Design and Bench Testing of a Novel, Pediatric, Non-Invasive, Bubble Bilevel Positive Pressure Ventilation Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
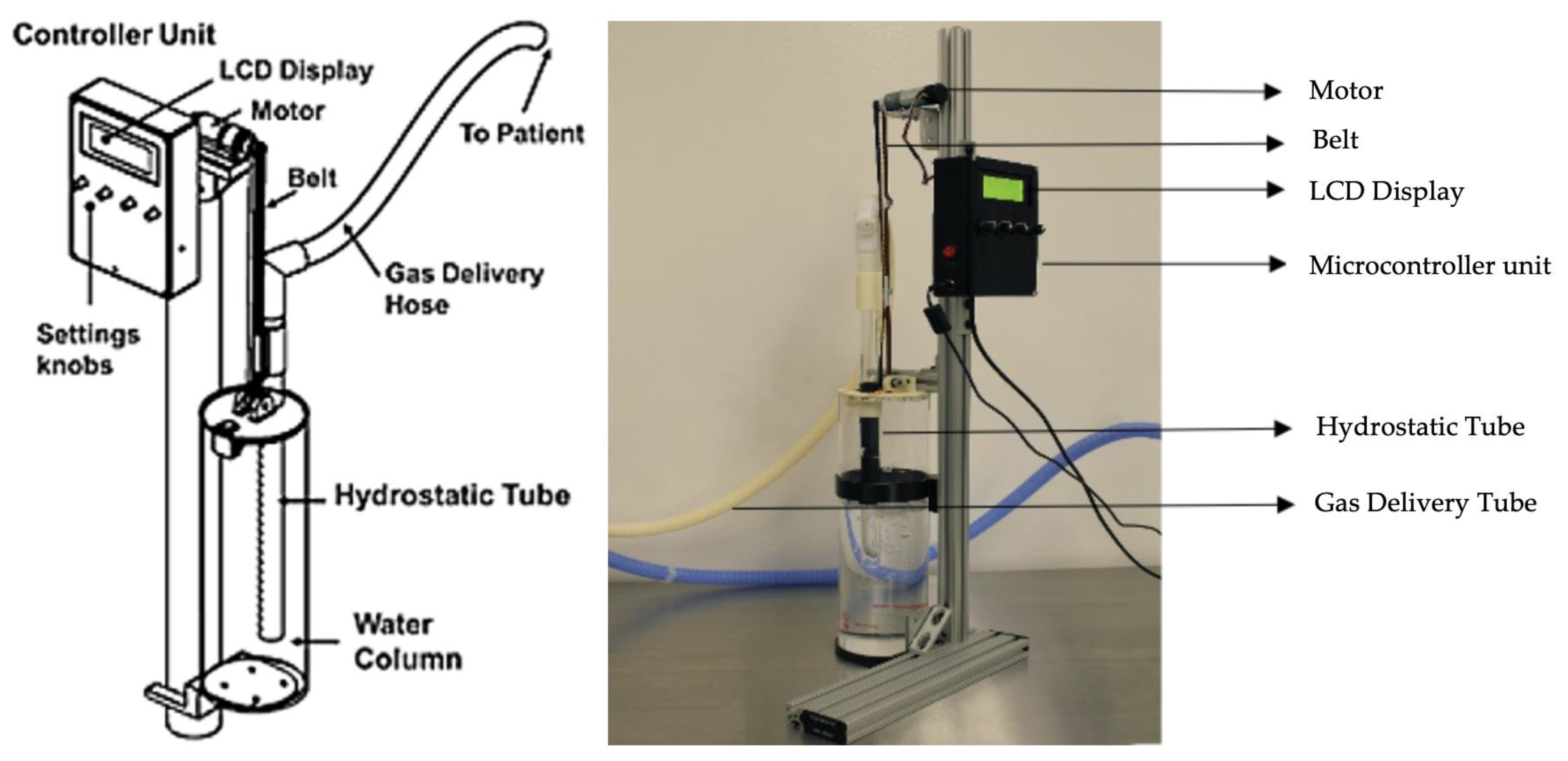
2.1. Bubble Bi-Vent Design
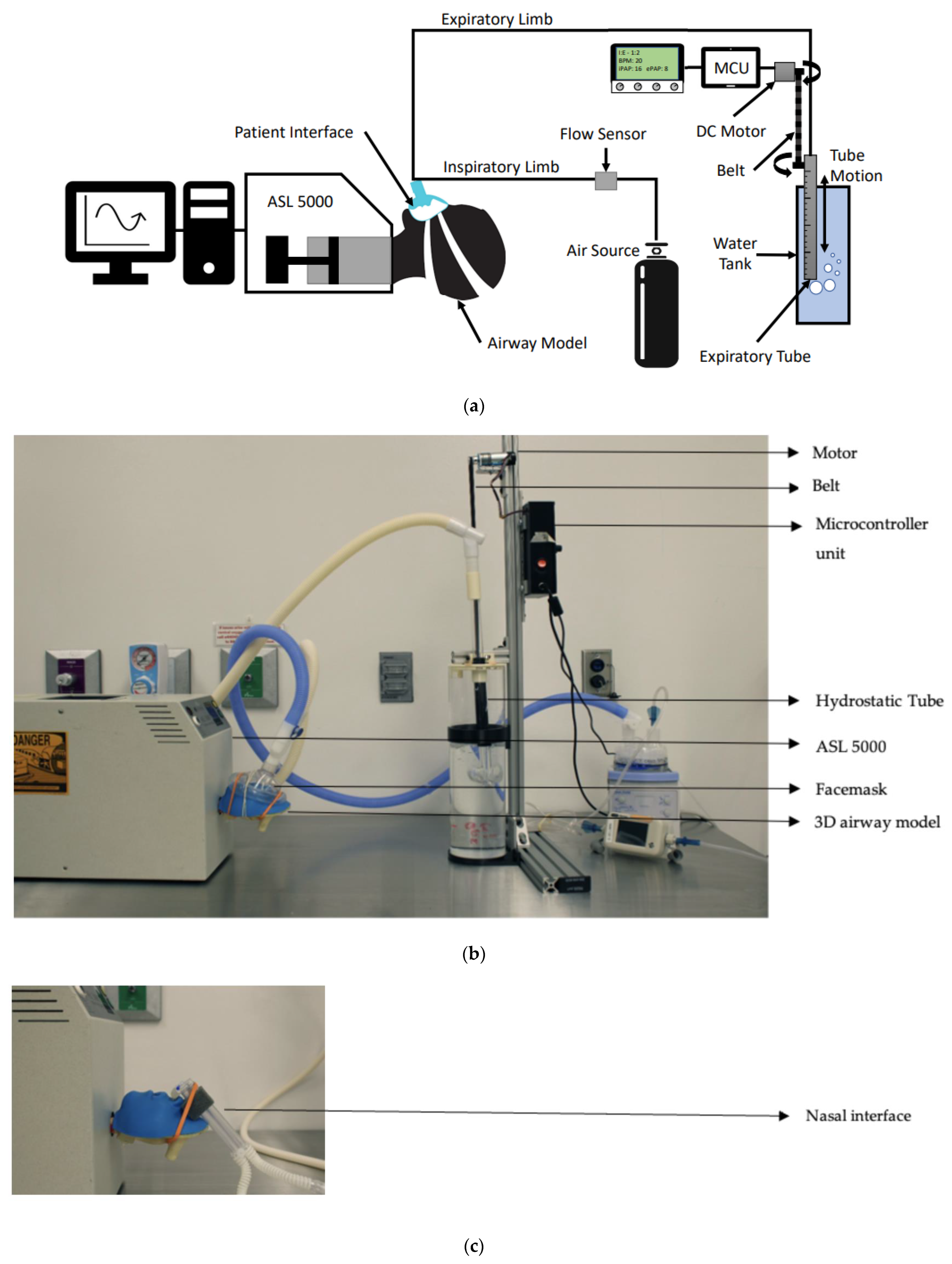
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
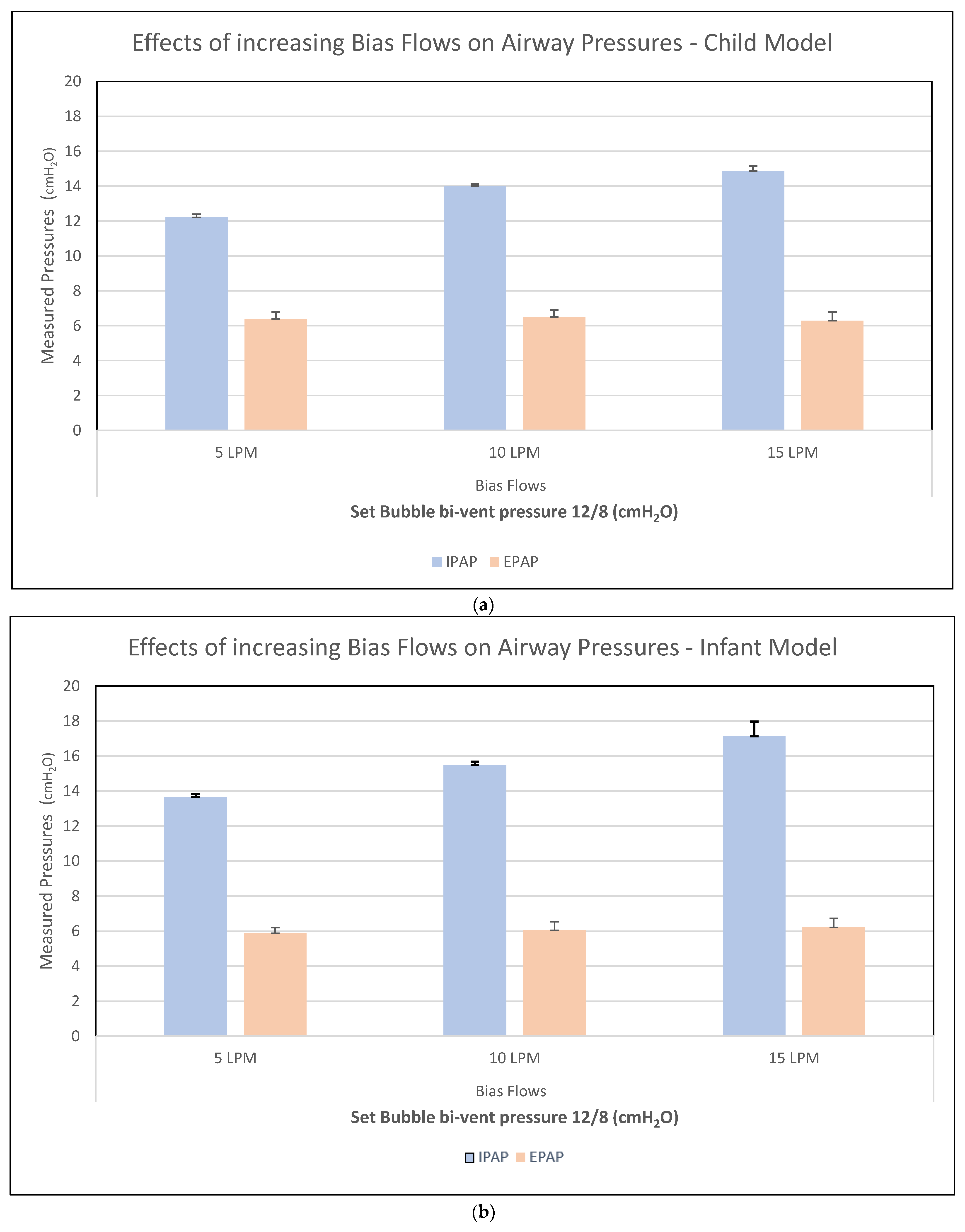
3.1. Test 1—Bias Flow Titration
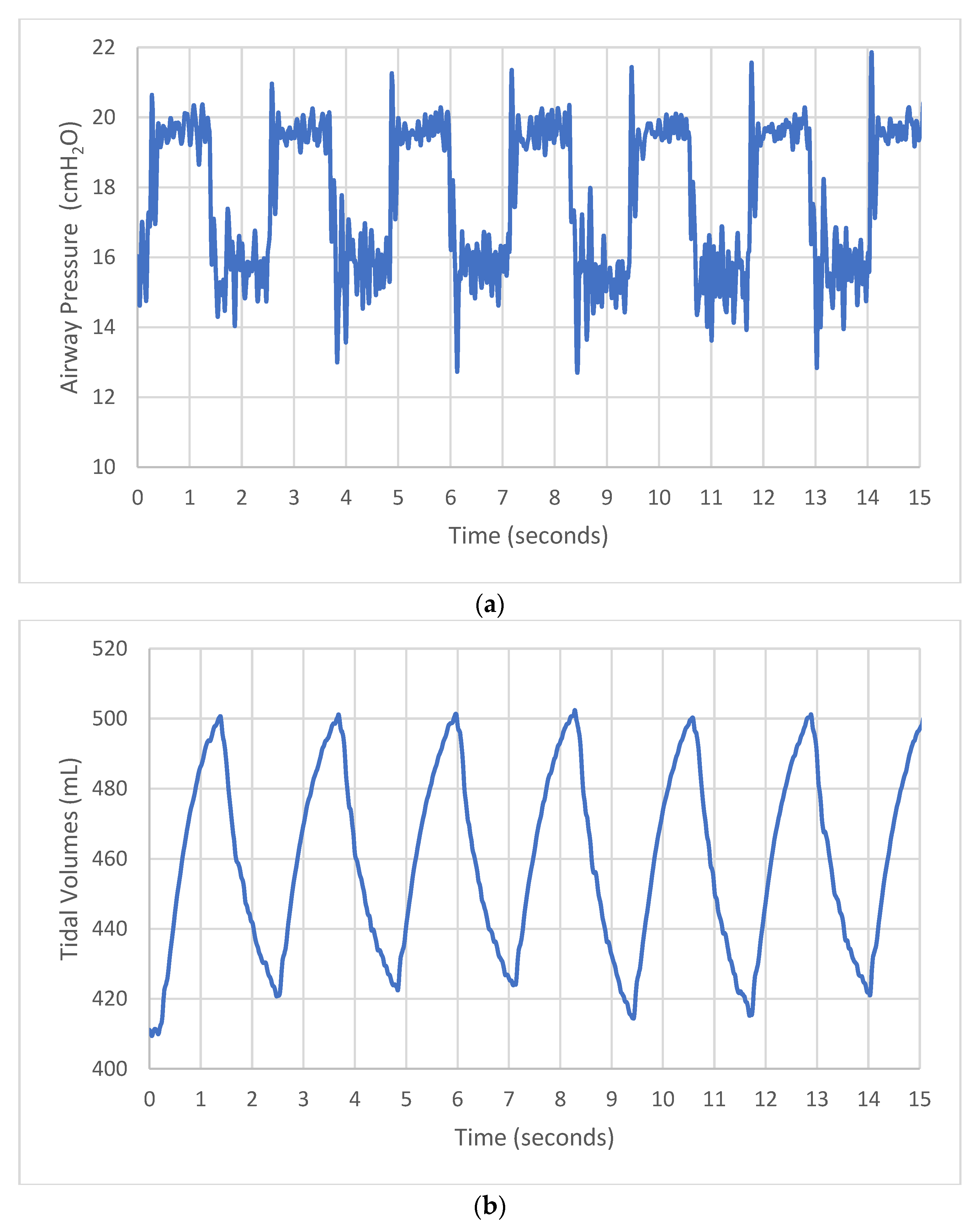
3.2. Test 2—Bubble Bi-Vent Testing in Healthy and Sick Lungs
3.3. Test 3—Bubble Bi-Vent Testing Across Different Interfaces
3.4. Test 4—Bubble Bi-Vent Comparison with Trilogy Ventilator
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LMICs | Low- and middle-income countries |
| CPAP | Continuous positive airway pressure |
| BiPAP | Bilevel positive airway pressure |
| ALRTI | Acute lower respiratory tract infections |
| NIV | Non-invasive ventilation |
| bCPAP | Bubble continuous positive airway pressure |
| IPAP | Inspiratory positive airway pressure |
| EPAP | Expiratory positive airway pressure |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
Appendix A

| Device Part | Unit Cost |
|---|---|
| Pololu 4.4:1 Metal Gearmotor HP 12 V with 48 CPR Encoder (electric motor) | $48.95 |
| Motor drivers shield for Arduino, 7 V–3 V, Peak 15 A | $17.90 |
| Sparkfun Qwicc breakout communication boards | $74.95 |
| Adafruit rotary encoder | $32.40 |
| 3D-printed parts | Lab resource |
| 5 M GT2 Timing Belt Upgrade Non-slip version | $12.99 |
| SunFounder Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Module Shield | $12.99 |
| Arduino REV3 [A000066] Microcontroller unit (MCU) | $27.6 |
| Peripherals and 5V USB connection (USBAB2MR) | $10.96 |
| Heavy-duty computer power cord | $18.49 |
| Steel structure for support | Lab resource |
| Submerged tube | Lab resource |
| Breathing circuit tubing supplies | Lab resource |
| Water bath | Lab resource |
References
