An Arthroscopic Robotic System for Meniscoplasty with Autonomous Operation Ability
Abstract
1. Introduction
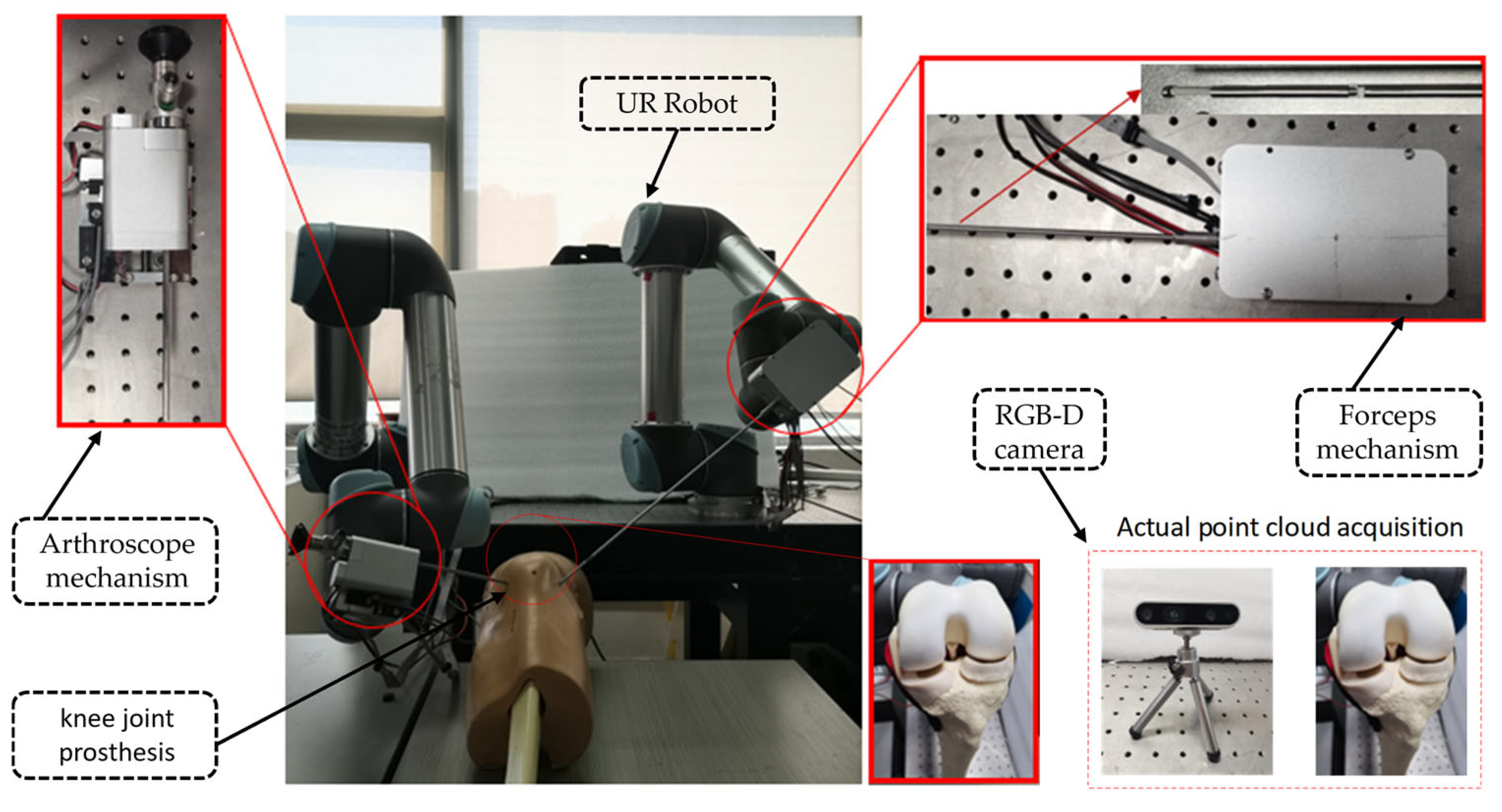
- An arthroscopic robotic system was constructed. This system consists of two UR5 robotic arms, an RGB-D camera, and a sawbones knee joint model. Meanwhile, the end of the robotic arm is equipped with customized surgical instruments for meniscoplasty.
