Improving Efficacy and Reducing Systemic Toxicity: An In Vitro Study on the Role of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofiber Membrane for Localized Melanoma Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
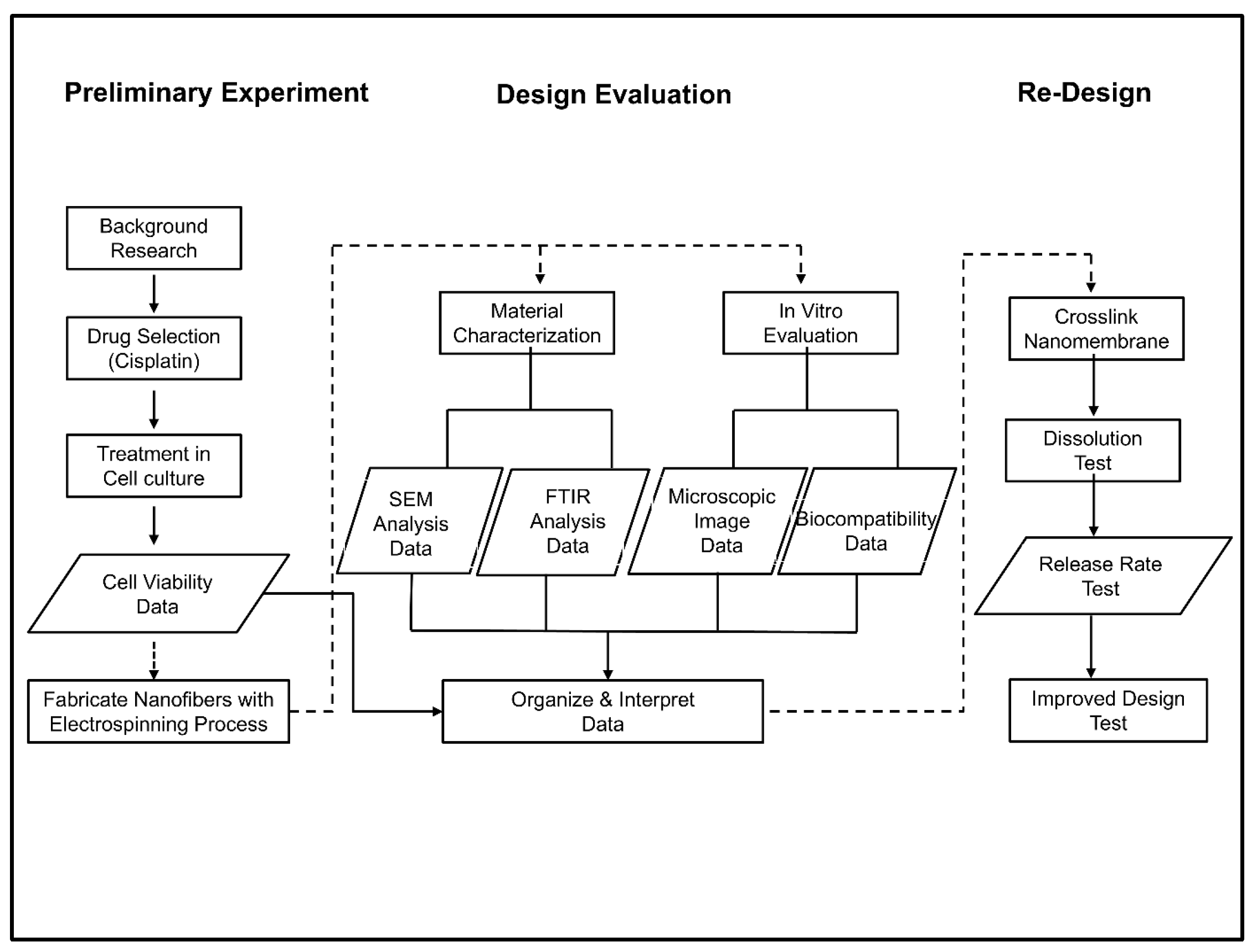
2.1. Design Plan
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. CCK-8 Cell Viability Assay
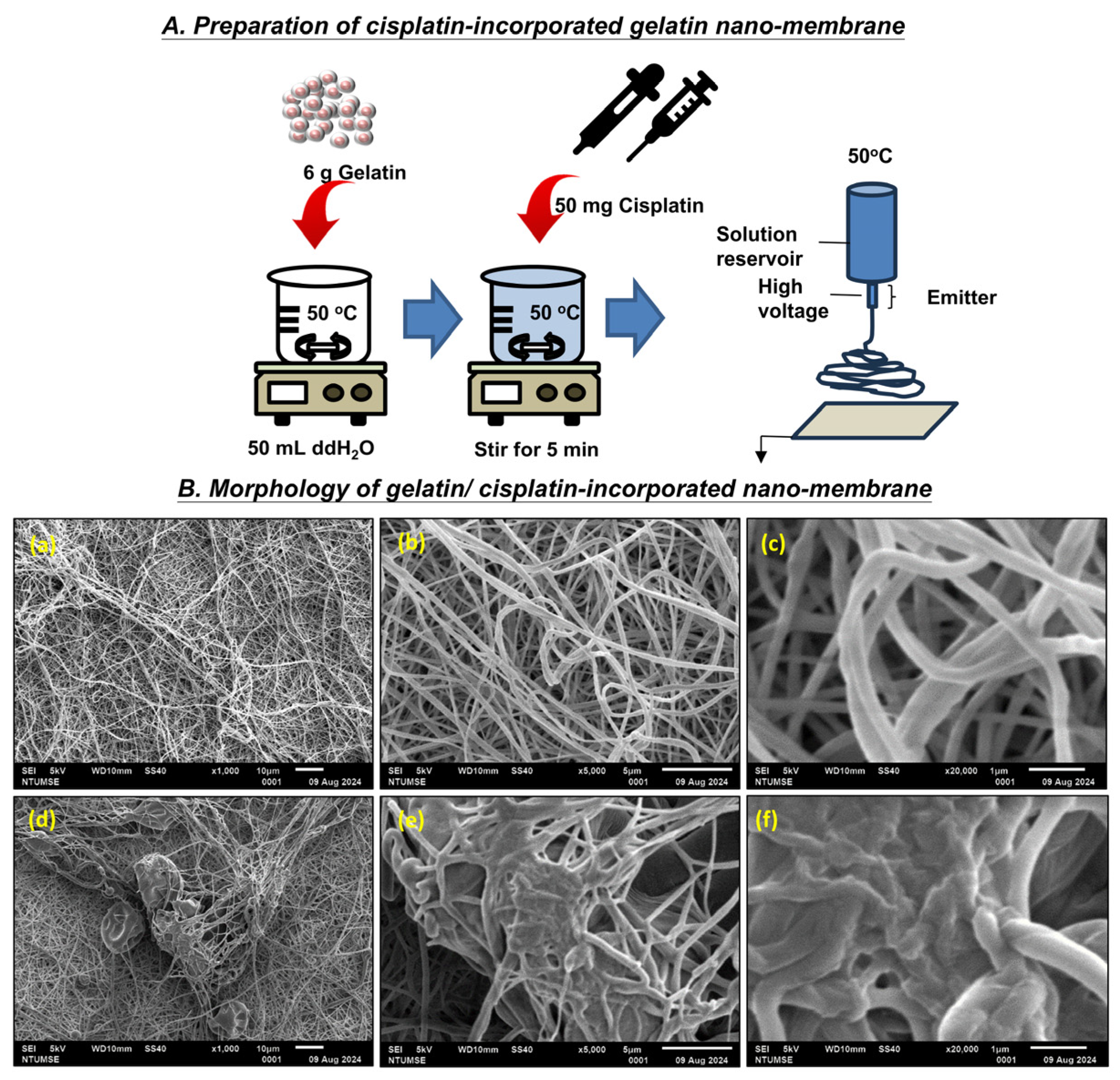
2.4. Electrospinning
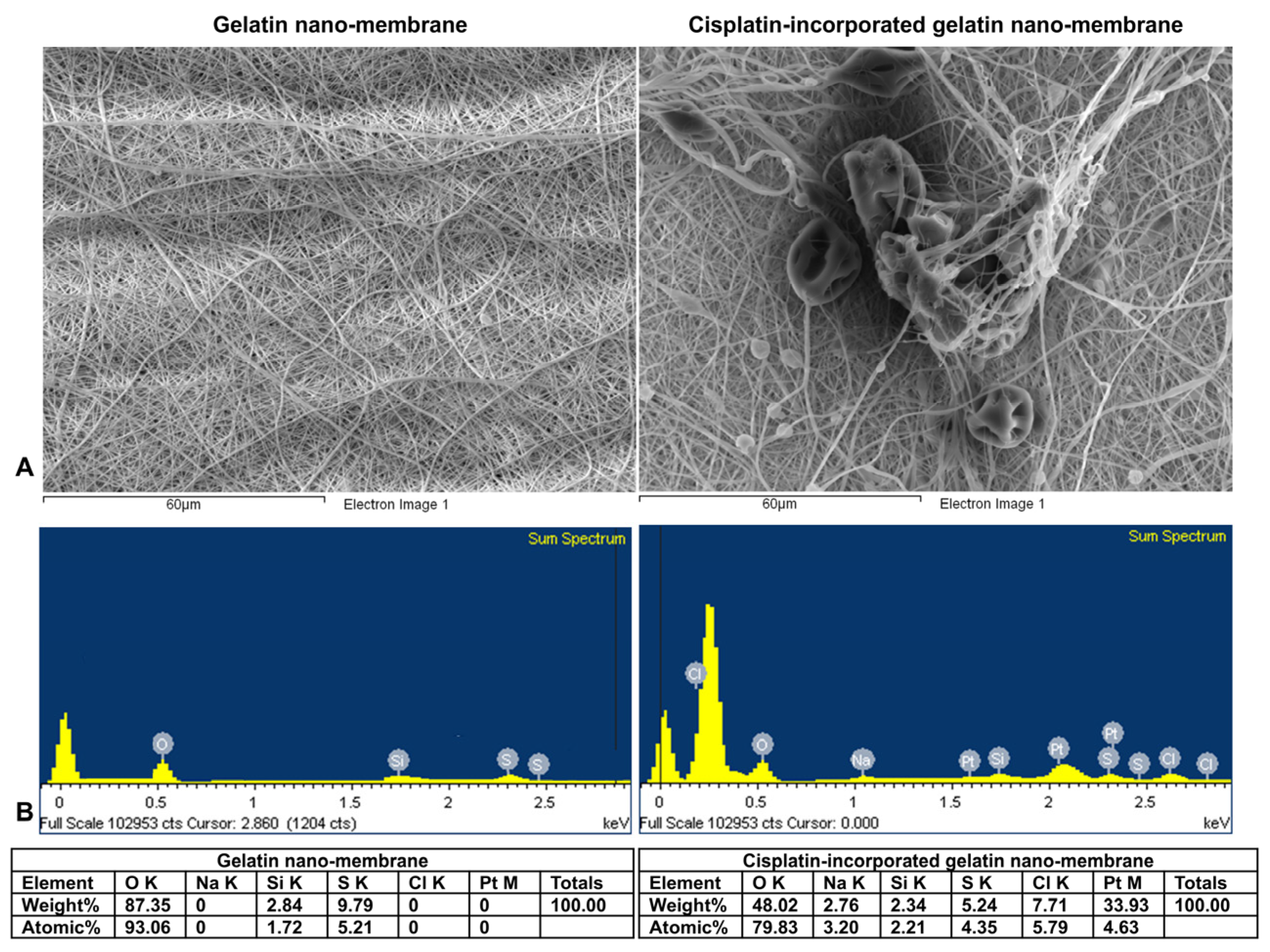
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDX)
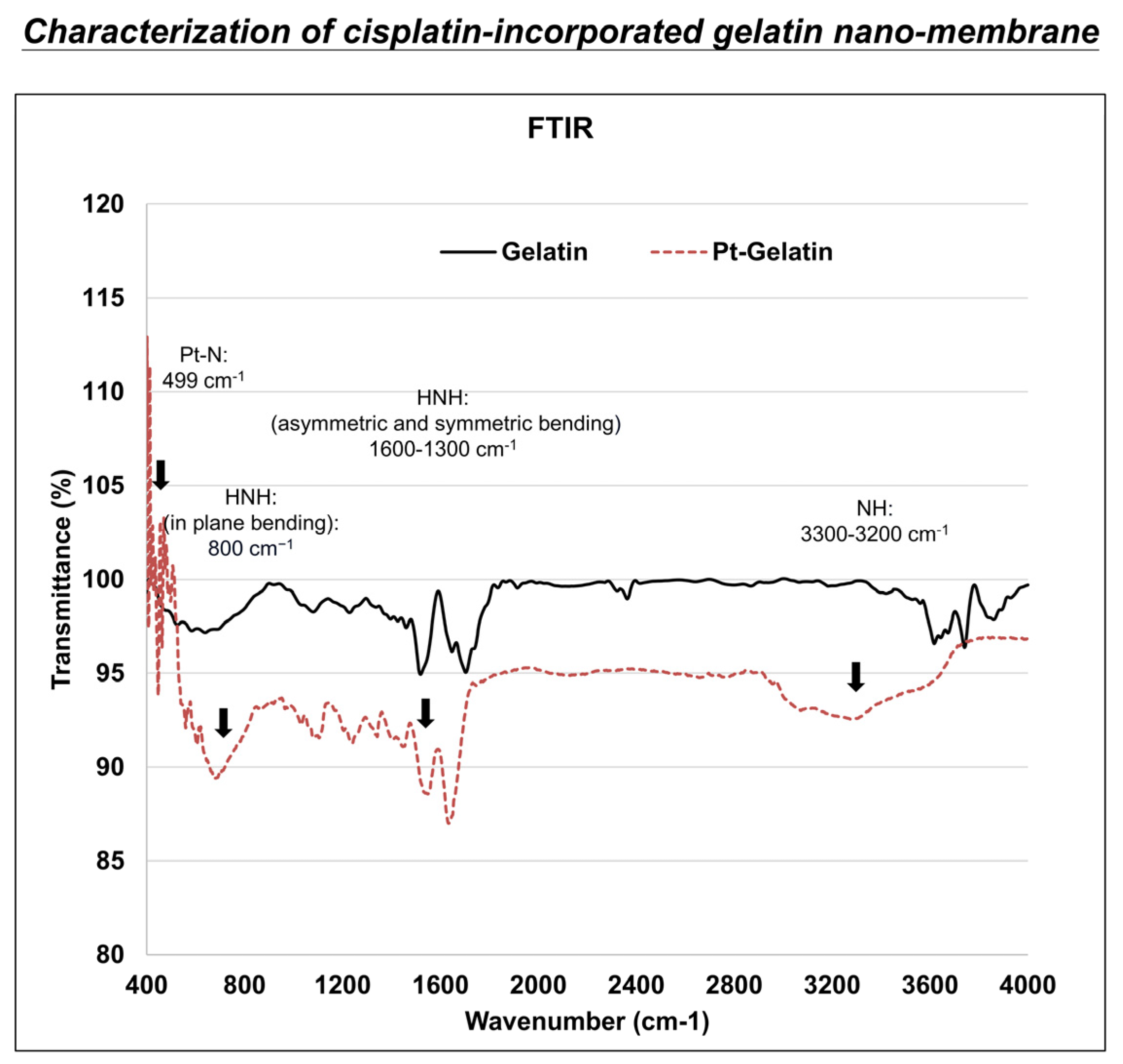
2.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.7. Cell Viability with Cisplatin-Incorporated Nanomembrane
2.8. Release Rate Studies
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
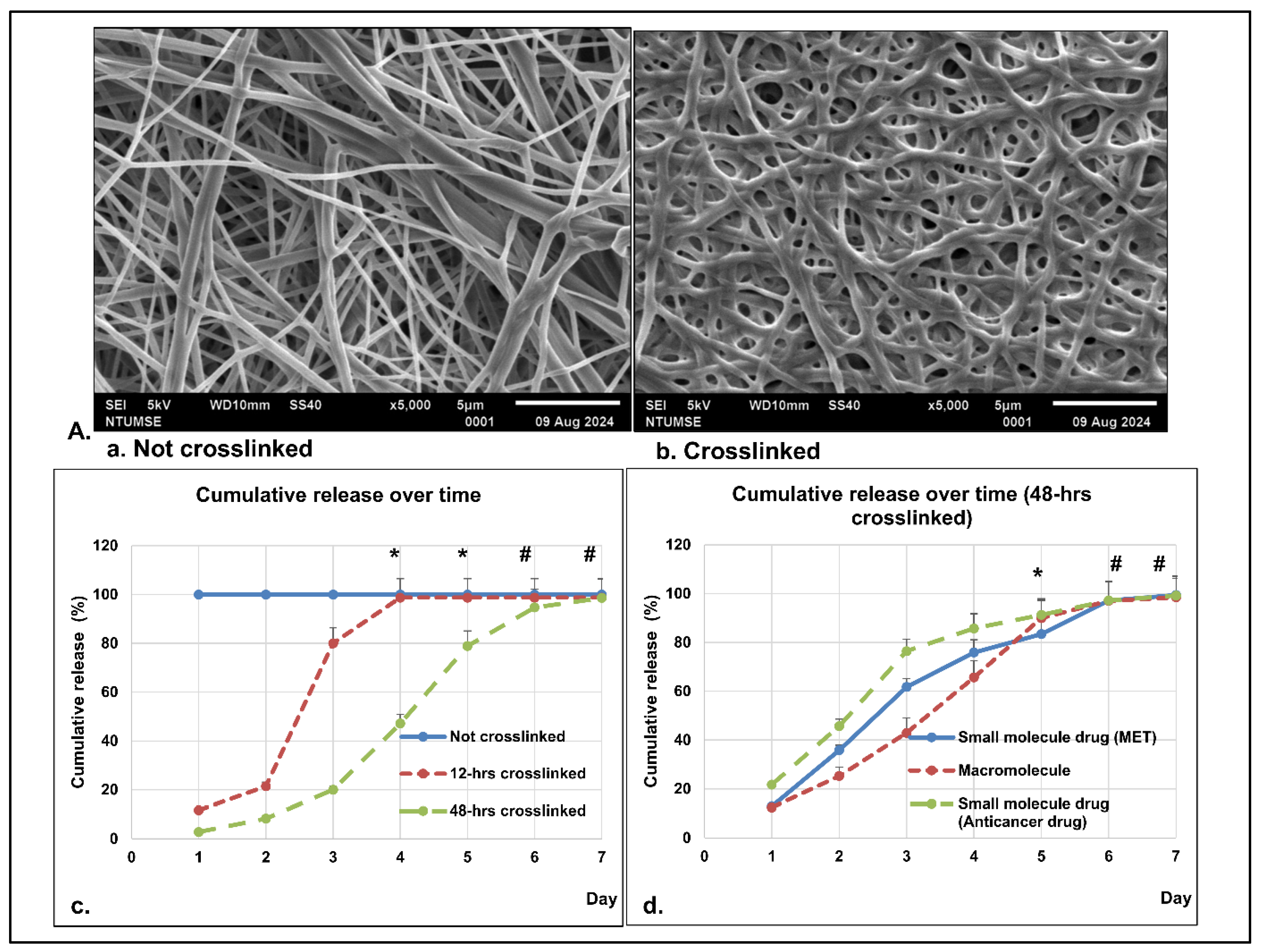
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy–Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) Analysis
3.1.1. Morphology
3.1.2. Characterization of Materials
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
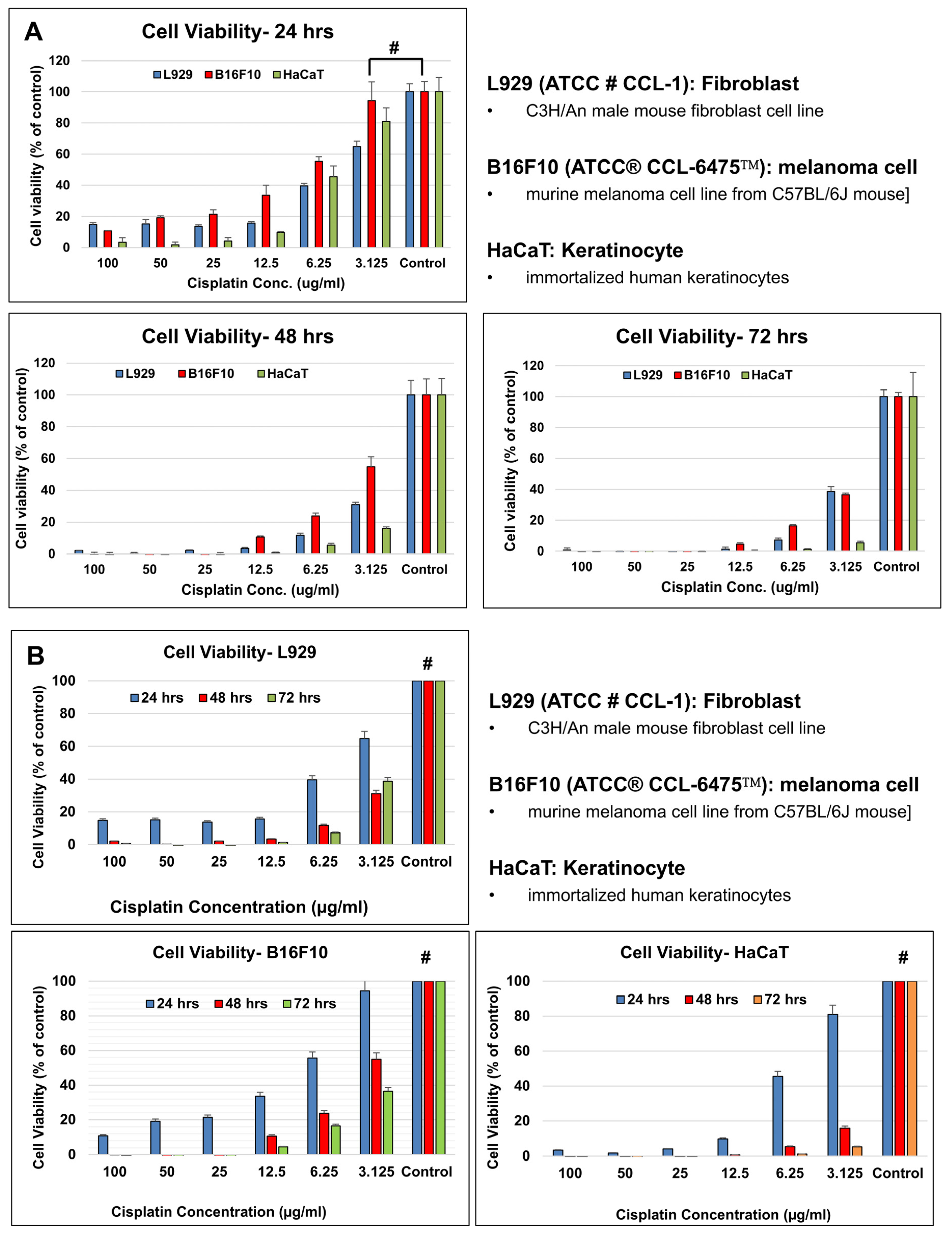
Cell Viability Assay
3.3. In Vitro Evaluation of Nanomembranes
3.3.1. Material Biocompatibility
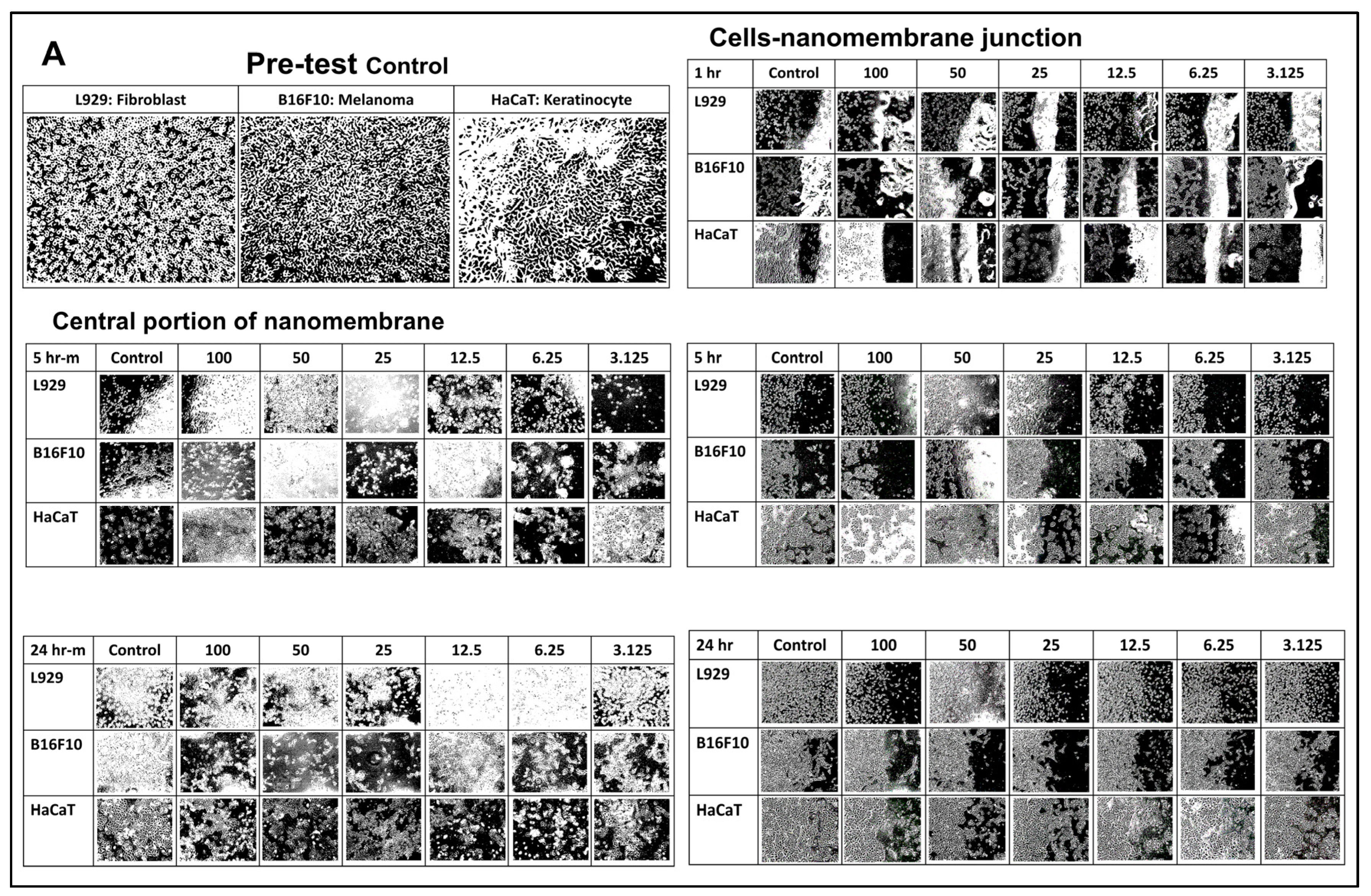
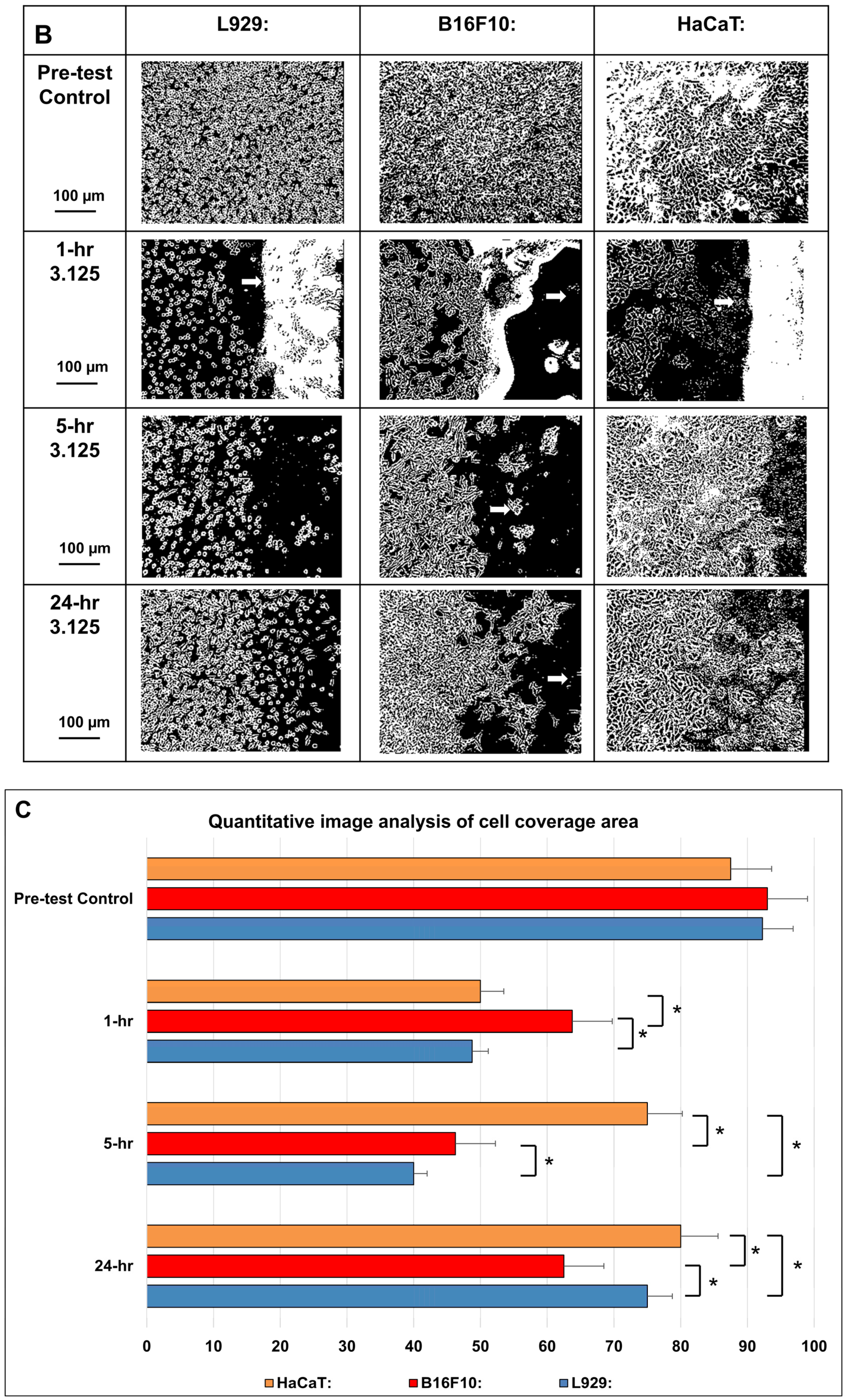
3.3.2. Cell Viability with Cisplatin-Incorporated Nanomembrane: 2D Qualitative Study
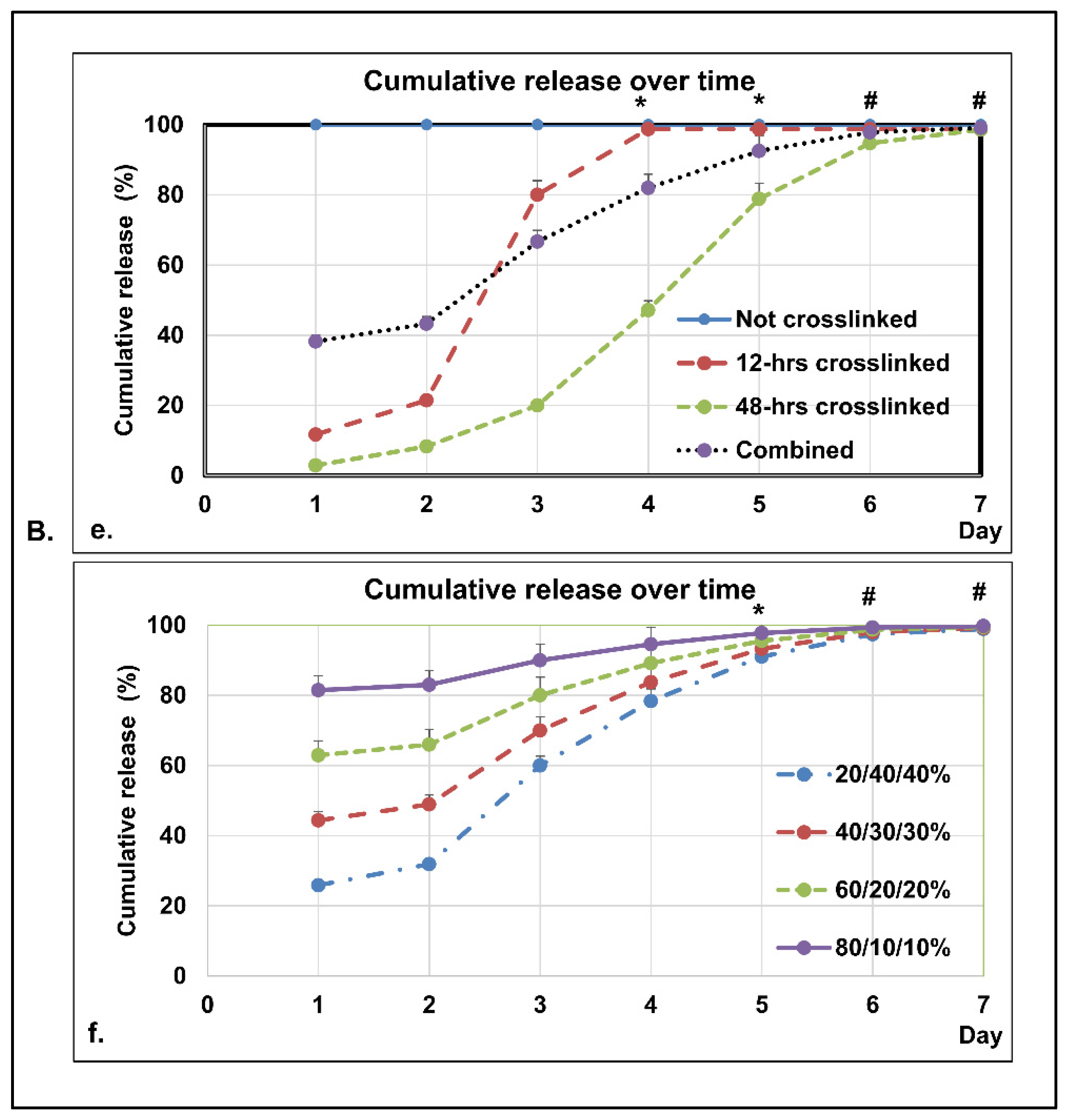
3.3.3. In Vitro Dissolution Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dzwierzynski, W.W. Managing Malignant Melanoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 446e–460e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Swetter, S.M.; Menzies, A.M.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Scolyer, R.A. Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet 2023, 402, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadadu, R.P.; Wei, M.L. Ultraviolet A radiation exposure and melanoma: A review. Melanoma Res. 2022, 32, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.; Ware, O.; Bosenberg, M. Genetics of metastasis: Melanoma and other cancers. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2018, 35, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Vaccarella, S.; Meheus, F.; Cust, A.E.; de Vries, E.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Cutaneous Melanoma in 2020 and Projections to 2040. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, J.P.; Joshua, A.M.; da Silva, I.P.; Dummer, R.; Goldinger, S.M. Chemotherapy in Cutaneous Melanoma: Is There Still a Role? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavri, S.N.; Clune, J.; Ariyan, S.; Narayan, D. Malignant Melanoma: Beyond the Basics. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 330e–340e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.; Karapetyan, L.; Kirkwood, J.M. Immunotherapy in Melanoma: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Cancers 2023, 15, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaft, N.; Dörrie, J.; Schuler, G.; Schuler-Thurner, B.; Sallam, H.; Klein, S.; Eisenberg, G.; Frankenburg, S.; Lotem, M.; Khatib, A. The future of affordable cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1248867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Haldar Neer, A.H. Chemotherapy. Cancer Treat. Res. 2023, 185, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livshits, Z.; Rao, R.B.; Smith, S.W. An approach to chemotherapy-associated toxicity. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 32, 167–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmorsy, E.A.; Saber, S.; Hamad, R.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; El-Kott, A.F.; AlShehri, M.A.; Morsy, K.; Salama, S.A.; Youssef, M.E. Advances in understanding cisplatin-induced toxicity: Molecular mechanisms and protective strategies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 203, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerich, D.F.; Thanos, C.G. Nanotechnology and medicine. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2003, 3, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.H.; Watkins, A.; Oh, M.J.; Babeer, A.; Schaer, T.P.; Steager, E.; Koo, H. Targeting biofilm infections in humans using small scale robotics. Trends Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abduljabbar, A.; Farooq, I. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers: Processing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.P.; Sell, S.A.; Boland, E.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Nanofiber technology: Designing the next generation of tissue engineering scaffolds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, L.B.; Dhand, C.; Venugopal, J.R.; Rajamani, L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Almeida, L. Nanotechnology for the treatment of melanoma skin cancer. Prog. Biomater. 2017, 6, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poláková, L.; Širc, J.; Hobzová, R.; Cocârță, A.-I.; Heřmánková, E. Electrospun nanofibers for local anticancer therapy: Review of in vivo activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 558, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Su, C.-H.; Yang, T.-C.; Chang, T.-M.; Kau, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-J. Concurrent delivery of carmustine, irinotecan, and cisplatin to the cerebral cavity using biodegradable nanofibers: In vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Lin, W.; Sun, T.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. The use of cisplatin-loaded mucoadhesive nanofibers for local chemotherapy of cervical cancers in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduna, L.; Patnaik, A. Challenges Associated with the Production of Nanofibers. Processes 2024, 12, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Su, S.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y. The Drug Combination of SB202190 and SP600125 Significantly Inhibit the Growth and Metastasis of Olaparib-resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, P.; Thirumurugan, S.; Chen, Y.L.; Dhawan, U.