- CME Info—Child Mortality Estimates. Available online: https://childmortality.org/causes-of-death/data?age=Y0T4&d_refArea=WORLD&type=DEATHS&causes=LRI (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- World Health Organization. Foundations of Medical Oxygen Systems, 17 February 2023. Art. no. WHO/2019-nCoV/Clinical/Oxygen/2023.1. 2023. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/366149 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Poletto, S.; Trevisanuto, D.; Ramaswamy, V.V.; Seni, A.H.A.; Ouedraogo, P.; Dellacà, R.L.; Zannin, E. Bubble CPAP respiratory support devices for infants in low-resource settings. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttalib, F.; González-Dambrauskas, S.; Lee, J.H.; Steere, M.; Agulnik, A.; Murthy, S.; Adhikari, N.K.J. Pediatric Emergency and Critical Care Resources and Infrastructure in Resource-Limited Settings: A Multicountry Survey. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.; Leligdowicz, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J. Intensive care unit capacity in low-income countries: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, T. CPAP: A guide for clinicians in developing countries. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2014, 34, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teague, W.G. Noninvasive ventilation in the pediatric intensive care unit for children with acute respiratory failure. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2003, 35, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooke, L.; Ehret, D.E.Y.; Okolo, A.; Dlamini-Nqeketo, S.; Joolay, Y.; Minto’o, S.; Pillay, S.; Abdallah, Y.; Naburi, H.; Ndour, D.; et al. Limited resources restrict the provision of adequate neonatal respiratory care in the countries of Africa. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 111, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, R.; Ayebale, E.; Schultz, M.J. Optimizing respiratory management in resource-limited settings. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansmann, A.; Morrow, B.M.; Lang, H.-J. Review of supplemental oxygen and respiratory support for paediatric emergency care in sub-Saharan Africa. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 7, S10–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, A.; Sankar, M.J.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Agarwal, R.; Paul, V.K. Efficacy and safety of CPAP in low- and middle-income countries. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Duke, T.; Davis, P. Efficacy and safety of bubble CPAP in neonatal care in low and middle income countries: A systematic review. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014, 99, F495–F504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, M.J.; Salam, M.A.; Smith, J.H.; Ahmed, T.; Pietroni, M.A.C.; Shahunja, K.M.; Shahid, A.S.M.S.B.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Ashraf, H.; Bardhan, P.K.; et al. Bubble continuous positive airway pressure for children with severe pneumonia and hypoxaemia in Bangladesh: An open, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diblasi, R.M.; Zignego, J.C.; Tang, D.M.; Hildebrandt, J.; Smith, C.V.; Hansen, T.N.; Richardson, C.P. Noninvasive Respiratory Support of Juvenile Rabbits by High-Amplitude Bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 67, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.T.; Baiden, F.; Brooks, J.C.; Morris, M.C.; Giessler, K.; Punguyire, D.; Apio, G.; Agyeman-Ampromfi, A.; Lopez-Pintado, S.; Sylverken, J.; et al. Continuous positive airway pressure for children with undifferentiated respiratory distress in Ghana: An open-label, cluster, crossover trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e615–e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollum, E.D.; Mvalo, T.; Eckerle, M.; Smith, A.G.; Kondowe, D.; Makonokaya, D.; Vaidya, D.; Billioux, V.; Chalira, A.; Lufesi, N.; et al. Bubble continuous positive airway pressure for children with high-risk conditions and severe pneumonia in Malawi: An open label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, M.; Haile, K.; Duke, T.; Faruk, T.; Kamal, M.; Kabir, F.; Uddin, F.; Shimelis, M.; Solomon, B.; Bayih, A.G.; et al. Effectiveness of Bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (BCPAP) for Treatment of Children Aged 1–59 Months with Severe Pneumonia and Hypoxemia in Ethiopia: A Pragmatic Cluster Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Tobias, J.D. A Five-Year Experience With the Use of BiPAP in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Population. J. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 22, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonescu-Turcu, A.; Parthasarathy, S. CPAP and bi-level PAP therapy: New and established roles. Respir. Care 2010, 55, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar]
- John, S.C.; Barnett, J.D.; Habben, N.D.; Le, H.T.; Cheng, E.; John, S.P.; A Gustafson, P. Development and Testing of a Bubble Bi-Level Positive Airway Pressure System. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.C.; John, A.V.; Moss, A.W.; Gustafson, P.A.; Fernando-Silva, L.; John, S.P. Bench Testing of a Bubble Noninvasive Ventilation Device in an Infant Lung Simulator. Respir. Care 2020, 65, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.C.; Mohammed, A.; Church, J.T.; John, A.V.; Perkins, E.M.; McLeod, J.S.; Carr, B.D.; Smith, S.; Barnett, J.H.; Gustafson, P.A.; et al. Bubble bilevel ventilation facilitates gas exchange in anesthetized rabbits. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, J.A.; Howard, C.; Garcia, A.J.; Remboski, D.; Littlewood, P.B.; Kress, J.P.; Kasthuri, N.; Comai, A.; Soni, K.; Kennedy, P.; et al. Performance Characteristics of a Novel 3D-Printed Bubble Intermittent Mandatory Ventilator (B-IMV) for Adult Pulmonary Support. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, E.M.; Goldman, S.L.; Brady, J.P. Pulmonary Function in the Sick Newborn Infant. Pediatr. Res. 1987, 21, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newth, C.J.L.; Stretton, M.; Deakers, T.W.; Hammer, J. Assessment of pulmonary function in the early phase of ARDS in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1997, 23, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilia, S.; Geromarkaki, E.; Briassoulis, P.; Bourmpaki, P.; Tavladaki, T.; Miliaraki, M.; Briassoulis, G. Longitudinal