Machine Learning Prediction of Left Ventricular Assist Device Thrombosis from Acoustic Harmonic Power
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HVAD Cohort and Acoustic Signature Data Acquisition
2.2. Spectral Analysis of Recordings
2.3. Acoustic Signature Characterization with Harmonic Power Distribution
2.4. Leave-Two-Out Cross Validation for Machine Learning Models
- The training dataset was created by removing the current validation pair of recordings from a copy of the dataset in Table 2;
- The machine learning algorithm being investigated was trained with this training dataset, using as inputs the harmonic power variables being investigated in the current model;
- The resulting trained classifier was then used to predict the outcomes of the current validation pair of recordings;
- The predicted and actual outcomes were collected in a confusion matrix.
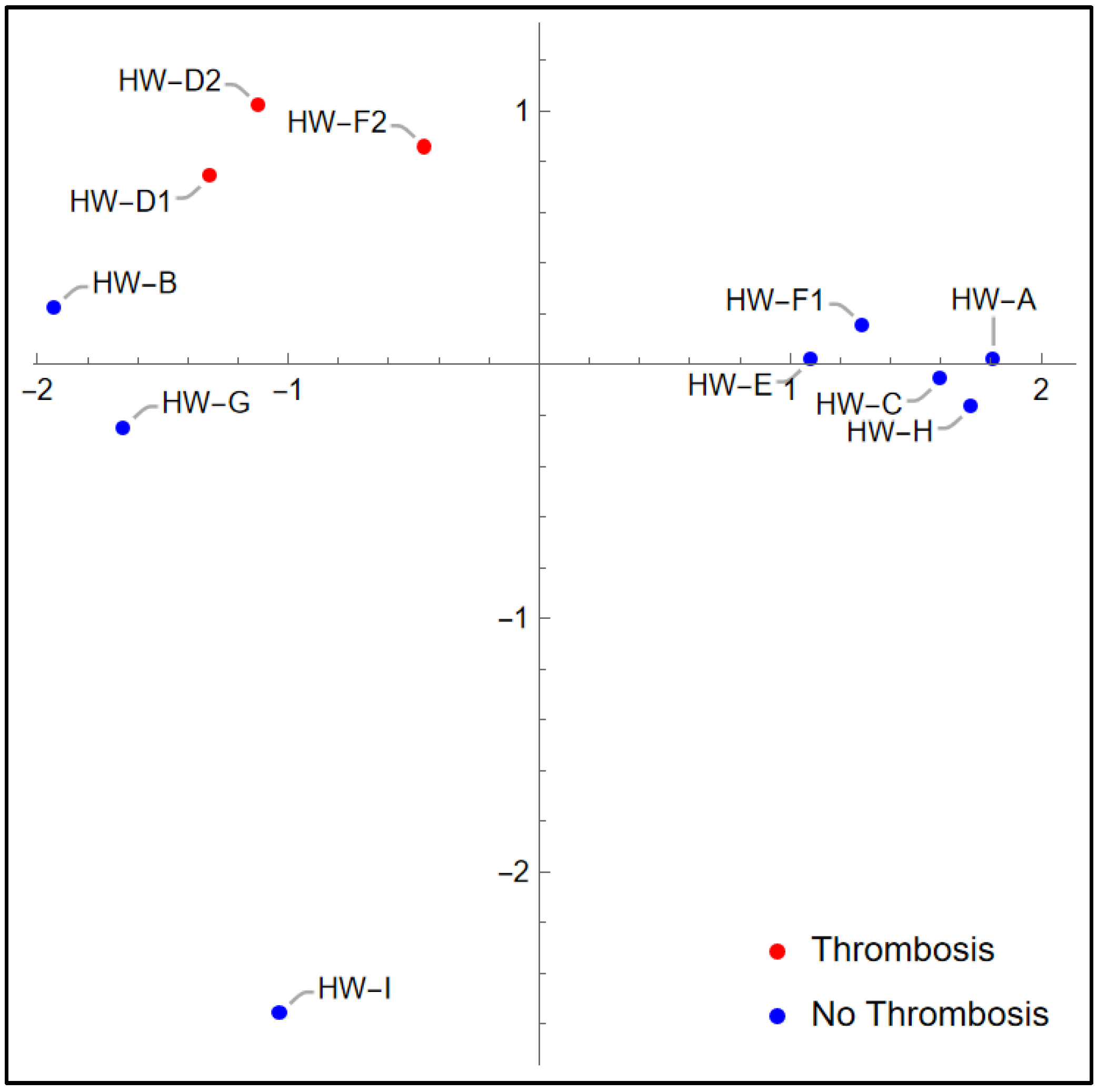
2.5. Principal Component Analysis
2.6. Leave-One-Out Cross Validation for KNN Models
3. Results
3.1. Harmonic Power Distributions
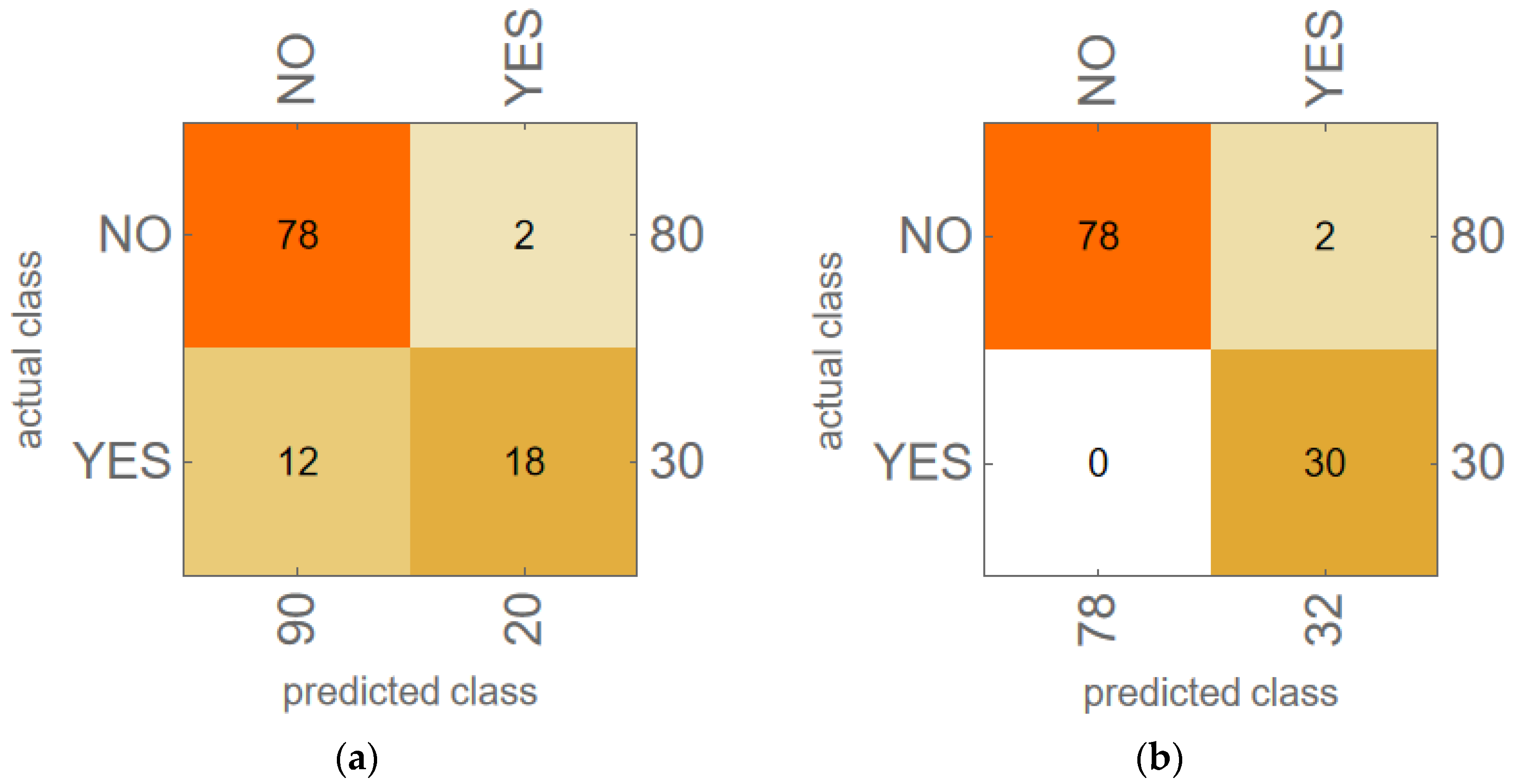
3.2. Machine Learning Model Results for LTOCV
3.3. KNN Model Results for LOOCV
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| dB | Decibels |
| FF | Fundamental frequency of HVAD pump (i.e., pump speed) |
| 2H, 3H | Higher harmonic frequencies of FF (2H = 2 × FF, 3H = 3 × FF, etc.) |
| PFF, P2H, P3H | Harmonic power values for frequencies FF, 2H, 3H, etc. |
| HVAD | HeartWare ventricular assist device |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors algorithm |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LOOCV | Leave-one-out cross validation |
| LTOCV | Leave-two-out cross validation |
| LVAD | Left ventricular assist device |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PSD | Power spectral density |
References
