Evaluating Accuracy of Smartphone Facial Scanning System with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- This smartphone scanner’s trueness is clinically acceptable for diagnosis and treatment planning, as the errors were of less than 2 mm in 91% of the subjects.
- The precision of this system was excellent, demonstrating scanning repeatability.
- The intraobserver agreement was rated as excellent, indicating the reliability of measurements conducted by the operator.
- This smartphone facial scanner offers three-dimensional scanning, which is a clinically acceptable alternative to traditional three-dimensional imaging systems. However, clinicians should be cautious when considering the lateral portions of those 3D images due to inherent inaccuracies.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plooij, J.M.; Swennen, G.; Rangel, F.; Maal, T.; Schutyser, F.; Bronkhorst, E.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.; Bergé, S. Evaluation of Reproducibility and Reliability of 3D Soft Tissue Analysis Using 3D Stereophotogrammetry. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, N.-K.; Moon, S.-W.; Jang, M.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Yun, P.-Y. Evaluation of Soft Tissue Changes around the Lips after Bracket Debonding Using Three-Dimensional Stereophotogrammetry. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baysal, A.; Ozturk, M.A.; Sahan, A.O.; Uysal, T. Facial Soft-Tissue Changes after Rapid Maxillary Expansion Analyzed with 3-dimensional Stereophotogrammetry: A Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, T.; Zhou, H.; Hou, Y. Lip Position Analysis of Young Women with Different Skeletal Patterns during Posed Smiling Using 3-dimensional Stereophotogrammetry. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 155, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erten, O.; Yılmaz, B.N. Three-Dimensional Imaging in Orthodontics. Turk. J. Orthod. 2018, 31, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, E.İ.; Gonzales, C.; Elekdag-Turk, S.; Isci, D.; Sahin-Saglam, A.M.; Alkis, H.; Turk, T.; Darendeliler, M.A. The Effect of Fluoride on Orthodontic Tooth Movement in Humans: A Two- and Three-Dimensional Evaluation. Australas. Orthod. J. 2011, 27, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindaroglu, F.; Kutlu, P.; Duran, G.S.; Görgülü, S.; Aslan, E. Accuracy and Reliability of 3D Stereophotogrammetry: A Comparison to Direct Anthropometry and 2D Photogrammetry. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoops, P.G.; Beaumont, C.A.A.; Borghi, A.; Rodriguez-Florez, N.; Breakey, R.W.; Rodgers, W.; Angullia, F.; Jeelani, N.O.; Schievano, S.; Dunaway, D.J. Comparison of Three-Dimensional Scanner Systems for Craniomaxillofacial Imaging. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2017, 70, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwilliam, J.; Cunningham, S.J.; Hutton, T. Reproducibility of Soft Tissue Landmarks on Three-Dimensional Facial Scans. Eur. J. Orthod. 2006, 28, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, L.; Zimmermann, A.; Brockmann, G.; Baurecht, H.; Schwenzer-Zimmerer, K.; Papadopulos, N.; Papadopoulos, M.; Sader, R.; Biemer, E.; Zeilhofer, H. Accuracy and Precision of the Three-Dimensional Assessment of the Facial Surface Using a 3-D Laser Scanner. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2006, 25, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, T.; Jun, L. Validation of a Three-Dimensional Facial Scanning System Based on Structured Light Techniques. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2009, 94, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Lv, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation of the Accuracy, Reliability, and Reproducibility of Two Different 3D Face-Scanning Systems. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 29, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaar, S.T.; Van Der Zel, J. Accuracy of Dental Digitizers. Int. Dent. J. 2006, 56, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akan, B.; Akan, E.; Şahan, A.O.; Kalak, M. Evaluation of 3D Face-Scan Images Obtained by Stereophotogrammetry and Smartphone Camera. Int. Orthod. 2021, 19, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apple, Inc. About Face ID Advanced Technology. Available online: https://support.apple.com/en-us/102381 (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Elbashti, M.E.; Sumita, Y.; Aswehlee, A.; Seelaus, R. Smartphone Application as a Low-Cost Alternative for Digitizing Facial Defects: Is It Accurate Enough for Clinical Application? Int. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 32, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellitteri, F.; Brucculeri, L.; Spedicato, G.A.; Siciliani, G.; Lombardo, L. Comparison of the Accuracy of Digital Face Scans Obtained by Two Different Scanners. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellus3D. Available online: https://swe-dent.se/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Scandy Inc. (2024). Scandy Pro (Version 1.8.5) [Mobile Application Software]. Apple App Store. Available online: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/scandy-pro/id1138160215 (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Kook, M.; Jung, S.; Park, H.-J.; Oh, H.-K.; Ryu, S.-Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Yoon, S.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Shin, H.-K. A Comparison Study of Different Facial Soft Tissue Analysis Methods. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerenhout, B.A.; Gelaude, F.; Swennen, G.R.; Casselman, J.W.; Van Der Sloten, J.; Mommaerts, M.Y. Accuracy and Repeatability of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Measurements Used in the Determination of Facial Indices in the Laboratory Setup. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 37, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, C.H.; Richmond, S.; Incrapera, A.; English, J.; Xia, J.J. Three-Dimensional Surface Acquisition Systems for the Study of Facial Morphology and Their Application to Maxillofacial Surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2007, 3, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5725-1:2023; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 1: General Principles and Definitions. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/69418.html (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Gibelli, D.; Dolci, C.; Cappella, A.; Sforza, C. Reliability of Optical Devices for Three-Dimensional Facial Anatomy Description: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, L.G. Anthropometry of the Head and Face, 2nd ed.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Maal, T.; van Loon, B.; Plooij, J.M.; Rangel, F.; Ettema, A.M.; Borstlap, W.A.; Bergé, S.J. Registration of 3-Dimensional Facial Photographs for Clinical Use. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, S.C.; Ngim, R.C.; Lee, S. Evaluation of the Laser Scanner as a Surface Measuring Tool and Its Accuracy Compared with Direct Facial Anthropometric Measurements. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1995, 48, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Cai, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liao, W. Accuracy of 3-Dimensional Stereophotogrammetry: Comparison of the 3dMD and Bellus3D Facial Scanning Systems with One Another and with Direct Anthropometry. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 160, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.; Alwafi, A.; Bichu, Y.M.; Pliska, B.T.; Mostafa, N.; Zou, B. Validation of Three-Dimensional Facial Imaging Captured with Smartphone-Based Photogrammetry Application in Comparison to Stereophotogrammetry System. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ettorre, G.; Farronato, M.; Candida, E.; Quinzi, V.; Grippaudo, C. A Comparison Between Stereophotogrammetry and Smartphone Structured Light Technology for Three-Dimensional Face Scanning. Angle Orthod. 2022, 92, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps-Perepérez, I.; Guijarro-Martínez, R.; Peiró-Guijarro, M.A.; Hernández-Alfaro, F. The value of cone beam computed tomography imaging in surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhammadi, M.S.; Al-Mashraqi, A.A.; Alnami, R.H.; Ashqar, N.M.; Alamir, O.H.; Halboub, E.; Reda, R.; Testarelli, L.; Patil, S. Accuracy and Reproducibility of Facial Measurements of Digital Photographs and Wrapped Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Photographs. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piedra-Cascón, W.; Meyer, M.J.; Methani, M.M.; Revilla-León, M. Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of a Dual-Structured Light Facial Scanner and Interexaminer Reliability. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asutay, H.C.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Benli, M.; Martinez, J.L. Transforming smiles using an intraoral scanner and face scan application on smartphone. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 1413–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rudy, H.L.; Wake, N.; Yee, J.; Garfein, E.S.; Tepper, O.M. Three-Dimensional Facial Scanning at the Fingertips of Patients and Surgeons: Accuracy and Precision Testing of iPhone X Three-Dimensional Scanner. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heike, C.L.; Upson, K.; Stuhaug, E.; Weinberg, S.M. 3D Digital Stereophotogrammetry: A Practical Guide to Facial Image Acquisition. Head Face Med. 2010, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühlman, D.C.; Almuzian, M.; Coppini, C.; Alzoubi, E.E. Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Four Tablet-Based Applications for Three-Dimensional Facial Scanning: An In-Vitro Study. J. Dent. 2023, 135, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.V.; Izadi, S.; Lovell, D. Modeling Kinect sensor noise for improved 3D reconstruction and tracking. In Proceedings of the 2012 Second Joint 3DIM/3DPVT Conference: 3D Imaging, Modeling, Processing, Visualization & Transmission, Zurich, Switzerland, 13–15 October 2012; pp. 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, R.J.; Liew, M.K.M.; Yong, C.W.; Wong, R.C.W. Validation of Low-Cost Mobile Phone Applications and Comparison with Professional Imaging Systems for Three-Dimensional Facial Imaging: A Pilot Study. J. Dent. 2023, 137, 104676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Menezes, M.; Rosati, R.; Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C. Accuracy and Reproducibility of a 3-Dimensional Stereophotogrammetric Imaging System. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2129–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, K.P.; Sun, A.Y.; Prihoda, T.J.; Sutton, A.J. Comparative Accuracy of Facial Models Fabricated Using Traditional and 3D Imaging Techniques. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 25, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, S.; Giberti, L.; Vigolo, P.; Stellini, E.; Di Fiore, A. Incorporating a facial scanner into the digital workflow: A dental technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 123, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apple Developer. Available online: https://forums.developer.apple.com/forums/thread/694147 (accessed on 6 March 2024).