PEEP Responses Differ Between Children with ARDS and at Risk for ARDS. Respir. Care 2021, 66, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, A.J.; Nielsen, K.R.; E Ellington, L.; Earley, M.; Johnson, K.; Smith, L.S.; DiBlasi, R.M. Tracheal pressure generated by high-flow nasal cannula in 3D-Printed pediatric airway models. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 145, 110719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essouri, S.; Carroll, C. Noninvasive Support and Ventilation for Pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Proceedings from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 16, S102–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Donn, S.M. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure: To Bubble or Not to Bubble? Clin. Perinatol. 2016, 43, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, J.A.; Richardson, C.P.; DiBlasi, R.M. Volume Oscillations Delivered to a Lung Model Using 4 Different Bubble CPAP Systems. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.R. Patient-Ventilator Interaction During Noninvasive Ventilation. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, M.; Stagstrup, C.; Lund, S.; Poulsen, A. To Bubble or Not? A Systematic Review of Bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Children in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2020, 66, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissauer, T.; Duke, T.; Mellor, K.; Molyneux, L. Nasal CPAP for neonatal respiratory support in low and middle-income countries. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2017, 102, F194–F196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, L.; Dellacà, R.L.; Penuelas, O.; Bellani, G.; Artigas, A.; Ferrer, M.; Navajas, D.; Pedotti, A.; Farre, R.; Dellaca, R.L.; et al. Actual performance of mechanical ventilators in ICU: A multicentric quality control study. Med. Devices 2012, 5, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussen, S.; Gainnier, M.; Michelet, P. Evaluation of ventilators used during transport of critically ill