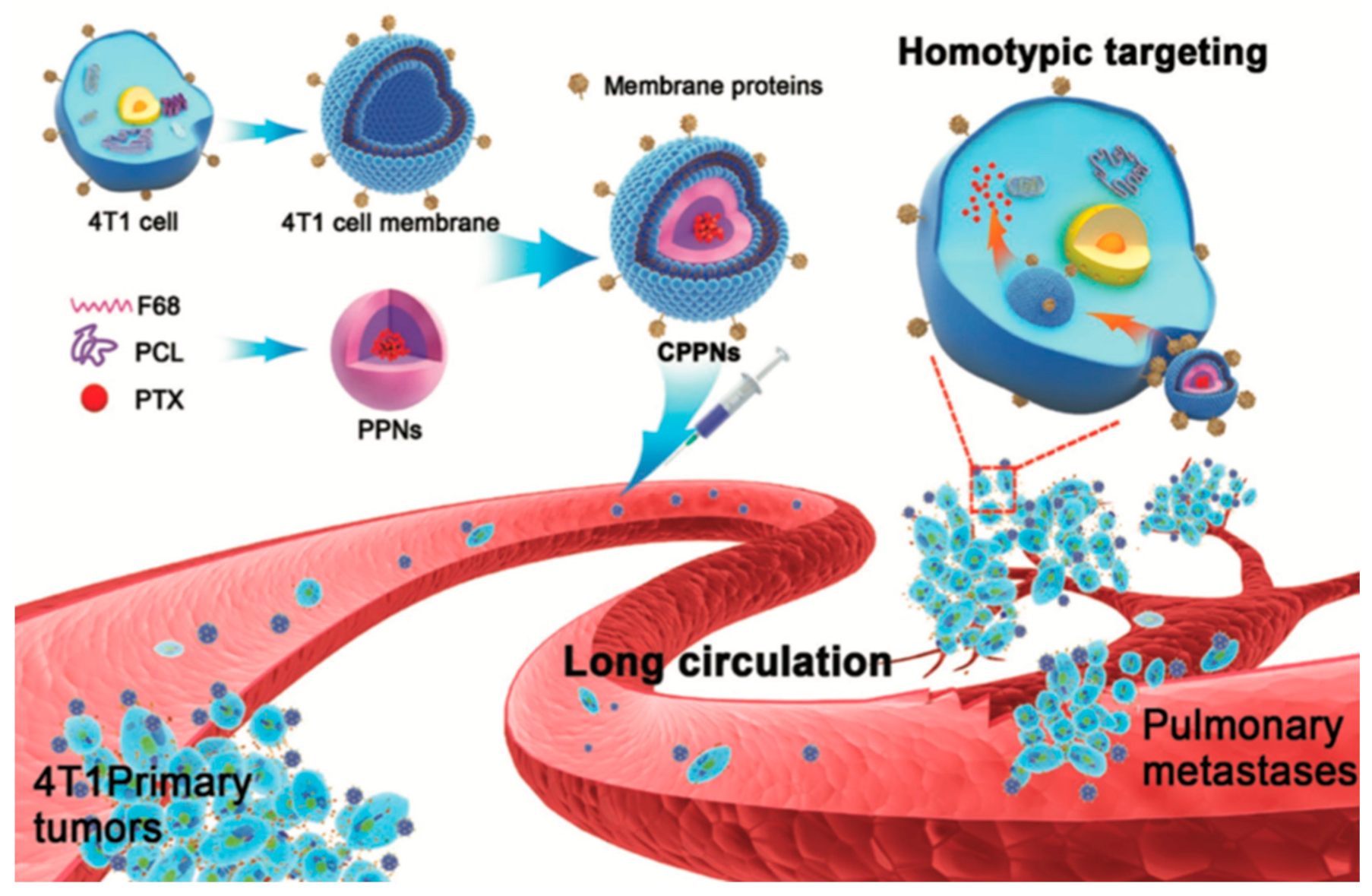
2. Cancer CMC NPs
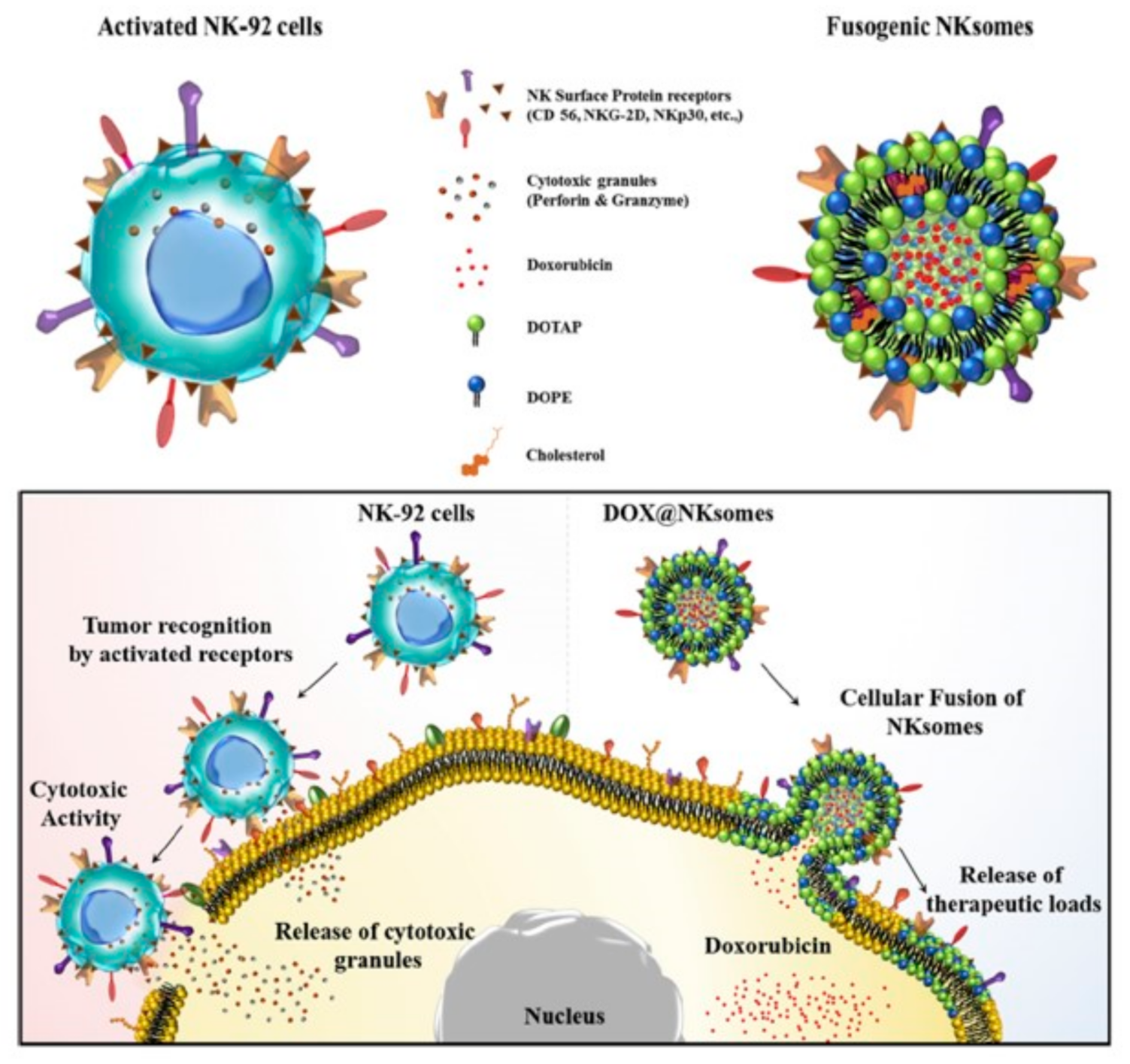
3. Leucocyte Cell Membrane-Covered NPs
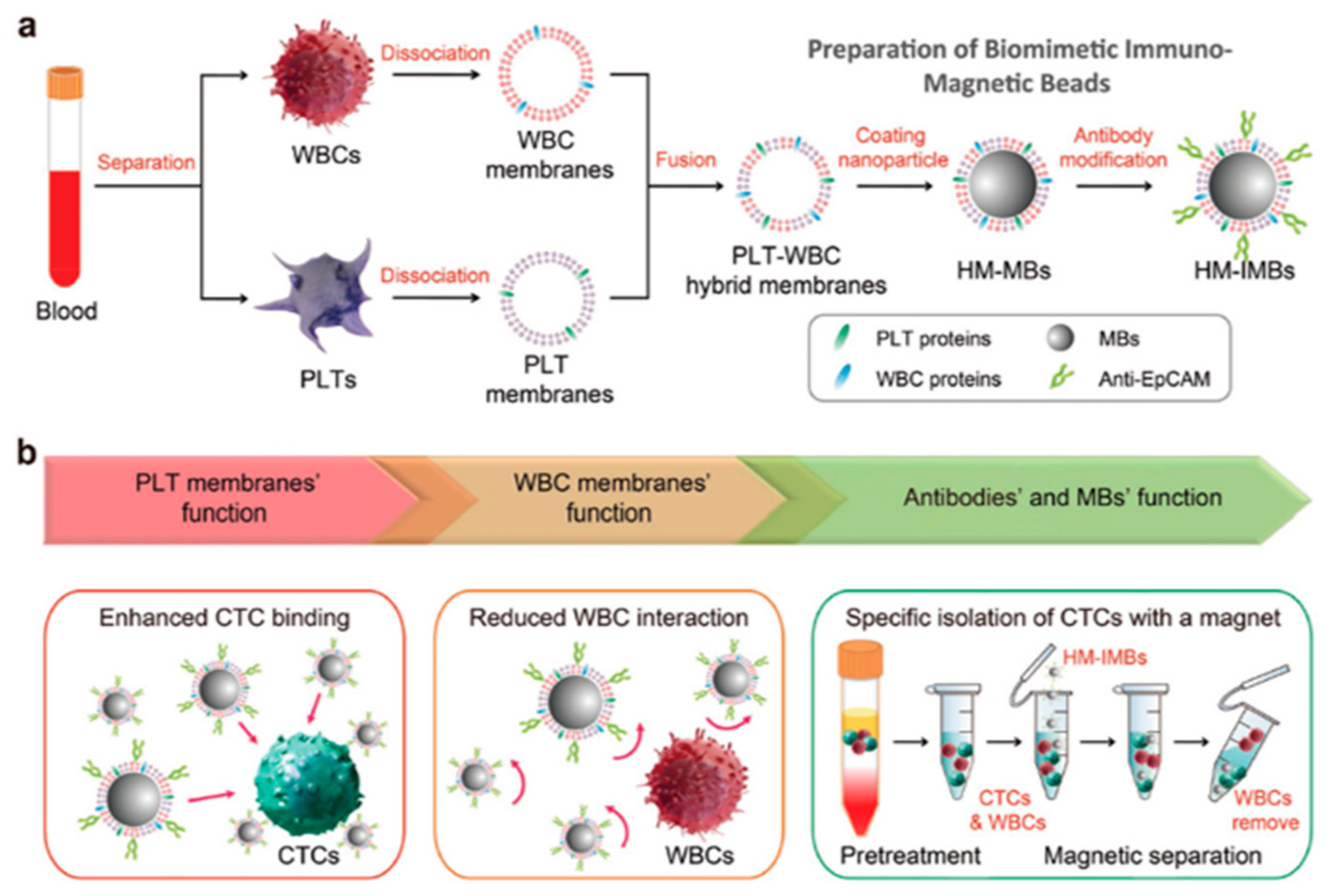
4. Platelet Cell Membrane Covered NPs
5. Stem Cell Membrane-Coated NPs
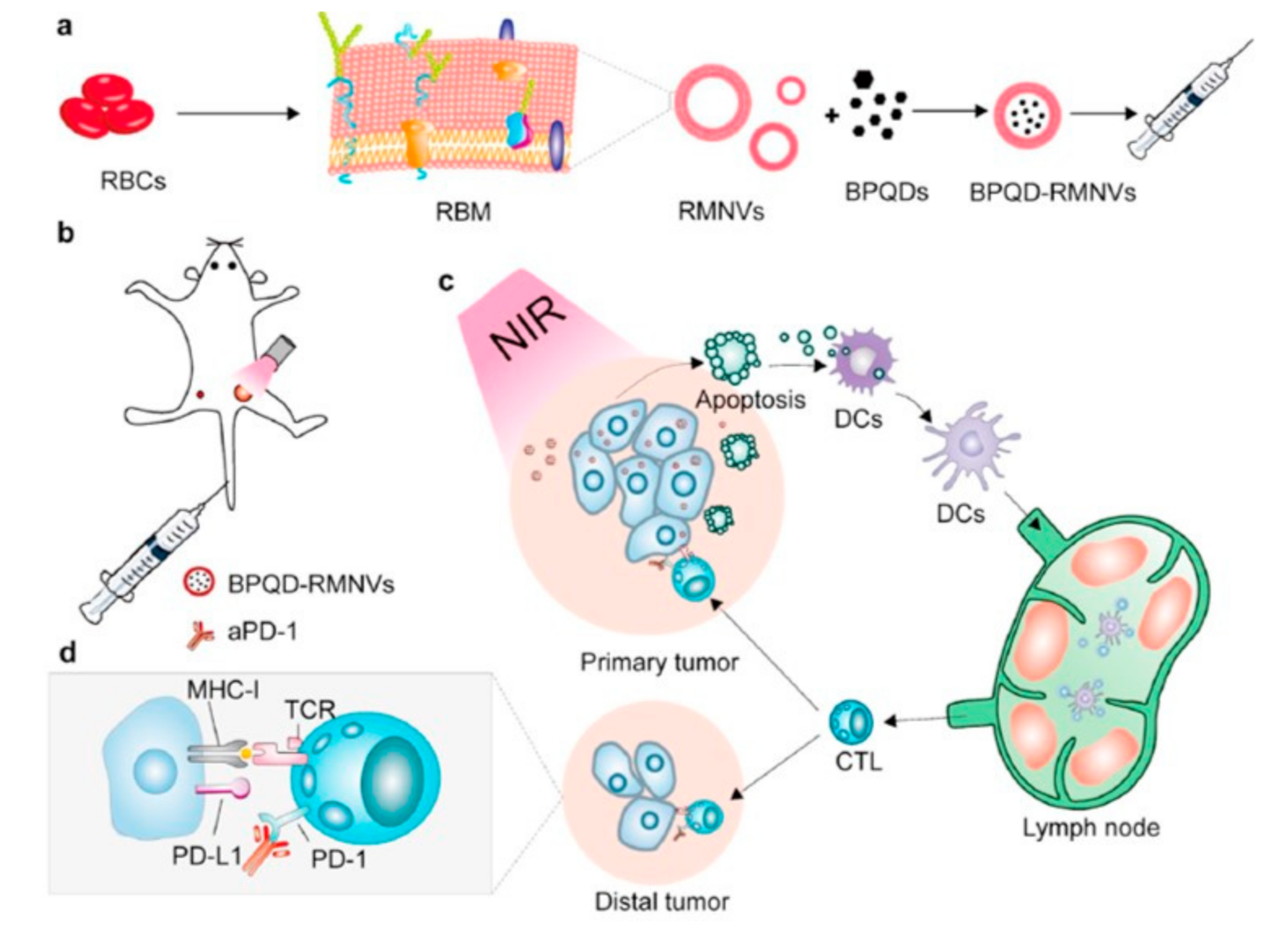
6. RBC Membrane-Covered NPs
7. Toxicity and Biological Impact of Biomimetic NPs
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, G.R.; Leong, D.P.; Rangarajan, S.; Lanas, F.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Gupta, R.; Diaz, R.; Avezum, A.; Oliveira, G.B.F.; Wielgosz, A.; et al. Variations in common diseases, hospital admissions, and deaths in middle-aged adults in 21 countries from five continents (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVita, V.T.; Chu, E. A History of Cancer Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, R.; Acharya, S.; Sahoo, S.K. Cancer nanotechnology: Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.; Batist, G.; Belt, R.; Rovira, D.; Navari, R.; Azarnia, N.; Welles, L.; Winer, E.; Group, T.D.-S. Liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin compared with conventional doxorubicin in a randomized multicenter trial as first-line therapy of metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 94, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, U.; Maeda, H.; Jain, R.K.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M.; Zamboni, W.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Barry, S.T.; Gabizon, A.; Grodzinski, P.; Blakey, D.C. Challenges and Key Considerations of the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect for Nanomedicine Drug Delivery in Oncology. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombek, S.K.; May, J.-N.; Theek, B.; Appold, L.; Drude, N.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Tumor targeting via EPR: Strategies to enhance patient responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 130, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeel, B. Hide and Seek: Nanomaterial Interactions with the Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberg, D. Iron oxide nanoparticles and the mechanisms of immune recognition of nanomedicines. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the nanoparticle-protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle size and surface properties determine the protein corona with possible implications for biological impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feiner-Gracia, N.; Beck, M.; Pujals, S.; Tosi, S.; Mandal, T.; Buske, C.; Linden, M.; Albertazzi, L. Super-Resolution Microscopy Unveils Dynamic Heterogeneities