Increasing Nebulizer Spray Efficiency Using a Baffle with a Conical Surface: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Breath-Actuated Nebulizer Operation
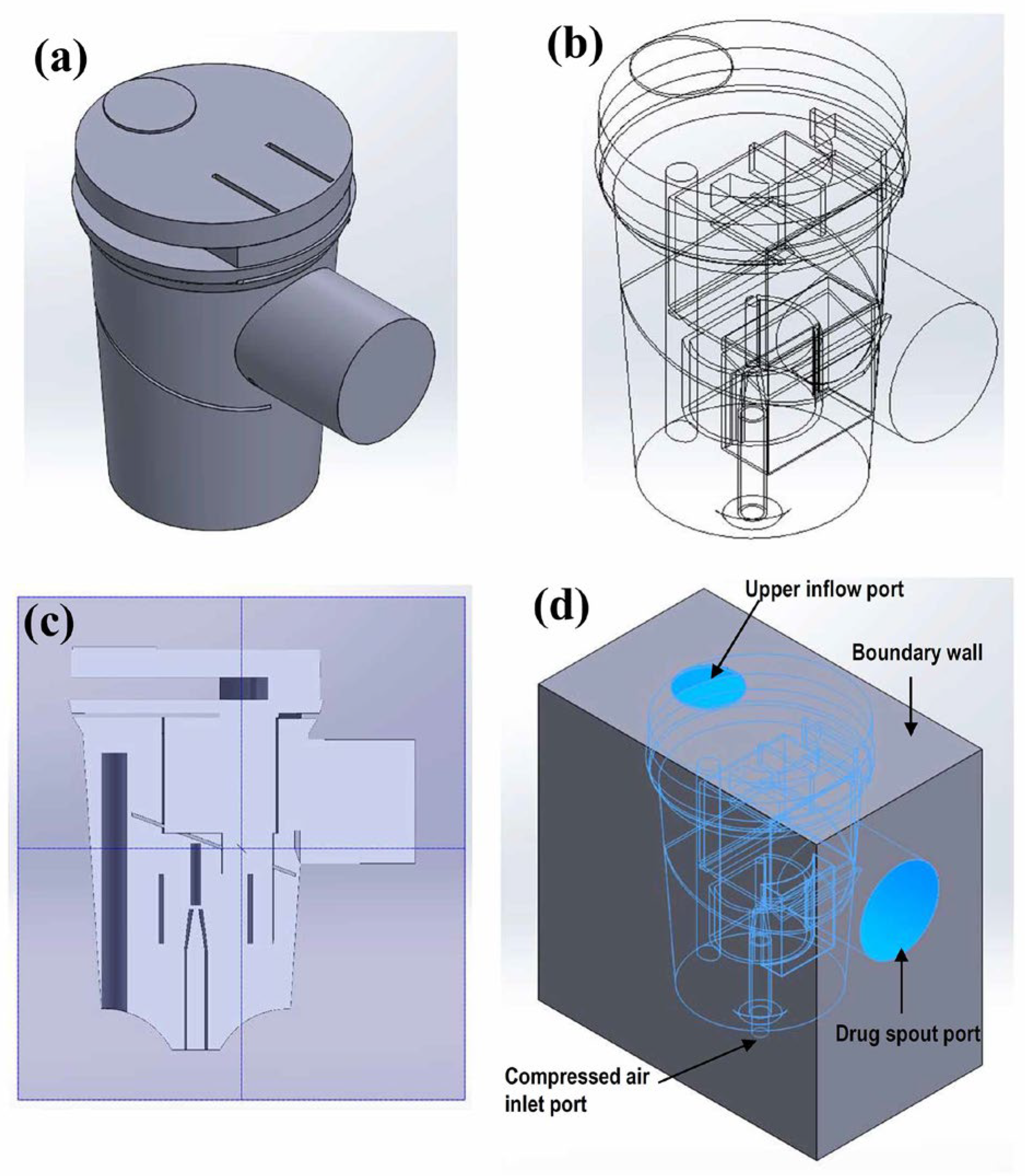
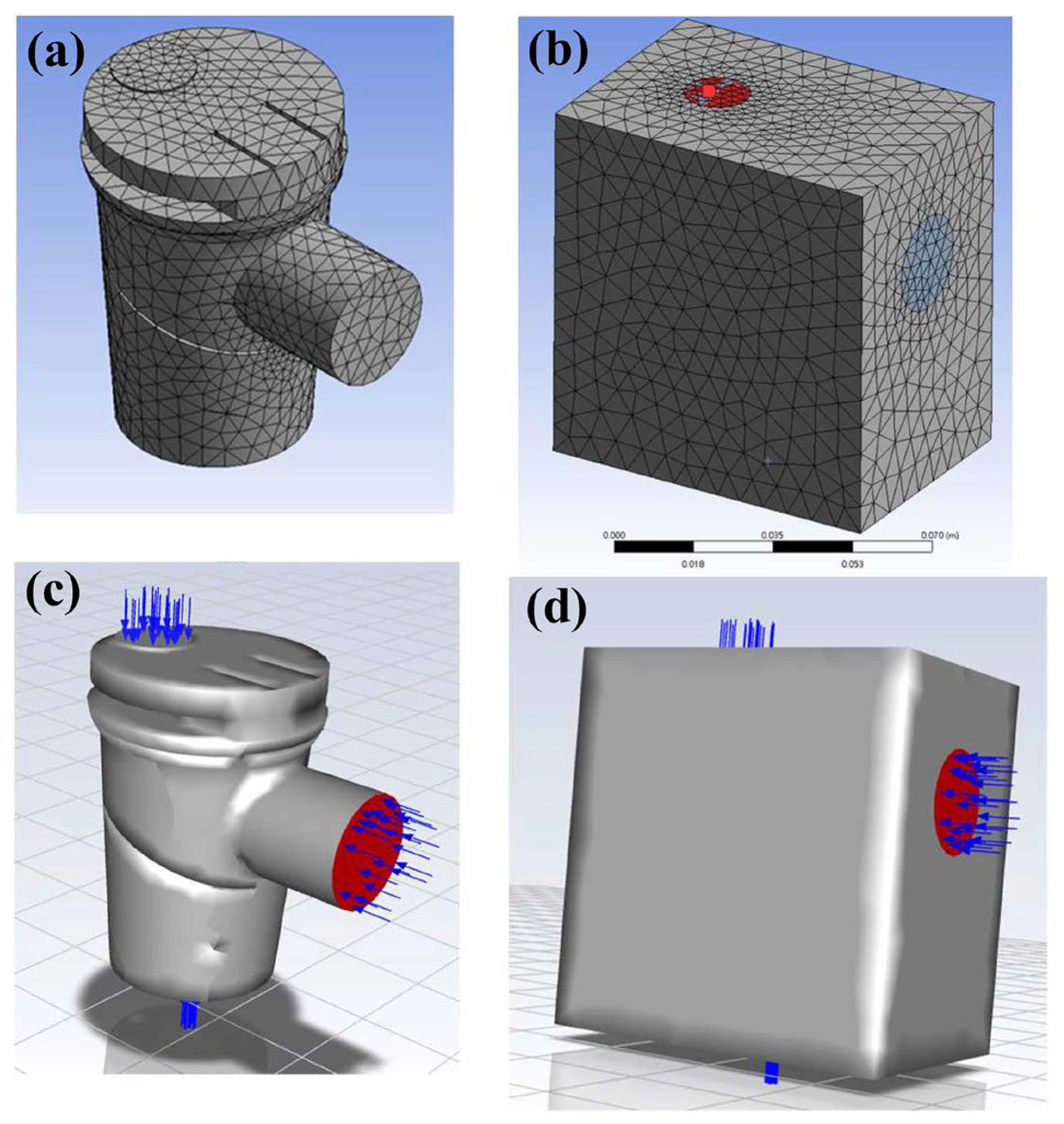
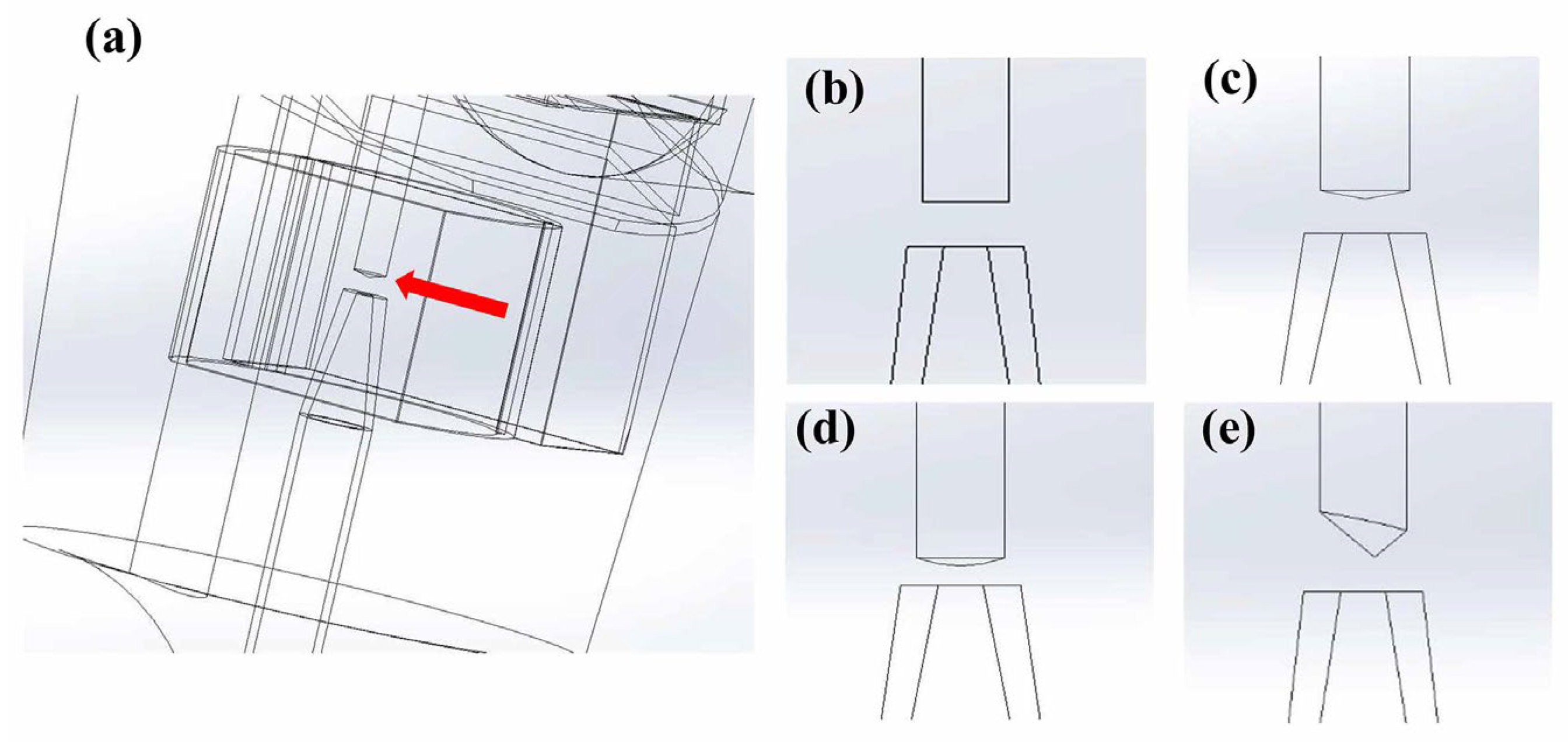
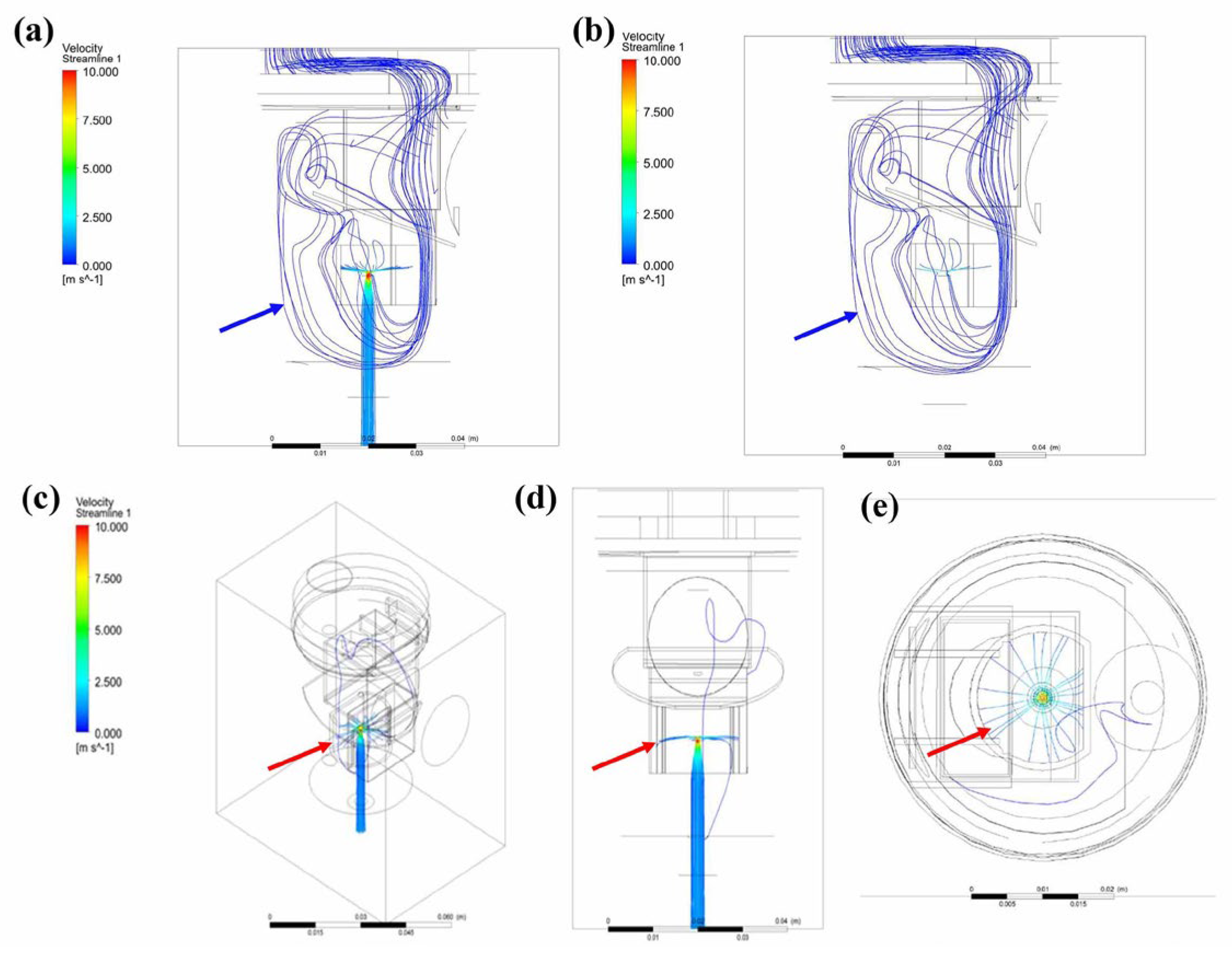
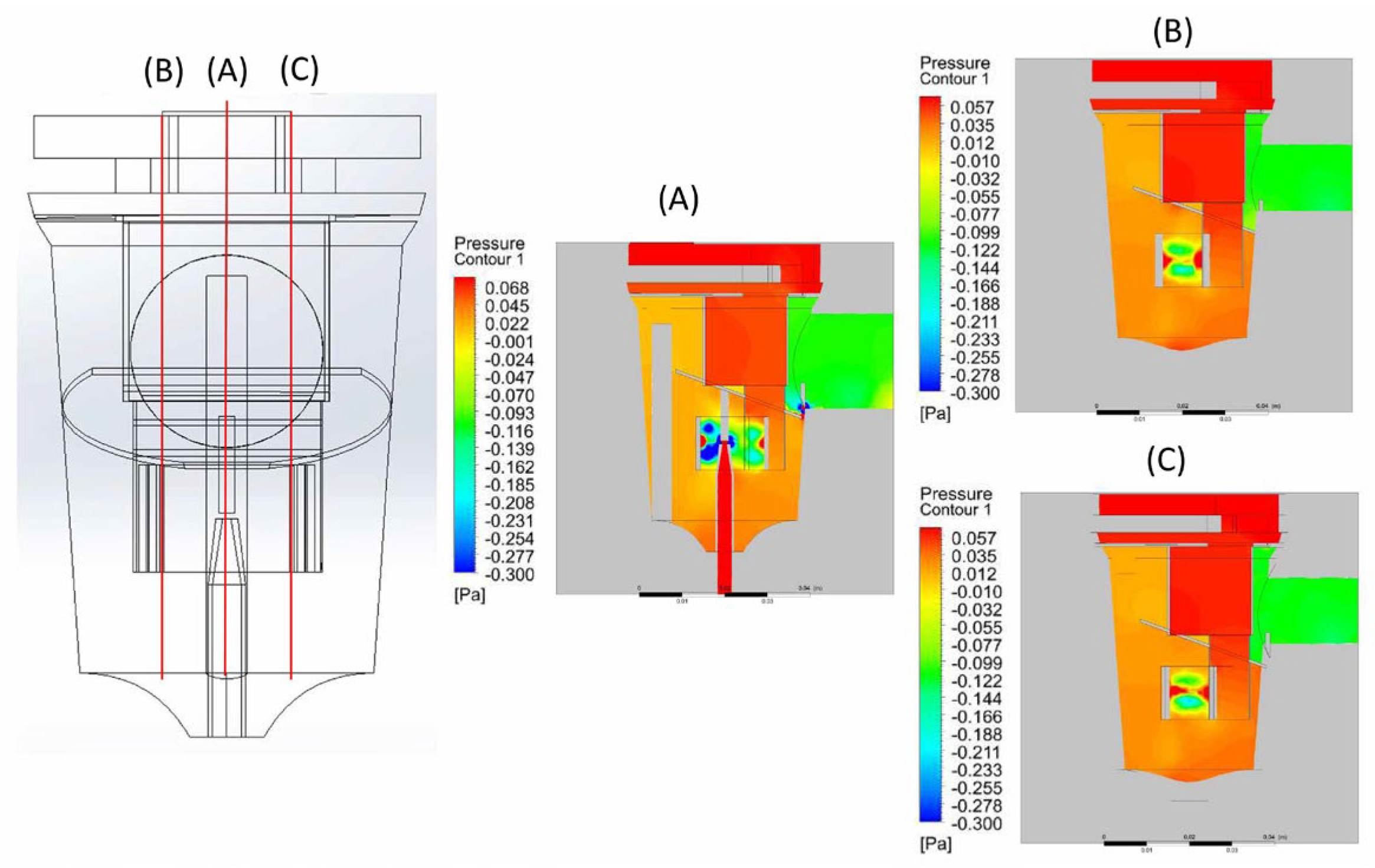
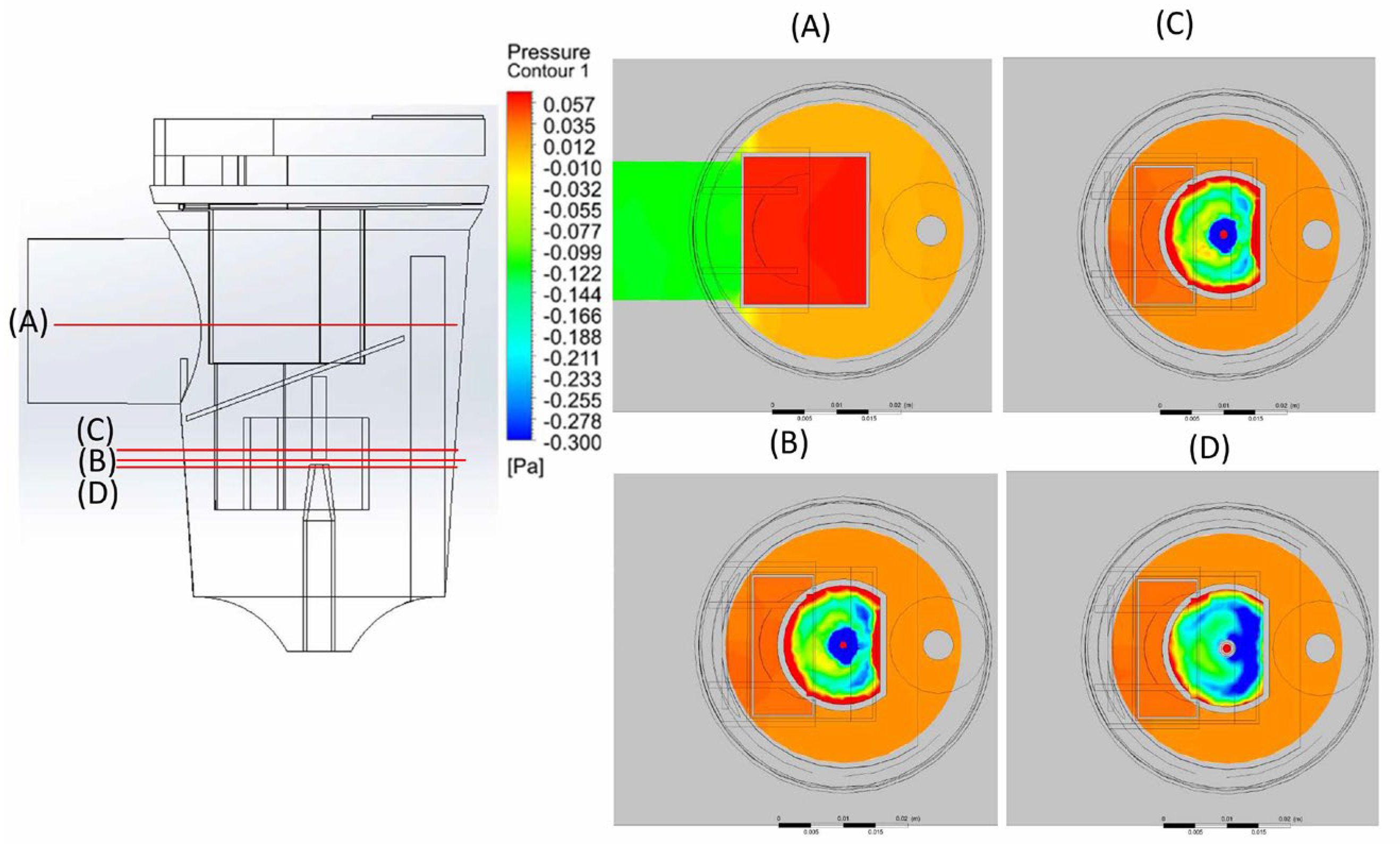
2.2. CFD Modeling
2.3. Parameter Settings of the CFD Model
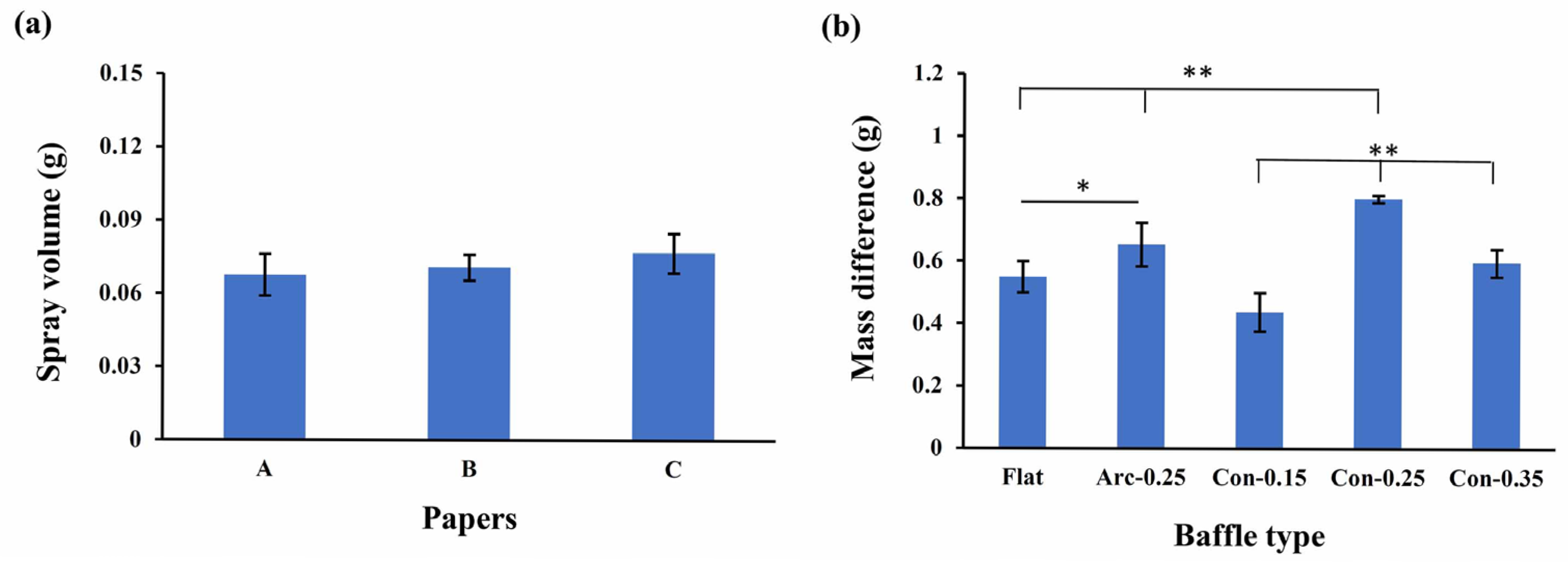
2.4. Nebulizer Efficiency Measurement
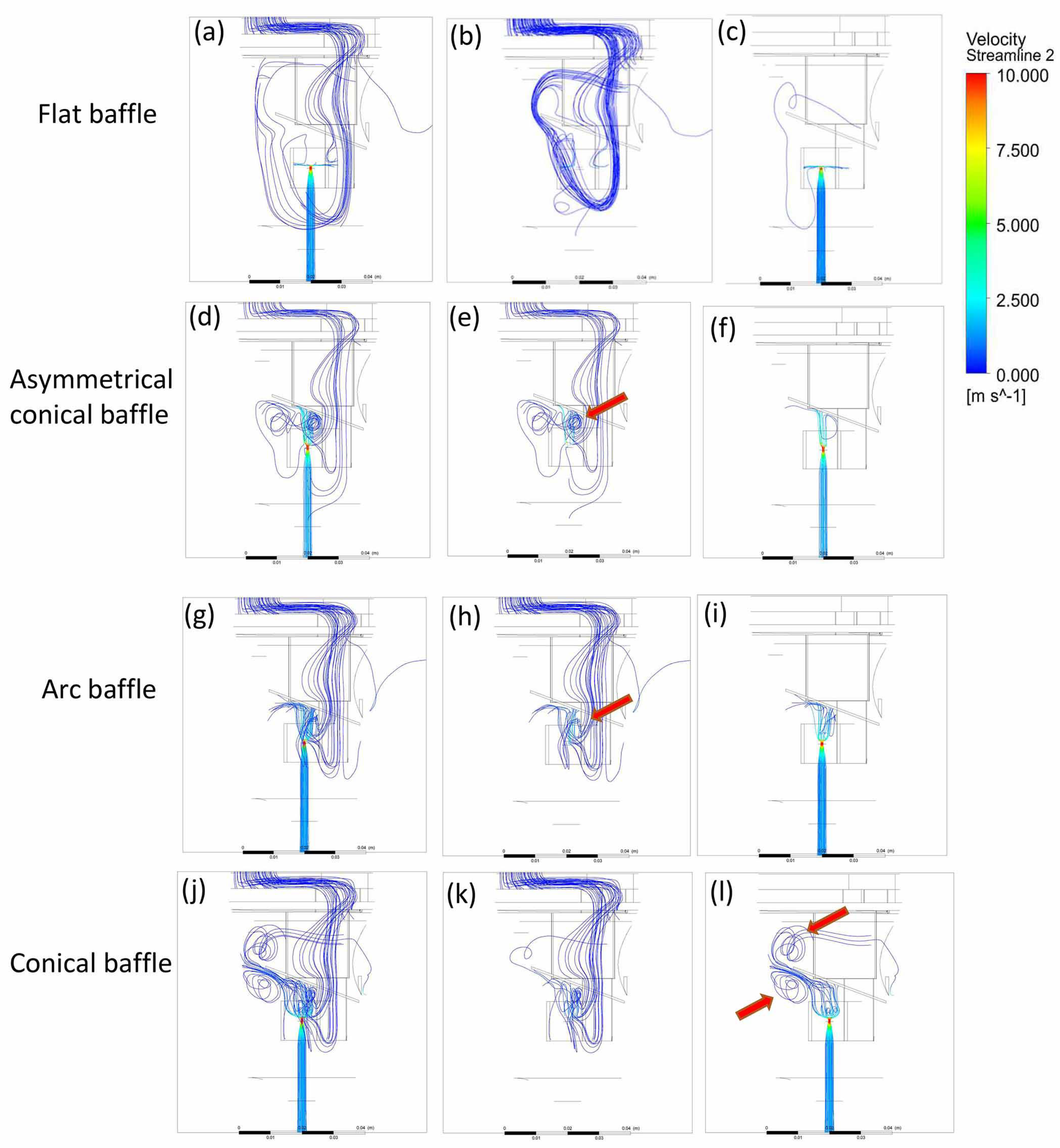
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| FVM | Finite volume method |
| LPM | Liters per minute |
References
- Drake, C.G.; Lipson, E.J.; Brahmer, J.R. Breathing new life into immunotherapy: Review of melanoma, lung and kidney cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, M.W. Aerosol therapy for obstructive lung diseases: Device selection and practice management issues. Chest 2011, 140, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanani, J.; Fraser, J.F.; Chan, H.K.; Rello, J.; Cohen, J.; Roberts, J.A. Fundamentals of aerosol therapy in critical care. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khilnani, G.C.; Banga, A. Aerosol therapy. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 2008, 50, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ari, A. Jet, ultrasonic, and nebulizers: An ealuation of nebulizers for better clinical outcomes. Eurasian J. Pulmonol. 2014, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexmond, A.; Forbes, B. Drug delivery devices for inhaled medicines. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 237, 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Artigas, A.; Camprubi-Rimblas, M.; Tantinya, N.; Bringue, J.; Guillamat-Prats, R.; Matthay, M.A. Inhalation therapies in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogliani, P.; Calzetta, L.; Coppola, A.; Cavalli, F.; Ora, J.; Puxeddu, E.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M. Optimizing drug delivery in COPD: The role of inhaler devices. Respir. Med. 2017, 124, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, V.; Murabito, A.; Ghigo, A. Inhaled biologicals for the treatment of cystic fibrosis. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2019, 13, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.C.; Swanson, J.M. An update on aerosolized antibiotics for treating hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia in adults. Ann. Pharmacother. 2017, 51, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, T.M.; Nahata, M.C.; Pai, V. Nebulized opioids for the palliation of dyspnea in terminally ill patients. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2017, 74, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knightly, R.; Milan, S.J.; Hughes, R.; Knopp-Sihota, J.A.; Rowe, B.H.; Normansell, R.; Powell, C. Inhaled magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, D.R. Nebulizers: Principles and performance. Respir. Care 2000, 45, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Finlay, W.H. Nebulizers for drug delivery to the lungs. Expert. Opin. 2015, 12, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitance, L.; Vecellio, L.; Leal, T.; Reychler, G.; Reychler, H.; Liistro, G. Delivery efficacy of a vibrating mesh nebulizer and a jet nebulizer under different configurations. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2010, 23, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komalla, V.; Wong, C.Y.J.; Sibum, I.; Muellinger, B.; Nijdam, W.; Chaugule, V.; Soria, J.; Ong, H.X.; Buchmann, N.A.; Traini, D. Advances in soft mist inhalers. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.; Louca, E.; Coates, A.L. Comparison of breath-enhanced to breath-actuated nebulizers for rate, consistency, and efficiency. Chest 2004, 126, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ari, A.; Fink, J.B. Breath-actuated nebulizer versus small-volume nebulizer: Efficacy, safety, and satisfaction. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1351–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.L.; Wan, G.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Fink, J.B.; Liu, W.Q.; Liu, K.Y. Influence of nebulizer type with different pediatric aerosol masks on drug deposition in a model of a spontaneously breathing small child. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, C.; Goniva, C.; Hager, A.; Amberger, S.; Pirker, S. Models, algorithms and validation for opensource DEM and CFD–DEM. Prog. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2012, 12, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraeye, T.; Blocken, B.; Koninckx, K.; Hespel, P.; Carmeliet, J. Aerodynamic study of different cyclist positions: CFD analysis and full-scale wind-tunnel tests. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaubhadel, M.N. CFD applications in the automotive industry. J. Fluids Eng. 1996, 118, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.L.; Albritton, J.R.; Ermak, D.L.; Kim, J. Computational fluid dynamics modeling for emergency preparedness and response. Environ. Model. Softw. 1997, 12, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantusheva, M.; Mitkov, R.; Hristov, P.O.; Petrova-Antonova, D. Air pollution dispersion modelling in urban environment using CFD: A systematic review. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Tauro, F.; Orrico, M.; Mangialardi, N.; Facci, A.L. Comparative analysis of patient-specific aortic dissections through computational fluid dynamics suggests increased likelihood of degeneration in partially thrombosed false lumen. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.W. High-order finite difference and finite volume WENO schemes and discontinuous Galerkin methods for CFD. Int. J. Comut. Fluid Dyn. 2003, 17, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmehran, O.; Psaltis, A.; Vreugde, S.; Zarei, K.; Shang, Y.; Inthavong, K.; Wormald, P.J. Evaluating nebulisation and nasal irrigation efficiency in post-operative chronic rhinosinusitis patients through computational fluid dynamics simulation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 264, 108697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Nof, E.; Amirav, I.; Kassinos, S.C.; Sznitman, J. Targeting inhaled aerosol delivery to upper airways in children: Insight from computational fluid dynamics (CFD). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Debbaut, C.; Ghorbaniasl, G.; Cosyns, S.; Willaert, W.; Ceelen, W. Optimization of intraperitoneal aerosolized drug delivery using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Pourmehran, O.; Gorji-Bandpy, M.; Inthavong, K.; Yeo, L.; Tu, J. CFD simulation of aerosol delivery to a human lung via surface acoustic wave nebulization. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 2035–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzycki, C.A.; Javaheri, E.; Finlay, W.H. The use of computational fluid dynamics in inhaler design. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, L.Y.; Chiu, W.T.; Lin, C.T.; Huang, H.M. Vibrational analysis of mandible trauma: Experimental and numerical approaches. Med. Bio. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisarciuc, C.; Dan, I.; Cioara, R. The influence of mesh density on the results obtained by finite element analysis of complex bodies. Materials 2023, 16, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, J. Randomized controlled trial of a breath-activated nebulizer in patients with exacerbation of COPD. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, D.R.; Acosta, F.L.; Ritz, R.H.; Kacmarek, R.M.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. The effect of heliox on nebulizer function using a beta-agonist bronchodilator. Chest 1999, 115, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.; Horney, D.; Snyder, T. Medication-delivery performance of eight small-volume, hand-held nebulizers: Effects of diluent volume, gas flowrate, and nebulizer model. Respir. Care 1989, 34, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, M.M.; Pavia, D.; Newman, S.P.; Lennard-Jones, T.; Clarke, S.W. Assessment of jet nebulisers for lung aerosol therapy. Lancet 1983, 2, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.H.; Stenton, S.C.; Beach, J.R.; Avery, A.J.; Walters, E.H.; Hendrick, D.J. Jet and ultrasonic nebuliser output: Use of a new method for direct measurement of aerosol output. Thorax 1990, 45, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.; González, H.; Higgins, B. Future trends in nebulized therapies for pulmonary disease. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, P.R.; Gonda, I. Droplets produced by medication nebulizers: Some factors affecting their size and solute concentration. Chest 1990, 97, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Callion, O.N.M.; Patel, M.J. Viscosity effects on nebulisation of aqueous solutions. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 130, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.W.; Windebank, W.J.; Bateman, J.R.M. Is driving gas flow rate clinically important for nebulizer therapy? Brit. J. Dis. Chest 1986, 80, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.-C.; Chen, F.-L.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lo, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Chang, W.-J.; Huang, H.-M. Increasing Nebulizer Spray Efficiency Using a Baffle with a Conical Surface: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070680
Wu H-C, Chen F-L, Chiang Y-C, Lo Y-J, Lin C-L, Chang W-J, Huang H-M. Increasing Nebulizer Spray Efficiency Using a Baffle with a Conical Surface: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070680
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hung-Chieh, Fu-Lun Chen, Yuan-Ching Chiang, Yi-June Lo, Chun-Li Lin, Wei-Jen Chang, and Haw-Ming Huang. 2025. "Increasing Nebulizer Spray Efficiency Using a Baffle with a Conical Surface: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070680
APA StyleWu, H.-C., Chen, F.-L., Chiang, Y.-C., Lo, Y.-J., Lin, C.-L., Chang, W.-J., & Huang, H.-M. (2025). Increasing Nebulizer Spray Efficiency Using a Baffle with a Conical Surface: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis. Bioengineering, 12(7), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070680







