Analytical Basal-State Model of the Glucose, Insulin, and C-Peptide Systems for Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basal-State Model Derivation Methodology
2.1. Foundational Dynamic Model
2.1.1. Glucose System
2.1.2. Insulin System
2.1.3. C-Peptide System
2.2. System of Literal Basal-State Equations
2.3. Methodology for Solving the System of Literal Basal-State Equations
3. Analytical Basal-State Model—Derivation and Result
3.1. Quartic Equation for
3.2. The Full Basal-State Model
3.3. Identifying Physical Basal Solutions
4. Analytical Basal-State Model—Applications and Model Verification
4.1. Basal Values Corresponding to Reported Median T2DM Parameter Values
4.2. Basal Model Parameter Study
4.3. Model Verification
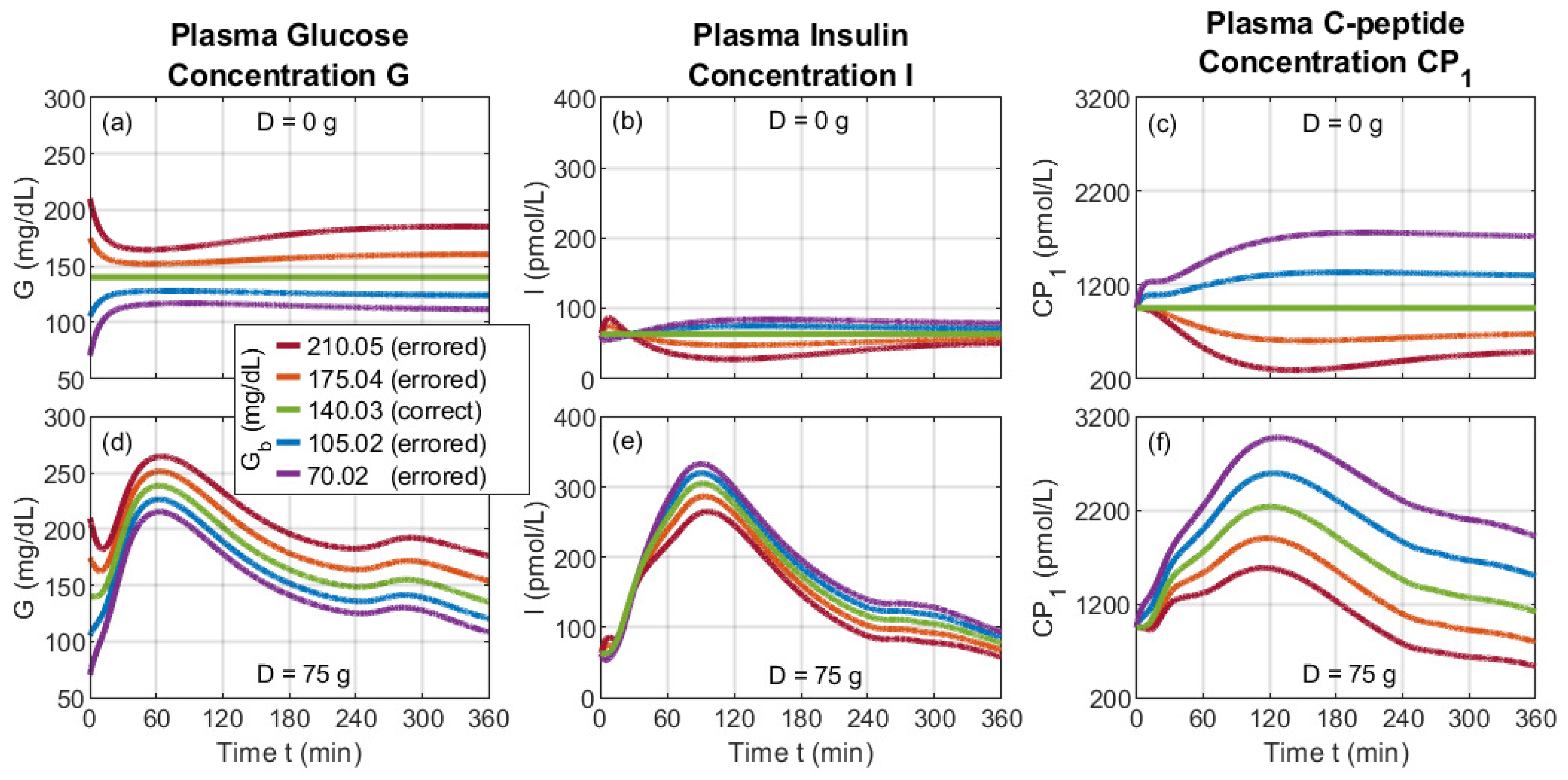
4.4. Misusing the Dynamic Model via Incorrect Basal Values
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| JSPS | Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science |
| LADA | Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults |
| MODY | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young |
| ODE | Ordinary differential equation |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
Appendix A. Physiological Model Parameters
| Subsystem | Symbol | Description | Units | Value | Origin | Basal? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate of Appearance | Maximum gastric emptying rate | 1/min | 0.0426 | [18] | No | |
| Minimum gastric emptying rate | 1/min | 0.0076 | [18] | No | ||
| Intestinal absorption rate | 1/min | 0.0542 | [18] | No | ||
| Stomach-grinding rate | 1/min | 0.0465 | [14] | No | ||
| f | Intestinal absorption fraction | Unitless | 0.9 | [18] | No | |
| b | Gastric-emptying reduction inflection point | Unitless | 0.73 | [18] | No | |
| c | Gastric-emptying recovery inflection point | Unitless | 0.1 | [18] | No | |
| Gastric-emptying reduction mass rate | 1/mg | 0.00010 | (D2) | No | ||
| Gastric-emptying recovery mass rate | 1/mg | 0.00037 | (D3) | No | ||
| Glucose Kinetics | Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.066 | [18] | Yes | |
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.043 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Glucose distribution volume | dL/kg | 1.00 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Glucose Excretion | Glomerular filtration rate | 1/min | 0.0005 | [18] | Yes | |
| Glucose excretion threshold | mg/kg | 339 | [18] | Yes | ||
| s | Excretion switch parameter | Unitless | 0 or 1 | (5b) | Yes | |
