Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Emerging Applications for Locoregional Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI)
3. DCE-MRI in Ablation Therapy
4. DCE-MRI in Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
5. DCE-MRI in 90Y Mapping and Dosimetry
6. Limitations in DCE-MRI
7. Limitations in Clinical Translation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DCE-MRI | Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| LRT | Locoregional Therapies |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| RFA | Radiofrequency Ablation |
| MWA | Microwave Ablation |
| TACE | Transarterial Chemoembolization |
| TARE | Transarterial Radioembolization |
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| CE-MRI | Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PK | Pharmacokinetic |
References
- Foglia, B.; Turato, C.; Cannito, S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Latest Research in Pathogenesis, Detection and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Yu, J.; Gamble, J.R.; McCaughan, G.W. Targeting the vasculature in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Starving versus normalizing blood supply. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronot, M.; Leporq, B.; Van Beers, B.E.; Vilgrain, V. CT and MR perfusion techniques to assess diffuse liver disease. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 3496–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, N.; Chandarana, H.; Rusinek, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Moy, L.; Sodickson, D.K.; Kim, S.G. Accuracy and precision of quantitative DCE-MRI parameters: How should one estimate contrast concentration? Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 52, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consul, N.; Sirlin, C.B.; Chernyak, V.; Fetzer, D.T.; Masch, W.R.; Arora, S.S.; Do, R.K.G.; Marks, R.M.; Fowler, K.J.; Borhani, A.A.; et al. Imaging Features at the Periphery: Hemodynamics, Pathophysiology, and Effect on LI-RADS Categorization. RadioGraphics 2021, 41, 1657–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.; Masthoff, M.; Kunz, W.G.; Seidensticker, M.; Bobe, S.; Gerwing, M.; Berdel, W.E.; Schliemann, C.; Faber, C.; Wildgruber, M. Multiparametric MRI for characterization of the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Adluru, G. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI: Basic Physics, Pulse Sequences, and Modeling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 321–344. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Chenevert, T.L.; Jambawalikar, S.; Schwartz, L.H.; Malyarenko, D.; Huang, W.; Noworolski, S.M.; Young, R.J.; Shiroishi, M.S.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers alliance (QIBA) recommendations for improved precision of DWI and DCE-MRI derived biomarkers in multicenter oncology trials. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e101–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronhime, S.; Calcagno, C.; Jajamovich, G.H.; Dyvorne, H.A.; Robson, P.; Dieterich, D.; Isabel Fiel, M.; Martel-Laferriere, V.; Chatterji, M.; Rusinek, H.; et al. DCE-MRI of the liver: Effect of linear and nonlinear conversions on hepatic perfusion quantification and reproducibility. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.P.; Meaney, J.F.; Fagan, A.J. DCE-MRI protocol for constraining absolute pharmacokinetic modeling errors within specific accuracy limits. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 3592–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-B. DCE-MRI in hepatocellular carcinoma-clinical and therapeutic image biomarker. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, F.; Soliman, A.; El-Baz, A.; Abou El-Ghar, M.; El-Diasty, T.; Gimel’Farb, G.; Ouseph, R.; Dwyer, A.C. Models and methods for analyzing DCE-MRI: A review. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz-Hansen, T.; Rostrup, E.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Søndergaard, L.; Ring, P.; Henriksen, O. Measurement of the arterial concentration of Gd-DTPA using MRI: A step toward quantitative perfusion imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G.J.M.; Roberts, C.; Macdonald, A.; Buonaccorsi, G.A.; Cheung, S.; Buckley, D.L.; Jackson, A.; Watson, Y.; Davies, K.; Jayson, G.C. Experimentally-derived functional form for a population-averaged high-temporal-resolution arterial input function for dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sourbron, S.P.; Buckley, D.L. Tracer kinetic modelling in MRI: Estimating perfusion and capillary permeability. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, R1–R33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.C.; Suzuki, Y.; Van Houdt, P.J.; Sourbron, S.; Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M. The road to the ISMRM OSIPI: A community-led initiative for reproducible perfusion MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S. Modeling tracer kinetics in dynamic Gd-DTPA MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofts, P.S.; Brix, G.; Buckley, D.L.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Henderson, E.; Knopp, M.V.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Lee, T.-Y.; Mayr, N.A.; Parker, G.J.M.; et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced t1-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: Standardized quantities and symbols. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999, 10, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, G.; Kiessling, F.; Lucht, R.; Darai, S.; Wasser, K.; Delorme, S.; Griebel, J. Microcirculation and microvasculature in breast tumors: Pharmacokinetic analysis of dynamic MR image series. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, M.M.S. Diffusion weighted and dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of malignant liver tumors after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2016, 47, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chiang, J.; Cristescu, M.; Lee, M.H.; Moreland, A.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Lee, F.T.; Brace, C.L. Effects of Microwave Ablation on Arterial and Venous Vasculature after Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2016, 281, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.; Yang, J.