Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
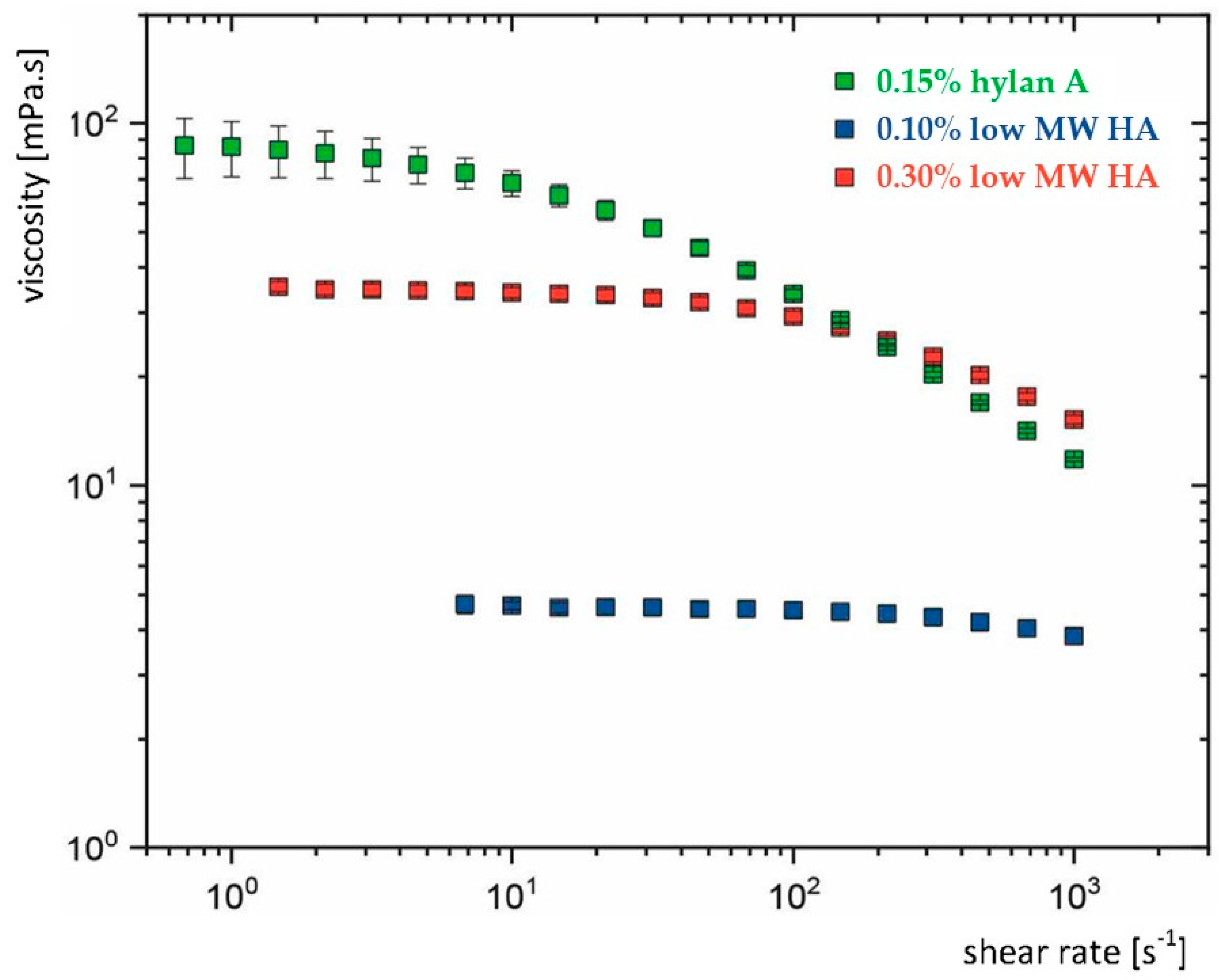
2. An Aqueous Hylan A Formulation with Optimal Viscoelastic Properties Enhances Ocular Surface Retention of APIs
3. An Aqueous Hylan A Formulation Improves API Solubilisation, Stability and Ocular Transport
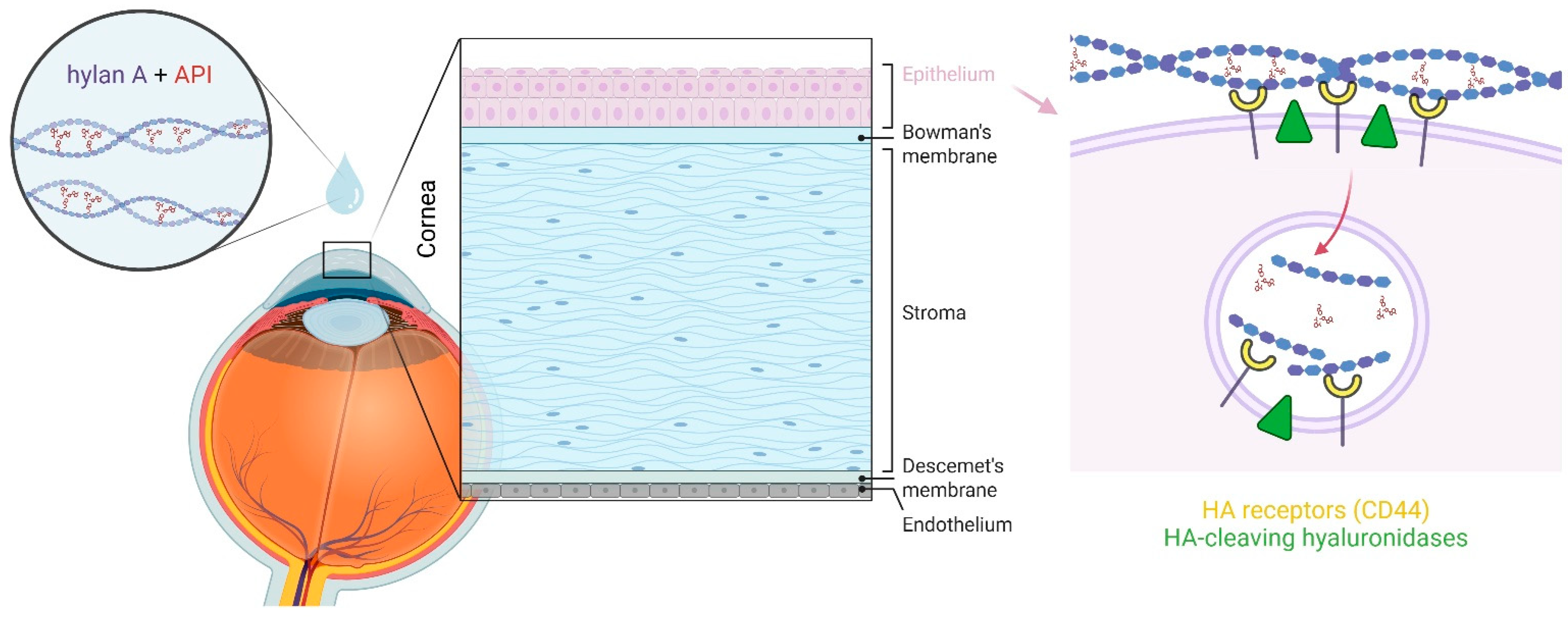
4. The Benefits of Using an Aqueous Hylan A Formulation for Ocular Surface Health
5. An Aqueous Hylan A Formulation as a New Vehicle for Latanoprost to Manage Elevated Intraocular Pressure
6. Hylan A-Based Eye Drops as Next Generation Vehicles for Therapeutic API Delivery
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allyn, M.M.; Luo, R.H.; Hellwarth, E.B.; Swindle-Reilly, K.E. Considerations for Polymers Used in Ocular Drug Delivery. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 787644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.E.; Ibrahim, Y.; Desai, T.A.; Koval, M. Nanostructure-Mediated Transport of Therapeutics through Epithelial Barriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Amin, M.M.; Sayed, S. Ocular Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseev, R.V.; Morrison, P.W.J.; Steele, F.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Penetration Enhancers in Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Shi, X.; Yang, J. High molecular weight hyaluronan decreases oxidative DNA damage induced by EDTA in human corneal epithelial cells. Eye 2012, 26, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahook, M.Y.; Rapuano, C.J.; Messmer, E.M.; Radcliffe, N.M.; Galor, A.; Baudouin, C. Preservatives and ocular surface disease: A review. Ocul. Surf. 2024, 34, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fineide, F.; Magno, M.; Dahlo, K.; Kolko, M.; Heegaard, S.; Vehof, J.; Utheim, T.P. Topical glaucoma medications—Possible implications on the meibomian glands. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Myers, J.S.; Van Tassel, S.H.; Goyal, N.A.; Martinez-de-la-Casa, J.; Ng, A.; Evans, J.S. Adherence and Persistence on Prostaglandin Analogues for Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 275, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedengran, A.; Kolko, M. The molecular aspect of anti-glaucomatous eye drops—Are we harming our patients? Mol. Aspects Med. 2023, 93, 101195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Novel Eye Drop Delivery Systems: Advance on Formulation Design Strategies Targeting Anterior and Posterior Segments of the Eye. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, H.; Kolko, M.; Friedman, D.S.; Gazzard, G. Glaucoma: Now and beyond. Lancet 2023, 402, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Lierheim, W.G.K. Why Chain Length of Hyaluronan in Eye Drops Matters. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, A.J.; Dogru, M.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Kojima, T.; Kovacs, I.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; van Setten, G.B.; Belmonte, C. Reflections on the Ocular Surface: Summary of the Presentations at the 4th Coronis Foundation Ophthalmic Symposium Debate: “A Multifactorial Approach to Ocular Surface Disorders” (August 31 2021). Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassiri, B.; Zambito, Y.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Strategies to prolong the residence time of drug delivery systems on ocular surface. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.R.; Jakka, D.; Sandoval, M.A.; Kulkarni, V.R.; Bao, Q. Advancements in Ocular Therapy: A Review of Emerging Drug Delivery Approaches and Pharmaceutical Technologies. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshinoff, S.; Hofmann, I.; Nae, H. Role of rheology in tears and artificial tears. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2021, 47, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffany, J.M. Viscoelastic properties of human tears and polymer solutions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1994, 350, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graessley, W.W. The Entanglement Concept in Polymer Rheology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–179. [Google Scholar]