in Nanoparticle Protein Corona. Small 2017, 13, 1701631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, F.M.; Pasut, G. PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Fujita, R.; Awata, M.; Kawanishi, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Okuhira, K.; Ishima, Y.; Ishida, T. A hydroxyl PEG version of PEGylated liposomes and its impact on anti-PEG IgM induction and on the accelerated clearance of PEGylated liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Shen, L.; Ji, S.; Hu, T. Effect of protein immunogenicity and PEG size and branching on the anti-PEG immune response to PEGylated proteins. Process Biochem. 2017, 52, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, T. Cell Membrane Coating Technology: A Promising Strategy for Biomedical Applications. Nano Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, R.J.; Paulmurugan, R.; Moon, J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H. Cell membrane-coated nanocarriers: The emerging targeted delivery system for cancer theranostics. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.H.; Hu, C.-M.J.; Luk, B.T.; Gao, W.; Copp, J.A.; Tai, Y.; O’Connor, D.E.; Zhang, L. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Anticancer Vaccination and Drug Delivery. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampado, R.; Crotti, S.; Caliceti, P.; Pucciarelli, S.; Agostini, M. Recent Advances in Understanding the Protein Corona of Nanoparticles and in the Formulation of “Stealthy ” Nanomaterials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, C.; Molinaro, R.; Taraballi, F.; Toledano Furman, N.E.; Hartman, K.A.; Sherman, M.B.; de Rosa, E.; Kirui, D.K.; Salvatore, F.; Tasciotti, E. Unveiling the in Vivo Protein Corona of Circulating Leukocyte-like Carriers. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3262–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Meng, Q.-F.; Bu, L.-L.; Cai, B.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z.-J.; Zhang, W.-F.; Li, A.; Guo, S.-S.; Liu, W.; et al. Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Upconversion Nanoparticles with Minimal Protein Adsorption for Enhanced Tumor Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Meng, Q.-F.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, G.-T.; Li, A.; Ma, W.; Zhang, N.; Guo, S.-S.; Zhao, X.-Z.; et al. Platelet-Leukocyte Hybrid Membrane-Coated Immunomagnetic Beads for Highly Efficient and Highly Specific Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Adjuvant Nanoparticles with Mannose Modification for Effective Anticancer Vaccination. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-H.; Zhou, Y.; Tabata, Y.; Gao, J.