Artificial Intelligence for Non-Invasive Prediction of Molecular Signatures in Spinal Metastases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Review
2.2. Search Strategy
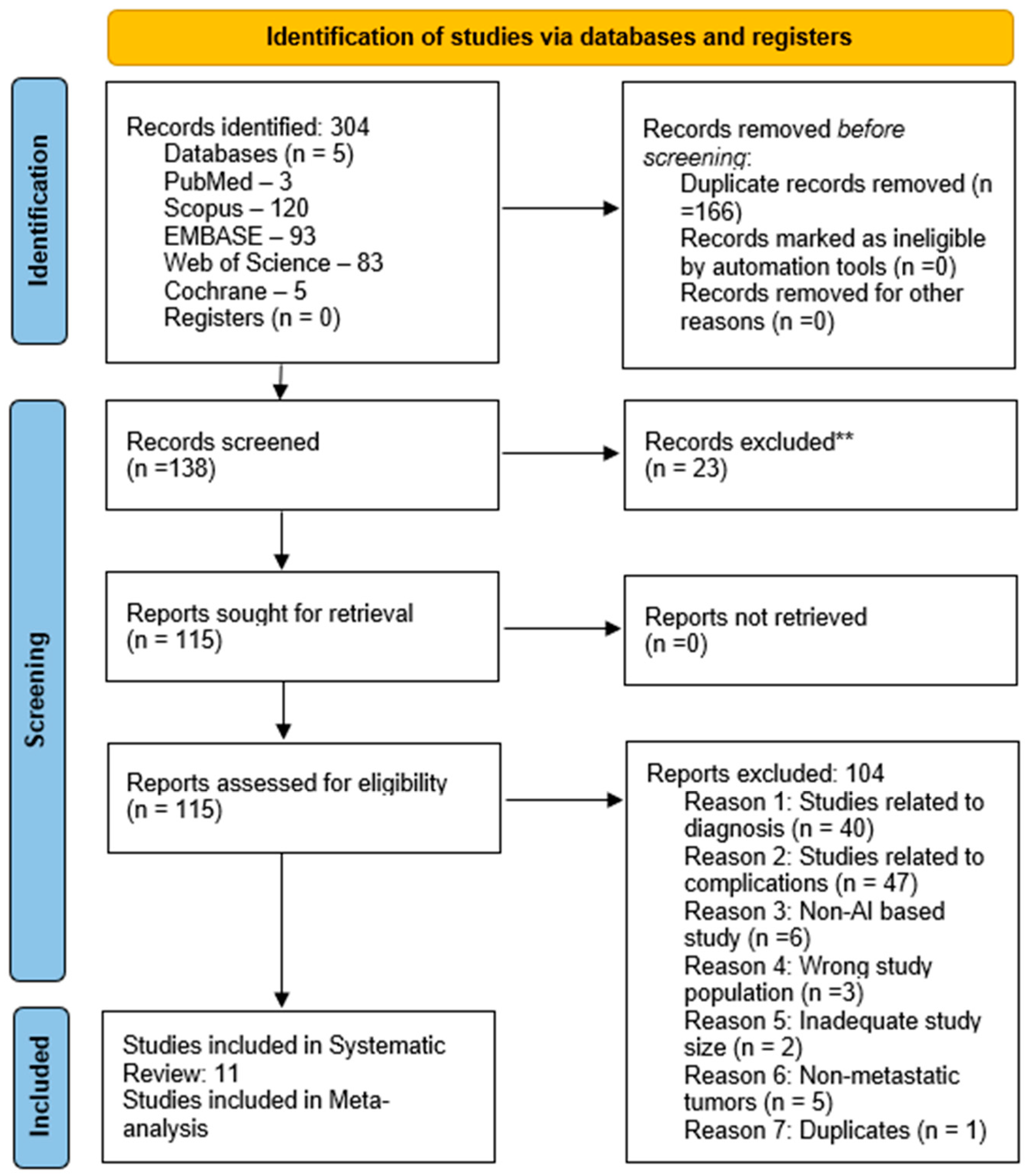
2.3. Screening of Studies
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Quality Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sciubba, D.M.; Petteys, R.J.; Dekutoski, M.B.; Fisher, C.G.; Fehlings, M.G.; Ondra, S.L.; Rhines, L.D.; Gokaslan, Z.L. Diagnosis and management of metastatic spine disease. A review. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2010, 13, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziu, E.; Viswanathan, V.K.; Mesfin, F.B. Spinal Metastasis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441950/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Van den Brande, R.; Cornips, E.M.; Peeters, M.; Ost, P.; Billiet, C.; Van de Kelft, E. Epidemiology of spinal metastases, metastatic epidural spinal cord compression and pathologic vertebral compression fractures in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review. J. Bone Oncol. 2022, 35, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, W.; Liang, Y.; Bian, C.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, G.; Dong, J. Gene expression profile analysis of the bone microenvironment in patients with spinal metastases. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schroeder, C.; Campilan, B.; Leary, O.P.; Arditi, J.; Michles, M.J.; De La Garza Ramos, R.; Akinduro, O.O.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Martinez Moreno, M.; Sullivan, P.L.Z. Therapeutic Opportunities for Biomarkers in Metastatic Spine Tumors. Cancers 2024, 16, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Xie, J. Association of mutation profiles with metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1451576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, W.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, W.; Kuah, T.; Lim, D.S.W.; Low, X.Z.; Thian, Y.L.; Teo, E.C.; Tan, J.H.; Kumar, N.; et al. Application of Artificial Intelligence Methods for Imaging of Spinal Metastasis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kourou, K.; Exarchos, T.P.; Exarchos, K.P.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Fotiadis, D.I. Machine learning applications in cancer prognosis and prediction. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 13, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, R.F.; Moons, K.G.M.; Riley, R.D.; Whiting, P.F.; Westwood, M.; Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Kleijnen, J.; Mallett, S.; PROBAST Group; et al. PROBAST: A Tool to Assess the Risk of Bias and Applicability of Prediction Model Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, L.; Huang, B.; Jiang, W. Improved Prediction of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Status by Combined Radiomics of Primary Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer and Distant Metastasis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2024, 48, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, W. Combined radiomics of primary tumour and bone metastasis improve the prediction of EGFR mutation status and response to EGFR-TKI therapy for NSCLC. Phys. Med. 2023, 116, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W. Radiomics of Spinal Metastases Originating from Primary Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer or Breast Cancer and Ability to Predict Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation/Ki-67 Levels. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2023, 47, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Sun, X.; Dong, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Yue, Z.