- Shah, P.; Mehta, V.M.; Cowger, J.A.; Aaronson, K.D.; Pagani, F.D. Diagnosis of hemolysis and device thrombosis with lactate dehydrogenase during left ventricular assist device support. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2014, 33, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, M.R.; Goldstein, D.J.; Cleveland, J.C.; Cowger, J.A.; Hall, S.; Salerno, C.T.; Naka, Y.; Horstmanshof, D.; Chuang, J.; Wang, A.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes in Patients With Fully Magnetically Levitated vs Axial-Flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices in the MOMENTUM 3 Randomized Trial. JAMA 2022, 328, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanelidis, A.J.; Prabhu, N.; Smith, B.; Kalantari, S.; Nguyen, A.; Chung, B.B.; Sarswat, N.; Shah, A.; Kim, G.H.; Pinney, S.P.; et al. Heart Mate 3 Pump Thrombosis After Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation: Pushing the Boundaries of Hemocompatibility. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2022, 41, S472–S473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, B.M. FDA: Stop Using Medtronic’s Heartware Ventricular Assist Device. JAMA 2021, 326, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, C.A.; Rogers, J.G.; Tatooles, A.J.; Bhat, G.; Slaughter, M.S.; Birks, E.J.; Mokadam, N.A.; Mahr, C.; Miller, J.S.; Markham, D.W.; et al. HVAD: The ENDURANCE Supplemental Trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boilson, B.A.; Bechtum, E.L.; Behnken, A.L.; Loga, L.A.; Luckhardt, A.J.; Schettle, S.D.; Clavell, A.L.; Dragomir-Daescu, D.; Stulak, J.M. Acoustic Properties of Axial and Centrifugal Flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices and Prediction of Pump Thrombosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagna, F.; Pan, S.; Garan, A.R.; Yuzefpolskaya, M.; Takeda, K.; Takayama, H.; Ross, K.; Torres, M.; Blum, R.A.; Singh, S.; et al. Acoustic Analysis of a Continuous-Flow Left Ventricular Assist Device before and after Suspected Pump Thrombosis. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2016, 35, S326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, C.; Deniz, E.; Stomps, A.; Knigge, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Wendl, R.; Hanke, J.S.; Dogan, G.; Napp, L.C.; Glasmacher, B.; et al. An acoustic method for systematic ventricular assist device thrombus evaluation with a novel artificial thrombus model. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S1711–S1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbert, L.; Sundbom, P.; Loebe, M.; Peterzén, B.; Granfeldt, H.; Ahn, H. Acoustic Analysis of a Mechanical Circulatory Support. Artif. Organs. 2014, 38, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, F.; Hörmandinger, C.; Stepanenko, A.; Kretzschmar, A.; Soltani, S.; Krabatsch, T.; Potapov, E.; Hetzer, R. Acoustic Spectral Analysis for Determining Pump Thrombosis in Rotary Blood Pumps. ASAIO J. 2014, 60, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilja, D.; Schalit, I.; Espinoza, A.; Pettersen, F.J.; Elle, O.J.; Halvorsen, P.S. Detection of inflow obstruction in left ventricular assist devices by accelerometer: An in vitro study. Med. Eng. Phys. 2022, 110, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Mainsah, B.; Milano, C.A.; Nowacek, D.P.; Collins, L.; Karra, R. Acoustic Signatures of Left Ventricular Assist Device Thrombosis. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 2, 0245011–0245014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalit, I.; Espinoza, A.; Pettersen, F.J.; Skulstad, H.; Fosse, E.; Fiane, A.E.; Halvorsen, P.S. Improved Detection of Thromboembolic Complications in Left Ventricular Assist Device by Novel Accelerometer-Based Analysis. ASAIO J. 2022, 68, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalit, I.; Espinoza, A.; Pettersen, F.J.; Snartland, S.; Ringdal, M.A.L.; Hoel, T.N.; Skulstad, H.; Fosse, E.; Fiane, A.E.; Halvorsen, P.S. Detection of Thromboembolic Events and Pump Thrombosis in HeartWare HVAD Using Accelerometer in a Porcine Model. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalit, I.; Espinoza, A.; Pettersen, F.J.; Thiara, A.P.S.; Karlsen, H.; Sorensen, G.; Fosse, E.; Fiane, A.E.; Halvorsen, P.S. Accelerometer Detects Pump Thrombosis and Thromboembolic Events in an HVAD Circuit. ASAIO J. 2018, 64, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semiz, B.; Hersek, S.; Pouyan, M.B.; Partida, C.; Blazquez-Arroyo, L.; Selby, V.; Wieselthaler, G.; Rehg, J.M.; Klein, L.; Inan, O.T. Detecting Suspected Pump Thrombosis in Left Ventricular Assist Devices via Acoustic Analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2020, 24, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yost, G.L.; Royston, T.J.; Bhat, G.; Tatooles, A.J. Acoustic Characterization of Axial Flow Left Ventricular Assist Device Operation In Vitro and In Vivo. ASAIO J. 2016, 62, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
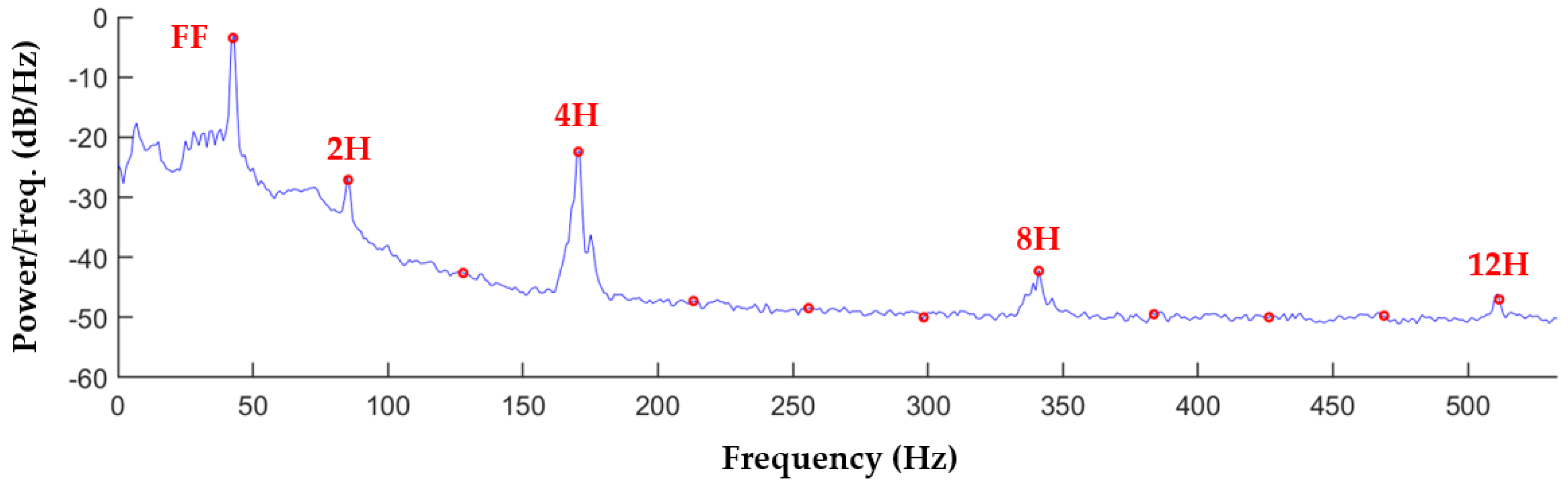
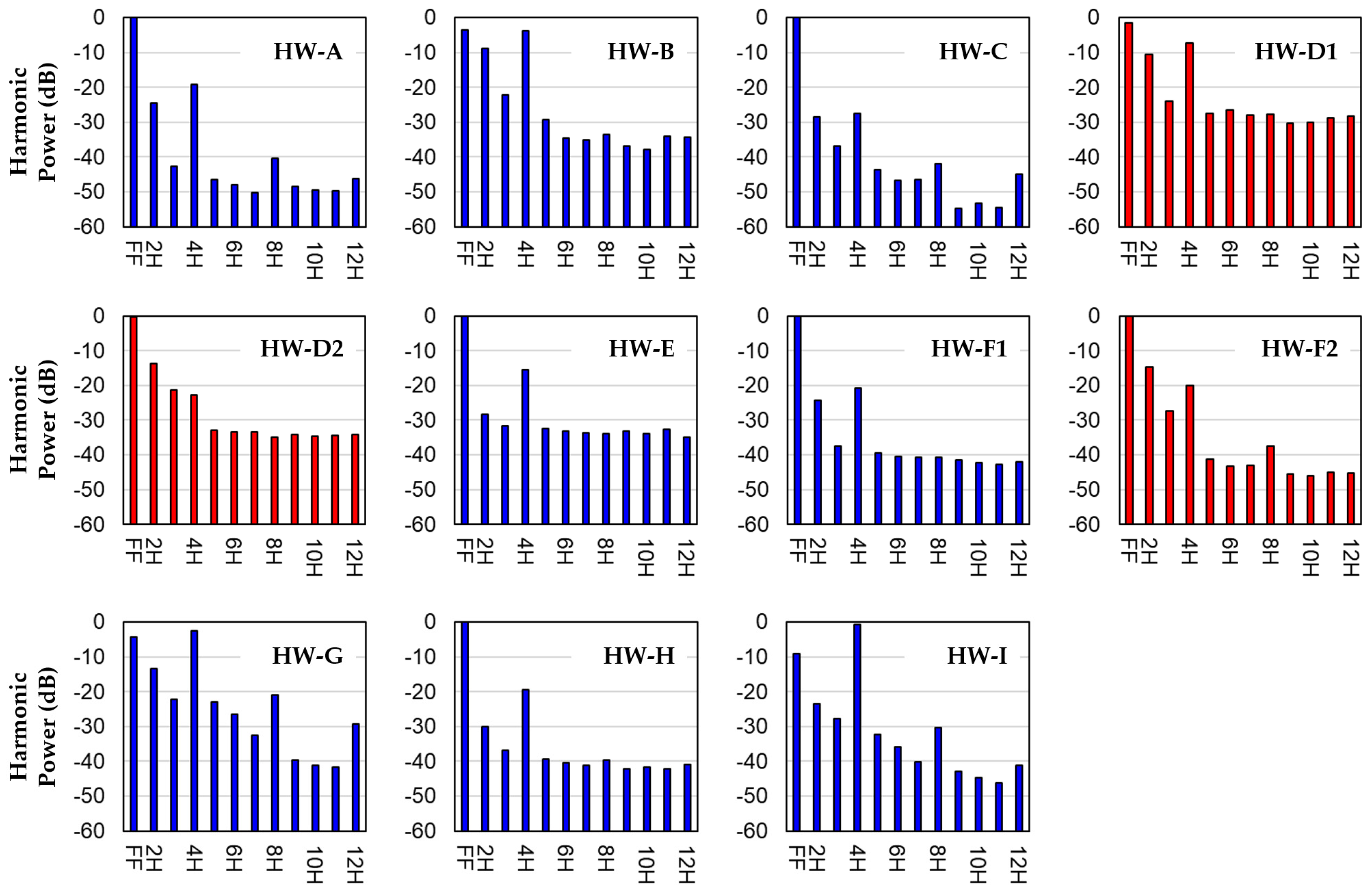
| Patient ID | LDH (U/L) | Pump Speed (rpm) | Pump Fund. Freq. (Hz) | Pump Power (W) | HVAD Age (Days) | Thrombosis Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW-A | 190 | 2560 | 42.67 | 3.1 | 1853 | NO |
| HW-B | 348 | 2600 | 43.33 | 3.6 | 1597 | NO |
| HW-C | 213 | 2620 | 43.67 | 3.9 | 959 | NO |
| HW-D1 | 4458 | 2540 | 42.33 | 7.0 | 2258 | YES |
| HW-D2 | 3585 | 2540 | 42.33 | 12.2 | 2262 | YES |
| HW-E | 275 | 2660 | 44.33 | 3.9 | 1472 | NO |
| HW-F1 | 292 | 2700 | 45 | 4.7 | 818 | NO |
| HW-F2 | 3330 | 2800 | 46.67 | 6.2 | 1253 | YES |
| HW-G | 253 | 2600 | 43.33 | 3.7 | 1444 | NO |
| HW-H | 154 | 2700 | 45 | 4.1 | 2034 | NO |
| HW-I | 311 | 2800 | 46.67 | 4.8 | 3461 | NO |