-Q. Mesenchymal stem cell-based drug delivery strategy: From cells to biomimetic. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Cai, B.; Bu, L.-L.; Liao, Q.-Q.; Guo, S.-S.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Dong, W.-F.; Liu, W. Microfluidic Electroporation-Facilitated Synthesis of Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Zheng, D.-W.; Zhang, M.-K.; Yu, W.-Y.; Qiu, W.-X.; Hu, J.-J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.-Z. Preferential Cancer Cell Self-Recognition and Tumor Self-Targeting by Coating Nanoparticles with Homotypic Cancer Cell Membranes. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5895–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, B. The role of adhesions between homologous cancer cells in tumor progression and targeted therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.S.; Xie, J.; LeBaron, M.J.; Ealley, E.L.; Nevalainen, M.T.; Rui, H. Stat5 promotes homotypic adhesion and inhibits invasive characteristics of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Kotani, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Matozaki, T. The CD47-SIRPα signalling system: Its physiological roles and therapeutic application. J. Biochem. 2014, 155, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, A.V.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Biointerfacing and Applications of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Su, J.; Meng, Q.; Yin, Q.; Chen, L.; Gu, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; et al. Cancer-Cell-Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Therapy of Homotypic Tumors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9581–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, B.; Pang, Z. Biomimetic nanoparticles for inflammation targeting. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qin, J.; Wang, J. Cell membrane-based nanoparticles: A new biomimetic platform for tumor diagnosis and treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, A.; Quattrocchi, N.; van de Ven, A.L.; Chiappini, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Martinez, J.O.; Brown, B.S.; Khaled, S.Z.; Yazdi, I.K.; Enzo, M.V.; et al. Synthetic nanoparticles functionalized with biomimetic leukocyte membranes possess cell-like functions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, R.; Parodi, A.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Acciardo, S.; Corbo, C.; de Rosa, E.; Yazdi, I.K.; Scaria, S.; Molinaro, R.; Furman, N.E.T.; et al. Biomimetic carriers mimicking leukocyte plasma membrane to increase tumor vasculature permeability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, K.