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, X. Deep learning for preoperative prediction of the EGFR mutation and subtypes based on the MRI image of spinal metastasis from primary NSCLC. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, E.N.; Jiang, W. Comprehensive analysis of prediction of the EGFR mutation and subtypes based on the spinal metastasis from primary lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1154327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Niu, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Radiomics signatures for predicting the Ki-67 level and HER-2 status based on bone metastasis from primary breast cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 11, 1220320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X. Development and validation of MRI-based radiomics signatures as new markers for preoperative assessment of EGFR mutation and subtypes from bone metastases. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, X. Development and externally validate MRI-based nomogram to assess EGFR and T790M mutations in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6739–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, N.; Yu, T.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Cui, E.N.; et al. MRI-Based Radiomics Nomogram as a Potential Biomarker to Predict the EGFR Mutations in Exon 19 and 21 Based on Thoracic Spinal Metastases in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, e9–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, T.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, X. Subregional radiomics analysis for the detection of the EGFR mutation on thoracic spinal metastases from lung cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 215008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Yang, H.; Lai, Q.; Shi, D.; Liu, G.; Shuang, X.; Su, J.; Xie, L.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, X. MRI-based radiomics analysis for predicting the EGFR mutation based on thoracic spinal metastases in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 5142–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.J.; Karthikesalingam, A.; Suleyman, M.; Corrado, G.; King, D. Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Past, present and future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Study | Cohort Size | Mean Age ± SD | Receptor Analyzed | Primary Tumor Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al. (2024) [18] | 359 | Training cohort = 58.21 ± 9.28 Validation cohort = 59.87 ± 7.23 | EGFR | NSCLC |
| Cheng et al. (2023) [19] | 203 | Training cohort (EGFR mutant) = 58.12 ± 9.62 (EGFR wild type) = 58.82 ± 10.14 Validation cohort (EGFR mutant) = 58.41 ± 9.04 (EGFR wild type) = 60.35 ± 9.61 | EGFR | NSCLC |
| Niu et al. (2023) [20] | 268 |
NSCLC =
57.88 ± 10.81 Breast cancer = 53.71 ± 9.77 | EGFR, Ki-67 | NSCLC Breast cancer |
| Jiang et al. (2023) [21] | 265 | Training cohort (EGFR-21) = 61.91 ± 10.75 (EGFR 19) = 57.43 ± 9.34 (EGFR wild type) = 59.18 ± 9.99 Validation cohort (EGFR-21) = 61.54 ± 10.85 (EGFR 19) = 58.71 ± 9.72 (EGFR wild type) = 60.13 ± 7.38 | EGFR | NSCLC |
| Cao et al. (2023) [22] | 299 | Training cohort (EGFR mutant) = 60.19 ± 9.99 (EGFR wildtype) = 59.28 ± 10.35 Validation cohort (internal) (EGFR mutant) = 61.15 ± 11.77 (EGFR wildtype) = 59.60 ± 10.42 (external) (EGFR mutant) = 60.17 ± 7.63 (EGFR wildtype) = 60.06 ± 6.78 | EGFR | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| Zhang et al. (2024) [23] | 110 | Training cohort (High Ki-67) = 54.48 ± 9.76 (Low Ki-67) = 54.31 ± 9.06 (HER-2 positive) = 49.73 ± 11.82 (HER-2 negative) = 53.90 ± 8.70 Validation cohort (High Ki-67) = 52.50 ± 9.22 (Low Ki-67) = 49.06 ± 9.51 (HER-2 positive) = 49.01 ± 9.23 (HER-2 negative) = 56.57 ± 10.01 | HER-2, Ki-67 | Breast cancer |
