Automated Measurement of Patient-Specific Tibial Slopes from MRI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
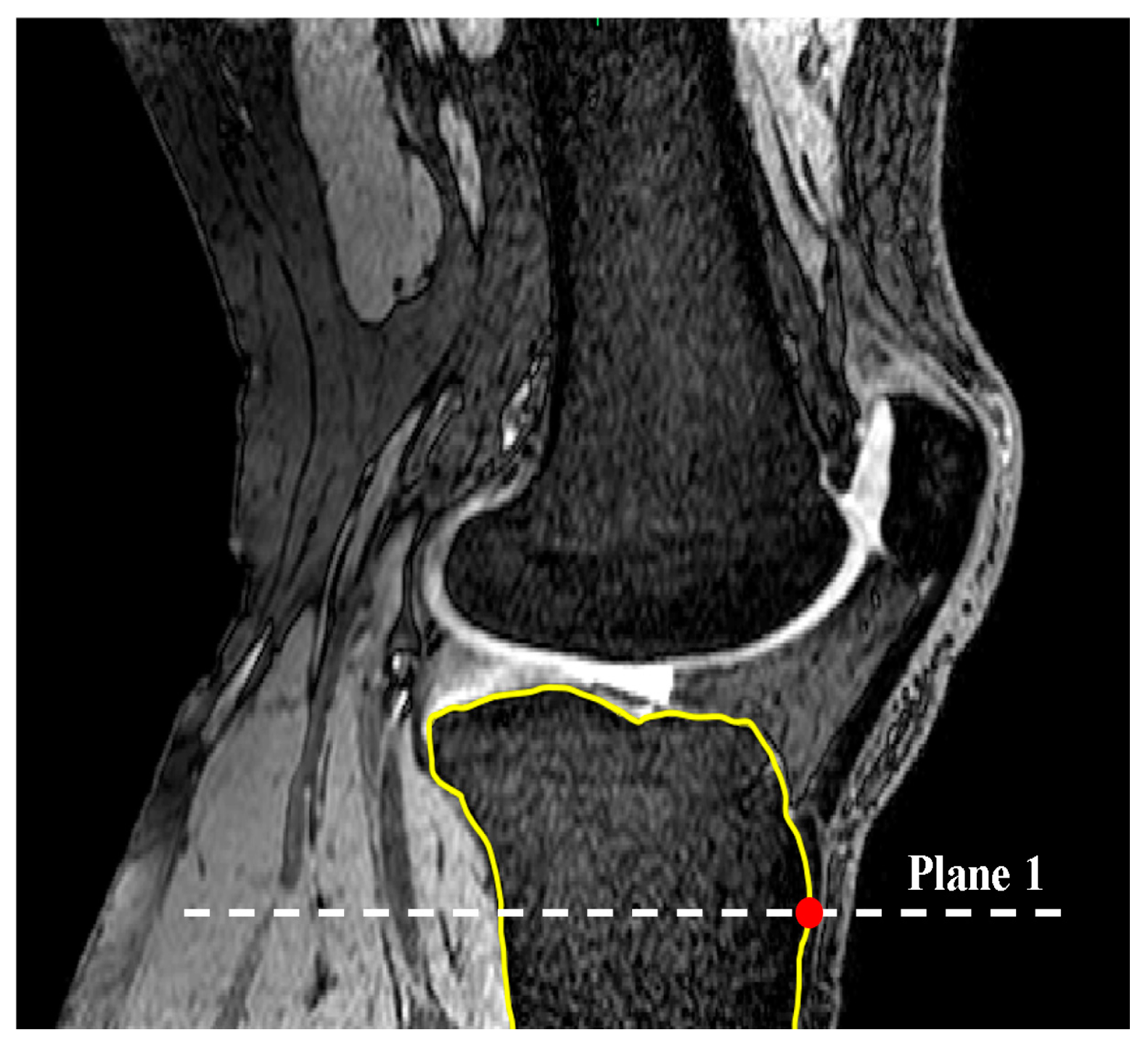
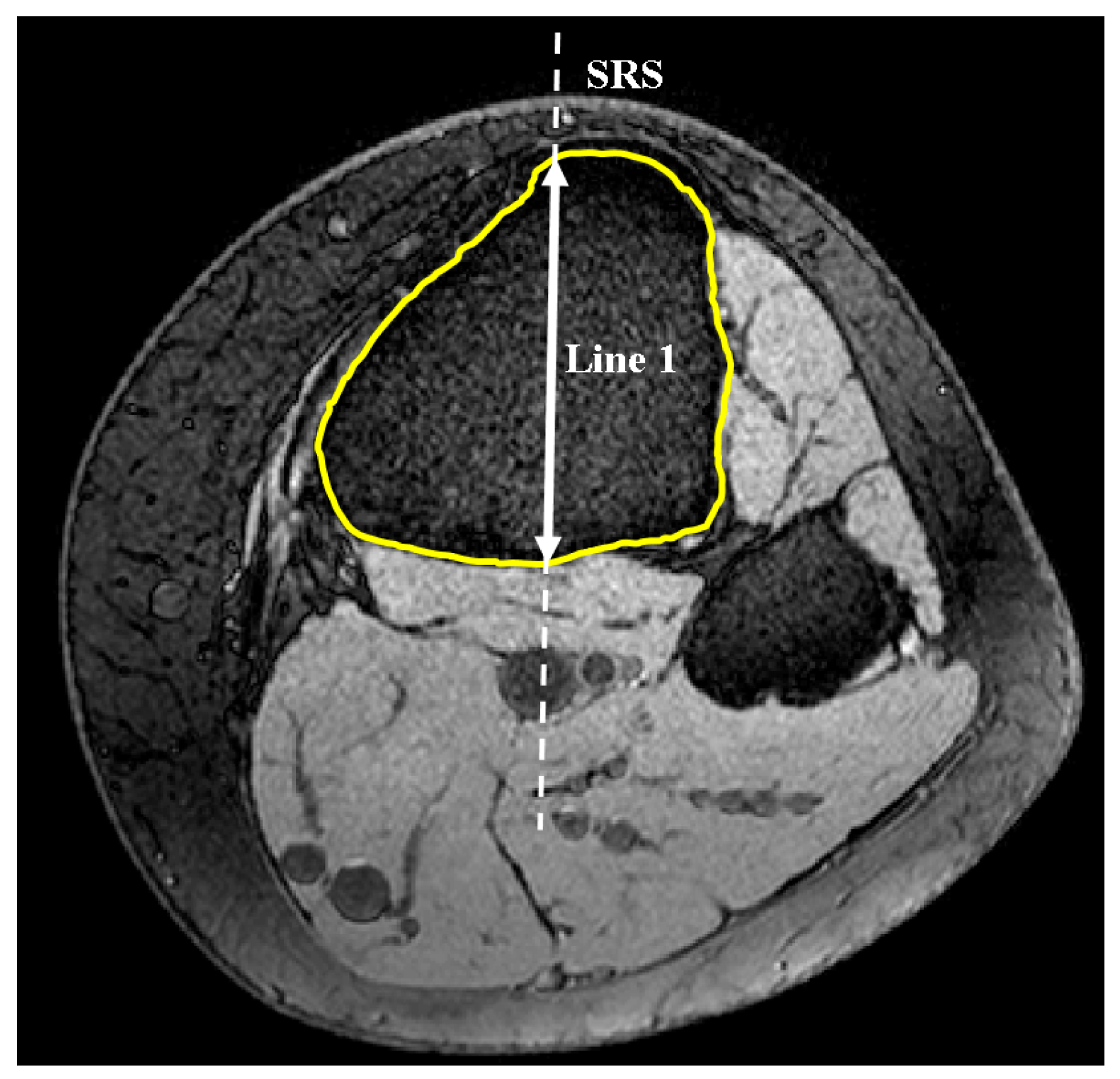
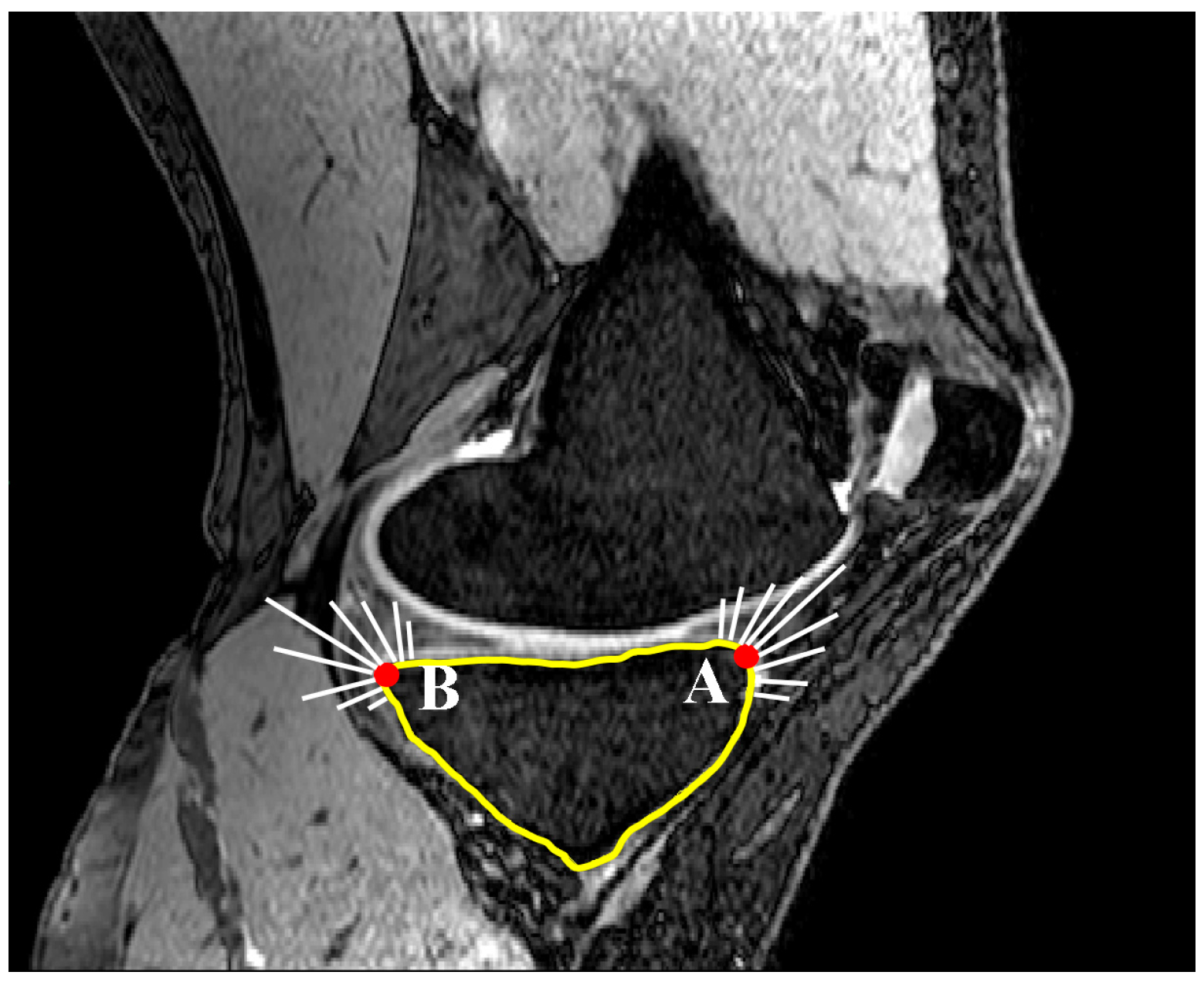
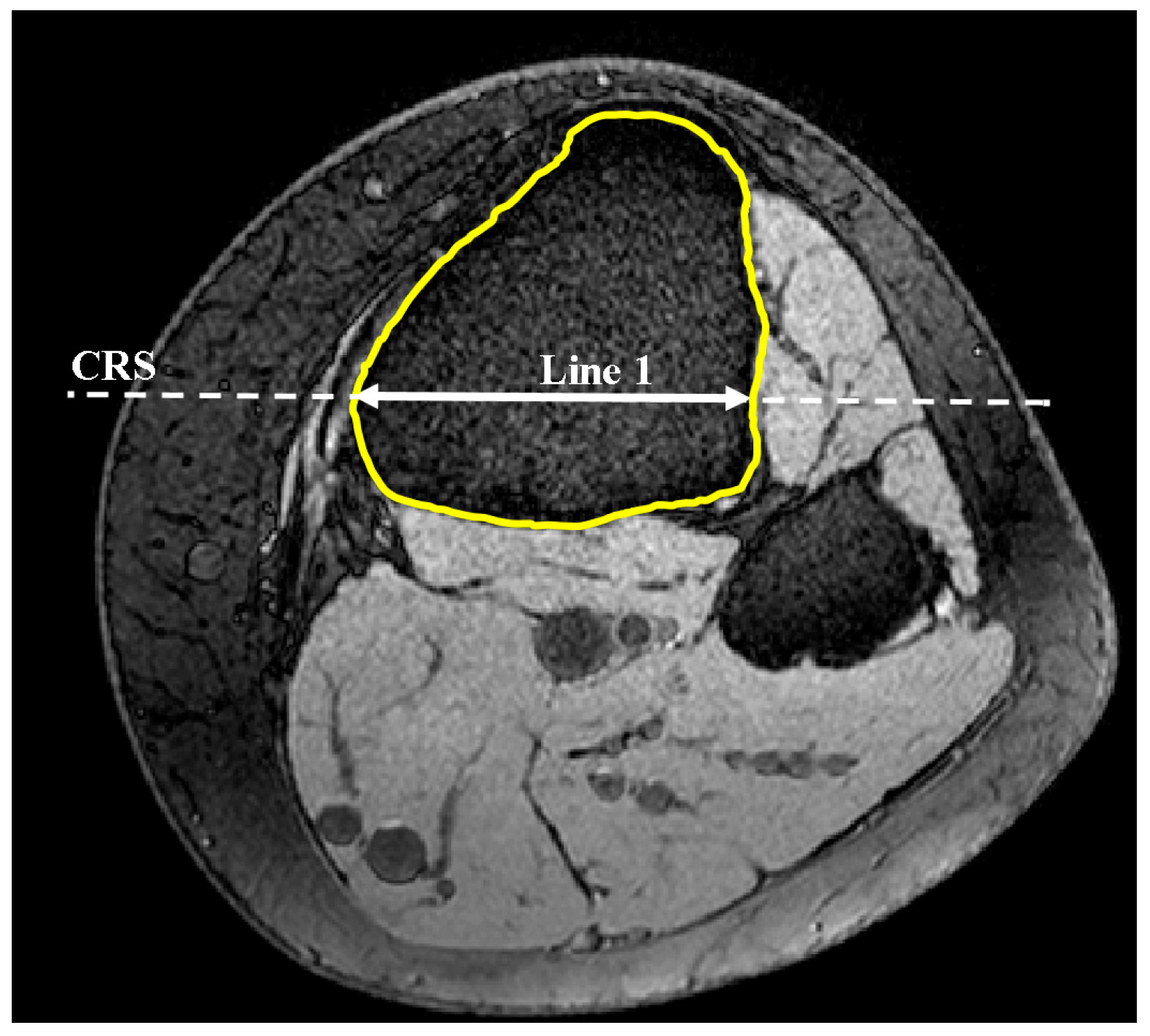
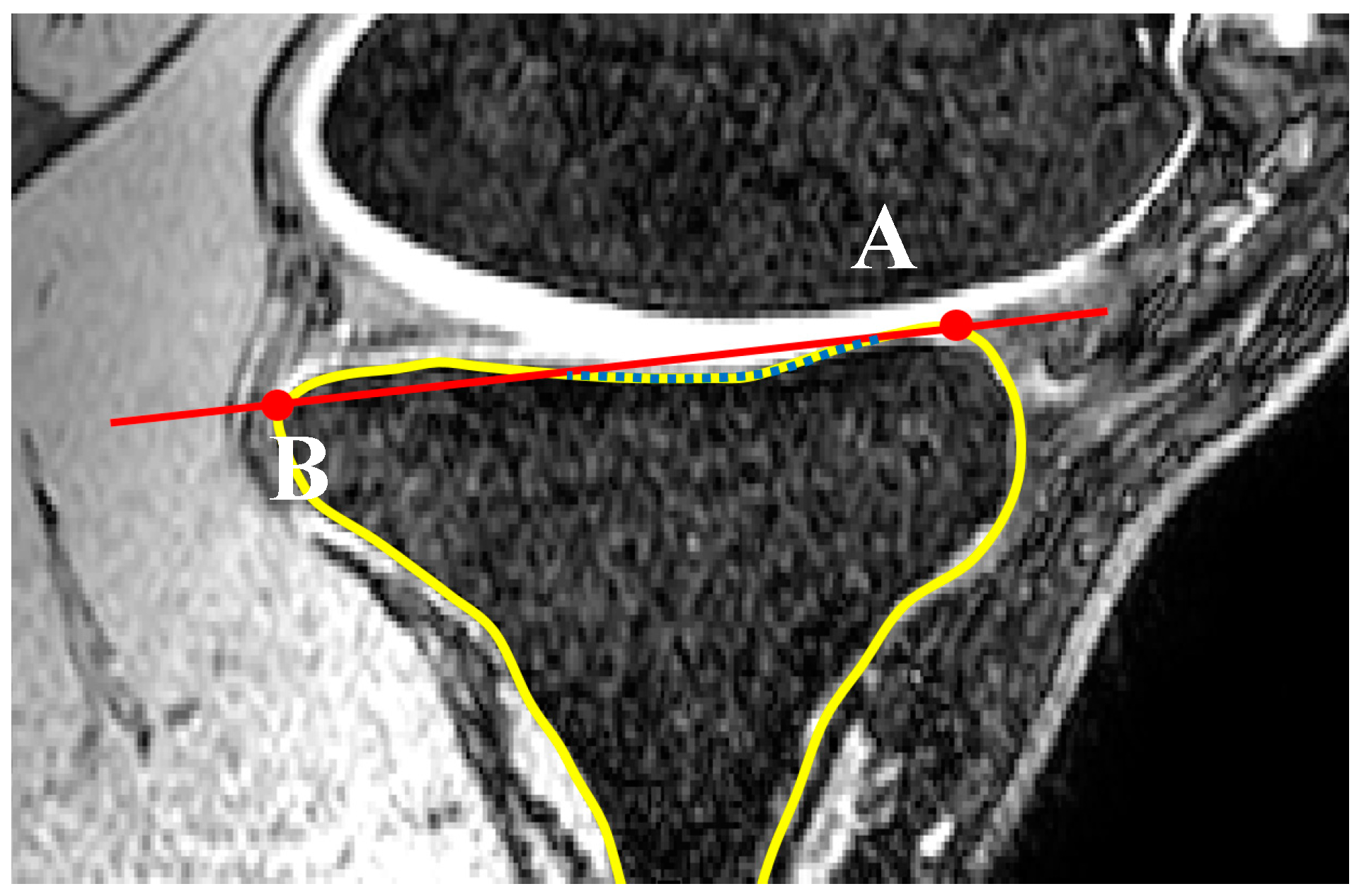
2.1. Medial and Lateral Tibial Slope Measurement Methodology
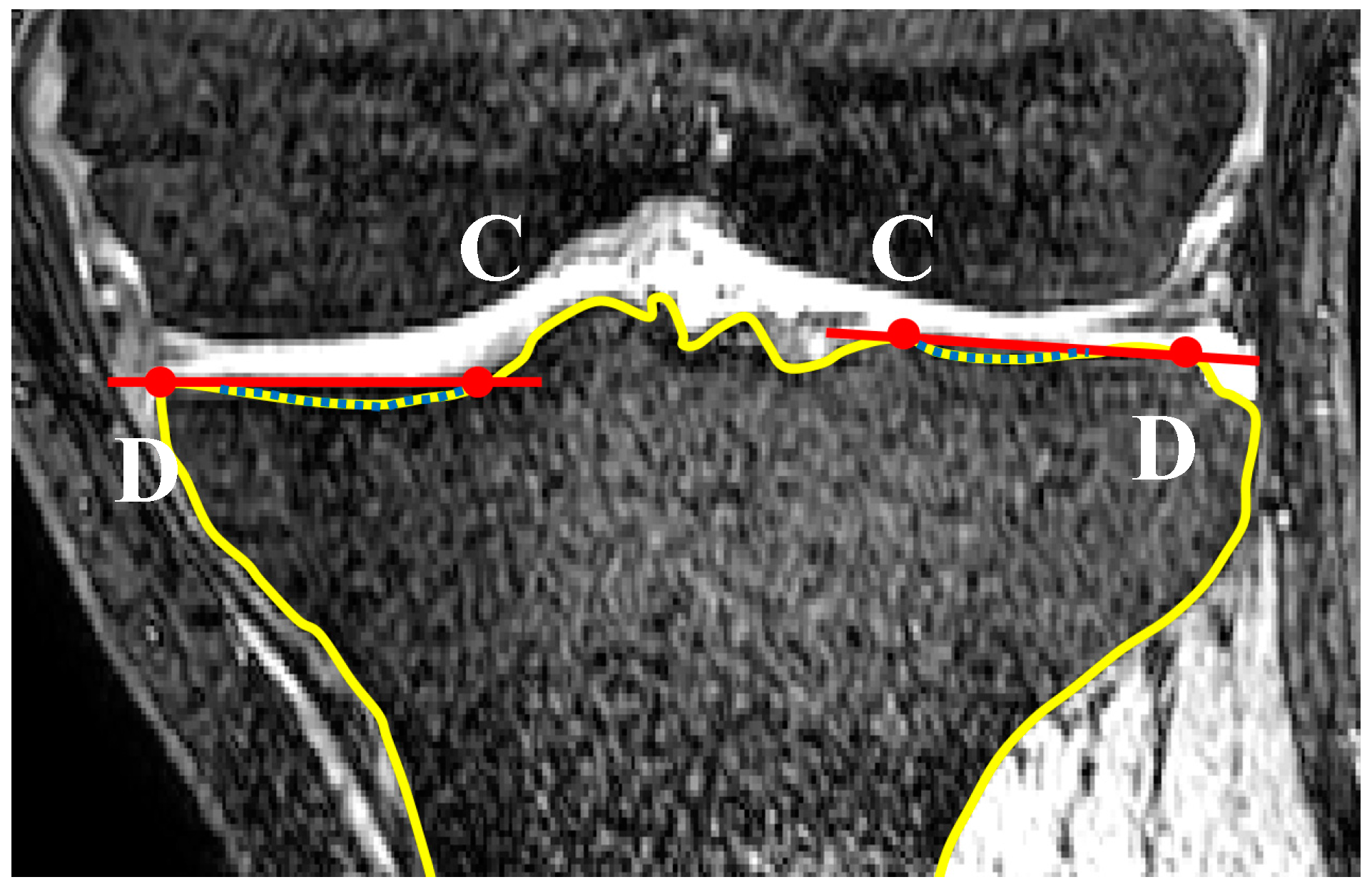
2.2. Coronal Tibial Slope Measurement Method
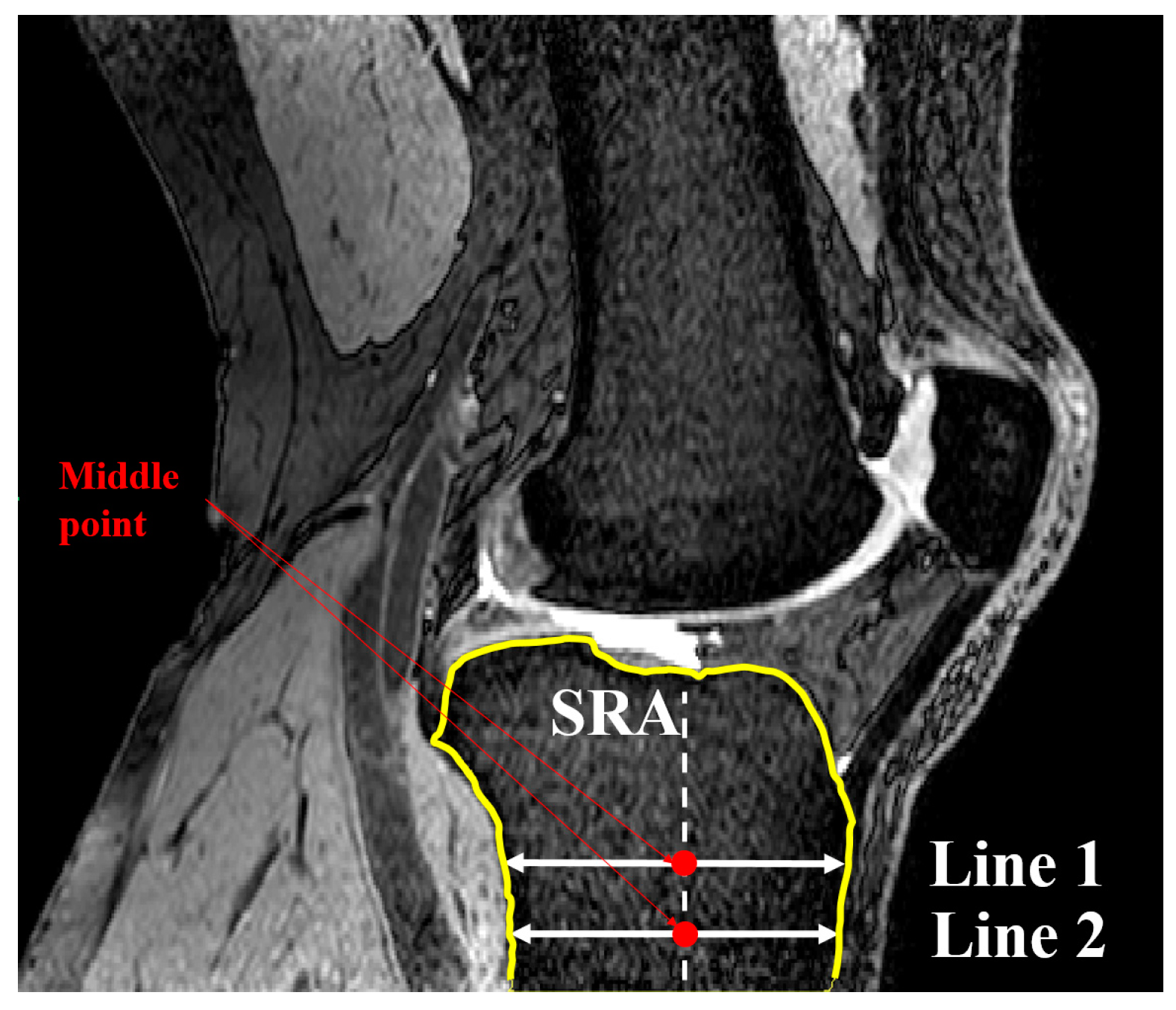
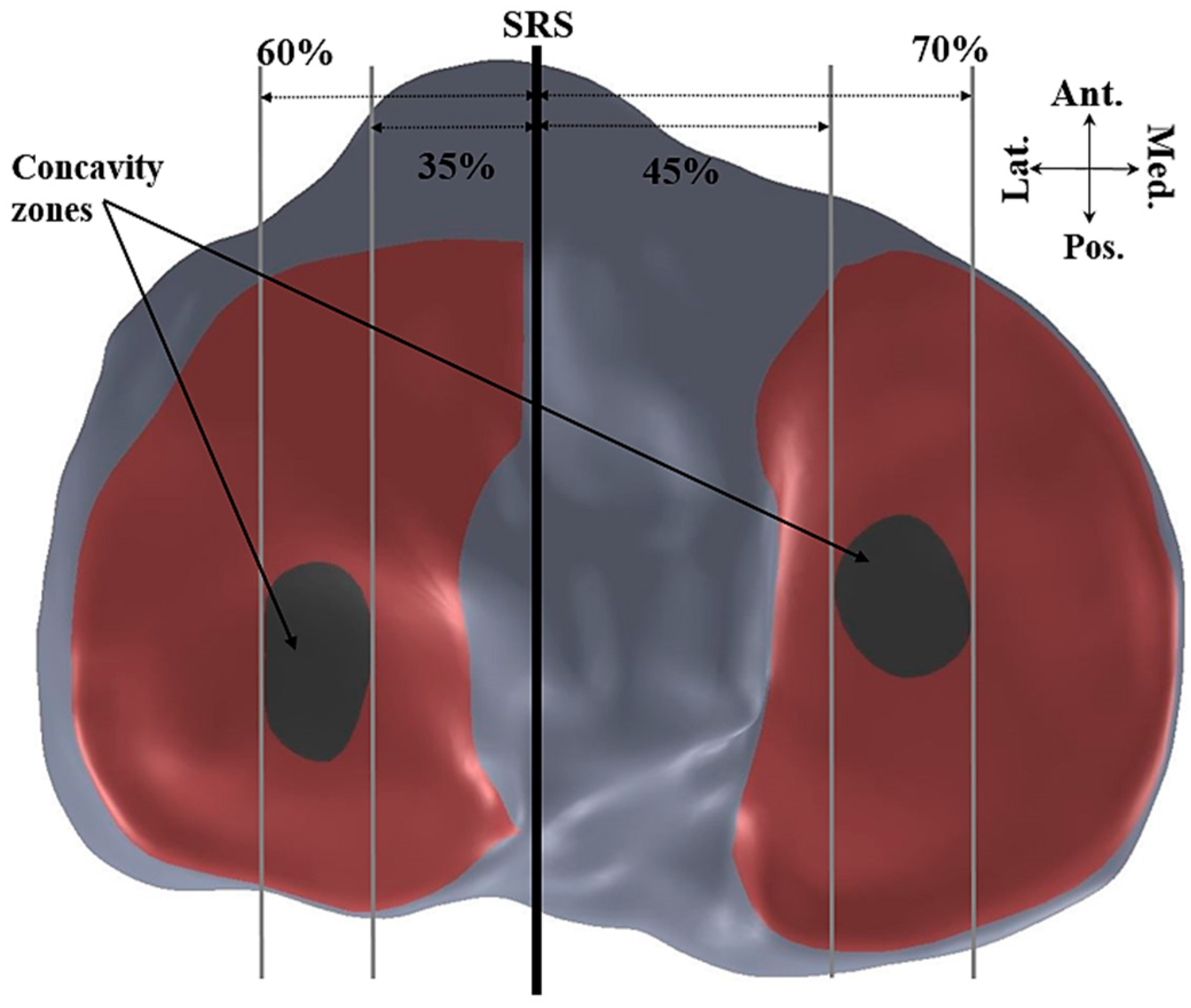
2.3. Concavity Zone
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brandon, M.L.; Haynes, P.T.; Bonamo, J.R.; Flynn, M.I.; Barrett, G.R.; Sherman, M.F. The association between posterior-inferior tibial slope and anterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2006, 22, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çullu, E.; Aydoğdu, S.; Alparslan, B.; Sur, H. Tibial slope changes following dome-type high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2005, 13, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejour, H.; Bonnin, M. Tibial translation after anterior cruciate ligament rupture. Two radiological tests compared. Bone Jt. J. 1994, 76, 745–749. [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann, E.; Bryant, A.; Imhoff, A.B. The effect of closed wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope: A radiographic study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2006, 14, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giffin, J.R.; Vogrin, T.M.; Zantop, T.; Woo, S.L.; Harner, C.D. Effects of increasing tibial slope on the biomechanics of the knee. Am. J. Sports Med. 2004, 32, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beynnon, B.D.; Hall, J.S.; Sturnick, D.R.; DeSarno, M.J.; Gardner-Morse, M.; Tourville, T.W.; Smith, H.C.; Slauterbeck, J.R.; Shultz, S.J.; Johnson, R.J. Increased slope of the lateral tibial plateau subchondral bone is associated with greater risk of noncontact acl injury in females but not in males a prospective cohort study with a nested, matched case-control analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, D.C.; Sturnick, D.R.; Vacek, P.M.; DeSarno, M.J.; Gardner-Morse, M.; Tourville, T.W.; Smith, H.C.; Slauterbeck, J.R.; Johnson, R.J.; Shultz, S.J. Relationship between the risk of suffering a first-time noncontact ACL injury and geometry of the femoral notch and ACL a prospective cohort study with a nested case-control analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnery-Cottet, B.; Archbold, P.; Cucurulo, T.; Fayard, J.-M.; Bortolletto, J.; Thaunat, M.; Prost, T.; Chambat, P. The influence of the tibial slope and the size of the intercondylar notch on rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2011, 93, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stijak, L.; Herzog, R.F.; Schai, P. Is there an influence of the tibial slope of the lateral condyle on the acl lesion? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2008, 16, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, J.; Chandrashekar, N.; Mansouri, H.; Gill, B.; Slauterbeck, J.R.; Schutt, R.C.; Dabezies, E.; Beynnon, B.D. Shallow medial tibial plateau and steep medial and lateral tibial slopes new risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, Y.; Sotozawa, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Kusayama, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Saito, T. Usefulness of long tibial axis to measure medial tibial slope for opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 3661–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, J.; Chandrashekar, N.; Gill, B.; Beynnon, B.D.; Slauterbeck, J.R.; Schutt, R.C.; Mansouri, H.; Dabezies, E. The geometry of the tibial plateau and its influence on the biomechanics of the tibiofemoral joint. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2008, 90, 2724–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, B.; Konan, S.; Mannan, K.; Scott, G. Evaluation of the posterior tibial slope on mr images in different population groups using the tibial proximal anatomical axis. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2012, 78, 757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudek, R.; Fuchs, B.; Regenfelder, F.; Koch, P. Is noncontact acl injury associated with the posterior tibial and meniscal slope? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipps, D.B.; Wilson, A.M.; Ashton-Miller, J.A.; Wojtys, E.M. Evaluation of different methods for measuring lateral tibial slope using magnetic resonance imaging. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 2731–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, S.; Goettinger, M.; Weber, P.; Horng, A.; Glaser, C.; Jansson, V.; Müller, P. Development and validation of a new method for the radiologic measurement of the tibial slope. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.H.; Chang, C.B.; Shin, K.S.; Seong, S.C.; Kim, T.K. Anatomical references to assess the posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty: A comparison of 5 anatomical axes. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudek, R.; Schmutz, S.; Regenfelder, F.; Fuchs, B.; Koch, P.P. Novel measurement technique of the tibial slope on conventional mri. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faschingbauer, M.; Sgroi, M.; Juchems, M.; Reichel, H.; Kappe, T. Can the tibial slope be measured on lateral knee radiographs? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 3163–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, J.; Migaud, H.; Gougeon, F.; Cotten, A.; Fontaine, C.; Duquennoy, A. [Evaluation of methods for radiographic measurement of the tibial slope. A study of 83 healthy knees]. Revue de Chirurgie Orthopédique et Réparatrice de l'Appareil Moteur 1995, 82, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Genin, P.; Weill, G.; Julliard, R. [The tibial slope. Proposal for a measurement method]. J. Radiol. 1993, 74, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Julliard, R.; Genin, P.; Weil, G.; Palmkrantz, P. [The median functional slope of the tibia. Principle. Technique of measurement. Value. Interest]. Revue de Chirurgie Orthopédique et Réparatrice de l'Appareil Moteur 1992, 79, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy, L.; Felson, D.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Lam, Y.-M.; Segal, N.; Lynch, J.; Cooke, T.D.V. Does measurement of the anatomic axis consistently predict hip-knee-ankle angle (hka) for knee alignment studies in osteoarthritis? Analysis of long limb radiographs from the multicenter osteoarthritis (most) study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, R.K.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Hewett, T.E.; Nyman, E., Jr.; Goel, V.K. Novel measurement of multi-planar proximal tibial slope: 2872 board# 4 june 3, 1:00 p.m.–3:00 p.m. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 803. [Google Scholar]