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.P.; Liu, W.C.; Tseng, C.L.; Chung, R.J. Development of iron oxide based-upconversion nanocomposites for cancer therapeutics treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 675, 125545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Zheng, S.; Wei, H. Comparison of histological structure and biocompatibility between human acellular dermal matrix (ADM) and porcine ADM. Burns 2009, 35, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleemullah, M.; Jiyauddin, K.; Thiban, E.; Rasha, S.; Al-Dhalli, S.; Budiasih, S.; Gamal, O.E.; Fadli, A.; Eddy, Y. Development and evaluation of Ketoprofen sustained release matrix tablet using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaves mucilage. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Khan, S.; Duplanty, M.; Lozano, H.C.; Morris, T.J.; Nguyen, T.; Rostovtsev, Y.V.; DeYonker, N.J.; Mirsaleh-Kohan, N. Raman and Infrared Studies of Platinum-Based Drugs: Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Oxaliplatin, Nedaplatin, and Heptaplatin. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 6934–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gemeinhart, R.A. Cisplatin delivery from poly(acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate) microparticles. J. Control Release 2005, 106, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, S.; Gao, W.; Li, T.; Zhou, Q.T. Pulmonary delivery of nanoparticle chemotherapy for the treatment of lung cancers: Challenges and opportunities. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashar, A.; Al-Zakwani, I.; Eriksson, T.; Sarakbi, A.; Al-Zadjali, B.; Al Mubaihsi, S.; Al Za’abi, M. Impact of medication reconciliation and review and counselling, on adverse drug events and healthcare resource use. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 40, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Abella, E.; Pettengell, R. Risk factors for febrile neutropenia among patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 90, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, R.C.; Xia, F.; Acklin, S. Targeting DNA Damage Response and Repair to Enhance Therapeutic Index in Cisplatin-Based Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, A.; Croce, E.; Ferrari, M.; Gili, R.; Massaro, G.; Marconcini, R.; Arecco, L.; Tanda, E.T.; Spagnolo, F. The treatment of advanced melanoma: Current approaches and new challenges. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 196, 104276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito, R.V.; Mancini, M.W.; Palumbo, M.D.N.; Moraes, L.H.O.; Rodrigues, G.J.; Cervantes, O.; Sercarz, J.A.; Paiva, M.B. The Rationale for “Laser-Induced Thermal Therapy (LITT) and Intratumoral Cisplatin” Approach for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Qin, X.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, H.; Chen, J. Comparison of Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Anticancer Drugs between Real-Time Cell Analysis and CCK-8 Method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12036–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ughachukwu, P.; Unekwe, P. Efflux pump-mediated resistance in chemotherapy. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ma, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cao, X.; Guo, Y. Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater. Lett. 2015, 140, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Chen, H.-l.; Guo, C. Polymeric Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications: A Recent Review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Du, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zaman, F.; Song, Z.; Guan, Y.; Yu, T.; Huang, Y. Gelatin-based anticancer drug delivery nanosystems: A mini review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1158749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Gao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, D. Nanotechnology-driven strategies to enhance the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Dhasmana, A.; Laskar, P.; Prasad, R.; Jain, N.K.; Srivastava, R.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Yallapu, M.M. Nanotechnology synergized immunoengineering for cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 163, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Dong, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Nanomedicine/materdicine-enabled sonocatalytic therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 205, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, W.; Chrisey, D.B.; Huang, Y. Study of gelatin as an effective energy absorbing layer for laser bioprinting. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnjanapratum, S.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; Benjakul, S.; O’Brien, N. Antioxidant, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative effects of gelatin hydrolysate from unicorn leatherjacket skin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Yong, Y.; Dong, X.; Du, J.; Guo, Z.; Gong, L.; Zhu, S.; Tian, G.; Yu, S.; Gu, Z.; et al. Therapeutic Nanoparticles Based on Curcumin and Bamboo Charcoal Nanoparticles for Chemo-Photothermal Synergistic Treatment of Cancer and Radioprotection of Normal Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14281–14291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jiang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Jing, X.; Jiang, H. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of multinuclear platinum(IV) prodrugs with enhanced drug uptake and the activity of overcoming drug resistance. Anticancer. Drugs 2016, 27, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghankhold, M.; Sadat Abolmaali, S.; Nezafat, N.; Mohammad Tamaddon, A. Peptide nanovaccine in melanoma immunotherapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 129, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, U.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Development and characterization of the cisplatin loaded nanofibers for the treatment of cervical cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 75, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, M.; Zanellato, I.; Gabano, E.; Perin, E.; Rangone, B.; Coppola, M.; Osella, D. Antiproliferative Activity of Pt(IV) Conjugates Containing the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Ketoprofen and Naproxen (†). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhäusler, A.; Rogg, K.; Schröder, S.; Spiehl, D.; Zora, H.; Arefaine, E.; Schettler, J.; Hartmann, H.; Blaeser, A. Electrospun microfibers to enhance nutrient supply in bioinks and 3D-bioprinted tissue precursors. Biofabrication 2024, 17, 015038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ou, H.; Pei, X.; Jiang, B.; Ma, Y.; Liu, N.; Wen, C.; Peng, C.; Hu, X. Chemo-drug Controlled-release Strategies of Nanocarrier in the Development of Cancer Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 6307–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Chim, H.; Soltanian, H.T. The effects of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy on the surgical outcomes of breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2012, 65, e267–e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cisplatin | Amount in 1 × 1 cm Nanomembrane | Amount in 1 mL Medium |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.083333 µg | 100 µg/mL × amount of medium (mL) |
| 50 | 1.042 µg | 50 µg/mL × amount of medium (mL) |
| 25 | 0.521 µg | 25 µg/mL × amount of medium (mL) |
| 12.5 | 0.26 µg | 12.5 µg/mL × amount of medium (mL) |
| 6.25 | 0.13 µg | 6.25 µg/mL × amount of medium (mL) |
| 3.125 | 0.065 µg | 3.125 µg/mL × amount of medium (mL) |
| Treatment Time | Cisplatin Concentration (µg/mL) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 50 | 25 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.125 | Control | |
| L929 Fibroblasts | |||||||
| 24 h | 14.7% | 15.1% | 13.7% | 15.7% | 39.5% | 64.8% | 100% |
| 48 h | 2.1% | 0.3% | 2.1% | 3.4% | 11.7% | 31.0% | 100% |
| 72 h | 0.7% | −0.8% | −0.7% | 1.3% | 7.2% | 38.7% | 100% |
| B16-F10 Melanoma Cells | |||||||
| 24 h | 10.8% | 19.2% | 21.4% | 33.7% | 55.5% | 94.5% * | 100% |
| 48 h | −0.2% | −1.7% | −1.8% | 10.6% | 23.8% | 54.8% | 100% |
