Machine and Deep Learning on Radiomic Features from Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Breast Cancer Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. Imaging Processing and Radiomic Analysis
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
- Z-score normalization applied to all features to ensure comparability across features and patients.
- Removal of highly correlated features to reduce redundancy.
- Synthetic balancing using the ROSE method to address class imbalance.
- Elastic Net Regularized Logistic Regression (LASSO)
- Random Forest (RF)
- Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM)
- Neural Network (NN)
- Classification and Regression Tree (CART)
- Their established effectiveness in radiomics literature for tabular feature classification.
- The need to compare interpretable models (e.g., LASSO, CART) with higher-capacity learners (e.g., GBM, NN).
- Use of grid search and cross-validation to optimize model performance based on AUC or Accuracy metrics.
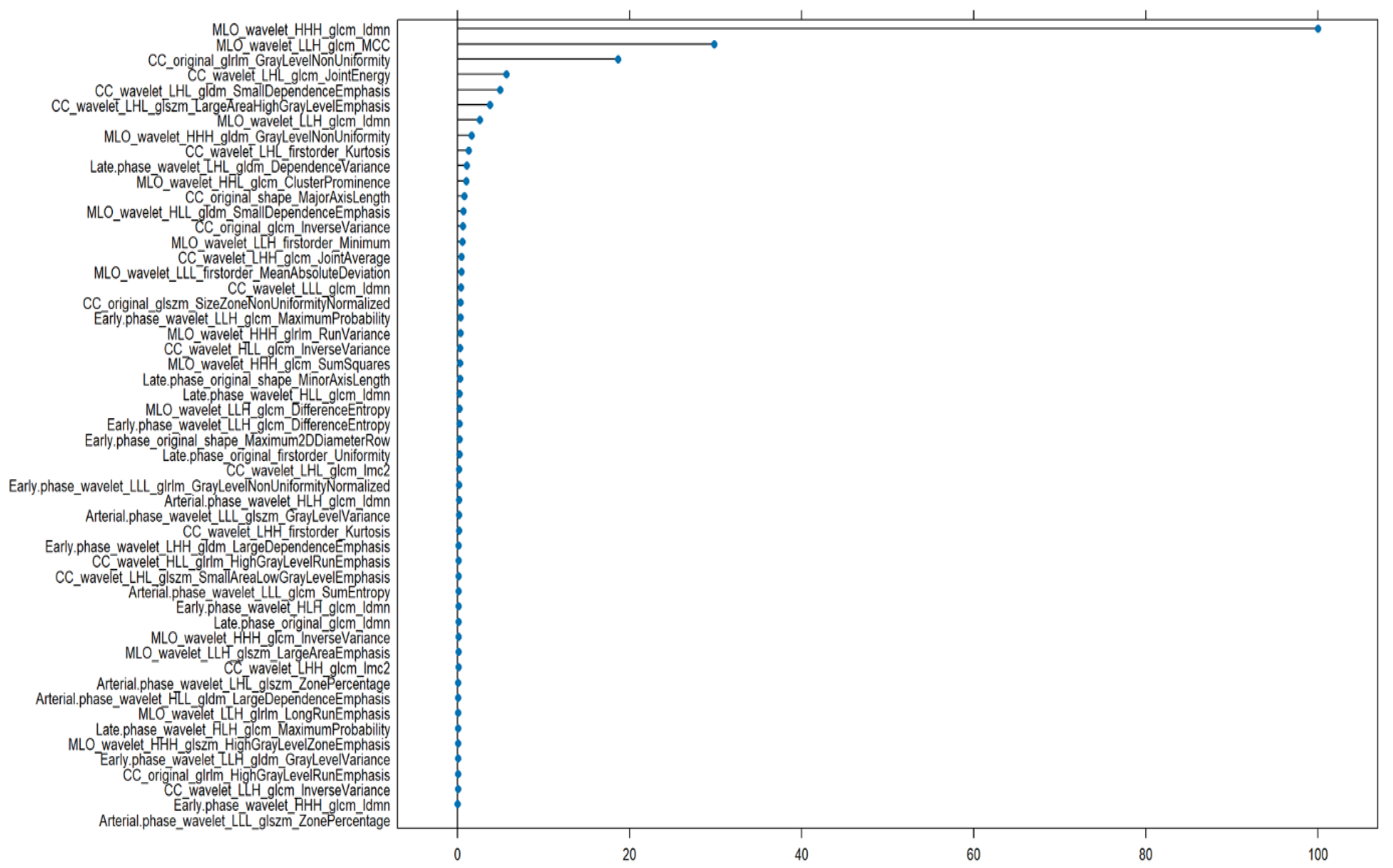
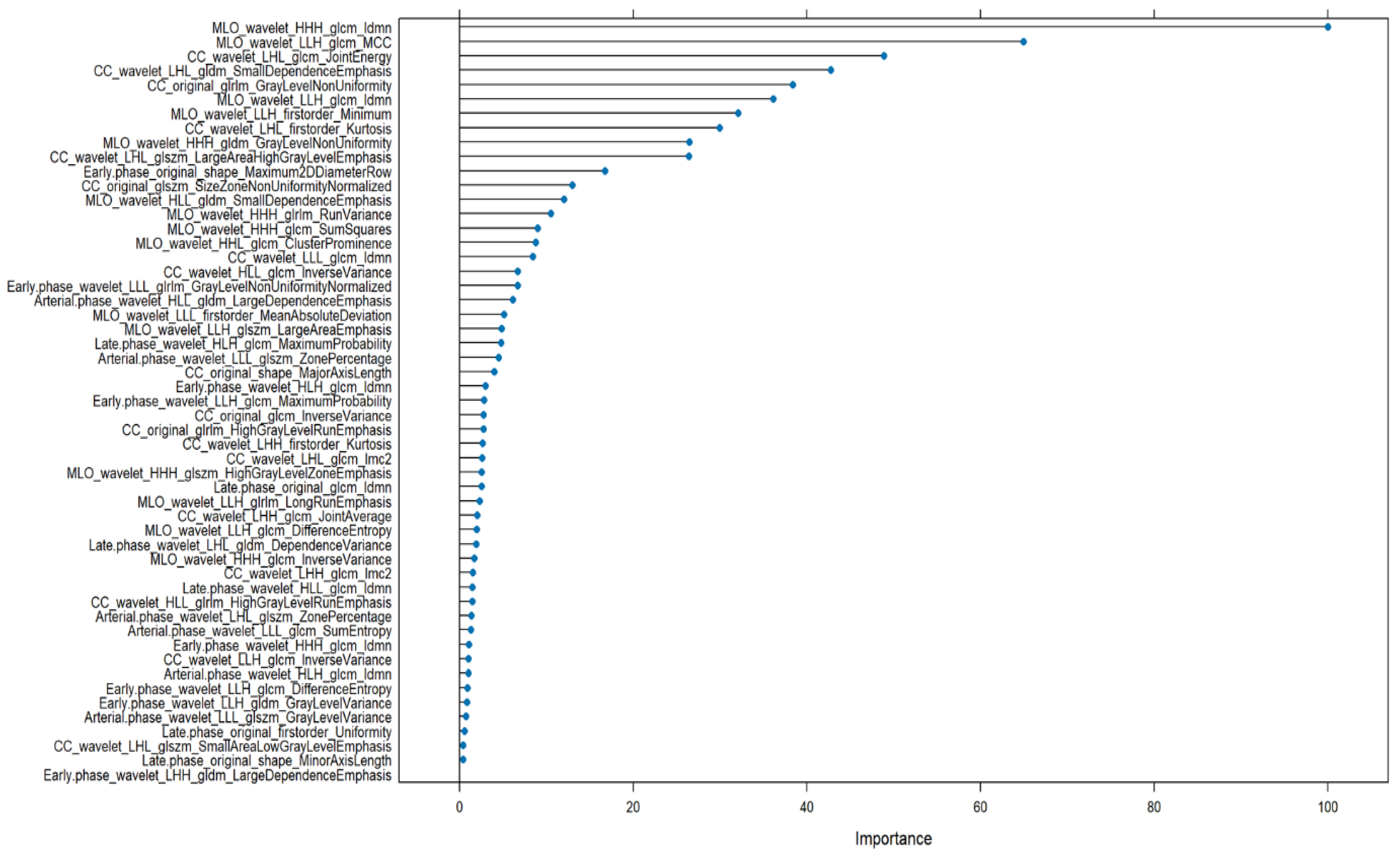
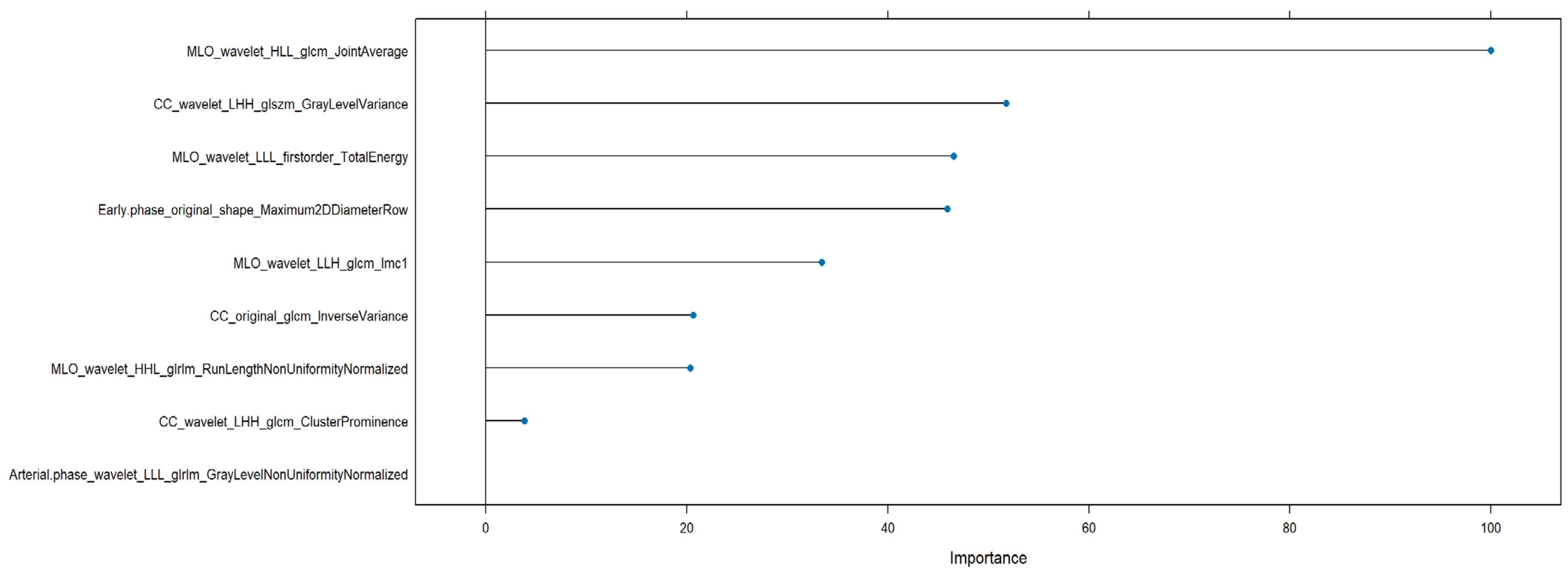
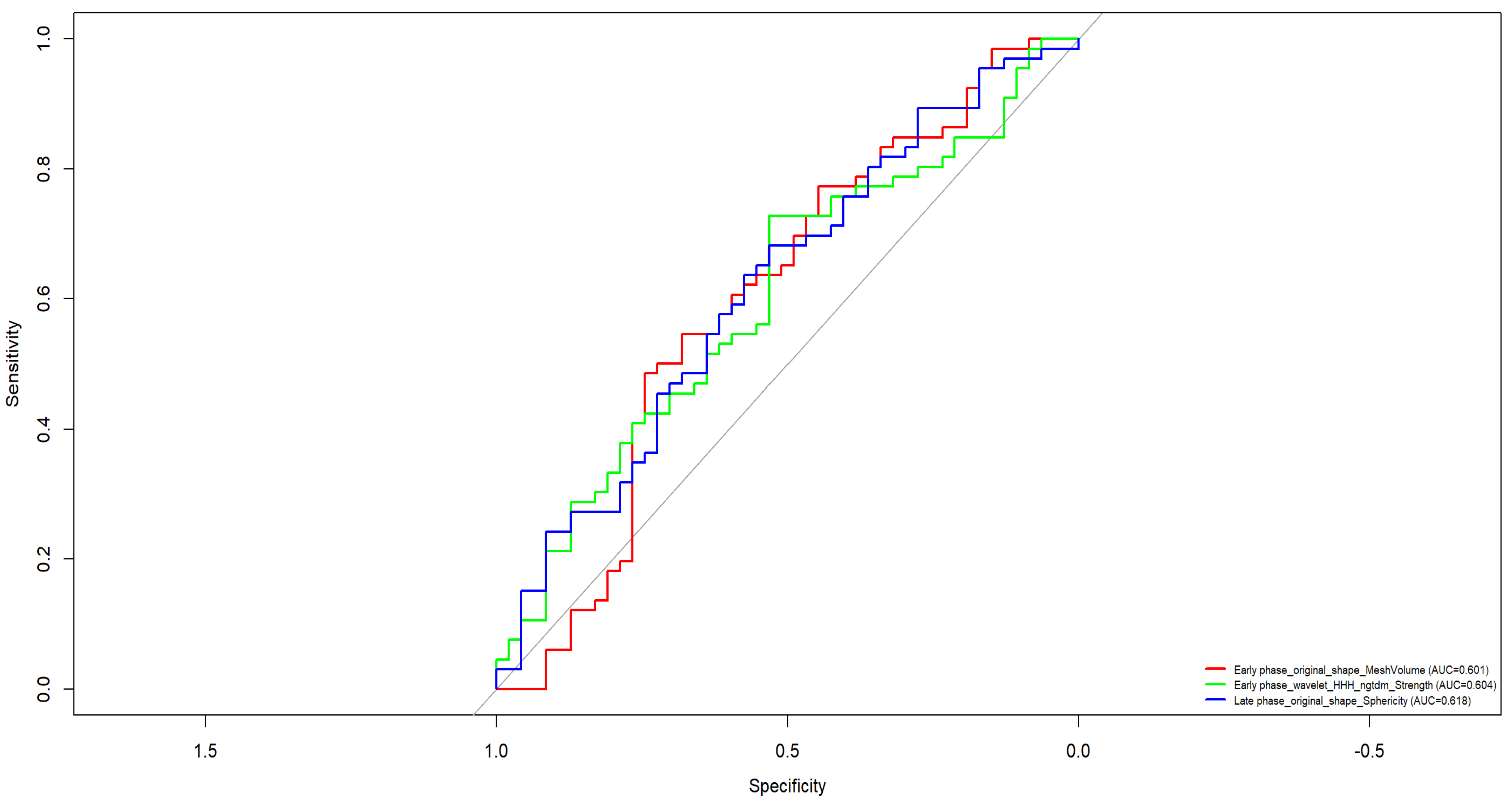
3. Results
- CC_wavelet_LLH_glrlm_LongRunEmphasis (AUC = 0.867)
- MLO_wavelet_LLH_glrlm_LongRunEmphasis (AUC = 0.867)
- CC_wavelet_LLH_firstorder_Kurtosis (AUC = 0.866)
- MLO_wavelet_LLH_glcm_Idmn (AUC = 0.841)
- MLO_wavelet_LLH_glrlm_RunVariance (AUC = 0.828)
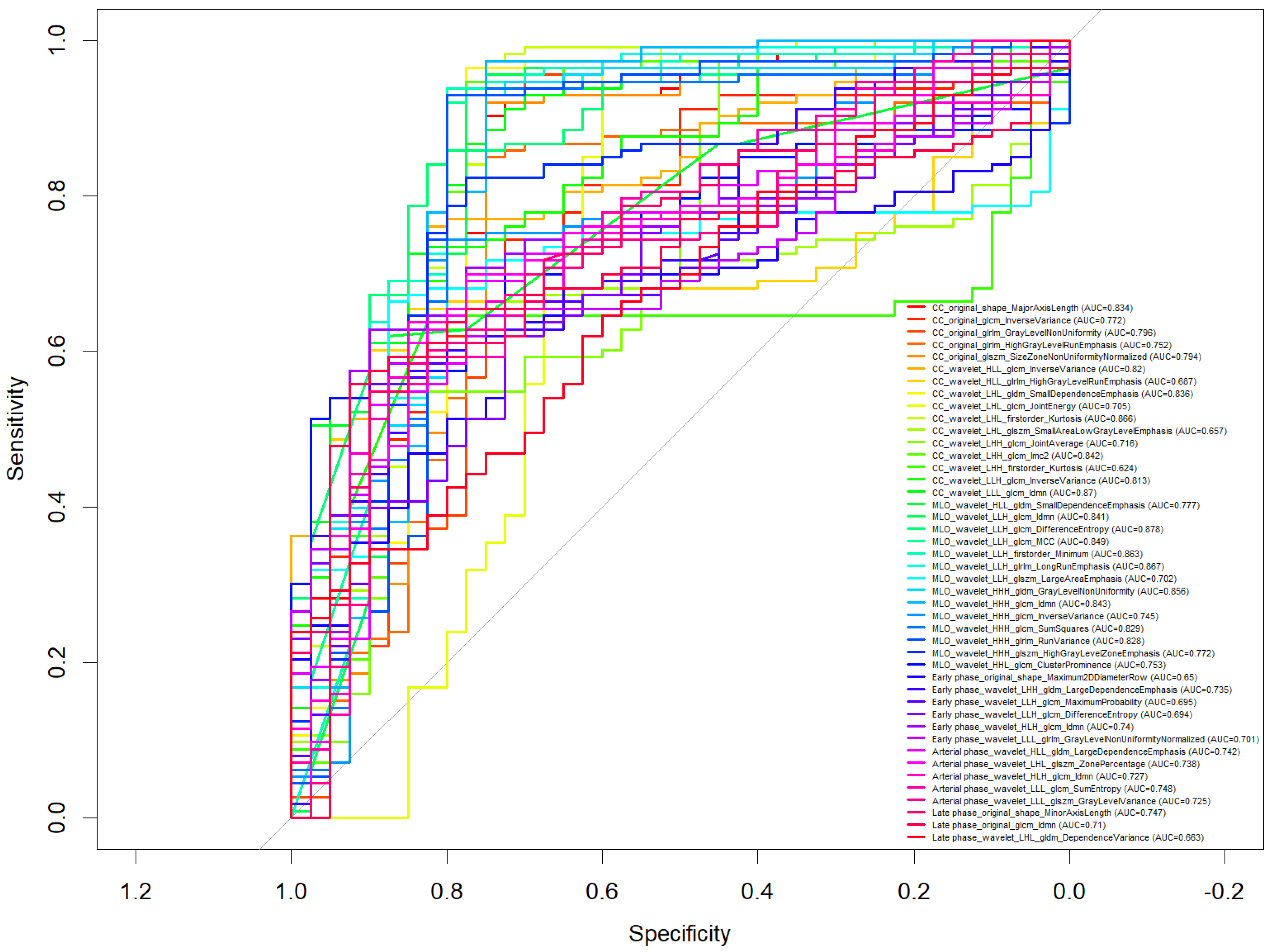
- MLO_wavelet_HHH_glcm_Idmn
- CC_wavelet_LLH_glrlm_LongRunEmphasis
- CC_wavelet_LLH_glcm_Correlation
- CC_wavelet_LLH_glcm_Imc1
- CC_wavelet_LLH_glcm_Imc2
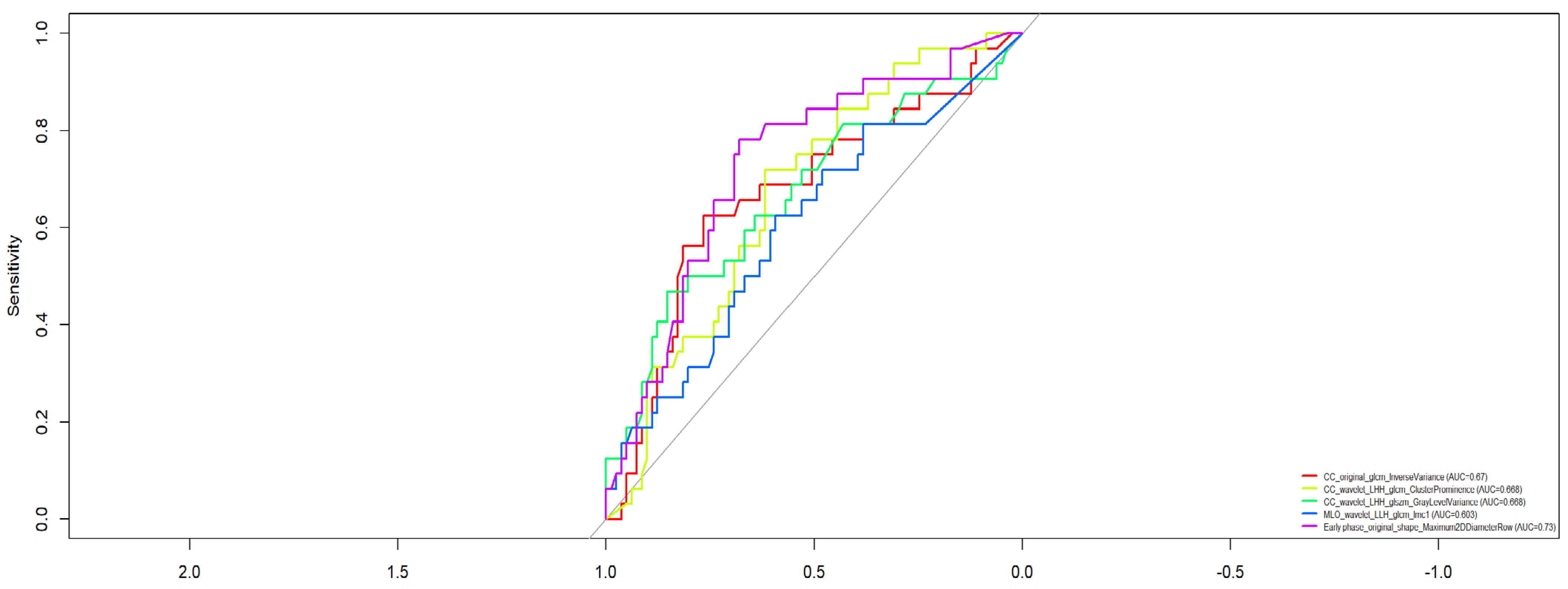
- CC_wavelet_LHH_glcm_ClusterProminence (AUC = 0.688)
- CC_wavelet_LHH_glszm_GrayLevelVariance (AUC = 0.688)
- CC_original_glcm_InverseVariance (AUC = 0.670)
- MLO_wavelet_LLH_glcm_Imc1 (AUC = 0.633)
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AIOM. I Numeri del Cancro in Italia; AIOM: Milano, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2019–2020; American Cancer Society Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures-2019-2020.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Schwab, F.D.; Huang, D.J.; Schmid, S.M.; Schötzau, A.; Güth, U. Self-detection and clinical breast examination: Comparison of the two “classical” physical examination methods for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywang-Köbrunner, S.; Viehweg, P.; Heinig, A.; Küchler, C. Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breast: Accuracy, value, controversies, solutions. Eur. J. Radiol. 1997, 24, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessouky, B.; Elsaid, N.; Shaaban, Y. Role of contrast-enhanced digital mammography in evaluation of breast lesions. Menoufia Med. J. 2017, 30, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, T.C.; Patel, B.K.; Pizzitola, V.J. Navigating contrast-enhanced digital mammography. Appl. Radiol. 2017, 46, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, V.; Houssami, N.; Ghirardi, M.; Ferrari, A.; Speziani, M.; Bellarosa, S.; Remida, G.; Gasparotti, C.; Galligioni, E.; Ciatto, S. Evidence of the effect of adjunct ultrasound screening in women with mammography-negative dense breasts: Interval breast cancers at 1year follow-up. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, M.R. Imaging the dense breast. Appl. Radiol. 2004, 33, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saslow, D.; Boetes, C.; Burke, W.; Harms, S.; Leach, M.O.; Lehman, C.D.; Morris, E.; Pisano, E.; Schnall, M.; Sener, S.; et al. American Cancer Society Guidelines for Breast Screening with MRI as an Adjunct to Mammography. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2007, 57, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Maglogiannis, I.; Zafiropoulos, E.; Anagnostopoulos, I. An intelligent system for automated breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis using SVM based classifiers. Appl. Intell. 2007, 30, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A.; Fusco, R.; Di Bernardo, E.; Petrosino, T.; Barretta, M.L.; Porto, A.; Granata, V.; Di Bonito, M.; Fanizzi, A.; Massafra, R.; et al. Prediction of Breast Cancer Histological Outcome by Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence Analysis in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography. Cancers 2022, 14, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Hwangbo, L.; Suh, H.B.; Son, Y.; Nickel, M.D.; Grimm, R. Ultrafast Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Using Compressed Sensing: Associations of Early Kinetic Parameters With Prognostic Factors of Breast Cancer. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, X. Breast magnetic resonance imaging: Kinetic curve assessment. Gland. Surg. 2013, 2, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillon-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yin, J. Radiomics of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parametric maps and apparent diffusion coefficient maps to