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, Y.L.; Rhim, M.H. Correlation of quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with microvascular density in necrotic, partial necrotic, and viable liver tumors in a rabbit model. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Feng, G.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Du, Y. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging assessment of residual tumor angiogenesis after insufficient microwave ablation and donafenib adjuvant therapy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.Y.; Bahig, S.; Shebrya, N.; Ahmed, A.Y. Value of dynamic and DWI MRI in evaluation of HCC viability after TACE via LI-RADS v2018 diagnostic algorithm. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2019, 50, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svecic, A.; Mansour, R.; Tang, A.; Kadoury, S. Prediction of post transarterial chemoembolization MR images of hepatocellular carcinoma using spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Li, R.; Jia, P.; Ye, W.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, R.; Wang, J.; Lin, S.; Pang, P.; Ji, W. MRI-Based Radiomics: Nomograms predicting the short-term response after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with diameter less than 5 cm. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeau-Antonacci, A.; Petitclerc, L.; Gilbert, G.; Bilodeau, L.; Olivié, D.; Cerny, M.; Castel, H.; Turcotte, S.; Huet, C.; Perreault, P.; et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI to assess hepatocellular carcinoma response to Transarterial chemoembolization using LI-RADS criteria: A pilot study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 62, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ledsam, J.; Sugimoto, K.; Sourbron, S.; Araki, Y.; Tokuuye, K. DCE-MRI for Early Prediction of Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma after TACE and Sorafenib Therapy: A Pilot Study. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2018, 102, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokuri, V.K.; Tomaszewski, G.M.; Ait-Oudhia, S.; Groman, A.; Khushalani, N.I.; Lugade, A.A.; Thanavala, Y.; Ashton, E.A.; Grande, C.; Fetterly, G.J.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Potential Biomarkers of Sunitinib and Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Combination in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hectors, S.J.; Lewis, S.; Kennedy, P.; Bane, O.; Said, D.; Segall, M.; Schwartz, M.; Kim, E.; Taouli, B. Assessment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Response to 90Y Radioembolization Using Dynamic Contrast Material–enhanced MRI and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted Imaging. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2020, 2, e190094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lee, K.S.; Talenfeld, A.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Prince, M.R.; Wang, Y. Prediction of Lung Shunt Fraction for Yttrium-90 Treatment of Hepatic Tumors Using Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI with Quantitative Perfusion Processing. Tomography 2022, 8, 2687–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; De Baere, T.; Kulik, L.; Haber, P.K.; Greten, T.F.; Meyer, T.; Lencioni, R. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hectors, S.J.; Wagner, M.; Bane, O.; Besa, C.; Lewis, S.; Remark, R.; Chen, N.; Fiel, M.I.; Zhu, H.; Gnjatic, S.; et al. Quantification of hepatocellular carcinoma heterogeneity with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Tang, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Xiao, Y.-D. Initial Incomplete Thermal Ablation Is Associated With a High Risk of Tumor Progression in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Feng, B.; Wang, P.; Wang, B.; Cai, W.; Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X. Bi-regional dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for prediction of microvascular invasion in solitary BCLC stage A hepatocellular carcinoma. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Sparks, H.; Rink, J.S.; Meloni, M.F.; Hao, F.; Sung, K.H.; Lee, E.W. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging Evaluation of Perfusional Changes and Ablation Zone Size after Combination Embolization and Ablation Therapy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 34, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, N.; Dong, W.-G.; Wang, J. The clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant ascites. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 3719–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, P.; Burrel, M.; Guiu, B.; De Rubeis, G.; Van Delden, O.; Helmberger, T. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Hepatic Transarterial Chemoembolisation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 1851–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Guo, R.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Mei, J.; Feng, S.; et al. Lack of Response to Transarterial Chemoembolization for Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Abandon or Repeat? Radiology 2021, 298, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taouli, B.; Johnson, R.S.; Hajdu, C.H.; Oei, M.T.H.; Merad, M.; Yee, H.; Rusinek, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Perfusion Quantification With Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashima, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Tateishi, U.; Kato, K.; Miyake, M.; Horita, Y.; Akiyoshi, K.; Takashima, A.; Okita, N.; Takahari, D.; et al. Pharmacokinetic parameters from 3-Tesla DCE-MRI as surrogate biomarkers of antitumor effects of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI in colorectal cancer with liver metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.H.; Lopes Vendrami, C.; Gabr, A.; Horowitz, J.M.; Kelahan, L.C.; Riaz, A.; Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J. Evolution of Radioembolization in Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Pictorial Review. RadioGraphics 2021, 41, 1802–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.; Johnson, G.E.; Kim, E.; Riaz, A.; Bishay, V.; Boucher, E.; Fowers, K.; Lewandowski, R.; Padia, S.A. Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for the Treatment of Solitary, Unresectable HCC: The LEGACY Study. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, F.E.; Maxwell, A.W.P. Beyond Mean Tumor Dose: The Importance of Particle Density in Radioembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 34, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, E.; Tselikas, L.; Guiu, B.; Chalaye, J.; Edeline, J.; De Baere, T.; Assenat, E.; Tacher, V.; Robert, C.; Terroir-Cassou-Mounat, M.; et al. Personalised versus standard dosimetry approach of selective internal radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (DOSISPHERE-01): A randomised, multicentre, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabr, A.; Riaz, A.; Johnson, G.E.; Kim, E.; Padia, S.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Salem, R. Correlation of Y90-absorbed radiation dose to pathological necrosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: Confirmatory multicenter analysis in 45 explants. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, A.W.P.; Mendoza, H.G.; Sellitti, M.J.; Camacho, J.C.; Deipolyi, A.R.; Ziv, E.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Maybody, M.; Humm, J.L.; et al. Optimizing 90Y Particle Density Improves Outcomes After Radioembolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasciak, A.S.; Abiola, G.; Liddell, R.P.; Crookston, N.; Besharati, S.; Donahue, D.; Thompson, R.E.; Frey, E.; Anders, R.A.; Dreher, M.R.; et al. The number of microspheres in Y90 radioembolization directly affects normal tissue radiation exposure. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsman, M.R.; Overgaard, J. The impact of hypoxia and its modification of the outcome of radiotherapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, i90–i98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.; Spencer, B.; Omidvari, N.; Foster, C.; Rusnak, M.; Hunt, H.; Caudle, D.T.; Pillai, R.T.; Vu, C.T.; Roncali, E. Radioembolization Dosimetry with Total-Body 90Y PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrenberg-Klee, E.; Gandhi, R.T.; Ganguli, S. Patient Selection and Clinical Outcomes of Y90 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 22, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouche, M.; Habib, A.; Ward, T.J.; Kim, E.; Kulik, L.; Ganger, D.; Mulcahy, M.; Baker, T.; Abecassis, M.; Sato, K.T.; et al. Unresectable Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Not Amenable to Radiofrequency Ablation: Multicenter Radiology-Pathology Correlation and Survival of Radiation Segmentectomy. Hepatology 2014, 60, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisen, M.; Fan, X.; Buurman, J.; Van Riel, N.A.W.; Karczmar, G.S.; Ter Haar Romeny, B.M. The influence of temporal resolution in determining pharmacokinetic parameters from DCE-MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, M.; Shen, D.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Q. Liver DCE-MRI registration based on sparse recovery of contrast agent curves. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 6916–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, A.C.; Wang, D.; Atassi, B.; Sato, K.T.; Ryu, R.K.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Nemcek, A.A.