patients: A bench study. Respir. Care 2013, 58, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.J.; Both, C.P.; Fries, D.; Wendel-Garcia, P.D.; Buehler, P.K.; Grass, B.; Cannizzaro, V.; Escher, C.; Schmitz, A.; Thomas, J. The in-vitro performance of a modern portable respirator in different lung models and as an alternative intensive care respirator: A simulation based cohort study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Care 2025, 4, e0069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Excess Mortality Collaborators. Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020–2021. Lancet 2022, 399, 1513–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranney, M.L.; Griffeth, V.; Jha, A.K. Critical Supply Shortages—The Need for Ventilators and Personal Protective Equipment during the COVID-19 Pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truog, R.D.; Mitchell, C.; Daley, G.Q. The Toughest Triage—Allocating Ventilators in a Pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1973–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguise, M.-O.; Lemyre, B. NIPPV vs CPAP: Lessons from meta-analyses. Semin. Perinatol. 2025, 152062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menniti, M.; Laganà, F.; Oliva, G.; Bianco, M.; Fiorillo, A.S.; Pullano, S.A. Development of Non-Invasive Ventilator for Homecare and Patient Monitoring System. Electronics 2024, 13, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, M.; Laganà, F.; Manin, L.; Angiulli, G. Soft computing and eddy currents to estimate and classify delaminations in biomedical device CFRP plates. J. Electr. Eng. 2025, 76, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.T.; Benckert, M.M.; Moresky, R.T.; Morris, M.C. Development and Implementation of a Training-of-Trainers Program for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Neonatal and Pediatric Patients in Five Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2017, 63, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]