| 72 h | −0.4% | −1.5% | −1.4% | 4.6% | 16.4% | 36.5% | 100% |
| HaCaT Keratinocytes | |||||||
| 24 h | 3.5% | 1.8% | 4.2% | 9.7% | 45.5% | 81.0% | 100% |
| 48 h | −0.6% | −0.6% | −0.5% | 0.7% | 5.5% | 15.9% | 100% |
| 72 h | −0.5% | −1.2% | −0.4% | 0.0% | 1.1% | 5.4% | 100% |
| Group | Cell Viability (%) | SD (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% | 109.4% | 18.3% | 0.252 |
| 75% | 121.3% | 20.4% | 0.031 |
| 50% | 113.7% | 19.6% | 0.126 |
| 25% | 87.5% | 15.1% | 0.079 |
| Negative Control (0%) | 100.0% | 4.4% | 1.000 |
| Positive Control (10% DMSO) | 0.0% | 0.6% | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Lai, Y.-C.; Shee, B.-W.; Fang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Sun, J.-S. Improving Efficacy and Reducing Systemic Toxicity: An In Vitro Study on the Role of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofiber Membrane for Localized Melanoma Treatment. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090910
Sun J, Lai Y-C, Shee B-W, Fang C-H, Chen C-Y, Sun J-S. Improving Efficacy and Reducing Systemic Toxicity: An In Vitro Study on the Role of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofiber Membrane for Localized Melanoma Treatment. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090910
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jason, Yi-Chung Lai, Bing-Wu Shee, Chih-Hsiang Fang, Ching-Yun Chen, and Jui-Sheng Sun. 2025. "Improving Efficacy and Reducing Systemic Toxicity: An In Vitro Study on the Role of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofiber Membrane for Localized Melanoma Treatment" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090910
APA StyleSun, J., Lai, Y.-C., Shee, B.-W., Fang, C.-H., Chen, C.-Y., & Sun, J.-S. (2025). Improving Efficacy and Reducing Systemic Toxicity: An In Vitro Study on the Role of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofiber Membrane for Localized Melanoma Treatment. Bioengineering, 12(9), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090910