| PatID | PFF | P2H | P3H | P4H | P5H | P6H | P7H | P8H | P9H | P10H | P11H | P12H | Thrombosis Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW-A | −0.0709 | −24.5376 | −42.7136 | −19.0600 | −46.5642 | −47.9261 | −50.3521 | −40.3536 | −48.5813 | −49.5637 | −49.7301 | −46.0885 | NO |
| HW-B | −3.5042 | −8.7993 | −22.1829 | −3.8459 | −29.3450 | −34.5989 | −35.1714 | −33.5871 | −36.9125 | −37.9513 | −34.1700 | −34.3805 | NO |
| HW-C | −0.0157 | −28.4070 | −36.9364 | −27.5495 | −43.5894 | −46.8234 | −46.3518 | −41.9392 | −54.6824 | −53.3172 | −54.4150 | −44.9496 | NO |
| HW-D1 | −1.4809 | −10.6403 | −23.9485 | −7.2912 | −27.4535 | −26.5844 | −27.9201 | −27.7818 | −30.2167 | −30.1508 | −28.6569 | −28.2910 | YES |
| HW-D2 | −0.2563 | −13.8401 | −21.2248 | −22.7990 | −32.9389 | −33.3901 | −33.4354 | −34.9352 | −34.0925 | −34.6498 | −34.4029 | −34.1315 | YES |
| HW-E | −0.1489 | −28.2704 | −31.7187 | −15.5442 | −32.5102 | −33.0632 | −33.5801 | −34.0536 | −33.0876 | −34.0219 | −32.7320 | −34.8687 | NO |
| HW-F1 | −0.0551 | −24.2720 | −37.3658 | −20.9277 | −39.5058 | −40.5999 | −40.6656 | −40.6629 | −41.5667 | −42.2361 | −42.7583 | −42.0199 | NO |
| HW-F2 | −0.2059 | −14.6536 | −27.4858 | −20.0872 | −41.3635 | −43.3848 | −43.0292 | −37.5080 | −45.6187 | −45.9965 | −45.1245 | −45.2195 | YES |
| HW-G | −4.1746 | −13.2433 | −22.2679 | −2.6211 | −22.8487 | −26.5414 | −32.6231 | −20.9933 | −39.5206 | −41.2349 | −41.5568 | −29.1602 | NO |
| HW-H | −0.0583 | −30.1282 | −36.7897 | −19.3974 | −39.3128 | −40.2933 | −41.0277 | −39.5763 | −42.1642 | −41.5989 | −42.2536 | −40.8596 | NO |
| HW-I | −9.1241 | −23.4190 | −27.7626 | −0.6080 | −32.2090 | −35.7505 | −40.1552 | −30.3619 | −42.9335 | −44.7409 | −46.1173 | −41.1794 | NO |
| Harmonic Power Variables | Machine Learning Algorithm LTOCV Model Accuracy 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-Nearest Neighbors | Logistic Regression | Random Forest | Gradient Boosted Trees | Support Vector Machine | Naïve Bayes | |