| Parameters | Infant 4 kg Healthy Model | Infant 4 kg ARDS Model | Small Child 20 kg Healthy Model | Small Child 20 kg ARDS Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance (mL/cm H2O) | 8 | 2 | 25 | 14 |
| Resistance (cm H2O/L/s) | 50 | 100 | 20 | 40 |
| Non-invasive interface | Ram Nasal Cannula | Ram Nasal Cannula | Nonny Full Face Pediatric Mask | Nonny Full Face Pediatric Mask |
| Invasive interface | ETT 3.5 mm | ETT 3.5 mm | ETT 4.5 mm | ETT 4.5 mm |
| Without interface | Direct | Direct | Direct | Direct |
| Experimental Procedures | Variable |  | Measured IPAP and EPAP in mechanical lung | |
| Test 1 | Bias flow | 5 10 15 20 | ||
| Test 2 | Lung compliance and resistance | Healthy lungs ARDS lungs | ||
| Test 3 | Interface | Non-invasive Invasive Direct connection | ||
| Test 4 | Device type | Trilogy ventilator Bubble bi-vent |
| (a) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vent Parameters | Healthy | ARDS | |||
| Set IPAP (cm H2O) | Set EPAP (cm H2O) | Measured IPAP (cm H2O) | Measured EPAP (cm H2O) | Measured IPAP (cm H2O) | Measured EPAP (cm H2O) |
| 12 | 6 | 13.6 ± 0.16 | 6.1 ± 0.55 | 15.1 ± 0.46 | 6.0 ± 0.39 |
| 15 | 8 | 16.5 ± 0.16 | 8.2 ± 0.41 | 18.1 ± 0.15 | 8.2 ± 0.29 |
| 18 | 10 | 18.4 ± 0.11 | 9.1 ± 0.46 | 20.2 ± 0.19 | 10.62 ± 1.82 |
| (b) | |||||
| Vent Parameters | Healthy | ARDS | |||
| Set IPAP (cm H2O) | Set EPAP (cm H2O) | Measured IPAP (cm H2O) | Measured EPAP (cm H2O) | Measured IPAP (cm H2O) | Measured EPAP (cm H2O) |
| 12 | 6 | 14.2 ± 0.16 | 6.6 ± 0.32 | 16.2 ± 0.31 | 6.3 ± 0.52 |
| 15 | 8 | 17.2 ± 0.09 | 8.4 ± 0.26 | 19.8 ± 0.22 | 8.5 ± 0.57 |
| 18 | 10 | 20.2 ± 0.04 | 10.6 ± 0.32 | 22.2 ± 0.21 | 10.6 ± 0.48 |
| (a) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ventilator Type | Set IPAP (cmH2O) | Set EPAP (cmH2O) | Measured IPAP (cmH2O) | IPAP Error % | Measured EPAP (cmH2O) | EPAP Error % | Tidal Volume (mL) | Tidal Volume (mL/kg) |
| Bubble bi-vent | 12 | 6 | 12.6 ± 0.03 | 5 | 6.7 ± 0.28 | 12 | 104.6 ± 1.34 | 5.2 |
| 15 | 8 | 15.5 ± 0.04 | 3 | 8.6 ± 0.26 | 7.5 | 119.6 ± 1.71 | 5.9 | |
| 20 | 10 | 20 ± 0.06 | 0 | 10.8 ± 0.45 | 8 | 157.1 ± 2.29 | 7.9 | |