- Almond, A. Hyaluronan. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshinoff, S.; Hofmann, I.; Nae, H. Rheological behavior of commercial artificial tear solutions. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2021, 47, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.M.; McNiece, M. The treatment of dry eyes with Na hyaluronate (Healon®). Cornea 1982, 1, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Setten, G.B.; Baudouin, C.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Bohringer, D.; Stachs, O.; Toker, E.; Al-Zaaidi, S.; Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Beck, R.; Al-Sheikh, O.; et al. The HYLAN M Study: Efficacy of 0.15% High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan Fluid in the Treatment of Severe Dry Eye Disease in a Multicenter Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.P.; Laverty, T.P.; Jones, D.S. Mucoadhesive polymeric platforms for controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Rolando, M.; Benitez Del Castillo, J.M.; Messmer, E.M.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Irkec, M.; Van Setten, G.; Labetoulle, M. Reconsidering the central role of mucins in dry eye and ocular surface diseases. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 71, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, J.D. The basics and underlying mechanisms of mucoadhesion. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Q. Hyaluronic acid in ocular drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 118006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, I.M.; Ebbesen, M.F.; Kaspersen, L.; Thomsen, T.; Bienk, K.; Cai, Y.; Malle, B.M.; Howard, K.A. Hyaluronic Acid Molecular Weight-Dependent Modulation of Mucin Nanostructure for Potential Mucosal Therapeutic Applications. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrani, A.M.; Farr, S.J.; Kellaway, I.W. Influence of molecular weight and formulation pH on the precorneal clearance rate of hyaluronic acid in the rabbit eye. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 118, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarise, C.; Acquasaliente, L.; Pasut, G.; Pavan, M.; Soato, M.; Garofolin, G.; Beninatto, R.; Giacomel, E.; Sartori, E.; Galesso, D. The role of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid in mucoadhesion on an ocular surface model. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 143, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenpattinam, S.S.; Bukke, S.P.N.; Kusuma, P.K.; Onohuean, H.; Mothilal, M.; Krishnamaraju, U.; Goruntla, N.; Yadesa, T.M. Self-assembled nanoparticles in ocular delivery: A comprehensive review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, Z. Hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles to deliver drugs to the ocular posterior segment. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2204206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Jiang, C. Biomacromolecules as carriers in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guter, M.; Breunig, M. Hyaluronan as a promising excipient for ocular drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 113, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, C.; Murphy, E.J.; Montgomery, T.R.; Major, I. Hyaluronic Acid: A Review of the Drug Delivery Capabilities of This Naturally Occurring Polysaccharide. Polymers 2022, 14, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, J.J.; Whateley, T.L.; Thomas, M.; Eccleston, G.M. Controlled drug delivery to the lung: Influence of hyaluronic acid solution conformation on its adsorption to hydrophobic drug particles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 330, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Hutadilok, N.; Adam, N.; Lentini, A. Interactions of hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) with phospholipids as determined by gel permeation chromatography, multi-angle laser-light-scattering photometry and 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1994, 16, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruffo, A.; Stamenkovic, I.; Melnick, M.; Underhill, C.B.; Seed, B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 1990, 61, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Han, W. Effects of molecular weights on the bioactivity of hyaluronic acid: A review. Carbohydr. Res. 2025, 552, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, S.M.; Hawn, T.R.; Arrigoni, A.; Wight, T.N.; Bollyky, P.L. Tissue integrity signals communicated by high-molecular weight hyaluronan and the resolution of inflammation. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sayer, S.S.; Dong, Y.; Arif, A.A.; Olsson, M.; Brown, K.L.; Johnson, P. The where, when, how, and why of hyaluronan binding by immune cells. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudson, W.; Chow, G.; Knudson, C.B. CD44-mediated uptake and degradation of hyaluronan. Matrix Biol. 2002, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garantziotis, S.; Savani, R.C. Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78–79, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardner, E.; van Setten, G.B. Detection of TSG-6-like protein in human corneal epithelium. Simultaneous presence with CD44 and hyaluronic acid. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2020, 43, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.N.; Nolle, B.; Duncker, G. Expression of adhesion molecule CD44 on human corneas. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1997, 81, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, L.E.; Schwartz, D.M.; Hwang, D.G.; Howes, E.L.; Stern, R. Hyaluronan and CD44 in the human cornea and limbal conjunctiva. Exp. Eye Res. 1998, 67, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Weigel, J.A.; Fauss, L.; Weigel, P.H. Identification of the hyaluronan receptor for endocytosis (HARE). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37733–37741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.N.; Baker, E. Role of the Hyaluronan Receptor, Stabilin-2/HARE, in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, M.; Schledzewski, K.; Hansen, B.; Goerdt, S. Expression of stabilin-2, a novel fasciclin-like hyaluronan receptor protein, in murine sinusoidal endothelia, avascular tissues, and at solid/liquid interfaces. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 120, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohaumilitzky, L.; Huber, A.K.; Stork, E.M.; Wengert, S.; Woelfl, F.; Boehm, H. A Trickster in Disguise: Hyaluronan’s Ambivalent Roles in the Matrix. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyphert, J.M.; Trempus, C.S.; Garantziotis, S. Size Matters: Molecular Weight Specificity of Hyaluronan Effects in Cell Biology. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 2015, 563818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monslow, J.; Govindaraju, P.; Pure, E. Hyaluronan—A functional and structural sweet spot in the tissue microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, A.; Pawlak, M.; Balazs, E.A.; Schmidt, R.F.; Belmonte, C. Effects of different molecular weight elastoviscous hyaluronan solutions on articular nociceptive afferents. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caires, R.; Luis, E.; Taberner, F.J.; Fernandez-Ballester, G.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.; Balazs, E.A.; Gomis, A.; Belmonte, C.; de la Pena, E. Hyaluronan modulates TRPV1 channel opening, reducing peripheral nociceptor activity and pain. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, I.J.M.; Araldi, D.; Khomula, E.V.; Bogen, O.; Green, P.G.; Levine, J.D. Mechanisms Mediating High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 6477–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, L.F.; Khomula, E.V.; Araldi, D.; Levine, J.D. CD44 Signaling Mediates High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonet, I.J.M.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Araldi, D.; Green, P.G.; Levine, J.D. Second messengers mediating high-molecular-weight hyaluronan-induced antihyperalgesia in rats with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2022, 163, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, Q.; Ford, N.C.; Limjunyawong, N.; Lin, Q.; Yang, F.; Cui, X.; Uniyal, A.; Liu, J.; Mahabole, M.; et al. Human birth tissue products as a non-opioid medicine to inhibit post-surgical pain. eLife 2024, 13, e101269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Nagata, T.; Kudo, H.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; van Setten, G.B.; Dogru, M.; Tsubota, K. The Effects of High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Eye Drop Application in Environmental Dry Eye Stress Model Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.; Stachs, O.; Koschmieder, A.; Mueller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; Peschel, S.; van Setten, G.B. Hyaluronic Acid as an Alternative to Autologous Human Serum Eye Drops: Initial Clinical Results with High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Eye Drops. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. 2019, 10, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Setten, G.B.; Stachs, O.; Dupas, B.; Turhan, S.A.; Seitz, B.; Reitsamer, H.; Winter, K.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Guthoff, R.F.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K. High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan Promotes Corneal Nerve Growth in Severe Dry Eyes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, N.; Boldin, I.; Berisha, B.; Matijak-Kronschachner, B.; Aminfar, H.; Schwantzer, G.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; van Setten, G.B.; Horwath-Winter, J. Application frequency—Key indicator for the efficiency of severe dry eye disease treatment—Evidence for the importance of molecular weight of hyaluronan in lubricating agents. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, e663–e671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, G.; Turhan, S.A.; Toker, E. Effect of high and low molecular weight sodium hyaluronic acid eye drops on corneal recovery after crosslinking in keratoconus patients. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2025, 10, e001890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheikh, O.; Alzaaidi, S.; Vargas, J.M.; Al-Sharif, E.; Alrajeh, M.; AlSemari, M.A.; Alhommadi, A.; Alsaati, A.; Aljwaiser, N.; Alshahwan, E.; et al. Effectiveness of 0.15% hylan A eye drops in ameliorating symptoms of severe dry eye patients in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 35, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Acosta, M.C.; Wassfi, M.A.; Diaz-Valle, D.; Gegundez, J.A.; Fernandez, C.; Garcia-Sanchez, J. Relation between corneal innervation with confocal microscopy and corneal sensitivity with noncontact esthesiometry in patients with dry eye. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, R.; Dua, H.S.; Tong, L.; Kundu, G.; Khamar, P.; Gorimanipalli, B.; D’Souza, S. Role of in vivo confocal microscopy in dry eye disease and eye pain. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 71, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galor, A.; Gallar, J.; Acosta, M.C.; Meseguer, V.; Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Stachs, O.; Szentmary, N.; Versura, P.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; Belmonte, C.; et al. CORONIS symposium 2023: Scientific and clinical frontiers in ocular surface innervation. Acta Ophthalmol. 