| Fan et al. (2022) [24] | 183 | Training cohort (EGFR mutant) = 58.71 ± 9.34 (EGFR wildtype) = 57.14 ± 11.28 Validation cohort (internal) (EGFR mutant) = 58.14 ± 12.11 (EGFR wildtype) = 59.21 ± 8.95 (external) (EGFR mutant) = 59.06 ± 7.78 (EGFR wildtype) = 60.14 ± 5.61 | EGFR | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| Fan et al. (2022) [25] | 192 | Training cohort (EGFR mutant) = 58.69 ± 10.31 (EGFR wildtype) = 58.37 ± 9.59 Validation cohort (internal) (EGFR mutant) = 61.5 ± 7.39 (EGFR wildtype) = 56.88 ± 10.10 (external) (EGFR mutant) = 63.06 ± 9.11 (EGFR wildtype) = 60.86 ± 6.64 | EGFR | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| Cao et al. (2022) [26] | 76 | Training cohort (EGFR-21) = 61.12 ± 11.45 (EGFR 19) = 59.44 ± 8.65 Validation cohort (EGFR-21) = 62.69 ± 11.44 (EGFR 19) = 53.54 ± 10.70 | EGFR | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| Fan et al. (2021) [27] | 94 | Training cohort (EGFR mutant) = 58.52 ± 9.84 (EGFR wild type) = 61.70 ± 10.75 Validation cohort (EGFR mutant) = 57.26 ± 9.43 (EGFR wild type) = 57.08 ± 10.66 | EGFR | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| Ren et al. (2021) [28] | 162 | Training cohort (EGFR mutant) = 60.60 ± 10 (EGFR wild type) = 59.10 ± 11.20 Validation cohort (EGFR mutant) = 61.10 ± 9.29 (EGFR wild type) = 60.00 ± 6.64 | EGFR | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| Study | Output/Prediction | Best Performing Model | AUC | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al. (2024) [18] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics (RS-SM-Com) | 0.929 | 0.886–0.973 |
| Study | Output/Prediction | Best Performing Model | AUC | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al. (2024) [18] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics (RS-SM-Com) | 0.896 | 0.781–1.000 | ||
| Cao et al. (2023) [22] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics (RS-Com-EGFR) | 0.806 2 | 0.745 3 | - | - |
| EGFR 1 Exon 19 mutation | Radiomics (RS-Com-Exon19) | 0.872 2 | 0.760 3 | - | - | |
| EGFR 1 Exon 21 mutation | Radiomics (RS-Com-Exon21) | 0.913 2 | 0.799 2 | - | - | |
| Cheng et al. (2023) [19] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics (RS-Com-EGFR) | 0.927 2 | 0.812 3 | 0.884–0.969 2 | 0.709–0.916 3 |
| Response to EGFR-TKI 4 | Radiomics (RS-Com-TKI) | 0.880 2 | 0.798 3 | 0.802–0.958 2 | 0.649–0.946 3 | |
| Jiang et al. (2023) [21] | EGFR 1 mutation status | CM-EfNet (CBAM 7 and MFM 8 and EfficientNet v2) | 0.866 2 | 0.851 3 | 0.800–0.916 2 | 0.750–0.923 3 |
| EGFR 1 mutations in Exons 19 and 21 | CM-EfNet (CBAM 7 and MFM 8 and EfficientNet v2) | 0.760 2 | 0.711 3 | 0.656–0.846 2 | 0.552–0.839 3 | |
| Niu et al. (2023) [20] | Differentiating NSCLC 5 and BC 6 spinal metastasis | Radiomics—logistic regression (Ori-RS) | 0.890 2 | 0.881 3 | 0.843–0.938 2 | 0.810–0.953 3 |
| EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics—logistic regression (EGFR-RS) | 0.793 2 | 0.744 3 | 0.703–0.833 2 | 0.601–0.887 3 | |
| Ki-67 expression level | Radiomics—logistic regression (Ki-67-RS) | 0.798 2 | 0.738 3 | 0.693–0.902 2 | 0.554–0.921 3 | |
| Zhang et al. (2024) [23] | Ki-67 level | Radiomics (RS-Ki-67) | 0.812 2 | 0.799 3 | 0.710–0.914 2 | 0.652–0.947 3 |
| HER-2 9 mutation status | Radiomics (RS-HER-2) | 0.796 2 | 0.705 3 | 0.686–0.906 2 | 0.506–0.904 3 | |
| Cao et al. (2022) [26] | Differentiating Exon 19 and Exon 21 in EGFR 1 mutation | Nomogram | 0.901 2 | 0.882 3 | 0.783–0.967 2 | 0.695–0.974 3 |