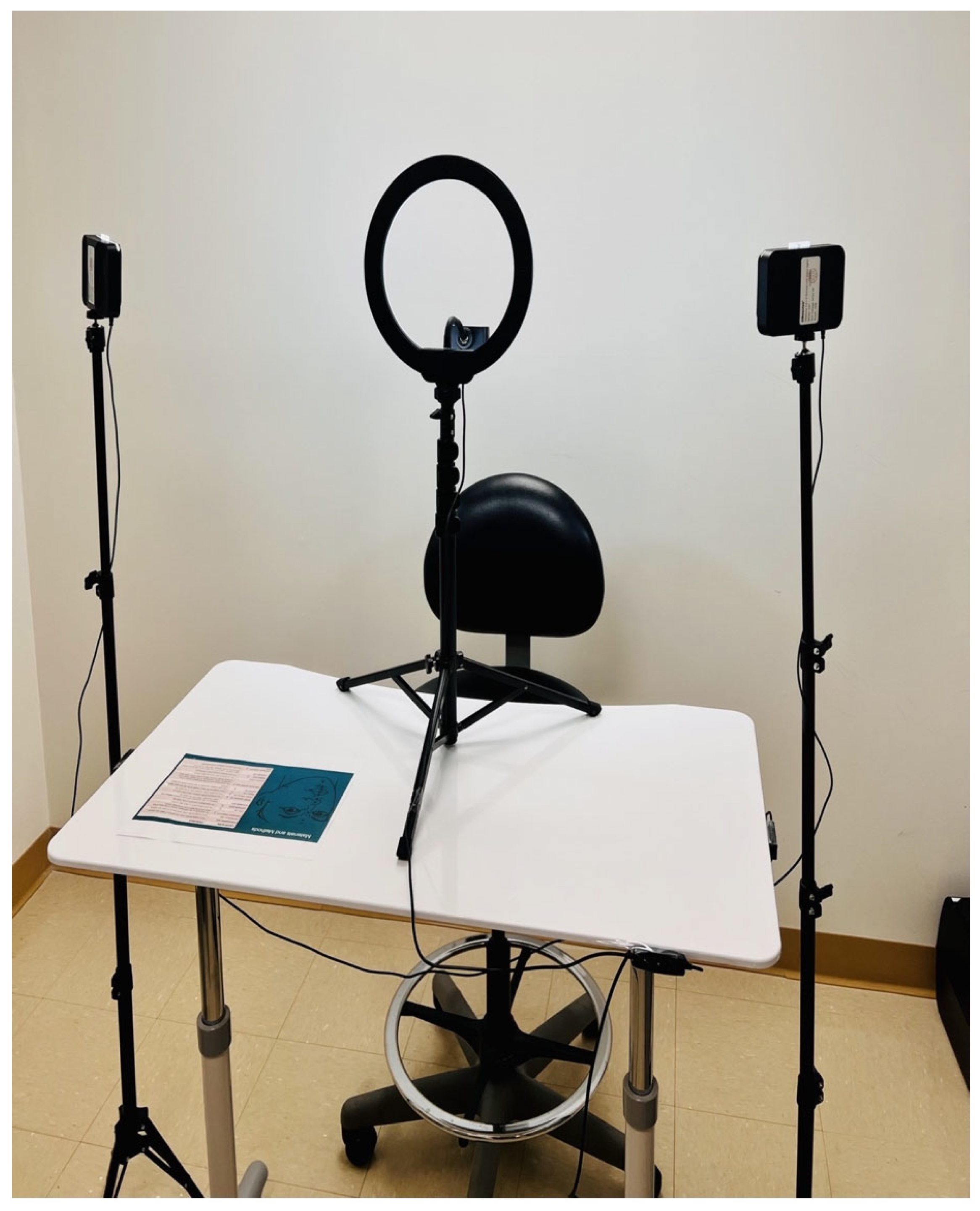
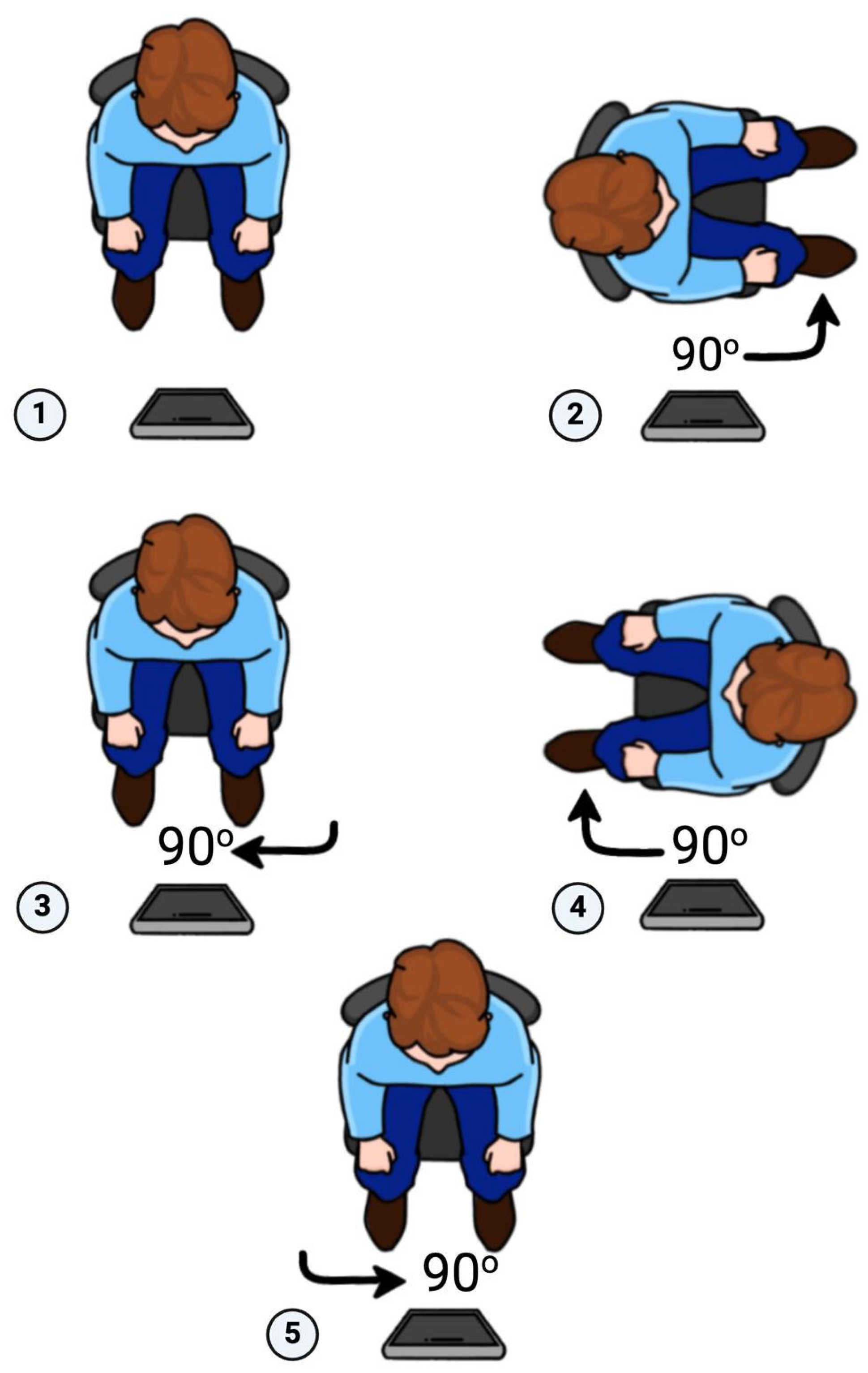
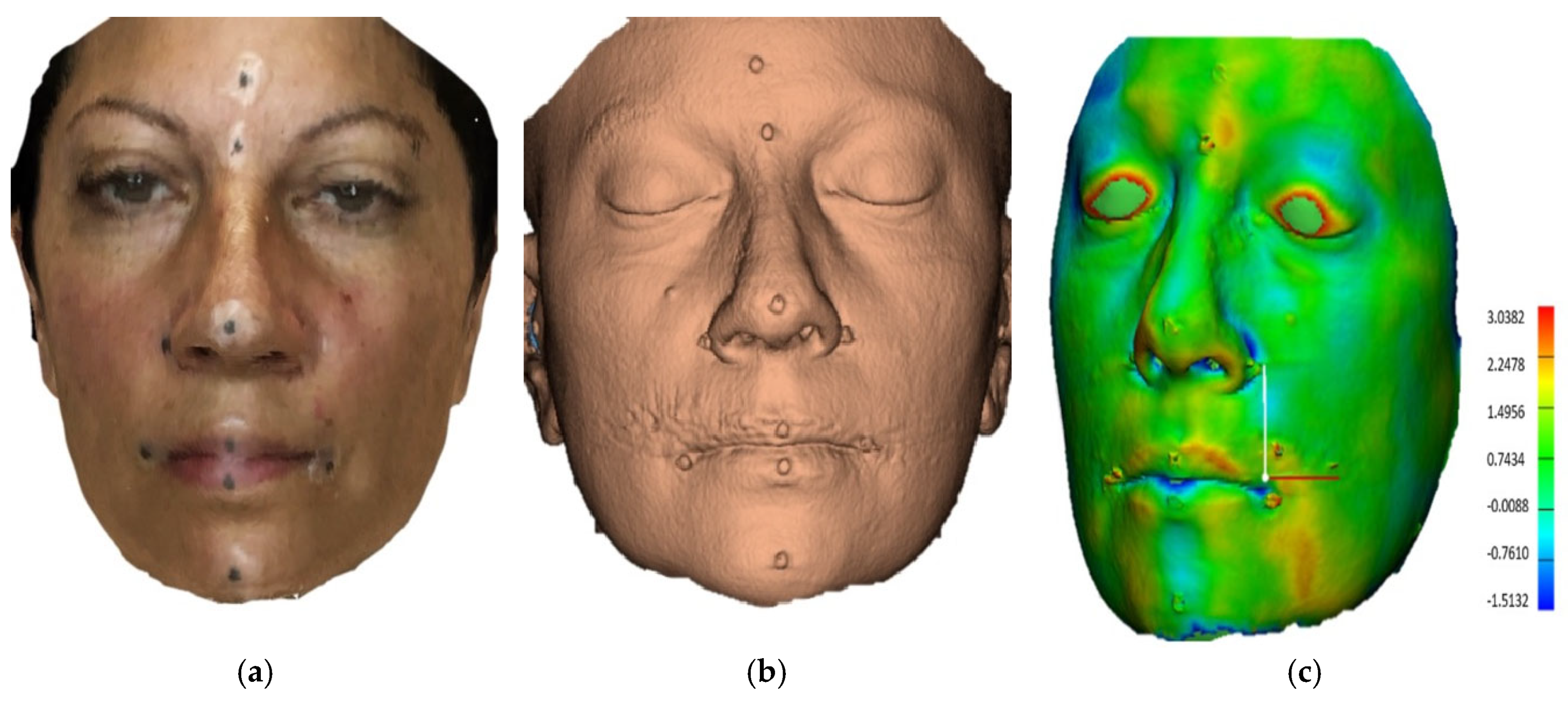
| Linear Measurements | ScandyPro | CBCT | Mean Absolute Diff | 95% CI of the Diff: Lower | 95% CI of the Diff: Upper | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| N-Pg (mm) | 107.91 | 7.03 | 109.2 | 7.44 | 1.29 | −6.05 | 2.54 | 0.416 |
| N-Sn (mm) | 55.47 | 5.80 | 56.65 | 5.79 | 1.18 | −4.91 | 1.97 | 0.435 |
| Sn-Pg (mm) | 53.78 | 5.93 | 54.83 | 5.58 | 1.05 | −4.48 | 2.37 | 0.538 |
| Sn-Sl (mm) | 39.37 | 5.11 | 40.53 | 5.43 | 1.16 | −4.29 | 1.97 | 0.461 |
| Ls-Li (mm) | 14.21 | 3.87 | 14.51 | 3.94 | 0.3 | −2.62 | 2.01 | 0.793 |
| Ch(R)-Ch(L) (mm) | 58.84 | 7.5 | 59.68 | 7.1 | 0.84 | −5.17 | 3.5 | 0.701 |
| Al(R)-Al(L) (mm) | 44.17 | 5.16 | 45.61 | 5.45 | 1.44 | −4.59 | 1.72 | 0.365 |