2025, 103, e240–e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lindsley, K.; Rouse, B.; Hong, H.; Shi, Q.; Friedman, D.S.; Wormald, R.; Dickersin, K. Comparative Effectiveness of First-Line Medications for Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolko, M.; Gazzard, G.; Baudouin, C.; Beier, S.; Brignole-Baudouin, F.; Cvenkel, B.; Fineide, F.; Hedengran, A.; Hommer, A.; Jespersen, E.; et al. Impact of glaucoma medications on the ocular surface and how ocular surface disease can influence glaucoma treatment. Ocul. Surf. 2023, 29, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Lin, X.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Tang, L.; Ye, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. 0.005% Preservative-Free Latanoprost Induces Dry Eye-Like Ocular Surface Damage via Promotion of Inflammation in Mice. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 3375–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Labbe, A.; Liang, H.; Pauly, A.; Brignole-Baudouin, F. Preservatives in eyedrops: The good, the bad and the ugly. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 312–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstas, A.G.; Labbe, A.; Katsanos, A.; Meier-Gibbons, F.; Irkec, M.; Boboridis, K.G.; Hollo, G.; Garcia-Feijoo, J.; Dutton, G.N.; Baudouin, C. The treatment of glaucoma using topical preservative-free agents: An evaluation of safety and tolerability. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollo, G.; Katsanos, A.; Boboridis, K.G.; Irkec, M.; Konstas, A.G.P. Preservative-Free Prostaglandin Analogs and Prostaglandin/Timolol Fixed Combinations in the Treatment of Glaucoma: Efficacy, Safety and Potential Advantages. Drugs 2018, 78, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Park, S.W.; Seong, M.; Ha, S.J.; Lee, J.W.; Rho, S.; Lee, C.E.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, T.W.; Sung, K.R.; et al. Comparison of the Safety and Efficacy between Preserved and Preservative-Free Latanoprost and Preservative-Free Tafluprost. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, E.; Sacchi, M.; Magnani, F.; Nicodemo, A.; Williams, S.E.; Rossi, A.; Ratiglia, R.; De Cilla, S.; Nucci, P. The Ocular Surface in Medically Controlled Glaucoma: An In Vivo Confocal Study. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, A.; Khopade, A.J. Physiochemical Properties and Cytotoxicity of a Benzalkonium Chloride-Free, Micellar Emulsion Ophthalmic Formulation of Latanoprost. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.A.P.; Azar, D.T.; Baudouin, C.; Efron, N.; Hirayama, M.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Kim, T.; Mehta, J.S.; Messmer, E.M.; Pepose, J.S.; et al. TFOS DEWS II iatrogenic report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 511–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechtner, R.D.; Godfrey, D.G.; Budenz, D.; Stewart, J.A.; Stewart, W.C.; Jasek, M.C. Prevalence of ocular surface complaints in patients with glaucoma using topical intraocular pressure-lowering medications. Cornea 2010, 29, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalicky, S.E.; Goldberg, I.; McCluskey, P. Ocular surface disease and quality of life in patients with glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 153, 1–9.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Renard, J.P.; Nordmann, J.P.; Denis, P.; Lachkar, Y.; Sellem, E.; Rouland, J.F.; Jeanbat, V.; Bouee, S. Prevalence and risk factors for ocular surface disease among patients treated over the long term for glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 23, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Denoyer, A.; Desbenoit, N.; Hamm, G.; Grise, A. In vitro and in vivo experimental studies on trabecular meshwork degeneration induced by benzalkonium chloride (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis). Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2012, 110, 40–63. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, R.; Tailor, R.; Mohamed, S. Ocular surface disease exacerbated glaucoma: Optimizing the ocular surface improves intraocular pressure control. J. Glaucoma 2014, 23, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudouin, C.; Kolko, M.; Melik-Parsadaniantz, S.; Messmer, E.M. Inflammation in Glaucoma: From the back to the front of the eye, and beyond. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 83, 100916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrulle, P.; Labbe, A.; Brasnu, E.; Liang, H.; Hamard, P.; Meziani, L.; Baudouin, C. Influence of Treating Ocular Surface Disease on Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma Patients Intolerant to Their Topical Treatments: A Report of 10 Cases. J. Glaucoma 2018, 27, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmer, E.M.; Baudouin, C.; Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Iester, M.; Anton, A.; Thygesen, J.; Topouzis, F. Expert Consensus Recommendations for the Management of Ocular Surface Inflammation in Patients With Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2024, 33, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemer, O.E.; Mekala, P.; Dave, B.; Kooner, K.S. Managing Ocular Surface Disease in Glaucoma Treatment: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Lierheim, W.G. Hylan a: A novel transporter for Latanoprost in the treatment of ocular hypertension. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2021, 37, 29176–29181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, K.; Kimoto, R.; Kojima, T.; Dogru, M.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; Shimazaki, J. Therapeutic Aqueous Humor Concentrations of Latanoprost Attained in Rats by Administration in a Very-High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Eye Drop. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogru, M.; Kojima, T.; Higa, K.; Igarashi, A.; Kudo, H.; Muller-Lierheim, W.G.K.; Tsubota, K.; Negishi, K. The Effect of High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid and Latanoprost Eyedrops on Tear Functions and Ocular Surface Status in C57/BL6 Mice. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Nguyen, D.D.; Lai, J.Y. Poly(l-Histidine)-Mediated On-Demand Therapeutic Delivery of Roughened Ceria Nanocages for Treatment of Chemical Eye Injury. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppieri, M.; Gagliano, C.; Tognetto, D.; Musa, M.; Rossi, F.B.; Greggio, A.; Gualandi, G.; Galan, A.; Babighian, S. Unraveling the Mechanisms, Clinical Impact, Comparisons, and Safety Profiles of Slow-Release Therapies in Glaucoma. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Sawale, G.; Ghuge, S.; Sathaye, S. Quintessence of currently approved and upcoming treatments for dry eye disease. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2025, 263, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.P.; Nichols, K.K.; Akpek, E.K.; Caffery, B.; Dua, H.S.; Joo, C.K.; Liu, Z.; Nelson, J.D.; Nichols, J.J.; Tsubota, K.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Definition and Classification Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Otake, H. Novel drug delivery systems for the management of dry eye. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 191, 114582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periman, L.M.; Mah, F.S.; Karpecki, P.M. A Review of the Mechanism of Action of Cyclosporine A: The Role of Cyclosporine A in Dry Eye Disease and Recent Formulation Developments. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 4187–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgoczi, E.; Molnar, Z.; Katko, M.; Ujhelyi, B.; Steiber, Z.; Nagy, E.V. Cyclosporin A inhibits PDGF-BB induced hyaluronan synthesis in orbital fibroblasts. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 396, 111045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, M.; Nagata, T.; Kojima, T.; Higa, K.; Okada, N.; Müller-Lierheim, W.; Fukagawa, K.; Fujishima, H.; Negishi, K. The effect of a novel high molecular weight hyaluronic acid and ketotifen eye drop on the ocular surface status in an allergic conjunctivitis mouse model. In Proceedings of the TFOS 2024 Conference, Venice, Italy, 30 October–2 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Study | Study Type | Model/ Patients | Comparisons | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kojima et al., 2020 [59] | Preclinical | Mouse model of environmental dry eye disease | Low MW HA eye drops, secretagogue eye drops | Improved tear film stability. Reduced ocular surface damage. Less inflammation with 0.15% hylan A eye drops. |
| Beck et al., 2019 [60] | Clinical | 11 patients treated with autologous serum eye drops | Autologous serum eye drops | Eye drops containing 0.15% hylan A effectively treat severe ocular disease. These 0.15% hylan A eye drops may replace eye drops with autologous serum. |
| van Setten et al., 2020a [23] | Clinical HYLAN M study | 84 patients with severe dry eye disease | Optimized artificial tear treatments | Symptoms rapidly improved by switching to 0.15% hylan A eye drops include: visual stability, discomfort and pain. |
| van Setten et al., 2020b [61] | Clinical. Subgroup analysis of the HYLAN M study | 16 patients | Optimized artificial tear treatments | Switching to 0.15% hylan A eye drops promotes corneal nerve growth. |
| Medic et al., 2024 [62] | Clinical Subgroup analysis of the HYLAN M study | 47 patients | HA containing artificial tears (15 commercial brands with HA of diverse MWs) | Fewer 0.15% hylan A eye drops required than those with lower MW HA. Eye drops containing 0.15% hylan A have better clinical effects. |
| Özkan et al., 2025 [63] | Clinical | 63 eyes from 55 patients with keratoconus following corneal crosslinking (CXL) | Low MW HA eye drops | After CXL, 0.15% hylan A eye drops produce: faster corneal nerve regeneration; faster recovery of sensitivity; improved ocular symptoms; and fewer inflammation-related immune cells than low MW HA eye drops. |
| Study | Study Type | Model/ Patients | Comparators | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Müller-Lierheim, 2021 [88] | Formulation solubility and stability | N/A | N/A | A preservative-free 0.15% hylan A solution in isotonic phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4) enhances latanoprost solubility by 75% |
| Dogru et al., 2023 [90] | Preclinical | Standard mouse strain | Commercial eye drops with 50 μg/mL latanoprost | A hylan A-based eye drop with 14 μg/mL latanoprost preserves ocular surface parameters while effectively lowering IOP |
| Higa et al., 2024 [89] | Preclinical | Standard strain rat | Commercial eye drops with 50 μg/mL latanoprost | A hylan A-based eye drop with 14 μg/mL latanoprost achieves comparable therapeutic latanoprost levels in aqueous humour as a 50 μg/mL commercial formulation |
| Müller-Lierheim, 2021 [88] | Proof-of-concept | One subject with ocular hypertension | Commercial eye drops with 50 μg/mL latanoprost | A hylan A-based eye drop with 20 μg/mL latanoprost lowers IOP better than a commercial latanoprost eye drop with a higher API concentration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pujol-Martí, J.; Müller-Lierheim, W.G.K. Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090907
Pujol-Martí J, Müller-Lierheim WGK. Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090907
Chicago/Turabian StylePujol-Martí, Jesús, and Wolfgang G. K. Müller-Lierheim. 2025. "Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090907
APA StylePujol-Martí, J., & Müller-Lierheim, W. G. K. (2025). Very High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid as an Enhanced Vehicle in Therapeutic Eye Drops: Application in a Novel Latanoprost Formulation for Glaucoma. Bioengineering, 12(9), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090907