| Fan et al. (2022) [24] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics (RS-EGFR) | 0.851 2 | 0.780 3 | 0.774–0.921 2 | 0.645–0.916 3 |
| EGFR 1 Exon 19 deletion | Radiomics (RS-19) | 0.816 2 | 0.789 3 | 0.716–0.917 2 | 0.636–0.942 3 | |
| EGFR 1 Exon 21 mutation | Radiomics (RS-21) | 0.814 2 | 0.770 3 | 0.714–0.914 2 | 0.609–0.931 3 | |
| Fan et al. (2022) [25] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Clinical-radiomics nomogram model (nomogram-EGFR) | 0.849 2 | 0.828 3 | 0.776–0.922 2 | 0.708–0.949 3 |
| T790M mutation status | Clinical-radiomics nomogram model (nomogram-T790M) | 0.842 2 | 0.823 3 | 0.717–0.927 2 | 0.633–0.940 3 | |
| Fan et al. (2021) [27] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Radiomics (multi-regional radiomics signature) | 0.879 2 | 0.777 3 | 0.766–0.947 2 | 0.612–0.967 3 |
| Ren et al. (2021) [28] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Combined rad score | 0.886 2 | 0.803 3 | 0.826–0.947 2 | 0.682–0.924 3 |
| Study | Output/Prediction | Best Performing Model | AUC | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al. (2024) [18] | EGFR mutation status | Radiomics (RS-SM-Com) | 0.865 | 0.731–0.998 |
| Cao et al. (2023) [22] | EGFR mutation status | Radiomics (RS-Com-EGFR) | 0.738 | - |
| EGFR Exon 19 mutation | Radiomics (RS-Com-Exon19) | 0.825 | - | |
| EGFR Exon 21 mutation | Radiomics (RS-Com-Exon21) | 0.811 | - | |
| Jiang et al. (2023) [21] | EGFR mutation status | CM-EfNet (CBAM 7 and MFM 8 and EfficientNet v2) | 0.764 | 0.615–0.914 |
| EGFR mutations in Exons 19 and 21 | CM-EfNet (CBAM 7 and MFM 8 and EfficientNet v2) | 0.687 | 0.476–0.897 | |
| Fan et al. (2022) [24] | EGFR mutation status | Radiomics (RS-EGFR) | 0.807 | 0.595–0.938 |
| EGFR Exon 19 deletion | Radiomics (RS-19) | 0.742 | 0.478–0.919 | |
| EGFR Exon 21 mutation | Radiomics (RS-21) | 0.792 | 0.530–0.946 | |
| Fan et al. (2022) [25] | EGFR 1 mutation status | Clinical-radiomics nomogram model (nomogram-EGFR) | 0.778 | 0.610–0.946 |
| T790M mutation status | Clinical-radiomics nomogram model (nomogram-T790M) | 0.800 | 0.548–0.948 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanker, V.; Sanikommu, S.; Thaller, A.; Li, Z.; Heesen, P.; Hariharan, S.; Nordin, E.O.R.; Cavagnaro, M.J.; Ratliff, J.; Desai, A. Artificial Intelligence for Non-Invasive Prediction of Molecular Signatures in Spinal Metastases: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080791
Sanker V, Sanikommu S, Thaller A, Li Z, Heesen P, Hariharan S, Nordin EOR, Cavagnaro MJ, Ratliff J, Desai A. Artificial Intelligence for Non-Invasive Prediction of Molecular Signatures in Spinal Metastases: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(8):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080791
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanker, Vivek, Sai Sanikommu, Alexander Thaller, Zhikai Li, Philip Heesen, Srinath Hariharan, Emil O. R. Nordin, Maria Jose Cavagnaro, John Ratliff, and Atman Desai. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence for Non-Invasive Prediction of Molecular Signatures in Spinal Metastases: A Systematic Review" Bioengineering 12, no. 8: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080791
APA StyleSanker, V., Sanikommu, S., Thaller, A., Li, Z., Heesen, P., Hariharan, S., Nordin, E. O. R., Cavagnaro, M. J., Ratliff, J., & Desai, A. (2025). Artificial Intelligence for Non-Invasive Prediction of Molecular Signatures in Spinal Metastases: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering, 12(8), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12080791