| Endogenous Glucose Production | Extrapolated EGP for zero glucose and insulin | mg/(kg·min) | 3.09 | [14] | Yes | |
| Hepatic glucose effectiveness | 1/min | 0.0008 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Hepatic insulin sensitivity | 0.0060 | [18] | Yes | |||
| Portal insulin sensitivity | 0.0484 | [18] | Yes | |||
| Glucose Utilization | Insulin-independent glucose utilization | mg/(kg·min) | 1 | [18] | Yes | |
| Michaelis–Menten parameter | mg/(kg·min) | 4.65 | [14] | Yes | ||
| Michaelis–Menten parameter | mg/kg | 466.2 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Insulin sensitivity to glucose utilization | 0.034 | [18] | No | |||
| Risk function parameter | Unitless | 0 | Appendix A | No | ||
| Risk function parameter | Unitless | 0 | Appendix A | No | ||
| Hypoglycemic threshold | mg/dL | 60 | [17] | No | ||
| Insulin Secretion | Delay between glucose and insulin secretion | 1/min | 0.034 | [18] | No | |
| Beta-cell responsivity to glucose | /min | 20.30 | [18] | No | ||
| Beta-cell responsivity to glucose rate of change | 286.0 | [18] | No | |||
| h | Glucose threshold for beta-cell secretion | mg/dL | (D20) | No | ||
| Insulin Kinetics | Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.314 | [18] | Yes | |
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.268 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.443 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.260 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.017 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Glucose control on HE | dL/mg | 0.005 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Extrapolated HE for zero glucose | Unitless | 1.16 | [14] † | Yes | ||
| Insulin distribution volume | L/kg | 0.041 | [18] | Yes | ||
| Insulin-action delay rate | 1/min | 0.0075 | [18] | No | ||
| Rate of insulin action on glucose utilization | 1/min | 0.058 | [18] | No | ||
| C-Peptide Kinetics | Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.062 | [23] | Yes | |
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.051 | [23] | Yes | ||
| Rate parameter | 1/min | 0.053 | [23] | Yes | ||
| C-peptide distribution volume | L | 4.18 | [23] | Yes | ||
| Basal plasma C-peptide concentration | pmol/L | 950 | [18] † | Yes |
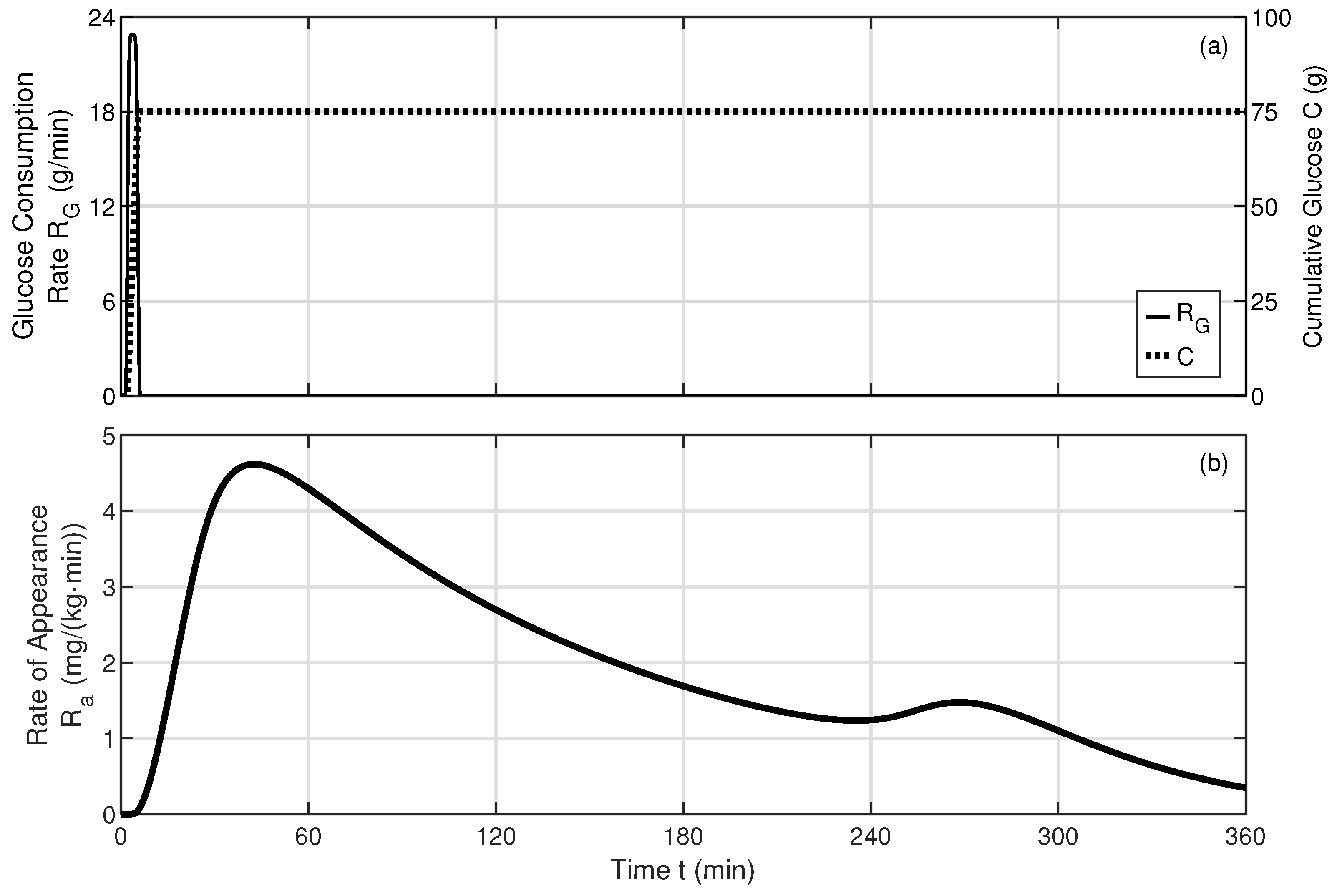
Appendix B. Dynamic Model Solver and Oral Glucose Consumption