predict Ki-67 status in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 847880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, L.; Pesapane, F.; Bozzini, A.C.; Latronico, A.; Rotili, A.; Ferrari, F.; Signorelli, G.; Raimondi, S.; Vignati, S.; Gaeta, A.; et al. Prediction of the Malignancy of a Breast Lesion Detected on Breast Ultrasound: Radiomics Applied to Clinical Practice. Cancers 2023, 15, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Kong, H.; Hu, N.; Wang, P.; Zuo, X.; Fan, W.; Yao, Y.; et al. Radiogenomic analysis of prediction HER2 status in breast cancer by linking ultrasound radiomic feature module with biological functions. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Lucas-Quesada, F.A.; DeBruhl, N.D.; Sayre, J.; Farria, D.; Gorczyca, D.P.; Bassett, L.W. Multifeature analysis of Gd-enhanced MR images of breast lesions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 7, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomweg, T.W.; Buscema, P.M.; Kauczor, H.U.; Teifke, A.; Intraligi, M.; Terzi, S.; Heussel, C.P.; Achenbach, T.; Rieker, O.; Mayer, D.; et al. Improved artificial neural networks in prediction of malignancy of lesions in contrast-enhanced MR-mammography. Med. Phys. 2003, 30, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, D.J.; Geetha, K. Mass classification in breast DCE-MR images using an artificial neural network trained via a bee colony optimization algorithm. Science 2013, 39, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A.; Fusco, R.; Barretta, M.L.; Granata, V.; Mattace Raso, M.; Porto, A.; Sorgente, E.; Fanizzi, A.; Massafra, R.; Lafranceschina, M.; et al. Radiomics and artificial intelligence analysis by T2-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to predict Breast Cancer Histological Outcome. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 1347–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrillo, A.; Fusco, R.; Petrosino, T.; Vallone, P.; Granata, V.; Rubulotta, M.R.; Pariante, P.; Raiano, N.; Scognamiglio, G.; Fanizzi, A.; et al. A multicentric study of radiomics and artificial intelligence analysis on contrast enhanced mammography to identify different histotypes of breast cancer. Radiol. Med. 2024, 129, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhard, A.; Tanner, C.; Hayes, C.; Hawkes, D.J.O.; Leach, M. The UK MRI Breast Screening Study Comparison between radiological and artificial neural network diagnosis in clinical screening. Physiol. Meas. 2002, 23, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, L.; Yin, J. Intratumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics Based on Functional Parametric Maps from Breast DCE-MRI for Prediction of HER-2 and Ki-67 Status. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.K.; Kim, J.Y. Dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MRI of estrogen receptor-positive invasive breast cancers: Associations between quantitative MR parameters and Ki-67 proliferation status. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Piccirillo, A.; Sansone, M.; Granata, V.; Vallone, P.; Barretta, M.L.; Petrosino, T.; Siani, C.; Di Giacomo, R.; Petrillo, A.; et al. Radiomic and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics, Morphological and Dynamic Perfusion Features Extracted by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Classification of Breast Lesions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Forgia, D.; Fanizzi, A.; Campobasso, F.; Bellotti, R.; Didonna, V.; Lorusso, V.; Moschetta, M.; Massafra, R.; Tam-borra, P.; Tangaro, S.; et al. Radiomic Analysis in Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography for Predicting Breast Cancer Histological Outcome. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.A.; Leithner, D.; Sung, J.; Avendano, D.; Morris, E.A.; Pinker, K.; Jochelson, M.S. Radiomics for Tumor Characterization in Breast Cancer Patients: A Feasibility Study Comparing Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Magnetic Reso-nance Imaging. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, A.; Bini, F.; Giovagnoli, E.; Dimarco, M.; Lauciello, N.; Narbonese, D.; Pasini, G.; Marinozzi, F.; Russo, G.; D’Angelo, I. Comparative Evaluation of Machine Learning-Based Radiomics and Deep Learning for Breast Lesion Classification in Mammography. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leithner, D.; Horvat, J.V.; Marino, M.A.; Bernard-Davila, B.; Jochelson, M.S.; Ochoa-Albiztegui, R.E.; Martinez, D.F.; Morris, E.A.; Thakur, S.; Pinker, K. Radiomic signatures with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of breast cancer receptor status and molecular subtypes: Initial results. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, B.; Baessler, B.; Bakas, S.; Cuocolo, R.; Fedorov, A.; Maier-Hein, L.; Mercaldo, N.; Müller, H.; Orlhac, F.; Pinto Dos Santos, D.; et al. CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): A step-by-step reporting guideline for authors and reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII. Insights Imaging. 