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Q.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Tumor-Targeted Chemotherapy. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Dan, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yin, Q.; Li, Y. Liposomes Coated with Isolated Macrophage Membrane Can Target Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7738–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Gnanasammandhan, M.K.; Xie, C.; Huang, K.; Cui, M.Y.; Chan, J.M. Monocyte cell membrane-derived nanoghosts for targeted cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 6981–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Massagué, J. Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Wei, J.; Qian, H.; Su, S.; Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Liu, B. Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles combined with low-dose irradiation: A new approach to enhance drug targeting in gastric cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitchaimani, A.; Nguyen, T.D.T.; Aryal, S. Natural killer cell membrane infused biomimetic liposomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 160, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Wei, D.; Feng, J.; Yao, J.; Jiang, T.; Song, Q.; Wei, X.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; et al. Nanoparticles Coated with Neutrophil Membranes Can Effectively Treat Cancer Metastasis. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1397–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, C.; Gu, Z. Platelet for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 58, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Bomba, H.N.; Gu, Z. Engineering platelet-mimicking drug delivery vehicles. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sun, W.; Qian, C.; Wang, C.; Bomba, H.N.; Gu, Z. Anticancer Platelet-Mimicking Nanovehicles. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7043–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Qu, H.; Wu, D.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zheng, J.; Shi, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y. Platelet-camouflaged nanococktail: Simultaneous inhibition of drug-resistant tumor growth and metastasis via a cancer cells and tumor vasculature dual-targeting strategy. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2683–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.W.; Lee, G.; Niidome, T.; Komohara, Y.; Lee, R.; Park, Y.I. Platelet-Like Gold Nanostars for Cancer Therapy: The Ability to Treat Cancer and Evade Immune Reactions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Bu, L.L.