In Vitro Characterization of a Novel Human Acellular Dermal Matrix (BellaCell HD) for Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ADMS
2.2. Decellularization Assessment
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Proliferation Assay
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Uniaxial Tensile Testing
2.7. Stiffness Testing
2.8. Suture Retention Strength Testing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
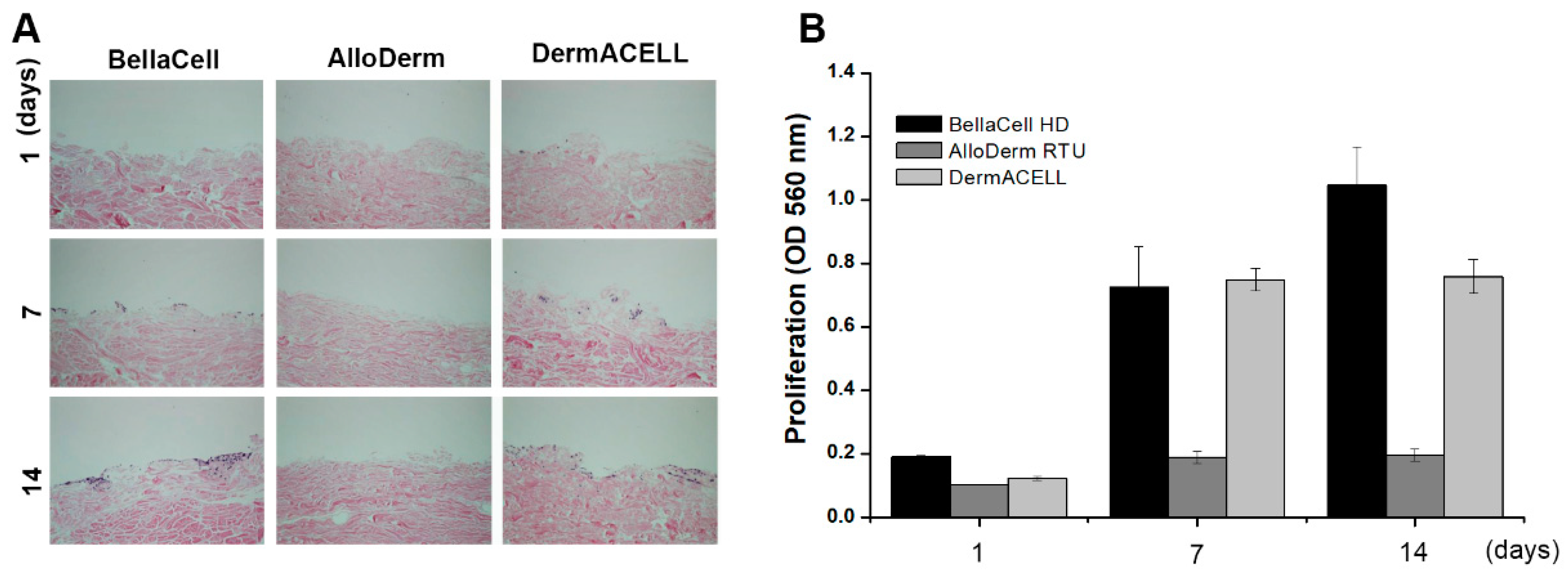
3.1. Decellularization Assessment
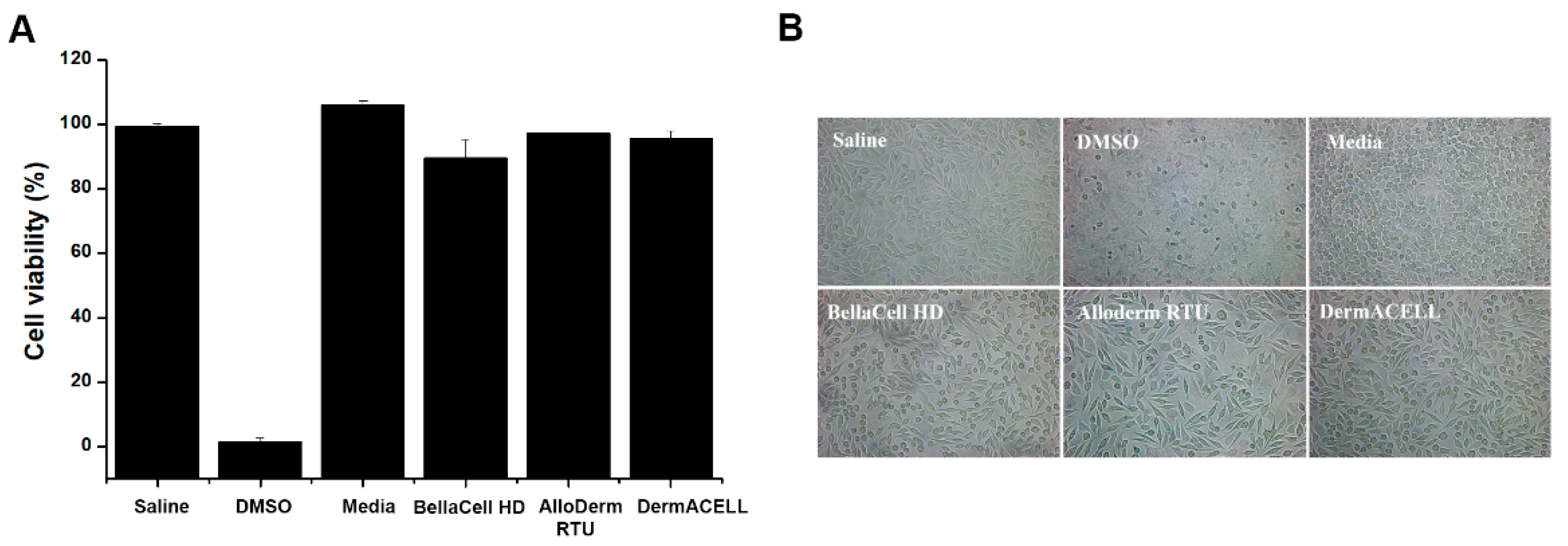
3.2. Biocompatibility Assessment
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
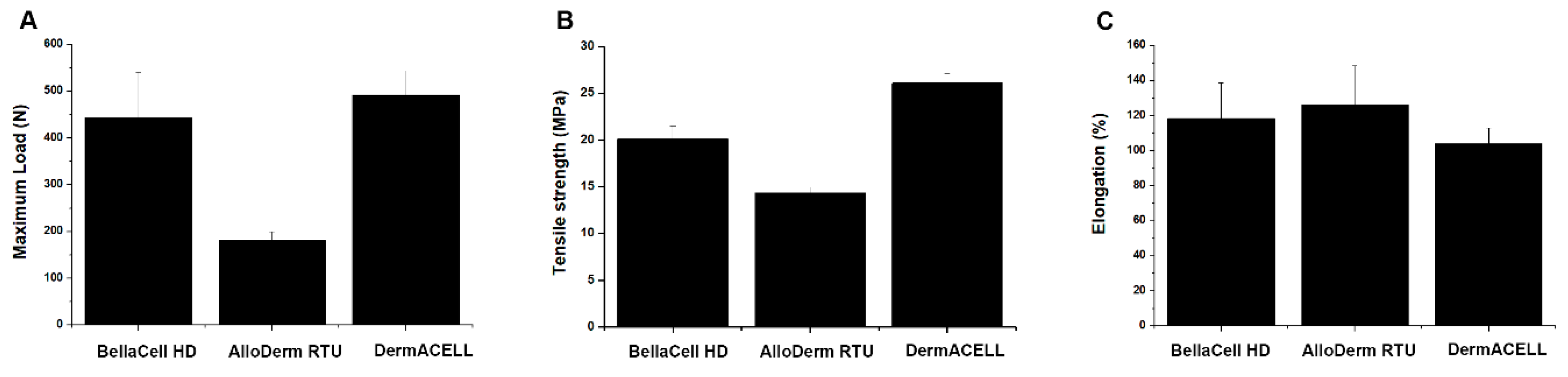
3.4. Uniaxial Tensile Test
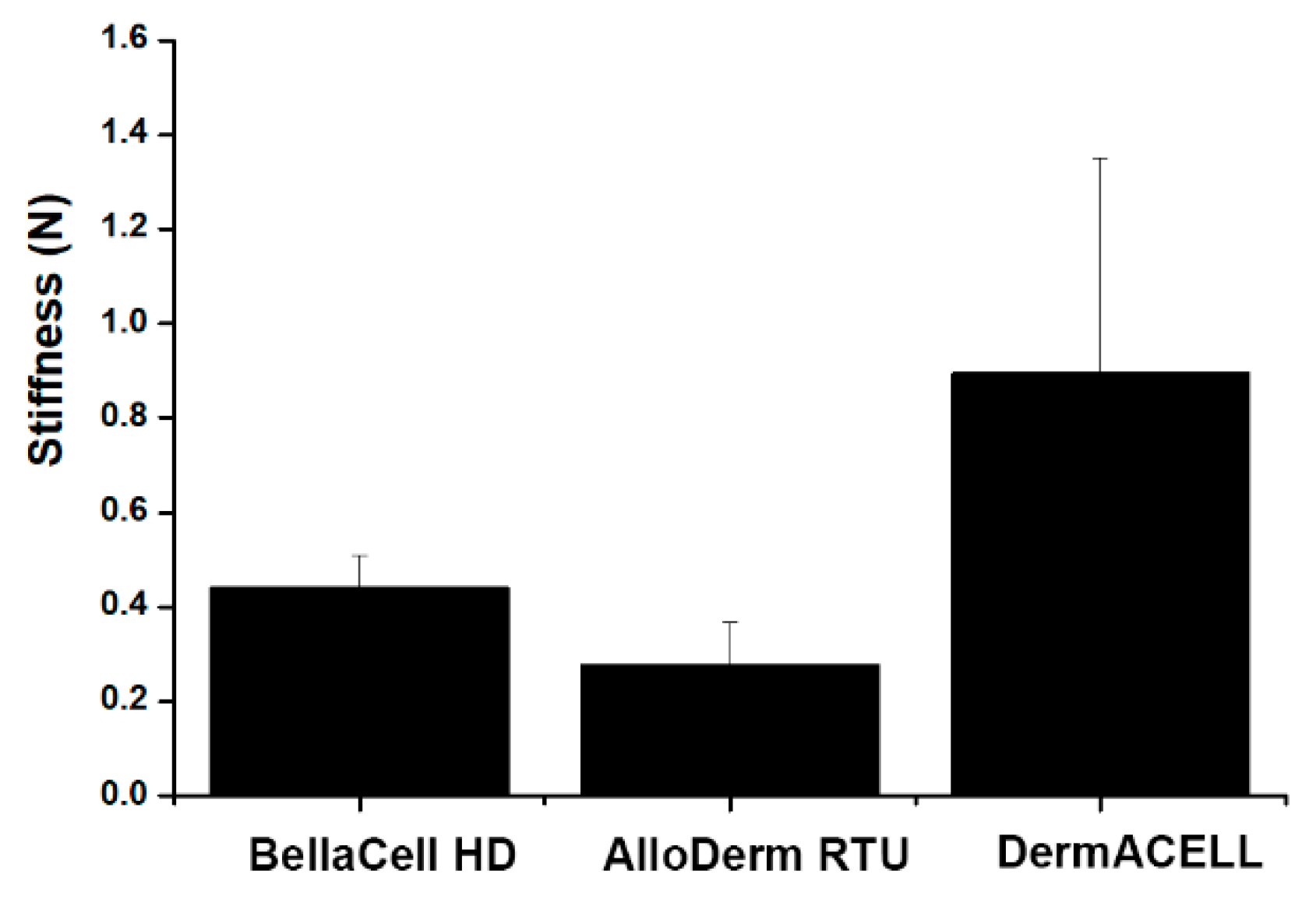
3.5. Stiffness Testing
3.6. Suture Retenstion Strength Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, W.J. Characterization and tissue incorporation of cross-linked human acellular dermal matrix. Biomaterials 2015, 44, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, C.; Schulz, C.; Vogt, N.; Warm, M. The Use of Acellular Dermal Matrices (ADM) in Breast Reconstruction: A Review. Surg. Technol. Int. 2017, 31, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reitsamer, R.; Peintinger, F. Prepectoral implant placement and complete coverage with porcine acellular dermal matrix: A new technique for direct-To-Implant breast reconstruction after nipple-Sparing mastectomy. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 68, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, D.J.; Oikonomou, A.; Hill, E.; Bayat, A. Development and functional evaluation of biomimetic silicone surfaces with hierarchical micro/nano-topographical features demonstrates favourable in vitro foreign body response of breast-Derived fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, M.; Stubert, J.; Gerber, B.; Reimer, T.; Richter, D.