2023, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Statist. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, P.; Buadu, L.D.; Naderimansh, H. Feature extraction and classification of breast cancer on dynamic magnetic resonance imaging using artificial neural network. Cancer Lett. 2001, 171, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agner, S.C.; Soman, S.; Libfeld, E.; McDonald, M.; Thomas, K.; Englander, S.; Rosen, M.A.; Chin, D.; Nosher, J.; Madabhushi, A. Textural Kinetics: A Novel Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE)-MRI Feature for Breast Lesion Classification. J. Digit. Imaging 2010, 24, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levman, J.; Leung, T.; Causer, P.; Plewes, D.; Martel, A.L. Classification of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance breast lesions by support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Piccirillo, A.; Sansone, M.; Granata, V.; Rubulotta, M.R.; Petrosino, T.; Barretta, M.L.; Vallone, P.; Di Giacomo, R.; Esposito, E.; et al. Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence Analysis with Textural Metrics Extracted by Contrast-Enhanced Mammography in the Breast Lesions Classification. Diagnostics 2021, 30, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizzi, A.; Losurdo, L.; Basile, T.M.A.; Bellotti, R.; Bottigli, U.; Delogu, P.; Diacono, D.; Didonna, V.; Fausto, A.; Lombardi, A.; et al. Fully Automated Support System for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Images. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massafra, R.; Bove, S.; Lorusso, V.; Biafora, A.; Comes, M.C.; Didonna, V.; Diotaiuti, S.; Fanizzi, A.; Nardone, A.; Nolasco, A.; et al. Radiomic Feature Reduction Approach to Predict Breast Cancer by Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Images. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losurdo, L.; Fanizzi, A.; Basile, T.M.A.; Bellotti, R.; Bottigli, U.; Dentamaro, R.; Didonna, V.; Lorusso, V.; Massafra, R.; Tam-borra, P.; et al. Radiomics Analysis on Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Images for Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Pilot Study. Entropy 2019, 21, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Samy, M.; Ali, A.M.; Hassan, R.A. Architectural distortion outcome: Digital breast tomosynthesis-detected versus dig-ital mammography-detected. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, A.; Orlandi, A.; Bufi, E.; Mercogliano, S.; Belli, P.; Manfredi, R. Automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) compared to handheld ultrasound (HHUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) in the early assessment of breast cancer during neoadjuvant chemotherapy: An emerging role to monitoring tumor response? Radiol. Med. 2021, 126, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, M.; Fusco, R.; Grassi, F.; Gatta, G.; Belfiore, M.P.; Angelone, F.; Ricciardi, C.; Ponsiglione, A.M.; Amato, F.; Galdiero, R.; et al. Machine Learning Approaches with Textural Features to Calculate Breast Density on Mammography. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Raiano, N.; Raiano, C.; Maio, F.; Vallone, P.; Mattace Raso, M.; Setola, S.V.; Granata, V.; Rubulotta, M.R.; Barretta, M.L.; et al. Evaluation of average glandular dose and investigation of the relationship with compressed breast thickness in dual energy contrast enhanced digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 126, 108912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicosia, L.; Mariano, L.; Gaeta, A.; Raimondi, S.; Pesapane, F.; Corso, G.; De Marco, P.; Origgi, D.; Sangalli, C.; Bianco, N.; et al. Preliminary Evaluation of Radiomics in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography for Prognostic Prediction of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Pan, H.; Huang, B.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B. Deep learning radiomic analysis of DCE-MRI combined with clinical characteristics predicts pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1041142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, L.; Hu, Y.; Shao, N.; Lin, Y.; He, S.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y. Multi-Parametric MRI-Based Radiomics Models for Predicting Molecular Subtype and Androgen Receptor Expression in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 706733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, V.; Fusco, R.; Avallone, A.; Catalano, O.; Filice, F.; Leongito, M.; Palaia, R.; Izzo, F.; Petrillo, A. Major and ancillary magnetic resonance features of LI-RADS to assess HCC: An overview and update. Infect. Agents Cancer 2017, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, V.; Fusco, R.; Setola, S.V.; De Muzio, F.; Dell’ Aversana, F.; Cutolo, C.; Faggioni, L.; Miele, V.; Izzo, F.; Petrillo, A. CT-Based Radiomics Analysis to Predict Histopathological Outcomes Following Liver Resection in Colorectal Liver Metastases. Cancers 2022, 14, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Filice, S.; Granata, V.; Catalano, O.; Amato, D.M.; Di Bonito, M.; D’Aiuto, M.; Capasso, I.; Rinaldo, M.; et al. Integration of DCE-MRI and DW-MRI Quantitative Parameters for Breast Lesion Classification. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 237863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.J.; Su, G.H.; You, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Shao, Z.M. Radiomics in breast cancer: Current advances and future directions. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, T.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Z. Radiomic Machine Learning in Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer: Prediction of Ki-67 Expression Level Based on Radiomics of DCE-MRI. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338241288751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, J.; Peng, Y.; Shang, T.; Pan, T. Radiomics Integration of Mammography and DCE-MRI for Predicting Molecular Subtypes in Breast Cancer Patients. Breast Cancer 2025, 17, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Settings | T1-Weigthed DCE | Units |
|---|---|---|
| TR/TE/FA | 4.4–5.1/2.0–2.4/15 | ms/msdeg/ |
| FOV | 250–500 × 450–500 | mm2 |
| Matrix size | 168–384 × 300–384 | pixel |
| Slice thickness | 3 | mm |
| Intersection gap | 0 | mm |
| Pixel spacing | 0.89–1 × 0.89–1 | mm2 |
| Model | Tuned Hyperparameters | Search Strategy | Selection Criterion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic Net Logistic Regression | α = 0.5 (Elastic Net) λ ∈ [0.001, 0.1] (100 values) | Cross-validation via cv.glmnet() | Minimum cross-validated error (lambda.min) |
| Random Forest | mtry = √(number of features) ntree = 200 min.node.size = {5, 10, 20} | Grid search | Highest AUC |
| Gradient Boosting Machine | n.trees = {50, 100, 200} interaction.depth = {2, 4, 6, 8} shrinkage = 0.01 n.minobsinnode = 10 | Grid search | Highest AUC |
| Neural Network | size = {2, 4, 6} decay = {0.1, 0.5} | Grid search | Highest Accuracy |
| Decision Tree (CART) | cp selected via pruning minsplit = 15 maxdepth = 15 | Cross-validation with cost-complexity pruning | Lowest cross-validated error |
| Model | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.844 | 0.879 | 0.75 | 0.906 | 0.692 | 0.905 |
| LASSO | 0.867 | 0.909 | 0.75 | 0.909 | 0.75 | 0.808 |
| GBM | 0.911 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.914 | 0.9 | 0.907 |
| NN | 0.844 | 0.879 | 0.75 | 0.906 | 0.692 | 0.861 |