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Wan, D.; Liu, J.F.; Li, A.; Guo, S.S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Platelet-Facilitated Photothermal Therapy of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Wei, W.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, D.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Qiao, C.; Yue, H.; Ma, G.; et al. Biomimetic Immuno-Magnetosomes for High-Performance Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7929–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- in’t Anker, P.S.; Scherjon, S.A.; Kleijburg-van der Keur, C.; de Groot-Swings, G.M.J.S.; Claas, F.H.J.; Fibbe, W.E.; Kanhai, H.H.H. Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Fetal or Maternal Origin from Human Placenta. Stem Cells 2004, 22, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanuja, M.Y.; Anupama, C.; Ranganath, S.H. Bioengineered cellular and cell membrane-derived vehicles for actively targeted drug delivery: So near and yet so far. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qu, X.; Zhao, R.C. Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledano Furman, N.E.; Lupu-Haber, Y.; Bronshtein, T.; Kaneti, L.; Letko, N.; Weinstein, E.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Reconstructed stem cell nanoghosts: A natural tumor targeting platform. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3248–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Lu, J.; Jiao, D. Stem cell membrane vesicle-coated nanoparticles for efficient tumor-targeted therapy of orthotopic breast cancer. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, K.; Huang, Y.; Taleb, M.; Zhao, J.; Dong, W.F.; et al. Surface Functionalization of Polymeric Nanoparticles with Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Membrane for Tumor-Targeted Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22963–22973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Lin, Z.; Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Lin, X.; Wu, Z.; He, Q. Stem Cell Membrane-Coated Nanogels for Highly Efficient In Vivo Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery. Small 2016, 12, 4056–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneti, L.; Bronshtein, T.; Malkah Dayan, N.; Kovregina, I.; Letko Khait, N.; Lupu-Haber, Y.; Fliman, M.; Schoen, B.W.; Kaneti, G.; Machluf, M. Nanoghosts as a Novel Natural Nonviral Gene Delivery Platform Safely Targeting Multiple Cancers. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sha, H.; Zhang, L.; Qian, H.; Chen, F.; Ding, N.; Ji, L.; Zhu, A.; Xu, Q.; Meng, F.; et al. Lipid insertion enables targeted functionalization of paclitaxel-loaded erythrocyte membrane nanosystem by tumor-penetrating bispecific recombinant protein. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 5347–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. Red Blood Cells as Smart Delivery Systems. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, W.M.; Pham, T.C.; Kwok, Y.Y.; Vu, L.T.; Ma, V.; Peng, B.; Chan, Y.S.; Wei, L.; Chin, S.M.; Azad, A.; et al. Efficient RNA drug delivery using red blood cell extracellular vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, M.; Hu, A.; Liu, Z. Remotely Controlled Red Blood Cell Carriers for Cancer Targeting and Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Drug Release in Combined Photothermal-Chemotherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, B.T.; Fang, R.H.; Hu, C.-M.J.; Copp, J.A.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Dehaini, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Safe and Immunocompatible Nanocarriers Cloaked in RBC Membranes for Drug Delivery to Treat Solid Tumors. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-M.J.; Zhang, L.; Aryal, S.; Cheung, C.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10980–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, S.; Hu, C.M.; Fang, R.H.; Dehaini, D.; Carpenter, C.; Zhang, D.E.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte membrane-cloaked polymeric nanoparticles for controlled drug loading and release. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Sun, H.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Yin, Q.; Li, Y. Enhanced Blood Suspensibility and Laser-Activated Tumor-specific Drug Release of Theranostic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Functionalizing with Erythrocyte Membranes. Theranostics 2017, 7, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Lv, P.; Chen, Z.; Ni, D.; Zhang, L.; Yue, H.; Yue, Z.; Wei, W.; Ma, G. Programmed co-delivery of paclitaxel and doxorubicin boosted by camouflaging with erythrocyte membrane. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4020–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, H.; Yang, M.; Li, R.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, B.; Qian, X. Gambogic acid-loaded biomimetic nanoparticles in colorectal cancer treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liang, M.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Gao, C.; Chu, X.