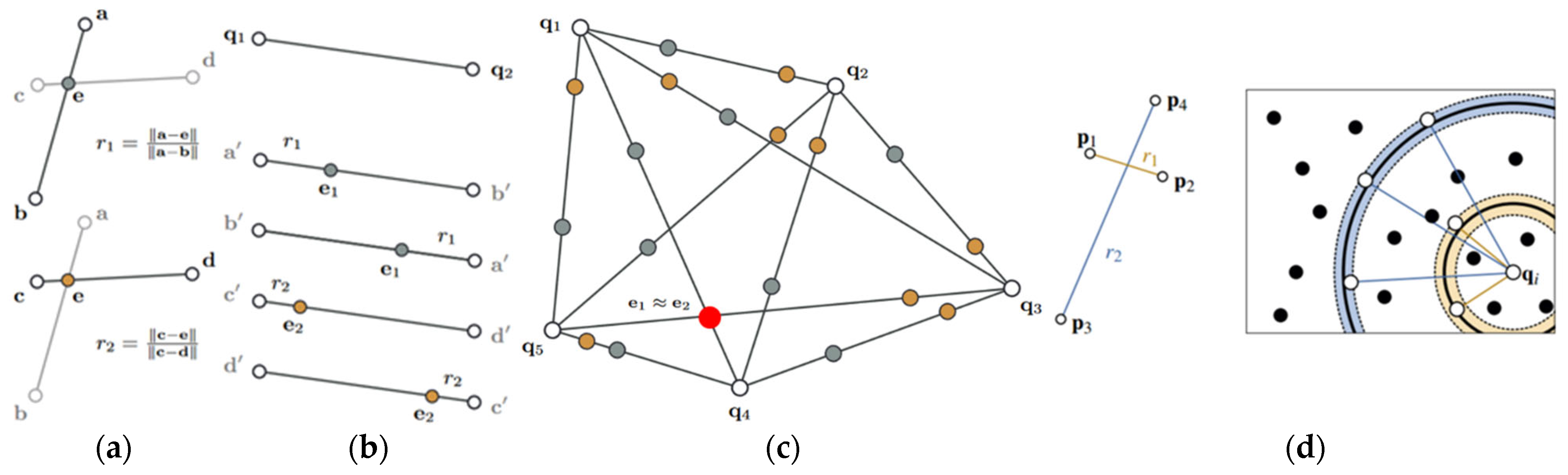
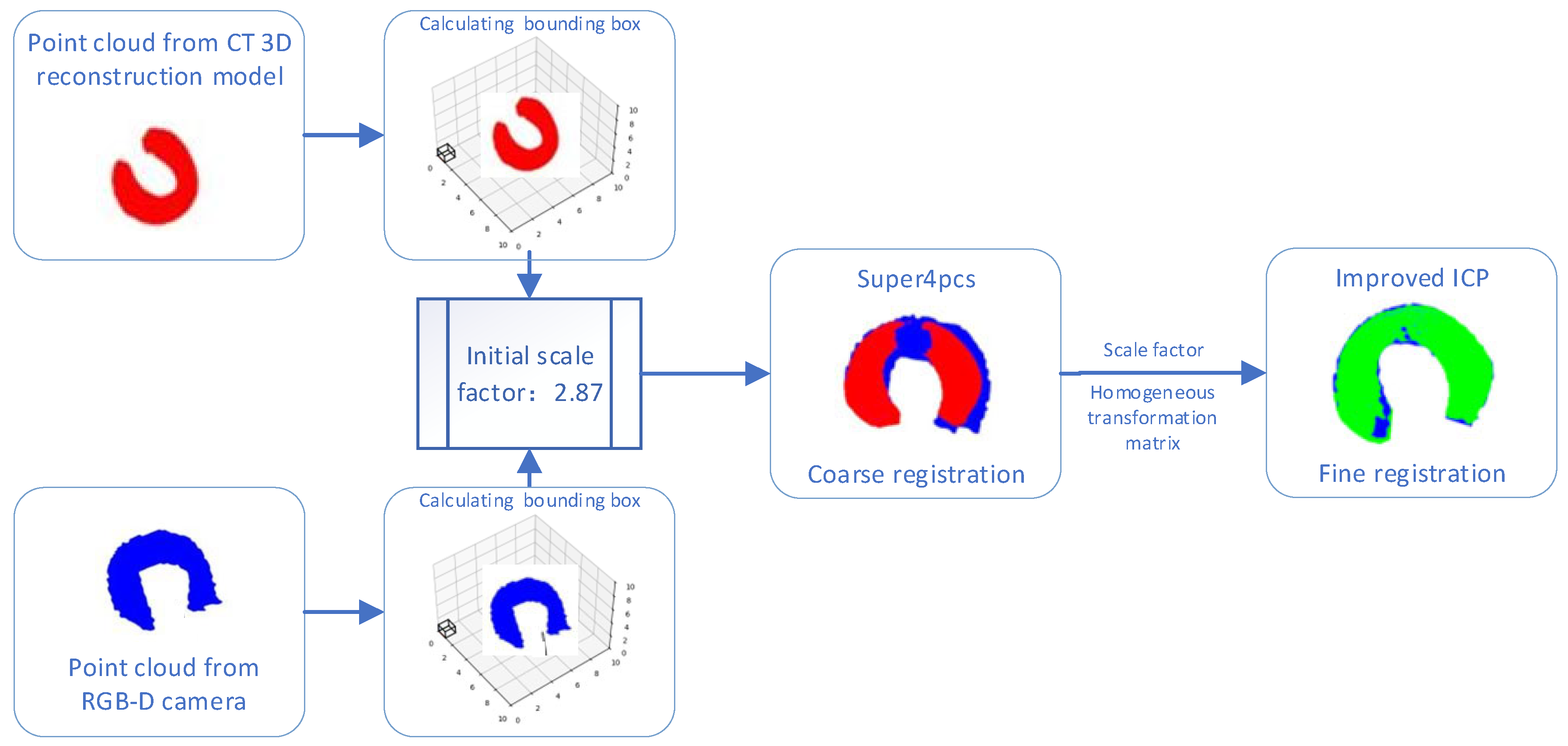
- A new two-stage cross-modal point cloud registration framework is proposed. Precise preoperative–intraoperative 3D point cloud alignment is achieved by fusing the Super4PCS algorithm with the improved ICP algorithm.
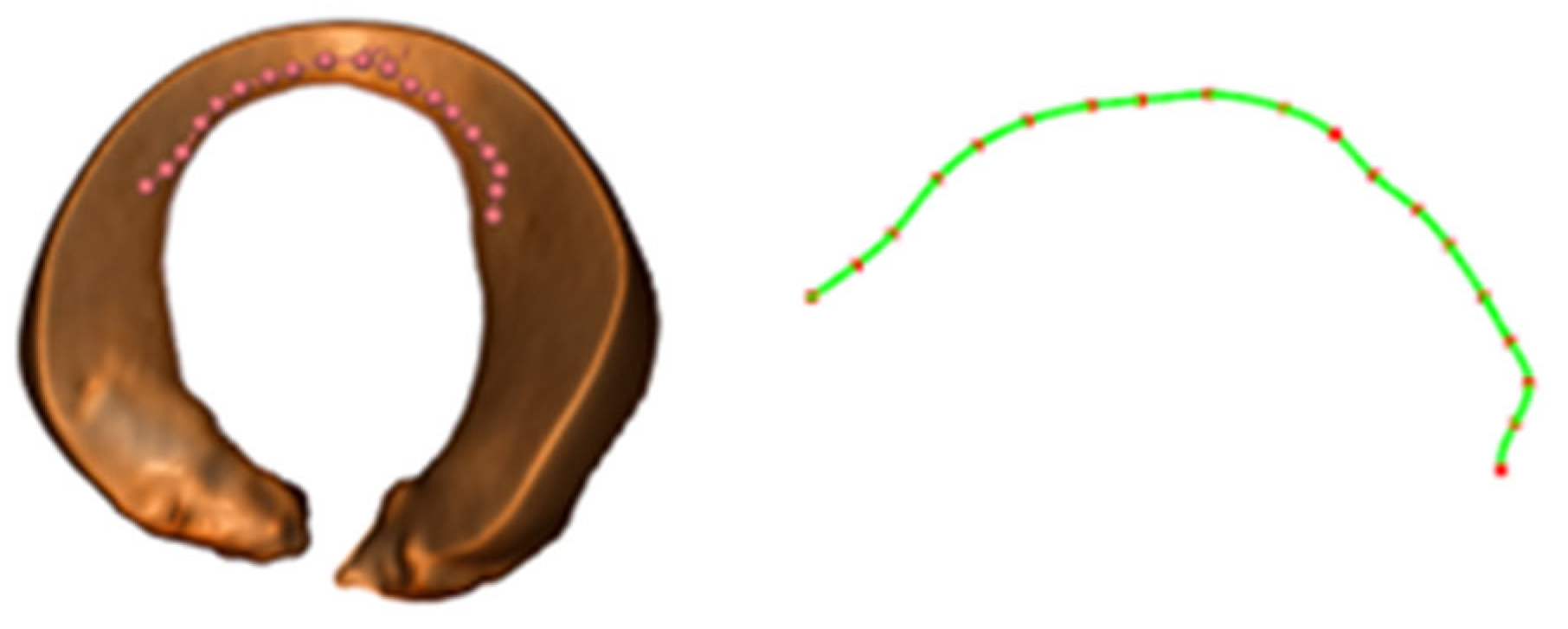
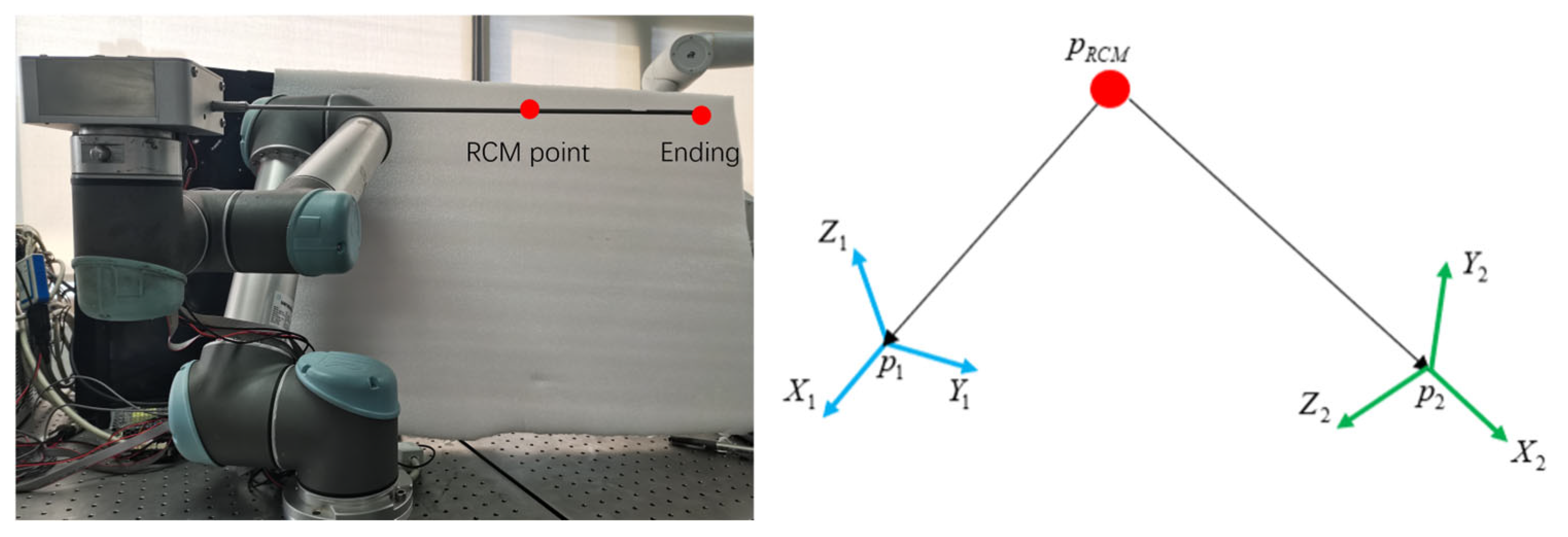
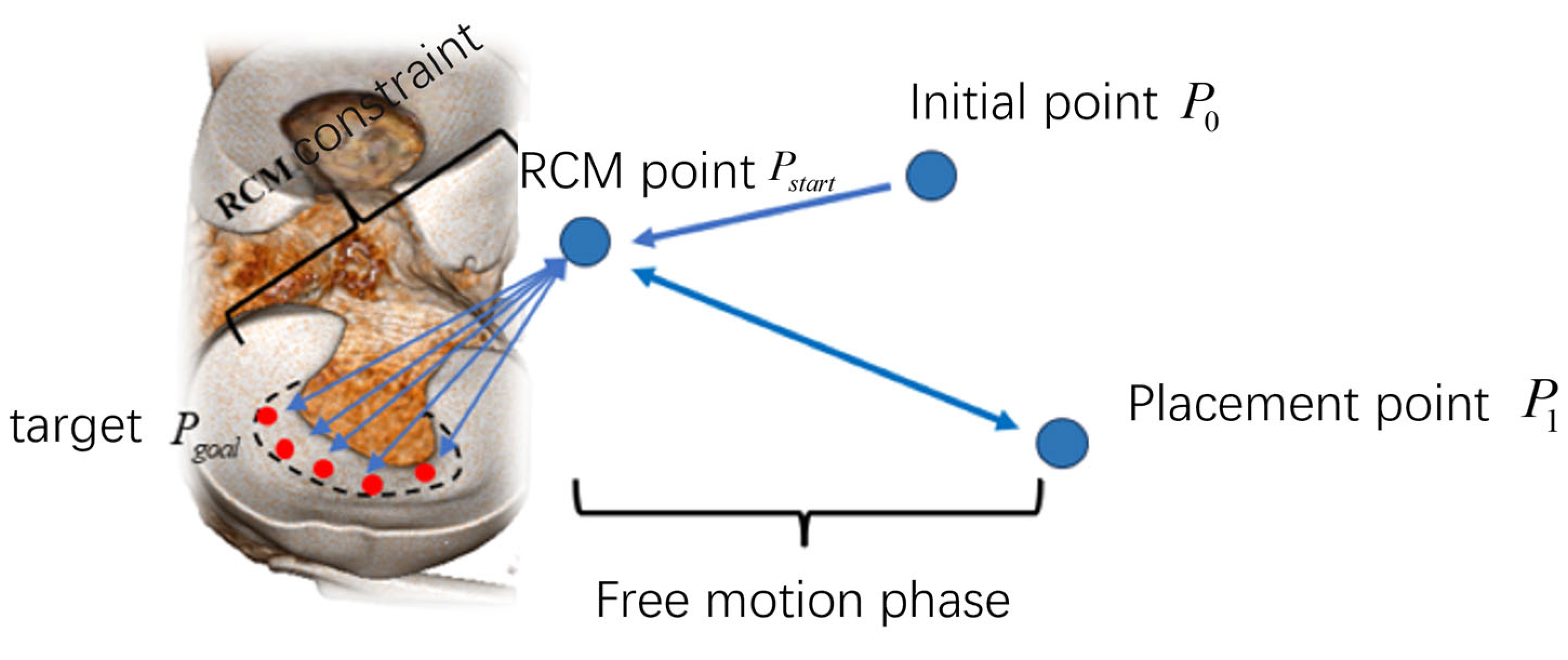
- A set of local autonomous motion-planning frameworks for robotic implementation is developed. We optimized the RRT path-planning algorithm to ensure that the paths planned by the algorithm can maintain the crescent shape of the meniscus. In addition, this study introduced the Remote Center of Motion constraints to enhance surgical safety.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Setup
2.2. Customized Surgical Instruments
2.3. Two-Stage Cross-Modal Point Cloud Registration
2.3.1. Coarse Registration Based on the Super4PCS Algorithm
2.3.2. Fine Registration Based on the Improved ICP Algorithm
2.4. Motion-Planning for Autonomous Operation
2.4.1. Path-Planning Based on the Improved RRT Algorithm
2.4.2. Remote Center of Motion Control
3. Results
3.1. Pre- and Intraoperative Point Cloud Registration Experiment
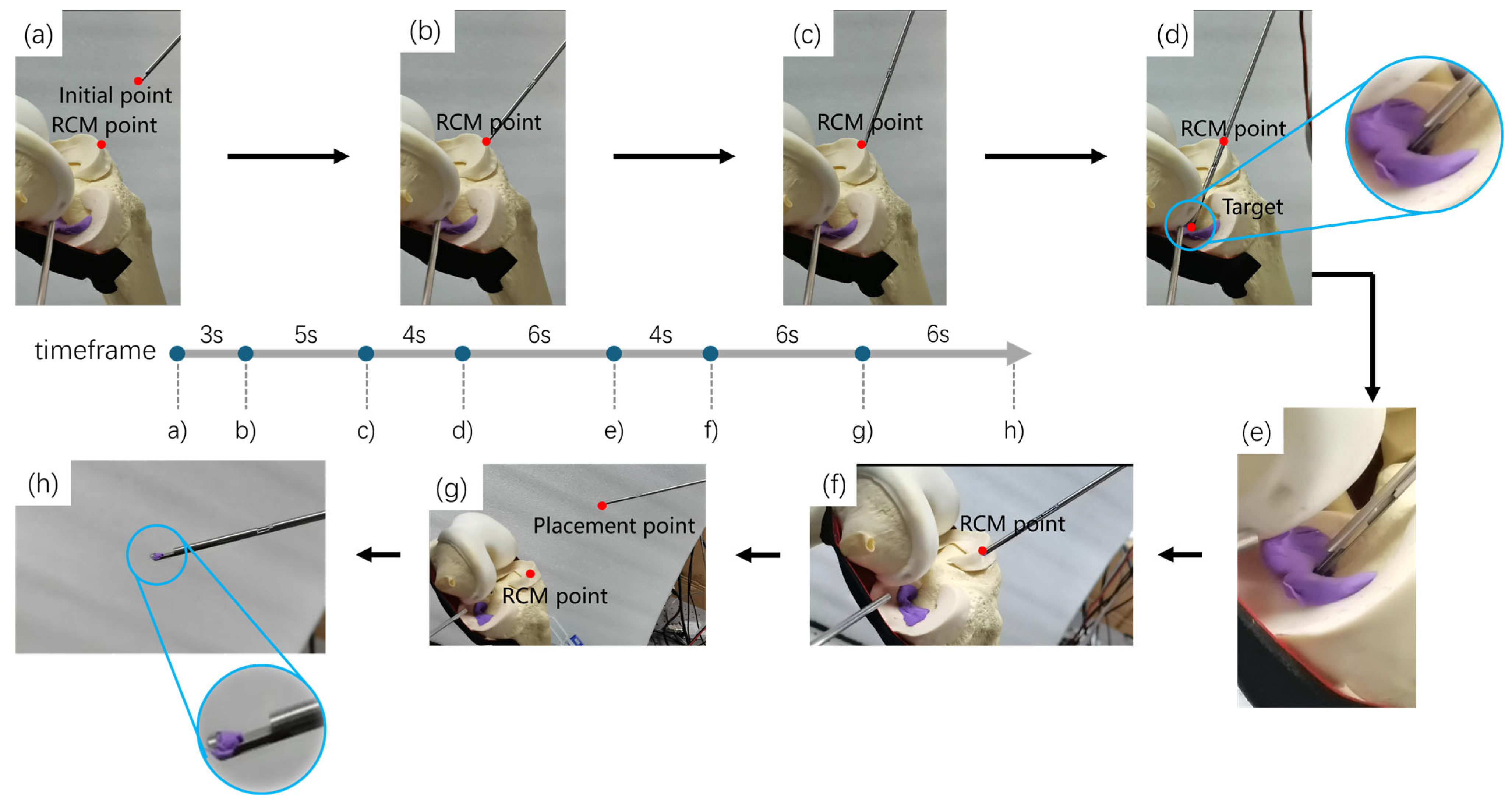
3.2. The Experiment of Motion-Planning and Robot Autonomous Operation
