From Pixels to Precision—A Dual-Stream Deep Network for Pathological Nuclei Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
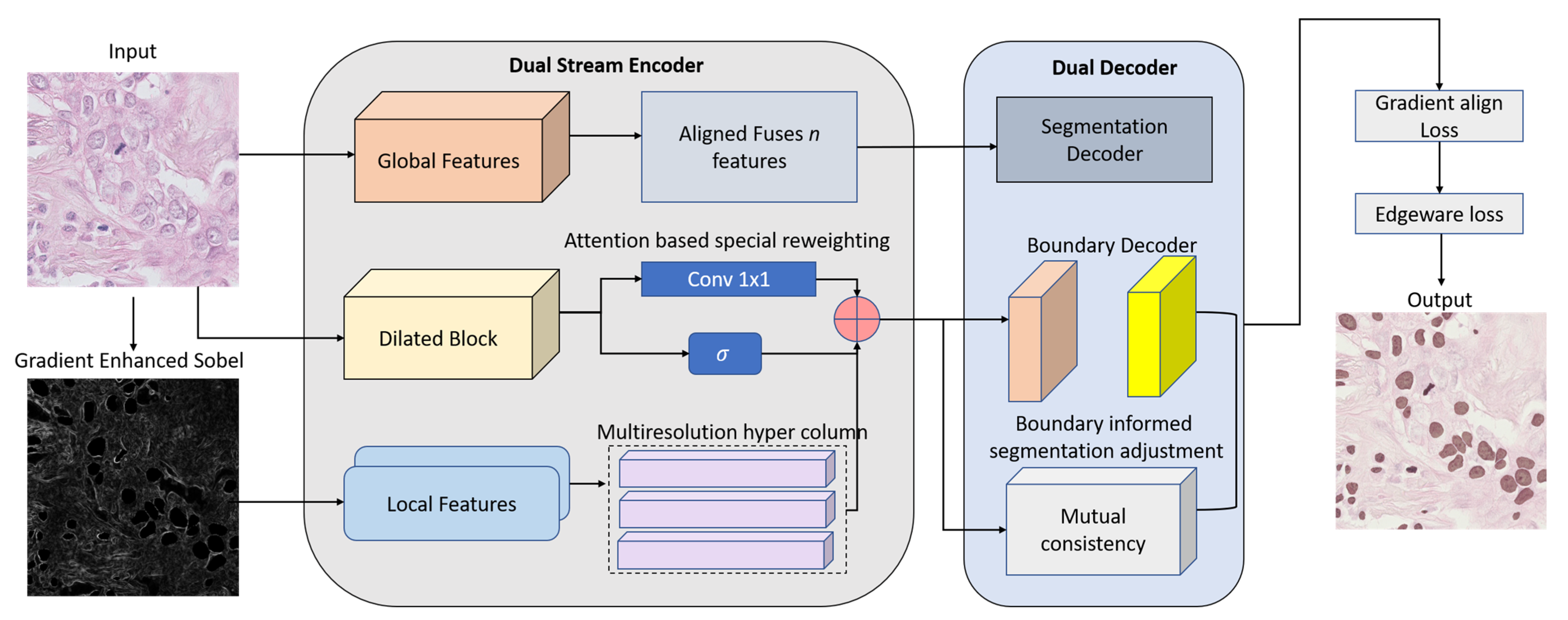
3.1. Dual-Stream Encoder
3.2. HyperFeature Embedding Module (HFEM)
3.3. Dual Decoders with Boundary-Aware Refinement
3.4. Gradient-Aligned Loss Function
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Training Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Shi, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y. PointFormer: Keypoint-Guided Transformer for Simultaneous Nuclei Segmentation and Classification in Multi-Tissue Histology Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2025, 34, 2883–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, A.; Kumar, P. Automated breast nuclei feature extraction for segmentation in histopathology images using Deep-CNN-based gaussian mixture model and color optimization technique. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, S.; Dura, E.; Domingo, J.; Martin, S. Advancing histopathology in Health 4.0: Enhanced cell nuclei detection using deep learning and analytic classifiers. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2025, 91, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Dong, W.; He, H.; Wang, S. HistoNeXt: Dual-mechanism feature pyramid network for cell nuclear segmentation and classification. BMC Med. Imaging 2025, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Chu, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Yi, B. Instance-level semantic segmentation of nuclei based on multimodal structure encoding. BMC Bioinform. 2025, 26, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Umirzakova, S.; Boymatov, E.; Zaripova, D.; Kamalov, S.; Temirov, Z.; Jeong, W.; Choi, H.; Whangbo, T.K. A Human-Centric, Uncertainty-Aware Event-Fused AI Network for Robust Face Recognition in Adverse Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhao, S.L.; Zhao, X.T.; Zhang, L.Z.; Gu, C.D.; Zhao, Y. Investigating lung cancer microenvironment from cell segmentation of pathological image and its application in prognostic stratification. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi Priya, C.V.; Biju, V.G.; Bhooshan, R.S. Enhancing nuclei segmentation in breast histopathology images using U-Net with backbone architectures. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 193, 110347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtiyorov, S.; Umirzakova, S.; Musaev, M.; Abdusalomov, A.; Whangbo, T.K. Real-Time Object Detector for Medical Diagnostics (RTMDet): A High-Performance Deep Learning Model for Brain Tumor Diagnosis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunesh Tripathi, J.; Saini, A.; Tiwari, S.; Kumari, S.; Taqui, S.N.; Almoallim, H.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Raghavan, S.S. Nucleus segmentation from the histopathological images of liver cancer through an efficient deep learning framework. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 84, 5025–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; He, J. UPHGAN: Generative Adversarial Network Based on Unet512 and PatchGAN Fusion with Huber Loss Function for Immunohistochemical Cell Nucleus Segmentation. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 88–101. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, S.; Prasad, K.; Robels-Kelly, A.; Lu, X. AI-based carcinoma detection and classification using histopathological images: A systematic review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 142, 105209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumbhare, P.; Dubey, Y.; Phuse, V.; Jamthikar, A.; Padole, H.; Gupta, D. November. Combining deep-learned and hand-crafted features for segmentation, classification and counting of colon nuclei in H &E Stained histology images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing, Nagpur, India, 4–6 November 2022; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 686–698. [Google Scholar]