| Ex(R)-Ex(L) (mm) | 94.71 | 7.4 | 96.83 | 7.16 | 2.12 | −6.95 | 1.7 | 0.229 |
| En(R)-En(L) (mm) | 35.92 | 3.49 | 36.67 | 3.63 | 0.75 | −2.87 | 1.36 | 0.477 |
| Tr(L)-Tr(R) (mm) | 145.78 | 9.79 | 149.38 | 9.33 | 3.05 | −9.29 | 2.08 | 0.358 |
| Go(L)-Go(R) (mm) | 126.5 | 13.11 | 129.03 | 13.54 | 2.53 | −10.44 | 5.39 | 0.524 |
| Angular Measurements | ScandyPro | CBCT | Mean Absolute Diff | 95% CI of the Diff: Lower | 95% CI of the Diff: Upper | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||||
| Prn-Sn-Ls (°) | 127.15 | 12.82 | 130.77 | 9.56 | 3.62 | −10.33 | 3.10 | 0.284 |
| N-Prn-Pg (°) | 134.25 | 8.46 | 133.47 | 8.45 | 0.78 | −4.24 | 5.80 | 0.756 |
| Prn-Sn-Pg (°) | 137.5 | 11.04 | 142.58 | 9.62 | 5.08 | −11.23 | 1.08 | 0.104 |
| Subject | Average Distance | RMS | Maximum Distance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | |||
| 1 | 0.65 | 1.54 | −0.78 | 5.14 |