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duong, V.; Oo, W.M.; Ding, C.; Culvenor, A.G.; Hunter, D.J. Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Pain: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habata, T.; Uematsu, K.; Kasanami, R.; Hattori, K.; Takakura, Y.; Tohma, Y.; Fujisawa, Y. Long-term clinical and radiographic follow-up of total resection for discoid lateral meniscus. Arthroscopy 2006, 22, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W. Research progress of knee meniscal repair techniques. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2023, 37, 885–894. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, H.; Shi, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Toward Bionic Arthroscopy: A Comprehensive Perspective of Continuum Robotics Principles and Prototypes for the Inception of Arthroscopic Surgery Robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2024, 6, 2300614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anooshahpour, F.; Yadmellat, P.; Polushin, I.G.; Patel, R.V. A Motion Transmission Model for a Class of Tendon-Based Mechanisms with Application to Position Tracking of the da Vinci Instrument. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Liu, H.; Hou, C.; Zhang, F.; Sun, L. Summary on the developments and applications of intelligent visual-tactile perception and autonomous technologies in surgical robots. Mach. Des. Manuf. Eng. 2023, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- De Virgilio, A.; Costantino, A.; Festa, B.M.; Sampieri, C.; Spriano, G. Compartmental Transoral Robotic Lateral Oropharyngectomy with the da Vinci Single-Port System: Surgical Technique. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5728–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kather, J.; Hagen, M.E.; Morel, P.; Fasel, J.; Markar, S.; Schueler, M. Robotic hip arthroscopy in human anatomy. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2010, 6, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, M.; Apaydin, N.; Işik, C.; Bilgetekin, Y.G.; Acar, H.I.; Elhan, A. Robotic arthroscopic surgery: A new challenge in arthroscopic surgery Part-I: Robotic shoulder arthroscopy; a cadaveric feasibility study. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2011, 7, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alletti, S.G.; Rossitto, C.; Cianci, S.; Perrone, E.; Pizzacalla, S.; Monterossi, G.; Vizzielli, G.; Gidaro, S.; Scambia, G. The SenhanceTM surgical robotic system (“Senhance”) for total hysterectomy in obese patients: A pilot study. J. Robot. Surg. 2018, 12, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, G.; Shirotake, S.; Oyama, M.; Koyama, I. Utility of a 3 mm Bipolar Instrument in Laparoscopic Renal Surgery Using the Senhance Robotic System. Cureus 2024, 