-U. Biocompatibility, cell growth and clinical relevance of synthetic meshes and biological matrixes for internal support in implant-based breast reconstruction. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 291, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.; Gertzman, A.A. Process Development and Manufacturing of Human and Animal Acellular Dermal Matrices. Skin Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Koolen, P.G.; Ganor, O.; Markarian, M.K.; Tobias, A.M.; Lee, B.T.; Lin, S.J.; Mureau, M.A.M. Does acellular dermal matrix really improve aesthetic outcome in tissue expander/implant-based breast reconstruction? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2015, 39, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan Delaney, R. The Biomechanics of ProLaye Acellular Dermal Matrix: Suture retention strength. Basic Sci. 2019, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander, F.; Lagergren, J.; Roy, P.G.; Johansson, H.; Brandberg, Y.; Eriksen, C.; Frisell, J. Implant based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: Safety data from an open-Label, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial in the setting of breast cancer treatment. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna, G.; Cawthorn, S.J. Long term follow-Up on prepectoral ADM-assisted breast reconstruction: Evidences after 4 years. Euro J. Plast. Surg. 2017, 40, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, M.S.F.; Farhadi, J. Radiation therapy and immediate breast reconstruction: Novel approaches and evidence base for radiation effects on the reconstructed breast. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2018, 45, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.A.; Samsell, B.; Wallis, G.; Triplett, S.; Chen, S.; Jones, A.L.; Qin, X. Decellularization of human dermis using non-denaturing anionic detergent and endonuclease: A review. Cell Tissue Bank 2015, 16, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, L.J.; Kovacs, T. Novel devices for