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Kulik, L.M.; Miller, F.H.; et al. Transcatheter Intraarterial Perfusion: MR Monitoring of Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma—Feasibility of Initial Clinical Translation. Radiology 2008, 246, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Padhani, A.R. Tumor response assessments with diffusion and perfusion MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Xiao, L.; Fan, X.; Huang, N.; Su, Z.; Xu, X. Free breathing DCE-MRI with motion correction and its values for benign and malignant liver tumor differentiation. Radiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, M.O.; Brindle, K.M.; Evelhoch, J.L.; Griffiths, J.R.; Horsman, M.R.; Jackson, A.; Jayson, G.C.; Judson, I.R.; Knopp, M.V.; Maxwell, R.J.; et al. The assessment of antiangiogenic and antivascular therapies in early-stage clinical trials using magnetic resonance imaging: Issues and recommendations. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wáng, Y.X.J.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Topics on quantitative liver magnetic resonance imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1840–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qu, C. Early Diagnosis Value of DCE-MRI Hemodynamic Parameters in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 9556589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safri, F.; Nguyen, R.; Zerehpooshnesfchi, S.; George, J.; Qiao, L. Heterogeneity of hepatocellular carcinoma: From mechanisms to clinical implications. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.P.B.; Rose, C.J.; Jackson, A.; Watson, Y.; Cheung, S.; Maders, F.; Whitcher, B.J.; Roberts, C.; Buonaccorsi, G.A.; Thompson, G.; et al. DCE-MRI biomarkers of tumour heterogeneity predict CRC liver metastasis shrinkage following bevacizumab and FOLFOX-6. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Chen, P.-J.; Chan, P.; Curtis, C.M.; Murphy, P.S.; Suttle, A.B.; Gauvin, J.; Hodge, J.P.; Dar, M.M.; Poon, R.T. Phase I Dose-Finding Study of Pazopanib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Evaluation of Early Efficacy, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6914–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, A.G.; Ma, C.; Ulahannan, S.V.; Rahma, O.E.; Makarova-Rusher, O.; Cao, L.; Yu, Y.; Kleiner, D.E.; Trepel, J.; Lee, M.-J.; et al. Phase I and Preliminary Phase II Study of TRC105 in Combination with Sorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

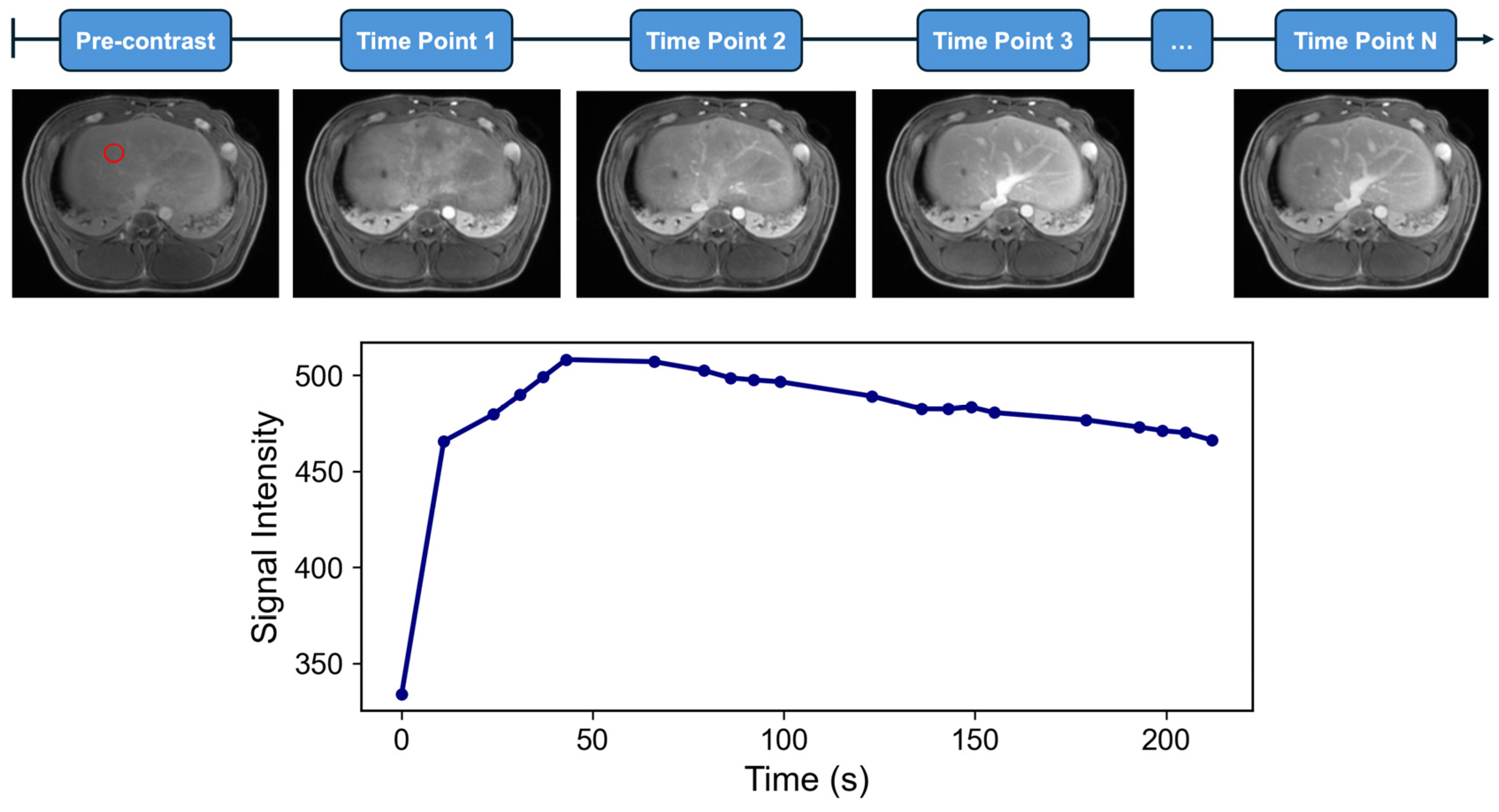
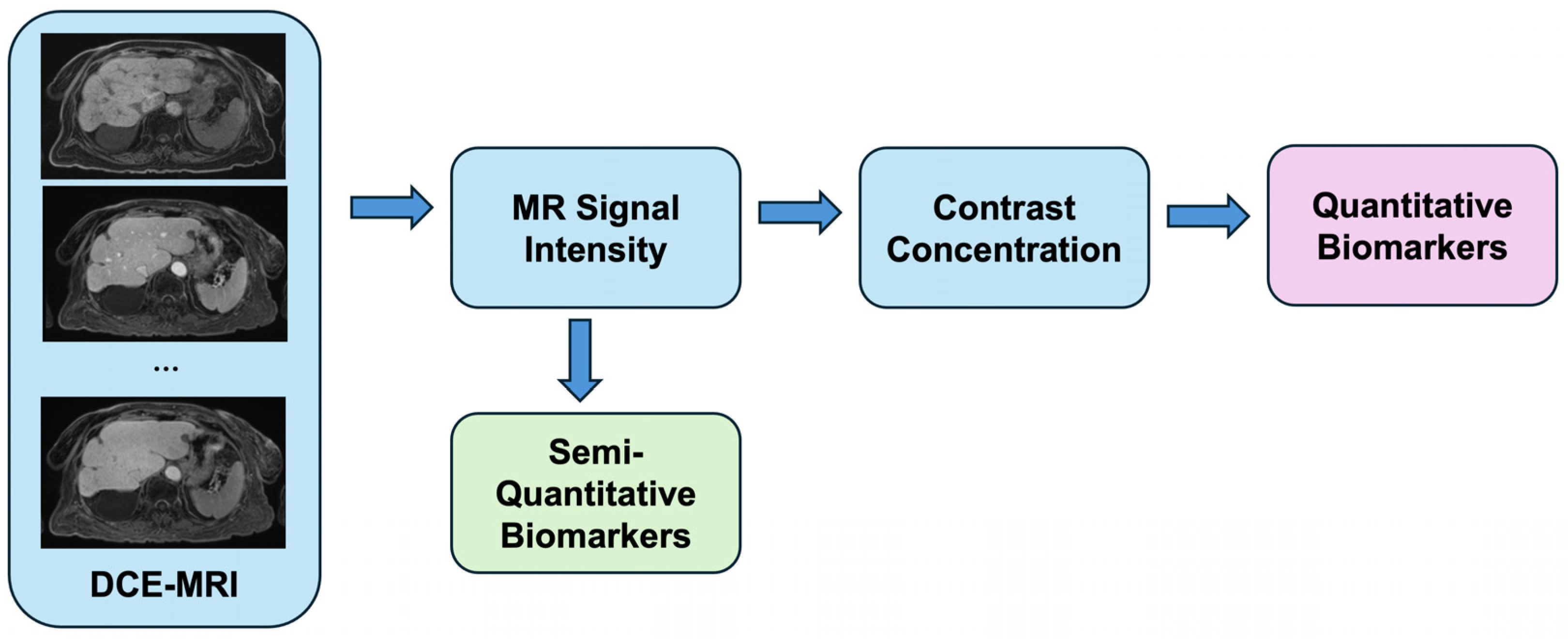
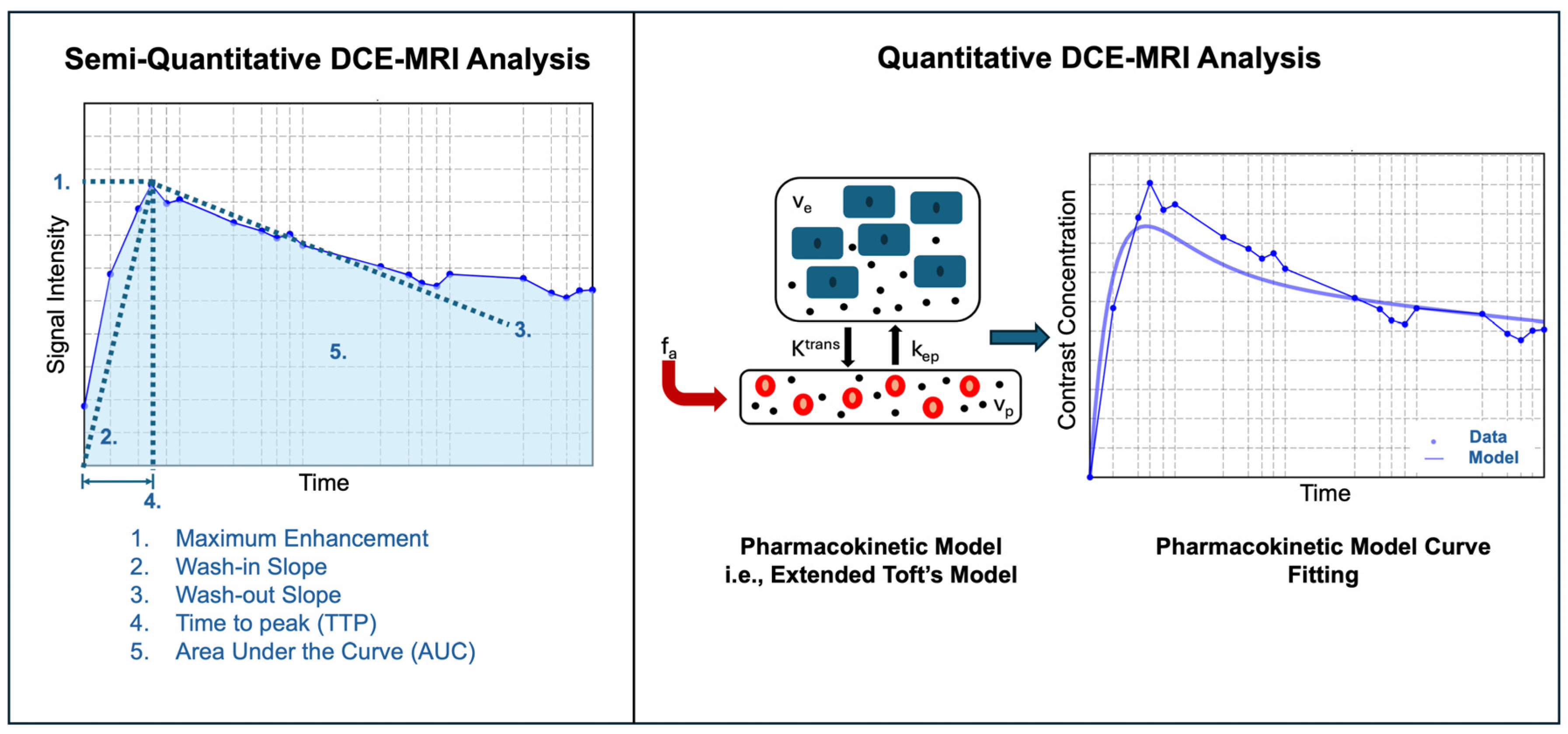
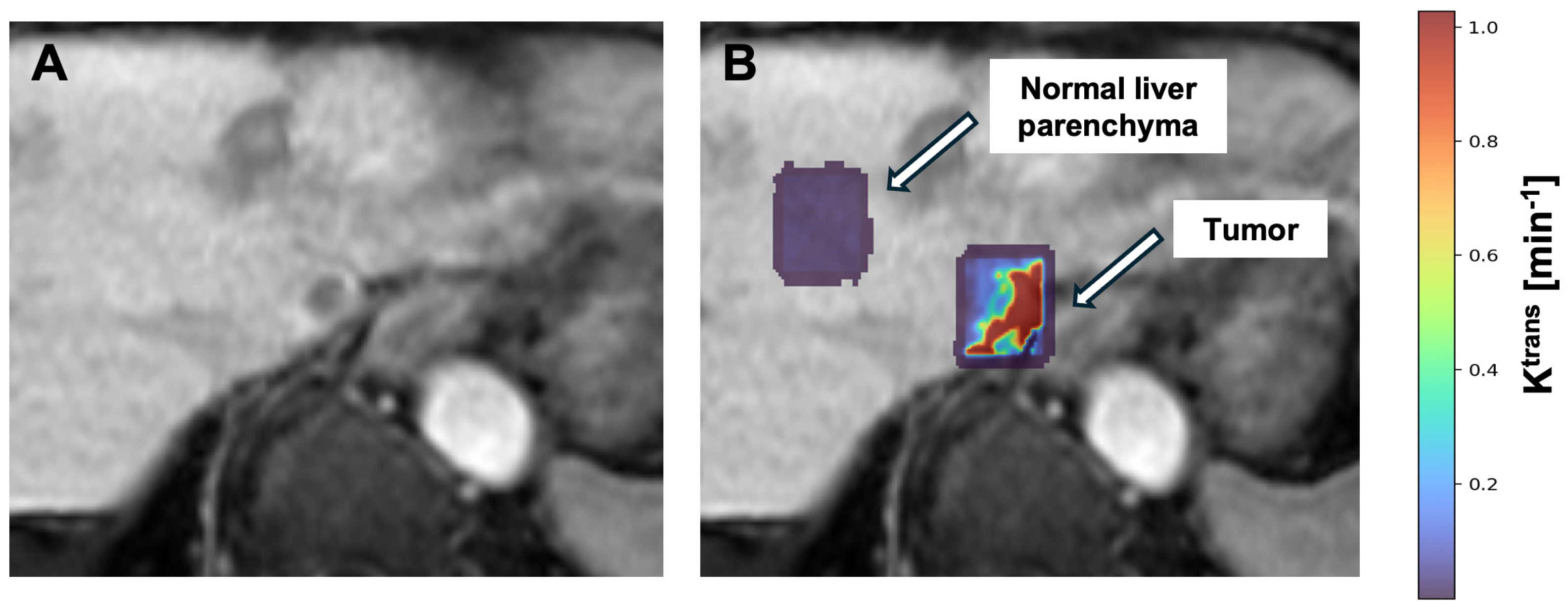
| Model | DCE-MRI Parameter Symbol | Units | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiquantitative | Onset Time | s | Time of contrast agent onset |
| Semiquantitative | TTP | s | Time to maximum contrast enhancement |
| Semiquantitative | Peak Enhancement | SI | Maximum signal intensity reached within a tissue region after contrast injection |
| Semiquantitative | Peak Enhancement Ratio | % | Peak enhancement relative to the signal intensity at time of onset |
| Semiquantitative | Wash-in Slope | % | Speed of contrast uptake |
| Semiquantitative | Wash-out Slope | % | Speed of contrast clearance |
| Semiquantitative | AUC | Area under the signal intensity-time curve | |