- Abdusalomov, A.; Mirzakhalilov, S.; Umirzakova, S.; Kalandarov, I.; Mirzaaxmedov, D.; Meliboev, A.; Cho, Y.I. Optimized Lightweight Architecture for Coronary Artery Disease Classification in Medical Imaging. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, W.; Wan, X.; Li, G.; Lou, X.; Li, C.; Gao, F.; Li, H. Structure embedded nucleus classification for histopathology images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024, 43, 3149–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.Z.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Nyberg, P.; Seppänen, T. Stain normalization methods for histopathology image analysis: A comprehensive review and experimental comparison. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V.; Artinger, A.; Daza Barragan, L.A.; Daza, J.; Winter, L.; Niedermair, T.; Itzel, T.; Arbelaez, P.; Teufel, A.; Cotarelo, C.L.; et al. Nuclei Detection and Segmentation of Histopathological Images Using a Feature Pyramidal Network Variant of a Mask R-CNN. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wan, X.; Zhou, L.; Song, W.; Zhu, S.; Yuan, X. Classes U-Net: A method for nuclei segmentation of photoacoustic histology imaging based on information entropy image classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 91, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Pan, J.; Jia, Z.; Xiao, S.; Tao, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Pan, L. A method of nucleus image segmentation and counting based on TC-UNet++ and distance watershed. Med. Eng. Phys. 2024, 133, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.J.; Ahmad, W.S.H.M.W.; Fauzi, M.F.A.; Lee, J.T.H.; Khor, S.Y.; Looi, L.M.; Abas, F.S. An Attention Based Model for Histopathology Image Nuclei Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 April 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kadaskar, M.; Patil, N. ANet: Nuclei Instance Segmentation and Classification with Attention-Based Network. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, B.; Lai, M.; Shou, J.; Fan, Y.; Xu, Y. MSNSegNet: Attention-based multi-shape nuclei instance segmentation in histopathology images. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Tan, X. BES-Net: Boundary Enhancing Semantic Context Network for High-Resolution Image Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Boundary Attention U-Net for Kidney and Kidney Tumor Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 1540–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, R.; Yazid, H.; Farhat, W.; Amara, N.E.B. SBC-UNet3+: Classification of Nuclei in Histology Imaging Based on Multi Branch UNET3+ Segmentation Model. Proc. Copyr. 2025, 601, 609. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Meng, Q.; Tan, D.; Wei, P.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, C. AER-Net: Attention-Enhanced Residual Refinement Network for Nuclei Segmentation and Classification in Histology Images. Sensors 2024, 24, 7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.M.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, G.; Ge, Y.; Ke, T.; Shi, K. Pancreatic cancer pathology image segmentation with channel and spatial long-range dependencies. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 169, 107844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zhou, X.; Tan, D.; Su, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yu, G.; Zheng, C. A deep multi-branch attention model for histopathological breast cancer image classification. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 4571–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Vu, Q.D.; Raza, S.E.A.; Azam, A.; Tsang, Y.W.; Kwak, J.T.; Rajpoot, N. Hover-net: Simultaneous segmentation and classification of nuclei in multi-tissue histology images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Yu, L.; Heng, P.A. DCAN: Deep contour-aware networks for accurate gland segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2487–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Onder, O.F.; Dou, Q.; Tsougenis, E.; Chen, H.; Heng, P.A. CIA-Net: Robust Nuclei Instance Segmentation with Contour-Aware Information Aggregation. In Information Processing in Medical Imaging; Chung, A., Gee, J., Yushkevich, P., Bao, S., Eds.; IPMI 2019; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufyan, A.; Fauzi, M.F.A.; Kuan, W.L. M3-Net: A Multi-Scale Nuclei Segmentation Model for Breast Cancer Histopathology Using Contextual Patches and Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 April 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Pan, K.; Ren, Y.; Lu, R.; Zhang, J. Multi-branch spectral channel attention network for breast cancer histopathology image classification. Electronics 2024, 13, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. DualBranch-FusionNet: A Hybrid CNN-Transformer Architecture for Cervical Cell Image Classification. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2025, 35, e70101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, S.P.; Palanisamy, R.; Swaminathan, R. An Approach to Segment Nuclei and Cytoplasm in Lung Cancer Brightfield Images Using Hybrid Swin-Unet Transformer. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2024, 44, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, S.; Memiş, A.; Varlı, S. Segmentation of Cell Nuclei in Histology Images with Vision Transformer Based U-Net Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 32nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Mersin, Turkey, 15–18 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mezei, T.; Kolcsár, M.; Joó, A.; Gurzu, S. Image Analysis in Histopathology and Cytopathology: From Early Days to Current Perspectives. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, E. Vision gnn: An image is worth graph of nodes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 8291–8303. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.W.; Yu, P.D.; Chen, S.; Poor, H.V. DeepTrace: Learning to optimize contact tracing in epidemic networks with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Netw. 2025, 11, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Zhong, D. MATNet: A multi-attention transformer network for nuclei segmentation in thymoma histopathology images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 60735–60759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, T.; Fattah, S.A.; Kung, S.Y. BAWGNet: Boundary aware wavelet guided network for the nuclei segmentation in histopathology images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 165, 107378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qu, Z.; Chen, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, K.T. Nuclei segmentation with point annotations from pathology images via self-supervised learning and co-training. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 89, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Dataset | Tissue Source(s) | Images | Annotation Type | Image Size | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNBC | Breast (TNBC) | 50 | Binary masks | 512 × 512 | Dense overlap, jagged contours |
| MoNuSeg | Multi-organ | 30 | Instance masks | ~2000 × 2000 | Cross-domain variability, scale heterogeneity |