- Amerinatanzi, A.; Summers, R.; Ahmadi, K.; Goel, V.K.; Hewett, T.E.; Nyman, E. A novel 3d approach for determination of frontal and coronal plane tibial slopes from mr imaging. Knee 2017, 24, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewett, T.E.; Myer, G.D.; Ford, K.R. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female athletes part 1, mechanisms and risk factors. Am. J. Sports Med. 2006, 34, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.G.; Baumer, T.G.; Slade, J.M.; Smith, W.E.; Haut, R.C. Tibiofemoral contact pressures and osteochondral microtrauma during anterior cruciate ligament rupture due to excessive compressive loading and internal torque of the human knee. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellemans, J.; Robijns, F.; Duerinckx, J.; Banks, S.; Vandenneucker, H. The influence of tibial slope on maximal flexion after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2005, 13, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malviya, A.; Lingard, E.; Weir, D.; Deehan, D. Predicting range of movement after knee replacement: The importance of posterior condylar offset and tibial slope. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2009, 17, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansara, D.; Markel, D.C. The effect of posterior tibial slope on range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2006, 21, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, K.; Talley, M.C.; Horodyski, M.B.; Indelicato, P.A.; Hartzel, J.S.; Batts, J. Caudal slope of the tibia and its relationship to noncontact injuries to the acl. Am. J. Knee Surg. 1997, 11, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.S.; Lalliss, S.; Garcia, E.S.; DeBerardino, T.M.; Cameron, K.L. The relationship between posterior tibial slope and anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




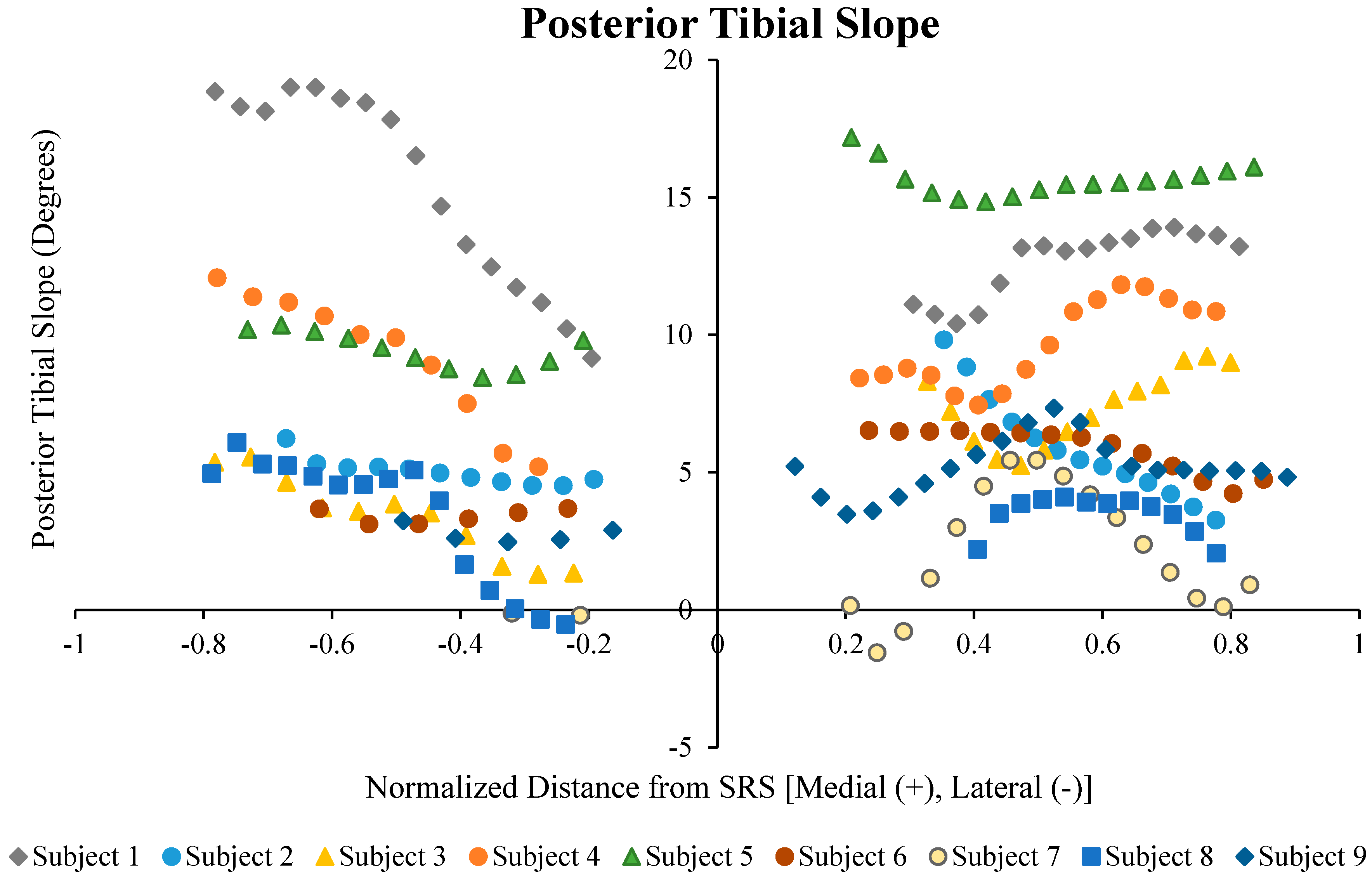
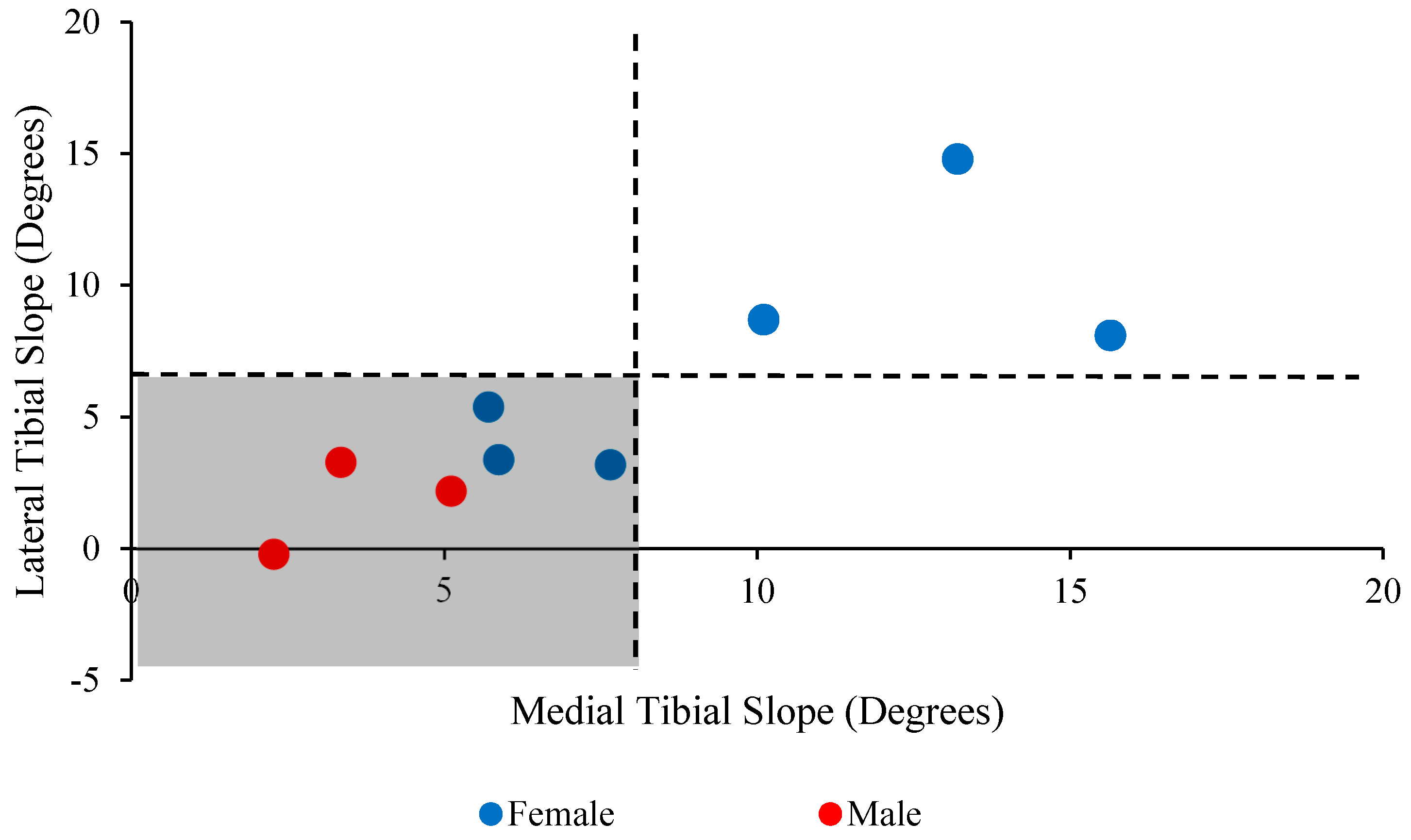
| Subject | Sex | Avg. LTS | Lat. Conc. | Avg. MTS | Med. Conc. | Coronal Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | F | 14.8° (3.5) | 18.5° (2.2) | 13.2° (1.5) | 13.5° (3.2) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Subject 2 | F | 5.4° (1.1) | 5.5° (0.2) | 5.7° (2.1) | 4.4° (3.9) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Subject 3 | F | 3.2° (1.6) | 4.4° (1.3) | 7.6° (1.4) | 8.1° (1.8) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Subject 4 | F | 8.7° (3.1) | 9.5° (1.8) | 10.1° (1.6) | 11.0° (3.6) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Subject 5 | F | 8.1° (4.8) | 7.2° (1.5) | 15.6° (0.6) | 15.7° (1.7) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Subject 6 | F | 3.4° (0.3) | 3.3° (0.3) | 5.9° (0.8) | 5.3° (0.5) | 2.4 (1.6) |