| PFF, P2H | 91.8% | 75.5% | 77.3% | 84.5% | 81.8% | 73.6% |
| PFF, P3H | 78.2% | 68.2% | 73.6% | 81.8% | 68.2% | 70.0% |
| PFF, P4H | 69.1% | 70.9% | 70.9% | 72.7% | 70.9% | 65.5% |
| P2H, P3H | 60.0% | 64.5% | 69.1% | 68.2% | 63.6% | 65.5% |
| P2H, P4H | 74.5% | 71.8% | 77.3% | 80.9% | 78.2% | 49.1% |
| P3H, P4H | 65.5% | 66.4% | 69.1% | 77.3% | 67.3% | 54.5% |
| PFF, P2H, P3H | 87.3% | 76.4% | 64.5% | 72.7% | 77.3% | 74.5% |
| PFF, P2H, P4H | 75.5% | 70.0% | 75.5% | 72.7% | 74.5% | 64.5% |
| PFF, P3H, P4H | 67.3% | 69.1% | 76.4% | 72.7% | 65.5% | 61.8% |
| P2H, P3H, P4H | 88.2% | 70.0% | 70.0% | 72.7% | 77.3% | 66.4% |
| PFF, P2H, P8H | 62.7% | 75.5% | 53.6% | 72.7% | 70.0% | 66.4% |
| PFF, P2H, P12H | 68.2% | 71.8% | 51.8% | 72.7% | 71.8% | 67.3% |
| PFF, P4H, P8H | 55.5% | 55.5% | 71.8% | 72.7% | 64.5% | 63.6% |
| PFF–P4H | 86.4% | 73.6% | 74.5% | 81.8% | 75.5% | 68.2% |
| PFF, P2H, P4H, P8H | 70.9% | 73.6% | 70.9% | 83.6% | 62.7% | 63.6% |
| PFF, P4H, P8H, P12H | 60.0% | 52.7% | 63.6% | 72.7% | 72.7% | 60.0% |
| PFF–P4H, P8H | 72.7% | 70.9% | 66.4% | 85.5% | 66.4% | 65.5% |
| PFF–P4H, P12H | 81.8% | 63.6% | 65.5% | 78.2% | 72.7% | 60.9% |
| PFF–P8H | 67.3% | 63.6% | 69.1% | 79.1% | 65.5% | 46.4% |
| PCA Variables Computed From | Machine Learning Algorithm LTOCV Model Accuracy 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-Nearest Neighbors | Logistic Regression | Random Forest | Gradient Boosted Trees | Support Vector Machine | Naïve Bayes | |
| PFF, P2H | 94.5% | 90.0% | 87.3% | 85.5% | 82.7% | 85.5% |
| PFF, P3H | 80.0% | -- | 86.4% | 91.8% | -- | -- |
| P2H, P4H | 82.7% | -- | 75.5% | 72.7% | 69.1% | -- |
| P3H, P4H | -- | -- | -- | 66.4% | -- | -- |
| PFF, P2H, P3H | 98.2% | 90.0% | -- | -- | 83.6% | 82.7% |