implant-Based breast reconstruction: Is the use of meshes to support the lower pole justified in terms of benefits? A review of the evidence. Ecancermedicalscience 2018, 12, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, H.R.; Hart, A.M.; Yeager, J.; Losken, A. A histological comparison of two human acellular dermal matrix products in prosthetic-based breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, K.; Santosa, K.B.; Lyons, D.A.; Mand, S.; Xin, M.; Kidwell, K.M.; Brown, D.L.; Wilkins, E.G.; Momoh, A.O. Use of acellular dermal matrix in postmastectomy breast reconstruction: Are all acellular dermal matrices created equal? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsicker, L.M.; Ashikari, A.Y.; Berry, C.; Koch, R.M.; Salzberg, C.A. Short-Term complications associated with acellular dermal matrix-assisted direct-to-implant breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2017, 78, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottler, P.S.; Olenczak, J.; Ning, B.; Seaman, S.A.; Thuman, J.M.; Sun, N.; Piñeros-Fernandez, A.; Hu, S.; DeGeorge, B.R. Fenestration improves acellular dermal matrix biointegration: An investigation of revascularization with photoacoustic microscopy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negenborn, V.L.; Young-Afat, D.A.; Dikmans, R.E.G.; Smit, J.M.; Winters, H.A.H.; Griot, J.P.W.D.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Ruhé, P.Q.; Mureau, M.A.M.; Lapid, O.; et al. Quality of life and patient satisfaction after one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction with an acellular dermal matrix versus two-Stage breast reconstruction (BRIOS): Primary outcome of a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.; Browning, D.; Savović, J.; Holcombe, C.; Blazeby, J.M. Systematic review and critical appraisal of the impact of acellular dermal matrix use on the outcomes of implant-Based breast reconstruction. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 102, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, H.C.; Weaver, M.R.; Schwarzbauer, J.E. Impact of Acellular Dermal Matrix on Postsurgical Wound Fluid Biomarkers in Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2018, 81, S89–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaretti, N.; Guarneri, G.F.; De Biasio, F.; Shoeib, M.A.; Parodi, P.C. The Use of Meshed Dermal Autograft in Breast Reconstruction. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2018, 42, 1704–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accurso, A.; Rocco, N.; Mattera, E.; D’Andrea, F. Innovative management of implant exposure in ADM/implant-based breast reconstruction with negative pressure wound therapy. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2017, 41, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, S.D.; Anderson, L.A.; Ying, J.; Boucher, K.M.; Neumayer, L.A.; Agarwal, J.P. The BREASTrial stage II: ADM breast reconstruction outcomes from definitive reconstruction to 3 months postoperative. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohac, M.; Danisovic, L.; Koller, J.; Dragunova, J.; Varga, I. What happens to an acellular dermal matrix after implantation in the human body? A histological and electron microscopic study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2018, 62, 2873. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, J.A.; Chun, Y.S. Minimizing the Risk of Postoperative Complications in Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix. In Breast Reconstruction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1509–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Bullocks, J.M. DermACELL: A novel and biocompatible acellular dermal matrix in tissue expander and implant-based breast reconstruction. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2014, 37, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.; Maxwell, G.P. AlloDerm RTU integration and clinical outcomes when used for reconstructive breast surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2018, 18, e1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.; Williams, L.; Anderson, E.; Neades, G.; Raine, C.; Young, O.; Kulkarni, D.; Young, I.; Dixon, J.M. Outcome of the use of acellular-dermal matrix to assist implant-based breast reconstruction in a single centre. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertozzi, N.; Pesce, M.; Santi, P.; Raposio, E. Tissue expansion for breast reconstruction: Methods and techniques. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 21, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, C.A.; Ashikari, A.Y.; Berry, C.; Hunsicker, L.M. Acellular dermal matrix–Assisted direct-To-Implant breast reconstruction and capsular contracture: A 13-Year experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, S.-Y.; Youn, D.; Kim, G.H.; Chai, J.H.; Lim, H.R.; Jung, H.H.; Heo, C.Y. In Vitro Characterization of a Novel Human Acellular Dermal Matrix (BellaCell HD) for Breast Reconstruction. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020039
Nam S-Y, Youn D, Kim GH, Chai JH, Lim HR, Jung HH, Heo CY. In Vitro Characterization of a Novel Human Acellular Dermal Matrix (BellaCell HD) for Breast Reconstruction. Bioengineering. 2020; 7(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Sun-Young, Dayoung Youn, Gyeong Hoe Kim, Ji Hwa Chai, Hyang Ran Lim, Hong Hee Jung, and Chan Yeong Heo. 2020. "In Vitro Characterization of a Novel Human Acellular Dermal Matrix (BellaCell HD) for Breast Reconstruction" Bioengineering 7, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020039
APA StyleNam, S.-Y., Youn, D., Kim, G. H., Chai, J. H., Lim, H. R., Jung, H. H., & Heo, C. Y. (2020). In Vitro Characterization of a Novel Human Acellular Dermal Matrix (BellaCell HD) for Breast Reconstruction. Bioengineering, 7(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020039