| CART | 0.822 | 0.879 | 0.667 | 0.879 | 0.667 | 0.798 |
| Model | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.818 | 0.333 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.887 |
| LASSO | 0.818 | 0.667 | 0.875 | 0.667 | 0.875 | 0.741 |
| GBM | 0.818 | 0.333 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.843 |
| NN | 0.848 | 0.556 | 0.958 | 0.833 | 0.852 | 0.741 |
| CART | 0.758 | 0.222 | 0.958 | 0.667 | 0.767 | 0.734 |
| Model | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.485 | 0.105 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.452 | 0.701 |
| LASSO | 0.545 | 0.737 | 0.286 | 0.583 | 0.444 | 0.53 |
| GBM | 0.424 | 0.0 | 1.0 | NA | 0.424 | 0.658 |
| NN | 0.727 | 0.842 | 0.571 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.669 |
| CART | 0.636 | 1.0 | 0.143 | 0.613 | 1.0 | 0.571 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusco, R.; Granata, V.; Petrosino, T.; Vallone, P.; Iasevoli, M.A.D.; Mattace Raso, M.; Setola, S.V.; Pupo, D.; Ferrara, G.; Fanizzi, A.; et al. Machine and Deep Learning on Radiomic Features from Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Breast Cancer Characterization. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090952
Fusco R, Granata V, Petrosino T, Vallone P, Iasevoli MAD, Mattace Raso M, Setola SV, Pupo D, Ferrara G, Fanizzi A, et al. Machine and Deep Learning on Radiomic Features from Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Breast Cancer Characterization. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090952
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusco, Roberta, Vincenza Granata, Teresa Petrosino, Paolo Vallone, Maria Assunta Daniela Iasevoli, Mauro Mattace Raso, Sergio Venanzio Setola, Davide Pupo, Gerardo Ferrara, Annarita Fanizzi, and et al. 2025. "Machine and Deep Learning on Radiomic Features from Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Breast Cancer Characterization" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090952
APA StyleFusco, R., Granata, V., Petrosino, T., Vallone, P., Iasevoli, M. A. D., Mattace Raso, M., Setola, S. V., Pupo, D., Ferrara, G., Fanizzi, A., Massafra, R., Lafranceschina, M., La Forgia, D., Greco, L., Ferranti, F. R., De Soccio, V., Vidiri, A., Botta, F., Dominelli, V., ... Petrillo, A. (2025). Machine and Deep Learning on Radiomic Features from Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Breast Cancer Characterization. Bioengineering, 12(9), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090952










