Identification of Key Genes and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Using Transformer and Machine Learning Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diagram of Study Flow and Data Collection
2.2. Sepsis and AKI-Related Gene Analysis
2.3. Gene Function Analysis
2.4. Diagnostic Signature Machine Learning Analysis
2.5. Diagnostic Signature Transformer Analysis
2.6. Model Construction and Evaluation
2.7. Drug Target Prediction
3. Results
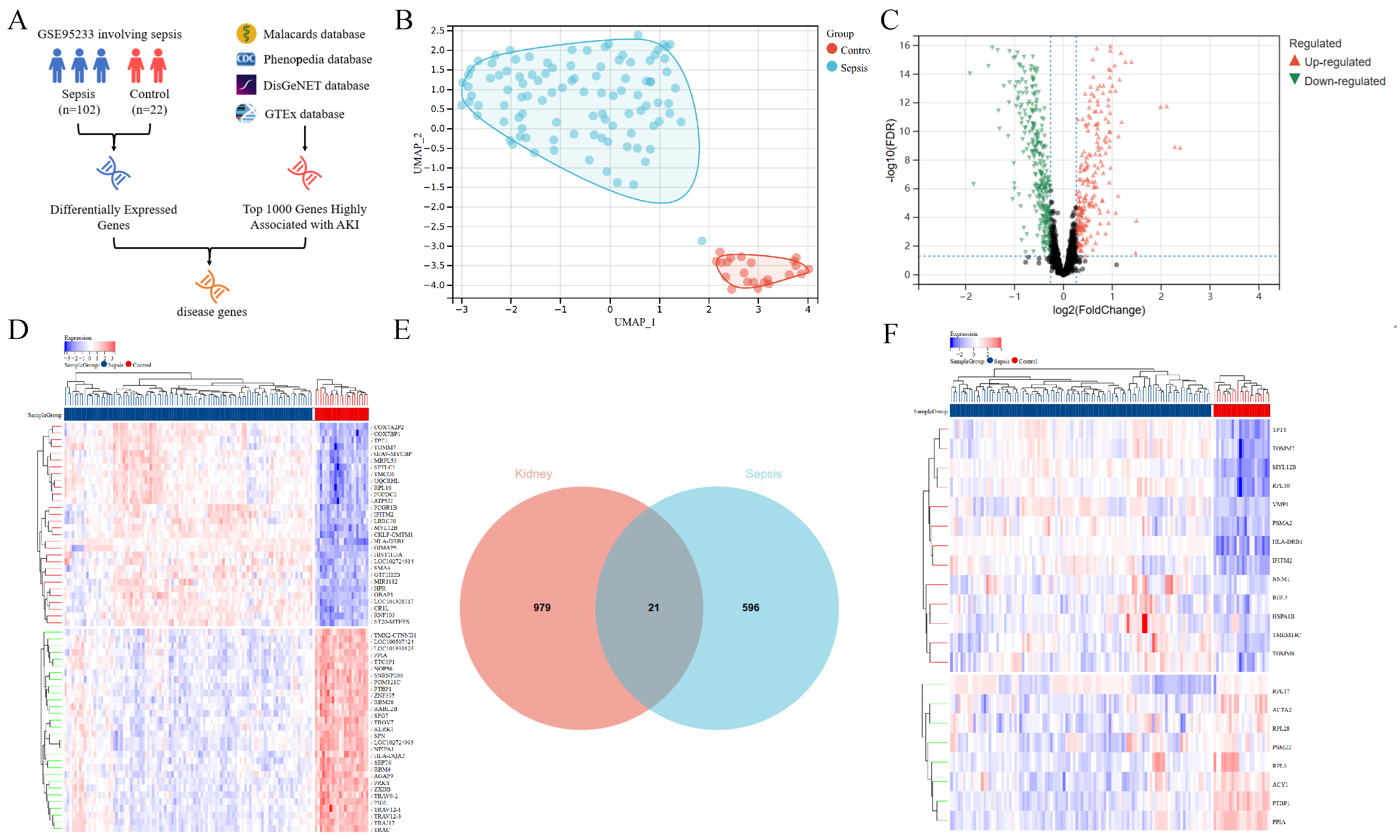
3.1. Analysis of Genes Associated with Sepsis and AKI
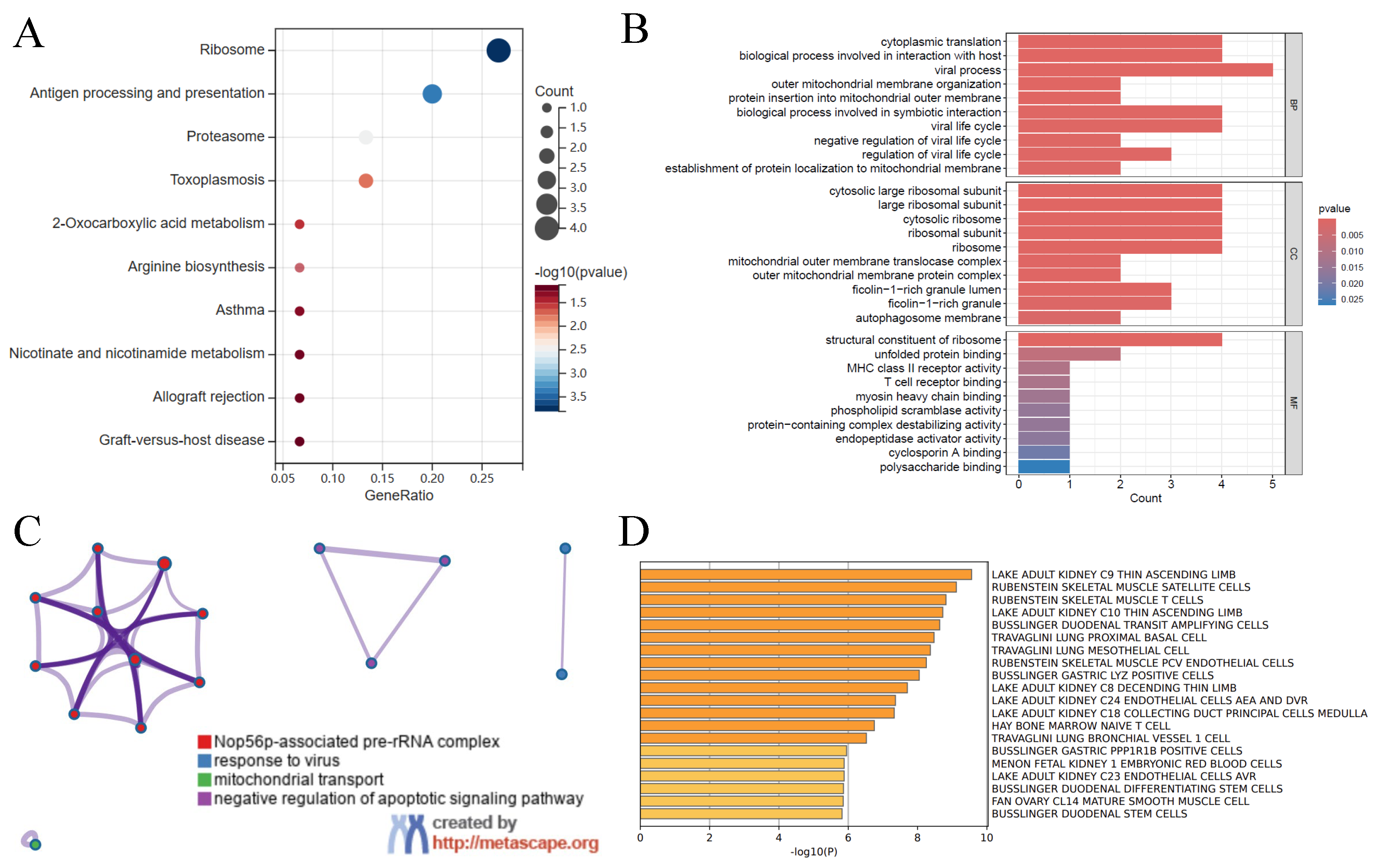
3.2. Gene Function Analysis
3.3. Diagnostic Signature Identification Analysis
3.4. Diagnostic Model Validation
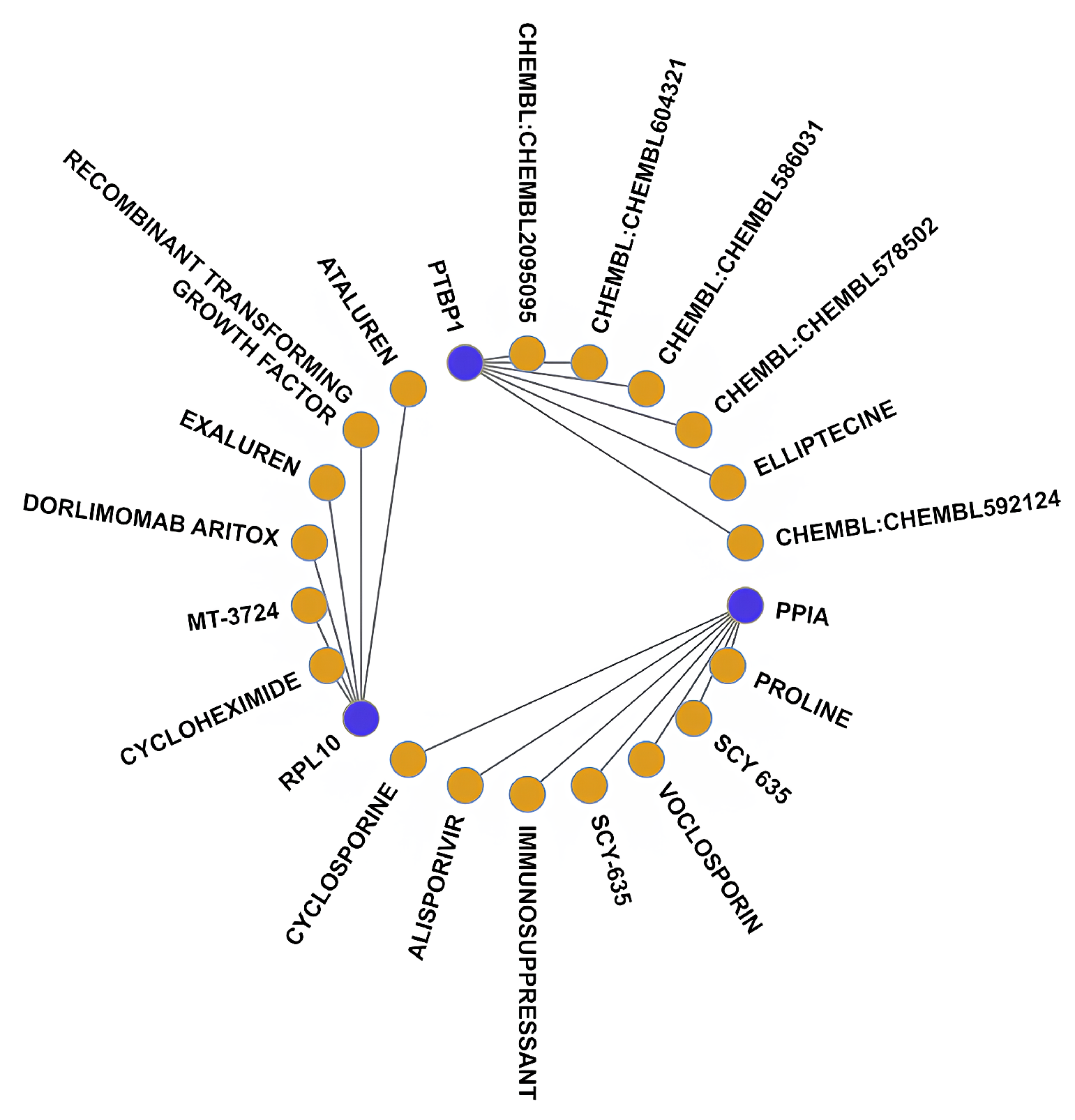
3.5. Drug–Gene Interaction Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SA-AKI | Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| SVM-RFE | Support Vector Machine Recursive Feature Elimination |
| RF | Random Forest |
| NNET | Artificial neural network |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| DGIdb | Drug Gene Interaction Database |
| UMAP | Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| TNF- | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| BP | Biological process |
| CC | Cellular Component |
| MF | Molecular Function |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
References
- Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; Wald, R.; Martensson, J.; Maiden, M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Glassford, N.J.; Lankadeva, Y.; Vaara, S.T.; et al. Acute kidney injury in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgili, B.; Haliloğlu, M.; Cinel, İ. Sepsis and Acute Kidney Injury. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2014, 42, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Del Rio-Pertuz, G.; Gomez, H. Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitoun, T.; Megahed, M.; Elghoneimy, H.; Emara, D.M.; Elsayed, I.; Ahmed, I. Renal arterial resistive index versus novel biomarkers for the early prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Rosner, M.H.; Okusa, M.D. Emerging therapeutic targets of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2015, 35, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårtensson, J.; Bellomo, R. Pathophysiology of Septic Acute Kidney Injury. Contrib. Nephrol. 