| Quantitative | Ktrans | min−1 | Forward volume transfer coefficient between blood plasma and EES |
| Quantitative | kep | min−1 | Reverse volume transfer coefficient between blood plasma and EES |
| Quantitative | ve | % | EES volume per unit volume of tissue |
| Quantitative | vp | % | Blood plasma volume per unit volume of tissue |
| Quantitative | DV | % | Distribution volume of contrast agent in the total volume of tissue |
| Quantitative | F | mL·g−1·min−1 | Total hepatic blood flow |
| Quantitative | Fa | mL·g−1·min−1 | Hepatic artery blood flow |
| Quantitative | Fp | mL·g−1·min−1 | Hepatic portal blood flow |
| Quantitative | MTT | s | Average time for plasma to traverse from arterial to the venous end of the vasculature |
| Study and Year | Treatment Method | Subject | Sample Size | Model | Valuable DCE Parameters | Major Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mostafa, 2016; [22] | RFA | Humans | 50 | Qualitative | Signal intensity, heterogeneity, pattern of enhancement, border definition | Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) showed early arterial enhancement and rapid wash-out in patients with recurrent and residual lesions at 1- and 3-month follow-ups. |
| Chiang et al., 2023; [23] | MWA | Porcine | 5 | Quantitative | Ktrans, kep | Perfusion parameters were significantly lower in embolized liver lobes than in nonembolized liver lobes, and there was a moderate but significant correlation between normalized kep and ablation volume. |
| Moon et al., 2016; [24] | RFA | Rabbit | 9 | Quantitative | Ktrans, ve, vp | Measuring from both the partial necrotic area (PNA) and viable tumor area (VTA), mean Ktrans values were positively correlated with mean microvascular density (MVD). |
| Ren et al., 2024; [25] | MWA, donafenib | Rabbit | 40 | Quantitative | Ktrans | Ktrans and tumor diameter were significantly greater in the insufficient MWA group than in the control sufficient MWA group. The serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) concentration, Ktrans, and tumor diameter were significantly lower in the combined treatment group than in the other two groups. |
| Saleh et al., 2019; [26] | TACE | Humans | 30 | Qualitative | Arterial-phase hyperenhancement | DCE-MRI showed a 100% level of sensitivity using the application of the LI-RADS v2018 (the Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System) diagnostic algorithmic approach to evaluate HCC viability following TACE. |
| Svecic et al., 2021; [27] | TACE | Humans | 366 | Quantitative | Spatial–temporal features of DCE-MRI images pre-TACE, Onset time (To), time to peak (TTP), peak enhancement (ΔS), peak enhancement ratio (PER), normalized maximum intensity time ratio (nMITR), wash-in slope, wash-out slope, distribution volume (DV), arterial fraction (ART), K2, Ka, Kp | The Spatial–Temporal Discriminant Graph Neural Network predicted post-TACE response with 93.5% accuracy and generated follow-up images with no significant differences in perfusion parameters compared to ground-truth post-TACE examinations. |