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diab. Res. Clin. Prac. 2022, 183, 110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekisz, S.; Holder-Pearson, L.; Chase, J.G.; Desaive, T. In silico validation of a new model-based oral-subcutaneous insulin sensitivity testing through Monte Carlo sensitivity analyses. Biomed. Sig. Proc. Cont. 2020, 61, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglay, K.; Hannachi, H.; Howie, P.J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Engel, S.S.; Moore, L.M.; Rajpathak, S. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: Standards of care in diabetes—2024. Diab. Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Turner, R.C. The basal plasma glucose: A simple relevant index of maturity-onset diabetes. Clin. Endoc. 1981, 14, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, S.; Huber, P.; Lamprinou, A.; Fritsche, L.; Stefan, N.; Peter, A.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Fritsche, A.; Heni, M.; Wagner, R. Reproducibility and discrimination of different indices of insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Bierman, E.L.; Porte, D., Jr. The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1967, 46, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E. Insulin resistance is central to the burden of diabetes. Diab. Metab. Rev. 1997, 13, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of insulin-action and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, R.N.; Ziya Ider, Y.; Bowden, C.R.; Cobelli, C. Quantitative estimation of insulin sensitivity. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 1979, 236, E667–E677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovorka, R.; Canonico, V.; Chassin, L.J.; Haueter, U.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Federici, M.O.; Pieber, T.R.; Schaller, H.C.; Schaupp, L.; Vering, T.; et al. Nonlinear model predictive control of glucose concentration in subjects with type 1 diabetes. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, C.D.; Camilleri, M.; Cobelli, C. A system model of oral glucose absorption: Validation on gold standard data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, C.D.; Rizza, R.A.; Cobelli, C. Meal simulation model of the glucose-insulin system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Jauslin, P.M.; Silber, H.E.; Frey, N.; Gieschke, R.; Simonsson, U.S.H.; Jorga, K.; Karlsson, M.O. An integrated glucose-insulin model to describe oral glucose tolerance test data in type 2 diabetics. J. Clin. Pharm. 2007, 47, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.D.; Raimondo, D.M.; Rizza, R.A.; Cobelli, C. GIM, simulation software of meal glucose–insulin model. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2007, 1, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Man, C.D.; Micheletto, F.; Lv, D.; Breton, M.; Kovatchev, B.; Cobelli, C. The UVA/PADOVA type 1 diabetes simulator: New features. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, R.; Cobelli, C.; Man, C.D. The Padova type 2 diabetes simulator from triple-tracer single-meal studies: In silico trials also possible in rare but not-so-rare individuals. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, J.; Visentin, R.; Man, C.D. Smart algorithms for efficient insulin therapy initiation in individuals with type 2 diabetes: An in silico study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2024, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, R.; Cobelli, C.; Sieber, J.; Man, C.D. Short- and long-term effects on glucose control of nonadherence to insulin therapy in people with type 2 diabetes: An in silico study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2024, 18, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, E.; Sainsbury, C.A.R.; Jones, G.C. A practical review of C-peptide testing in diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.G.; Hattersley, A.T. The clinical utility of C-peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes. Diabetes Med. 2013, 30, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, F.; Man, C.D.; Vella, A.; Cobelli, C. A model for the estimation of hepatic insulin extraction after a meal. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauter, E.V.; Mestrez, F.; Sturis, J.; Polonsky, K.S. Estimation of insulin secretion rates from C-peptide levels: Comparison of individual and standard kinetic parameters for C-peptide clearance. Diabetes 1992, 41, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; The WHO Consultation. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetes Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, L.; Man, C.D.; Nandy, D.K.; Saad, A.; Bharucha, A.E.; Levine, J.A.; Rizza, R.A.; Basu, R.; Carter, R.E.; Cobelli, C.; et al. Diurnal pattern of insulin action in type 1 diabetes: Implications for a closed-loop system. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, Y.; Romeres, D.; Cobelli, C.; Man, C.D.; Carter, R.; Basu, A.; Basu, R. Impaired diurnal pattern of meal tolerance and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes: Implications for therapy. Diabetes 2023, 72, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shampine, L.F.; Reichelt, M.W. The MATLAB ODE suite. SIAM J. Sci. Comp. 1997, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| k | (mg/dL) | (mg/(kg·min)) | (unitless) | (pmol/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | 586.92 | 61.58 | ||