2016, 187, 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Takasu, O.; Gaut, J.P.; Watanabe, E.; To, K.; Fagley, R.E.; Sato, B.; Jarman, S.; Efimov, I.R.; Janks, D.L.; Srivastava, A.; et al. Mechanisms of cardiac and renal dysfunction in patients dying of sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounatidis, D.; Tzivaki, I.; Daskalopoulou, S.; Daskou, A.; Adamou, A.; Rigatou, A.; Sdogkos, E.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M.; Vallianou, N.G. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: What’s new regarding its diagnostics and therapeutics? Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Yan, L. Predictive models of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury based on machine learning: A scoping review. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2380748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; Lameire, N.H.; Vanholder, R.C.; Benoit, D.D.; Decruyenaere, J.M.; Colardyn, F.A. Acute renal failure in patients with sepsis in a surgical ICU: Predictive factors, incidence, comorbidity, and outcome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Fu, P.; Cai, D.; Yang, L. A simple risk score for prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, W.; Wu, J. Machine learning for the prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Q.; Yan, P.; Duan, S.B.; Kang, Y.X.; Deng, Y.H.; Liu, Q.; Wu, T.; Wu, X. Development and validation of machine learning models for real-time mortality prediction in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 853102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, R.; Zhao, W.; Shi, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Wang, D. Machine learning algorithm to predict mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lin, J.; Duan, M. Application of machine learning to predict acute kidney disease in patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 792974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, R.; Jin, W.; Du, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R. A prediction model of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury based on antithrombin III. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Shui, P.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, K.; et al. Gene signature for the prediction of the trajectories of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Nadim, M.K.; Pickkers, P.; Gomez, H.; Bell, S.; Joannidis, M.; Kashani, K.; Koyner, J.L.; Pannu, N.; Meersch, M.; et al. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: Consensus report of the 28th Acute Disease Quality Initiative workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, J.C.C.; Khondker, A.; Lajkosz, K.; McDermott, M.B.A.; Frigola, X.B.; McCradden, M.D.; Mamdani, M.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Johnson, A.E.W. APPRAISE-AI tool for quantitative evaluation of AI studies for clinical decision support. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2335377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carithers, L.J.; Ardlie, K.; Barcus, M.; Branton, P.A.; Britton, A.; Buia, S.A.; Compton, C.C.; DeLuca, D.S.; Peter-Demchok, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; et al. A novel approach to high-quality postmortem tissue procurement: The GTEx Project. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2015, 13, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, N.; Twik, M.; Plaschkes, I.; Nudel, R.; Iny Stein, T.; Levitt, J.; Gershoni, M.; Morrey, C.P.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. MalaCards: An amalgamated human disease compendium with diverse clinical and genetic annotation and structured search. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D877–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Clyne, M.; Khoury, M.J.; Gwinn, M. Phenopedia and Genopedia: Disease-centered and gene-centered views of the evolving knowledge of human genetic associations. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Saüch, J.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET Cytoscape app: Exploring and visualizing disease genomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Xiong, Y.; Han, G.; Luo, T.; Peng, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, T.; Zha, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. Unraveling the genetic and molecular landscape of sepsis and acute kidney injury: A comprehensive GWAS and machine learning approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 137, 112420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Huang, J.Q.; Ming, Y.Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Xia, H. Screening of key biomarkers of tendinopathy based on bioinformatics and machine learning algorithms. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawagreh, K.; Medhat, G.M.; Elyan, E. Random forests: From early developments to recent advancements. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2014, 2, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.W. NeuralNetTools: Visualization and analysis tools for neural networks. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Yang, L. Identification of an immune-related gene diagnostic model and potential drugs in sepsis using bioinformatics and pharmacogenomics approaches. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 5665–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Su, W.; Chen, F.; Lai, T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D. Mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of 4-octyl itaconate in treating sepsis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1056405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Fan, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Jia, K.; Ma, C. Single-cell sequence analysis combined with multiple machine learning to identify markers in sepsis patients: LILRA5. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1236–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Hou, H.; Guo, Z.; Yang, H.; Tang, H.; Chen, B. Interleukin-36 is overexpressed in human sepsis and IL-36 receptor deletion aggravates lung injury and mortality through epithelial cells and fibroblasts in experimental murine sepsis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshour, S.L.; Kiwala, S.; Cotto, K.C.; Coffman, A.C.; McMichael, J.F.; Song, J.J.; Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Wagner, A.H. Integration of the Drug–Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb 4.0) with open crowdsource efforts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1144–D1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; He, L.; Yan, F.; Li, J.; Liao, X.; Ling, M.; Jing, R.; Pan, L. Identification of hub genes associated with acute kidney injury induced by renal ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 951855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, H.D.; Jackson, N.M.; O’Connor, R.P.; Hunt, D.A.; White, M.D. Pathogenetic mechanisms of nephrotoxicity: Insights into cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Transplant. Proc. 1985, 17 (Suppl. S1), 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hadpech, S.; Thongboonkerd, V. Current update on theranostic roles of cyclophilin A in kidney diseases. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4067–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.N. The unsolved cyclosporine-induced kidney injury: Is paricalcitol a feasible new renoprotective option? Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hałka, J.; Spaleniak, S.; Kade, G.; Antosiewicz, S.; Sigorski, D. The nephrotoxicity of drugs used in causal oncological therapies. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 9681–9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, F.R.; Shang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lv, X.F.; Yuan, J.N.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, K.; Lin, X.C.; Liu, X.; et al. Renal inhibition of miR-181a ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced mesangial cell apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Nassiri, V.; Srivastava, S.; Yang, A.; Brar, S.; McDuffie, E.; Sachs, C. Artificial intelligence and machine learning models for predicting drug-induced kidney injury in small molecules. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Huang, S.-T.; Wu, P.-H. Detection of drug–drug and drug–disease interactions inducing acute kidney injury using deep rule forests. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y. The ufmylation modification of ribosomal protein L10 in the development of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Dong, X.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Q.L.; Su, L. Identification of phosphorylated MYL12B as a potential plasma biomarker for septic acute kidney injury using a quantitative proteomic approach. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14409–14416. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhong, W.; Tao, J.; Ao, Y.; Niu, B.; Zhu, L. Identification of Key Genes and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Using Transformer and Machine Learning Approaches. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050536
Zhai Z, Peng J, Zhong W, Tao J, Ao Y, Niu B, Zhu L. Identification of Key Genes and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Using Transformer and Machine Learning Approaches. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Zhendong, JunZhe Peng, Wenjun Zhong, Jun Tao, Yaqi Ao, Bailin Niu, and Li Zhu. 2025. "Identification of Key Genes and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Using Transformer and Machine Learning Approaches" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050536
APA StyleZhai, Z., Peng, J., Zhong, W., Tao, J., Ao, Y., Niu, B., & Zhu, L. (2025). Identification of Key Genes and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Using Transformer and Machine Learning Approaches. Bioengineering, 12(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050536