| 2 | 0.67 | 1.4 | −1.39 | 4.57 |
| 3 | 0.32 | 1.12 | −1.87 | 3.26 |
| 4 | 0.49 | 1.93 | −5.07 | 4.84 |
| 5 | 0.91 | 1.84 | −2.09 | 5.34 |
| 6 | 1.14 | 2.15 | −3.7 | 6.12 |
| 7 | 0.17 | 1.11 | −3.22 | 3.54 |
| 8 | 1.11 | 1.91 | −1.47 | 5.37 |
| 9 | 0.4 | 1.69 | −2.71 | 4.88 |
| 10 | 0.61 | 1.51 | −2.99 | 3.94 |
| 11 | 0.94 | 2.05 | −4.02 | 5.91 |
| 12 | 0.43 | 1.36 | −4.47 | 4.09 |
| 13 | 0.48 | 1.27 | −1.77 | 3.81 |
| 14 | 0.55 | 1.13 | −1.51 | 3.03 |
| 15 | 0.84 | 1.77 | −2.64 | 5.86 |
| 16 | 0.48 | 1.38 | −4.32 | 3.34 |
| 17 | 0.4 | 1.35 | −1.79 | 4.43 |
| 18 | 0.54 | 0.98 | −0.89 | 3.05 |
| 19 | 0.56 | 1.21 | −2 | 4.12 |
| 20 | 0.11 | 1.76 | −5.18 | 5.12 |
| 21 | 0.18 | 1.44 | −3.71 | 3.89 |
| 22 | 0.35 | 0.96 | −1.15 | 2.78 |
| 23 | 0.56 | 1.15 | −2.67 | 3.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Megkousidis, K.; Amm, E.; Motro, M. Evaluating Accuracy of Smartphone Facial Scanning System with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080792
Megkousidis K, Amm E, Motro M. Evaluating Accuracy of Smartphone Facial Scanning System with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(8):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080792
Chicago/Turabian StyleMegkousidis, Konstantinos, Elie Amm, and Melih Motro. 2025. "Evaluating Accuracy of Smartphone Facial Scanning System with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images" Bioengineering 12, no. 8: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080792
APA StyleMegkousidis, K., Amm, E., & Motro, M. (2025). Evaluating Accuracy of Smartphone Facial Scanning System with Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images. Bioengineering, 12(8), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080792