| Kuang et al., 2021; [28] | TACE | Humans | 153 | Quantitative | DCE-MRI arterial phase features pre-TACE | Nomograms combining DCE-MRI arterial phase radiomics features with clinical variables predicted short-term response in HCC ≤ 5 cm with AUC = 0.83 (training) and 0.81 (validation), outperforming radiomics-only and clinical-only models. |
| Thibodeau-Antonacci et al, 2019; [29] | TACE | Humans | 28 | Semiquantitative | Onset time (To), time to peak (TTP), peak enhancement (ΔS), peak enhancement ratio (PER), normalized maximum intensity time ratio (nMITR), wash-in slope, wash-out slope | For non-viable tumors, time to peak increased after TACE. For equivocal or viable tumors, time to peak and mean transit time significantly increased and the transfer constant from the extracellular, and extravascular space to the central vein significantly decreased. |
| Saito et al., 2018; [30] | TACE, Sorafenib | Humans | 11 | Quantitative | Distribution volume of contrast agent (DV), Ktrans | DV was reduced in responders at 3 and 10 days post-TACE. DV fell in non-responders at three days but was not significantly changed from pre-TACE values after sorafenib. |
| Pokuri et al., 2018; [31] | TACE, Sunitinib | Humans | 16 | Quantitative | Ktrans | Mean Ktrans and viable tumor percent decreased with combination therapy. |
| Hectors et al., 2020; [32] | 90Y | Humans | 24 | Semiquantitative/Quantitative | Arterial–venous blood flow, portal venous blood flow, total liver blood flow, arterial flow fraction, mean transit time, ve, intracellular uptake rate (Ki), uptake fraction (fi) | Tumor DCE-MRI parameters of arterial–venous blood flow, arterial fraction, and ve showed a significant reduction at 6 weeks post radioembolization compared with baseline values, whereas fi showed a significant increase. |
| Zhang et al., 2022; [33] | 90Y | Humans | 25 | Quantitative | Ktrans, ve, Quantitative transport mapping (QTM) velocity | DCE-MRI with quantitative transport mapping demonstrated significant correlation between QTM velocity (|u|) and lung shunting fraction (LSF), along with increased Ktrans and ve in the high LSF group. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.M.; Nguyen, T.; Sparks, H.D.; Sung, K.; Chiang, J. Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Emerging Applications for Locoregional Therapy. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080870
Li XM, Nguyen T, Sparks HD, Sung K, Chiang J. Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Emerging Applications for Locoregional Therapy. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(8):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080870
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyi M., Tu Nguyen, Hiro D. Sparks, Kyunghyun Sung, and Jason Chiang. 2025. "Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Emerging Applications for Locoregional Therapy" Bioengineering 12, no. 8: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080870
APA StyleLi, X. M., Nguyen, T., Sparks, H. D., Sung, K., & Chiang, J. (2025). Quantitative Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DCE-MRI) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Emerging Applications for Locoregional Therapy. Bioengineering, 12(8), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080870