| Parameter | Value/Setting |
|---|---|
| Framework | PyTorch v2.1.0 (CUDA 11.8) |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Initial Learning Rate | 1 × 10−4 |
| Learning Rate Schedule | Cosine annealing with warm restarts |
| Weight Decay | 0.01 |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Epochs | 200 |
| Early Stopping Patience | 15 epochs |
| Mixed Precision Training | Enabled (PyTorch AMP) |
| Gradient Clipping Norm | 5.0 |
| Convolution Initialization | He initialization |
| Input Size | 256 × 256 |
| Image Preprocessing | Grayscale conversion, standardization |
| Data Augmentation | Rotation, flipping, elastic deformation |
| Random Seed | 42 |
| Prediction Threshold | 0.5 |
| Loss Function Weights (α/β/γ) | 0.6/0.2/0.2 |
| Checkpointing Criterion | Best validation Dice score |
| Edge Enhancement Method | Sobel filter (3 × 3 kernel) |
| Train–Validation–Test Split | 5-fold cross-validation with stratified sampling |
| Model | Dice Score | IoU | BF1 Score | Hausdorff Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS-HFN (ours) | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 8.2 |
| Xu et al. [1] | 0.89 | 0.738 | 0.68 | 13.69 |
| Chen et al. [4] | 0.89 | 0.793 | 0.729 | 10 |
| Guan et al. [5] | 0.89 | 0.788 | 0.736 | 16.18 |
| Liu et al. [18] | 0.873 | 0.702 | 0.79 | 16.04 |
| Hasan et al. [20] | 0.869 | 0.779 | 0.685 | 12.19 |
| Kadaskar et al. [21] | 0.866 | 0.788 | 0.708 | 14.06 |
| Qian et al. [22] | 0.865 | 0.756 | 0.716 | 15.39 |
| Jaafar et al. [25] | 0.861 | 0.768 | 0.756 | 10.33 |
| Cao et al. [26] | 0.859 | 0.822 | 0.725 | 15.7 |
| Ding et al. [28] | 0.857 | 0.775 | 0.738 | 13.63 |
| Sufyan et al. [32] | 0.853 | 0.817 | 0.715 | 16.21 |
| Cao et al. [33] | 0.852 | 0.753 | 0.8 | 15.24 |
| Sreekumar et al. [35] | 0.846 | 0.84 | 0.731 | 18.87 |
| Xu et al. [1] | 0.843 | 0.765 | 0.758 | 14.89 |
| Imtiaz et al. [41] | 0.882 | 0.801 | 0.791 | 11.6 |
| Lin et al. [42] | 0.871 | 0.783 | 0.764 | 13.8 |
| Variant | Dice Score | IoU | BF1 Score | Hausdorff Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full DS-HFN (proposed) | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 8.2 |
| w/o Global Stream (Local Only) | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 14.5 |
| w/o Local Stream (Global Only) | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 17.3 |
| w/o HFEM Fusion | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 15.8 |
| w/o Boundary Decoder | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 13.4 |
| w/o Gradient-Aligned Loss LGLGA | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 15.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasimov, R.; Zohirov, K.; Dauletov, A.; Abdusalomov, A.; Cho, Y.I. From Pixels to Precision—A Dual-Stream Deep Network for Pathological Nuclei Segmentation. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080868
Nasimov R, Zohirov K, Dauletov A, Abdusalomov A, Cho YI. From Pixels to Precision—A Dual-Stream Deep Network for Pathological Nuclei Segmentation. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(8):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080868
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasimov, Rashid, Kudratjon Zohirov, Adilbek Dauletov, Akmalbek Abdusalomov, and Young Im Cho. 2025. "From Pixels to Precision—A Dual-Stream Deep Network for Pathological Nuclei Segmentation" Bioengineering 12, no. 8: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080868
APA StyleNasimov, R., Zohirov, K., Dauletov, A., Abdusalomov, A., & Cho, Y. I. (2025). From Pixels to Precision—A Dual-Stream Deep Network for Pathological Nuclei Segmentation. Bioengineering, 12(8), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080868