16, e65694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badre, A.; Tavakoli, M. Robotic Assistance and Haptic Feedback in Arthroscopic Procedures: Design and Preliminary Evaluation of a Two-Arm System. J. Med. Robot. Res. 2024, 9, 2450004. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Jaiprakash, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Fontanarosa, D.; Jonmohamadi, Y.; Antico, M.; Strydom, M.; Razjigaev, A.; Sasazawa, F.; Roberts, J.; et al. 29—Robotic and Image-Guided Knee Arthroscopy. In Handbook of Robotic and Image-Guided Surgery; Abedin-Nasab, M.H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 493–514. ISBN 9780128142455. [Google Scholar]
- Pedram, S.A.; Shin, C.; Ferguson, P.W.; Ma, J.; Dutson, E.P.; Rosen, J. Autonomous Suturing Framework and Quantification Using a Cable-Driven Surgical Robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osa, T.; Harada, K.; Sugita, N.; Mitsuishi, M. Trajectory planning under different initial conditions for surgical task automation by learning from demonstration. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 6507–6513. [Google Scholar]
- Osa, T.; Sugita, N.; Mitsuishi, M. Online Trajectory Planning and Force Control for Automation of Surgical Tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, A.; Sen, S.; Kehoe, B.; Garg, A. Learning by observation for surgical subtasks: Multilateral cutting of 3D viscoelastic and 2D Orthotropic Tissue Phantoms. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, Washington, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1202–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Fast Point Feature Histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3212–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Salti, S.; Tombari, F.; Di Stefano, L. SHOT: Unique signatures of histograms for surface and texture description. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2014, 125, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L. Quick solution algorithm for quasi-minimum bounding box of similar to cuboid. Appl. Res. Comput. 2020, 37, 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Zheng, N.; Ying, S.; Wei, J. ICP with Bounded Scale for Registration of M-D Point Sets. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Beijing, China, 2–5 July 2007; pp. 1291–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Han, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Qi, Q.; Feng, N.; Tang, S. Research on Two-Stage Variable Scale Three-Dimensional Point Cloud Registration Algorithm. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, J.; Veloso, M. Real-time randomized path planning for robot navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 September–4 October 2002; Volume 3, pp. 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunoth, A.; Lyche, T.; Sangalli, G.; Serra-Capizzano, S. Splines and PDEs: From Approximation Theory to Numerical Linear Algebra; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Hanwen, S. Optimal robot-world and hand-eye calibration with rotation and translation coupling. Robotica 2022, 40, 2953–2968. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yu, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X. An Arthroscopic Robotic System for Meniscoplasty with Autonomous Operation Ability. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050539
Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Zhao B, Yu G, Zhang P, Wang Q, Yang X. An Arthroscopic Robotic System for Meniscoplasty with Autonomous Operation Ability. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050539
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zijun, Yijun Zhao, Baoliang Zhao, Gang Yu, Peng Zhang, Qiong Wang, and Xiaojun Yang. 2025. "An Arthroscopic Robotic System for Meniscoplasty with Autonomous Operation Ability" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050539
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhao, B., Yu, G., Zhang, P., Wang, Q., & Yang, X. (2025). An Arthroscopic Robotic System for Meniscoplasty with Autonomous Operation Ability. Bioengineering, 12(5), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050539