| PFF, P2H, P4H | 85.5% | -- | 84.5% | -- | 75.5% | -- |
| PFF, P3H, P4H | -- | -- | 82.7% | -- | -- | -- |
| P2H, P3H, P4H | 86.4% | -- | -- | -- | 74.5% | -- |
| PFF, P2H, P8H | -- | 83.6% | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| PFF–P4H | 88.2% | 82.7% | 80.0% | 80.0% | 78.2% | -- |
| PFF, P2H, P4H, P8H | -- | 81.8% | -- | 78.2% | -- | -- |
| PFF–P4H, P8H | -- | -- | -- | 76.4% | -- | -- |
| PFF–P4H, P12H | 70.9% | -- | -- | 85.5% | -- | -- |
| PFF–P8H | -- | -- | -- | 78.2% | -- | -- |
| Harmonic Power Variables | LOOCV Model Accuracy 1 with Harmonic Power Variables | LOOCV Model Accuracy 1 with PCA Variables |
|---|---|---|
| PFF, P2H | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| PFF, P3H | 81.8% | 72.7% |
| PFF, P2H, P3H | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| P2H, P3H, P4H | 90.9% | 72.7% |
| PFF–P4H | 90.9% | 90.9% |
| PFF–P4H, P12H | 81.8% | 72.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carlson, K.D.; Dragomir-Daescu, D.; Boilson, B.A. Machine Learning Prediction of Left Ventricular Assist Device Thrombosis from Acoustic Harmonic Power. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050484
Carlson KD, Dragomir-Daescu D, Boilson BA. Machine Learning Prediction of Left Ventricular Assist Device Thrombosis from Acoustic Harmonic Power. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050484
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarlson, Kent D., Dan Dragomir-Daescu, and Barry A. Boilson. 2025. "Machine Learning Prediction of Left Ventricular Assist Device Thrombosis from Acoustic Harmonic Power" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050484
APA StyleCarlson, K. D., Dragomir-Daescu, D., & Boilson, B. A. (2025). Machine Learning Prediction of Left Ventricular Assist Device Thrombosis from Acoustic Harmonic Power. Bioengineering, 12(5), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050484