| Respironics Trilogy 202 | 12 | 6 | 11 ± 0.02 | −8 | 5.8 ± 0.01 | −3 | 95.7 ± 0.19 | 4.8 |
| 15 | 8 | 13.6 ± 0.02 | −9 | 7.7 ± 0.02 | −3 | 109.0 ± 0.15 | 5.5 | |
| 20 | 10 | 17.9 ± 0.03 | −11 | 9.6 ± 0.02 | −4 | 151.5 ± 0.11 | 7.6 | |
| (b) | ||||||||
| Ventilator Type | Set IPAP (cmH2O) | Set EPAP (cmH2O) | Measured IPAP (cmH2O) | IPAP Error % | Measured EPAP (cmH2O) | EPAP Error % | Tidal Volume (mL) | Tidal Volume (mL/kg) |
| Bubble bi-vent | 12 | 6 | 12.2 ± 0.04 | 1.6 | 6.3 ± 0.18 | 5 | 60.9 ± 0.54 | 3.0 |
| 15 | 8 | 15.2 ± 0.04 | 1.3 | 8.4 ± 0.27 | 5 | 71.1 ± 0.63 | 3.6 | |
| 20 | 10 | 20.6 ± 0.05 | 3 | 10.4 ± 0.17 | 4 | 104.2 ± 0.95 | 5.2 | |
| Respironics Trilogy 202 | 12 | 6 | 11.2 ± 0.02 | −6.6 | 5.7 ± 0.01 | −5 | 61.8 ± 0.08 | 3.1 |
| 15 | 8 | 13.9 ± 0.03 | −7.3 | 7.6 ± 0.02 | −5 | 70.7 ± 0.08 | 3.5 | |
| 20 | 10 | 18.4 ± 0.02 | −8 | 9.5 ± 0.02 | −5 | 100 ± 0.16 | 5.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sonaike, I.; DiBlasi, R.M.; Poli, J.A.; Vamos, A.; Yanay, O.; von Saint Andre-von Arnim, A. Design and Bench Testing of a Novel, Pediatric, Non-Invasive, Bubble Bilevel Positive Pressure Ventilation Device. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070697
Sonaike I, DiBlasi RM, Poli JA, Vamos A, Yanay O, von Saint Andre-von Arnim A. Design and Bench Testing of a Novel, Pediatric, Non-Invasive, Bubble Bilevel Positive Pressure Ventilation Device. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070697
Chicago/Turabian StyleSonaike, Ibukun, Robert M. DiBlasi, Jonathan Arthur Poli, Andrew Vamos, Ofer Yanay, and Amelie von Saint Andre-von Arnim. 2025. "Design and Bench Testing of a Novel, Pediatric, Non-Invasive, Bubble Bilevel Positive Pressure Ventilation Device" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070697
APA StyleSonaike, I., DiBlasi, R. M., Poli, J. A., Vamos, A., Yanay, O., & von Saint Andre-von Arnim, A. (2025). Design and Bench Testing of a Novel, Pediatric, Non-Invasive, Bubble Bilevel Positive Pressure Ventilation Device. Bioengineering, 12(7), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070697