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Gong, W.; Yang, M.; et al. Dual-Modified Novel Biomimetic Nanocarriers Improve Targeting and Therapeutic Efficacy in Glioma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, H.; Huang, J.; Sha, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Liu, B.; Hua, D.; Qian, X. Anti-EGFR-iRGD recombinant protein modified biomimetic nanoparticles loaded with gambogic acid to enhance targeting and antitumor ability in colorectal cancer treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4961–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Ye, X.; Wang, C.; Xing, C.; Miao, Q.; Xie, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Mei, L. Photothermal cancer immunotherapy by erythrocyte membrane-coated black phosphorus formulation. J. Control. Release 2019, 296, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Williams, G.R.; Fan, Q.; Niu, S.; Wu, J.; Xie, X.; Zhu, L.M. Platelet-membrane-biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted antitumor drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Yu, W.; Ji, B.; Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Du, Y.; Song, M.; Cai, H.; Yan, F.; Su, R. Saikosaponin D loaded macrophage membrane-biomimetic nanoparticles target angiogenic signaling for breast cancer therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelopoulos, M.; Parodi, A.; Martinez, J.O.; Yazdi, I.K.; Cevenini, A.; van de Ven, A.L.; Quattrocchi, N.; Boada, C.; Taghipour, N.; Corbo, C.; et al. Cell source determines the immunological impact of biomimetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2016, 82, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, C.; Molinaro, R.; Parodi, A.; Furman, N.E.T.; Salvatore, F.; Tasciotti, E. The impact of nanoparticle protein corona on cytotoxicity, immunotoxicity and target drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Emerging Approaches to Functionalizing Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Biochemistry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guido, C.; Maiorano, G.; Cortese, B.; D’Amone, S.; Palamà, I.E. Biomimetic Nanocarriers for Cancer Target Therapy. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030111
Guido C, Maiorano G, Cortese B, D’Amone S, Palamà IE. Biomimetic Nanocarriers for Cancer Target Therapy. Bioengineering. 2020; 7(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuido, Clara, Gabriele Maiorano, Barbara Cortese, Stefania D’Amone, and Ilaria Elena Palamà. 2020. "Biomimetic Nanocarriers for Cancer Target Therapy" Bioengineering 7, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030111
APA StyleGuido, C., Maiorano, G., Cortese, B., D’Amone, S., & Palamà, I. E. (2020). Biomimetic Nanocarriers for Cancer Target Therapy. Bioengineering, 7(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030111