| Subject 7 | M | −0.2° (0.9) | −0.2° (1.2) | 2.3° (0.7) | 2.8° (1.1) | 2.4 (2.8) |
| Subject 8 | M | 3.3° (2.2) | 3.9° (1.0) | 3.3° (1.1) | 3.6° (1.2) | 0.4 (0.2) |
| Subject 9 | M | 2.2° (1.5) | 3.1° (1.0) | 5.1° (1.5) | 5.2° (1.6) | 0.4 (0.2) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amerinatanzi, A.; Summers, R.K.; Ahmadi, K.; Goel, V.K.; Hewett, T.E.; Nyman, E., Jr. Automated Measurement of Patient-Specific Tibial Slopes from MRI. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4030069
Amerinatanzi A, Summers RK, Ahmadi K, Goel VK, Hewett TE, Nyman E Jr. Automated Measurement of Patient-Specific Tibial Slopes from MRI. Bioengineering. 2017; 4(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmerinatanzi, Amirhesam, Rodney K. Summers, Kaveh Ahmadi, Vijay K. Goel, Timothy E. Hewett, and Edward Nyman, Jr. 2017. "Automated Measurement of Patient-Specific Tibial Slopes from MRI" Bioengineering 4, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4030069
APA StyleAmerinatanzi, A., Summers, R. K., Ahmadi, K., Goel, V. K., Hewett, T. E., & Nyman, E., Jr. (2017). Automated Measurement of Patient-Specific Tibial Slopes from MRI. Bioengineering, 4(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4030069