| 1 | + | − | 140.03 | 2.32 | 0.46 | 62.95 |
| 1 | − | + | 1669.25 | 5.58 | ||
| 1 | − | − | 6.54 | 10.19 | ||
| 2 | + | + | 1669.25 | 5.58 | ||
| 2 | + | − | 586.92 | 61.58 | ||
| 2 | − | + | 140.03 | 2.32 | 0.46 | 62.95 |
| 2 | − | − | 6.54 | 10.19 | ||
| 3 | + | + | 1669.25 | 5.58 | ||
| 3 | + | − | 140.03 | 2.32 | 0.46 | 62.95 |
| 3 | − | + | 586.92 | 61.58 | ||
| 3 | − | − | 6.54 | 10.19 |
| System | Symbol | Basal Quantity Description | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Plasma-glucose concentration | mg/dL | 140.03 | |
| Plasma-glucose mass | mg/kg | 140.03 | ||
| Endogenous glucose-production rate | mg/(kg·min) | 2.32 | ||
| Glucose-excretion rate | mg/(kg·min) | 0 | ||
| Tissue-glucose mass | mg/kg | 184.30 | ||
| Insulin-dependent utilization rate | mg/(kg·min) | 1.32 | ||
| Insulin-independent utilization rate | mg/(kg·min) | 1 | ||
| Insulin | Insulin-secretion rate | pmol/min | 246.20 | |
| Hepatic-extraction ratio | unitless | 0.46 | ||
| Hepatic-extraction parameter | 1/min | 0.27 | ||
| Plasma-insulin mass | pmol/kg | 2.58 | ||
| Liver-insulin mass | pmol/kg | 5.84 | ||
| Extravascular-insulin mass | pmol/kg | 39.47 | ||
| Plasma-insulin concentration | pmol/L | 62.95 | ||
| Anticipated insulin signal | pmol/L | 62.95 | ||
| Delayed insulin signal | pmol/L | 62.95 | ||
| C-Peptide | Peripheral C-peptide concentration | pmol/L | 987.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chichester, C.C.; Yamakuchi, M.; Takenouchi, K.; Hashiguchi, T.; Maywar, D.N. Analytical Basal-State Model of the Glucose, Insulin, and C-Peptide Systems for Type 2 Diabetes. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050553
Chichester CC, Yamakuchi M, Takenouchi K, Hashiguchi T, Maywar DN. Analytical Basal-State Model of the Glucose, Insulin, and C-Peptide Systems for Type 2 Diabetes. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050553
Chicago/Turabian StyleChichester, Ched C., Munekazu Yamakuchi, Kazunori Takenouchi, Teruto Hashiguchi, and Drew N. Maywar. 2025. "Analytical Basal-State Model of the Glucose, Insulin, and C-Peptide Systems for Type 2 Diabetes" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050553
APA StyleChichester, C. C., Yamakuchi, M., Takenouchi, K., Hashiguchi, T., & Maywar, D. N. (2025). Analytical Basal-State Model of the Glucose, Insulin, and C-Peptide Systems for Type 2 Diabetes. Bioengineering, 12(5), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050553







